Abstract
Land use change accounts for a large proportion of the carbon emissions produced each year, especially in highly developed traditional heavy industry and agriculture areas. In this study, we estimated the carbon emissions from land use in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China (BSRNC) from 1990 to 2020. We utilized seven periods of land use remote sensing image data spanning the years 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, with a 30-m grid resolution. Additionally, socio-economic data was incorporated into the analysis. The preprocessing of the remote sensing images involved several steps using ENVI 5.5, including radiometric correction, fusion, mosaic, and cropping. The land types were classified into six major categories: cropland, forest land, grassland, water area, construction land, and unused land, using the LUCC classification system. The IPCC coefficient method was used to calculate the trends in carbon emissions from land use, and the logarithmic mean Divisia index (LMDI) method was applied to analyze the influencing factors. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) From 1990 to 2020, the net carbon emissions from land use in the BSRNC increased from 11.91 × 104 t to 253.29 × 104 t, with an annual growth rate of 8.04%. (2) Spatially, land use carbon emissions exhibited an agglomeration pattern that gradually weakened and the regional emission differences gradually narrowed. (3) Income level was identified as the most important factor influencing land use carbon emissions in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020. Land use efficiency had a inhibitory effect on net carbon emissions, reducing land use carbon emissions by 1730.63 × 104 t.
1. Introduction
Since the onset of the industrial revolution, human activities have significantly altered land use/land cover at various temporal and spatial scales, leading to drastic changes in the state of land cover [1,2,3]. These changes have caused significant alterations in the material cycle and energy flow of ecosystems, directly impacting the carbon regulation process of land ecosystems, and have emerged as one of the key drivers of global climate change [4,5,6]. Carbon emissions resulting from land use changes have become one of the critical factors influencing global warming [7], and associated land use changes are considered the second most significant factor in the increase in atmospheric CO2 content on a global scale [8,9]. The most recent report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) indicates that human activities are responsible for over 90% of global carbon emissions [10]. The surge in global carbon emissions in recent decades has led to various environmental problems, including climate anomalies, sea level rise, and frequent extreme weather events, significantly impacting human production and daily life [11,12]. In summary, the rapid changes in land use/land cover have significantly altered carbon emissions and contributed to the current global climate crisis, requiring urgent and effective measures to mitigate their impacts.
In order to tackle climate change and pursue sustainable development, global agreements have been developed since the late twentieth century to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. One such agreement is the Paris Agreement, which was adopted in 2015 with the objective of limiting global temperature rise to 2 °C, and aiming to limit it to 1.5 °C [13]. The role of land use in contributing to greenhouse gas emissions is significant, with agriculture, forestry, and other land use activities accounting for 23% of human emissions [14]. Additionally, natural processes on land absorb nearly one-third of the global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels and industry [15]. It is evident that land plays a crucial role in the climate system, and to achieve the goal of limiting temperature rise, emissions from all sectors, including land, must be reduced [16,17]. Human activities such as economic development, population growth, and energy consumption are closely linked to carbon emissions, and are ultimately dependent on various land use activities [18,19]. These activities include heating in settlements, tailpipe emissions from transportation on land, and process emissions from industrial and mining activities on land [20,21,22]. All of these activities contribute to anthropogenic carbon emissions on different types of land [23]. Therefore, to achieve sustainable development and address climate change, it is essential to reduce emissions from all sectors and consider the impact of land use activities on the climate system.
In 1950, a total of 60 × 108 t of CO2 were emitted globally. By 1990, this number had increased to over 220 × 108 t. CO2 emissions have continued to grow rapidly, with annual emissions now exceeding 340 × 108 t. In 2020, China, the United States, and India collectively accounted for half of the global CO2 emissions. From 1850 to 2021, the United States has cumulatively emitted over 5090 × 108 t of CO2, representing 20.3% of the global total. It is the largest emitter in terms of cumulative emissions and has contributed to a global warming of approximately 0.2 °C font. China ranks second, with cumulative CO2 emissions of 2884 × 108 t, accounting for 11.4% of the global total and resulting in a global warming of approximately 0.1 °C. Russia ranks third, accounting for 6.9% of the cumulative global CO2 emissions. Brazil (4.5%) and Indonesia (4.1%) follow, with their carbon emissions primarily attributed to land use changes and deforestation.
Since 2006, China has become the world’s largest carbon emitter [24], contributing nearly 63% to the growth in global carbon emissions from 2006–2013 [25]. With this significant role, China has a responsibility to reduce global carbon emissions [26]. To achieve this goal, the Chinese government has made a commitment to “peak CO2 emissions” by 2030 and achieve “carbon neutrality” by 2060, making climate change mitigation and sustainable development a top priority in its national planning [27,28]. However, accurate and reliable carbon accounting is crucial in setting emission reduction policies and targets [29]. China is a vast country with varying regional characteristics such as economy, natural resources, and population [30]. The potential for carbon emission reduction through land use structure optimization is about one-third of that through conventional low-carbon policies. Therefore, it is essential to account for carbon emissions by region and formulate targeted regional emission reduction policies to effectively achieve national carbon emission reduction targets [31,32]. Examining regional carbon emissions from land use change is of great practical significance in achieving low-carbon land use and developing a low-carbon economy.
The relationship between land use and land cover change (LUCC) and carbon emissions has attracted the attention of scientists worldwide. Previous research on land use carbon emissions both domestically and abroad has primarily focused on the accounting and temporal and spatial characteristics of land use carbon emissions [33,34], the mechanisms by which land use affects carbon emissions [35,36,37], and the factors that influence land use carbon emissions [38,39,40]. Researchers have proposed carbon emission coefficient methods for calculating carbon emissions from cultivated land [41,42,43], forest land [44,45,46], grassland [47,48,49], and construction land [50,51], and explored the impact of land use change on carbon emissions. Most studies have been conducted at the provincial and municipal levels, investigating the temporal and spatial characteristics of regional land use carbon emissions [52,53]. Lai et al. conducted a detailed analysis of the impact of land use changes and related management practices on soil carbon stocks in China between 1990 and 2010. Their study highlighted the crucial role of land use management [54]. Similarly, Xu et al. focused on the Pearl River Delta region as their research area and identified the influence of land structure and urbanization levels on carbon sequestration levels in the land [55]. Scholars have extensively discussed the driving factors of land use carbon emissions, with most using various econometric methods to explore the factors that affect carbon emissions, such as the decomposition method [56,57], Laspeyres decomposition [58,59,60], and logarithmic mean Divisia index (LMDI) model [61,62]. Scholars have also calculated the driving factors of carbon emissions in various sectors in China, such as per capita carbon emissions, industrial carbon emissions, and energy consumption carbon emissions [63,64]. Ang et al. empirically demonstrated through several methods that the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) model can be widely applied in energy and environmental decomposition studies [65]. Cao et al. utilized the LMDI model and geographic detectors to explore the main influencing factors of carbon emissions from land use in Chongqing City, identifying total energy consumption, per capita GDP, and urbanization rate as significant factors [4]. Wu et al. analyzed the factors influencing carbon emissions in China using an improved Kaya identity formula, revealing that increasing urbanization rate, energy carbon emission coefficient, and energy intensity contribute to the rise in carbon emissions [66]. Shuai et al. employed the STIRPAT model to confirm that per capita GDP significantly increases carbon emissions, while urbanization rate significantly inhibits carbon emissions [67]. Zhao et al. conducted an analysis of agricultural carbon emissions and the matching degree of water and soil resources at the provincial level, followed by calculations using the LMDI model to examine the impact of water and soil resource development on agricultural carbon emissions [68]. In addition, population growth, economic output, industrial structure, land structure, urbanization, and spatial expansion are important factors that promote the growth of land use carbon emissions [69,70,71]; energy efficiency and land intensity of GDP are the main limiting factors for land use carbon emissions [72]. These studies indicate that LMDI is an effective method for analyzing the factors behind carbon emissions, providing a valuable reference for exploring a series of related issues concerning carbon emissions in land use change [73]. However, most of these studies emphasize the impact of economic development and energy consumption on carbon emissions, and relatively few studies have analyzed the factors that influence carbon emissions from a land use perspective, which also have an important impact on carbon emissions.
The BSRNC is a vital grain-producing area and a traditional stronghold of heavy industry in China. However, it is also a significant contributor to the country’s carbon emissions, accounting for 10–11% of the national total, a figure that surpasses the region’s GDP and population proportions [74]. The region is faced with new and more demanding challenges for synergistic development in light of China’s carbon peaking and carbon neutrality targets. Additionally, the BSRNC is one of China’s most climate-sensitive areas, with significant potential impacts from climate change. Over the past 50 years, the region’s average temperature has risen by 0.38 °C per decade, exceeding the national average. It is projected that temperatures in the region will continue to increase in the future. Climate change has resulted in severe degradation of wetland ecosystems in the BSRNC, along with increased occurrences of extreme weather events and other negative impacts. With the comprehensive implementation of the Northeast revitalization strategy, the economic and social development of the Northeast China region has been rapidly progressing. At the same time, the BSRNC is undergoing a transition from the transformation and revitalization of old industrial bases to a new era of industrialization. Consequently, this transformation inevitably leads to further expansion of energy consumption, land development, and changes in various land use types, which in turn contribute to increased carbon emissions. In the fourteenth Five-Year Plans of the provinces in the BSRNC, it is emphasized that the peaking of carbon emissions in China by 2030 should be implemented, and active actions to achieve this goal are being undertaken. However, as an important energy and industrial base in China, the BSRNC has a relatively high proportion of primary and secondary industries, which have a significant scale. By 2018, the annual average growth rate of energy consumption had reached 4%. With the vigorous economic development in the BSRNC in recent years, it is difficult to change the energy consumption structure in the short term. The irrational utilization of land resources caused by land development and expansion exacerbates problems such as low land use efficiency. Therefore, based on the current land use data of the BSRNC in the past 30 years, this study aims to investigate the spatio-temporal patterns of land use carbon emissions and to identify their influencing factors. Furthermore, the study proposes some suggested measures, with the aim of assisting in the carbon reduction efforts in the BSRNC and helping achieve the carbon emissions peaking target set in the national fourteenth Five-Year Plans by 2030.
This study employs a land use perspective to estimate the net carbon emissions resulting from land use change in the BSRNC. Through decomposition of the influencing factors of land use change carbon emissions, we quantitatively assess the impact of these factors on carbon emissions, with the ultimate goal of improving regional land use planning and promoting low-carbon economic development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The BSRNC (120°30′ E–134°06′ E, 41°04′ N–51°37′ N) is located in the middle temperate zone, covering an area of nearly 4656.48 km2 in northeast China (Figure 1). The study area is characterized by diverse geomorphologic landscapes, including mountains and plains such as Daxing’anLing, Xiaoxing’anling, Changbai Mountains, Sanjiang Plain, Songnen Plain, and Liaohe Plain. The BSRNC is characterized by a temperate continental monsoon climate, with long and harsh winters and short, hot summers. There is a significant variation in temperature throughout the year, with average temperatures decreasing from south to north. In the coldest month, January, the average temperature ranges from −6 to −32 °C from south to north, while in the hottest month, July, temperatures generally range between 20 and 23 °C. The average annual precipitation in this region ranges from 400 to 1200 mm, with significant spatial and temporal variations. Spatially, the precipitation gradually decreases from southeast to northwest, with the eastern Three Rivers Plain receiving around 500 to 600 mm, while the western Daxing’anling region and the southern Liaohe Plain receive only 300 to 400 mm. Temporally, the majority of precipitation occurs from June to September, accounting for 60% to 70% of the annual total, with heavy rain concentrated in July and August. The natural vegetation in the area mainly consists of deciduous broad-leaved forests, coniferous forests, and grasslands. The dominant soil types include brown soil, loam, dark brown soil, black soil, and black calcareous soil. The BSRNC have high organic matter content, loose texture, and are suitable for cultivation.
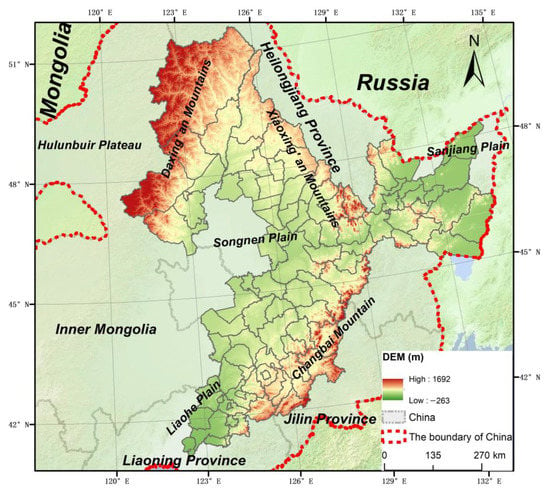
Figure 1.
Study area.
Since 1990, the BSRNC has experienced significant changes in land use structure, mainly cultivated land and construction land, due to industrialization, urbanization, and black soil protection policies. These changes have led to drastic alterations in land use carbon emissions, highlighting the urgent need to study the spatiotemporal evolution of carbon emissions resulting from land use change in the region.
2.2. Data Sources
This study utilized two primary data types and sources:
(1) Land use remote sensing data: The land use raster data used in this study is sourced from the Resource and Environment Science Data Center (RESDC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 29 May 2023). The primary remote sensing images utilized are Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 8 TM images, obtained from the Geospatial Data Cloud Platform (https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 3 June 2023), with a spatial resolution of 30 m. Preprocessing and interpretation of the remote sensing images from seven time periods: 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020. The remote sensing images were processed using Envi 5.5, which involved radiometric correction, atmospheric correction, and geometric correction. Additionally, image fusion, mosaicking, and cropping were performed. Based on the LUCC classification system and “Current land use classification” (GB/T21010-2017) [75], taking into account the actual conditions of the study area, the ArcGIS 10.2 was utilized to process remote sensing images using supervised classification and visual interpretation methods. The land use types were reclassified into cultivated land, woodland, grassland, water, construction land, and unused land. A classification confusion matrix was established and the Kappa coefficient was utilized to evaluate the accuracy of the interpreted remote sensing images. The research findings revealed that the Kappa coefficients for the data from all seven time periods were above 0.75, indicating that the accuracy met the requirements for practical usage.
(2) Socioeconomic development data: Population, GDP, and energy consumption data related to the study area were obtained from the China Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistics Yearbook, and China Rural Statistical Yearbook.
2.3. Methods
LUCC is a critical aspect of human-induced climate change, which alters the structure, functions, and processes of ecosystems at various scales and levels. This transformation has significant implications for the carbon regulation process of ecosystems and ultimately contributes to the global climate change phenomenon. The present study investigated the impact of LUCC on carbon emissions in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020. The IPCC carbon emission factor method was utilized to calculate land use carbon emissions while a quantitative analysis was performed to assess the temporal characteristics of carbon emissions. Additionally, spatial autocorrelation analysis was conducted to ascertain the spatial correlation of land use carbon emissions within the study area. Lastly, factor decomposition analysis was employed to identify and quantify the specific impact of various factors on carbon emissions. This interdisciplinary approach offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between LUCC and carbon emissions and provides valuable information for policymakers and other stakeholders working towards mitigating climate change. The specific process is shown in Figure 2.
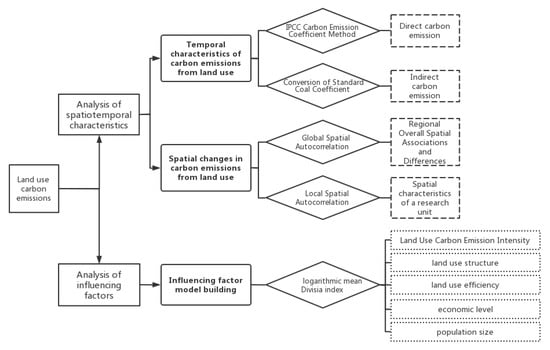
Figure 2.
Method flowchart.
2.3.1. Computation of Carbon Storage Change Caused by LUCC
Land use/land cover change (LUCC) refers to the transformation of original land use types by human activities in the process of production and living, resulting in changes in land use patterns and management. LUCC is the most obvious manifestation of human activities affecting the Earth’s surface system and is critically important for global ecological environmental changes. This study calculated the carbon absorption of forest land, grassland, water bodies, and unused land, as well as the carbon emissions from cropland and construction land. The IPCC-based direct carbon emission factor method was used to estimate the carbon emissions (or absorption) of farmland, forest land, grassland, water, and unused land. The land use carbon emission (or absorption) factors were determined based on relevant literature from previous studies (as shown in Table 1), and the carbon emission measurement equation was:
where, E represents the total amount of carbon emissions, measured in tons (t); ei represents the carbon emissions caused by different land use types, measured in tons (t); Si represents the area of different land use types, measured in hectares (hm2); δi represents the emission coefficient of each land use type per unit area, measured in tons per hectare (t/hm2).

Table 1.
Emission (absorption) coefficient of the five types of land use studied in the BSRNC.
In regard to the carbon emission coefficient of cultivated land, cultivated land serves as both a carbon source and a carbon sink. The carbon sink function of cultivated land includes carbon sequestration by crops, organic carbon storage in the soil, and carbon sequestration through the return of crop residues to the land. However, agricultural production activities such as pesticide use, fertilization, and agricultural machinery usage also contribute to carbon emissions, which represent the carbon source of cultivated land. Therefore, the net carbon emission coefficient of cultivated land is calculated by subtracting the carbon absorption coefficient from the carbon emission coefficient. According to research by Cai et al., the carbon emission coefficient of cultivated land is determined to be 0.504 t/hm2, while the carbon absorption coefficient is 0.007 t/hm2. Consequently, the net carbon emission coefficient of cultivated land is 0.497 t/hm2 [76].
In regard to the carbon emission coefficient of forest land, forest land plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration within terrestrial ecosystems. In the research conducted by Fang Jingyun et al. the carbon absorption of forest land in China was estimated for the 20-year period after 1981. Subsequently, some scholars calculated the weighted average of the Chinese forest system, resulting in a carbon emission coefficient for forest land of −0.581 t/hm2 [77]. In this study, the carbon emission coefficient of forest land is defined as −0.581 t/hm2.
In regard to the carbon emission coefficient of grassland, grassland plays a vital role in carbon sequestration and has the capacity to effectively absorb carbon emissions. Through calculations conducted by Shi Hongxin et al., the carbon emission coefficient of grassland was determined to be −0.021 t/hm2 [78]. This study draws upon the findings of their research regarding the carbon emission coefficient of grassland.
In regard to the carbon emission coefficient of water ecosystems, Duan Xiaonan et al. conducted a study on wetlands in China, aiming to investigate the carbon sequestration rate and potential in this region. After calculating the carbon sequestration rate and carbon sink coefficients in the five major lake areas, the obtained values were averaged, resulting in the determination of −0.253 t/hm2 as the carbon emission coefficient for aquatic ecosystems [79].
In regard to the carbon emission coefficient of unused land, in the BSRNC, unused land exhibits both carbon absorption and carbon emission, but to a relatively lesser extent, with low-carbon emissions. Referring to the research by Yan Jing et al., the carbon emission coefficient of unused land is determined to be −0.005 t/hm2 [80].
Carbon emissions from construction sites are estimated indirectly through the carbon emission coefficients of each energy consumption. Mainly, the consumption of energy consumption generated in production and living is converted into tons of standard coal, and then converted into carbon emissions according to the carbon emission coefficients of different energy sources. With reference to the actual situation of the BSRNC, the energy sources calculated in this study included coal, coke, gasoline, kerosene, diesel, fuel oil, liquefied petroleum gas and natural gas. The carbon emission measurement of construction land was based on the reference model provided by IPCC, and the calculation formula used was:
where, EC denotes the CO2 emissions from energy consumption; eci is various energy consumption of construction land produces carbon emissions; Eni is the consumption of a certain energy source; σi is the carbon content conversion coefficient [37]; φi is the carbon emission coefficient of a certain energy source.
2.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
Spatial Autocorrelation is measured based on both the feature location and feature value. Given a set of features and a related attribute, it evaluates whether the expressed pattern is clustered, dispersed, or random. This method calculates the Moran’s I index value, as well as the Z-score and p-value to assess the significance of this index. The p-value is an approximate numerical value of the area under a known distribution curve, constrained by the test statistic. The Moran’s I statistic of spatial autocorrelation was:
where, zi is the deviation of the attribute of feature i from its mean, wi,j is the spatial weight between features i and j, n is equal to the total number of features, and So is the sum of all spatial weights:
The calculation method of statistical Zi score is:
Among them,
Starting from a local perspective, conducting spatial autocorrelation analysis can explore the aggregation and differentiation characteristics of a specific unit area in space. The local Moran’s I measures the concentration level of high or low values of a particular study area. The spatial correlation of the Local Moran’s I statistic is:
where xi is the attribute of feature i, X is the mean value of the corresponding attribute, and wij is the spatial weight between feature i and j. Additionally,
where n is equal to the total number of features.
The calculation of the ZIi score in the statistics is as follows:
Among them,
2.3.3. Factor Decomposition Method
In order to adopt more targeted carbon reduction measures or formulate more effective emission reduction policies, it is necessary to further understand the influencing factors of carbon emissions after calculating regional carbon emissions. The Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) is one of the main approaches used in the field of low-carbon economy to study the factors affecting energy consumption. This method is widely applied in the research of energy consumption and carbon emissions due to its strong operability, complete decomposition, absence of residuals, and unique results. The LMDI model can decompose the influencing factors based on the research focus and adapt them to multiple factors for time series analysis. Therefore, in this study, the LMDI model is used to decompose the factors influencing carbon emissions, with the aim of identifying the direction and specific impacts of these factors on carbon emissions. To analyze the impact of different factors on land use carbon emissions, this study considers socioeconomic factors and introduces land use-related factors. A decomposition model for the influencing factors of land use carbon emissions in the BSRNC is constructed, considering five factors: land use carbon emission intensity, land use structure effect, land use efficiency, economic level, and population size effect. The decomposition model of the influencing factors in this article is as follows:
where, C represents the total carbon emissions from land use in thousands of tons, Ci represents the carbon emissions from different types of land use, Li represents the area of different types of land use in thousands of hectares, L represents the total area of land in the region in thousands of hectares, G represents the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in thousands of yuan, and p represents the number of permanent residents in thousands of people.
Therefore, let:
The total carbon emissions in the region can be represented as the product of the factors in the formula, which is expressed as follows:
where, fi represents the carbon emission intensity of land use, si represents the land use structure, l represents the land use efficiency, g represents the per capita GDP, and p represents the population size.
By using the LMDI model to decompose the contribution values of each influencing factor, C0 is defined as the carbon emissions at the beginning of the study period, and Ct is the carbon emissions during period t of the study. The effect of changes in carbon emissions during the study period can be expressed as follows:
where, ΔCfi, ΔCsi, ΔCl, ΔCg, ΔCp are the contribution values for the selected indicators (fi, si, l, g, p).
Assumption:
According to the LMDI decomposition method, the decomposition results and contribution rates of each influencing factor are expressed as follows:
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Land Use Related Carbon Storage Change
3.1.1. Characteristics of Land Use Change in the BSRNC
After pre-processing the images, specific information about land use classification were obtained. ArcGIS 10.2 software was used to generate land use type maps at a temporal scale of 5 years. With the aid of ArcGIS 10.2 software, it was possible to calculate the areas of different land use types, as presented in Table 2. In the table, the areas of different land use types were compared to the total land area, thereby obtaining the proportions of land use types.

Table 2.
Land use area and proportion in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020.
Table 2 reflected the land use status and changes in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020. It can be observed that the dominant land use types in the region are cropland and forestland, accounting for over 70% of the total land area. From 1990 to 2020, there was a general decreasing trend in the areas of forestland, grassland, and water bodies, while cropland and urban land areas showed an expanding trend, exhibiting phase-specific characteristics during different time periods. The farmland area showed a consistent increasing trend, with an increase of approximately 6.07% of the total land area of the study region from 1990 to 2020. The woodland area decreased gradually but with a relatively small reduction, accounting for around 2% of the total land area from 1990 to 2020. The grassland area exhibited a decreasing trend, with a reduction of over 50% from 1990 to 2020. The water area showed fluctuating changes, with a slight overall decrease from 1990 to 2020, while the total remained relatively stable. The urban land area showed an increasing trend, experiencing rapid growth after 2005 and reaching a relatively stable level by 2020. The unused land area decreased annually from 1990 to 2005, followed by an increasing trend from 2005 to 2020, but with relatively small changes overall.
3.1.2. The Overall Change Characteristics of Land Use Carbon Emissions from 1990 to 2020
Using the formulas for direct and indirect carbon emissions mentioned in the previous text, the carbon emissions from land use in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020 are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Carbon emissions of land use in BSRNC from 1990 to 2020 (104 t).
Overall, from 1990 to 2020, net carbon emissions from land use in the BSRNC showed an increasing trend, as shown in Table 3. Analyzing the carbon emissions and carbon sinks in the BSRNC, human activities on cropland were the main carbon source, showing an increasing trend. The percentage of carbon emissions from cropland increased from 76.82% in 1990 to 90.01% in 2020. In terms of carbon absorption, forests contributed the most, accounting for over 96.00% of the total carbon sink. Forests in the region have an important carbon sequestration ability, and with 37.29% of the total area covered by forests, their carbon absorption role is very significant. Grasslands, water bodies, and unused land have relatively low-carbon absorption, with a combined proportion of only 13.52%.
In terms of changes in carbon emissions/carbon absorption, from 1990 to 2020, the net carbon emissions from land use in the BSRNC showed an increasing trend, increasing from 11.91 × 104 t to 253.29 × 104 t. The total amount of carbon emissions increased from 1070.51 × 104 t in 1990 to 1236.11 × 104 t in 2020, with an average annual growth rate of 0.52%. Carbon emissions from construction land grew rapidly, from 107.16 × 104 t in 1990 to 132.34 × 104 t in 2020, but the growth rate had a “slow first, then fast” characteristic, increasing from 0.25% from 1990–2005 to 1.35% from 2005–2020. Carbon emissions from cropland showed a staged upward trend, increasing from 963.35 × 104 t in 1990 to 1103.78 × 104 t in 2020, with an annual growth rate of 0.49%. From 1990 to 2020, the rate of carbon absorption decreased slowly, with a reduction of 75.77 × 104 t. During this period, the ability of forests to absorb carbon emissions changed significantly, while the carbon sinks of grasslands, water bodies, and unused land remained relatively stable.
3.1.3. Temporal Variation Characteristics of Land Use Carbon Emissions from 1990 to 2020
By inputting land use data and energy consumption data into the land use carbon emission accounting model, the carbon emissions from land use for each county (district and city) research unit in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020 were calculated, and the growth trends of carbon emissions from land use were classified and shown in Figure 3.
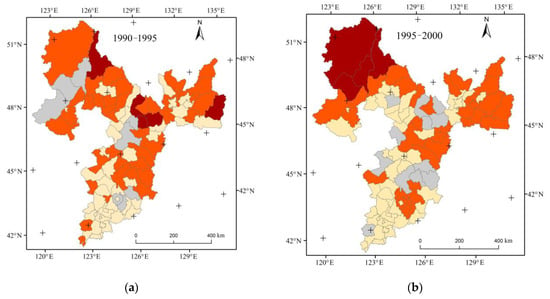
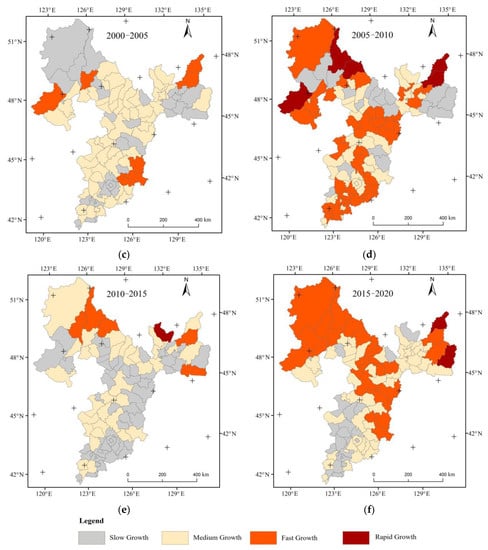
Figure 3.
Growth trend of land use carbon emissions in county-level research units in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020. (a) Growth trend of carbon emissions from land use in BSRNC during 1990–1995. (b) Growth trend of carbon emissions from land use in BSRNC during 1995–2000. (c) Growth trend of carbon emissions from land use in BSRNC during 2000–2005. (d) Growth trend of carbon emissions from land use in BSRNC during 2005–2010. (e) Growth trend of carbon emissions from land use in BSRNC during 2010–2015. (f) Growth trend of carbon emissions from land use in BSRNC during 2015–2020.
From a time-series perspective, the BSRNC experienced significant changes in land use carbon emissions from 1990 to 1995. The total amount of carbon emissions increased by 95.68 × 104 t, with one-third of the research units experiencing rapid growth, including Nenjiang City, Qing’an County, Mulan County, Tonghe County, and Hulin City. From 1995 to 2000, the growth rate of land use carbon emissions remained high, with the total carbon emissions increasing by 44.85 × 104 t. The fastest growth rate of carbon emissions occurred in Arong Banner, Morin Dawa Daur Autonomous Banner, Oroqen Autonomous Banner, and Nenjiang City. Between 2000 and 2005, the carbon emission of land use changed little, with most counties experiencing slow or medium growth. From 2005 to 2010, the growth trend of carbon emissions changed significantly in areas such as Zhalantun, Nenjiang, Wudalianchi, Tongjiang, and Fujin, which experienced rapid growth. Between 2010 and 2015, most counties in the BSRNC had a relatively stable land use carbon emission trend, with only Luobei County experiencing a relatively large growth rate, which belonged to the rapid growth type. From 2015 to 2020, the total carbon emissions increased by 60.90 × 104 t, with the fastest growth rate occurring in Hulin City and Tongjiang City.
Overall, from 1990 to 2020, the carbon emissions of the research units at the county level in the BSRNC continued to increase, with Dehui City, Nehe City, and Changchun City having the largest total carbon emissions. Longjiang County, Yushu City, and Nong’an County also rank high in carbon emissions, accounting for 42.23% of the total emissions. Counties and cities such as Oroqen Autonomous Banner, Zhalantun City, and Daqingshan County showed carbon absorption. These trends are consistent with the economic development and urban positioning of the BSRNC. Economically developed areas such as Changchun City and Harbin City have large areas of construction land and high energy consumption for economic development, while ecologically positioned areas such as Oroqen Autonomous Banner and Zhalan City have a large area of grassland. The total amount of carbon emissions in most counties in the BSRNC shows a continuous increasing trend, with counties in the west of Heilongjiang Province, Nenjiang City, Wudalianchi City, Moli Dawa Daur Autonomous Banner, and Zhalaite Banner in Inner Mongolia, Dongfeng County in Jilin Province, and Jilin City experiencing a relatively large range of change in carbon emissions. The rest of the regions show a trend of increasing fluctuations and the range of change is relatively small.
3.2. Analysis of Spatial Variation in Land Use Carbon Emissions
3.2.1. Global Autocorrelation Analysis
In order to examine the spatial autocorrelation of carbon emissions from land use in the BSRNC, this study used global Moran’s I to assess the correlation of carbon emissions based on remote sensing inversion data. The global Moran’s I results for carbon emissions from 1990 to 2020 are shown in Table 4 (Expected value is 0.010526.).

Table 4.
Global Moran index of carbon emissions in BSRNC from 1990 to 2020.
The significance of Moran’s I index and Z-Score test lies in their ability to indicate the significance of spatial autocorrelation of a variable when Moran’s I > 0 and Z-Score > 1.96 (p-Value < 0.05). The study detected significant spatial autocorrelation of carbon emissions in the research area from 1990 to 2020 (p-Value < 0.05) using Moran’s I, indicating an aggregated spatial distribution of carbon emissions. Among them, the Z-values were higher in 1990, 1995, and 2010, with values of 2.8646, 2.6978, and 2.6544, respectively, and p-values close to 0, indicating strong spatial clustering in these three years. The Z-values were lower in 2005, 2000, and 2020, with values of 2.5459, 2.5575, and 2.5699, respectively, and p-values less than 0.05, indicating weaker spatial clustering in these three years. The Moran’s I index decreased from 0.0630 in 1990 to 0.0556 in 2020, suggesting that with the passage of time, the spatial clustering phenomenon has weakened, and the differences in carbon emissions between regions are gradually narrowing.
3.2.2. Local Autocorrelation Analysis
In order to further explore the spatial and temporal distribution and heterogeneity of carbon emissions in the research area, based on ArcGIS 10.2, the Euclidean distance method was used to construct a spatial weight matrix with counties as the basic research unit to obtain the local spatial autocorrelation of carbon emissions in the research area. This study produced a cluster map of the Local Indicators of Spatial Association (LISA) for the BSRNC between 1990 and 2020, as shown in Figure 4.
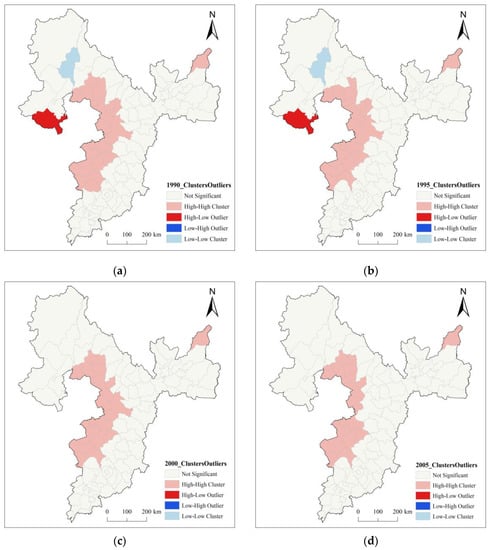
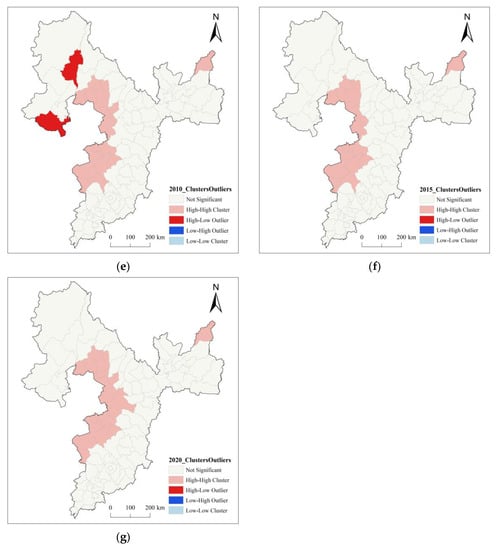
Figure 4.
Cluster map of LISA for the BSRNC between 1990 and 2020. (a) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 1990. (b) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 1995. (c) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 2000. (d) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 2005. (e) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 2010. (f) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 2015. (g) LISA Cluster Diagram of BSRNC in 2020.
The Local Indicators of Spatial Association index values divide the space into four parts, “high-high (H-H),” “low-low (L-L),” “high-low (H-L),” and “low-high (L-H).” H-H aggregation, which represents high-carbon emissions areas being surrounded by other high-carbon emissions areas, is particularly significant in land use carbon emissions. H-L aggregation represents a relatively high level of carbon emissions in the central area and relatively low levels in the adjacent areas, exhibiting a more pronounced polarization effect in spatial association. L-H aggregation represents a relatively low level of carbon emissions in the central area and relatively high levels in the adjacent areas, which are considered transition zones. Some counties that are not significant represent areas where carbon emissions do not exhibit strong spatial patterns. Based on the LISA clustering map derived from the treatment of land use carbon emissions in this study, the carbon emissions in the study area mainly exhibit the H-H aggregation type, with clear patchy aggregation distribution characteristics in space. The L-L, H-L, and L-H types show less significant aggregation effects in space. H-H aggregation areas are mainly concentrated in the southwest of the study area, indicating that this area has excessive carbon emissions and requires strengthened carbon emission control measures, vigorous development of clean industries, and continuous reduction of carbon emissions. When formulating pollution control plans, the characteristics of H-H aggregation areas should be considered. In addition, we can see from Figure 4 that the number of counties exhibiting H-H aggregation decreased from twenty-two in 1990 to nineteen in 2020, indicating that the carbon emissions in this area have been decreasing year-by-year, and the high-value aggregation phenomenon in space has begun to weaken, which is consistent with the trend shown by the global Moran’s I index. However, it should not be ignored that the orientation of high-value aggregation has remained unchanged over the years, and it is mostly distributed in the southwest of the BSRNC, indicating that although carbon emissions in this area’s southwest have been decreasing year-by-year, it remains a key area for emissions.
3.3. Decomposing the Influencing Factors of Land Use Related Carbon Emissions
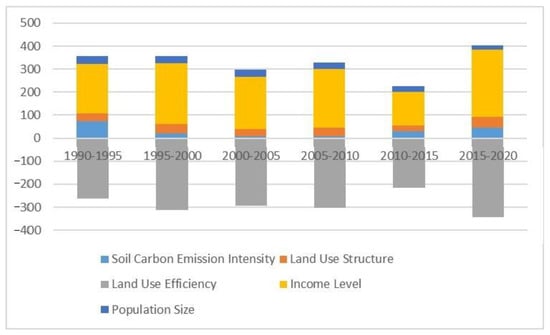
According to the LMDI decomposition method, based on the calculation formula mentioned above, the carbon emissions from land use can be additively decomposed. This allows for the calculation of the effects of five factors during the study period on the change in land use carbon emissions in the BSRNC relative to the base period in 1990. These factors include the effects of land carbon emission intensity, land use structure, land use efficiency, income level, and population size. These effects are the contribution values obtained from the decomposition. In the additive decomposition model, the results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 5, which enables an overall analysis of the direction and magnitude of the impact of each factor on land use carbon emissions in the BSRNC.

Table 5.
The decomposition results of carbon emission factors in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020.
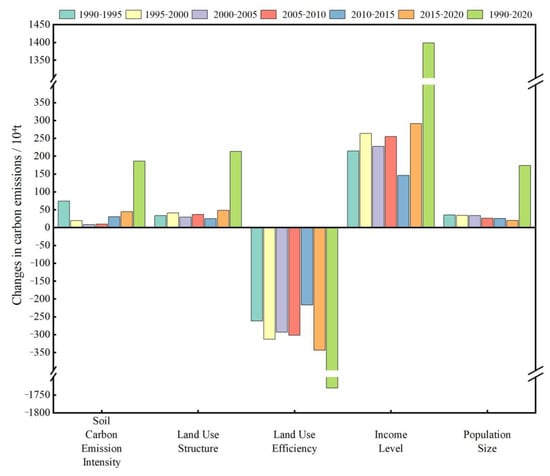
Figure 5.
The decomposition results of carbon emission factors in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020. Between 1990 and 2020, various influencing factors had different effects on net carbon emissions in the BSRNC. The contributions of different influencing factors to net carbon emissions also varied. The cumulative contributions of each factor to net carbon emissions were different, and their directions were not consistent, as shown in Figure 6.
From a holistic perspective, the income level was the most significant factor influencing carbon emissions in the BSRNC between 1990 and 2020. In other words, changes in per capita gross domestic product had the greatest impact on net carbon emissions in this region. Among all the influencing factors, per capita gross domestic product played the most prominent role, resulting in a growth of carbon emissions by 1398.35 × 104 t over the entire period. Three factors, namely land use structure, land carbon emission intensity, and population size, also had a positive impact on carbon emissions, increasing them by 213.44 × 104 t, 186.26 × 104 t, and 173.95 × 104 t, respectively. Land efficiency had a negative impact on carbon emissions, meaning that the more output per unit area of land, the lower the carbon emissions. The reduction in land use carbon emissions due to land efficiency was 1760.63 × 104 t. Overall, these five factors led to a net increase in land use carbon emissions of 241.37 × 104 t. The suppressive effect of land efficiency on carbon emissions is increasing, but its impact cannot completely offset the promoting effect of economic activities and other factors on carbon emissions. In addition, during the study period, the structure of land use had a continuously promoting effect on carbon emissions. Therefore, it is difficult to achieve carbon reduction solely by continuously improving land use efficiency. To achieve carbon neutrality, the BSRNC should accelerate the transformation of the economic growth and agricultural development model, quickly adjust the land use structure, enhance the intensive use of land, improve efficiency, and adopt various measures to achieve low-carbon economic development.
(1) Factor of Land Carbon Emission Intensity
Between 1990 and 2020, the decomposition results of the factor of land carbon emission intensity were positive values. The unit factor of land carbon emission intensity had a promoting effect on the growth of carbon emissions, contributing to an increase of 186.26 × 104 t in carbon emissions. From the results of the decomposition of annual effects, the contribution value of the unit factor of land carbon emission intensity to the net carbon emissions from land use fluctuated significantly.
(2) Factor of Land Use Structure
According to the cumulative decomposition results, land use structure is the second largest factor contributing to the increase in carbon emissions from land use, with a positive impact and a contribution of 235.43 × 104 t of carbon emissions. Whether it is analyzed annually or cumulatively, the contribution of land use structure to carbon emissions is positive, and this factor has a significant promoting effect on carbon emissions in all study periods. During the study period, the proportion of cultivated land and construction land, which act as carbon sources, continued to increase. Agricultural production on cultivated land significantly increased carbon emissions, while the continuous increase in construction land area resulted in the consumption of fossil fuels, leading to a continuous increase in net carbon emissions within the study area. Land with carbon sequestration potential has remained largely unchanged or has even decreased overall, so the carbon emissions resulting from the increase in carbon source area cannot be offset.
(3) Factor of Land Use Efficiency
Based on the yearly and cumulative decomposition results, it is evident that land use efficiency has a fluctuating impact on carbon emissions from land use, with an overall increasing trend, and is an important factor in reducing the increase in carbon emissions from land use. Between 1990 and 2020, the improvement in land use efficiency in the BSRNC has played a significant role in slowing down the growth of carbon emissions, resulting in a cumulative reduction of 1760.63 × 104 t of carbon emissions.
(4) Factor of Income Level
Per capita GDP is an important indicator reflecting the level of per capita income in the region, which can characterize the level of economic development in the region. Economic development is the main factor affecting carbon emissions from land use, contributing 1398.35 × 104 t to the total amount, accounting for 69%. Regardless of gradual or cumulative effects, this factor has a positive impact on carbon emissions, and compared with other factors, it has the most significant promoting effect. With the continuous development of the economy, the consumption of energy also continues to increase, accompanied by a continuous increase in carbon emissions.
(5) Factor of Population Size
According to the results of year-by-year and cumulative decomposition, the population size has the smallest promoting effect on land use related carbon emissions, contributing 173.95 × 104 t to the increase in net carbon emissions. However, its impact on land use carbon emissions is smaller than that of land use structure and land carbon emission intensity. After 2010, the number of permanent residents in the BSRNC continued to decline, and its impact on land use carbon emissions decreased from 35.56 × 104 t from 1990 to 1995 to 19.83 × 104 t from 2015 to 2020.
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Findings
The results of this study are generally highly reliable and consistent with previous research. For example, some prior studies have indicated that the expansion of coal-intensive industries and resulting per capita GDP growth are the main drivers of carbon emissions in China [81,82]. This study also suggests that per capita GDP plays a dominant role in promoting carbon emissions growth in the BSRNC, demonstrating consistency with the main driving factors in China. Both the Northeast China Black Soil Zone and other regions in China rely heavily on coal, and although there are slight differences in energy utilization technology levels, the carbon emission patterns in both regions are similar [83,84]. According to Gao Zhenjun et al., various factors contribute to the increased intensity of carbon emissions in the surrounding areas of Northeast China [85]. These factors include population growth, improved economic development, industrialization, enhanced living standards, predominantly agricultural and construction land use structure, and increased urbanization. In addition, this study estimated carbon emissions using data extracted from authoritative statistical yearbooks and performed a decomposition analysis of carbon emission influencing factors using the relatively mature LMDI model, both of which are roughly consistent with previous research, ensuring the reliability of the results.
Chen et al. obtained energy-related carbon emissions, including those from various fossil fuels such as raw coal and gasoline, through county-level carbon emission statistics [86]. Haiming Yan et al. believed that per capita GDP growth is the main driving factor of carbon emissions [18]. Since land use carries a large amount of human production and life activities, we believe that land use has an impact on carbon emissions. Furthermore, arable land and construction land have been identified as major sources of carbon in several studies [21,72]. Therefore, we consider land use structure as one of the factors influencing carbon emissions. The results suggest that land use structure has a significant positive impact on the growth of carbon emissions.
4.2. Policy Implications
Over the past few decades, the economic development of the BSRNC has mainly relied on the development of primary and secondary industries, and carbon emissions generated by agricultural and industrial activities have been the main source of carbon emissions. The Black Soil Region needs to adjust its industrial structure, develop clean and low-carbon energy, improve energy efficiency, reduce the consumption of traditional energy such as coal, and gradually change the current situation where coal consumption is the main energy source. Promoting energy technology innovation, optimizing energy structure, and reducing the proportion of high-polluting energy sources such as coal are necessary steps. Improving agricultural infrastructure construction and increasing agricultural intensification can enhance the productivity of farmland, thereby preventing the over-expansion of land resources. Improving agricultural production technology can effectively save farmland. Increasing soil carbon content in farmland and guiding agriculture towards low-energy, circular, and organic farming models can also help. Gradually reducing the use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture is also essential. According to local conditions, there is a need for adjusting and optimizing the agricultural product structure reasonably, at the same time, increasing the construction and protection of agricultural infrastructure. Additionally, the government should provide appropriate low-carbon agricultural development compensation to farmers to enhance their enthusiasm.
By promoting the policy of returning farmland to forests and grasslands, more low- and medium-yield fields (such as slopes, barren mountains, and wasteland) can be transformed into forests and grasslands, thereby increasing the carbon sequestration capacity of these two ecosystems. The frequent land use transformation between arable land, forests, and grasslands should focus on protecting high-quality arable land and reducing destructive encroachment behavior. The forest area in the BSRNC is large and existing forest land should be strictly controlled from being converted to other types of land. Urban development boundaries should be delineated and urban scale should be effectively controlled to improve the utilization efficiency of construction land. The expansion of urban green space and the construction of ecological cities should be promoted. Village land should be scientifically planned and projects such as village consolidation and old village renovation should be carried out. For the inefficient land use with scattered layout and poor ecological environment in some urban-rural fringe areas of the BSRNC, carbon emissions should be reduced.
To promote the green development objectives and achieve sustainable growth, it is suggested to leverage the role of a market economy and establish a carbon rights trading market. Additionally, it is important to construct a high-quality, highly liquid, mandatory, and intelligent system for carbon emission certification and trading. In order to effectively implement these measures, relevant policy frameworks need to be improved. It is crucial to actively explore green development policy mechanisms that are effective in achieving policy objectives. This includes establishing ecological and environmental element quotas, such as carbon emission quotas and pollutant emission quotas, that can be utilized by different regions and stakeholders. Furthermore, policies should reflect fairness in terms of ecological benefit sharing, ecological maintenance costs and responsibilities, ecological element allocation, and ecological-economic benefit exchanges. Feasibility factors should also be taken into full consideration to ensure the practicality and effectiveness of these policies, thereby driving genuine green transformation across society. Efforts should be made to develop regional green collaborative development policies based on balanced interests. This involves promoting market systems that facilitate the optimal allocation of ecological and environmental elements among market participants, including carbon emission rights, pollution emission rights, and carbon sink trading.
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
5.1. Conclusions
This study was based on seven periods of remote sensing data from 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 in the BSRNC. Using ArcGIS10.2, the current land use status of the BSRNC in the past 30 years was extracted and analyzed. Previous experience coefficients were referenced and the carbon emissions of different land use types in the BSRNC were calculated using the relevant carbon emission estimation methods from the ”2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories”. The spatial variation in carbon emissions from land use in the BSRNC was analyzed using the Moran’s I. Finally, the LMDI model was used to analyze the influencing factors of land use carbon emissions in the BSRNC from 1990 to 2020.
(1) During the study period, cultivated land and construction land were the main sources of carbon emissions in the BSRNC. The carbon emissions from land use showed a significant increasing trend, while carbon absorption gradually decreased. The total carbon emissions in the study area increased from 11.91 × 104 t in 1990 to 253.29 × 104 t in 2020. Cultivated land was the main source of carbon, with carbon emissions rapidly increasing from 963.35 × 104 t in 1990 to 1103.78 × 104 t in 2020, with a growth rate of 0.49%. Forest land accounted for more than 96% of the total carbon absorption but still could not offset the carbon emissions from cultivated land.
(2) The total carbon emissions in most counties in the study area showed a continuous increasing trend, and the spatial distribution was in an agglomeration state, but the spatial agglomeration phenomenon gradually weakened, and the difference in emissions between regions gradually decreased.
(3) Per capita GDP made the largest contribution to the growth of carbon emissions, resulting in an accumulated increase of 1398.35 × 104 t in carbon emissions. Land use structure, land carbon emission intensity, and population size caused increases of 213.44 × 104 t, 186.26 × 104 t, and 173.95 × 104 t, respectively, in carbon emissions. In comparison, land use efficiency had a restraining effect on carbon emissions, and with the increase in land use intensity, the restraint of land use efficiency also increased, resulting in a total reduction of 1730.63 × 104 t in carbon emissions.
5.2. Limitations and Future Directions
There have been significant differences in the carbon emission coefficients of land use in various regions due to differences in geographical location, latitude and longitude, and climatic conditions. It is difficult to determine the special coefficients for each city in the BSRNC. This study follows the previous research approach, using the same coefficients to estimate the carbon emission levels of different cities in the region. However, this method leads to uncertainty as it cannot identify differences among cities. Furthermore, the impact of administrative division adjustments on the accurate estimation of carbon emissions for different research units and the regional differences cannot be neglected.
Therefore, future research on land use carbon emissions needs to consider more factors and improve the calculation methods to increase accuracy. The research units need to be further refined to more accurately measure the relationship and differences in carbon emissions from land use in different regions, providing a basis for achieving low-carbon goals in the BSRNC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C. and Q.L.; methodology, L.C.; validation, L.C., Y.H. and Q.L.; formal analysis, L.C.; investigation, L.C. and Q.L.; resources, Q.L.; data curation, L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C.; writing—review and editing, L.C., Y.H. and Q.L.; visualization, L.C.; supervision, L.C. and Q.L.; project administration, L.C.; funding acquisition, Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2021M700738 and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2022T150103.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or other restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, M.; Li, M.; Xia, B. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Ecosystem Service Value in Response to Land-Use/Cover Changes in the Pearl River Delta. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Inácio, M.; Neves, O.; Almeida, A.A.; Pinto, E.; Oliveiros, B.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. Human Health Risk Assessment Due to Agricultural Activities and Crop Consumption in the Surroundings of an Industrial Area. Expo Health 2020, 12, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.S.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. Heavy Metals of Santiago Island (Cape Verde) Alluvial Deposits: Baseline Value Maps and Human Health Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yuan, X. Region-County Characteristic of Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factor on Land Use-Related CO2 Emissions in Chongqing of China, 1997–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, T.N.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Kittel, T.G.F.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Simulated Impacts of Historical Land Cover Changes on Global Climate in Northern Winter. Clim. Dyn. 2000, 16, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.K.; Solomon, A.M.; Brown, S.; Houghton, R.A.; Trexier, M.C.; Wisniewski, J. Carbon Pools and Flux of Global Forest Ecosystems. Science 1994, 263, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Zhang, K.; Radhamani, A.V. The Role of Carbon Capture and Storage in the Energy Transition. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 7364–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Burney, J.A.; Pongratz, J.; Nabel, J.E.M.S.; Mueller, N.D.; Jackson, R.B.; Davis, S.J. Global and Regional Drivers of Land-Use Emissions in 1961–2017. Nature 2021, 589, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Frolking, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, G. Urbanization Contributes Little to Global Warming but Substantially Intensifies Local and Regional Land Surface Warming. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, S.; Fan, J.; Cai, Y. Examining the Effects of Land Use on Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A. Magnitude, Distribution and Causes of Terrestrial Carbon Sinks and Some Implications for Policy. Clim. Policy 2002, 2, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quay, P.D.; Tilbrook, B.; Wong, C.S. Oceanic Uptake of Fossil Fuel CO2: Carbon-13 Evidence. Science 1992, 256, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.-M.; Han, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, B.; Liang, Q.-M.; Yuan, X.-C.; Chang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liao, H.; Tang, B.; et al. Self-Preservation Strategy for Approaching Global Warming Targets in the Post-Paris Agreement Era. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.A.; House, J.I.; Pongratz, J.; van der Werf, G.R.; DeFries, R.S.; Hansen, M.C.; Le Quéré, C.; Ramankutty, N. Carbon Emissions from Land Use and Land-Cover Change. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5125–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Deng, J.; Zhou, M.; Gan, M.; Jiang, R.; Wang, K.; Shahtahmassebi, A. Carbon Emissions Induced by Land-Use and Land-Cover Change from 1970 to 2010 in Zhejiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knodt, M.; Schoenefeld, J.J. Harder Soft Governance in European Climate and Energy Policy: Exploring a New Trend in Public Policy. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2020, 22, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhne, N.; Gidden, M.J.; den Elzen, M.; Hans, F.; Fyson, C.; Geiges, A.; Jeffery, M.L.; Gonzales-Zuñiga, S.; Mooldijk, S.; Hare, W.; et al. Wave of Net Zero Emission Targets Opens Window to Meeting the Paris Agreement. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Guo, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H. Variation of Net Carbon Emissions from Land Use Change in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region during 1990–2020. Land 2022, 11, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Dong, Y.; Ren, B.; Geng, Y. Land Use/Cover Changes in the Oriental Migratory Locust Area of China: Implications for Ecological Control and Monitoring of Locust Area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosan, T.M.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Ganzenmüller, R.; O’Sullivan, M.; Pongratz, J.; Mercado, L.M.; Aragao, L.E.O.C.; Heinrich, V.; Randow, C.V.; Wiltshire, A.; et al. A Multi-Data Assessment of Land Use and Land Cover Emissions from Brazil during 2000–2019. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 074004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, C. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emissions in China. Land 2021, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Aziz, N.; Raza, A. Short and Long-Run Causal Effects of Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use on Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Evidence from China Using VECM Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2021, 28, 64419–64430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Liu, Z.; Luo, M.; Fang, C.; Lin, H. The Effects of Anthropogenic Land Use Changes on Climate in China Driven by Global Socioeconomic and Emission Scenarios. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 784–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.S.; Andres, R.J.; Marland, G. China: Emissions Pattern of the World Leader in CO2 Emissions from Fossil Fuel Consumption and Cement Production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L08806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Jiang, J.; Li, C.; Miao, L.; Tang, J. Quantification and Driving Force Analysis of Provincial-Level Carbon Emissions in China. Appl. Energy 2017, 198, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Hay, I.; Huang, X. Decoding National New Area Development in China: Toward New Land Development and Politics. Cities 2019, 87, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Niu, D.; Zhou, W.; Fan, Y. Decomposition Analysis of Carbon Emissions from Energy Consumption in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China: A Weighted-Combination Model Based on Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index and Shapley Value. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Meng, J.; Reiner, D.M.; Zhang, N.; Shan, Y.; Mi, Z.; Shao, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Davis, S.J. Structural Decline in China’s CO2 Emissions through Transitions in Industry and Energy Systems. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Wei, W.; Davis, S.J.; Ciais, P.; Bai, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hubacek, K.; Marland, G.; et al. Reduced Carbon Emission Estimates from Fossil Fuel Combustion and Cement Production in China. Nature 2015, 524, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Meng, J.; Guan, D.; Shan, Y.; Song, M.; Wei, Y.-M.; Liu, Z.; Hubacek, K. Chinese CO2 Emission Flows Have Reversed since the Global Financial Crisis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Peng, W. Exploring Spatiotemporal Variation of Carbon Storage Driven by Land Use Policy in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Land 2021, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pei, J.; Geng, J.; Niu, Z. Tracking the Spatial–Temporal Evolution of Carbon Emissions in China from 1999 to 2015: A Land Use Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Niu, H.; Guo, J.; Zhao, S.; Fan, L. Carbon Storage Change Analysis and Emission Reduction Suggestions under Land Use Transition: A Case Study of Henan Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wen, X.; Guo, Y.; Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Spatiotemporal Variability of Carbon Flux from Different Land Use and Land Cover Changes: A Case Study in Hubei Province, China. Energies 2014, 7, 2298–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienert, S.; Joos, F. A Bayesian Ensemble Data Assimilation to Constrain Model Parameters and Land-Use Carbon Emissions. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2909–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. Net Carbon Flux from Agriculture: Carbon Emissions, Carbon Sequestration, Crop Yield, and Land-Use Change. Biogeochemistry 2003, 63, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, M.; Gingrich, S.; Roux, N.; Le Noë, J.; Kastner, T.; Matej, S.; Schwarzmueller, F.; Erb, K.-H. Quantifying and Attributing Land Use-Induced Carbon Emissions to Biomass Consumption: A Critical Assessment of Existing Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Raza, M.Y. Analysis of Energy Related CO2 Emissions in Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Dong, B.; Gu, G.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q. Carbon Emissions from Energy Consumption in China: Its Measurement and Driving Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, D. Industrial Energy-Related CO2 Emissions and Their Driving Factors in the Yangtze River Economic Zone (China): An Extended LMDI Analysis from 2008 to 2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Min, W.; Liu, H. Decomposition and Decoupling Analysis of Carbon Emissions from Cultivated Land Use in China’s Main Agricultural Producing Areas. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Li, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z. Dynamic Evolution of Regional Discrepancies in Carbon Emissions from Agricultural Land Utilization: Evidence from Chinese Provincial Data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpel, J.; Schüngel, J.; Schaldach, R.; Meurer, K.H.E.; Jungkunst, H.F.; Franko, U.; Boy, J.; Strey, R.; Strey, S.; Guggenberger, G.; et al. Future Land Use and Land Cover in Southern Amazonia and Resulting Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agricultural Soils. Reg. Environ. Change 2018, 18, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehr, R.; Munger, J.W.; Nelson, D.D.; McManus, J.B.; Zahniser, M.S.; Wofsy, S.C.; Saleska, S.R. Long-Term Eddy Covariance Measurements of the Isotopic Composition of the Ecosystem–Atmosphere Exchange of CO2 in a Temperate Forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 181, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, G.G. Changes in Forest Biomass Carbon Storage in the South Carolina Piedmont between 1936 and 2005. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y. Spatial Patterns of Vegetation Carbon Sinks and Sources under Water Constraint in Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Rasmussen, J.; Eriksen, J. Grassland Carbon Sequestration and Emissions Following Cultivation in a Mixed Crop Rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 153, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanca, P.; Vuichard, N.; Campbell, C.; Viovy, N.; Cozic, A.; Fuhrer, J.; Soussana, J.-F. Simulating the Fluxes of CO2 and N2O in European Grasslands with the Pasture Simulation Model (PaSim). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Banner, J.L.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Pockman, W.T.; Wall, D.H. Ecosystem Carbon Loss with Woody Plant Invasion of Grasslands. Nature 2002, 418, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, R.; Lu, J. Spatiotemporal Changes of Built-Up Land Expansion and Carbon Emissions Caused by the Chinese Construction Industry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13021–13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hu, S.; Frazier, A.E. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors of Carbon Emissions in Three Industrial Land Spaces in China from 1997 to 2016. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 169, 120837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Spatial Spillover Effect and Driving Forces of Carbon Emission Intensity at the City Level in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Lv, Q.; Wang, Y.D. Economic Development, Technological Progress, and Provincial Carbon Emissions Intensity: Empirical Research Based on the Threshold Panel Model. Appl. Econ. 2022, 54, 3495–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Chuai, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Thompson, J.R. Carbon Emissions from Land-Use Change and Management in China between 1990 and 2010. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Yang, R. Influence of Different Geographical Factors on Carbon Sink Functions in the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, R. Determinants of Decoupling Economic Output from Carbon Emission in the Transport Sector: A Comparison Study of Four Municipalities in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.; Lu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, D. Provincial Cultivated Land Use Efficiency in China: Empirical Analysis Based on the SBM-DEA Model with Carbon Emissions Considered. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 151, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.C.; Matsumura, W. Changes in the GHG Emission Intensity in EU-15: Lessons from a Decomposition Analysis. Energy 2010, 35, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Shao, S.; Lin, B. Exploring the Driving Forces and Mitigation Pathways of CO2 Emissions in China’s Petroleum Refining and Coking Industry: 1995–2031. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Benjamin, N.I. Influencing Factors on Carbon Emissions in China Transport Industry. A New Evidence from Quantile Regression Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 150, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, R.; Cansino, J.M.; Rodas, J.A. Analysis of the Main Drivers of CO2 Emissions Changes in Colombia (1990–2012) and Its Political Implications. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández González, P.; Landajo, M.; Presno, M.J. Tracking European Union CO2 Emissions through LMDI (Logarithmic-Mean Divisia Index) Decomposition. The Activity Revaluation Approach. Energy 2014, 73, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y. Influencing Factors and Regional Discrepancies of the Efficiency of Carbon Dioxide Emissions in Jiangsu, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Sun, Y. Review on Carbon Emissions, Energy Consumption and Low-Carbon Economy in China from a Perspective of Global Climate Change. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.; Zhang, F.; Choi, K. Factorizing Changes in Energy and Environmental Indicators through Decomposition. Energy 1998, 23, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Skitmore, M.; Lu, W. The Impact of Urbanization on Carbon Emissions in Developing Countries: A Chinese Study Based on the U-Kaya Method. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L. Identifying the Key Impact Factors of Carbon Emission in China: Results from a Largely Expanded Pool of Potential Impact Factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.; Tian, M.; Ding, M.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chuai, X.; Xiao, L.; Yao, L. Impacts of Water and Land Resources Exploitation on Agricultural Carbon Emissions: The Water-Land-Energy-Carbon Nexus. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, R.; Dong, Y.-X.; Liu, Y.-X.; Qiu, L.-R. The Influence of Rapid Urbanization and Land Use Changes on Terrestrial Carbon Sources/Sinks in Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. The Relationship between Urbanization, Economic Growth and Energy Consumption in China: An Econometric Perspective Analysis. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5609–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing Urban Forms and Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China: A Case Study of 30 Provincial Capital Cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, T.; Ding, M.; Chuai, X. Carbon Emission of Regional Land Use and Its Decomposition Analysis: Case Study of Nanjing City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffhammer, M.; Carson, R.T. Forecasting the Path of China’s CO2 Emissions Using Province-Level Information. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2008, 55, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Duan, Z.; Shan, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.; Song, J.; Wang, X. Low-Carbon Developments in Northeast China: Evidence from Cities. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21010-2017; Current Land Use Classification. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=224BF9DA69F053DA22AC758AAAADEEAA (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- TSURUTA, H.; MOSIER, A. Estimate of CH_4 Emissions from Year-Round Flooded Rice Fields During Rice Growing Season in China. Pedosphere 2005, 15, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Yuan, X.; Li, B.; Yan, W. The Effects of Land Use Changes on Carbon Emission C: Take Chongqing as an Example. J. Chongqing Norm. Univ. 2012, 29, 38–42+115. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Mu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, M. Effects of Different Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emission in Guangyuan City of Sichuan Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 32, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, F.; Ou, Y. Carbon sequestration and its potential by wetland ecosystems in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Assessment, Prediction and Control of Carbon Emissions in Land Use Planning-A Case Study of Nanqiao Zone, Chuzhou, Anhui Province. Sci. Technol. Manag. Land Resour. 2010, 27, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, C.; Ma, L.; Li, Z.; Ni, W.; Song, S. Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) Decomposition of Coal Consumption in China Based on the Energy Allocation Diagram of Coal Flows. Energy 2015, 85, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X. Land-Use Carbon Emissions Estimation for the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration Using 1994–2016 Landsat Image Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, Y.; Guan, B.; Jing, X. Analysis of Energy Industry Upgrading in Northeast China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 113, 012121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Z.; Sun, J. Efficiency Evaluation of Energy in Northeastern China Based on Data Envelopment Analysis. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 5725850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, S.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. Carbon Emission Intensity Characteristics and Spatial Spillover Effects in Counties in Northeast China: Based on a Spatial Econometric Model. Land 2022, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.; Hou, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, Y. County-Level CO2 Emissions and Sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci Data 2020, 7, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).