Agrochemical Input Behavior and Cleaner Production Adoption Willingness of Farmers in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Probit Model Introduction
2.3.2. Variable Description
2.3.3. Model Building
2.3.4. Model Running
3. Results
3.1. Agrochemical Input
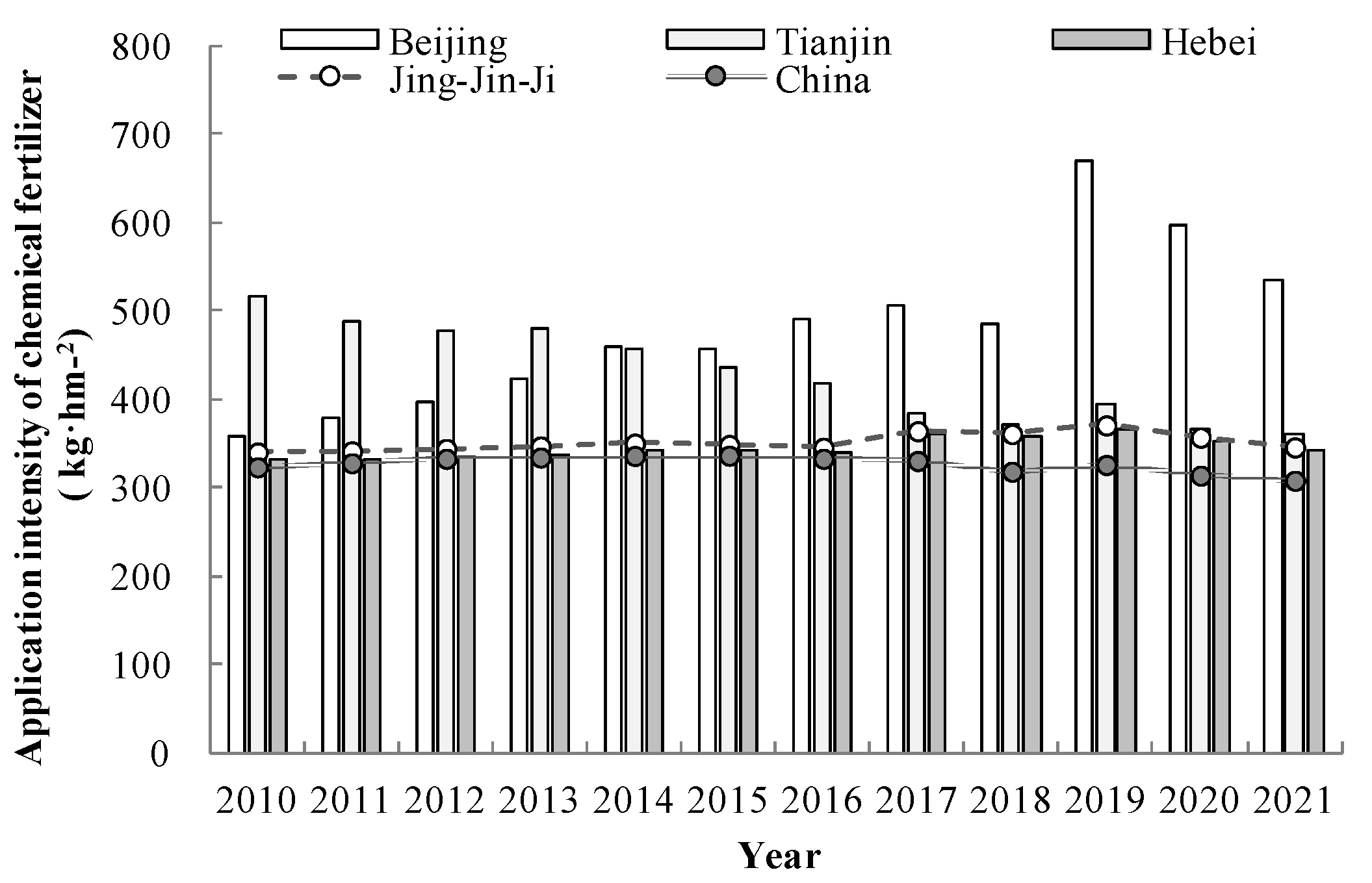
3.1.1. Total Quantity of Agrochemical Input
3.1.2. Application Intensity of Agrochemical Input
3.2. Farmers’ Behavior of Agrochemical Input
3.2.1. Different Kinds of Fertilizer Input
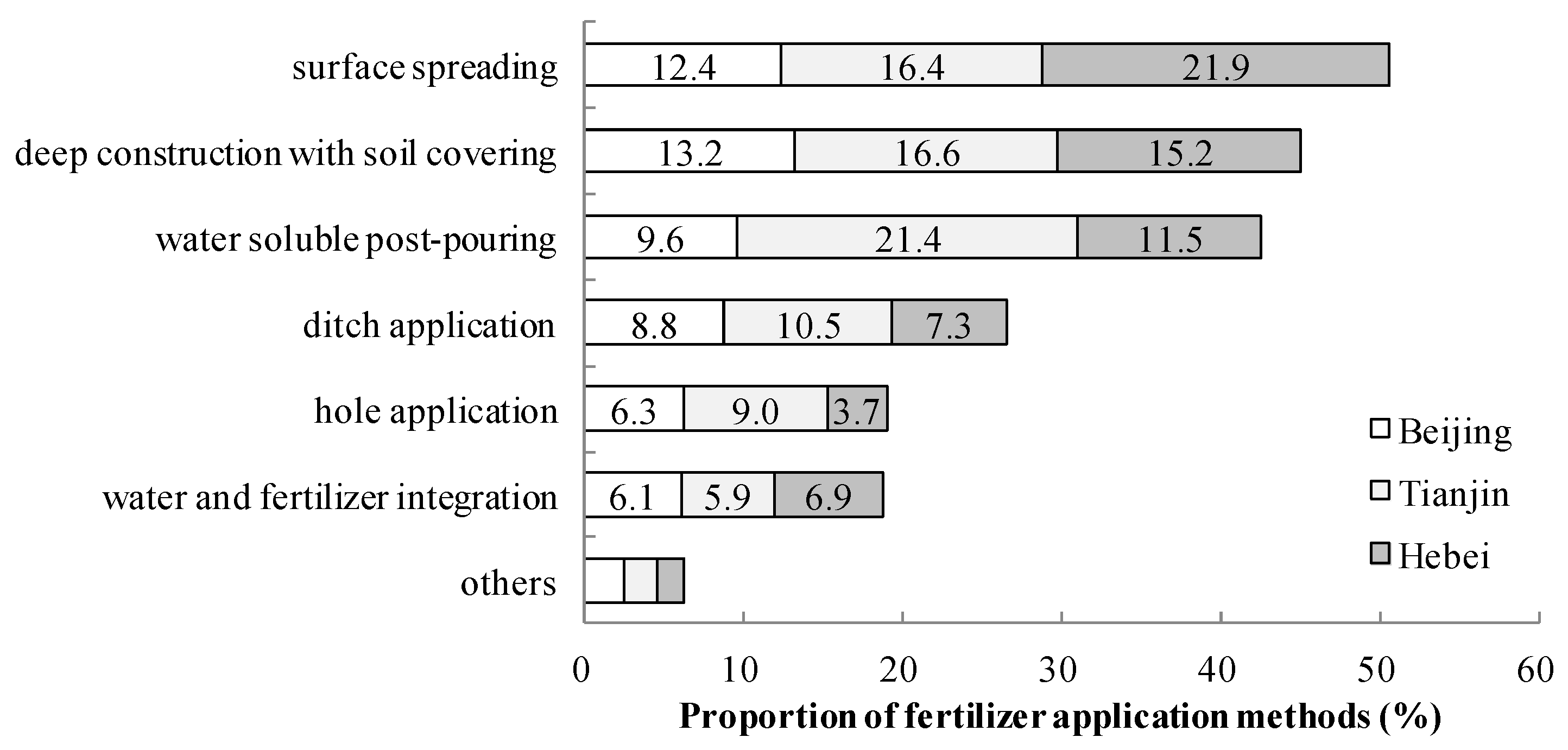
3.2.2. Fertilizer Application Method
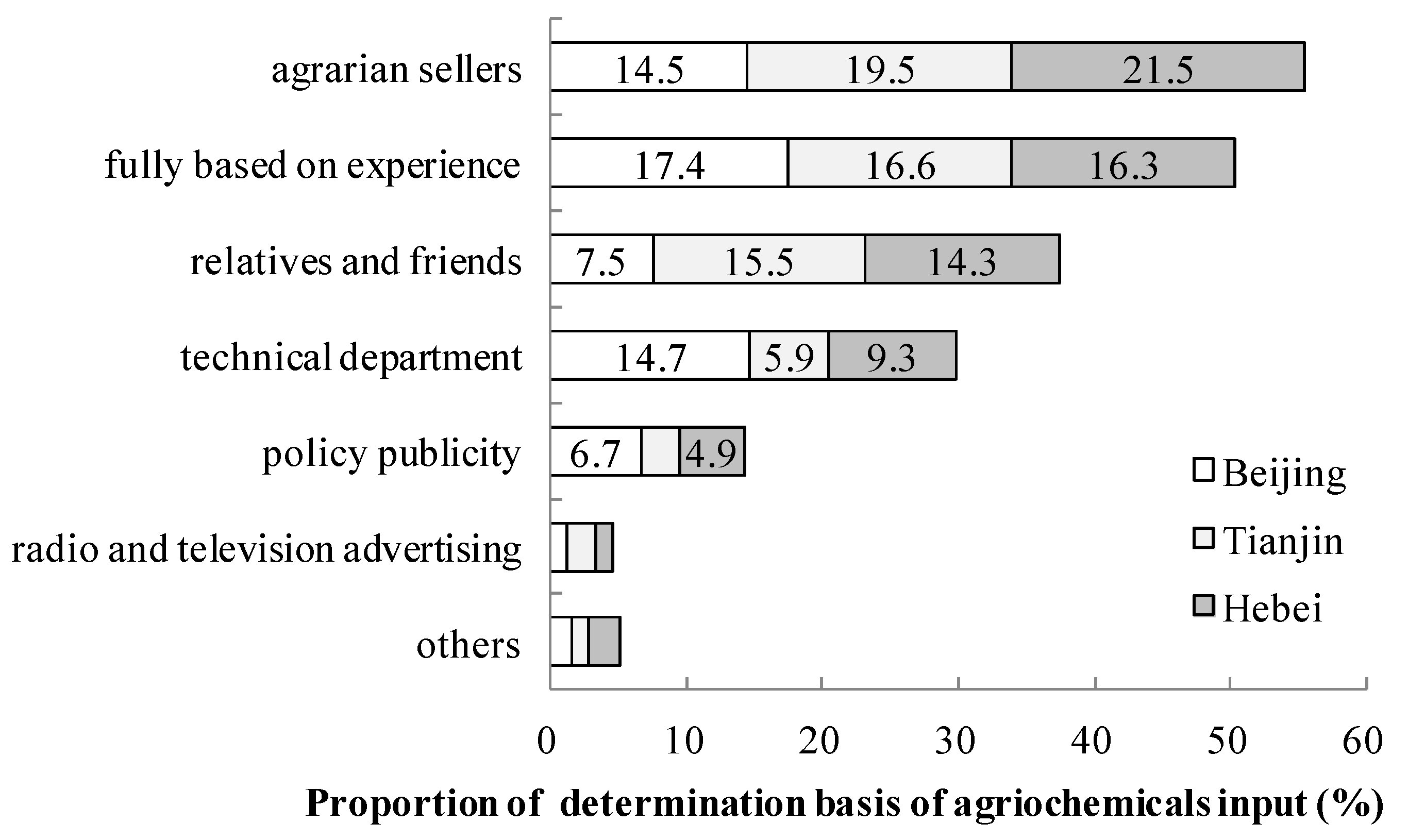
3.2.3. Agrochemical Use Determination
3.2.4. Treatment of Pesticide Packaging Waste
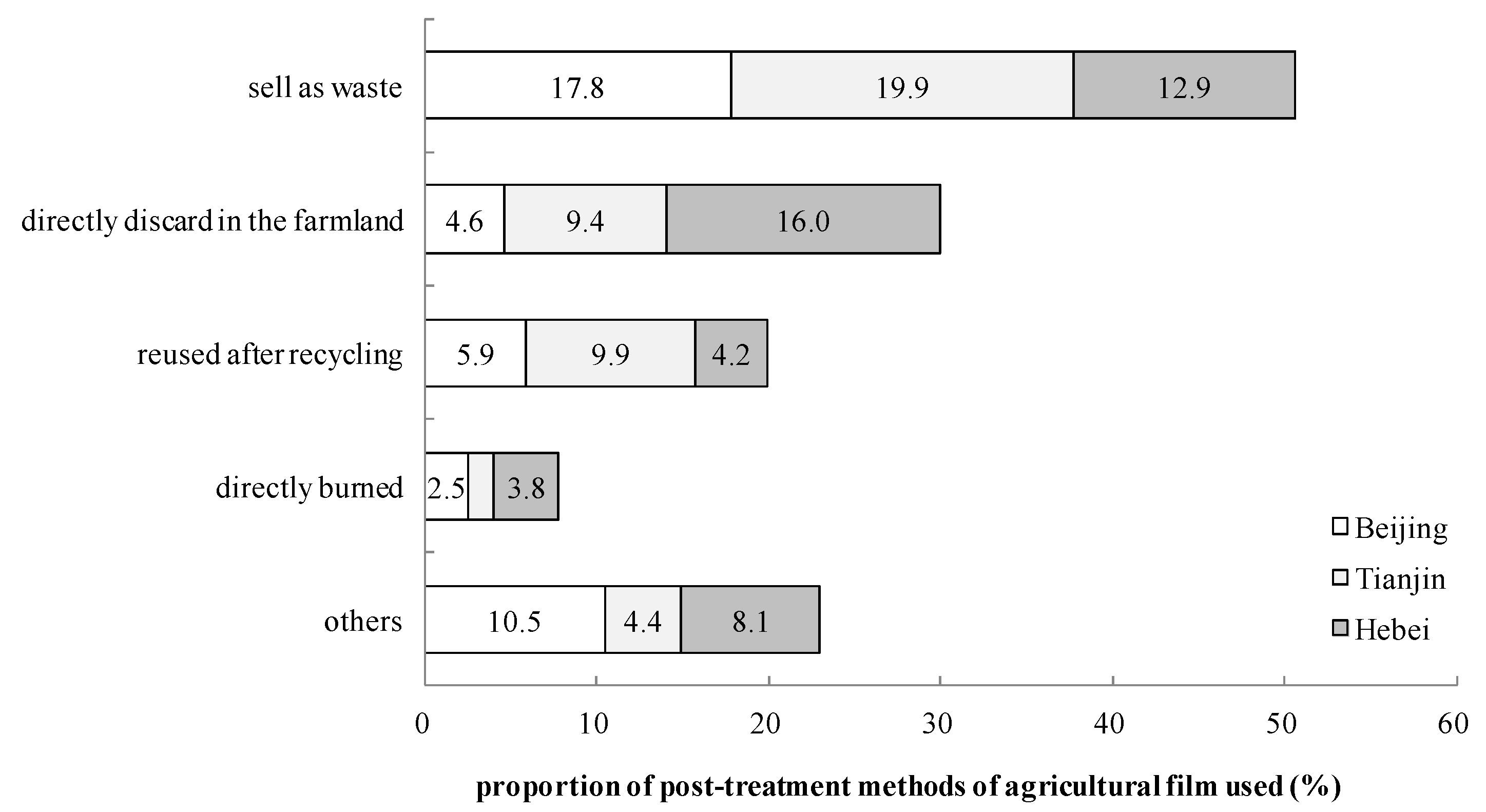
3.2.5. Disposal of the Agricultural Film
3.2.6. Application of Cleaner Agricultural Production Technology
3.3. Farmers’ Environmental Cognition
3.4. Influencing Factors of Farmers’ Behavior toward Agrochemical Input
3.5. Influencing Factors of Farmers’ Willingness to Adopt Cleaner Production
3.5.1. Age
3.5.2. Years of Planting
3.5.3. Types of Work
3.5.4. Viewpoint of Excessive Use of Agrochemicals
3.5.5. Cognition of the Pollution Degree
3.5.6. Urgency of Saving and Rational Use of Agrochemicals
3.5.7. Pre-Production Technical Guidance
3.5.8. Technical Training
4. Discussion
4.1. Positive Effects Resulting from Reducing Agrochemical Inputs
4.2. Strategies for Agrochemical Reduction and Effciency Improvement
4.2.1. Improve the Scientific Level and Promote the Reduction and Efficiency
4.2.2. Improve Farmers’ Willingness to Participate in and Promote Emission Reduction
4.2.3. Strengthen the Publicity and Training of Agricultural Technology Departments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.D.; Li, C.; Huang, Y. Study on regional differences of pesticide and fertilizer application in China based on provincial data. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chuan, L.M.; Zheng, H.G.; Wang, A.L.; Zhao, J.J.; Yan, Z.H.; Qi, S.J. Chemical fertilizer input characteristics, pollution prevention and control measures in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook 2020; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Zhuang, Z.; Mu, H.Y.; Fu, P.N.; Wan, Y.N.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.F. Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soil and scenario analysis of cadmium inputs by fertilization: A case study in Quzhou county. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.Q.; Kong, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Shan, Z.J. Pollution of chemical pesticides on environment and suggestion for prevention and control countermeasures. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.X.; Li, E.L.; Deng, Q.Q.; Cui, Z.Z. Characteristics of chemical fertilizer application and environmental risk assessment of three major food crops in China. Resour. Environ. YZ Basin 2019, 28, 2936–2947. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.X.; Meng, T.T.; Li, J.M.; Qiu, W. Changing from dry field to paddy field intensifying water pollution by nitrogen and phosphorus loads in Jiangchuan irrigation area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sjerps, R.M.A.; Kooij, P.J.F.; van Loon, A.; van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence of peptides in Dutch drinking water sources. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.H.; Huang, Z.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Tong, L.; Xiao, H. Pollution characteristics and spatial-temporal variation of organochlorine pollutants (OCs) in eastern areas of Ningbo city, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 787–797. [Google Scholar]
- Linhart, C.; Panzacchi, S.; Belpoggi, F.; Clausing, P.; Zaller, J.G.; Hertoge, K. Year-round pesticide contamination of public sites near intensively managed agricultural areas in South Tyrol. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to peptides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Qin, Q.Q.; Zhang, Z.G.; Yang, G.F. Effects of farmers’ behavior on agricultural non-point source pollution in Simian Mountain, Chongqing. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan. 2021, 42, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mugandani, R.; Mafongoya, P. Behavior of smallholder farmers towards adoption of conservation agriculture in Zimbabwe. Soil Use Manag. 2019, 35, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukchin, S.; Kerret, D. Food for hope: The role of personal resources in farmers’ adoption of green technology. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.Y. Study on Fertilizer Application Behavior and Influencing Factors of Large Growers in Henan Province. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, L. Study on influence factors of chemical fertilizer application intensity of households taking Xuzhou city of Jiangsu Province as an example. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2017, 49, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.J.; Shi, Q.H. The impacts of rural households’ productive characteristics on pesticide application: Mechanism and evidence. Chin. Rural Econ. 2019, 11, 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.J.; Peng, C.; Shi, Q.H. Study on the high chemical fertilizers consumption and fertilization behavior of small rural household in China: Discovery from 1995~2016 national fixed point survey data. J. Manag. World 2019, 35, 120–132. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.; He, J.Y.; Fu, Y.Z. Study on influencing factors of farmers’ safe pesticide application behavior-taking Zhejiang province as an example. Chin. Collec. Econ. 2020, 26, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, G.Y. Heterogeneity in adoption of technology by farmers and measurement of its technical efficiency -based on the survey data of 1208 farmers in Heilongjiang province. Rural Econ. 2020, 8, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.D.; Yu, Z.G. An empirical study on farmers’ willingness to reduce agricultural chemicals use and its influencing factors-Based on the questionnaire survey of 208 vegetable farmers in H Town, Shandong province. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 20, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Qi, Y.B. Analysis on the risk cognition of excess fertilizer application and the adoption behavior of environment-friendly technology and its reason-based on the survey of 380 citrus growers in Sichuan province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan. 2020, 41, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.Y. Study on the Influence of Incentive Policies of Cultivated Land Ecological Protection on Farmers’ Behavior-Based on the Analysis of Farmers’ Behavior of Fertilization and Application. Doctoral Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Li, H.; Xu, B.B. Green Cognition, reality, and farmers’ biological pesticide application behaviors—Explaining the deviation between farmers’ willingness and their behaviors. Res. Agric. Modern. 2020, 41, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.L.; Lu, X.Y. Research on farmers’ green control techniques adoption behavior and its effect evaluation. J. Chin. Agri. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2020, 37, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.D.; Li, X.Z. Farmers’ characteristics, external environment and scientific fertilization. J. South Chin. Agri. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 20, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.C.; Bashir, M.A.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.H.; Liu, X.T.; Li, F.; Wang, H.Y.; Raza, Q.U.A.; Rehim, A.; Zhang, X.J.; et al. Long-Term Fertilizer Reduction in Greenhouse Tomato-Cucumber Rotation System to Assess N Utilization, Leaching, and Cost Efficiency. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Y.; Muminov, M.A.; Wu, G.L.; Liang, X.T.; Li, C.H.; Meng, J.; Li, L.J.; Cheng, D.; Song, Y.J.; Gu, X.; et al. Large reductions in pesticides made possible by use of an insect-trapping lamp: A case study in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechenet, M.; Dessaint, F.; Py, G.; Makowski, D.; Munier-Jolain, N. Reducing pesticide use while preserving crop productivity and profitability on arable farms. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, J.W.; Xu, C.S.; Zhou, W.Q.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, X. Research progress analysis on key technology of chemical fertilizer reduction and efficiency increase. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Machin. 2019, 50, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.X. Analysis of factors influencing the willingness of organic fertilizer application in facility vegetable growers. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 22, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Jin, S.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Wu, S.X. Analysis of the reasons for overuse of chemical fertilizer-from a seller’s perspective. Strat. Study CAE 2018, 20, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.J. The Impact of Fertilizer Service Market Development on Fertilizer Use Behavior of Farmers with Different Farm Size—An Example of Fertilizer Dealers. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]




| Variables | Assignment | |
|---|---|---|
| Are you willing to rationally adjust the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and agricultural films? | Unwilling = 0, willing = 1 | |
| Are you willing to participate in the activities of reducing the amount and increasing efficiency? | Unwilling = 0, willing = 1 | |
| Farmers characteristics | Age | 30 years old and below = 1, 31~40 years old = 2, 41~50 years old = 3, 51~60 years old = 4, 61 years old and above = 5 |
| Education level | Junior middle school and below = 1, senior middle school = 2, associate or bachelor’s degree = 3, master’s degree and above = 4 | |
| Planting years | 5 years and below = 1, 6~10 years = 2, 11~20 years = 3, 21~30 years = 4, 31 years and above = 5 | |
| Identity category | Small-holder farmers = 1, large planting households = 2, agricultural cooperatives = 3 | |
| Types of work | Full-time agriculture = 1, part-time agriculture = 2, non-agricultural work = 3 | |
| Household income 1 | CNY 50,000 and below = 1, CNY 50,000~100,000 = 2, CNY 100,000~150,000 = 3, CNY 150,001 and above = 4 | |
| Cultivated land area | 0.2 ha and below = 1, 0.2~0.3 ha = 2, 0.3~0.6 ha = 3, 0.6~1.0 ha = 4, 1.0 ha and above = 5 | |
| Agrochemical input | Fertilizer cost | CNY 500 and below = 1, CNY 501~1000 = 2, CNY 1001~2000 = 3, CNY 2001~3000 = 4, CNY 3001~4000 = 5, CNY 4000 and above = 6 |
| Pesticide cost | CNY 200 and below = 1, CNY 201~400 = 2, CNY 401~600 = 3, CNY 601~800 = 4, CNY 801~1000 = 5, CNY 1001 and above = 6 | |
| Agricultural film cost | CNY 0 = 1, CNY 1~1000 = 2, CNY 1001~2000 = 3, CNY 2001~3000 = 4, CNY 3001 and above = 5 | |
| Environmental awareness | Is the amount of fertilizer used clear? | No = 0, yes = 1 |
| Is there overuse? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Do you pay attention to agricultural film pollution? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| What is the severity of pollution? | Not serious = 1, average = 2, serious = 3, very serious = 4 | |
| Do you think saving is necessary? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Are you aware of the urgency? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Technical cognition | Is there guidance before production? | No = 0, yes = 1 |
| Have you participated in training? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Do you receive subsidies? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Do you understand the zero growth action? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Do you know the agricultural film recycling plan? | No = 0, yes = 1 | |
| Variables | Are You Willing to Rationally Adjust the Use of Chemical Fertilizers, Pesticides and Agricultural Films | Are You Willing to Participate in the Activities of Reducing Amount and Increasing Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics of farmers | Age | −0.546 ** 1 | −1.013 *** 2 |
| Education level | −0.162 | 0.434 | |
| Planting years | −0.455 * 3 | −0.418 * | |
| Identity category | 0.636 | −0.44 | |
| Types of work | −1.172 *** | −0.362 | |
| Household income | −0.326 | −0.158 | |
| Cultivated land area | 0.057 | −0.076 | |
| Agrochemical input | Fertilizer cost | −0.268 | −0.137 |
| Pesticide cost | −0.041 | 0.132 | |
| Agricultural film cost | −0.215 | −0.301 | |
| Environmental cognition | Is the amount of fertilizer used clear? | 0.014 | 0.206 |
| Is there an overuse problem? | 1.272 ** | 0.858 ** | |
| Are you concerned about white pollution? | 0.315 | 0.344 | |
| What is the severity of pollution? | 0.739 ** | 0.419 * | |
| Do you think saving is necessary? | 0.759 | 1.260 ** | |
| Are you aware of the urgency? | 1.615 *** | 0.363 | |
| Technical cognition | Is there guidance before production? | 1.602 ** | 1.498 ** |
| Have you participated in training? | −0.079 | 1.196 ** | |
| Do you receive subsidies? | −0.270 | −0.389 | |
| Do you understand the zero growth action? | 0.028 | −0.354 | |
| Do you know the agricultural film recycling plan? | 0.264 | 0.915 | |
| Constant | 4.101 ** | 0.038 | |
| Number | 413 | 413 | |
| Prob > Chi 2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Log likelihood | −68.251 | −73.951 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuan, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Shan, N.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A. Agrochemical Input Behavior and Cleaner Production Adoption Willingness of Farmers in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118479
Chuan L, Zhao J, Zhao J, Shan N, Zhang H, Wang A. Agrochemical Input Behavior and Cleaner Production Adoption Willingness of Farmers in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118479
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuan, Limin, Jiang Zhao, Jingjuan Zhao, Nan Shan, Hui Zhang, and Ailing Wang. 2023. "Agrochemical Input Behavior and Cleaner Production Adoption Willingness of Farmers in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118479
APA StyleChuan, L., Zhao, J., Zhao, J., Shan, N., Zhang, H., & Wang, A. (2023). Agrochemical Input Behavior and Cleaner Production Adoption Willingness of Farmers in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Sustainability, 15(11), 8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118479





