Scientometrics-Based Research Status and Hot Topics Analysis of Chinese Private Colleges under Policy Guidance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Source and Methods
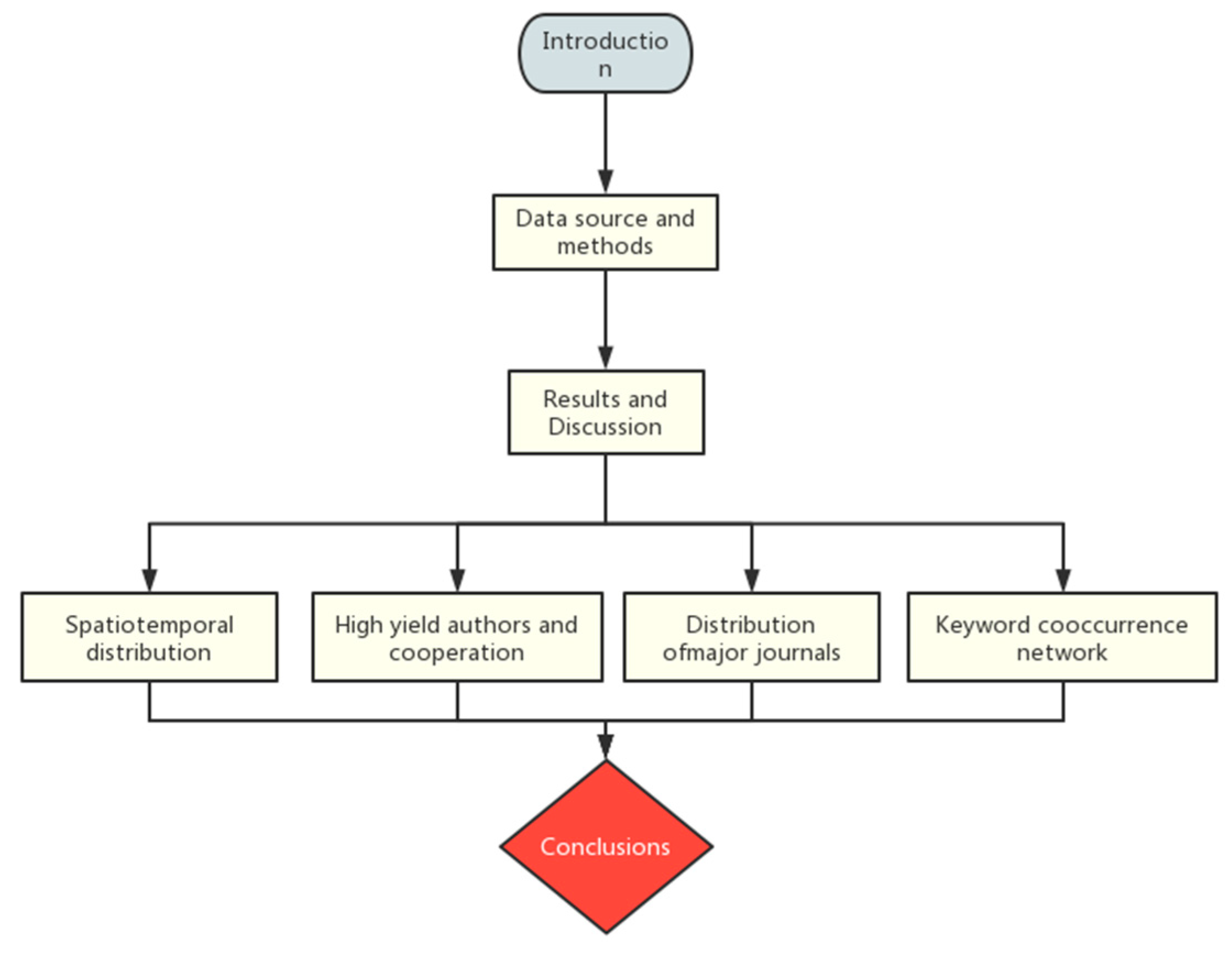
3. Results and Discussion
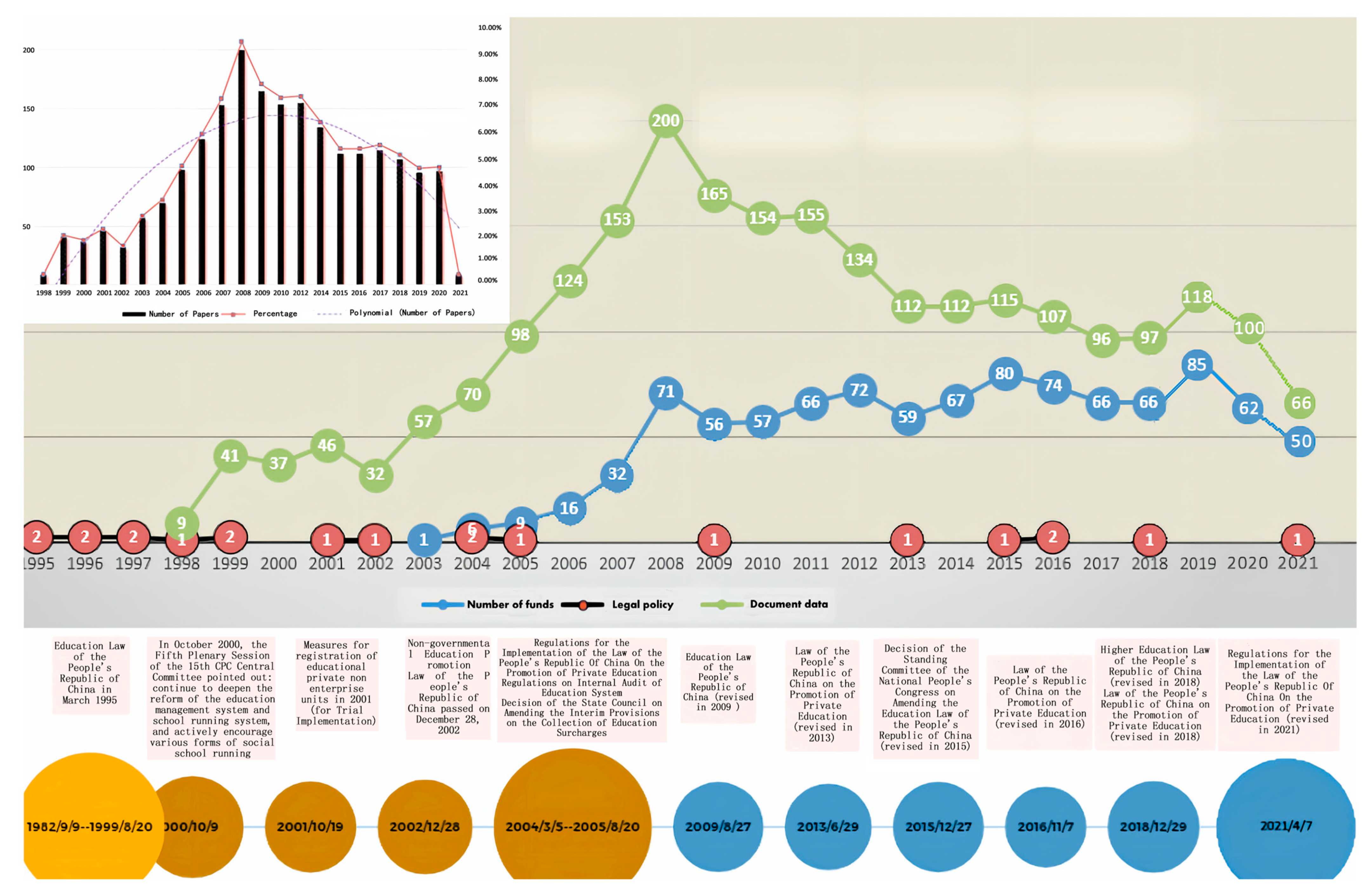
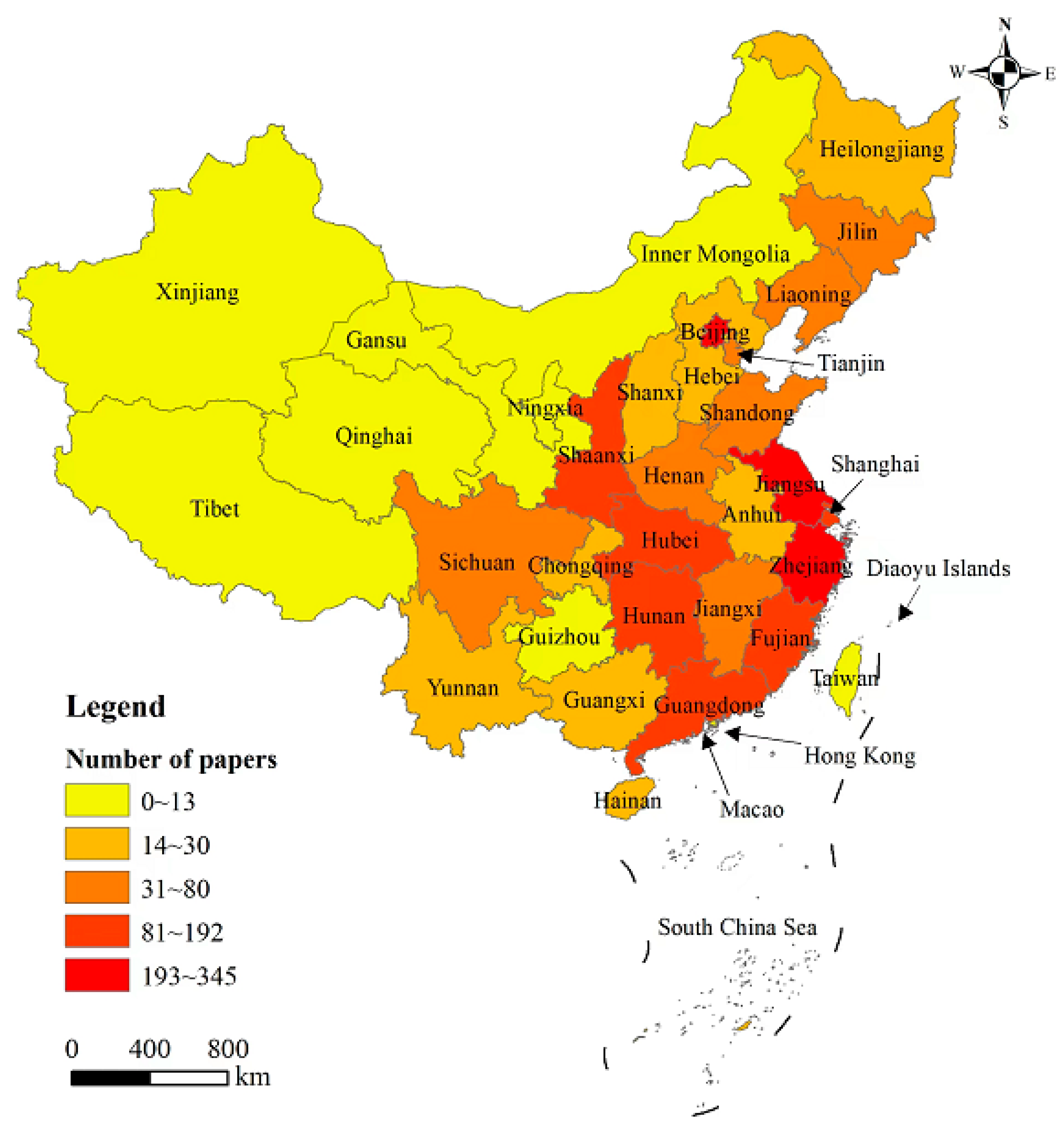
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution
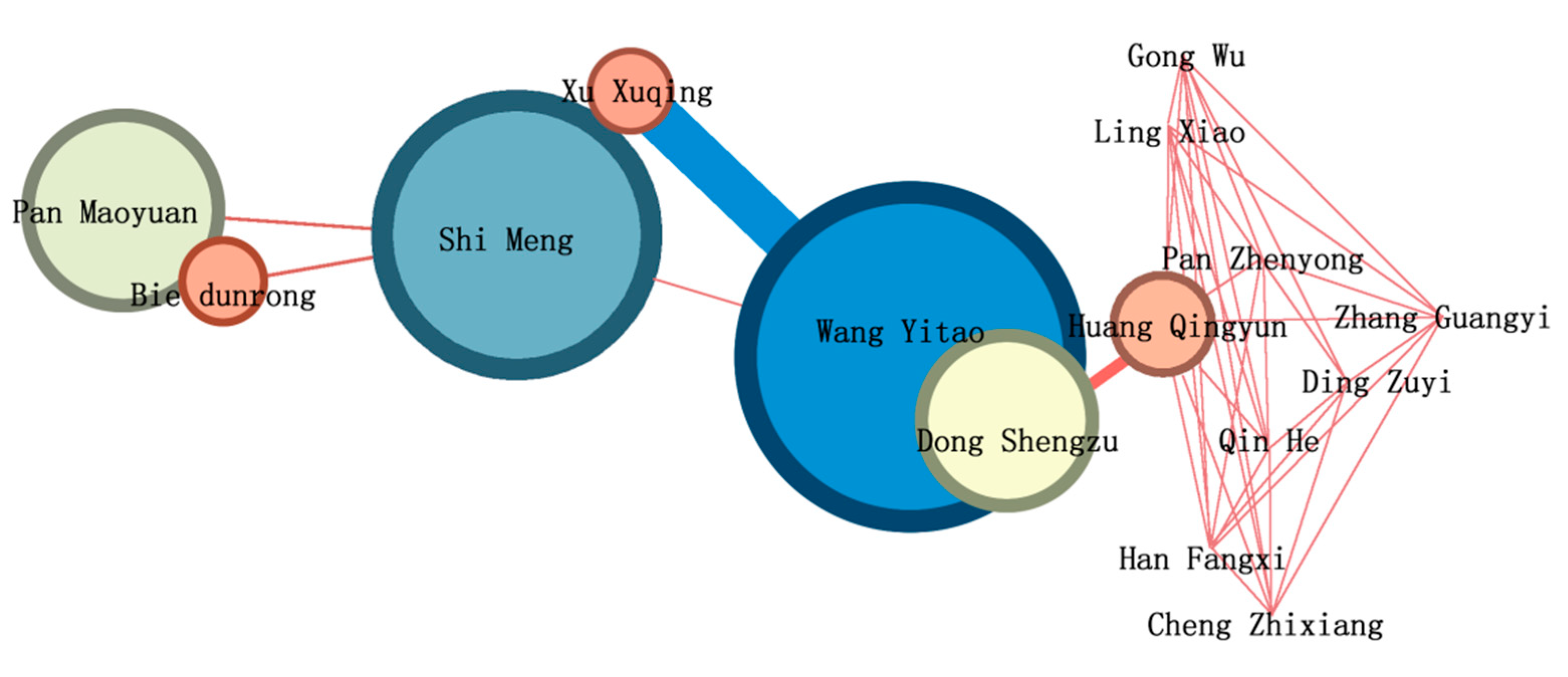
3.2. High Yield Authors and Cooperation
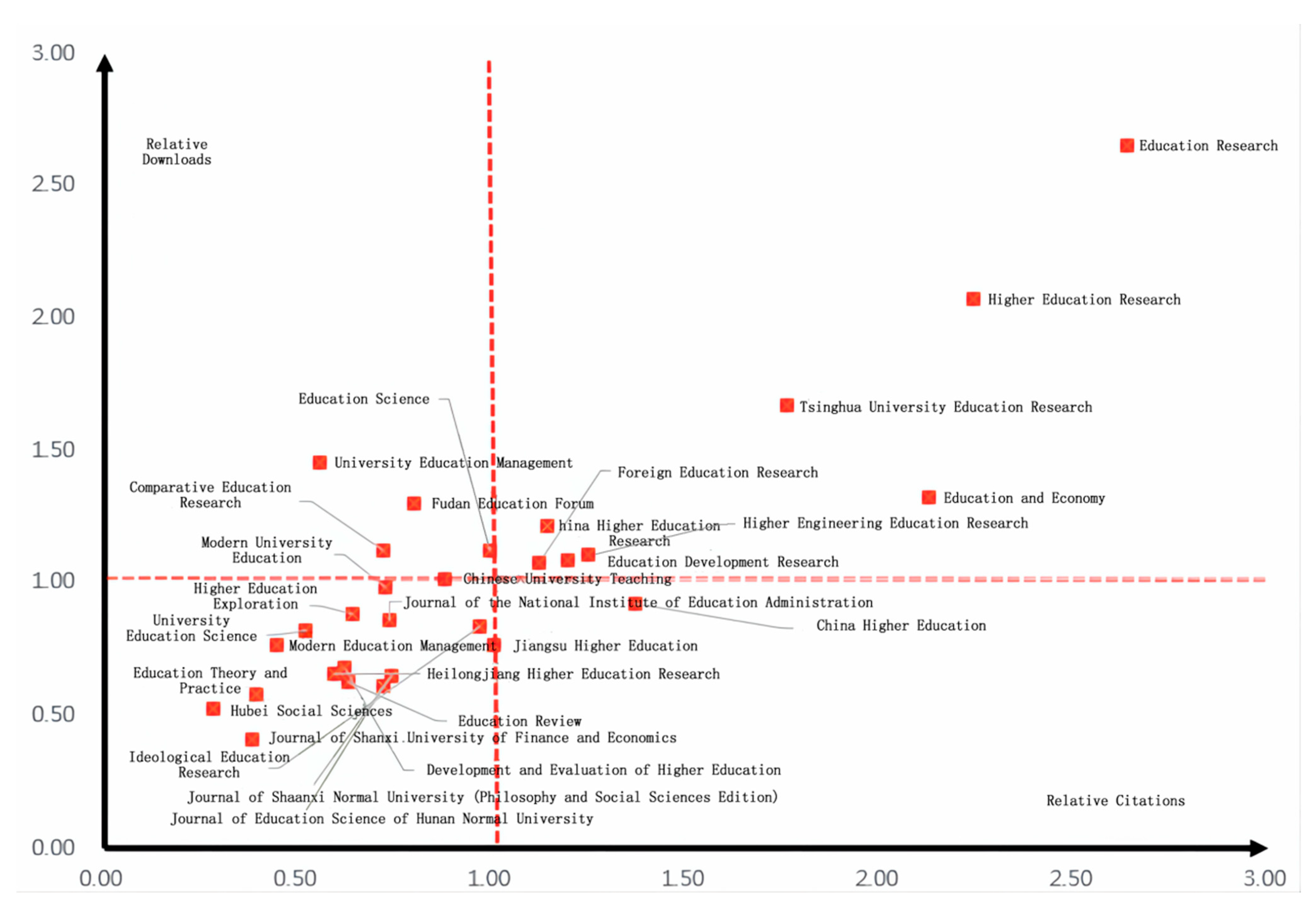
3.3. Distribution of Major Journals
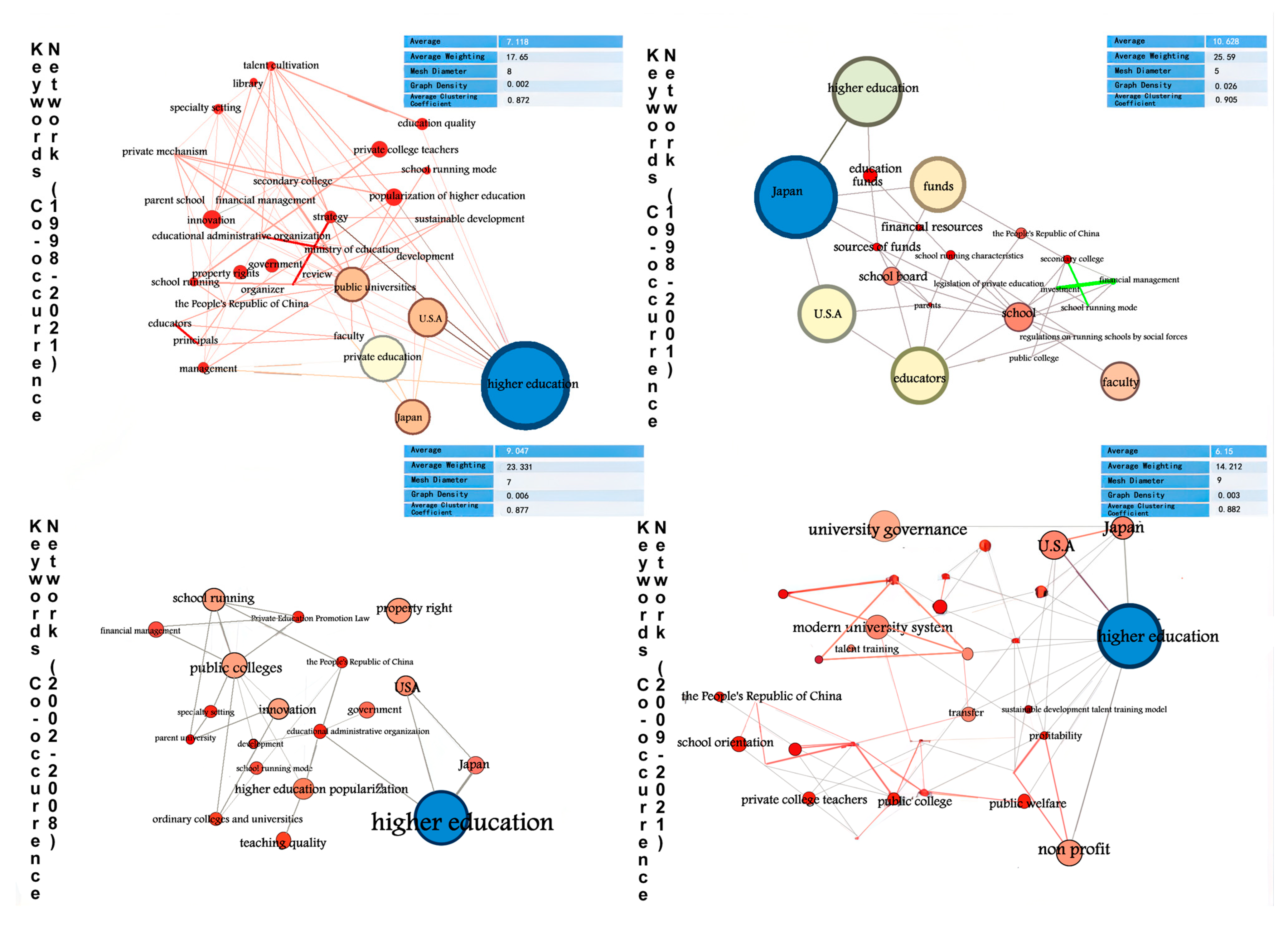
3.4. Keyword Cooccurrence Network
3.4.1. The First Stage (1998–2001): The Leading Period of Private University Research
3.4.2. The Second Stage (2002–2008): The Growth Period of Private University Research
3.4.3. The Third Stage (2009–2021): The Adjustment Period of Private University Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P. Research on the Development of Private Universities in Liaoning Province; Dongbei University of Finance and Economics: Dalian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Omus, R.M. International Comparative Education: Practice, Issue and Prospects; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H. Comparative analysis of the development of private education at home and abroad. J. Linyi Norm. Univ. 2006, 2, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Higher Education: The Lessons of Experience; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D. Analysis on the marketization characteristics and policy trend of private higher education in China. China High. Educ. 2001, 11, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, H. The road to becoming a strong country in Higher Education—How far is China from a strong country in Higher Education in the world? Educ. Res. Tsinghua Univ. 2010, 1, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.-Y. A Study on Changing Roles of Market and Government in High School Economic Education of China; Korean Association for Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction: Anyang, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shank, M.; Walker, M.; Hayes, T. Understanding professional service expectations: Do we know what our students expect in a quality education? Serv. Mark. Q. 1995, 13, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, A. Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. J. Doc. 1969, 25, 348. [Google Scholar]
- Garfield, E. Citation indexes for science. A new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhu, T. Theoretical fallacy and its harm: Take the Theory of Higher Education Industrialization as an Example. Mod. Univ. Educ. 2006, 6, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Law of the People’s Republic of China on Compulsory Education (2018 Revision)-Peking University Magic Treasure Official Website. Available online: pkulaw.com (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Chae, J.-E.; Hong, H.K. The expansion of higher education led by private universities in Korea. Asia Pac. J. Educ. 2009, 29, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Exploring the potential rationale for the privatization of higher education in China. Asia Pac. J. Educ. 2011, 31, 421–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. Prospects of Private Education in China. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2009, 42, 40–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W. Formational Mechanism and Regional Growth Patterns of Private Higher Education in China. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2009, 42, 74–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Revitalizing Private Schools: Japan’s Important Measures for Developing through Education. Res. Educ. Dev. 1999, 6, 27–30, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Ehara, T.; Sugimoto, H. Great Management Reform-Japan’s Trend and Other Foreign Trends, 1st ed.; Eastcom Hall: Tokyo, Japan, 2005; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.A. Demographic factors, compensation, job satisfaction and organizational commitment in private university:an analysis using SEM. J. Glob. Responsib. 2020, 11, 407–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, Y. Competitive Finance and Reform; Modern Education: Hong Kong, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. The popularization of Japanese higher education from the perspective of higher education policy. Foreign Educ. Res. 1999, 1, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F. Policies on Private Education. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2009, 6, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, M.-H.; Jungblut, J.; Ravinet, P.; Vukasovic, M. Higher education governance and policy: An introduction to multi-issue, multi-level and multi-actor dynamics. Policy Soc. 2017, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Promote the sustained, healthy and rapid development of independent colleges and universities. Educ. Dev. Res. 2003, 8, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M. The Necessity and Content of Culture Teaching in Chinese Teaching in Senior High School. Chin Lit 2008, 57, 507–529. [Google Scholar]
- Si, R.; Gong, S.; Zou, X. Exploration on the training mode of applied innovative talents in independent colleges. Res. High. Eng. Educ. 2005, 1, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Leonnard, L. The performance of servqual to measure service quality in private university. J. Effic. Responsib. Educ. Sci. 2018, 11, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Hu, J. Research on the practice and innovation of application-oriented talent training mode in private colleges. Educ. Rev. 2018, 2, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Research on talent training mode of private colleges in the perspective of supply side structural reform. Contin. Educ. Res. 2018, 2, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W. Value chain management of talent training in private universities—From the perspective of human capital operation. High. Educ. Res. 2019, 8, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. Give play to the respective advantages of public and private universities, implement the concept of “one school, two systems” joint school running mode. Mod. Educ. Manag. 1997, 4, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K. A Critical Analysis of Accountability in Higher Education. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2009, 42, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Wu, M. The rise and prospect of independent colleges. China High. Educ. 2004, 13, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F. Effective governance of non-profit private colleges under the guidance of common values: Problems and ideas. Jiangsu High. Educ. 2019, 1, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z. A Study on the Mixed Ownership Reform in Vocational Colleges in China. J. Digit. Converg. 2022, 1, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, L. Research on educational donation of higher education institutions in China during the Republic of China era. Jiangsu High. Educ. 2018, 8, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Bao, R. The orientation and development of private universities in the new situation. Educ. Dev. Res. 2000, 12, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Tandberg, D.A. Politics, Interest Groups and State Funding of Public Higher Education. Res. High. Educ. 2010, 51, 416–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J. Exploration on the supply side structural reform of private colleges—From the perspective of the transformation and development of colleges and universities. China’s Adult Educ. 2017, 18, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S. From Beneficial Supplement to Common Development—The Road to Reform and Development of Private Education; East China Normal University Press: Shanghai, China, 2018; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Tandberg, D.A.; Fowles, J.T.; McLendon, M.K. The Governor and the State Higher Education Executive Officer: How the Relationship Shapes State Financial Support for Higher Education. J. High. Educ. 2017, 88, 110–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. Exploration of private higher education development fund on raising funds for managing private universities. Jiangsu High. Educ. 2001, 1, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen, R.G. Private Foreign-Affiliated Universities, the State, and Soft Power: The American University of Beirut and the American University in Cairo. Foreign Policy Anal. 2012, 8, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Bie, D.; Shi, M. On the commonweal and profit of private universities. Educ. Res. 2013, 3, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S. A Study on the Effect of Gender Differences on the Return to Chinese Higher Education based on CGSS Database. J. Chin. Stud. 2019, 63, 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, D.C. Public Policy for Private Higher Education: A Global Analysis. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. 2011, 13, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H. Research on Private College Teachers’ Incentive Mechanism in View of Potter-Lawler Model:Taking Shandong Province as an Example. High. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2013, 4, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, K.H.; Han, X. Higher education governance and policy in China: Managing decentralization and transnationalism. Policy Soc. 2017, 36, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B. An analysis of some important issues in the development of private higher education in China. China High. Educ. Res. 2011, 7, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.-S.; Rha, K.-H. Analyzing Recent Trends and Efforts for Developing Teaching Competences in China’s Higher Education. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2020, 20, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D. The development and innovation of private universities under the demand of Talents—A review of the reference study of the enterprise operation mode of private colleges in China on the management of public colleges and universities. China Educ. J. 2018, 9, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, K.H. The growing importance of the privateness in education: Challenges for higher education governance in China. Comp. J. Comp. Int. Educ. 2009, 39, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhou, H. Analysis of internal governance and power balance of non-profit private universities. Mod. Educ. Manag. 2018, 1, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H. Path Choice for Sustainable Development of Private Colleges; China Business Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 202–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Formulate the Law of Private Higher Education to regulate the behavior of private colleges. High. Educ. Res. 2021, 21, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S. Stories of the ‘Qualification-Building’ Experiences of Local Private College Job Seekers. J. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2017, 2, 161–194. [Google Scholar]
- Bilimoria, D.; Buch, K.K. The Search is On: Engendering Faculty Diversity through More Effective Search and Recruitment. Chang. Mag. High. Learn. 2010, 42, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.; Lankford, H.; Loeb, S.; Ronfeldt, M.; Wyckoff, J. The Role of Teacher Quality in Retention and Hiring: Using Applications-to-Transfer to Uncover Preferences of Teachers and Schools. J. Policy Anal. Manag. 2011, 30, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Cho, Y.-H. The Relationships among Distributed Leadership of University Organization, Administrative Staffs’ Self-Efficacy, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Commitment: Based on Comparison between National and Private Universities. In Korean Education Inquiry; The Research Institute of Korean Education: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
| Organization Name | Number of Articles Issued | Organization Name | Number of Articles Issued | Organization Name | Number of Articles Issued |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiamen University | 115 | Shanghai Normal University | 36 | Sanjiang University | 17 |
| Beijing Normal University | 90 | Suzhou University | 32 | Beijing City University | 16 |
| Peking University | 89 | Nanjing Normal University | 31 | Nankai University | 13 |
| Zhejiang Shuren University | 89 | Xi’an Institute of Foreign Affairs | 28 | Ningbo Dahongying University | 13 |
| Huazhong University of Science and Technology | 77 | Sichuan Normal University | 28 | Shandong Yingcai University | 12 |
| Zhejiang University | 75 | South China Normal University | 23 | Huanghe University of Science and Technology | 10 |
| WuHan University | 46 | Shanghai Jianqiao College | 23 | Hebei University | 9 |
| East China Normal University | 44 | Renmin University of China | 22 | Qingdao Huanghai University | 9 |
| Jiangxi Lantian School | 39 | Fudan University | 20 | Liaoning Education Research Institute | 7 |
| Hunan International Economics College | 33 | Tsinghua University | 18 | Jilin Huaqiao Foreign Languages Institute | 8 |
| Author | Frequency | Author | Frequency | Author | Frequency | Author | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang Yitao | 23 | Luo Kun | 8 | Xiao Hao | 6 | Zhong Binglin | 5 |
| Xu Xuqing | 15 | Liu Juqin | 8 | Zhou Guoping | 6 | Chen Zhidan | 5 |
| Que Haibao | 13 | Bo Yun | 7 | Wu Daguang | 5 | Jin Xin | 5 |
| Dong Shengzu | 10 | Zhang Liguo | 6 | Shi Meng | 5 | Liu Gendong | 5 |
| Pan Maoyuan | 9 | Zhu Jian | 6 | Chen Weixu | 5 | ||
| Chen Wuyuan | 9 | Bie Dunrong | 6 | Li guonian | 5 | ||
| Zhou Haitao | 9 | Pan Liuxian | 6 | Que Mingkun | 5 |
| Serial Number | Name | Issuance Frequency | Highest Cited Literature | Citation Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wang Yitao | 23 | Is education a public product?—Questioning a popular view | 99 |
| 2 | Xu Xuqing | 15 | Faculty construction: the foundation of sustainable development of private colleges | 61 |
| 3 | Que Haibao | 13 | Analysis and countermeasures on the construction of teaching staff in independent colleges | 37 |
| 4 | Dong Shengzu | 10 | Exploring “mixed ownership” in the field of Education: connotation, pattern and strategy | 59 |
| 5 | Pan Maoyuan | 9 | The classification and orientation of colleges and universities | 919 |
| 6 | Chen Wuyuan | 9 | Popularization of higher education: Japan’s experience and lessons | 83 |
| 7 | Zhou Haitao | 9 | An investigation and analysis of the students’ sense of gain in private colleges and universities in China | 111 |
| 8 | Luo Kun | 8 | The realization of industry-university-institute cooperation in local universities from the perspective of collaborative innovation | 50 |
| 9 | Liu Juqin | 8 | Reform the talent training program and cultivate high-quality applied talents | 61 |
| 10 | Bo Yun | 7 | Research on the funding policy of private higher education in Korea, Malaysia and the Philippines | 23 |
| Rank | Number of Documents Issued | Citation Frequency | Downloads |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Education Development Research (12.01%) | Education Development Research (14.37%) | Education Development Research (12.97%) |
| 2 | Higher Education in China (8.29%) | Higher Education Research (12.03%) | Higher Education Research (11.14%) |
| 3 | Higher Education Research (5.37%) | Higher Education in China (11.37%) | Higher Education in China (7.60%) |
| 4 | Jiangsu Higher Education (5.04%) | China Higher Education Research (5.75%) | China Higher Education Research (6.11%) |
| 5 | China Higher Education Research (5.04%) | Jiangsu Higher Education (5.06%) | Education Research (4.50%) |
| 6 | Higher Education Exploration (3.86%) | Education Research (4.47%) | Jiangsu Higher Education (3.87%) |
| 7 | Heilongjiang Higher Education Research (3.72%) | Higher Engineering Education Research (3.52%) | Higher Education Exploration (3.40%) |
| 8 | Modern Education Management (3.16%) | Education and Economy (2.50%) | Higher Engineering Education Research (3.12%) |
| 9 | Higher Engineering Education Research (2.83%) | Higher Education Exploration (2.44%) | Heilongjiang Higher Education Research (2.45%) |
| 10 | Journal of National Institute of Education Administration (2.40%) | Heilongjiang Higher Education Research (2.21%) | Modern Education Management (2.43%) |
| Dimension | Pearson Correlation Coefficient r | Significance (Bi-Side) P |
|---|---|---|
| Cited Frequency | 0.974 | 0.005 |
| Number of Downloads | 0.951 | 0.005 |
| Number of Documents Issued | 0.948 | 0.005 |
| Item | Description | More than 1 | Equal to 1 | Less than 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Citations of Journals | It refers to the ratio of the average citation frequency of a journal in a subject field to that of all journals in the same field. | The cited frequency of this journal is higher than that of all journals in this field, and it is in a high influential position. | The citation frequency of the journal is equal to the average of The citation frequencies of all journals in the same subject field, which is at the level of moderate influence. | Indicating that it is at a low level of influence. |
| Relative Downloads of Journals | It refers to the ratio of the average downloads of a journal in a subject area to that of all journals in the same area. | The download volume of this journal is higher than that of all journals in this field, and it is in a high attention position. | The download volume of this journal is equal to the average value of all journals in the same subject area, which is at the level of moderate attention. | Indicating that it is in a neglected position. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Yang, J. Scientometrics-Based Research Status and Hot Topics Analysis of Chinese Private Colleges under Policy Guidance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010646
Kuang Z, Jia Y, Yang J. Scientometrics-Based Research Status and Hot Topics Analysis of Chinese Private Colleges under Policy Guidance. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010646
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Zhongqin, Yan Jia, and Jun Yang. 2023. "Scientometrics-Based Research Status and Hot Topics Analysis of Chinese Private Colleges under Policy Guidance" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010646
APA StyleKuang, Z., Jia, Y., & Yang, J. (2023). Scientometrics-Based Research Status and Hot Topics Analysis of Chinese Private Colleges under Policy Guidance. Sustainability, 15(1), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010646







