Experimental Characterisation of Different Ecological Substrates for Use in Green Roof Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate Samples
2.2. Test Methods
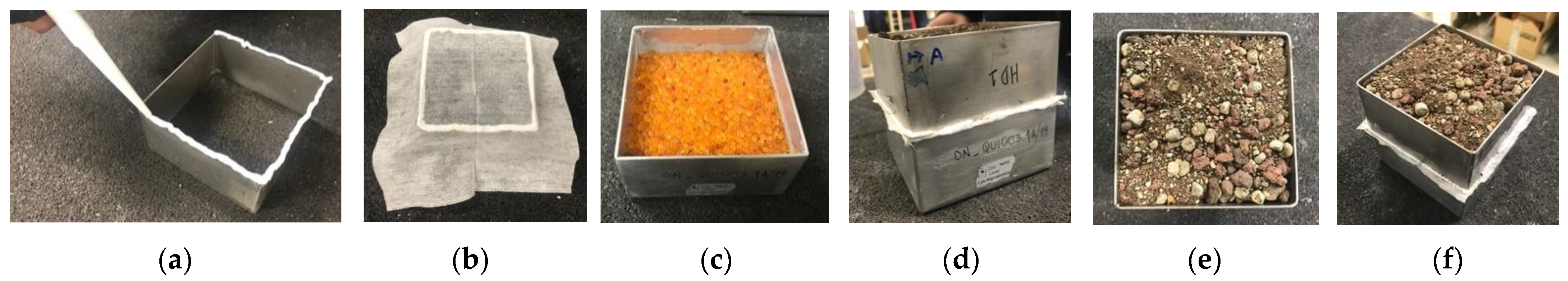
2.2.1. Thermal Conductivity
2.2.2. Specific Heat Capacity
2.2.3. Emissivity
2.2.4. Water Vapour Transmission
2.2.5. Hygroscopic Sorption Properties
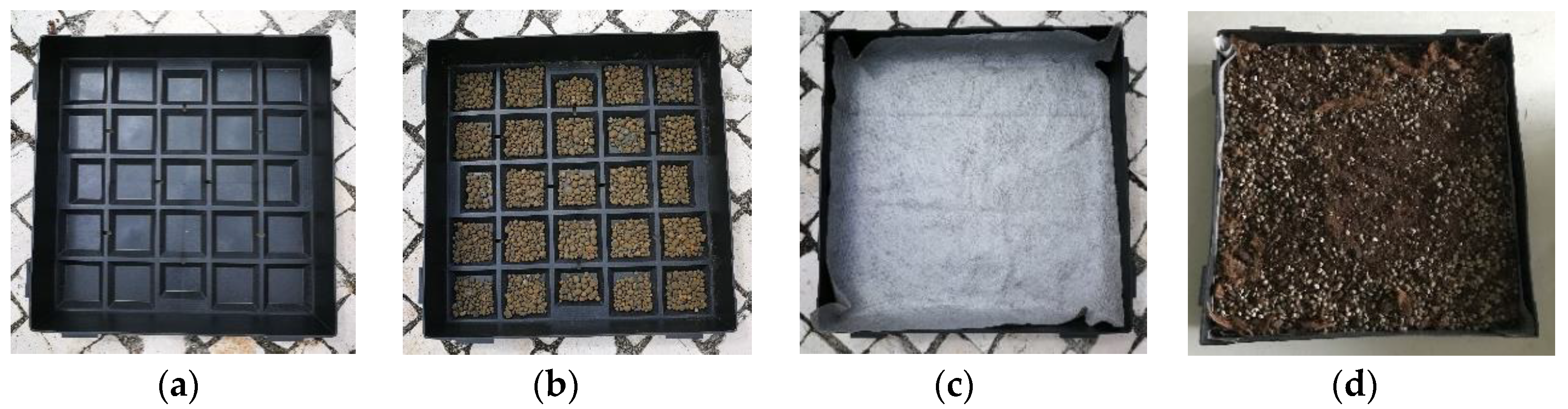
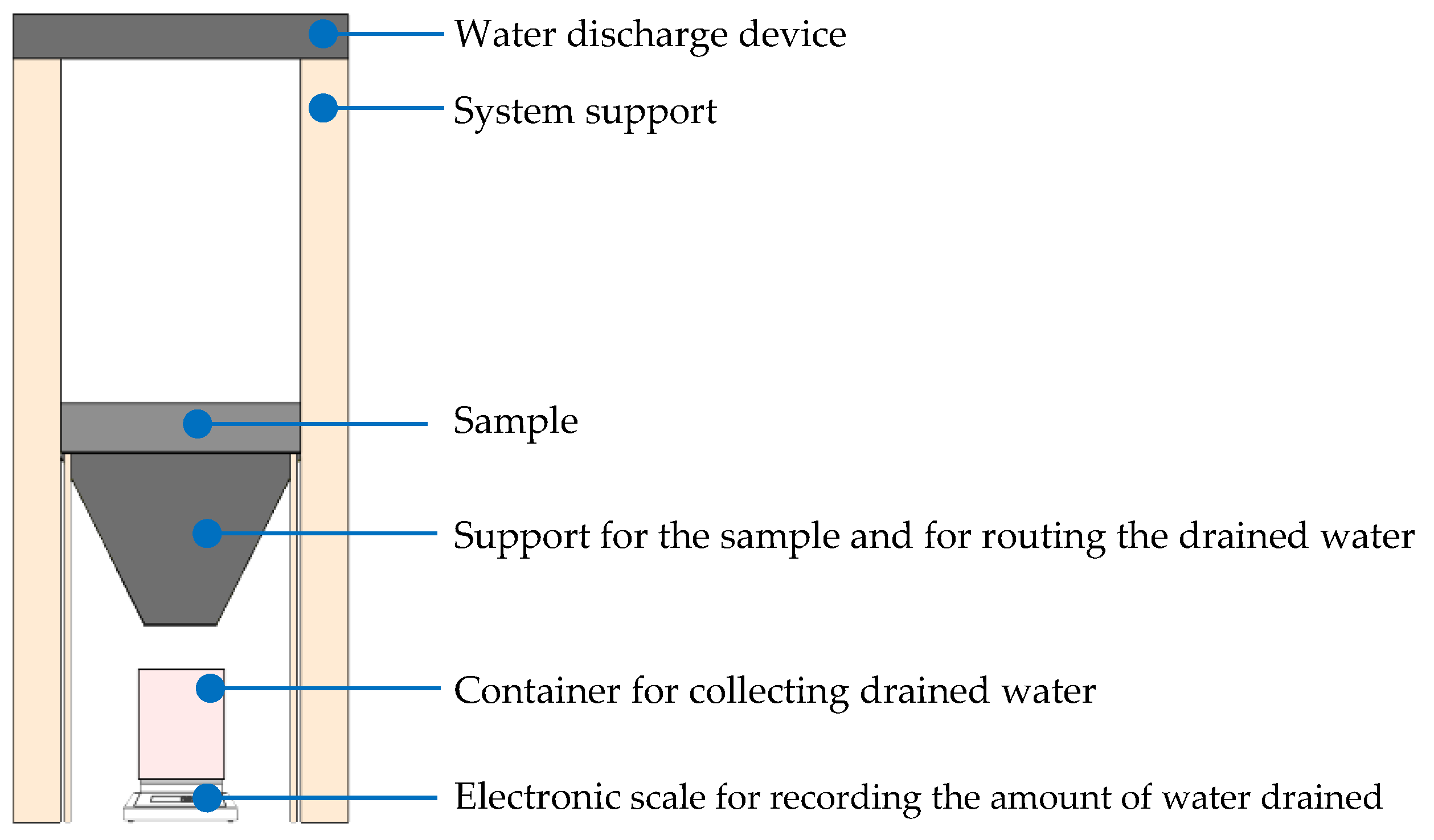
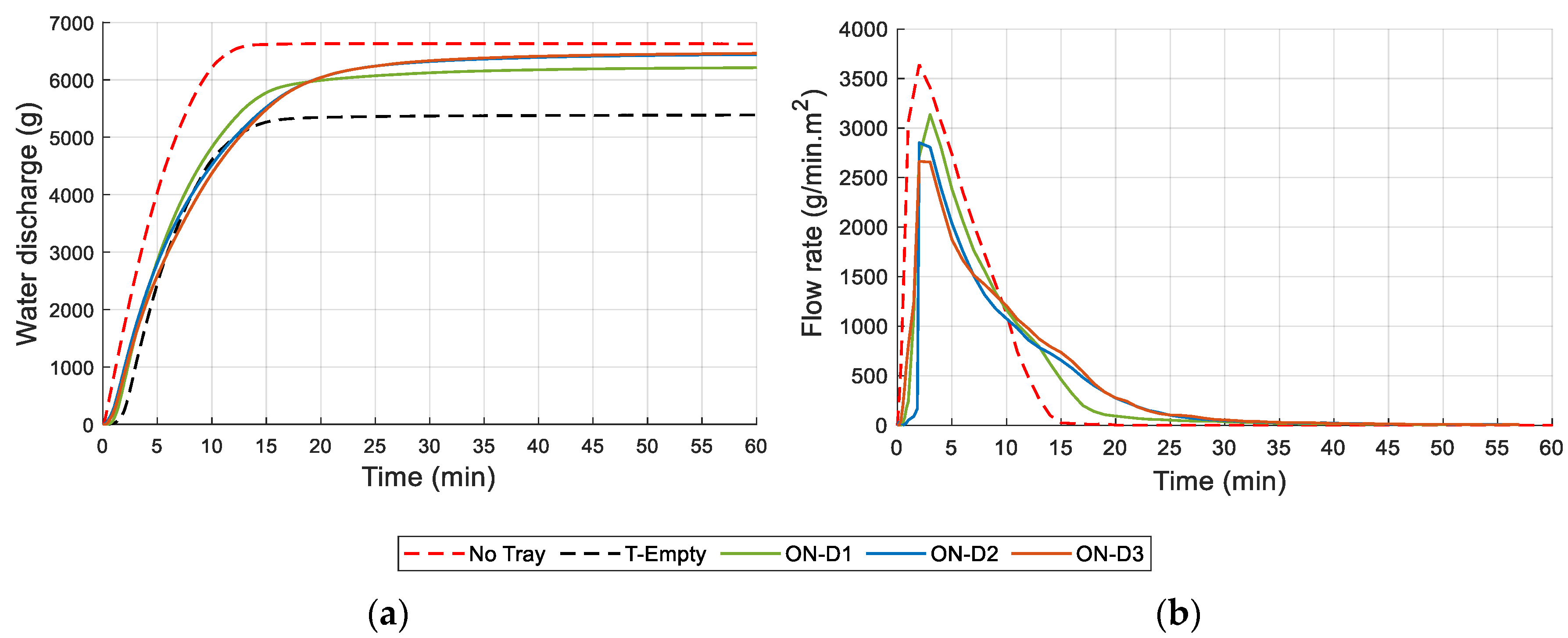
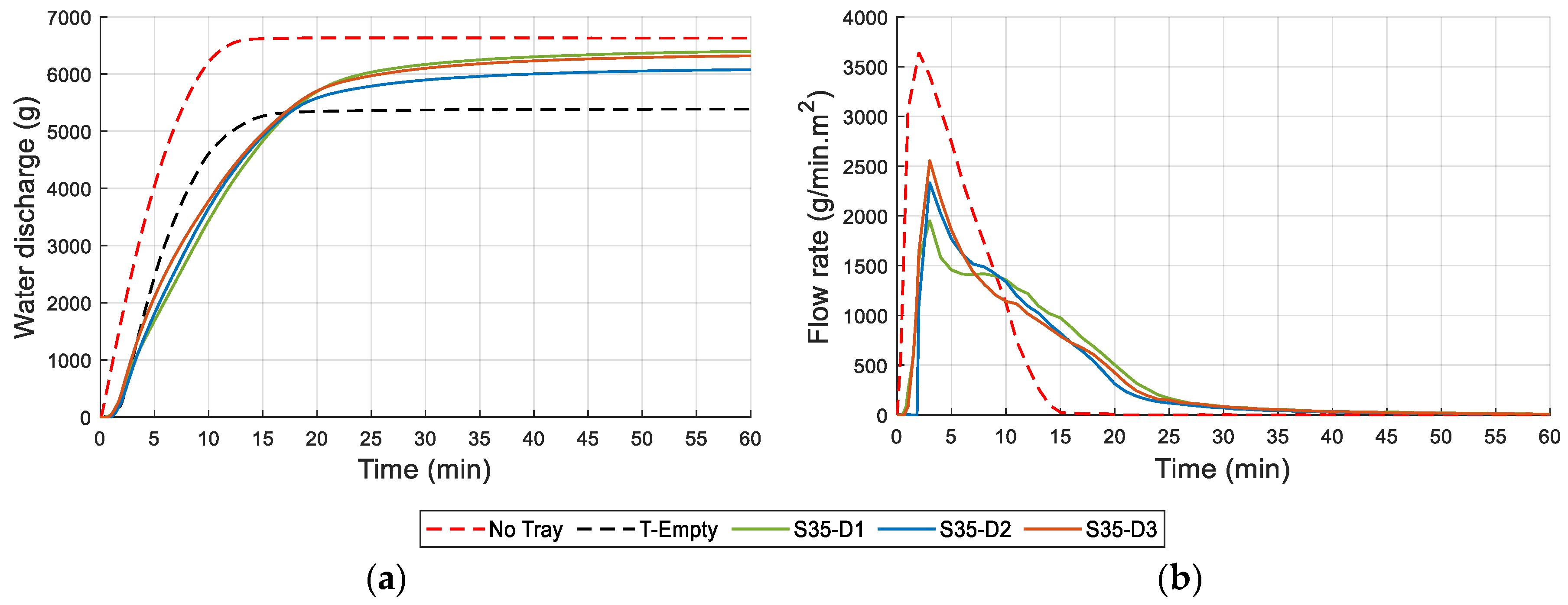
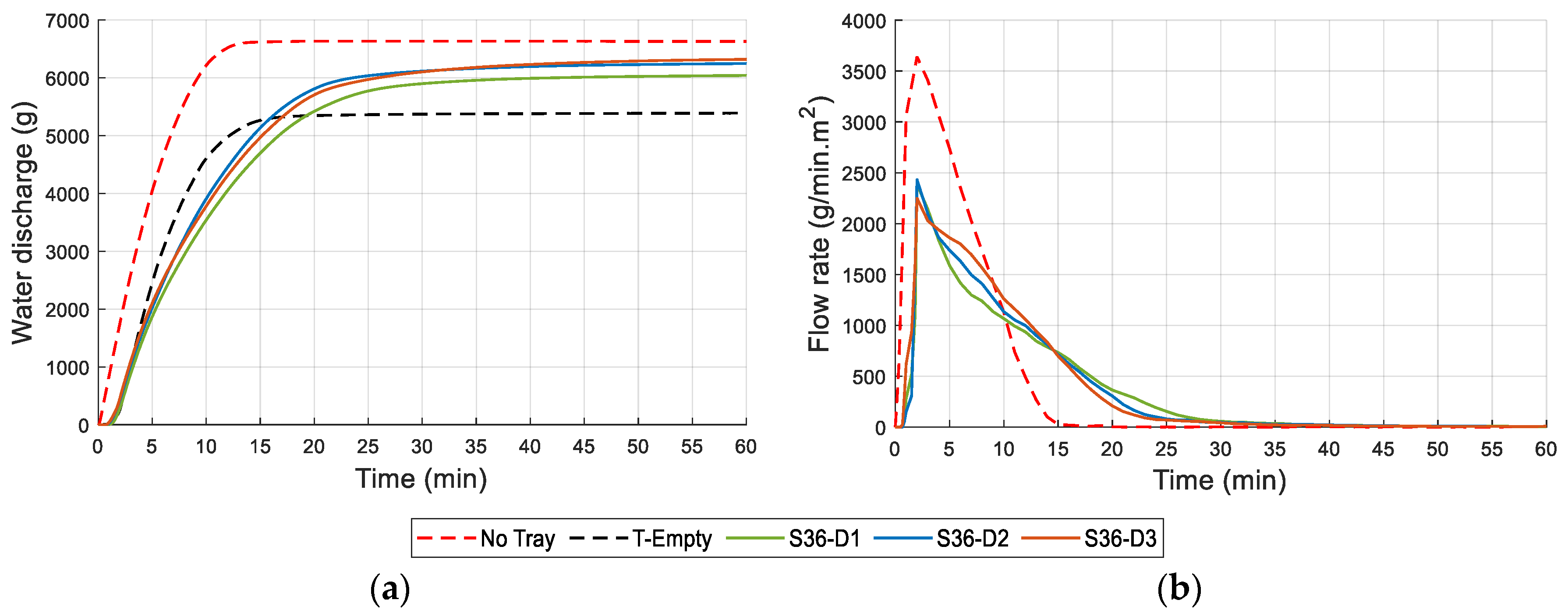
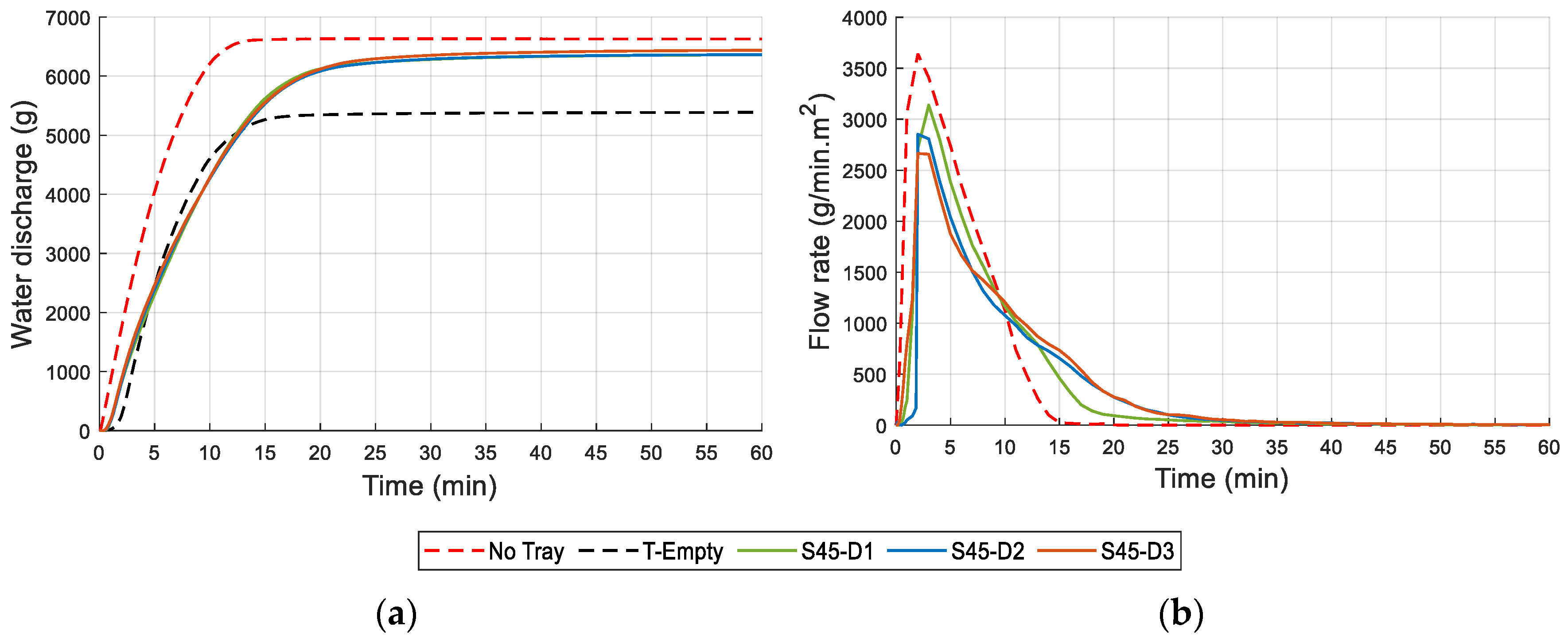
2.2.6. Water Drainage and Retention Capacity
3. Results and Discussion
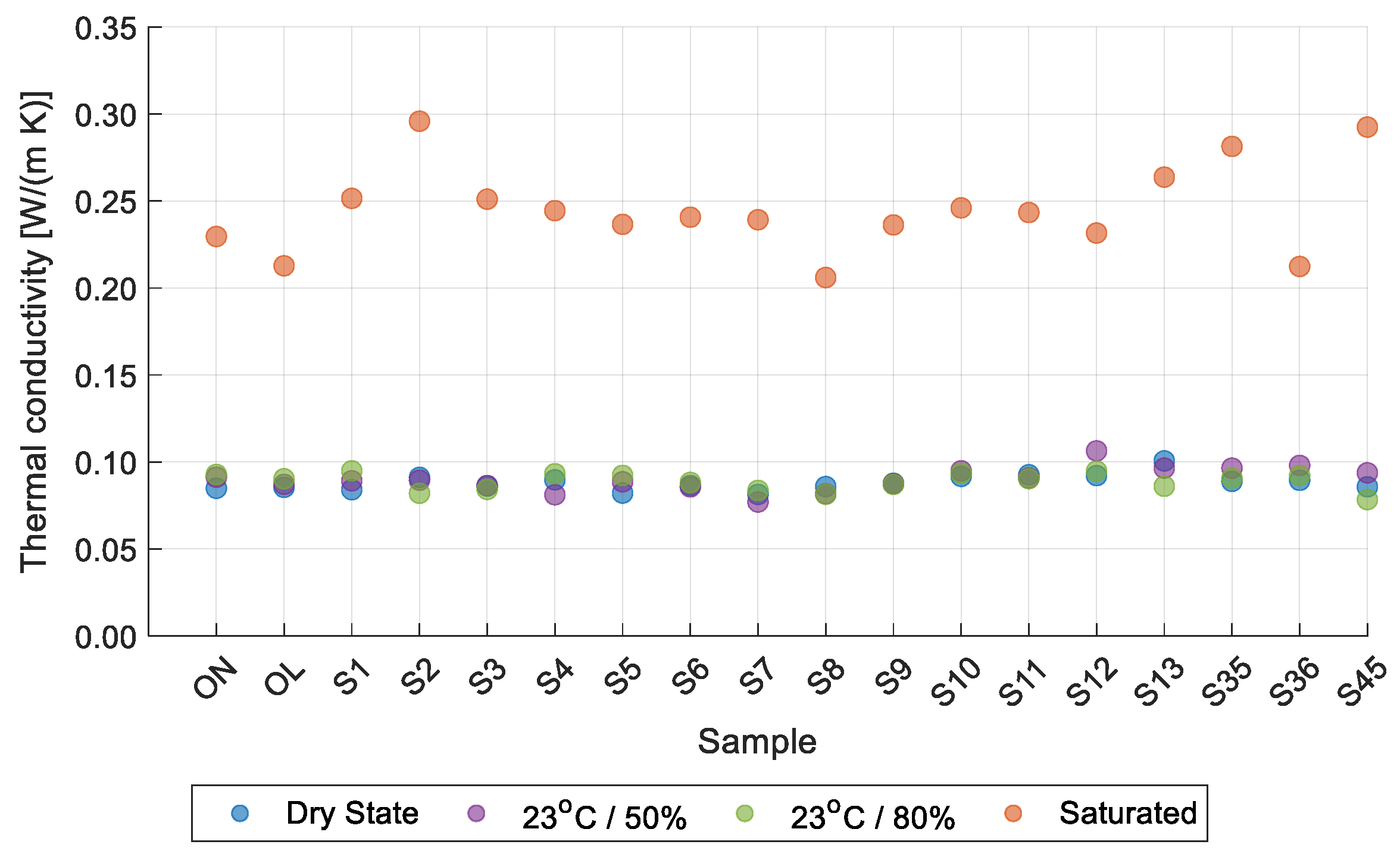
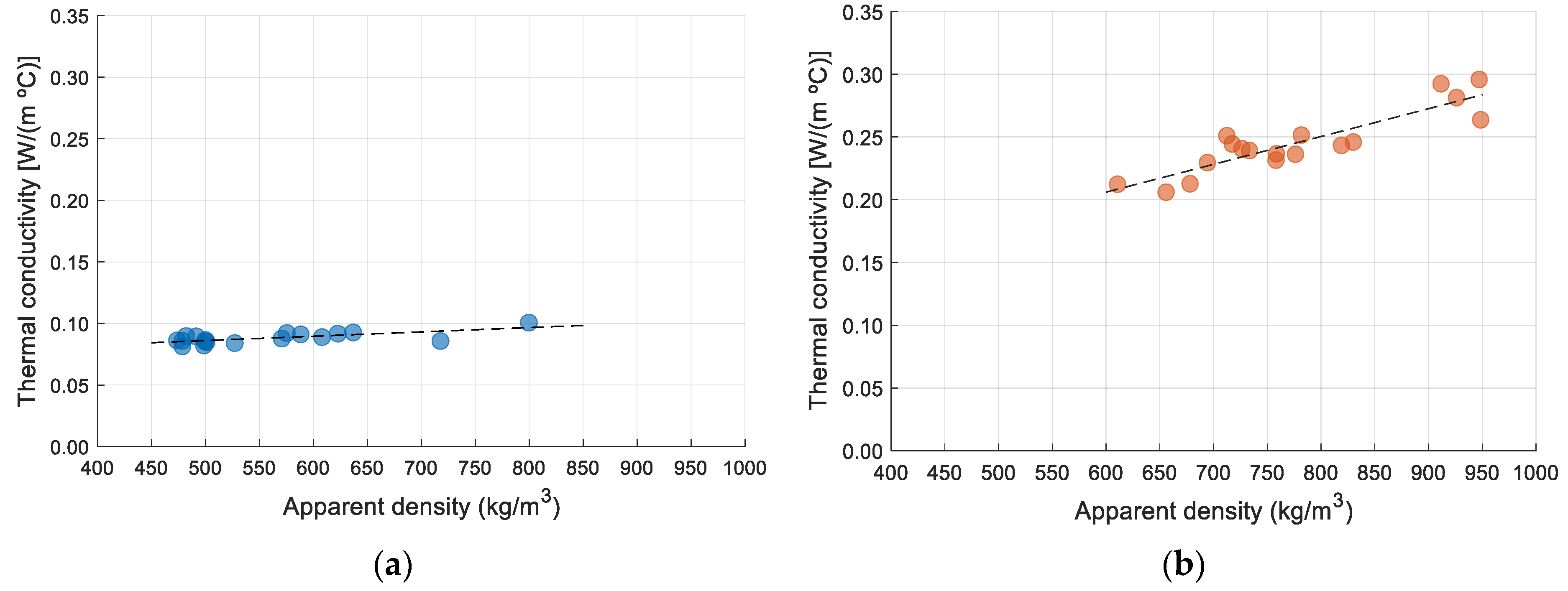
3.1. Thermal Conductivity
3.2. Specific Heat Capacity
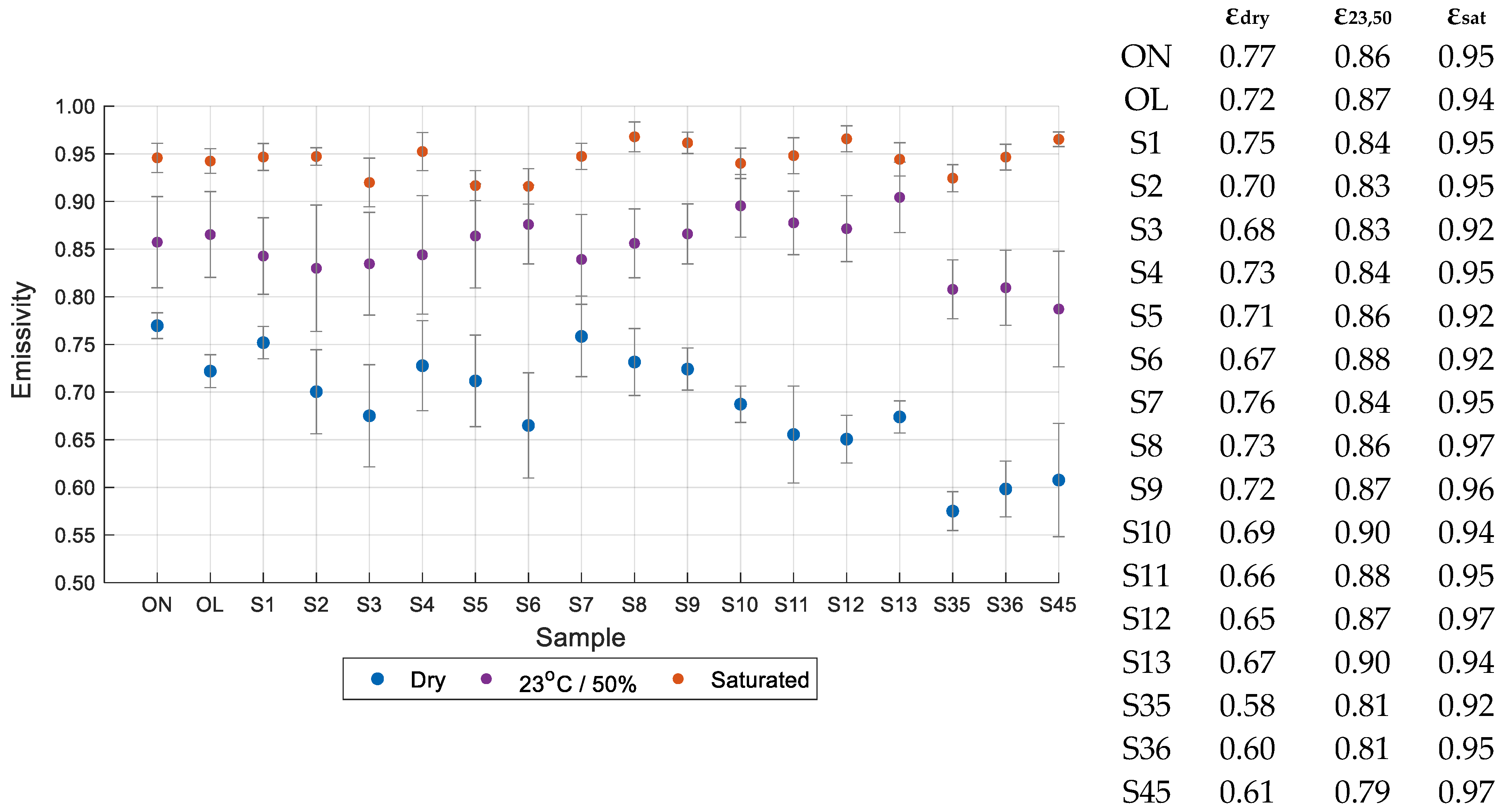
3.3. Emissivity
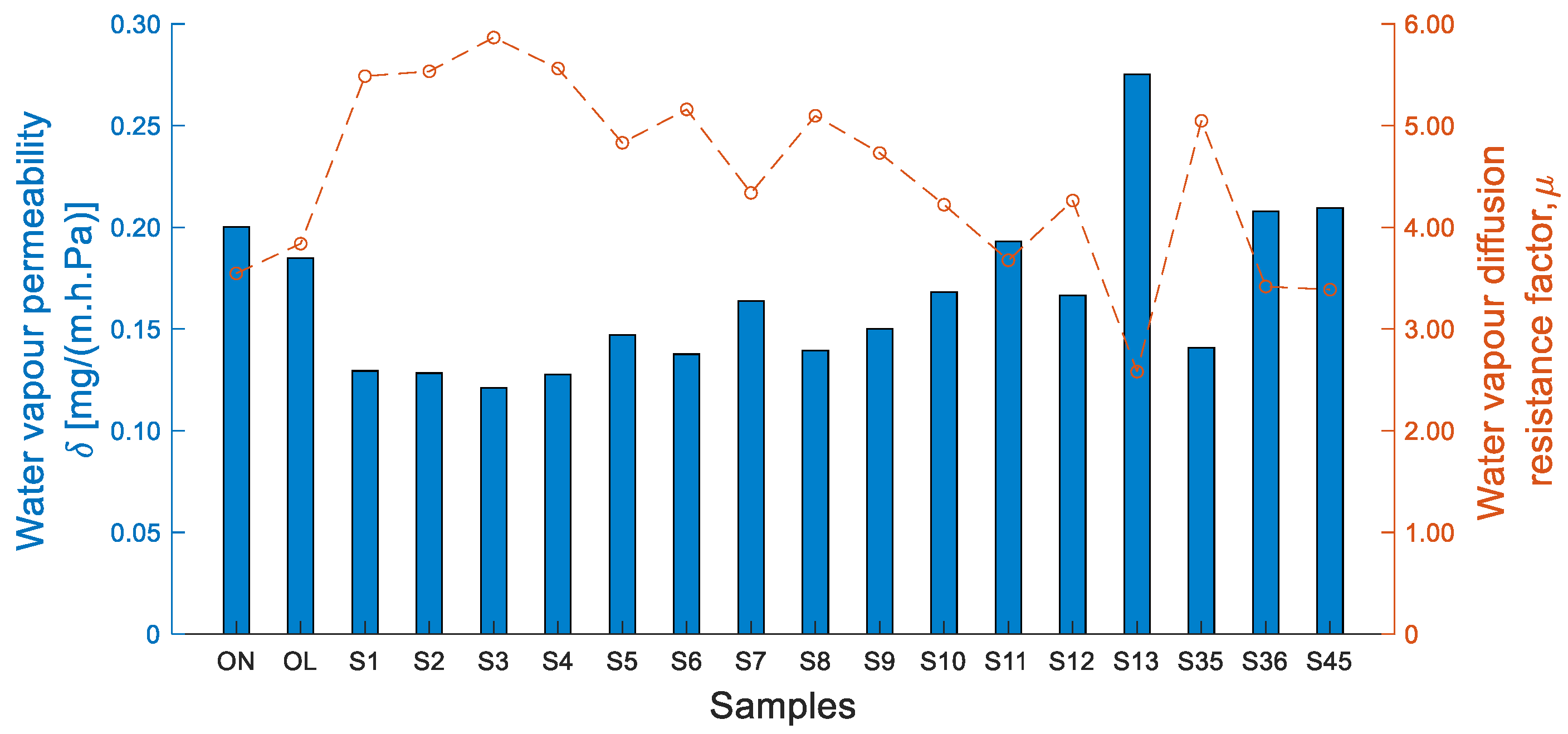
3.4. Water Vapour Transmission
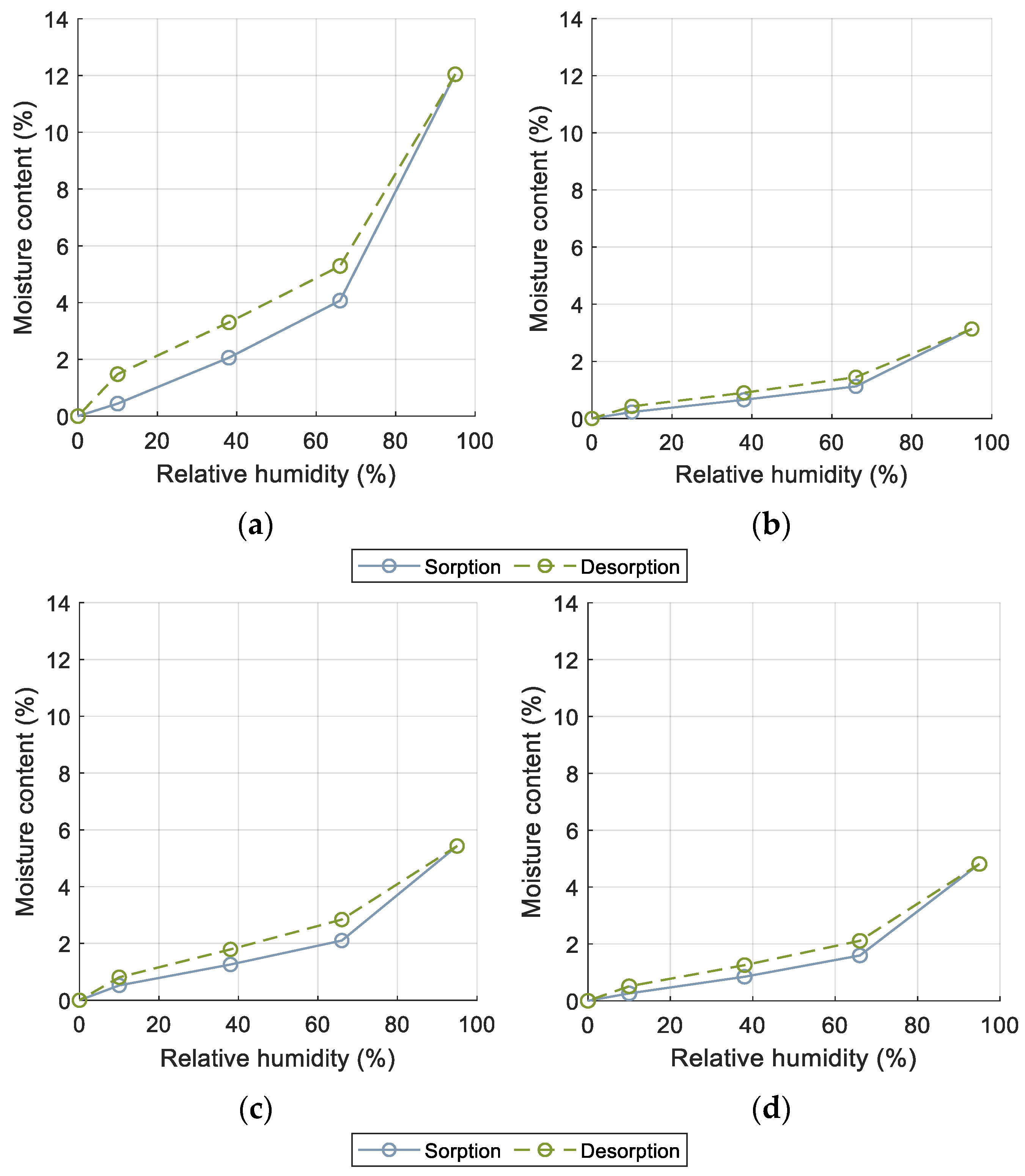
3.5. Hygroscopic Sorption Properties
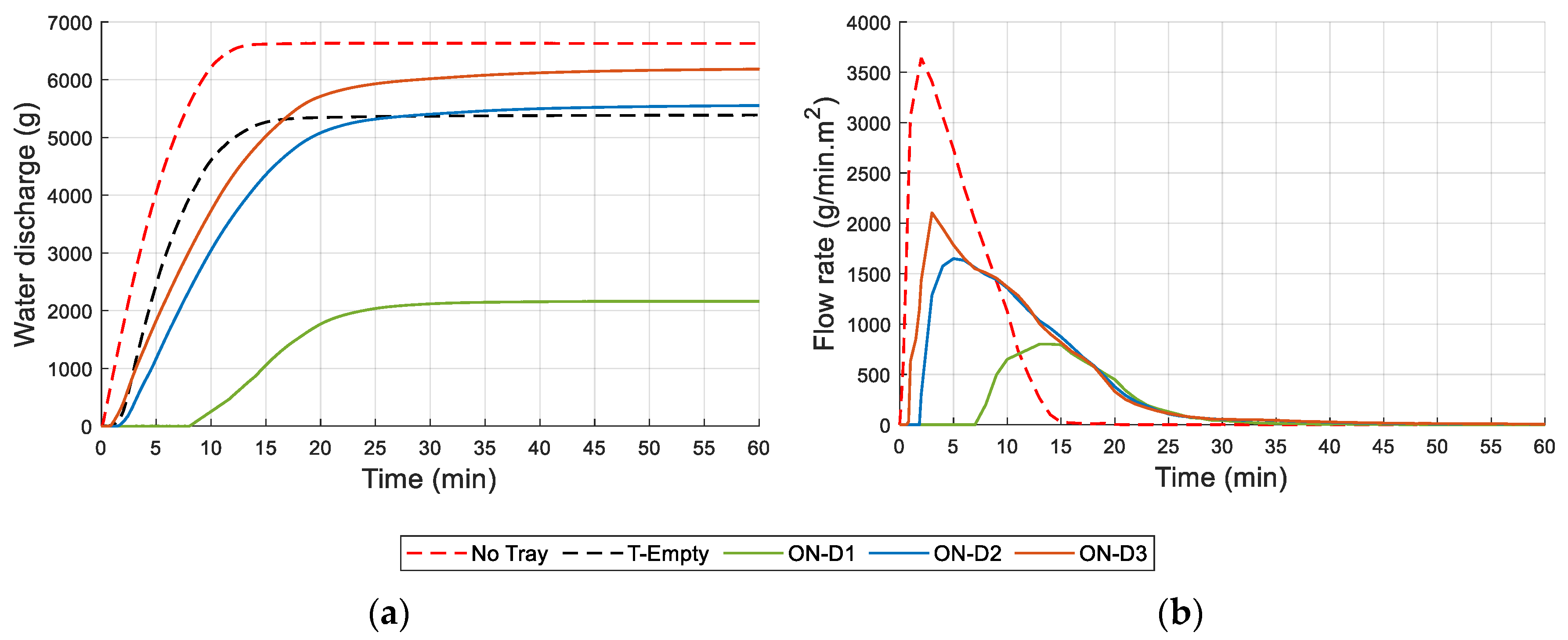
3.6. Drainage and Water Retention
3.7. Final Remarks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations (UB). Global Perspective Human Stories. 2019. Available online: https://news.un.org/pt/story/2019/02/1660701 (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Reuters in Geneva, More than 7000 Extreme Weather Events Recorded Since 2000, Says UN, Guard. 2020. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/oct/12/un-highlights-dramatic-global-rise-in-extreme-weather-since-2020 (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction. Towards a Zero-Emissions, Efficient and Resilient Buildings, and Construction Sector. UN Environment Programme. 2021. Available online: https://globalabc.org/sites/default/files/2021-10/GABC_Buildings-GSR-2021_BOOK.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Zhang, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ge, D. Stormwater retention and detention performance of green roofs with different substrates: Observational data and hydrological simulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 291, 112682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T. Analysis and modelling of stormwater control volume control performance of rainwater harvesting systems in four climatic zones of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2649–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, S.; Mahdiyar, A.; Durdyev, S.; Mohandes, S.; Ismail, S. An assessment model of benefits, opportunities, costs, and risks of green roof installation: A multi criteria decision making approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Exl, J.; Geisendorf, S. The Potential of Stormwater Management in Addressing the Urban Heat Island Effect: An Economic Valuation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, F.; Urbano, B. Green Roofs and Walls Design Intended to Mitigate Climate Change in Urban Areas across All Continents. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastran, M.; Kobal, M.; Eler, K. Urban heat islands in relation to green land use in European cities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 37, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Shin, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; An, K. Efficient plant types and coverage rates for optimal green roof to reduce urban heat island effect. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korol, E.; Shushunova, N.; Feoktistova, O.; Shushunova, T.; Rubtsov, O. Technical and economical factors in green roof using to reduce the aircraft noise. International Science Conference SPbWOSCE-2017 “Business Technologies for Sustainable Urban Development”, Russia, 20–22 December 2017. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Connelly, M.; Hodgson, M. Experimental investigation of the sound absorption characteristics of vegetated roofs. Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renterghem, V. Green roofs for noise reduction: Literature review and new approaches. In 46th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering; Inter-Noise: Hong Kong, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lundholm, J. Green roof plant species diversity improves ecosystem multifunctionality. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susca, T. Green roofs to reduce building energy use? A review on key structural factors of green roofs and their effects on urban climate. Build. Environ. 2019, 162, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, N.; Almeida, R.; Tadeu, A.; Brett, M.; Almeida, J. Comparison between cork-based and conventional green roof solutions. Build. Environ. 2020, 175, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Cameron, D.; Sorrill, J.; Edwards, T.; Phoenix, G. Importance of different components of green roof substrate on plant growth and physiological performance. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksi, M.; Rowe, B. Green roof substrates: Effect of recycled crushed porcelain and foam glass on plant growth and water retention. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, J.; Gracia, A.; Cháfer, M.; Pérez, G.; Cabeza, L. Thermal characterization of different substrates under dried conditions for extensive green roofs. Energy Build. 2017, 144, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadeu, A.; Škerget, L.; Almeida, J.; Simões, N. Canopy contribution to the energy balance of a building’s roof. Energy Build. 2021, 244, 111000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tabares-Velasco, P.; Srebric, J.; Komarneni, S.; Berghage, R. Effects of plant and substrate selection on thermal performance of green roofs during the summer. Build. Environ. 2014, 78, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianella, A.; Clarke, R.; Williams, N.; Chen, Z.; Aye, L. Steady-state and transient thermal measurements of green roof substrates. Energy Build. 2016, 131, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Courard, L.; Attia, S. Water permeability, water retention capacity, and thermal resistance of green roof layers made with recycled and artificial aggregates. Build. Environ. 2023, 227, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Courard, L.; Hubert, J. Coarse recycled materials for the drainage and substrate layers of green roof system in dry condition: Parametric study and thermal heat transfer. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryla, A.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Bus, A. Role of substrates used for green roofs in limiting rainwater runoff. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Farrell, C. Use of organic wastes to create lightweight green roof substrates with increased plant-available water. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dong, W.; Cheng, R.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Effect of highly efficient substrate modifier, super-absorbent polymer, on the performance of the green roof. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomello, E.; Gaspari, J. Hydrologic Performance of an Extensive Green Roof under Intensive Rain Events: Results from a Rain-Chamber Simulation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forschungsgesellschaft Landschaftsentwicklung Landschaftsbau e.V. (Landscape Development and Landscaping Research Society). Green Roof Guidelines. Guidelines for the Planning, Construction and Maintenance of Green Roofs; Landscape Development and Landscaping Research Socitety: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- EAD 220009-00-0401: 2015-04; Kits for Green Roofs, Edition 03/2021. EOTA European Organisation for Technical Assessment: Brussels, Belgium, 2021.
- ISO 8302:1991; Thermal Insulation—Determination of Steady-State Thermal Resistance and Related Properties—Guarded Hot Plate Apparatus. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991.
- European Standard EN 12664:2001; Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Thermal Resistance by Means of Guarded Hot Plate and Heat Flow Meter Methods—Dry and Moist Products of Medium and Low Thermal Resistance. CEN-CENELEC: Brussels, Belgium, 2001.
- Simões, I.; Simões, N.; Tadeu, A. Thermal delay simulation in multilayer systems using analytical solutions. Energy Build. 2012, 49, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, B.; Tadeu, A.; Almeida, J.; António, J.; Brito, J. Characterisation of sustainable building walls made from rice straw bales. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28, 101041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Simões, N.; Serra, C.; Flores-Colen, I.; Rottenbacher, K.; Almeidad, F. Study of the edge thermal bridging effect in vacuum insulation panels: Steady and unsteady-state approaches using numerical and experimental methods. Energy Build. 2022, 258, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononogova, E.; Adibekyan, A.; Monte, C.; Hollandt, J. Characterization, calibration, and validation of an industrial emissometer. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2019, 8, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 12572:2016; Hygrothermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Water Vapour Transmission Properties—Cup Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 12571:2013; Hygrothermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Hygroscopic Sorption Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Ferrer, G.; Barreneche, C.; Solé, A.; Martorell, I.; Cabeza, L. New proposed methodology for specific heat capacity determination of materials for thermal energy storage (TES) by DSC. J. Energy Storage 2017, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavoni, S.; D’Alessandro, F.; Bianchi, F.; Asdrubali, F. Insulation materials for the building sector: A review and comparative analysis. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 62, 988–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
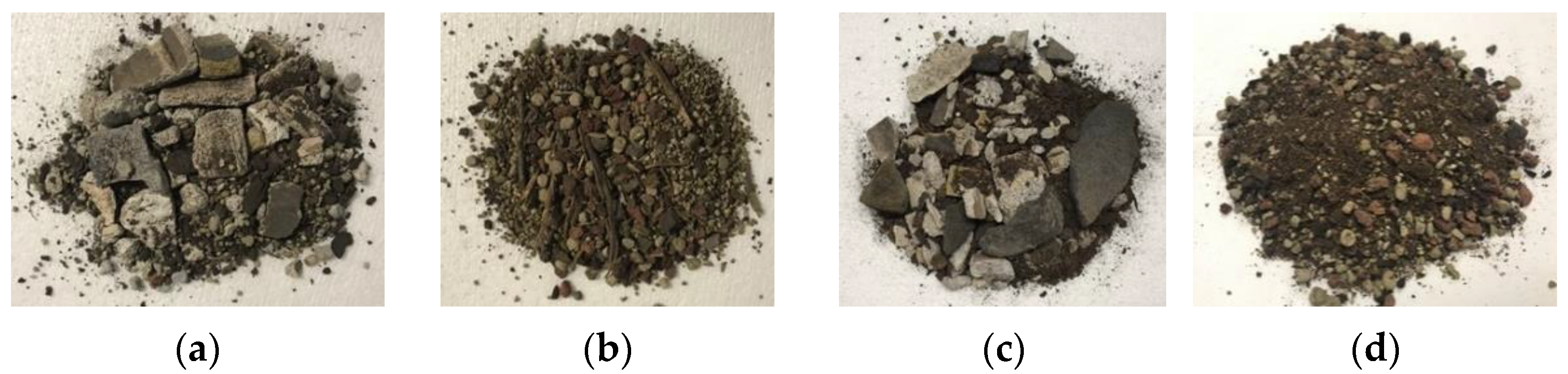
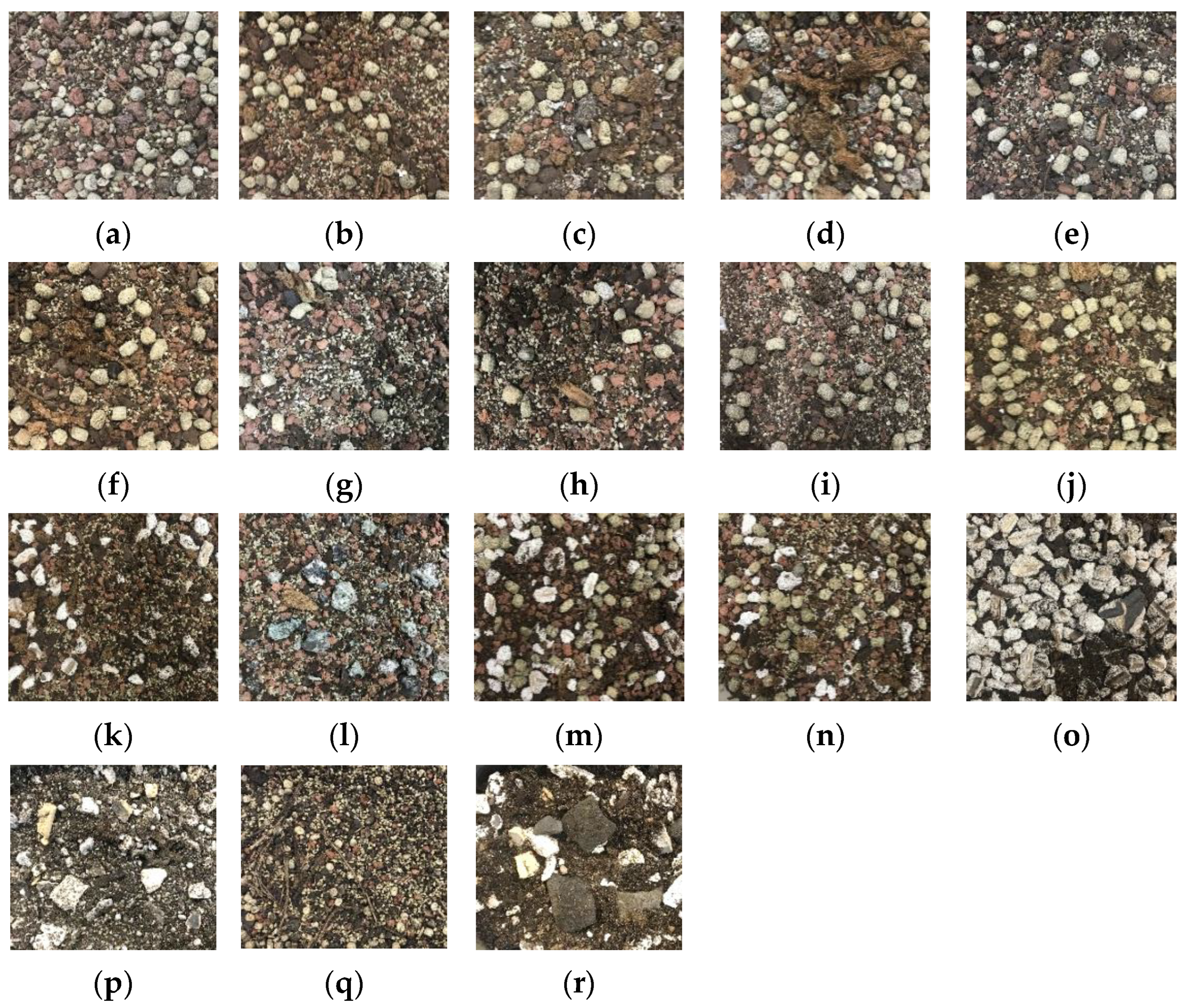
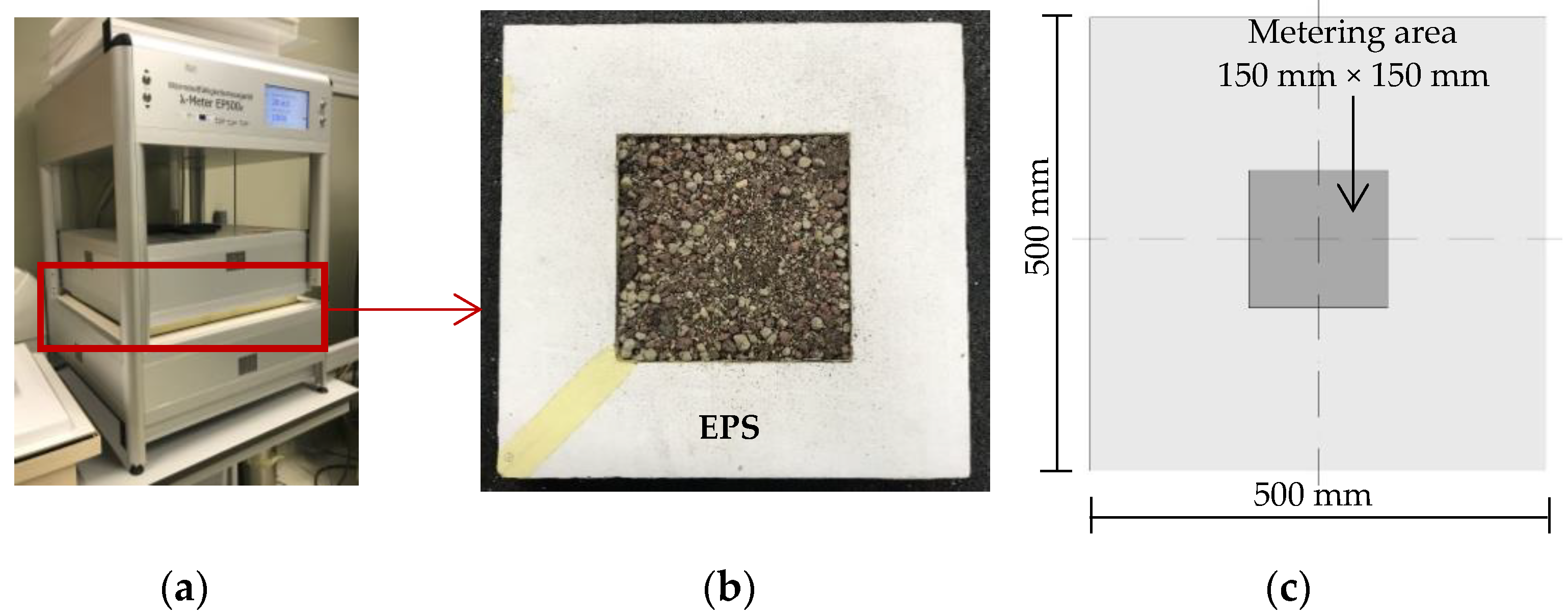
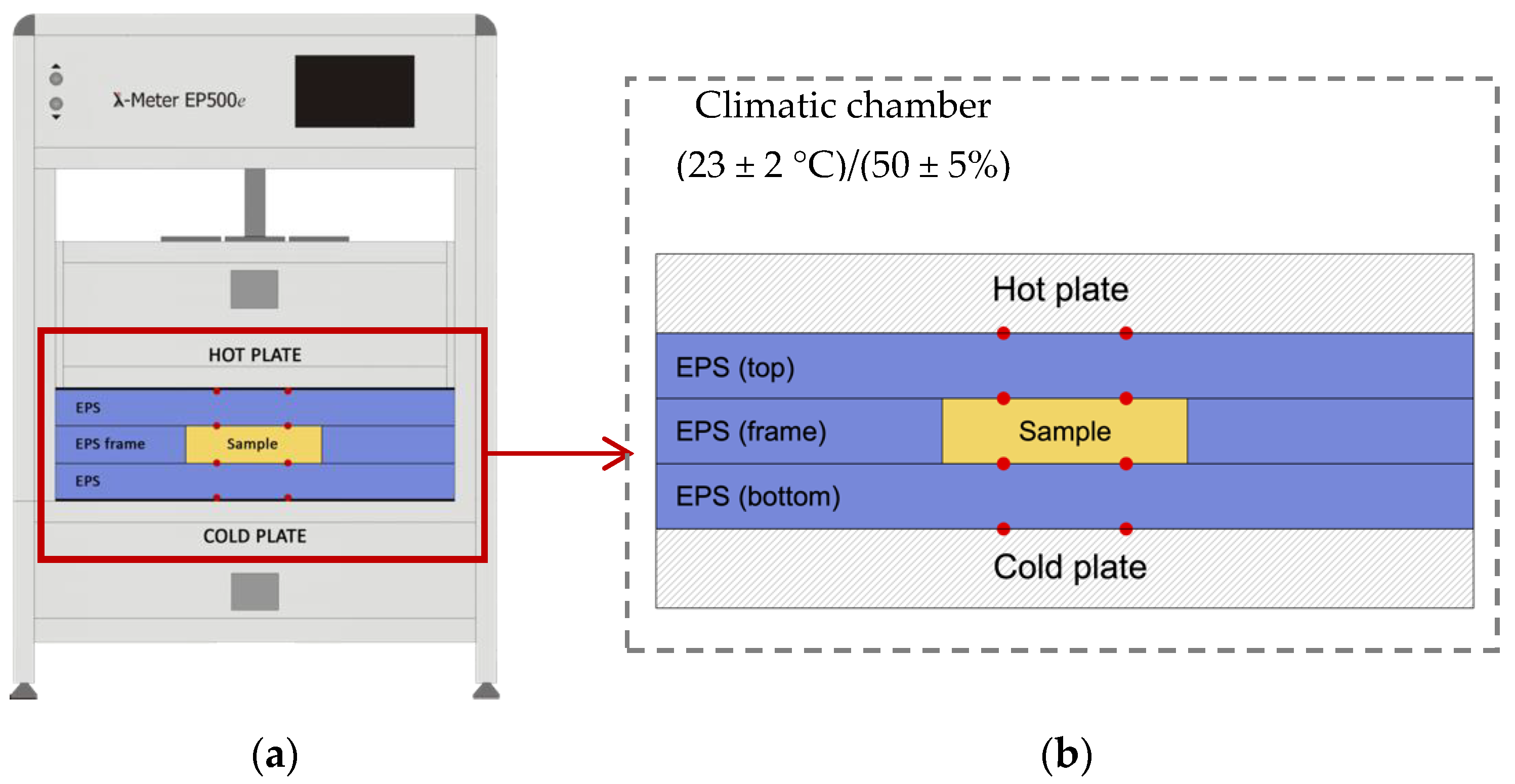
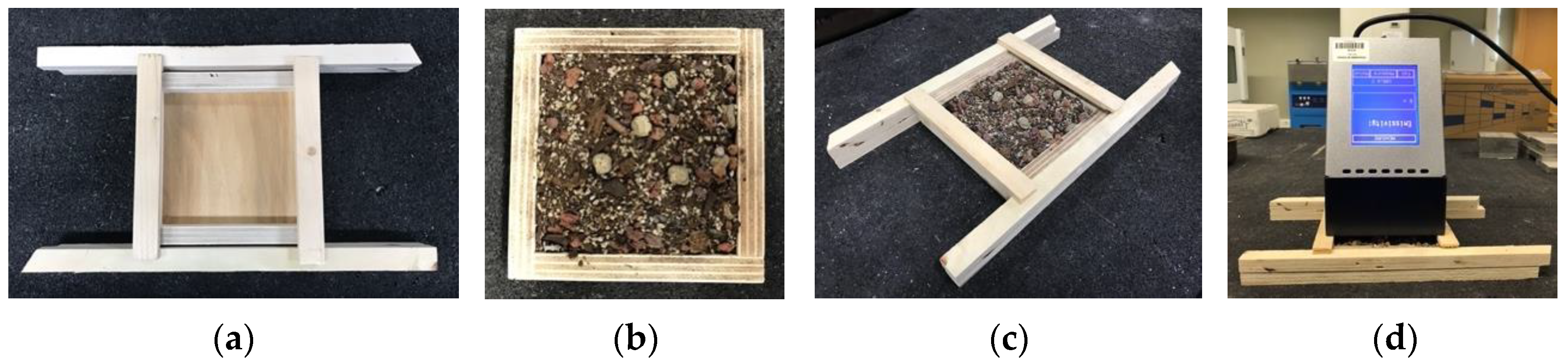

| Substrate | Compost | Forest Residues | Blond Peat | Coco Peat | Iron Slag | Steel Slag | Refractories | Geopolymer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 |
| S2 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 40 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| S3 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| S4 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 0 |
| S5 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 10 |
| S6 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 0 |
| S7 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 30 |
| S8 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 20 |
| S9 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 30 |
| S10 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 35 |
| S11 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 35 | 15 |
| S12 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 40 | 10 | 0 |
| S13 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 10 |
| S35 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 25 | 15 | 10 | 0 |
| S36 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| S45 | 20 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| Specific Heat Capacity, Cp, dry | Specific Heat Capacity, Cp, (23,50) | |
|---|---|---|
| [J/(kg °C)] | [J/(kg °C)] | |
| ON | 1413 | 1658 |
| S45 | 536 | 2069 |
| Water Vapour Permeance, W | Water Vapour Resistance, Z | Water Vapour Permeability, δ | Water Vapour Diffusion Resistance Factor, μ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mg/(m2·h·Pa)] | [(m2·h·Pa)/mg] | [mg/(m·h·Pa)] | - | |
| ON | 4.00 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 3.55 |
| OL | 3.70 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 3.84 |
| S1 | 2.59 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 5.49 |
| S2 | 2.57 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 5.53 |
| S3 | 2.42 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 5.87 |
| S4 | 2.55 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 5.56 |
| S5 | 2.94 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 4.83 |
| S6 | 2.75 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 5.16 |
| S7 | 3.27 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 4.34 |
| S8 | 2.79 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 5.10 |
| S9 | 3.00 | 0.33 | 0.15 | 4.73 |
| S10 | 3.36 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 4.22 |
| S11 | 3.86 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 3.68 |
| S12 | 3.33 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 4.26 |
| S13 | 5.50 | 0.18 | 0.28 | 2.58 |
| S35 | 2.81 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 5.05 |
| S36 | 4.16 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 3.42 |
| S45 | 4.90 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 3.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, K.; Almeida, J.; Castro, F.; Ribeiro, A.; Teixeira, T.; Palha, P.; Simões, N. Experimental Characterisation of Different Ecological Substrates for Use in Green Roof Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010575
Coelho K, Almeida J, Castro F, Ribeiro A, Teixeira T, Palha P, Simões N. Experimental Characterisation of Different Ecological Substrates for Use in Green Roof Systems. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010575
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, Katya, João Almeida, Fernando Castro, André Ribeiro, Tiago Teixeira, Paulo Palha, and Nuno Simões. 2023. "Experimental Characterisation of Different Ecological Substrates for Use in Green Roof Systems" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010575
APA StyleCoelho, K., Almeida, J., Castro, F., Ribeiro, A., Teixeira, T., Palha, P., & Simões, N. (2023). Experimental Characterisation of Different Ecological Substrates for Use in Green Roof Systems. Sustainability, 15(1), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010575









