Fate of Sulfate in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants and Its Effect on Sludge Recycling as a Fuel Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
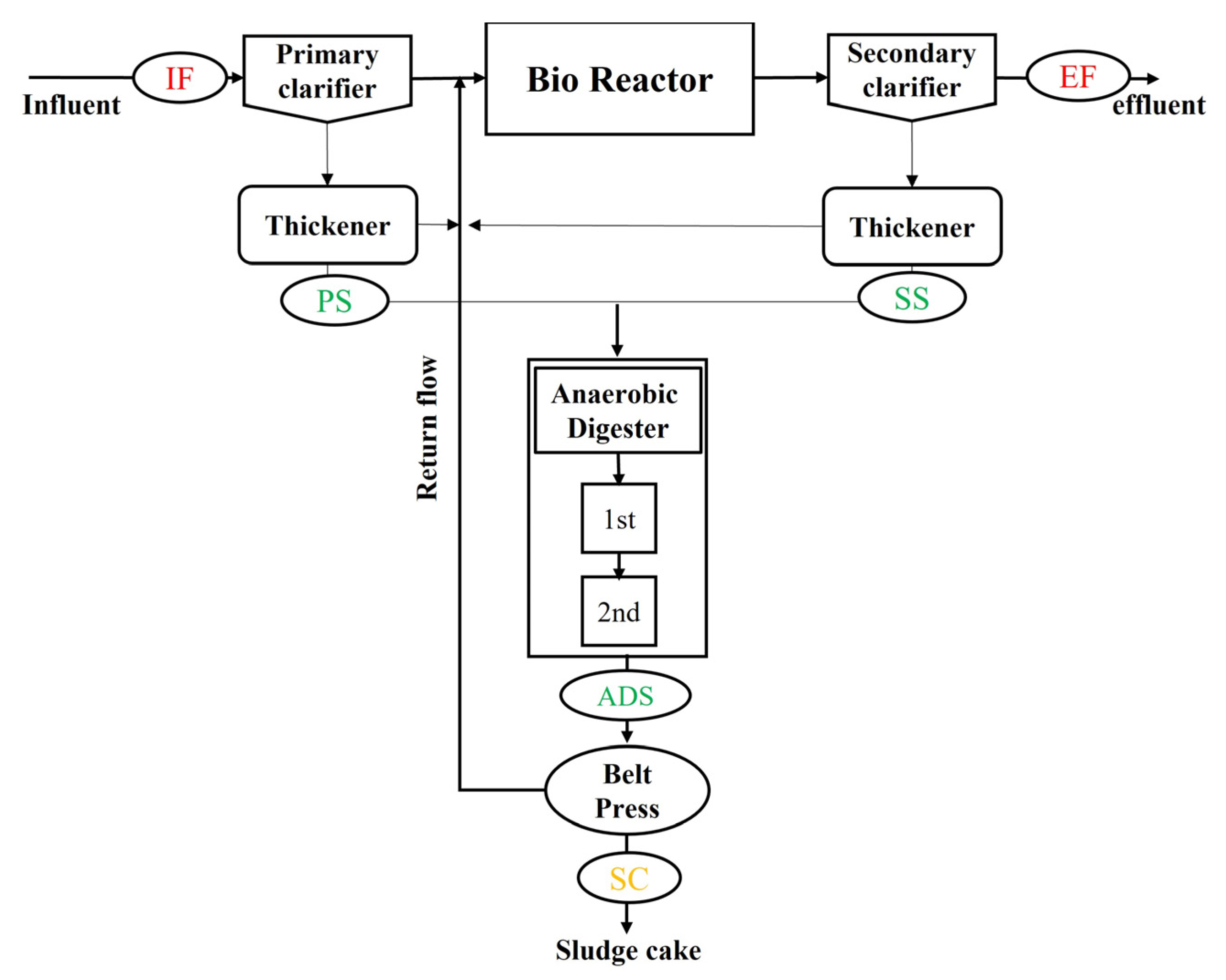
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Procedure
2.3. Measurement of the Liquid Phase Sulfate and Solid Phase Sulfate and Iron
2.4. Sulfate Reduction Rate (SRR) Test
2.5. Genetic Identification of Archaea, Bacteria, and Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria (SRB)
3. Results
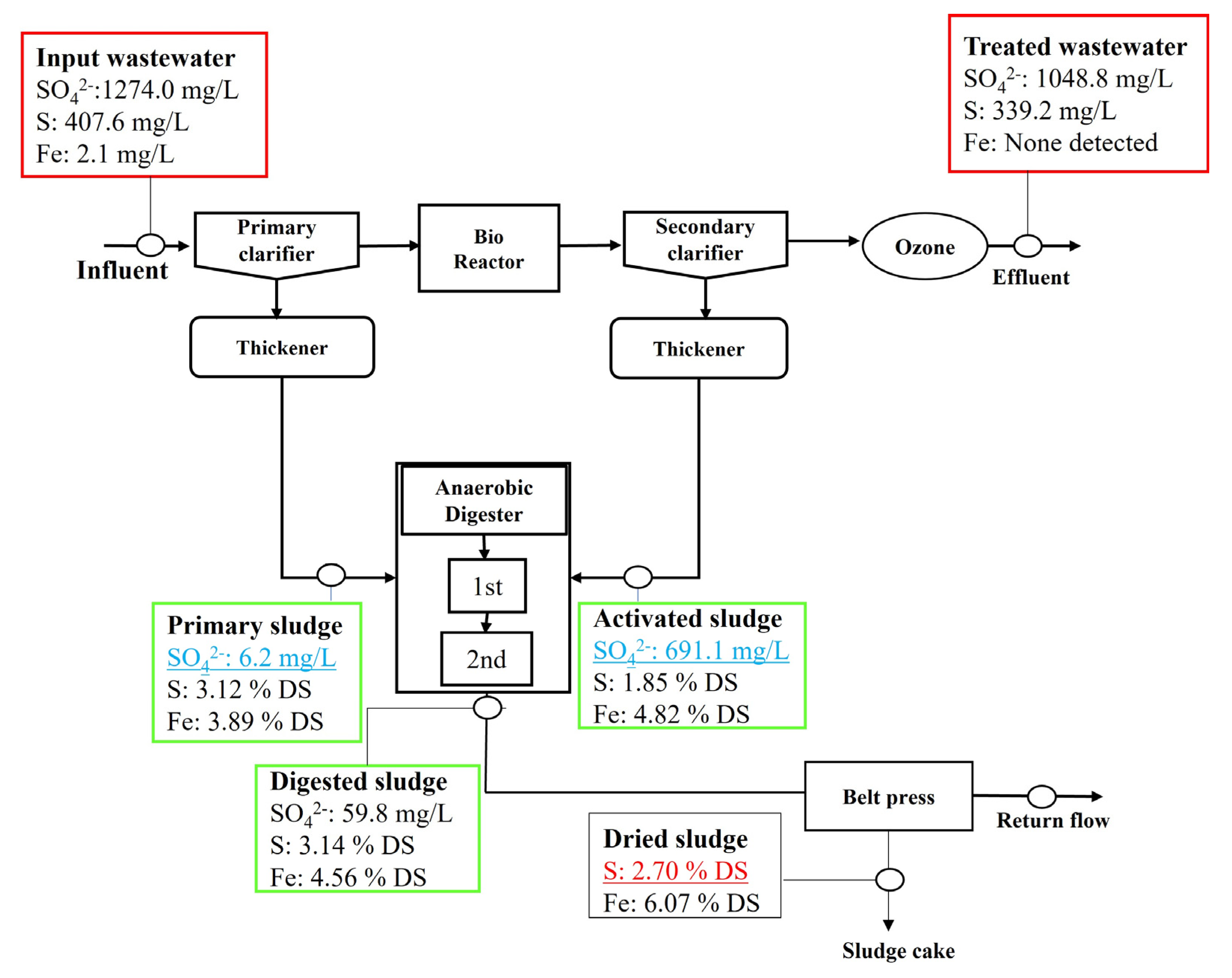
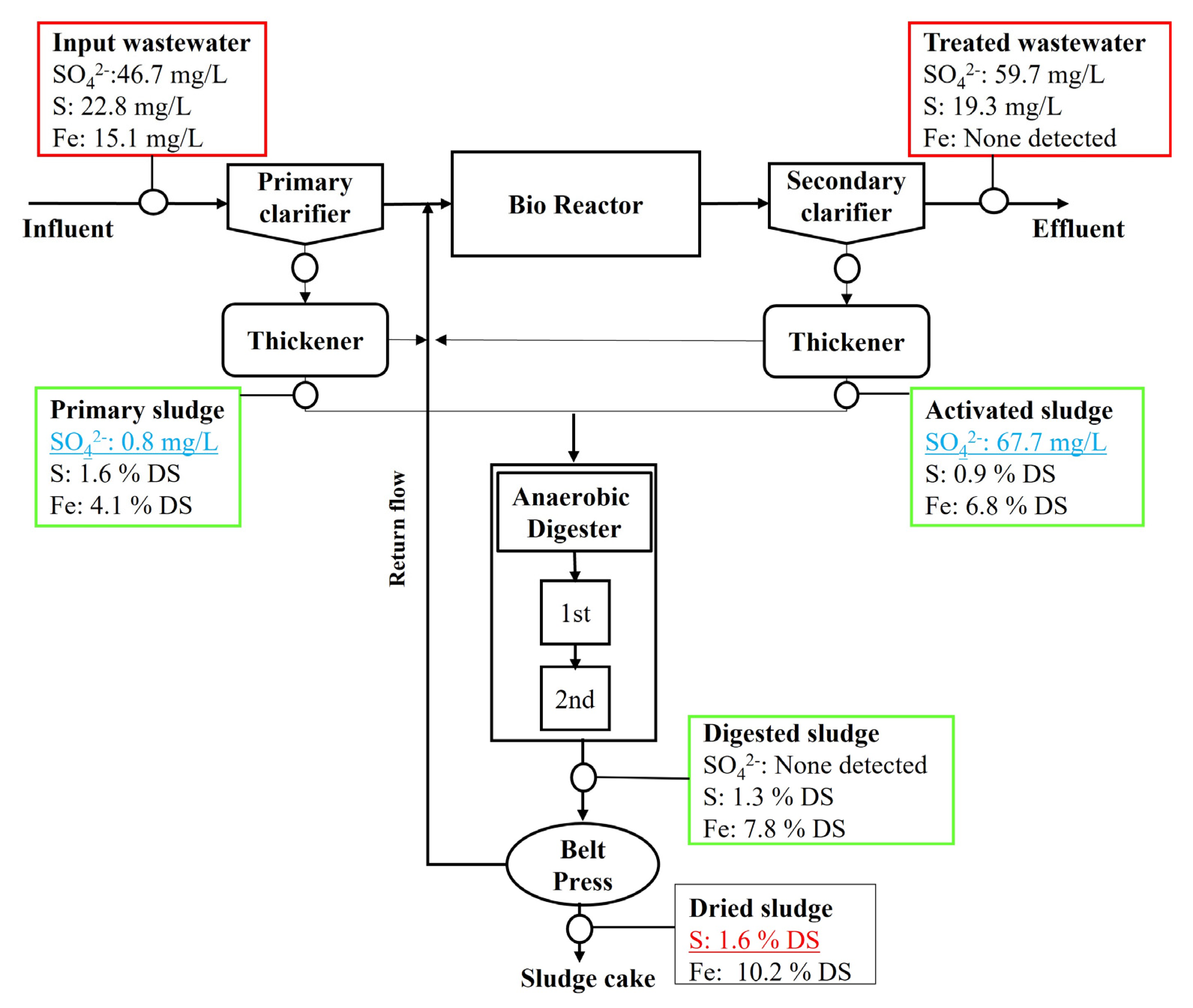
3.1. Fate and Transformation of Sulfate, Sulfur, and Iron
3.2. Sulfate Reduction Rate (SRR) Test
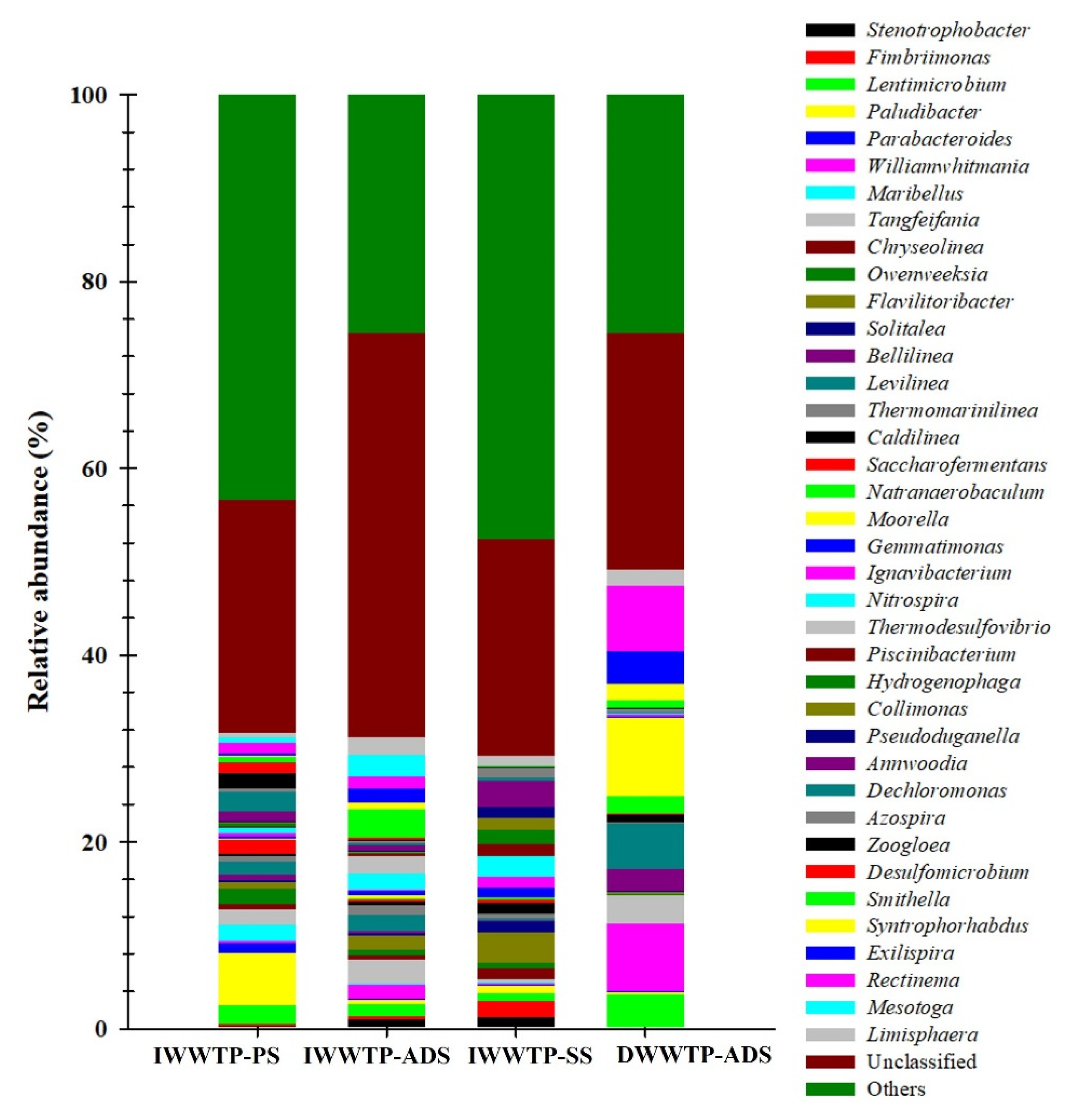
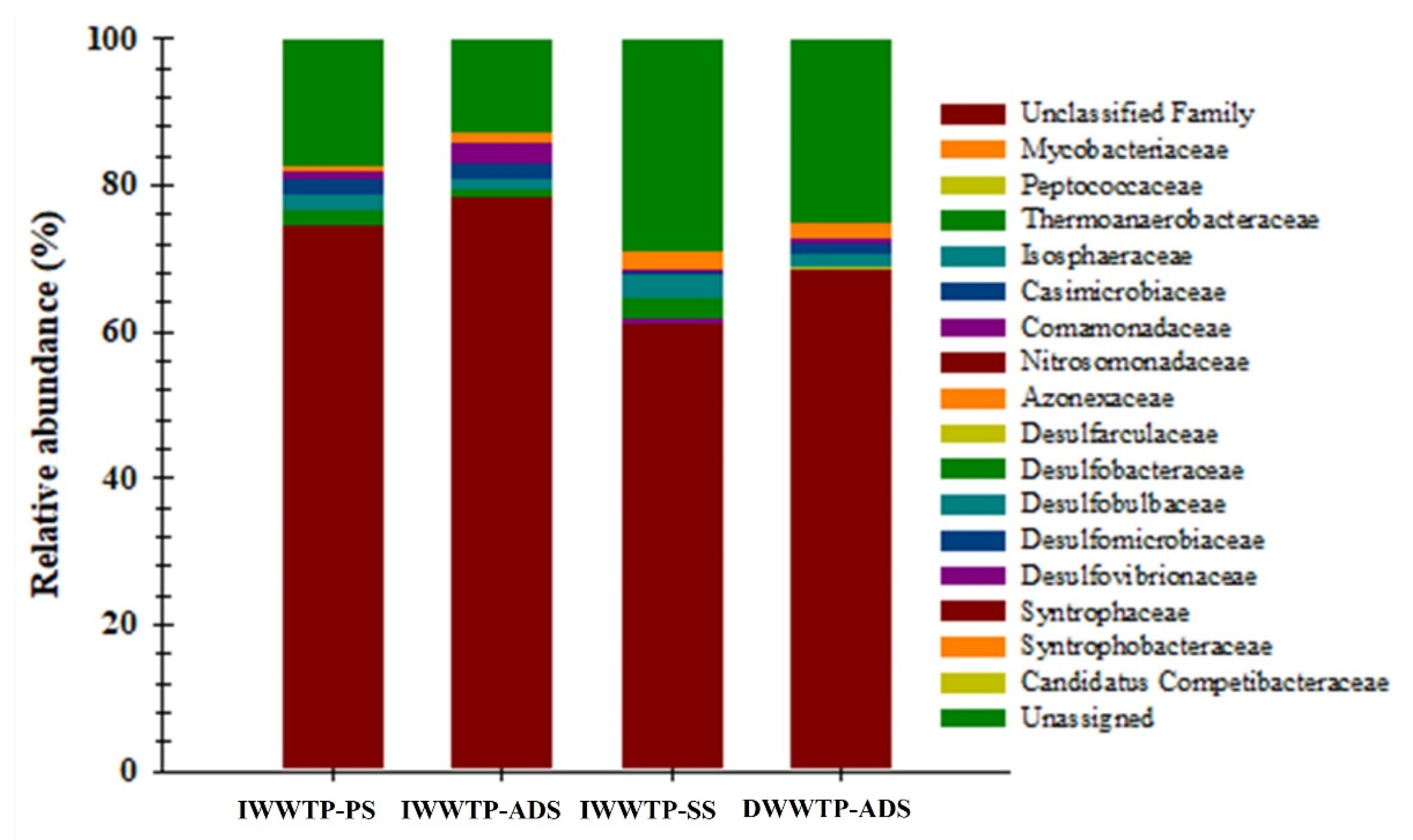
3.3. Identification of Archaea and Bacteria with 16S rRNA Gene Analysis
3.4. Identification of SRBs with dsrB Gene Analysis
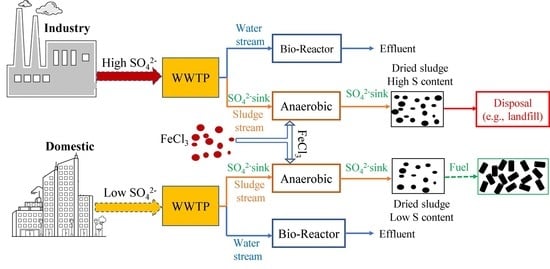
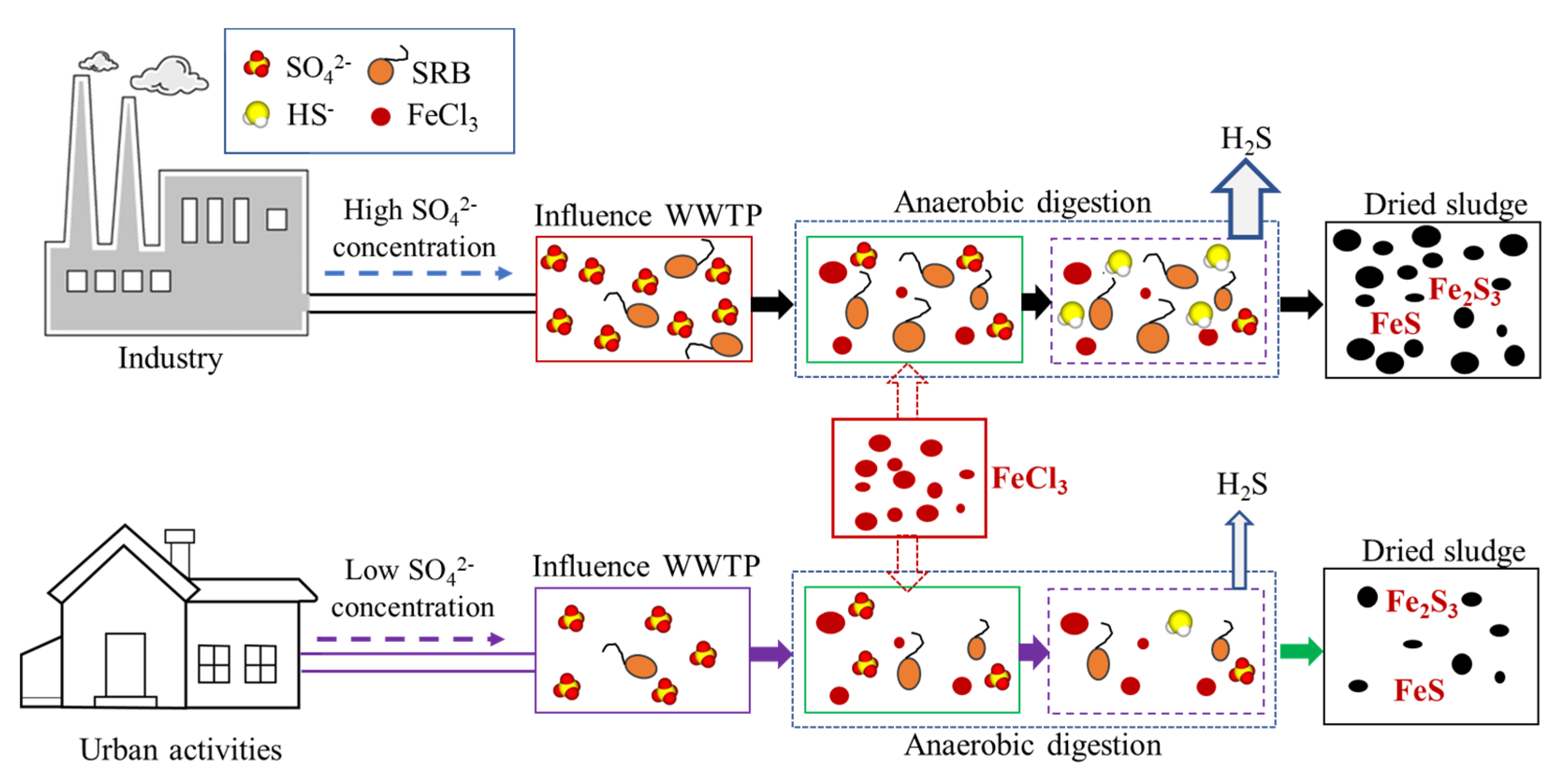
4. Implication
5. Conclusions
- The primary clarifier and anaerobic digester played prominent roles in reducing sulfate in the IWWTP and DWWTP because of biological sulfate reduction under anaerobic conditions.
- The activity of SRB in the IWWTP, receiving a large amount of sulfate from the dyeing industrial complex, was much higher than that in the DWWTP. The results from the batch SRR test indicated that the SRR of the IWWTP sludge was twice as high as that of the DWWTP.
- The high-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA and dsrB genes achieved almost complete coverage (>99%) and revealed the high diversity, richness, and number of ASV communities in both the WWTPs. The results of 16S rRNA and dsrB gene sequencing analyses also indicated the diversity of microorganisms involved in biochemical sulfate reduction in the sulfur cycle.
- Biological sulfate reduction and Fe-S complexation, induced by excessive sulfate and iron in the WWTP, were the primary causes of the high sulfur content in the WWTP sludge.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahuja, S.; Larsen, M.C.; Eimers, J.L.; Patterson, C.L.; Sengupta, S.; Schnoor, J.L. Comprehensive Water Quality and Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Raheem, A.; Ding, L.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Lin, S.-L. Pretreatment, modification and applications of sewage sludge-derived biochar for resource recovery-A review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Sulfur removal from crude oil using supercritical water. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, H. Sludge management–future issues and trends. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkens, W. Sewage sludge as a biomass resource for the production of energy: Overview and assessment of the various options. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B.R. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, P.; Xu, M.; Ning, C.; Lin, C.S.K.; McKay, G. A critical review on preparation, characterization and utilization of sludge-derived activated carbons for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccia, J.; Westerhoff, P. We should expect more out of our sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8271–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: Fundamentals, challenges and considerations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 888–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đurđević, D.; Blecich, P.; Jurić, Ž. Energy recovery from sewage sludge: The case study of Croatia. Energies 2019, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijo-Kleczkowska, A.; Środa, K.; Kosowska-Golachowska, M.; Musiał, T.; Wolski, K. Combustion of pelleted sewage sludge with reference to coal and biomass. Fuel 2016, 170, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Peng, X.; Mao, M.; Chi, Y.; Wang, F. Effect of sludge pellets addition on combustion characteristics and ash behaviour of municipal solid waste. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5351–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatachi, N. Wastewater sludge to energy production. A review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering: 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012053. [Google Scholar]
- Leckner, B. Co-combustion: A summary of technology. Therm. Sci. 2007, 11, 5–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Ogada, T. Sewage sludge combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 55–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Roels, J.; Van De Steene, B. Evolution of the total sulphur content in full-scale wastewater sludge treatment. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Rao, N.C.; Prasad, K.K.; Sarma, P. Bioaugmentation of an anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (AnSBBR) with immobilized sulphate reducing bacteria (SRB) for the treatment of sulphate bearing chemical wastewater. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elferink, S.J.O. Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Anaerobic Bioreactors; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, K.; Ma, G.; Qiao, Y.; Cheng, D.; Jiang, Q. Insights into the effects of operating parameters on sulfate reduction performance and microbial pathways in the anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z. Role of indigenous iron in improving sludge dewaterability through peroxidation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vazquez, C.; Welles, L.; Lotti, T.; Ficara, E.; Rene, E.; van den Brand, T.; Brdjanovic, D.; van Loosdrecht, M. Activated sludge activity tests. In Experimental Methods In Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhen, Y.; Mi, T.; He, H.; Yu, Z. Microbial diversity and community structure of sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in sediment cores from the East China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, C.F.; Pedas, P.; Glaring, M.A.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Stougaard, P. Bacterial diversity in Greenlandic soils as affected by potato cropping and inorganic versus organic fertilization. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geets, J.; Borremans, B.; Diels, L.; Springael, D.; Vangronsveld, J.; van der Lelie, D.; Vanbroekhoven, K. DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 66, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Vela, J. Nitrogen and Sulfur Cycling during Wastewater Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.; Alvarez-Gaitan, J.P.; Stuetz, R.; Moore, S. Sulfur flows and biosolids processing: Using Material Flux Analysis (MFA) principles at wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.L.; Fardeau, M.-L.; Fauque, G.D. Hydrogen sulfide: A toxic gas produced by dissimilatory sulfate and sulfur reduction and consumed by microbial oxidation. In The Metal-Driven Biogeochemistry of Gaseous Compounds in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 237–277. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, A. The Anaerobic Treatment of Sulfate Containing Wastewater. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lens, P.; De Poorter, M.-P.; Cronenberg, C.; Verstraete, W. Sulfate reducing and methane producing bacteria in aerobic wastewater treatment systems. Water Res. 1995, 29, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-J.; Yang, S.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Gu, J.-D. Microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation at different organic loading rates. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, C.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Larsson, M.; Alm, E.; Yekta, S.S.; Svensson, B.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Karlsson, A. 454 pyrosequencing analyses of bacterial and archaeal richness in 21 full-scale biogas digesters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Whitman, W.B. Metabolic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of the methanogenic archaea. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2008, 1125, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Xia, Y.; Lau, F.T.; Tang, D.T.; Fung, W.C.; Fang, H.H.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis of sludge from full-scale anaerobic digesters operated in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5709–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Taylor, M.W.; Turner, S.J. dsrAB-based analysis of sulphate-reducing bacteria in moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7211–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratby, J. Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment; IWA publishing: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, Q.N.; Anam, G.B.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Lee, T.-U.; Jeon, J.-Y.; Choi, Y.-Y.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Lee, B.J. Fate of Sulfate in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants and Its Effect on Sludge Recycling as a Fuel Source. Sustainability 2023, 15, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010311
Ho QN, Anam GB, Kim J, Park S, Lee T-U, Jeon J-Y, Choi Y-Y, Ahn Y-H, Lee BJ. Fate of Sulfate in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants and Its Effect on Sludge Recycling as a Fuel Source. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010311
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Que Nguyen, Giridhar Babu Anam, Jaein Kim, Somin Park, Tae-U Lee, Jae-Young Jeon, Yun-Young Choi, Young-Ho Ahn, and Byung Joon Lee. 2023. "Fate of Sulfate in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants and Its Effect on Sludge Recycling as a Fuel Source" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010311
APA StyleHo, Q. N., Anam, G. B., Kim, J., Park, S., Lee, T.-U., Jeon, J.-Y., Choi, Y.-Y., Ahn, Y.-H., & Lee, B. J. (2023). Fate of Sulfate in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants and Its Effect on Sludge Recycling as a Fuel Source. Sustainability, 15(1), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010311