Abstract
Plant-based food (PBF) is on the rise as an alternative for animal-based food. Europe is leading in the market size compared with the global market. However, the high failure rate for new food products is challenging the success of new PBF in the market. This paper aims to unravel the key success factors (KSFs) from existing brands, contributing to the knowledge on how to achieve success in PBF market. Two subsequent studies employing online surveys were included, which targeted food expert participants. Study 1 focused on the collection of KSFs related to PBF brands utilizing the card sorting approach. Study 2 employed cluster analysis to further investigate the KSFs among different PBF brands. The findings identified six clusters of KSFs under the external and internal factors supporting the success of the PBF brands. Two (‘Consumer’ and ‘Trend’) and four (‘Ideology’, ‘Marketing strategy’, ‘Innovation management’, and ‘Management structure’) clusters were assigned into external and internal factors, respectively. Furthermore, cluster analysis identified four brand clusters: ‘Mature’, ‘Targeted’, ‘Newcomer’, and ‘Established but diversifying’ clusters. Each brand cluster utilized different KSFs into their strategies; however, both external and internal factors were applied, suggesting that there is no one-size-fits-all KSF to succeed in the market.
1. Introduction
The growing world population, estimated to rise to 9.7 billion people by 2050, will create challenges to fulfill the global demand of food for every living individual [1]. In parallel with the growing pressure of the global food supply, the demand for high-quality protein sources is equally increasing, as it is undeniable that protein is an important element in the human diet, and believed to be mainly provided by animal sourced foods (ASF) [2]. Hence, the increased demand for animal-based protein leads to additional challenges, which are mainly related to environmental, sustainability, and health issues [3,4]. Meat production, particularly from ruminants, contributes to the excess greenhouse gas emissions thus resulting in the global warming, as well as polluting the environment, for instance, through the release of chemical substances in fresh water [5,6]. Meat consumption increases the risk of chronic diseases, such as colorectal cancer, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease [5,7,8]. These challenges have also contributed to the development of new plant-based food (PBF) products and increased consumer interest to decrease meat consumption and shift to a plant-based diet [9,10]. Consuming a plant-based diet is deemed to be more sustainable due to the lower utilization of natural resources and lower environmental burden, compared with meat-based diet consumption [11,12]. Additionally, the consumption of PBF is believed to have a beneficial role in health, such as decreasing the risk of certain cancer types, type II diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases [13,14,15].
‘Plant-based’ is a term that reflects the current consumer trend where PBF alternatives are chosen instead of animal-based products, or the decreased consumption of animal-based food in the overall diet [9]. The growing consumer demand sparks reactions in the food industry, who increasingly aim to develop new PBFs with the intention to imitate the sensorial qualities of animal-based food products. Successful products include plant-based meat (such as sausages and burgers) and plant-based dairy products (such as oat and almond milk). On the European market, meat and dairy alternatives are available with various ingredients, such as from soybeans, legume, nuts, and fungi [16]. From a business point of view, the prospect of plant-based protein market is promising. The market growth of plant-based alternatives is expected to expand across the world. In terms of PBF market size, Europe is leading with a 40% market share of the global meat-alternative market [17]. Based on the retail scanning data from Nielsen MarketTrack, the total sales value of PBF in Europe was USD 4.2 billion in terms of Moving Annual Total (MAT) in 2020, an increase of 49% compared with the MAT in 2018 [18]. Despite the promising growth of the PBF market, the industry is still relatively premature, providing opportunities to grow [17].
There are various challenges that hinder the success of newly launched food products, including PBF products. In the FMCG business, the failure rate of consumer goods is as high as 50% to 75% [19]. The high failure rate for new food products highlights the complexity of a successful interplay between many related functions, such as research and development, technology, and marketing [20]. In terms of PBF products, barriers such as habits, familiarity, and beliefs about meat consumption are among the major challenges for consumers to shift towards a PBF lifestyle [9]. Additionally, PBFs are often considered to be inconvenient and less tasty than meat-based foods [21,22]. Therefore, new PBF products should tackle these consumer challenges, while also addressing the importance of health and sustainability issues for consumers [12].
To understand and ensure the success of future PBF products in Europe, relevant guidance and insights are needed. It is necessary for future brands to learn from existing players that have been established in the market, e.g., by utilizing a case study approach to explore and examine the key success factors (KSFs) in a particular market [23], and PBF products or brands are no exception. Alpro and Oatly, two successful first-generation plant-based alternative dairy products, could set the guidance for the future new PBF products innovation or development [9,12]. In every business, there are KSFs which support the company to gain success in a certain market. KSFs could be connected to the competencies or resources from the company or utilized as a tool to aid the managers to sharpen their thinking at the managerial level [23]. They are applicable in every component of a business, such as for a product launch or within their general brand management. Furthermore, KSFs enable a company to distinguish itself from the competitors and to provide unique products or services to the customers. In general, the KSFs of a successful company might set an example for what has to be settled to compete in a certain industry [24,25].
The principal aim of this research was to identify and investigate the KSFs of PBF brands in a European context. This research focuses mainly on the marketing perspective and carried out two subsequent studies to unravel the relevant KSFs from these brands. The first study focused on the collection of success factors related to the PBF brands utilizing the card sorting approach, yielding a set of relevant KSFs in PBFs sector (Study 1). Building upon the results of Study 1, the second study aimed to investigate the KSFs from different PBF brands (Study 2). Therefore, food experts’ views were investigated in both studies to ensure the credibility of KSFs from different perspectives. The findings of this research will provide a better understanding into the marketing of PBF products and give insights for future PBF brands to market their new products successfully.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study 1 Gathering and Identification of KSFs from the PBF Brands
2.1.1. Selection of PBF Brands (Study 1)
The study was initiated with the selection of successful PBF brands, which are representing several food product categories, such as dairy, meat, baked goods, and cheese. Several food experts from universities, institution, NGO, and a European policy officer provided a number of successful PBF brands. Based on the discussion and suggestions of the food experts, researchers in the present study shortlisted the 10 successful brands from different countries, which cover different food categories. The overview of the selected brands is presented in Table 1. Following the brands selection, an online questionnaire was developed, and an ethical approval was obtained by the ethical committee of Ghent University Hospital (BC-08826) for this study.

Table 1.
Overview of the selected cases.
2.1.2. Procedures (Study 1)
Online survey was selected as the data collection method, mostly based on the time restriction of the participants and the fact that participation in the study was voluntary. The study started with the recruitment of participants, which were food experts, defined as people who were active in either a private company, institution, or NGO related to food sector, in Europe. The food experts were initially identified based on the network of the researchers involved, and recruited through personal interaction via several communication channels, such as email and social media. All participants provided the informed consent before starting with the questionnaire. Respondents were provided a link to access the online survey, designed in the software package Eyequestion v.4.1.7 (Logic8 BV, Elst, The Netherlands). Participants were shown 5 random brands (Table 1) based on the William Latin Square design to prevent order effects [26]. Each participant provided success factors based on an open-ended question and could provide as many success factors as possible. Afterwards, few key socio-demographic questions were presented, which included: age, gender, job-related questions.
2.1.3. Data Analysis (Study 1)
The data processing stage was conducted to identify the KSFs, and started with proper data cleaning. The data cleaning process contained removing misspelling, editing the sentences into uniform typologies and only retaining the essential words which explicitly pointed to success factors. The content analysis in this research included the identification of certain keywords mentioned by the participants, followed by inductive coding where we based the code on the identified keywords earlier. The number of occurrences of each keyword was recorded. In order to minimize researchers’ bias, the qualitative data analysis was carried out by multiple researchers and the emerging disagreement was resolved by consensus. KSFs were mapped and higher order clusters for KSFs were formed. Thereby, success factors were later grouped and sub-grouped based on their similarity by utilizing the card sorting approach, where this technique allowed us to arrange and structure the information obtained into systematic groups. Subsequently, the relevant KSFs were shortlisted, yielding a specific number of KSFs for further analysis in Study 2.
2.2. Study 2—Evaluation of the Selected KSFs for PBF Brands
2.2.1. Procedures (Study 2)
As the participation in this study was voluntary and the time restriction of the participants, online survey was selected as the data collection approach. The target participants were food experts who were familiar with the PBF business as well as active in the food sector (industry, institution, or NGO). Specifically, we were targeting food experts from industry related to food manufacturing, NGO focusing on sustainable food products and consumption, and research groups focused on sustainable agri-food or food-related research. The recruitment of the participants was similar with the one from Study 1, with the additional approach in promoting the online questionnaire during an online event where the participants were people involved in the food industry in Europe. Informed consent from all participants was obtained prior to participating in this study. Respondents were given a link to access the online survey, designed in Qualtrics (Qualtrics International Inc, United States). Participants were screened for their familiarity with PBF business, where they would be excluded if they responded ‘No’. Afterwards, participants indicated their awareness of the 10 brands provided (Table 1), by which they were only asked to evaluate the brands they were familiar with. They were shown a matrix of shortlisted KSFs obtained from the result of Study 1 and their selected brand(s). As such, they could indicate the applicability of each factor for each brand they knew. Following this section, participants responded to socio-demographic-related questions similar to the ones in the first questionnaire, which included: age, gender, and job-related questions.
2.2.2. Data Analysis (Study 2)
After data collection, data cleaning and analysis were performed consecutively. Only the completed response data were considered for the data analysis. The statistical data analysis was performed with IBM SPSS version 27 software (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
Two-step cluster analysis, a combination of hierarchical and non-hierarchical K-means clustering [27], was carried out to cluster the brands and the KSFs separately. The values inserted into the cluster analysis were calculated in terms of matrix operations, based on the following formula:
where i is the brand (10 in total, from Table 1) and j is the number of selected KSF obtained from the result of Study 1 (n). Xij is the average value for the selected KSF j, given the brand i. Nij is the total times KSF j has been selected in the scope of brand i and Ni is the total times brand i has been selected. As 10 brands and n KSFs were included in this study, the data transformation yielded a matrix table of 10×n.
Xij = Nij/Ni
Afterwards, hierarchical clustering utilizing Ward’s method was performed to identify the distinct clusters generated based on the similarity of the cases (KSFs or brands) using the distance index of ‘Squared Euclidean Distance’. The dendrogram generated in this step was observed to determine the optimal number of the clusters. This output served as the input for the non-hierarchical K means clustering in order to generate mean scores for each variable which represent the characteristics of the members of each cluster. The cluster analysis was performed two times: for clustering KSFs based on the brands as cluster variables and, vice versa, e.g., for clustering brands.
The relationships between the KSFs were examined using the Spearman Rho correlation coefficient, utilizing the values (Xij) as calculated previously. The significance level was corrected with Bonferroni correction. The network of significant correlations between KSFs were plotted utilizing a force-directed algorithm [28]. The size of the nodes (KSFs) and the thickness of the edges (connection between KSFs) were adapted based on the value of correlation coefficient accordingly. The bigger the node size and the thickness of the edge, the higher the correlation coefficient. Additionally, nodes were assigned to different colors based on their clusters to better visualize the relationship between KSF clusters and the outcome of the correlation analysis. The plot was constructed utilizing the NetworkX library in Python v3.7 (Python Software Foundation, PSF, Fredericksburg, VA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Study 1—Gathering and Identification of Key Success Factors from the Plant-Based Food (PBF) Brands
3.1.1. Participants (Study 1)
In total, 80 participants completed the questionnaire, of which 47 females and 33 males, each providing key success factors for the selected cases. The average age of the participants was 36.33 ± 10.11 years old. Around 70% of the participants had European nationalities, with Belgian, Danish and German being the majority of the European participants. Most of the participants (91.3%) were employed as full-time employees. Around 50% and 20% of the participants worked in the industry and in research institutions, respectively. Among those who worked in the industry, around 30% of them represented large enterprises (e.g., with a total of more than 250 employees). In terms of job level, almost half (44%) of the total participants were in the staff/working category, whereas over 50% of the participants were working in higher levels as managers, advisors, directors, or executives.
3.1.2. Results (Study 1)
One hundred success factor keywords were collected. Some of them were mentioned more frequently than others, such as ‘taste’/‘flavor’ (40 times), ‘quality’ (17 times), ‘innovative’ (15 times), ‘pioneer’ (15 times), ‘variety’ (15 times), and ‘design’ (9 times). Subsequently, the grouping of the KSFs were conducted and six distinct clusters emerged: ‘Consumer’, ‘Trend’, ‘Ideology’, ‘Marketing Strategy’, ‘Innovation Management’, and ‘Management Structure’. Each cluster includes related KSFs or groups of KSFs. Figure 1 presents the map of the clusters and groups of the success factors.
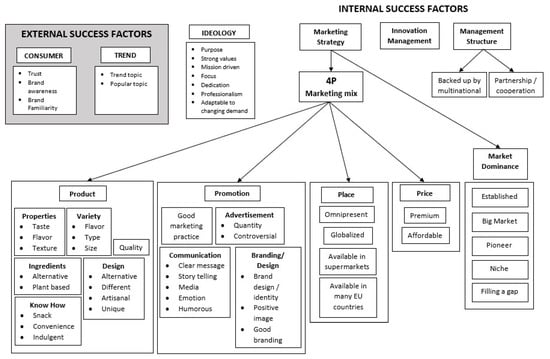
Figure 1.
Map of the clusters and groups of KSFs, generated based on card sorting approach.
Among the clusters, four of them (‘Ideology’, ‘Marketing Strategy’, ‘Innovation Management’, and ‘Management Structure’) are considered as internal success factors. The other clusters (‘Consumer’ and ‘Trend’) represent external success factors. In line with the concept of SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis, the internal factors are defined as factors within the business and can be controlled by the company or brands, such as the strengths (and the weaknesses) of the brands [29]. External factors are linked to aspects external to the organization of the brand, such as the opportunities (and threats) that are wider in the market or business field [29].
External Success Factors
Participants mentioned ‘Trust’, ‘Brand awareness’, and ‘Brand familiarity’ as KSFs related to consumers’ connection to the brand, hence they were classified into the ‘Consumer’ cluster. Participants also referred to ‘Trend topic’ and ‘Popular topic’, which were both implying an external movement or a (societal) trend towards PBF as a success factor of the brands. These two KSFs were further grouped together under the ‘Trend’ cluster.
Internal Success Factors
Four clusters were classified under the internal success factors. ‘Innovative’ and ‘innovation’ were among the most used keywords to explain the success factors of the brands, and were grouped under ‘Innovation management’ cluster. In the ‘Management structure’ cluster, brands were considered successful when they had a ‘partnership or cooperation’ with other brand(s) or organization(s) and also when they were ‘backed up or supported by a multinational organization’.
Another cluster, namely ‘Marketing strategy’, houses many success factors which includes two groups: ‘4P’ and ‘Market dominance’. The former, ‘4P’, refers to the common marketing mix of tools which include Product, Promotion, Price, and Place [30]. In the Product subgroup, the KSFs of the successful PBF brands described the characteristics of the physical product the brands offered, and comprise aspects such as ‘quality’, ‘properties’, ‘variety’, ‘design’, ‘know-how’, and ‘ingredients’. The Promotion includes ‘general good marketing practice’, ‘advertisement’, ‘communication’, and ‘branding’. Meanwhile, Place subgroup covered the point of sales of the products, or how easy the products are to be found by the consumers (‘omnipresent’), but also the strategized point of sales, which includes ‘many different supermarkets’, ‘different EU countries’, or other non-European countries (‘globalized’). The KSFs under the Price subgroup were two contradicting factors, namely ‘premium price’ and ‘affordable price’. In the ‘Market Dominance’ group, the prominent KSFs mentioned by the participants were ‘being the pioneer’ and ‘being established in the PBF market’. The other KSFs in this group included ‘focusing on a niche market’, ‘targeting the big market’, and ‘filling the gap’ in the PBF market. Finally, the cluster ‘Ideology’ includes KSFs related to the philosophical value or practice of the PBF brands, such as ‘having a purpose’ and ‘focus’. Some other KSFs were also mentioned for this cluster, such as ‘mission driven’, ‘having dedication’, ‘professionalism action’, and ‘the ability to adapt to the changing demand’.
Building Study 2 from the Result of Study 1
As the result of Study 1 was the basis for Study 2, KSFs from each cluster were shortlisted and selected by the researchers. A KSF was selected if it was among the top two from each of the group/subgroup in terms of total times being mentioned by the participants of the first study. In total, 19 KSFs were selected from Study 1. The shortlisted KSFs, as presented in Table 2, were utilized in the second survey for further food expert evaluation. In order to avoid potential misinterpretation of the KSFs in Study 2, each KSF was shown to the participants in a full sentence.

Table 2.
The shortlisted KSFs for Study 2.
3.2. Study 2—Evaluation of the Selected Key Success Factors for Plant-Based Food Brands
3.2.1. Participants (Study 2)
In total, 108 respondents participated in Study 2. However, due to incomplete data and failure to comply with the screening question (familiarity in the PBF business), 35 respondents were eliminated, leaving 73 valid responses for analysis. Out of the total number of valid participants, 49 were female and 24 were male participants. The average age of the participants was 36.55 ± 11.21 years old. Around 86% of the participants were European and similar with Study 1, the majority of these participants were Belgian, Danish and German people. Around 48% of the participants were employed in the industry, 20% in academic, 15% in NGO, and 12% in research institution. Among participants who were employed in the industry, 57% were employed in a large company with more than 250 employees. Regarding the job level, around 50% were in a higher-level position (managerial or executive level), whereas the other participants were employed at staff level or lower. Approximately 57% of the participants were employed in a research and development function, whereas the rest were employed in various functions, such as in marketing, communications, management, and sales.
3.2.2. Results (Study 2)
Two-step cluster analysis was performed with the 10 brands as the cases to be clustered against the 19 KSFs as cluster variables, and vice versa, yielding two clustering results: brand clusters and KSF clusters. Based on the dendrograms generated by hierarchical clustering, four clusters were considered to be optimal for clustering both brand clusters and KSFs. The similarities and differences of the clusters were further interpreted based on the mean values generated from the K-means clustering process. Table 3 presents the membership of KSFs and brands in their respective clusters, as well as the mean values of each KSF within each brand cluster. Thereby mean values are used to identify the characteristics of the brand clusters.

Table 3.
Mean scores of key success factors (KSFs) within each brand cluster.
Regarding brand clusters, cluster 1, labelled as ‘Mature’ brands, included two brands (Alpro and Ben & Jerry’s) and was characterized by high scores in five KSFs, namely ‘Established/recognized in the market’, ‘Brand familiarity’, ‘Easily accessible (Place)’, ‘Brand design (Promotion)’, and ‘Product variety (Product)’. These scores were highest when compared to the other clusters. Cluster 2 included Simply V, Violife, and GoodDot and within its own cluster was marked by overall low scores for KSFs, except for ‘Trend topic’, which scored high but still lower compared to cluster 3. The label for this cluster was ‘Newcomer’ brands. Cluster 3 consisted of Oatly and Beyond Meat. Compared to the other clusters, this cluster was characterized by high scores in many KSFs, prominently in ‘Trend topic’, ‘Focus’, ‘Pioneer’, ‘Clear message (Promotion)’, and ‘Innovative’. This cluster was dubbed as ‘Targeted’ brands. Cluster 4 (Oreo, Greggs, and Silk) had overall moderate KSF scores, with higher scores for ‘Brand familiarity’, ‘Established/recognized in the market’, ‘Brand design (Promotion)’, and ‘Affordable price (Price)’. This cluster was referred as ‘Established but diversifying’ brands.
The Relationship among KSFs
Figure 2 presents the network of significant correlations among KSFs. In general, KSFs that scored high in a particular cluster (observed with the same color) were strongly correlated. For instance, the “members” of KSF cluster 2 (‘Trend Topic’, ‘Pioneer’, ‘Innovative’) were connected to each other, implying a stronger correlation as compared to their correlation with other KSFs. However, there were also strong correlations among KSFs which belonged to different clusters. Some KSFs of cluster 3 also had significant correlations with those of cluster 4 (‘Focus’, ‘Product Flavor’ with ‘Premium Price’; ‘Positive image’, ‘Clear message’ with ‘Product Quality’). Other significant correlations across clusters were also observed in one KSF of cluster 4, namely ‘Advertising Strategy’, where it was directly connected with ‘Well established marketing approach’ from cluster 3 as well as with ‘Brand design’ and ‘Easily accessible’ from cluster 1.
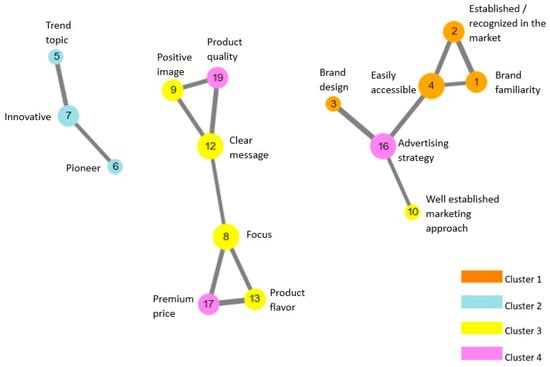
Figure 2.
Network correlation among KSFs according to their clusters. Note. Only significant correlations among KSFs are shown.
4. Discussion
The general aim of this study was to identify the KSFs of the 10 selected PBF brands through the perspectives of food experts in Europe, and to investigate the similarities as well as the differences of KSFs applied in those brands. In Study 1, various KSFs were gathered and classified into two factors, namely external and internal KSFs, in line with the strengths and opportunities of SWOT analysis. While this implies that PBF company/brands should take into account both internal and external factors, these factors should be considered as connected and not independent.
Two external factors emerged from this study, namely ‘Consumer’ and ‘Trend’. KSFs related to the former were ‘Brand familiarity’ and ‘Trust’. Indeed, increased familiarity of PBF brands is expected to increase the market shares of those products [31]. As consumers become familiar and build more trust towards a certain brand, they might also consider trying different products from this brand, as illustrated for plant-based milk brands [32]. The other external factor, ‘Trend’, was also related to consumers. The PBF trend emerged as consumers become more aware of the health, sustainability, and environmental issues caused by meat production and consumption. This consumer trend increased the market demand for meat-alternatives and other types of PBF products in Europe [9]. Thus, companies which acted upon the trend by developing and marketing their PBF brands have a better chance to succeed in the market. For example, a German meat producer Rügenwalder Mühle developed and produced their own meat-alternative products and achieved success in plant-based meat market in Germany. Their journey started by observing and responding to the early emerging trend where consumers demanded more meat-alternative products [33]. Given that both external factors relate to consumers’ demands and have been typically considered as important drivers for the success of a brand or product [34,35], they could be valuable for the initial guidance of companies when planning their journey in the PBF market.
For the internal factors, the majority of the identified KSFs in our first study were in the cluster ‘Marketing Strategy’, specifically in the ‘4P’ group. The KSFs in this group were in line with the concept of the marketing mix, in particular the Product and Promotion subgroups [30]. Three KSFs related to the product characteristics were dominant according to the experts: taste/flavor, quality, and type/variety. Both taste and quality are among the most important attributes for consumers when considering purchasing plant-based products, such as plant-based meat products [36]. Product type/variety as a KSF could offer a brand increased opportunities to expand their markets, resulting in increased volume of sales and revenues by reaching both new and existing consumer segments [37]. This KSF was highlighted in, for example, plant-based cheese and ice cream [38]. Different KSFs were mentioned in relation to the ‘Promotion’ subgroup, especially when it comes to branding. Indeed, branding is the fundamental aspect of marketing processes and the driver for achieving success in business [39], including in the food industry [40]. Other KSFs in ‘Promotion’ subgroup were linked to communication and advertising. These KSFs were reflected in a successful case such as Oatly, which thrives in the dairy-alternative market by creative branding in the packaging design, which also serves as their communication and advertising channel to deliver provocative and humorous messages [41].
Another important element of the marketing mix is the ‘Price’. Some experts mentioned ‘Affordable price’, whereas others stated ‘Premium price’ as a KSF. Although the messages seem conflicting, each advice could be applied according to the brand strategy. For example, one can set the premium price to target specific consumer segments with the aid of certain product properties or by providing more information. Consumers might be willing to pay a premium price for novel food products, given a careful information about the said products is provided [42]. A significant increase in willingness to pay for plant-based meat products was reported after presenting nutrition information to the consumers [43]. On the other hand, one could opt for affordable prices by aiming on a mass production strategy, or by considering private label products. For instances supermarkets in the United Kingdom (e.g., Tesco and Sainsbury) support PBF with both pricing strategies, by providing branded products and private label products [17]. Another example are plant-based eggs, with a higher price compared to the conventional egg products, due to the limited scale of production, including the high cost of the ingredients [44]. In this case, the producers focus on targeting a specific segment of consumers who are willing to pay the premium price, unless the production cost can be lowered to provide lower price and target the broader public. The last element of marketing mix is ‘Place’, which indicate the placement of the products to be accessible to the consumers. Increasing the visibility and accessibility of PBF is important and the placement of PBF products in retail grocery stores might influence consumers in substituting the conventional products [31]. For example, PB meat products in grocery stores are mostly placed close to the conventional meat products. Additionally, other strategies could be considered to increase the prospects of consumers to access these products, such as utilizing an online shop or meal-delivery service [17].
‘Pioneer’ was also mentioned as a KSF by many food experts, which was the member of the ‘Market dominance’ group under the same cluster. Consumers have a tendency to favor the pioneering brands instead of brands which enter the market later, a phenomenon dubbed as ‘pioneering advantage’ [45], and this is also observed for novel food products [46]. Another fundamental internal KSF from the experts’ point of view was ‘Innovation’, under the ‘Innovation Management’ cluster. Innovative products, including in the food industry, have a higher chance to succeed in the market due to the rapid saturation in the market [35].
To be successful in the market, a brand must take into account both external and internal factors. One example is the story of Ben & Jerry’s ice cream. While they originally only offered non-vegan ice cream products, they launched vegan ice cream to the US market in 2016 as response to the growing consumer demand for a non-dairy version of Ben & Jerry’s products. By responding to the trend and consumers’ demand through delivering innovative products as the first in the market, brands might thus become the pioneering brands in the market [33].
Our study further illustrated substantial differences in KSFs between brands in order to become successful. All brands in the ‘Mature’ cluster, which included Alpro and Ben & Jerry’s, utilized both the external and internal factors, with the consumers’ brand familiarity and establishment in the market as their main KSFs. This cluster was also characterized by its abundance of easily accessible sales channels. Consumer research also identified easy of purchase as one of the key drivers to stimulate the adoption of PBF products [47]. Another study targeting both food experts and consumers underlined the need for providing clear information regarding PBFs availability [48]. Product variety, another KSF in this cluster, also increased the success of brands in the ‘Mature’ cluster. Lack of variety has been reported as one of the barriers from the consumers to consume PBF [48].
In the ‘Targeted’ cluster, Oatly and Beyond Meat are also considered successful due to a mixture of external and internal factors. The success of these brands mainly relies on its capacity to anticipate on the PBF trend, followed by their position as pioneers in the market, allowing them to innovate with the right products for the market. Their focus in their marketing efforts, illustrated by their clear, targeted messaging, aided the brands to further establish their position in the market. According to Cooper [34], a clear ‘focus’ supports the success in new product development (NPD), such as narrowing down to a specific strategic arena and portfolio management. Regarding the latter, for instance, prioritization could be achieved in terms of resource utilization in order to invest in the best project and disinvest in less promising projects, which will shorten the time to deliver product the market. One major example is Oatly, which is oriented towards functional health benefits of plant-based dairy. Following their success as a global player in Europe, USA and China, this brand later on focused on global challenges, such as public health and climate change [41]. As such, their focus was a KSF to support its brands positioning strategy. Furthermore, the importance of clear message of marketing activities as a KSF confirms previous research of Aschemann-Witzel [24]. As consumers often put only limited attention towards the content of products and advertisement [49], a clear communication strategy in the domain of PBF products could be only targeted towards the most important content of the message, e.g., the product benefits [50]. As an example, Oatly applied this KSF by focusing on a message related to the functional and health benefits before shifting the focus to the environmental and sustainability issue [41].
The other two clusters namely ‘Newcomer’ and ‘Established but diversifying’ were less focused on specific KSFs. For example, the latter cluster, which included Oreo, Greggs, and Silk, applied similar KSFs as the ‘Mature’ cluster, but to a lesser extent. However, this cluster also utilized pricing strategy (‘Affordable price’) as a KSF compared with the other clusters. Not surprisingly, affordable price is among the most important drivers for consumers to purchase PBF products [36]. Nevertheless, the price of PBF products such as PB meat and PB milk is relatively higher compared with the conventional meat- and dairy products, due to their low supply and niche status [51]. Meanwhile, the ‘Newcomer’ cluster consisted of relatively new entrants (Simply V, Violife, GoodDot), whose KSFs were mainly related to the emerging PBF trend, rather than being considered successful due to specific marketing mix characteristics.
In terms of practical implications, our research indicated that there is no ‘one-size fits all’ KSFs framework, by which future PBF brands could elaborate on our findings to apply and invest in the most suitable KSFs given their business structure and the (competitor) environment. Based on our findings, external and internal success factors should be taken into consideration in order to have success in the PBF market. From an external consumer point of view, it is the right time to anticipate the fact that this market is still trending and consumer demand is not stagnating. Meanwhile, regarding internal success factors, our results from both studies indicated the importance of the 4Ps of the marketing mix. Suwannaporn and Speece [52] stated that managers were prioritizing internal strategy and other elements related to planning in new product development (NPD) over marketing strategy, whereas the results of this study found that some of the most important KSFs of the observed brands were related to marketing and communication. As an illustration, especially in the food processing industry where the stake of competition is high, brands can reinforce their marketing strategy, such as improving brand design and providing a clear message in the promotion. Indeed, consumers as individuals might respond differently to diverse marketing messages based on one’s prior beliefs. Nevertheless, consumers’ behavioral intention towards PBF could potentially be enhanced by the repeated exposure of PBF-related message [32,53]. Therefore, brands could adjust their promotional message accordingly to support the marketing strategy. Other elements of the marketing mix should also be considered, particularly those related product components such as taste, quality and product variety, which are essential for consumers [36,37]. Additionally, increasing the visibility and ease of access for consumers to purchase PBF products [17,31] as well as drawing attention to the message to promote such products will be necessary. Although it might depend on one’s feasibility to decide on the pricing strategy, adjusting the price according to target the consumers is also fundamental. One might be unable to focus on all KSFs related to the marketing mix altogether. Therefore, adaptation and careful targeting to the market is also important to thrive in the market, as it allows brands to distinguish themselves among the competitors. As consumers and markets are not static, brands should also be dynamic in terms of applying the suitable marketing strategy, by taking into account of the KSFs as a guidance to achieve success. A combination of these external and internal KSFs inspired by the PBF brands will potentially increase the success of future PBF brands in the European market.
Finally, we would like to address some limitations of our research. The focus of this research was limited to the European market and oriented towards the evaluation of ten PBF brands. Additionally, a qualitative approach was utilized at the early stage of this research. The approach we took for the purpose of data collection was through online questionnaires for both studies. The decision of this approach was mostly based on the time restriction of the industry experts. Incorporation of verbal interviews or focus group approach might be interesting for more elaborate and comprehensive data collection, which future research should take into consideration. Although some might consider the number of participants (80 in Study 1 and 73 in Study 2) in this research as insufficient to conclude the results for the European level, one should bear the qualitative approach in mind and that the participants were experts active in the European food sector. However, future studies may recruit on a broader scale, thus offering a better chance to reach more experts along the agri-food chain. The recruitment approach was limited to online channels considering time and budget constraints. Therefore, future research could explore expert recruitment in-person, in combination with online expert recruitment (e.g., via the professional social media platform LinkedIn). One possible opportunity for in-person recruitment is by approaching expert participants attending international food events such as trade fairs, (scientific) conferences, etc. Furthermore, we are aware that the majority of the participants were from northern and western European countries; thus, the findings should not be generalized. Nonetheless, especially in this era where the market is dynamic and not much predictable, this research contributed to the literature by exploring the insights to the success in the PBF market. Furthermore, this research included several alternative product types (dairy, meat, cheese, and baked goods); however, the brand clusters generated in study 2 were not based on product types. For example, the members of the ‘Targeted’ cluster were Oatly and Beyond Meat, which were focusing on dairy- and meat-alternatives, respectively. Hence, the results of our research should be treated cautiously and interpreted from a generic PBF market point of view. The present study showed relevant KSFs from the experts’ point of views, which were utilized by the brands to succeed in the PBF market regardless of the product types. Nevertheless, it would be interesting for future research to also dive into the KSFs for a single product type. Since the focus of our research was mainly on marketing perspectives, the KSFs obtained and analyzed in this research might be complemented with other relevant success factors for PBF brands. As such, future research could validate our findings on a larger scale, but also identify and investigate the success factors from other angles, such as from a research and development perspective.
5. Conclusions
The production and consumption of PBF in Europe is continuously rising, mostly driven by health and environmental concerns. Although the market is promising, there are still opportunities to grow in terms of marketing new PBF products. This research brings new insights into how to market new PBF products successfully, based on the lessons learned in the form of KSFs from the current PBF brands in the market. The present study identified external KSFs which were related to consumers and trends, whereas the internal KSFs were typically factors associated with the concept of the marketing mix (4P: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion). Several KSFs were more highlighted by food experts, especially those related to the product (taste/flavor, quality, type/variety), or promotion (branding). The observed brands utilized both external and internal KSFs, indicating the importance of KSF combinations instead of emphasizing a single KSF. Brands were classified based on their similarities in terms of the KSFs they focused on, resulting in four brand clusters: ‘Mature’, ‘Newcomer’, ‘Targeted’, and ‘Established but diversifying’. Although this study showed that there was no ‘one-size fits all’ KSFs framework, future brands could build upon our research and adjust accordingly based on their business environment to support their success in the PBF market.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.R., J.J.S. and H.D.S.; methodology, L.R., J.J.S. and H.D.S.; software, L.R.; validation, J.J.S. and H.D.S.; formal analysis, L.R.; investigation, L.R.; resources, F.J.A.P.-C. and X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.R.; writing—review and editing, L.R., J.J.S., and I.F.; visualization, L.R.; supervision, J.J.S., H.D.S., X.G., F.J.A.P.-C. and K.-B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, grant number 862957.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration, the EU General Data Protection Regulation 2016/679 and approved by the ethical committee of Ghent University Hospital (BC-08826).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schneider, U.A.; Havlík, P.; Schmid, E.; Valin, H.; Mosnier, A.; Obersteiner, M.; Böttcher, H.; Skalský, R.; Balkovič, J.; Sauer, T.; et al. Impacts of population growth, economic development, and technical change on global food production and consumption. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewy, M.W.; Patel, A.; Abdelmagid, M.G.; Mohamed Elfadil, O.; Bonnes, S.L.; Salonen, B.R.; Hurt, R.T.; Mundi, M.S. Plant-Based Diet: Is It as Good as an Animal-Based Diet When It Comes to Protein? Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2022, 11, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature 2014, 515, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zanten, H.H.E.; Mollenhorst, H.; Klootwijk, C.W.; van Middelaar, C.E.; de Boer, I.J. Global food supply: Land use efficiency of livestock systems. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 21, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Aveyard, P.; Garnett, T.; Hall, J.W.; Key, T.J.; Lorimer, J.; Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Scarborough, P.; Springmann, M.; Jebb, S.A. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science 2018, 361, eaam5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. A global assessment of the water footprint of farm animal products. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, S.; Overvad, K.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Jakobsen, M.U.; Egeberg, R.; Tjønneland, A.; Nailler, L.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Krogh, V.; et al. Meat consumption and mortality-results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norat, T.; Bingham, S.; Ferrari, P.; Slimani, N.; Jenab, M.; Mazuir, M.; Overvad, K.; Olsen, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Clavel, F.; et al. Meat, fish, and colorectal cancer risk: The European Prospective Investigation into cancer and nutrition. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Gantriis, R.F.; Fraga, P.; Perez-Cueto, F.J. Plant-based food and protein trend from a business perspective: Markets, consumers, and the challenges and opportunities in the future. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M. Consumer acceptance of blending plant-based ingredients into traditional meat-based foods: Evidence from the meat-mushroom blend. Food Qual. Preference 2020, 79, 103758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabate, J.; Soret, S. Sustainability of plant-based diets: Back to the future. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100 (Suppl. 1), 476S–482S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Sustainability, health and consumer insights for plant-based food innovation. Int. J. Food Des. 2020, 5, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, M.; Karhu, E. The role of plant-based nutrition in cancer prevention. J. Unexplor. Med. Data 2018, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, C.K.; Skulas-Ray, A.C.; Champagne, C.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Plant protein and animal proteins: Do they differentially affect cardiovascular disease risk? Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 712–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonstad, S.; Butler, T.; Yan, R.; Fraser, G.E. Type of vegetarian diet, body weight, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Agriculture and Rural Development. Market Developments and Policy Evaluation Aspects of the Plant Protein Sector in the EU; Final Report; Agrosynergie EEIG for the European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deloitte. Plant-Based Alternatives—Driving Industry M & A; Deloitte: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Proveg International and University of Copenhagen. Plant-based foods in Europe: How big is the market? In Smart Protein Plant-based Food Sector Report; Proveg International: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dijksterhuis, G. New product failure: Five potential sources discussed. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, A.; Behdani, B.; Fogliano, V.; Luning, P.A. A systems approach to dynamic performance assessment in new food product development. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, J.; Godinho, C.A.; Truninger, M. Reducing meat consumption and following plant-based diets: Current evidence and future directions to inform integrated transitions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reipurth, M.F.S.; Hørby, L.; Gregersen, C.G.; Bonke, A.; Perez-Cueto, F.J. Barriers and facilitators towards adopting a more plant-based diet in a sample of Danish consumers. Food Qual. Preference 2019, 73, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G.; Ellegaard, C. The Concept of Key Success Factors: Theory Method; MAPP: Toronto, ON, USA, 1992; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.; Niedzwiedzka, B.; Verbeke, W.; Bech-Larsen, T. Lessons for public health campaigns from analysing commercial food marketing success factors: A case study. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelhöhn, W. What is a key success factor? Eur. Manag. J. 1998, 16, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFie, H.J.; Bratchell, N.; Greenhoff, K.; Vallis, L.V. Designs to balance the effect of order of presentation and first-order carry-over effects in hall tests. J. Sens. Stud. 1989, 4, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. Multivariate Data Analysis, 8th ed.; Cengage Learning EMEA: Hampshire, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fruchterman, T.M.; Reingold, E.M. Graph drawing by force-directed placement. Softw. Pract. Exp. 1991, 21, 1129–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, L.G. The SWOT Analysis: Using Your Strength to Overcome Weaknesses, Using Opportunities to Overcome Threats; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.E.; Perreault, W. Basic Marketing, A Managerial Approach; US McGrow Hill: Columbus, OH, USA, 2000; Volume 40, p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loo, E.J.; Caputo, V.; Lusk, J.L. Consumer preferences for farm-raised meat, lab-grown meat, and plant-based meat alternatives: Does information or brand matter? Food Policy 2020, 95, 101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beacom, E.; Bogue, J.; Repar, L. Market-oriented Development of Plant-based Food and Beverage Products: A Usage Segmentation Approach. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2021, 27, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, U.A.; Herstatt, C.; Tiwari, R.; Dedehayir, O.; Mäkinen, S.J. The vegan trend and the microfoundations of institutional change: A commentary on food producers’ sustainable innovation journeys in Europe. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.G. The drivers of success in new-product development. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2019, 76, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart-Knox, B.; Mitchell, P. What separates the winners from the losers in new food product development? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, J.; Mitchell, R. Assessing the General Population’s Implicit Perception of the Plant-Based Food Category; The Good Food Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ElMaraghy, H.; Schuh, G.; ElMaraghy, W.; Piller, F.; Schönsleben, P.; Tseng, M.; Bernard, A. Product variety management. Cirp Ann. 2013, 62, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry. Winning with Plant-Based Unlocking the Keys to Success for a Growing Market; Kerry: Wisconsin, WI, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, S. Marketing Management: A Relationship Marketing Perspective; Macmillan: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Davčik, N.S.; Rundquist, J. An Exploratory Study of Brand Success: Evidence From the Food Industry. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2012, 24, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.H. Brands as activists: The Oatly case. J. Brand Manag. 2020, 27, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavari, M.; Castellini, A.; Xhakollari, V. A short review on willingness to pay for novel food. In Case Studies on the Business of Nutraceuticals, Functional and Super Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Bao, J. Paying for the Greater Good?-What Information Matters for Beijing Consumers’ Willingness to Pay for Plant-Based Meat? Foods 2022, 11, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondoni, A.; Millan, E.; Asioli, D. Plant-based Eggs: Views of Industry Practitioners and Experts. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2021, 34, 564–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, G.S.; Nakamoto, K. Consumer preference formation and pioneering advantage. J. Mark. Res. 1989, 26, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florack, A.; Koch, T.; Haasova, S.; Kunz, S.; Alves, H. The Differentiation Principle: Why Consumers Often Neglect Positive Attributes of Novel Food Products. J. Consum. Psychol. 2021, 31, 684–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejda, K.; Urbanovich, T.; Wilks, M. Accelerating Consumer Adoption of Plant-Based Meat; Good Food Inst: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, B.; Hadwiger, K. Plant-Based Foods for Future—Results of Consumer and Professional Expert Interviews in Five European Countries—EIT-Food Project “The V-Place”; Universität Hohenheim, Institut für Agrarpolitik und Landwirtschaftliche Marktlehre: Stuttgart, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peschel, A.O.; Orquin, J.L.; Loose, S.M. Increasing consumers’ attention capture and food choice through bottom-up effects. Appetite 2019, 132, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschel, A.O.; Kazemi, S.; Liebichová, M.; Sarraf, S.C.M.; Aschemann-Witzel, J. Consumers’ associative networks of plant-based food product communications. Food Qual. Preference 2019, 75, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.J. We Can’t Keep Meating Like This: Attitudes towards Vegetarian and Vegan Diets in the United Kingdom. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannaporn, P.; Speece, M.W. Assessing new product development success factors in the Thai food industry. Br. Food J. 2010, 112, 364–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, A.; Irz, X.; Hartikainen, H. How effective are messages and their characteristics in changing behavioural intentions to substitute plant-based foods for red meat? The mediating role of prior beliefs. Appetite 2018, 1, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).