Sustainable Management and Valorization of Agri-Food Industrial Wastes and By-Products as Animal Feed: For Ruminants, Non-Ruminants and as Poultry Feed
Abstract
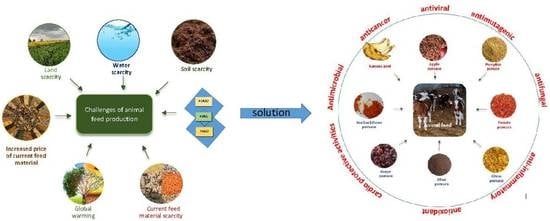
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
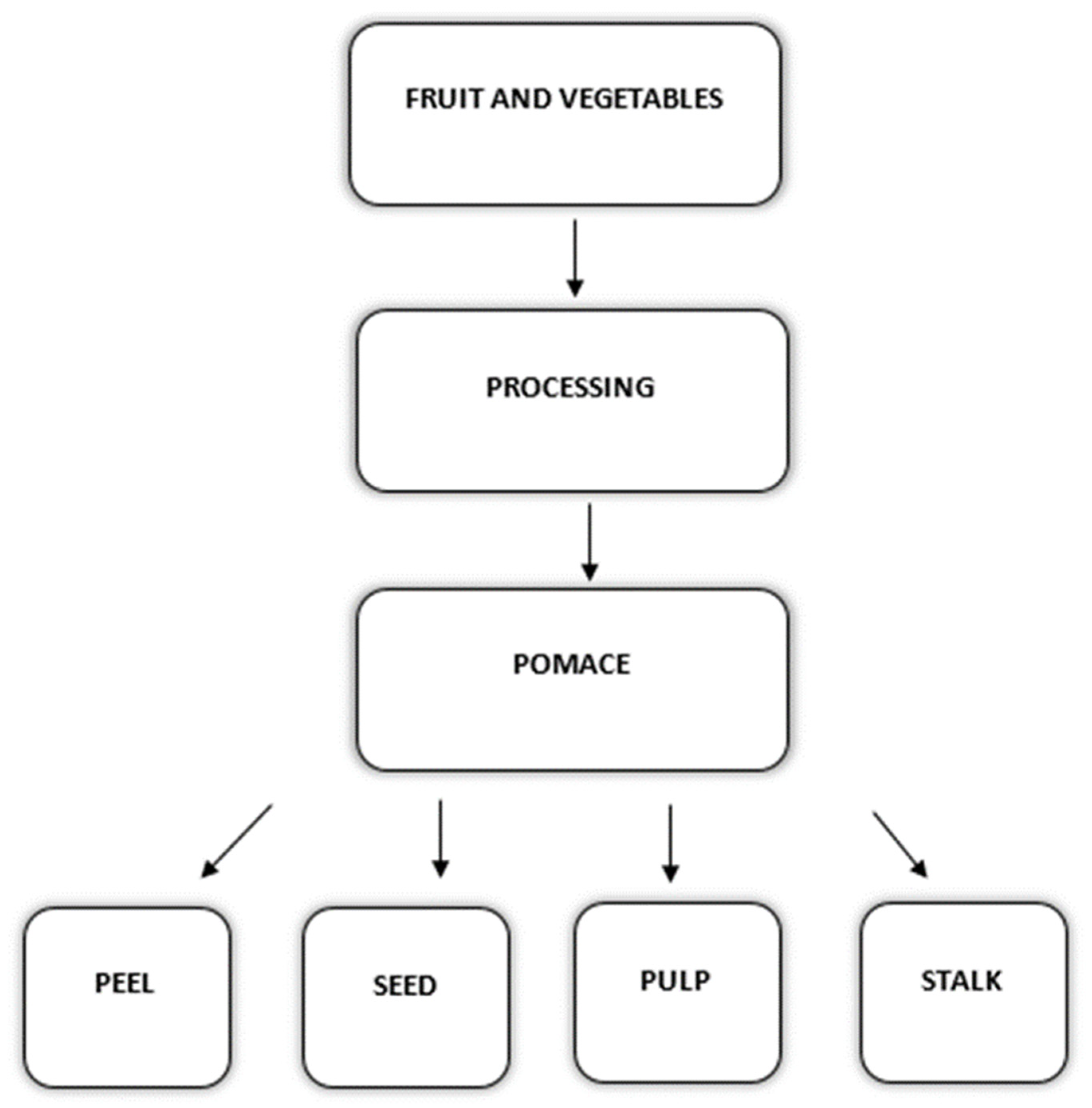
3. Composition of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes
3.1. Proteins and Enzymes
| Feed | Crude Protein (% of DM) | Metabolizable Protein (g/kg DM) | Protein Degradability (% DM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean meal | 53. 60 | 95 | 58.50 | [70] |
| Heat treated Rapeseed cake | 36.30 | 166 | 53.40 | [71] |
| Cold pressed Rapeseed cake | 33.20 | 102 | 89.20 | [71] |
| Maize grain | 10.28 | 95.26 | 6.73 | [72] |
| Wheat bran | 15.68 | 107.11 | 9.23 | [72] |
| Maize fodder | 9.77 | 72.01 | 5.37 | [72] |
| Canola meal | 40.10 | 92 | 4.75 | [70,73] |
| Tomato pomace | 22.21 | 6.30 | 9.74% | [74] |
| Beetroot pulp | 93.40 | 4.8 | 3.46% | [74] |
3.2. Dietary Fibre
3.3. Polyphenolic Compounds
Phenolic Compounds in Wastes and By-Products
3.4. Essential Oils and Lipids
3.5. Organic Acids
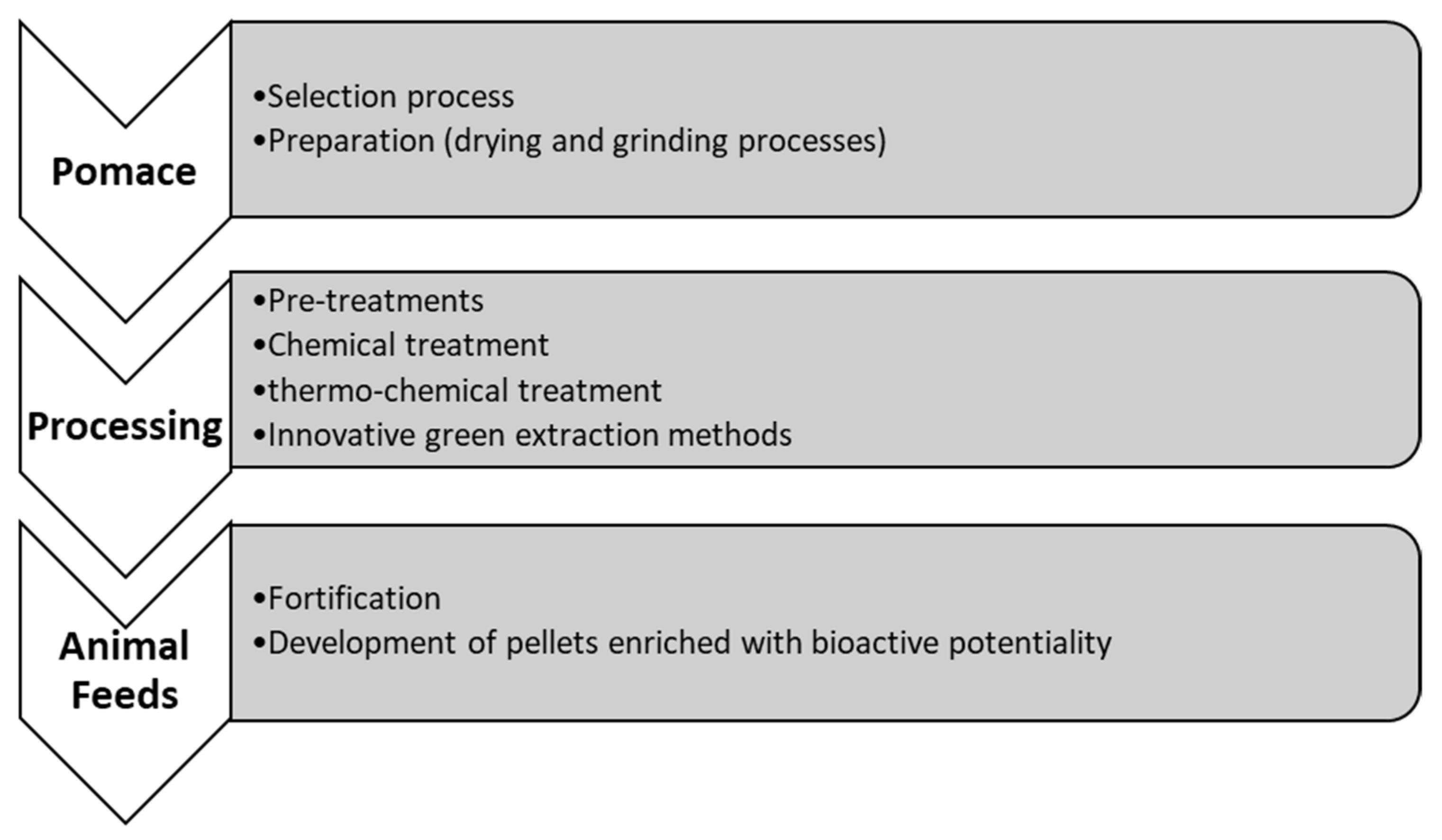
4. FVWs in Animal Feeds
4.1. Utilization of FVW in Ruminant Feed
4.2. Utilization of FVW in Poultry Feed
5. Safety and Regulations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sagar, N.A.; Pareek, S.; Sharma, S.; Yahia, E.M.; Lobo, M.G. Fruit and vegetable waste: Bioactive compounds, their extraction, and possible utilization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurostat. 2022. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/safety/food-waste_en (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Coman, V.; Teleky, B.E.; Mitrea, L.; Martău, G.A.; Szabo, K.; Călinoiu, L.F.; Vodnar, D.C. Bioactive potential of fruit and vegetable wastes. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 91, 157–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FAO. Definitional Framework of Food Losses and Waste; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/at144e/at144e.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Salunkhe, D.K.; Kadam, S. (Eds.) Handbook of Fruit Science and Technology: Production, Composition, Storage, and Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Barta, J.; Balla, C.; Vatai, G. Dehydration preservation of fruits. In Handbook of Fruits and Fruit Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 133–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, N.K.; Sidhu, J.; Barta, J.; Wu, J.; Cano, M.P. (Eds.) Handbook of Fruits and Fruit Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Plazzotta, S.; Manzocco, L.; Nicoli, M.C. Fruit and vegetable waste management and the challenge of fresh-cut salad. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R. (Ed.) Valorization of Agri-Food Wastes and By-Products: Recent Trends, Innovations and Sustainability Challenges; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Joudu, I.; Bhat, R. Dietary fiber from underutilized plant resources—A positive approach for valorization of fruit and vegetable wastes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perussello, C.A.; Zhang, Z.; Marzocchella, A.; Tiwari, B.K. Valorization of apple pomace by extraction of valuable compounds. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 776–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiles, A.; Campbell, G.M.; Struck, S.; Rohm, H.; Hernando, I. Fiber from fruit pomace: A review of applications in cereal-based products. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, V.; Trabert, A.; Keller, J.; Bunzel, M.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Defined shear and heat treatment of apple pomace: Impact on dietary fiber structures and functional properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapidou, E.; Sossidou, E.; Mitlianga, P. Fruit and vegetable co-products as functional feed ingredients in farm animal nutrition for improved product quality. Agriculture 2015, 5, 1020–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, F.V.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, E.H.; Pintea, A. Phenolic compounds, flavonoids, lipids and antioxidant potential of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) pomace fermented by two filamentous fungal strains in solid state system. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xie, M. Comparison of (poly) phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of pomace extracts from kiwi and grape juice. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilonu, M.; Shale, K.; Arthur, G.; Naidoo, K.; Mbatha, M. Phytochemical benefits of agroresidues as alternative nutritive dietary resource for pig and poultry farming. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1035071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.; Singh, R.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; MacFarlane, D.; Patti, A.F.; Arora, A. Bioactives from fruit processing wastes: Green approaches to valuable chemicals. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, N.; Sharma, K.; Koteswararao, R.; Sinha, M.; Baral, E.; Cho, M.H. Citrus essential oils: Extraction, authentication and application in food preservation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmemies-Beauchet-Filleau, A.; Rinne, M.; Lamminen, M.; Mapato, C.; Ampapon, T.; Wanapat, M.; Vanhatalo, A. Alternative and novel feeds for ruminants: Nutritive value, product quality and environmental aspects. Animal 2018, 12, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Arjona, L.P.; Ramírez-Mella, M. Pumpkin waste as livestock feed: Impact on Nutrition and Animal Health and on Quality of Meat, Milk, and Egg. Animals 2019, 9, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayengwa, T.; Mapiye, C. Citrus and winery wastes: Promising dietary supplements for sustainable ruminant animal nutrition, health, production, and meat quality. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Wu, W. Soil and crop management strategies to ensure higher crop productivity within sustainable environments. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balehegn, M.; Duncan, A.; Tolera, A.; Ayantunde, A.A.; Issa, S.; Karimou, M.; Zampaligré, N.; Kiema, A.; Gnanda, I.; Varijakshapanicker, P.; et al. Improving adoption of technologies and interventions for increasing supply of quality livestock feed in low- and middle-income countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitbarek, M.B. Some Selected Vegetable and Fruit Wastes for Poultry Feed. J. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rauw, W.M.; Rydhmer, L.; Kyriazakis, I.; Øverland, M.; Gilbert, H.; Dekkers, J.C.; Hermesch, S.; Bouquet, A.; Gómez Izquierdo, E.; Louveau, I.; et al. Prospects for sustainability of pig production in relation to climate change and novel feed resources. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, M.; Bakshi, M.P.; Makkar, H.P. Waste to worth: Fruit wastes and by-products as animal feed. CAB Rev. 2015, 10, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi MP, S.; Wadhwa, M.; Makkar, H.P. Waste to worth: Vegetable wastes as animal feed. CAB Rev. 2016, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesogan, A.T. What are feeds worth? A critical evaluation of selected nutritive value methods. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium, Gainesville, FL, USA, 10–11 January 2002; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chikwanha, O.C.; Raffrenato, E.; Muchenje, V.; Nolte JV, E.; Mapiye, C. Effect of grape (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Pinotage) pomace supplementation on nutrient utilization in finisher lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 179, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyard, J.R.; Myers, C.A.; Murdoch, G.K.; Rezamand, P.; Chibisa, G.E. Optimum grape pomace proportion in feedlot cattle diets: Ruminal fermentation, total tract nutrient digestibility, nitrogen utilization, and blood metabolites. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanušovský, O.; Gálik, B.; Bíro, D.; Šimko, M.; Juráček, M.; Rolinec, M.; Zábranský, L.; Philipp, C.; Puntigam, R.; Slama, J.A.; et al. The Nutritional Potential of Grape By-Products from the Area of Slovakia and Austria. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinerio, C.A.; Fadel, J.G.; Asmus, J.; Heguy, J.M.; Taylor, S.J.; DePeters, E.J. Tomato seeds as a novel by-product feed for lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4811–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, S.; Viveros, A.; Centeno, C.; Romero, C.; Arija, I.; Brenes, A. Effects of dietary grape seed extract on growth performance, amino acid digestibility and plasma lipids and mineral content in broiler chicks. Animal 2013, 7, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiplakou, E.; Zervas, G. The effect of dietary inclusion of olive tree leaves and grape marc on the content of conjugated linoleic acid and vaccenic acid in the milk of dairy sheep and goats. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; IFIF. Good practices for the feed industry—Implementing the Codex Alimentarius Code of Practice on Good Animal Feeding. In FAO Animal Production and Health Manual No. 9; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kasza, G.; Szabó-Bódi, B.; Lakner, Z.; Izsó, T. Balancing the desire to decrease food waste with requirements of food safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Jörundsdóttir, H.Ó. Food in the bioeconomy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, D.E.A.; Scarioni, S.; Tava, A.; Panseri, S.; Zuorro, A. Fruit and Vegetable Wholesale Market Waste: Safety and Nutritional Characterisation for Their Potential Re-Use in Livestock Nutrition. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Espinoza, M.A.; Ayed, C.; Foster, T.; Camacho MD, M.; Martínez-Navarrete, N. The impact of freeze-drying conditions on the physico-chemical properties and bioactive compounds of a freeze-dried orange puree. Foods 2020, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mphahlele, R.R.; Fawole, O.A.; Makunga, N.P.; Opara, U.L. Effect of drying on the bioactive compounds, antioxidant, antibacterial and antityrosinase activities of pomegranate peel. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbondo, N.N.; Owino, W.O.; Ambuko, J.; Sila, D.N. Effect of drying methods on the retention of bioactive compounds in African eggplant. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgilevich, A.; Birge, T.; Kentala-Lehtonen, J.; Korhonen-Kurki, K.; Pietikäinen, J.; Saikku, L.; Schösler, H. Transition towards circular economy in the food system. Sustainability 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriela MM, I.; Ganjyal, G. Fruit Processing By-Products: A Rich Source for Bioactive Compounds and Value-Added Products. In Food Processing By-Products and their Utilization; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gowe, C. Review on potential use of fruit and vegetables by-products as a valuable source of natural food additives. Food Sci. Qual. Manag. 2015, 45, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- De la Torre, I.; Acedos, M.G.; Ladero, M.; Santos, V.E. On the use of resting L. delbrueckii spp. delbrueckii cells for D-lactic acid production from orange peel wastes hydrolysates. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 145, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerska, J.; Michalska, A.; Figiel, A. A review of new directions in managing fruit and vegetable processing by-products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, I.; Segliņa, D. Content of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Fresh Apple, Pomace and Pomace Water Extract—Effect of Cultivar. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B. Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 2019, 73, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruczek, M.; Gumul, D.; Kačániová, M.; Ivanišhová, E.; Mareček, J.; Gambuś, H. Industrial Apple Pomace By-Products as A Potential Source Of Pro-Health Compounds In Functional Food. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2017, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, I.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Bimbela, F.; Ancín-Azpilicueta, C.; Gandía, L.M. Fruit and vegetable waste management: Conventional and emerging approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Anwar, Z.; Irshad, M.; Asad, M.J.; Ashfaq, H. Cellulase production from species of fungi and bacteria from agricultural wastes and its utilization in industry: A review. Adv. Enzym. Res. 2016, 4, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.R.; Pandey, A. Novel enzymatic processes applied to the food industry. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, C.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K. Utilization of pomegranate peel waste for the production and characterization of invertase using Cladosporium sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2016, 5, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Uygut, M.A.; Tanyildizi, M.Ş. Optimization of alpha-amylase production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens grown on orange peels. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2018, 42, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedeji, O.; Bakare, M.K.; Adewale, I.O.; Olutiola, P.O.; Omoboye, O.O. Optimized production and characterization of thermostable invertase from Aspergillus niger IBK1, using pineapple peel as alternate substrate. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 9, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, P.; Mahajan, R. Cellulase and xylanase synergism in industrial biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8711–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Pitarch, A.; Hermans, D.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Bindelle, J.; Everaert, N.; Beckers, Y.; Torrallardona, D.; Bruggeman, G.; Gardiner, G.E.; Lawlor, P.G. Effect of feed enzymes on digestibility and growth in weanedpigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2017, 233, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, B.; Zhang, R.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Dietary Sea buckthorn Pomace induces beige adipocyte formation in inguinal white adipose tissue in lambs. Animals 2019, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, L.; Hong, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Z.; Che, L.; Feng, B.; et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with exogenous catalase on growth performance, oxidative stress, and hepatic apoptosis in weaned piglets challenged with lipopolysaccharide. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallès, J.P.; Montoya, C.A. Dietary alternatives to in-feed antibiotics, gut barrier function and inflammation in piglets post-weaning: Where are we now? Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 274, 114836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Ghosh, U. Statistical Optimization of Fermentation Parameters for Cellulase Production Utilizing Banana Peel. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uday, U.S.P.; Majumdar, R.; Tiwari, O.N.; Mishra, U.; Mondal, A.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Bhunia, B. Isolation, screening and characterization of a novel extracellular xylanase from Aspergillus niger (KP874102. 1) and its application in orange peel hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashetty, S.B.; Biradar, V. Orange peel as novel substrate for enhanced invertase production by a. niger in solid state fermentation. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.; Waghorn, G.C. Dietary nitrogen-definitions, digestion, excretion and consequences of excess for grazing ruminants. Proc. New Zld Grassl. Assoc. 2008, 70, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadele, Y.; Amha, N. Use of different non protein nitrogen sources in ruminant nutrition: A review. Adv. Life Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M. Nutritional value of proteins from different food sources. A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 6–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesseraud, S.; Temim, S.; Le Bihan-Duval, E.; Chagneau, A.M. Increased responsiveness to dietary lysine deficiency of pectoralis major muscle protein turnover in broilers selected on breast development. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.W.; Kidd, M.T.; Chrystal, P.V.; McQuade, L.R.; McInerney, B.V.; Selle, P.H.; Liu, S.Y. Assessment of limiting dietary amino acids in broiler chickens offered reduced crude protein diets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, S.; Hvelplund, T.; Weisbjerg, M.R. Ideal amino acid profiles as a basis for feed protein evaluation. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2000, 64, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtanen, P.; Hetta, M.; Swensson, C. Evaluation of canola meal as a protein supplement for dairy cows: A review and a meta-analysis. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 91, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldmäe, H.; Leming, R.; Kass, M.; Lember, A.; Tölp, S.; Kärt, O. Chemical composition and nutritional value of heat-treated and cold-pressed rapeseed cake. Vet. Ir. Zootech. 2010, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Das, L.K.; Kundu, S.S.; Kumar, D.; Datt, C. The evaluation of metabolizable protein content of some indigenous feedstuffs used in ruminant nutrition. Vet. World 2014, 7, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maxin, G.; Ouellet, D.R.; Lapierre, H. Ruminal degradability of dry matter, crude protein, and amino acids in soybean meal, canola meal, corn, and wheat dried distillers grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5151–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, A.; Safamehr, A.; Palangi, V.; Mehmannavaz, Y.M. The Determination of metabolizable protein of some feedstuffs used in ruminant. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 3, 804–806. [Google Scholar]
- Zebeli, Q.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Tafaj, M.; Boguhn, J.; Ametaj, B.N.; Drochner, W. Invited review: Role of physically effective fiber and estimation of dietary fiber adequacy in high-producing dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, G.G.; Fondevila, G.; Cámara, L. The importance of the fibre fraction of the feed in non-ruminant diets. In The Value of Fibre. Engaging the Second Brain for Animal Nutrition; González-Ortiz, G., Bedford, M.R., Knudsen, K.E.B., Courtin, C.M., Classen, H.L., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publisher: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 61–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kheravii, S.K.; Morgan, N.K.; Swick, R.A.; Choct, M.; Wu, S.B. Roles of dietary fibre and ingredient particle size in broiler nutrition. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2018, 74, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, B.A. Advances in the understanding of dietary fibre and its components in relation to the use of alternative feed ingredients in modern poultry and livestock production. In Proceedings of the 2018 Animal Nutrition Conference of Canada, Cutting Edge Nutritionalstrategies for Improving Performance, Profitability and Sustainability, Edmonton, AL, Canada, 2–3 May 2018; pp. 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.A.; Mikkelsen, D.; Flanagan, B.M.; Gidley, M.J. “Dietary fibre”: Moving beyond the “soluble/insoluble” classification for monogastric nutrition, with an emphasis on humans and pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, S.; Medina-Remón, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Estruch, R. Effects of Dietary Fiber Intake on Cardiovascular Risk Factors. In Recent Advances in Cardiovascular Risk Factors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D. The interaction between insoluble and soluble fiber. In Dietary Fiber for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 35–59. [Google Scholar]
- Montagne, L.; Pluske, J.R.; Hampson, D.J. A review of interactions between dietary fibre and the intestinal mucosa, and their consequences on digestive health in young non-ruminant animals. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2003, 108, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, H.M.J.; Davids, M.; Maes, D.; Millet, S.; Possemiers, S.; Den Hartog, L.A.; van Kempen, T.A.T.G.; Janssens, G.P.J. Dietary fibre enrichment of supplemental feed modulates the development of the intestinal tract in suckling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblet, J.; Le Goff, G. Effect of dietary fibre on the energy value of feeds for pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2001, 90, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.D.; Kawas, J.R.; Mahgoub, O.G. Fibre digestion and utilization in goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2005, 60, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtanen, P.; Ahvenjärvi, S.; Weisbjerg, M.R.; Nørgaard, P. Digestion and Passage of Fibre in Ruminants. In Ruminant Physiology: Digestion, metabolism and Impact of Nutrition on Gene Expression, Immunology and Stress; Wageningen Academic Publisher: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 87–138. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, G.A.; Kolver, E.S. Microbial and animal limitations to fiber digestion and utilization. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 819S–823S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchtová, V.; Karovičová, J.; Kohajdová, Z.; Minarovičová, L. Chemical composition and functional properties of pumpkin pomace-incorporated crackers. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2016, 9, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Sánchez, I.; Cueva, C.; Sanz-Buenhombre, M.; Guadarrama, A.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Bartolomé, B. Dynamic gastrointestinal digestion of grape pomace extracts. Bioacessible phenolic metabolites and impacto on human gut microbiota. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 68, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gu, B.J.; Ganjyal, G.M. Impacts of the inclusion of various fruit pomace types on the expansion of corn starch extrudates. Lebensm. -Wiss. Technol. 2019, 110, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Sampers, I.; Raes, K. Dietary fiber concentrates recovered from agro-industrial by-products: Functional properties and application as physical carriers for probiotics. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharoba, A.M.; Farrag, M.A.; Abd El-Salam, A.M. Utilization of some fruits and vegetables waste as a source of dietary fiber and its effect on the cake making and its quality attributes. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2013, 19, 429–444. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, A.B.B.; Speroni, C.S.; Moro, K.I.B.; Morisso, F.D.P.; dos Santos, D.R.; da Silva, L.P.; Penna, N.G. Effects of micronization on dietary fiber composition, physicochemical properties, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant capacity of grape pomace and its dietary fiber concentrate. Lebensm. -Wiss. Technol. 2020, 117, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turksoy, S.; Özkaya, B. Pumpkin and carrot pomace powders as a source of dietary fiber and their effects on the mixing properties of wheat flour dough and cookie quality. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2011, 17, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Bartley, G.E.; Yokoyama, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, A. Plasma and hepatic cholesterol-lowering effects of tomato pomace, tomato seed oil and defatted tomato seed in hamsters fed with high-fat diets. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, C.M.; Dias, M.I.; Alves, M.J.; Calhelha, R.C.; Barros, L.; Pinho, S.P.; Ferreira, I.C. Grape pomace as a source of phenolic compounds and diverse bioactive properties. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, R.C.; Gigliotti, J.C.; Ku, K.M.; Tou, J.C. A comprehensive analysis of the composition, health benefits, and safety of apple pomace. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Moilanen, J.; Laaksonen, O.; Yang, W.; Tenhu, E.; Yang, B. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of tea-type infusions processed from sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides) leaves. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, F.; Chinnici, F.; Caboni, M.F.; Verardo, V. Recovery of oligomeric proanthocyanidins and other phenolic compounds with established bioactivity from grape seed by-products. Molecules 2019, 24, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, D.K.; Ringseis, R.; Siebers, M.; Keller, J.; Kloster, J.; Wen, G.; Eder, K. Inhibition of the pro-inflammatory NF-κB pathway by grape seed and grape marc meal extract in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Y.I.; Kosir, V.; Yin, X.; Ross, K.; Diarra, M.S. Grape pomace as a promising antimicrobial alternative in feed: A critical review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9705–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liimatainen, J.; Alanne, A.; Lindstedt, A.; Liu, P.; Sinkkonen, J.; Kallio, H.; Yang, B. Phenolic compounds extracted by acidic aqueous ethanol from berries and leaves of different berry plants. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Puganen, A.; Alakomi, H.; Uusitupa, A.; Saarela, M.; Yang, B. Antioxidative and antibacterial activities of aqueous ethanol extracts of berries, leaves, and branches of berry plants. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytařová, I.; Orsavová, J.; Snopek, L.; Mlček, J.; Byczyński, Ł.; Mišurcová, L. Impact of phenolic compounds and vitamins C and E on antioxidant activity of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries and leaves of diverse ripening times. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, B.; Kontek, R.; Żuchowski, J.; Stochmal, A. Novel bioactive properties of low-polarity fractions from sea-buckthorn extracts (Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson)—(in vitro). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 135, 111141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolk, K.; Pällin, R.; Kärner, T.; Oraste, O. Sea buckthorn as a home garden crop. Agraarteadus 2004, 15, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Piir, R. Hippophae rhamnoides L. in Estonia for fruit growing. Agraarteadus 1996, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Nemzer, B.V.; Kalita, D.; Yashin, A.Y.; Yashin, Y.I. Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant Activities, and Health Beneficial Effects of Selected Commercial Berry Fruits: A Review. J. Food Res. 2020, 9, 78–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienaitė, L.; Pukalskas, A.; Pukalskienė, M.; Pereira, C.V.; Matias, A.A.; Venskutonis, P.R. Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities of Defatted Sea Buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) Berry Pomace Fractions Consecutively Recovered by Pressurized Ethanol and Water. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, T.; Destandau, E.; Le Floch, G.; Lucchesi, M.E.; Elfakir, C. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and phytochemical investigations of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) leaf, stem, root and seed. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepa, L.; Zolnere, E.; Dūrītis, I.; Segliņa, D. Preliminary results of the effect of the seabuckthorn leaves and fruit marc extract on the health indices of calves. In Proceedings of the 4th European Workshop on Seabuckthorn EuroWorks 2016 RPD Abstracts, Riga, Latvia, 17–19 August 2016; Volume 2, p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Morar, R.; Cimpeanu, S.; Morar, E.; Mărghitaș, L.; Rozalia, Z. Results of the use of certain phytotherapeutic preparations in the feeding of weaned piglets. Bul. Inst. Agron. Cluj-Napoca Ser. Zooteh. Și Med. Vet. 1990, 44, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, G.P.; Sharma, N.; Mane, B.G.; Sharma, D.; Krofa, D.; Khurana, S.K. Effect of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides)-leaves, pulp and oil on growth performance, carcass characteristics and meat quality of broilers chicken. J. Poult. Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, N.K.; Auer, A.D.; Garza Jr, F.; Keowen, M.L.; Kearney, M.T.; McMullin, R.B.; Andrews, F.M. Effect of sea buckthorn berries and pulp in a liquid emulsion on gastric ulcer scores and gastric juice pH in horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ositis, U.; Seglina, D.; Strikauska, S.; Bula, S. Influence of sea buckthorn by-products premix feeding on the mare and foal blood biochemical indices. In Proceedings of the 1st Nordic Feed Science Conference, Uppsala, Sweden, 22–23 June 2010; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Varshneya, C.; Bharadwaj, P. Ochratoxin induced immunosupression and its protection by seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and glucomannan in Japanese quail (Courtunix Courtunix Japonica). Indian Vet. J. 2013, 90, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Patial, V.; Asrani, R.K.; Patil, R.D.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, R. Protective effect of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) leaves on ochratoxin-A induced hepatic injury in Japanese quail. Vet. Res. 2015, 3, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Souilem, S.; Fki, I.; Kobayashi, I.; Khalid, N.; Neves, M.A.; Isoda, H.; Sayadi, S.; Nakajima, M. Emerging technologies for recovery of value-added components from olive leaves and their applications in food/feed industries. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, C.D.; Vuong, Q.V.; Stathopoulos, C.E.; Roach, P.D.; Scarlett, C.J. Ultrasound increases the aqueous extraction of phenolic compounds with high antioxidant activity from olive pomace. Lebensm. -Wiss. Technol. 2018, 89, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, M.K.E.S.; Galal, S.M.; Alabdulla, O. Ultrasound assisted extraction of polyphenols with high antioxidant activity from olive pomace (Olea europaea L.). Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Irakli, M.; Chatzopoulou, P.; Ekateriniadou, L. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds: Oleuropein, phenolic acids, phenolic alcohols and flavonoids from olive leaves and evaluation of its antioxidant activities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 124, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilali, S.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Ruiz, K.; Hejjaj, A.; Ait Nouh, F.; Idlimam, A.; Bily, A.; Mandi, L.; Chemat, F. Green extraction of essential oils, polyphenols, and pectins from orange peel employing solar energy: Toward a zero-waste biorefinery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11815–11822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, M.; Bakshi, M.P.S. Utilization of fruit and vegetable wastes as livestock feed and as substrates for generation of other value-added products. Rap Publ. 2013, 4, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Azhdarzadeh, F.; Hojjati, M. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of leaf, ripe and unripe peel of bitter orange (Citrus aurantium) essential oils. Nutr. Food Sci. Res. 2016, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, J.; van Stempvoort, S.; García-Gallarreta, M.; Houghton, J.A.; Briers, H.K.; Budarin, V.L.; Matharu, A.S.; Clark, J.H. Microwave assisted hydro-distillation of essential oils from wet citrus peel waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, K.A.; de Oliveira Monteschio, J.; Mottin, C.; Ramos, T.R.; de Moraes Pinto, L.A.; Eiras, C.E.; Guerrero, A.; do Prado, I.N. Effects of diet supplementation with clove and rosemary essential oils and protected oils (eugenol, thymol and vanillin) on animal performance, carcass characteristics, digestibility, and ingestive behavior activities for Nellore heifers finished in feedlot. Livest. Sci. 2019, 220, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Nanon, A.; Suksombat, W.; Yang, W.Z. Effects of essential oils supplementation on in vitro and in situ feed digestion in beef cattle. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014, 196, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.M.; Ávila, V.A.D.; Bonin, E.; Matos, A.M.; do Prado, R.M.; Castilho, R.A.; Silva, R.R.; de Abreu Filho, B.A.; do Prado, I.N. Effect of extracts from baccharis, tamarind, cashew nut shell liquid and clove on animal performance, feed efficiency, digestibility, rumen fermentation and feeding behavior of bulls finished in feedlot. Livest. Sci. 2021, 244, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottin, C.; Ornaghi, M.G.; Carvalho, V.M.; Guerrero, A.; Vital, A.C.P.; Ramos, T.R.; Bonin, E.; Lana de Araújo, F.; de Araújo Castilho, R.; do Prado, I.N. Carcass characteristics and meat evaluation of cattle finished in temperate pasture and supplemented with natural additive containing clove, cashew oil, castor oils, and a microencapsulated blend of eugenol, thymol, and vanillin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monrroy, M.; Rueda, L.; Aparicio, A.L.; García, J.R. Fermentation of Musa paradisiaca Peels to Produce Citric Acid. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 8356712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukas, T.; Kotzekidou, P. Pomegranate peel waste: A new substrate for citric acid production by Aspergillus niger in solid-state fermentation under non-aseptic conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 12, 13105–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.R.; Anwar, Z.; Irshad, M.; Mukhtar, S.; Warraich, N.T. Bio-synthesis of citric acid from single and co-culture-based fermentation technology using agro-wastes. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekoai, P.T.; Ayeni, A.O.; Daramola, M.O. Parametric optimization of citric acid production from apple pomace and corn steep liquor by a wild type strain of Aspergillus niger: A Response surface methodology approach. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2018, 36, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, E.; Mantzouridou, F.T. Citric acid production from the integration of Spanish-style green olive processing wastewaters with white grape pomace by Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.; Akpan, I.; Alebiowu, O. Production of citric acid by Aspergillus niger using pineapple waste. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2010, 6, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, N.; Safdar, W.; Ali, S.; Choudhry, S.; Elahi, S. Citric acid production from Aspergillus niger using mango (Mangifera indica L.) and sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) peels as substrate. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2016, 7, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, A.M.; Cortés, S.; Salgado, J.M.; Max, B.; Rodríguez, N.; Bibbins, B.P.; Converti, A.; Domínguez, J.M. Citric acid production from orange peel wastes by solid-state fermentation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correddu, F.; Lunesu, M.F.; Buffa, G.; Atzori, A.S.; Nudda, A.; Battacone, G.; Pulina, G. Can Agro-Industrial By-Products Rich in Polyphenols be Advantageously Used in the Feeding and Nutrition of Dairy Small Ruminants. Animals 2020, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltan, M.; Elsamadony, M.; Mostafa, A.; Awad, H.; Tawfik, A. Harvesting zero waste from co-digested fruit and vegetable peels via integrated fermentation and pyrolysis processes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10429–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmo-García, L.; Monasterio, R.P.; Sánchez-Arévalo, C.M.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Olmo-Peinado, J.M.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A. Characterization of new olive fruit derived products obtained by means of a novel processing method involving stone removal and dehydration with zero waste generation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9295–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schader, C.; Muller, A.; Scialabba, N.E.H.; Hecht, J.; Isensee, A.; Erb, K.H.; Smith, P.; Makkar, H.P.; Klocke, P.; Leiber, F.; et al. Impacts of feeding less food-competing feedstuffs to livestock on global food system sustainability. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20150891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, K.; Pries, M.; Tholen, E.; Schmithausen, A.J.; Büscher, W.; Südekum, K.H. Effect of condensed tannins in rations of lactating dairy cows on production variables and nitrogen use efficiency. Animal 2018, 12, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, K.M.; Beauchemin, K.A. Effect of feeding condensed tannins in high protein finishing diets containing corn distillers grains on ruminal fermentation, nutrient digestibility, and route of nitrogen excretion in beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 4398–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, S.A.; Luciano, G.; O’Grady, M.N.; Biondi, L.; Newbold, C.J.; Kerry, J.P.; Priolo, A. Sustainability of feeding plant by-products: A review of the implications for ruminant meat production. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 251, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.M.; Dragomir, C.; Gras, M.A.; Ropotă, M. Inclusion of rapeseed and pumpkin seed cakes in diets for Murciano-Granadina goats alters the fatty acid profile of milk. South Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 51, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannelli, F.; Cappucci, A.; Pini, F.; Pastorelli, R.; Decorosi, F.; Giovannetti, L.; Mele, M.; Minieri, S.; Conte, G.; Pauseli, M.; et al. Effect of different types of olive oil pomace dietary supplementation on the rumen microbial community profile in Comisana ewes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, J.; Mateos, I.; Saro, C.; González, J.S.; Carro, M.D.; Ranilla, M.J. Replacing forage by crude olive cake in a dairy sheep diet: Effects on ruminal fermentation and microbial populations in Rusitec Fermenters. Animals 2020, 10, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terramoccia, S.; Bartocci, S.; Taticchi, A.; Di Giovanni, S.; Pauselli, M.; Mourvaki, E.; Urbani, S.; Servili, M. Use of dried stoned olive pomace in the feeding of lactating buffaloes: Effect on the quantity and quality of the milk produced. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, A. Influence of feeding mixture of tomato and apple pomace silage to lactating goats on productive performance. Egypt. J. Sheep Goats Sci. 2019, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Cao, Y.; Matsuzaki, M.; Suzuki, H. Effects of apple pomace proportion levels on the fermentation quality of total mixed ration silage and its digestibility, preference and ruminal fermentation in beef cows. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdani, D.; Hernaman, I.; Nurmeidiansyah, A.A.; Heryadi, D.; Nurachma, S. Potential Use of Banana Peels Waste at Different Ripening Stages for Sheep Feeding on Chemical, Tannin, and In Vitro Assessments. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 334, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Diao, X.; Yu, S.; Ding, N.; Mu, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J. Nutrient digestibility, rumen microbial protein synthesis, and growth performance in sheep consuming rations containing sea buckthorn pomace. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.Y.; Ding, N.; Mu, C.T.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, J.X. Effects of sea buckthorn pomace supplementation on energy partitioning and substrate oxidation in male lambs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 247, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, T.; Cao, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Effects of dietary sea buckthorn pomace supplementation on skeletal muscle mass and meat quality in lambs. Meat Sci. 2020, 166, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuernberg, K.; Nuernberg, G.; Priepke, A.; Dannenberger, D. Sea buckthorn pomace supplementation in the finishing diets of pigs—Are there effects on meat quality and muscle fatty acids? Arch. Anim. Breed. 2015, 58, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenberger, D.; Tuchscherer, M.; Nürnberg, G.; Schmicke, M.; Kanitz, E. Sea Buckthorn Pomace Supplementation in the Diet of Growing Pigs—Effects on Fatty Acid Metabolism, HPA Activity and Immune Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palade, L.M.; Dore, M.I.; Marin, D.E.; Rotar, M.C.; Taranu, I. Assessment of Food By-Products’ Potential for Simultaneous Binding of Aflatoxin B1 and Zearalenone. Toxins 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qu, H.; Bai, S.; Yan, L.; You, M.; Gou, W.; Li, P.; Gao, F. Effect of wet sea buckthorn pomace utilized as an additive on silage fermentation profile and bacterial community composition of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, T.; Gallardo, B.; Salvá, A.; Guerra-Rivas, C.; Mantecón, A.R.; Lavín, P.; De la Fuente, M.A. Influence of dietary grape pomace combined with linseed oil on fatty acid profile and milk composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rivas, C.; Gallardo, B.; Mantecón, Á.R.; del Álamo-Sanza, M.; Manso, T. Evaluation of grape pomace from red wine by-product as feed for sheep. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, D.P.; Boskou, G.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Polyphenolic content and vitro antioxidant characteristics of wine industry and otheragri-food solid waste extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarghuei, M.J.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Alipour, D. The influence of the grape pomace on the ruminal parameters of sheep. Livest. Sci. 2010, 132, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilonu, M.C.; Nwafor, I.C.; Umesiobi, D.O.; Sedibe, M.M. Biochemical proximates of pumpkin (Cucurbitaeae spp.) and their beneficial effects on the general well-being of poultry species. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Francis, G.; Becker, K. Bioactivity of phytochemicals in some lesser-known plants and their effects and potential applications in livestock and aquaculture production systems. Animal 2007, 1, 1371–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, A.H.; Toghyani, M.; Tabeidian, S.A. Effect of incremental levels of apple pomace and multi enzyme on performance, immune response, gut development and blood biochemical parameters of broiler chickens. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarisafar, Z.; Sadeghi, G.; Karimi, A.; Azizi, O. Apple peel waste as a natural antioxidant for heat-stressed broiler chickens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, S.; Ohh, S.J.; Ahammed, M.; Lohakare, J. Supplementation of grape pomace (Vitis vinifera) in broiler diets and its effect on growth performance, apparent total tract digestibility of nutrients, blood profile, and meat quality. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, K.; Kocaoglu-guclu, B. The effects of different molting methods and supplementation of grape pomace to the diet of molted hens on post-molt performance, egg quality and peroxidation of egg lipids. J. Fac. Vet. Med. Erciyes Univ. 2012, 9, 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lichovnikova, M.; Kalhotka, L.; Adam, V.; Klejdus, B.; Anderle, V. The effects of red grape pomace inclusion in grower diet on amino acid digestibility, intestinal microflora, and sera and liver antioxidant activity in broilers. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2015, 39, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, Y.; Valdivié, M.; Martínez, O.; Estarrón, M.; Córdova, J. Utilization of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) seed in broiler chicken diets. Cuba. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 44, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hajati, H.; Hasanabadi, A.; Waldroup, P.W. Effects of dietary supplementation with pumpkin oil (Cucurbita pepo) on performance and blood fat of broiler chickens during finisher period. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2011, 6, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Modirsanei, M.; Kiaei, M.M. Influence of dried tomato pomace as an alternative to wheat bran in maize or wheat based diets, on the performance of laying hens and traits of produced eggs. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 9, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Panaite, T.D.; Mironeasa, S.; Iuga, M.; Vlaicu, P.A. Liquid egg products characterization during storage as a response of novel phyto-additives added in hens diet. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2019, 31, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orczewska-Dudek, S.; Pietras, M.; Nowak, J. The effect of amaranth seeds, sea buckthorn pomace and black chokeberry pomace in feed mixtures for broiler chickens on productive performance, carcass characteristics and selected indicators of meat quality. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2018, 18, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Rana, D.; Wadhwa, D.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Effect of feeding seabuckthorn cake (Hippophae L.) on egg production and egg quality in poultry birds. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2017, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dvořák, P.; Suchý, P.; Straková, E.; Doležalová, J. The effect of a diet supplemented with sea-buckthorn pomace on the colour and viscosity of the egg yolk. Acta Vet. Brno 2017, 86, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mushtaq, M.; Sharma, V.K.; Daisy, R.; Sharma, A. Effect of dietary replacement of protein with seabuckthorn products alone and in combination on the performance of broiler birds. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2017, 5, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
| Trait | TDF (%) | IDF (%) | SDF (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple pomace | 53.1 | 47.0 | 6.10 | [90] |
| Banana peel | 65.55 | 54.06 | 11.49 | [91] |
| Black currant pomace | 76.87 | 68.73 | 8.14 | [91] |
| Blueberry pomace | 59.1 | 56.7 | 2.4 | [90] |
| Cranberry pomace | 59.3 | 56.2 | 3.0 | [90] |
| Carrot pomace | 69.85 | 45.12 | 24.73 | [92] |
| Grape pomace | 65.56 | 61.20 | 4.06 | [93] |
| Potato peels | 73.25 | 53.39 | 19.86 | [92] |
| Pumpkin pomace | 76.94 | 57.69 | 19.25 | [94] |
| Peach pomace | 54.5 | 35.5 | 19.1 | [1] |
| Pear pomace | 43.9 | 36.3 | 7.6 | [1] |
| Tomato pomace | 58.8 | 47.3 | 11.5 | [95] |
| Fruit & Vegetable Wastes/By-Products | Phenolic Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Grape pomace | Gallic acid, galloyl glucose, quinic acid, protocatechuic acid vanillic acid glycoside, feruloytartaric acid, p-coumaric acid O-Glycoside, caffeic acid, eriodictyol hexoside, myricetin-O-glycoside, quercetin, quercetin 3-O-galactoside, quuercetin 3-O-glucoside, quercetin 3-O-glucoronide, quercein 3-O-rhamnoside, quercetin-glucoronide, Laricitrin 3-O-galactoside, laricitrin-3-O-rhamnose-7-O-trihydroxycinnamic acid, syringetin -3-O-galactoside, Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside, robinin, catechin, epicatechin, Procyanidin B3, Procyanidin B1, Procyanidin B4, procyanidin B2; cyanidin glucoside or galactoside; peonidin 3-glucoside or galactoside; malic acid, critic acid, tryptophan; malvidin-hexoside malvidin-acetylhexoside, delphinidin-rutinoside, malvidin-dihexoside, petunidin-rutinoside, peonidin-rutinoside, malvidin-rutinoside | [16,96] |
| Apple pomace | proanthocyanidins, flavonoids: quercetin 3-O- rutinoside, quercetin 3-O-galactoside, quercetin 3-O-glucoside, quercetin 3-O- xyloside, Quercetin 3-O-arabinoside and quercetin 3-O-rhamnosidehydroxycinnamates, and dihydrochalcones, phloridzin, chlorogenic acid, coumaric acid, chlorogenic acid, gallic acid, | [49,97] |
| Pumpkin waste | Gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, 4-hydrxybenzoic acid, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, p-coumaric acid, feluric acid, sinapic acid, and vanilic acid Flavonols: Astragalin, Rutin, kaempferol, isoquercetin, myricetin, and quercetin | [21] |
| Sea buckthorn pomace | Flavanoid glycosides, elllagitannins, flavonoids, isorhametim, quercetin derivatives, anthocyanins, tocopherols and carotenoids | [98] |
| Apricots pomace | Neochlorogenic and chlorogenic acids, proantocynidin, kaempferol glycosides, cyanidin 3-glucoside and certain quercetin derivatives | [15] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malenica, D.; Kass, M.; Bhat, R. Sustainable Management and Valorization of Agri-Food Industrial Wastes and By-Products as Animal Feed: For Ruminants, Non-Ruminants and as Poultry Feed. Sustainability 2023, 15, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010117
Malenica D, Kass M, Bhat R. Sustainable Management and Valorization of Agri-Food Industrial Wastes and By-Products as Animal Feed: For Ruminants, Non-Ruminants and as Poultry Feed. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010117
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalenica, Dunja, Marko Kass, and Rajeev Bhat. 2023. "Sustainable Management and Valorization of Agri-Food Industrial Wastes and By-Products as Animal Feed: For Ruminants, Non-Ruminants and as Poultry Feed" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010117
APA StyleMalenica, D., Kass, M., & Bhat, R. (2023). Sustainable Management and Valorization of Agri-Food Industrial Wastes and By-Products as Animal Feed: For Ruminants, Non-Ruminants and as Poultry Feed. Sustainability, 15(1), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010117