Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review and Theoretical Background
1.1.1. System Theory and Systems Thinking
1.1.2. Strategic Management and Complexity
1.1.3. Growth and Development
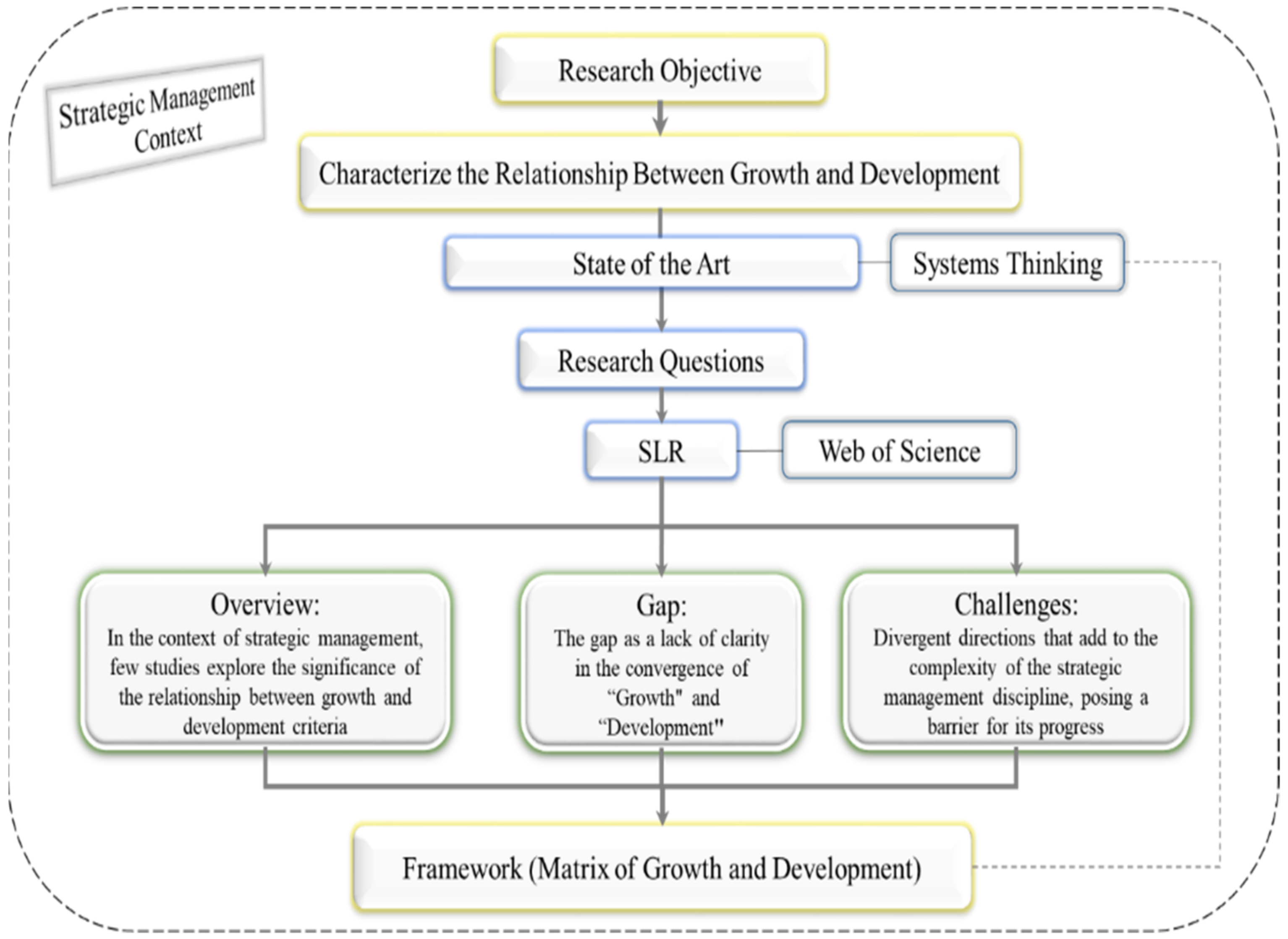
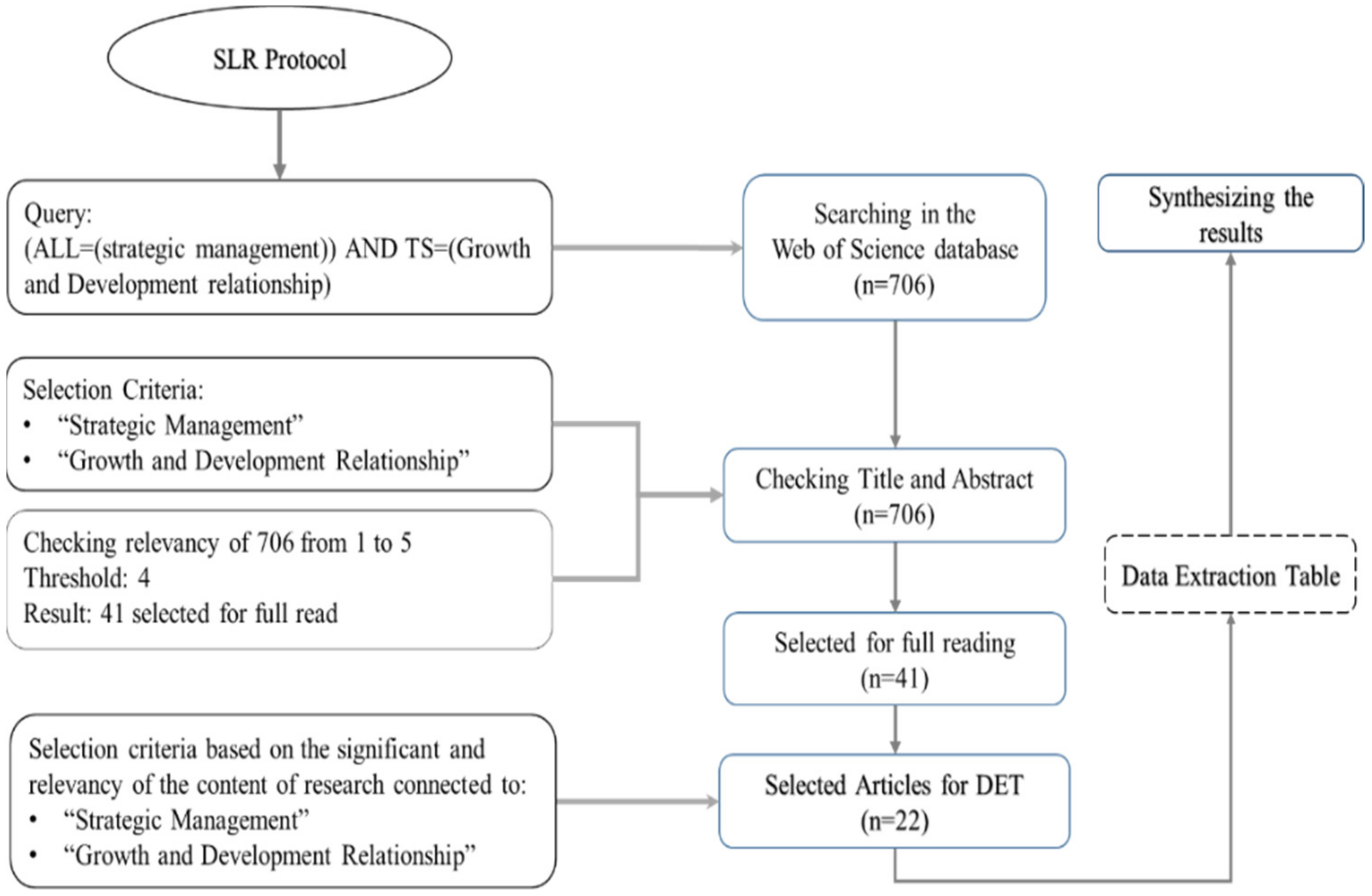
2. Materials and Methods
- RQ1: In the strategic management literature, do we have any studies that focus on the significance of the relationship between growth and development?
- RQ2: If any studies have been conducted, what are their remarks and contributions?
- RQ3: Is there any gap in the strategic management literature that shows a lack of convergence in growth and development synchronization?
- RQ4: What are the possibilities for future research?
- (ALL = (strategic management)) AND TS = (growth and development relationship)
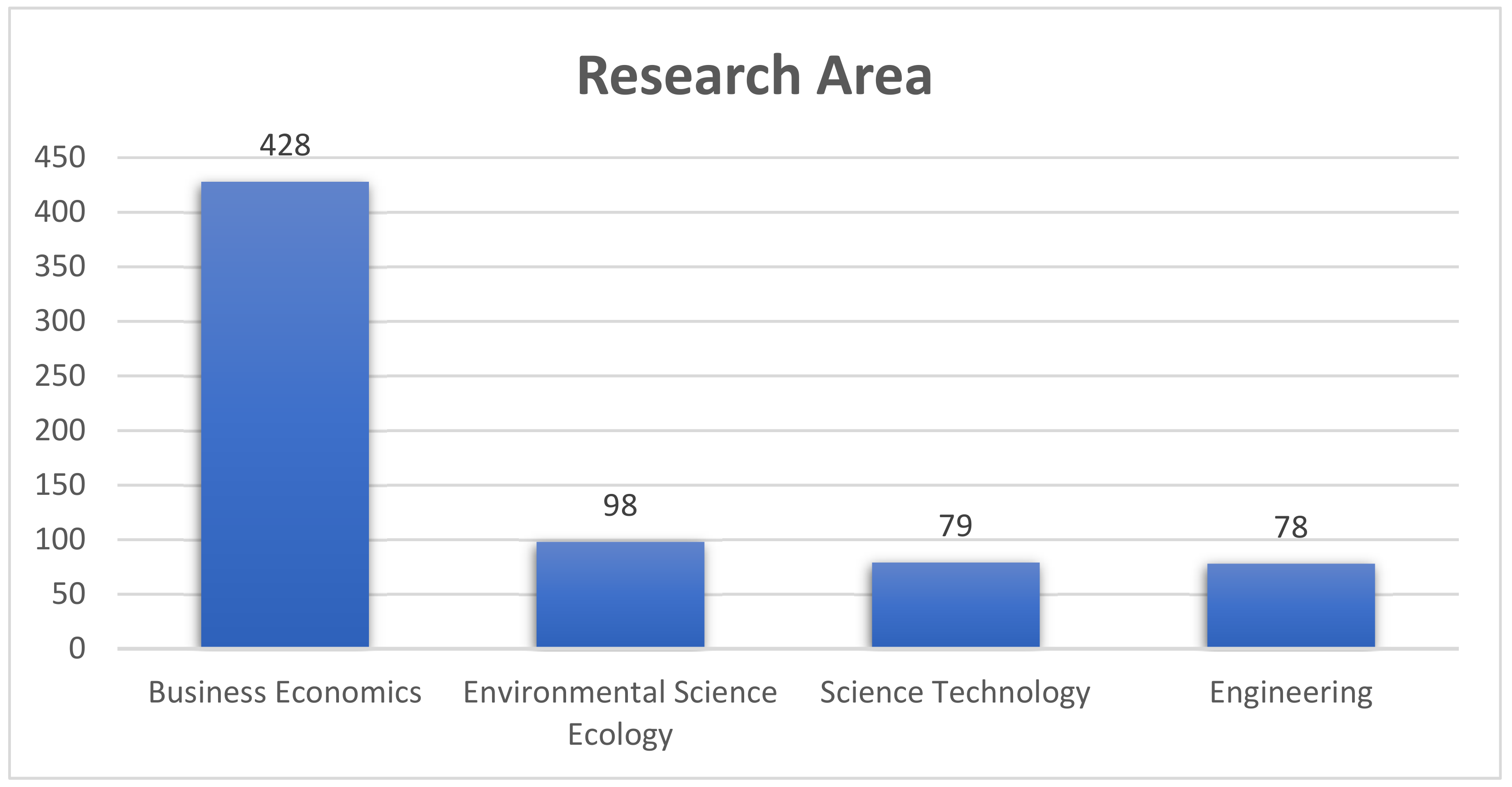
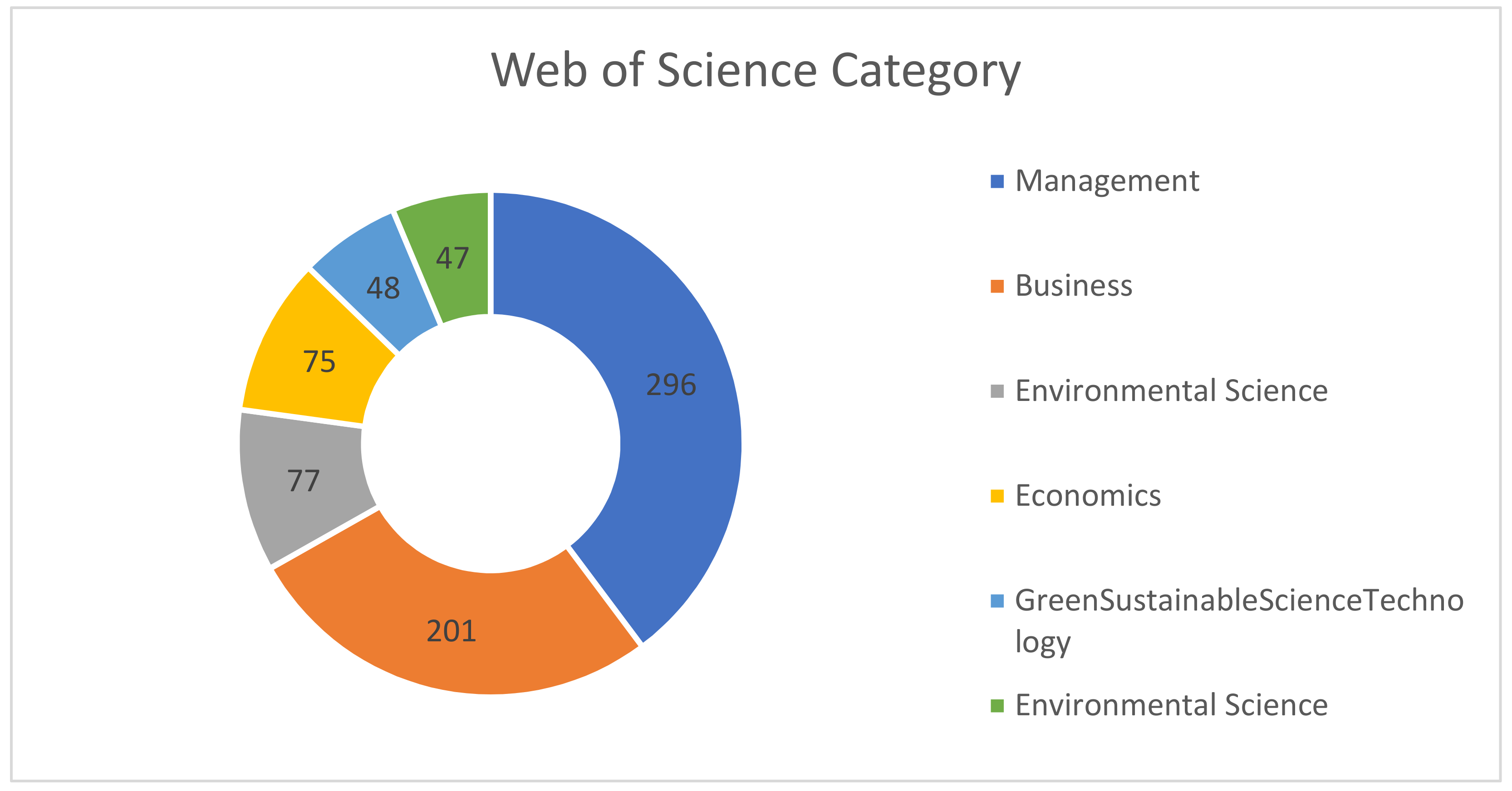
3. Results
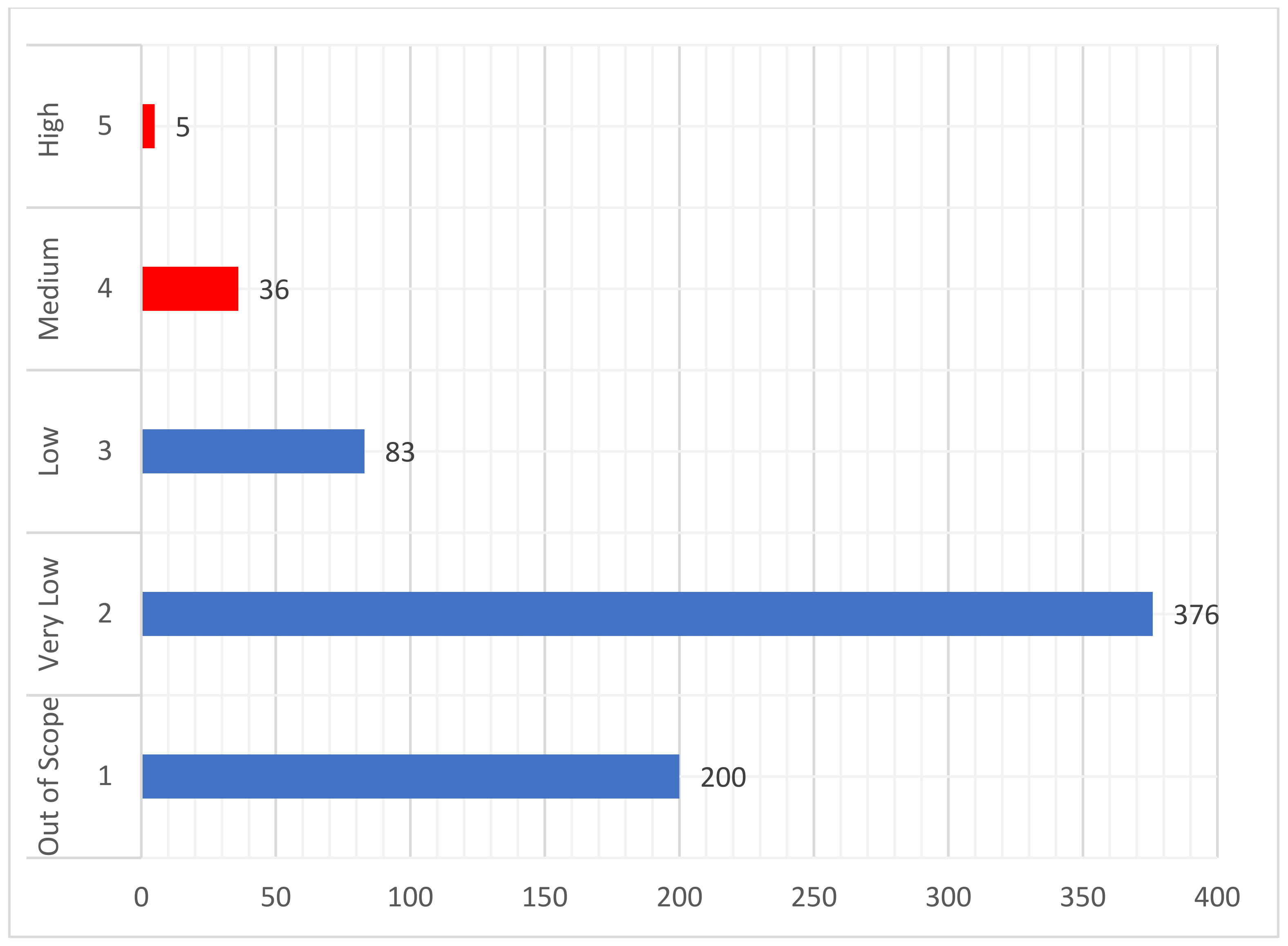
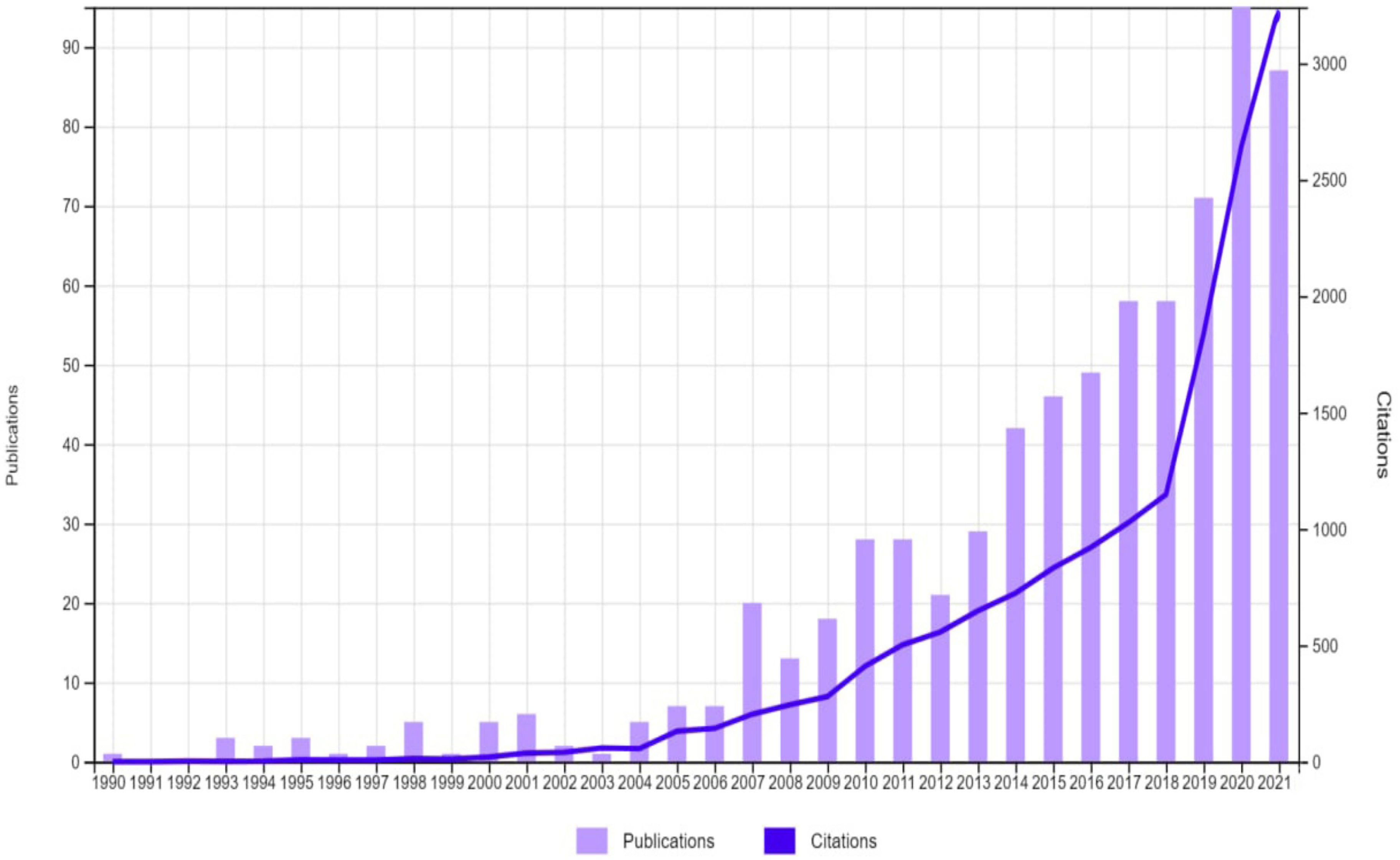
3.1. Analysis of the Web of Science Results
3.2. Network Analysis Results (VOSviewer)
3.3. Data Extraction Table
| Articles | Subject/Topic | Contribution/Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| [47] | Exploring the relationship between a business’s growth and organizational development in 150 Polish small, medium, and large enterprises in the context of strategic management. | According to the study, the relationship between business growth and organizational development in the examined enterprises is complex and hence unclear. The study’s key result is that when businesses grow, their strategic management direction changes as well, but not always in all of the examined enterprises in this research. |
| [48] | Using the strategic management accounting (SMA) spectrum, examine the growth and development of a China SNS service firm. | This study provides insight into the connections between company strategy, accountancy, and social life. |
| [49] | The paper investigates how growth-oriented businesses in Wales have implemented management strategies to develop the entrepreneurial ability needed to maintain growth. | This work supports earlier research that asserts that support programs and activities that communicate the value of management practice adoption are critical for small business development and growth. |
| [50] | Investigating Edith Penrose’s contributions and theory of the growth of the firm, the nature of the firm, and stakeholders criteria. | Overviewing Edith Penrose’s theory of the growth of the firm, exploring the definitions and peripheral criteria that led to the development of the stakeholders theory of the firm. |
| [51] | The goal of this research is to see if enterprises’ cooperative efforts, notably “coopetition,” have an impact on company success. | The findings of this study may be utilized to address and diagnose problems in Korean companies by examining links between cooperative activities, innovation outputs, and management performance in the structural environment. |
| [52] | Using banking sector and stock market development indicators, this study investigates the link between financial development and economic growth for five key rising economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South (BRICS) from 1993 to 2014. | The study’s key finding is that financial development and economic growth in certain economies have a substantial and favorable relationship. The expansion of bank and stock market activity at the same time is critical to an economy’s progress. |
| [53] | Entrepreneurial leadership behavior, top management team heterogeneity, and environmental dynamism are all examined in the context of new venture performance. | This study highlights the complexities of executive leadership by demonstrating critical connections between individual, team, and firm-level characteristics. |
| [54] | From the perspective of decision making and business success, this study examines the link between boards and board activities and subsequent company performance in the setting of high-growth enterprises. | Indicating the importance of the influence of the board in being involved in the strategic development process, assessment, options, and strategic management criteria. |
| [55] | This study explores the organization’s growth and development lifecycle model to find the relationship between high-performance work systems and performance in firms within human resource management criteria. | This article contributes to the literature on strategic human resource management with the focus on high-performance work systems’ relationships with SME performances. |
| [56] | In this research on a freshwater fishery, the authors use the Morris and Sobol techniques to conduct a complete global sensitivity analysis to determine the life-history characteristics that have the greatest impact on model outputs. | This study discovered that growth-related factors, such as the von Bertalanffy growth coefficient and asymptotic mass, had the biggest impact on the outcomes of our size spectrum model (contributing to fisheries’ management). |
| [57] | A conceptual study to overview major innovation (MI) and its importance for the growth of an enterprise, using system theory and dynamic capability theory to develop a framework for MI dynamic capability. | Comprehensive overview to develop MI dynamic capability. |
| [58] | Strategic alliances and the nature of international business. The goal of this research is to see if a realignment of company incentives and the use of game theory may help to promote stable collaboration and improved alliance performance. | The literature on strategic alliances and game theory criteria is expanded in this study. In addition, it determines whether game theory is appropriate for forming strategic alliances. |
| [59] | In this study, the link between a manager’s Strategic Intelligence (SI), Organizational Development (OD), and Entrepreneurial Behavior (EB) in governmental agencies in developing nations is investigated. | According to this study, there is a substantial positive association between the manager’s SI and organizational development, as well as a significant positive relationship between the manager’s SI and entrepreneurial activity. |
| [60] | As markets evolve from fledgling to growth stage, this study examines how varying degrees of uncertainty and competitiveness impact interfirm connections of entrepreneurial enterprises. | Due to the variation in their relationships and power compared to partners, the findings of this study suggest that shifting degrees of uncertainty and competitiveness in growth stage marketplaces might have various effects for enterprises. The findings pave the way for a better understanding of the relationships between firms, interfirm linkages, and market dynamics. |
| [61] | The implications of social capital in critical customer connections on knowledge acquisition and exploitation are investigated in this study. | According to the findings of this study, the social contact and network linkages of social capital are certainly connected with better knowledge acquisition; however, the relationship quality component is inversely associated with knowledge acquisition. |
| [62] | This study proposes a framework for the organizational effectiveness model in continuation of the previous research framework for organizational development strategy by Eric Flamholtz (1995). | The current research improves on this earlier framework by conducting an empirical examination of the proposed link between “organizational growing pains” and corporate financial performance. |
| [63] | This study develops a system dynamic model to investigates how CEO attitudes influence organizational transformation (change) that leads to high performance (case study of General Electric Corporation). | This study employed a simulation model (system dynamic) to show how a leader’s belief system affects organizational transformation, which in turn affects the company’s strategy for reaching a better financial outcome. |
| [64] | The goal of this research is to see how strategic innovation affects company development, organizational effectiveness, and business performance in Thailand’s Industrial Estate. | With a focus on research-based theory and contingency theory, this study finds that strategic innovation has a favorable impact on organizational development, organizational effectiveness, and firm success. According to the findings, strategic innovation is critical for businesses to grow. |
| [65] | This study analyzes the growth, profitability, and productivity via concentration-based entropy as an instrument for quantification. | This study proposes criteria to define the relationship between innovation and performance, taking into account the level of innovation and the size of the business. It develops a novel methodology for analyzing the impact of innovation and performance based on information theory. |
| [67] | The objective of this paper is to highlight how phases of growth models have been used in management research to explain a variety of organizational phenomena. | This study adds to the development of a framework for assessing an industrial organization’s current stage and determining its strategic direction in the future. |
| [68] | This article examines the importance of creating sustainable firms and the extension of sustainable development standards in industry from a systems perspective. | This article navigates the importance of creating a sustainable enterprise and also how businesses are changing due to the transformation of concepts via a systems perspective. |
| [66] | The topic of this paper is how Chinese economic development can achieve sustainable development of enterprises via an examination of the link between intellectual capital and corporate sustainable growth. | This research backs up the idea that intellectual capital has a favorable impact on a corporate sustainable growth. |
4. Discussion
4.1. An Overview of the Study’s Findings
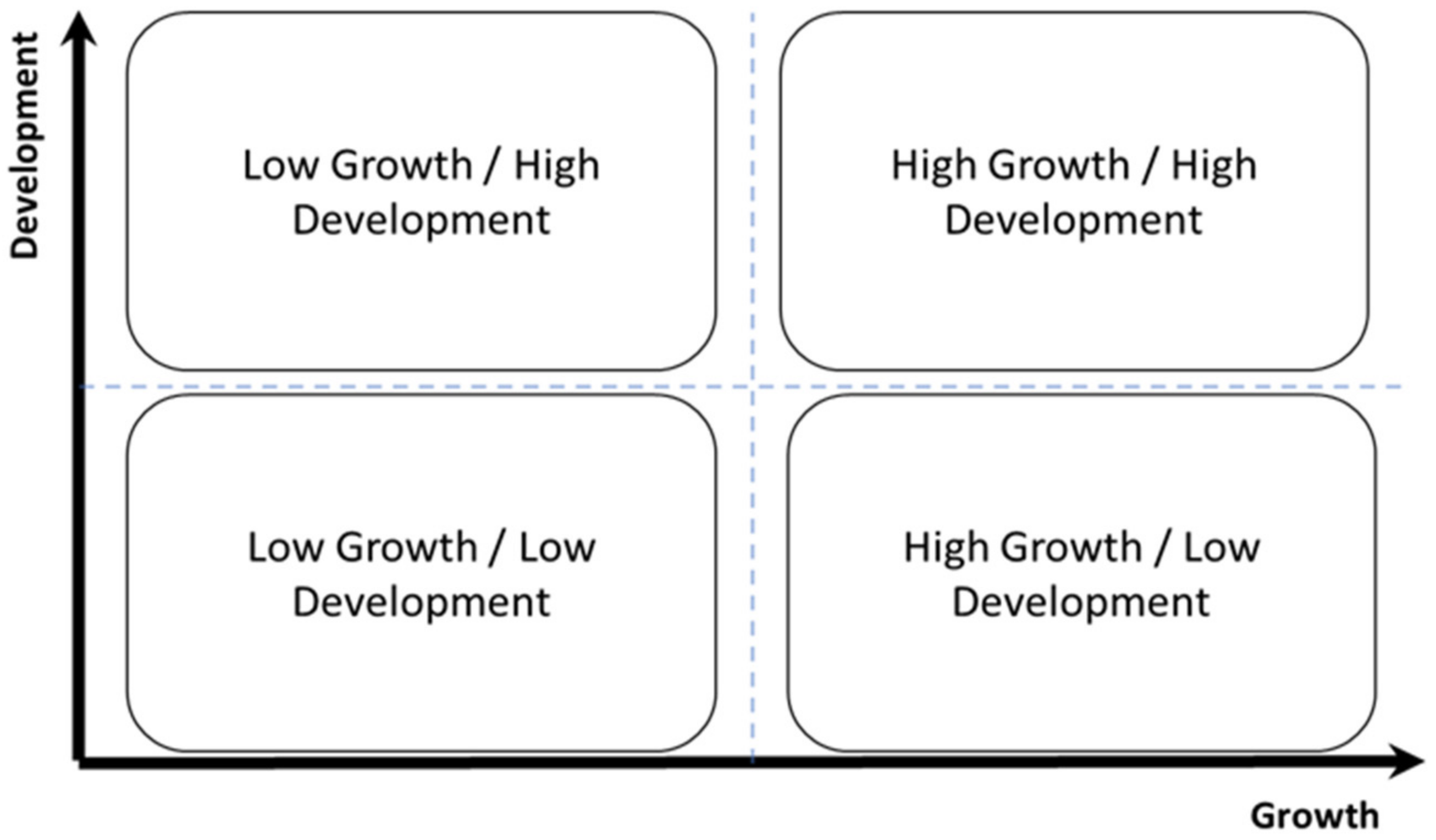
4.2. The Gap in the Convergence of Growth and Development
4.3. Challenges and Opportunities
5. The Conceptual Framework and Future Research
6. Conclusions
- A few publications have investigated the relationship between organizational growth and development in the context of strategic management. However, the significance of this process has not been investigated enough, regardless of the importance of the topic.
- The gap was discovered to be due to a lack of clarity in this research area regarding the convergence of growth and development processes, as well as a lack of research focus.
- A challenge stems from the increased complexity caused by various approaches that investigate growth and development processes in a divergent rather than convergent manner.
- An opportunity was identified to use an integrated systems approach to provide a framework for future research in order to chart a path for converging the growth and development processes in the management field.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Articles | Research Method | Keywords | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| [47] | Hybrid, Qualitative and Quantitative. | Business growth; organizational development; strategic management | 5 |
| [48] | Qualitative | China, Business formation, Management accounting, Social networking sites, Popular culture | 0 |
| [49] | Qualitative | Management development; Business development; Small enterprises; Small to medium-sized enterprises; United Kingdom. | 5 |
| [50] | Qualitative | The growth of the firm, Firms nature, Stakeholders | 20 |
| [51] | Quantitative | Coopetition; cooperation; innovation performance; management performance; structural equation model (SEM) | 3 |
| [52] | Hybrid, Qualitative and Quantitative. | Growth | 0 |
| [53] | Quantitative | Entrepreneur leadership behavior empowering, Top management team, Industry environmental dynamism, New venture performance. | 165 |
| [54] | Qualitative | Corporate governance; Strategic management; Agency theory; Critical realism; Black box | 5 |
| [55] | Quantitative | HPWS; small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs); performance; best fit; organizational growth and development | 42 |
| [56] | Quantitative | Ecosystem-based approach, Fisheries modelling, | 0 |
| [57] | Qualitative | Major Innovation, Dynamic capability, System theory | 169 |
| [58] | Hybrid, Qualitative and Quantitative | Strategic alliances; intercountry differences; structure-performance relationship; game theory; interfirm cooperation | 131 |
| [59] | Quantitative | Intelligence; Strategic intelligence; Organization development; Entrepreneurial behavior | 1 |
| [60] | Qualitative, Multiple case study | competition; entrepreneurial firms; interfirm ties; market growth; uncertainty | 18 |
| [61] | Qualitative | social capital; knowledge acquisition and knowledge exploitation; young technology-based firm. | 1526 |
| [62] | Hybrid, Quantitative and Quantitative | Strategic organizational development; stages of growth developmental gap; growing pains; pyramid of organizational development | 6 |
| [63] | Hybrid, Quantitative and Qualitative, | System dynamics; organizational change; belief system; time delay; limit to growth | 5 |
| [64] | Quantitative | Strategic Innovation; Organization Development; Organizational Effectiveness; Firm Performance | 0 |
| [65] | Quantitative | Entropy; innovation; business performance | 15 |
| [67] | Qualitative | Management research; Business development; Outsourcing; Modelling | 8 |
| [68] | Qualitative | Sustainable enterprise, Systems thinking, Sustainable development | 185 |
| [66] | Quantitative | Intellectual capital efficiency; Capital employed efficiency; Corporate sustainable growth; MVAIC (Modified value-added intellectual coefficient) model | 1 |
References
- Abreu Pederzini, G.D. Managerial learning challenges in a complex world. J. Work-Appl. Manag. 2019, 11, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BCG. The End of Management as We Know It. Available online: https://www.bcg.com/publications/2020/end-management-as-we-know-it (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- O’Neill, R.; Nalbandian, J. Change, Complexity, and Leadership Challenges. Public Adm. Rev. 2018, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laylavi, F. Social Vulnerability to COVID-19: Preliminary Indicators and Research Agenda; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zarghami, A. A reflection on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Australian businesses: Toward a taxonomy of vulnerabilities. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 64, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzeń-Mitka, I.; Okręglicka, M. Managing Complexity: A Discussion of Current Strategies and Approaches. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 27, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grewatsch, S.; Kennedy, S.; Bansal, P. Tackling wicked problems in strategic management with systems thinking. Strateg. Organ. 2021, 14761270211038635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Aguilera, J.; Anderson, W.; Bridges, A.; Fernández, M.; Hansen, W.; Maurer, M.; Nébié, E.; Stock, A. Supporting interdisciplinary careers for sustainability. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. A foundational framework for smart sustainable city development: Theoretical, disciplinary, and discursive dimensions and their synergies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 758–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, Z.; Böhme, J.; Wamsler, C. Towards a relational paradigm in sustainability research, practice, andeducation. Ambio 2021, 50, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.D.; Wade, J.P. A Definition of Systems Thinking: A Systems Approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 44, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Murray, D.; Furlong, K.; Coco, E.; Dablander, F. A breeding pool of ideas: Analyzing interdisciplinary collaborations at the Complex Systems Summer School. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryani, S.M.; Amini, A. Management and Organizational Complexity. Procedia - Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 230, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, P.M. The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization; Random House Business Books: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ackoff, R.L. Systems thinking and thinking systems. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1994, 10, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C. Fifty years of systems thinking for management. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009, 60, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchen, D.; Boyd, B.; Bergh, D. Research Methodology in Strategic Management: Past Accomplishments and Future Challenges. Organ. Res. Methods 2007, 11, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bertalanffy, L. General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications; G. Braziller: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Condorelli, R. Complex Systems Theory: Some Considerations for Sociology. Open J. Appl. Sci. 2016, 06, 422–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, B. There is a Relationship Between Systems Thinking and W. Edwards Deming’s Theory of Profound Knowledge. 2006. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/There-is-a-Relationship-Between-Systems-Thinking-W-Berry/a09048ae9c5cd2efbe90f3feb8a2b9ca57a9f6e9 (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Miller, J.G. General Living Systems Theory. In Biological Psychiatry, Higher Nervous Activity; Pichot, P., Berner, P., Wolf, R., Thau, K., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, J.W. System dynamics, systems thinking, and soft OR. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1994, 10, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checkland, P.B. Soft Systems Methodology. Hum. Syst. Manag. 1989, 8, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansoff, H.I.; Kipley, D.; Lewis, A.O.; Helm-Stevens, R.; Ansoff, R. Implanting Strategic Management; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bettis, R.; Blettner, D. Strategic Reality Today: Extraordinary Past Success, but Difficult Challenges Loom. Strateg. Manag. Rev. 2020, 1, 75–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintzberg, H. Patterns in Strategy Formation. Manag. Sci. 1978, 24, 934–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engert, S.; Rauter, R.; Baumgartner, R.J. Exploring the integration of corporate sustainability into strategic management: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2833–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiblein, M.; Reuer, J. Foundations and Futures of Strategic Management. Strateg. Manag. Rev. 2020, 1, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G. What theories are needed for strategic management? Nankai Bus. Rev. Int. 2015, 6, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, C.A. Growth and development. J. Pediatrics 1933, 2, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirásek, M.; Bilek, J. The Organizational Life Cycle: Review and Future Agenda. Qual. Innov. Prosper. 2018, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filley, A.C.; Aldag, R. Organizational Growth and Types: Lessons from Small Institutions. Res. Organ. Behav. 1990, 2, 279–320. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277559527_Organizational_Growth_and_Types_Lessons_from_Small_Institutions (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Bogin, B. Human Growth and Development. Basics Hum. Evol. 2015, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, M.; Papaluca, O.; Sasso, P. The System Thinking Perspective in the Open-Innovation Research: A Systematic Review. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2018, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basadur, M.; Basadur, T.; Licina, G. Chapter 26—Organizational Development. In Handbook of Organizational Creativity; Mumford, M.D., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 667–703. [Google Scholar]
- Schreyögg, G. Development: Organizational. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Wright, J.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, S.; Halliday, M. Organisations as Systems. Hum. Relat. 1980, 33, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackoff, R.L. Re-Creating the Corporation: A Design of Organizations for the 21st Century; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, J.; Sims, D.; Fineman, S.; Gabriel, Y. Organizing and Organizations: An Introduction. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1995, 46, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M. Organizational Life Cycles; University of Wisconsin-Oshkosh: Oshkosh, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, R.; Adams, R.; Bessant, J. Life Cycles of Growing Organizations: A Review with Implications for Knowledge and Learning. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2007, 9, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, U.; Schneider, N.; Ben Jebli, M. How coal and geothermal energies interact with industrial development and carbon emissions? An autoregressive distributed lags approach to the Philippines. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.; Monni, S. Environment, human development and economic growth. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 64, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Criado, A.R. The art of writing literature review: What do we know and what do we need to know? Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R., Jr.; Clark, L.A.; Clark, W.; Raffo, D. Re-examining systematic literature review in management research: Additional benefits and execution protocols. Eur. Manag. J. 2020, 39, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek-Crabb, A. Business Growth Versus Organizational Development Reflected in Strategic Management of Polish Small, Medium and Large Enterprises. Procedia - Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 150, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fong, C.C. Strategic management accounting of social networking site service company in China. J. Technol. Manag. China 2011, 6, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, G.; Brooksbank, D.; Miller, C.; Thomas, B. Climbing the mountain: Management practice adoption in growth oriented firms in Wales. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2005, 12, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitelis, C.N.; Wahl, M.W. Edith penrose: Pioneer of stakeholder theory. Long Range Plan. 1998, 31, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Lee, C. Effect of Coopetitive Activity on Innovation and Management Performances in the Structural Context. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2019, 24, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guru, B.K.; Yadav, I.S. Financial development and economic growth: Panel evidence from BRICS. J. Econ. Financ. Adm. Sci. 2019, 24, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmieleski, K.M.; Ensley, M.D. A contextual examination of new venture performance: Entrepreneur leadership behavior, top management team heterogeneity, and environmental dynamism. J. Organ. Behav. 2007, 28, 865–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, P.R.; Lockhart, J.C. How boards influence business performance: Developing an explanation. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2016, 37, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hoque, K.; Bacon, N.; Llusar, J. High performance work systems and workplace performance in small, medium-sized and large firms. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 2015, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, D.M.; Giacomini, H.C.; Chu, C.; Jackson, D.A. Identifying influential parameters of a multi-species fish size spectrum model for a northern temperate lake through sensitivity analyses. Ecol. Model. 2021, 460, 109740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, G.C. Major Innovation as a Dynamic Capability: A Systems Approach*. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2008, 25, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhe, A. Partner Nationality and the Structure-Performance Relationship in Strategic Alliances. Organ. Sci. 1993, 4, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Baei, F.; Hosseini-Amiri, S.-M.; Moarefi, A.; Suifan, T.S.; Sweis, R. Proposing a model of manager’s strategic intelligence, organization development, and entrepreneurial behavior in organizations. J. Manag. Dev. 2020, 39, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, P. Growing with the Market: How Changing Conditions During Market Growth Affect Formation and Evolution of Interfirm Ties. Strateg. Manag. J. 2017, 39, 295–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Renko, H.; Autio, E.; Sapienza, H.J. Social capital, knowledge acquisition, and knowledge exploitation in young technology-based firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 587–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamholtz, E.; Hua, W. Strategic Organizational Development, Growing Pains and Corporate Financial Performance:: An Empirical Test. Eur. Manag. J. 2002, 20, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Young, S.; Li, S.-J.; Huang, Y.-Y. Using System Dynamics to Investigate How Belief Systems Influence the Process of Organizational Change. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2017, 34, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dararat, T. The Effect of Strategic Innovation on Company Performance: A Case Study of the Industrial Estate of Thailand. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolacci, F.; Castellano, N.G.; Cerqueti, R. The impact of innovation on companies’ performance: An entropy-based analysis of the STAR market segment of the Italian Stock Exchange. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2015, 27, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, X. The intellectual capital efficiency and corporate sustainable growth nexus: Comparison from agriculture, tourism and renewable energy sector. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, P.; Solli-Sæther, H. Towards a stage theory for industrial management research. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2009, 109, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, P.M.; Carstedt, G. Innovating Our Way to the Next Industrial Revolution. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2001, 42, 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- Roetzel, P.G. Information overload in the information age: A review of the literature from business administration, business psychology, and related disciplines with a bibliometric approach and framework development. Bus. Res. 2019, 12, 479–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saemundsson, R. On the Interaction between the Growth Process and the Development of Technical Knowledge in Young Technology-based Firms. Technovation 2005, 25, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, C.; Pels, J.; Polese, F. A Brief Review of Systems Theories and Their Managerial Applications. Serv. Sci. 2010, 2, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, L. Information: A Very Short Introduction; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
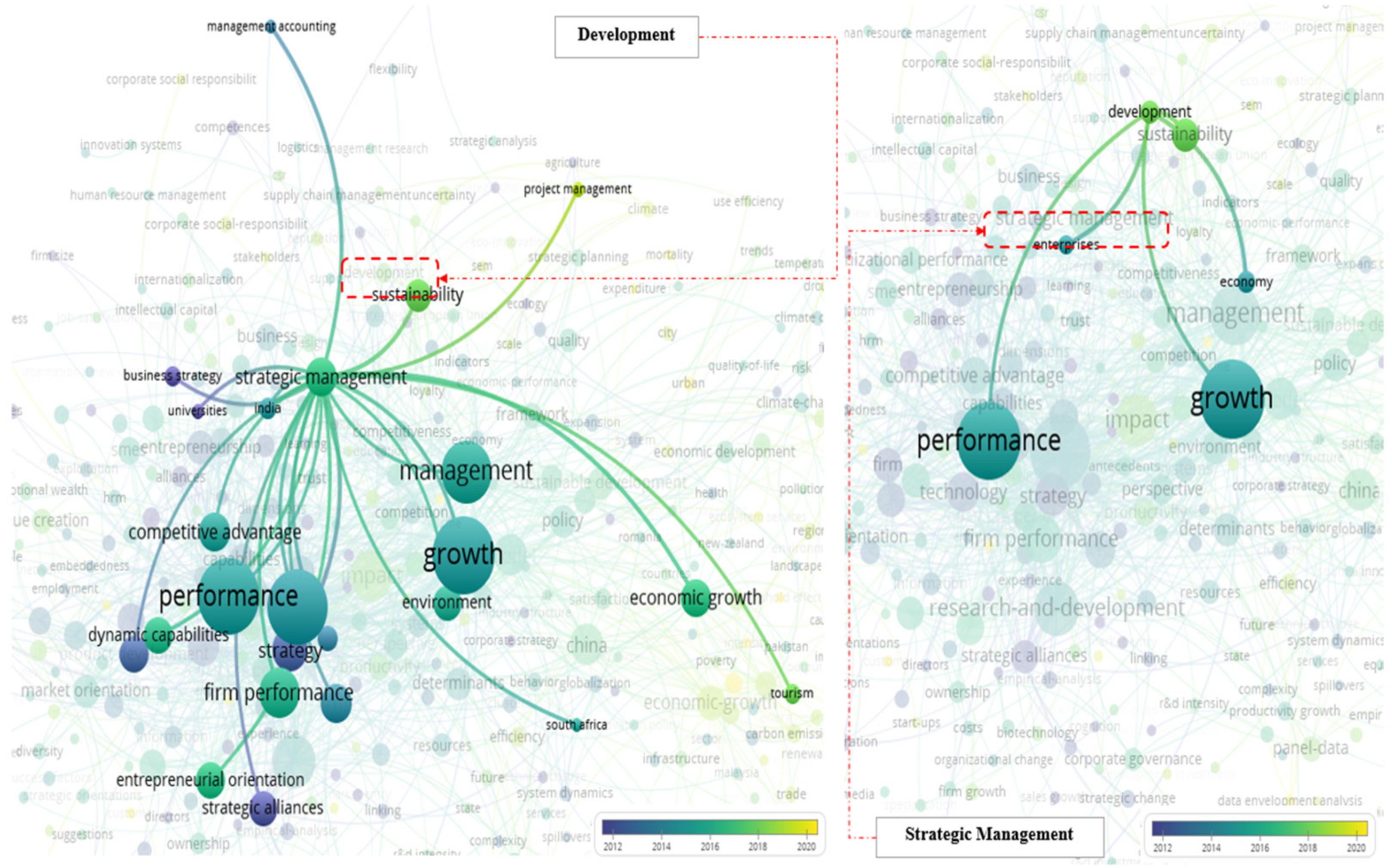

| Keywords | Occurrence | Links | Total Link Strength | Average Publication per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Management | 30 | 100 | 26 | 2016 |
| Growth | 122 | 256 | 117 | 2014 |
| Development | 9 | 32 | 8 | 2017 |
| Articles | Growth and Development | Strategic Management | Growth | Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [47] | High | High | High | High |
| [48] | Low | Low | High | Medium |
| [49] | Medium | Low | High | Medium |
| [50] | Non | Low | High | Medium |
| [51] | Non | Low | Low | Low |
| [52] | Non | Non | High | High |
| [53] | Non | Low | High | Medium |
| [54] | Non | Medium | Low | Low |
| [55] | Low | Low | Medium | Low |
| [56] | Non | Non | High | Low |
| [57] | Non | Medium | Low | High |
| [58] | Non | Low | Low | Low |
| [59] | Low | Low | Medium | High |
| [60] | Non | Low | High | Low |
| [61] | Non | Low | Medium | High |
| [62] | Low | Low | High | High |
| [63] | Non | Low | High | Low |
| [64] | Non | Low | Medium | High |
| [65] | Non | Low | High | Low |
| [66] | Non | Low | High | Medium |
| [67] | Non | Low | High | Low |
| [68] | Non | Low | Medium | Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pourahmadi, B.; Kalkowska, J. Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095561
Pourahmadi B, Kalkowska J. Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095561
Chicago/Turabian StylePourahmadi, Behnam, and Joanna Kalkowska. 2022. "Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095561
APA StylePourahmadi, B., & Kalkowska, J. (2022). Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability, 14(9), 5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095561






