Abstract
The landscape scaling relation challenges catchment ecological management; however, how the scaling relations change among naturally and anthropogenically differentiated catchments is still unknown. In this study, approximately 1500 soil samples were determined; more than 800 households were surveyed; and the landscape pattern was investigated in 120 sub-catchments of a subtropical Chinese urbanizing agricultural catchment. A scalogram and a coefficient of variation of the commonly used landscape metrics were estimated among various grain sizes, to quantify the Strength of Landscape Scale Effects (SSE) among sub-catchments. Natural and anthropogenic determinants for the SSE were determined. Then, the determinants incorporating landscape scaling relation were applied to classify the sub-catchments through the k-means clustering analysis. The SSE presented different spatial heterogeneity across the 120 sub-catchments and was not expectedly related to the scaling relation over the entire catchment, especially for the Contagion index and Shannon’s Evenness Index. The SSE were significantly related to natural and anthropogenic factors including the soil sand content, the population density, the relief ratio, and the ratio of arable land to woodland. The four factors combing with landscape scaling relations contributed to the four gratifying convergent categories for the 120 sub-catchments. Category I with a large relief and less anthropogenic disturbance had higher spatially non-stationary relationship, while categories II, III, and IV, with varying degrees of relatively small relief and strong intensities of anthropogenic disturbance, had a lower spatial heterogeneity of the landscape scaling relation. The results implied that category I was required to strengthen environmental protection of spatial differences, and categories II, III, and IV could ignore the landscape scale effects and even upscaling management to save management resources when carrying out ecological management within. Our findings could minimize uncertainty in ecological planning and provide opportunities for the application of multiple-scale management.
1. Introduction
The landscape scaling relation, termed as the landscape pattern heterogeneity changing with scales of observation or analysis, usually induces highly spatially non-stationary and uncertain relationships between the catchment landscape and ecological processes [1,2,3], and it consequently challenges catchment ecological management, e.g., urbanization planning, environment protection, and water resource utilization [4,5,6,7,8]. Natural and anthropogenic processes form catchment landscape heterogeneity across various spatial scales [1,3]. This means that the catchments with approximate natural and anthropogenic features are supposed to possess a spatial consistency of the landscape scaling relation. Although numerous studies widely examined the relationships between the natural and anthropogenic features and the landscape pattern [6,9], few studies have been carried out on the influencing factors and applications of the landscape scaling relation; even these studies can benefit to clarify the relationship between the catchment landscape and the ecological processes and can further facilitate catchment ecological management.
Natural catchment and anthropogenic factors structure the landscape pattern and drive landscape evolution and thus determine the landscape scaling relation. For instance, soil properties determine agricultural productivity to influence the size and spatial distribution of agricultural fields [1,4]; high mountains are usually covered by woodland and also can redirect trends of rives and roads [10]; urbanization generally expands along roads and rivers and gradually fragment a distribution of agricultural landscape in urbanizing agricultural catchments [11]. As the landscape pattern is spatially correlated and scale-dependent and the landscape evolution occurs at various spatial scales, landscape spatial heterogeneity and its relationship to the natural and anthropogenic factors may resultantly change with the spatial scales. Some studies were carried out at a single spatial scale and suggested that the local-scale anthropogenic factors include population density, urbanization, and agriculture development intensities, and regional-scale differences in climate, geologic parent material, and topography structure catchment landscape heterogeneity [1,3,5]. These studies, neglecting the multi-scale effects, probably miss some essential details and cause a failure to capture the spatial dependence of landscape heterogeneity [3,8]. The other studies have presented light on the issue of landscape spatial scale effects, and have summarized scaling relations and functions [12,13], whereas they mainly focus on the change in landscape heterogeneity in itself but rarely consider its relationship to natural catchment and anthropogenic features, e.g., soil, topography, and anthropogenic activities. Therefore, the specific determinants and relationships between natural catchment and anthropogenic factors and the landscape scaling relation are needed for further study in catchments.
The landscape scaling relation induces high risk and the uncertainty of catchment ecological management among different catchments due to the highly spatially non-stationary and uncertain relationships between the catchment landscape and ecological processes. Given the strong effects of the natural and the anthropogenic on the landscape scaling relation, one method to minimize the risk and uncertainty is to incorporate landscape scale effects into catchment classification for regional naturally and anthropogenically differentiated catchments [14,15]. Previous studies reported that the catchments, having similar natural and anthropogenic features, possess a spatial consistency of the landscape scaling relation among neighborhood catchments for specific landscape features such as division, fragmentation, and aggregation [16,17]. These spatial consistencies of the landscape scaling relation facilitate a ready and accurate extrapolation or interpolation of landscape features in a certain catchment class [13]. Catchment classification has been considered an essential step towards improving catchment ecological management [15]. Some catchment classification studies have been conducted based on catchment physiographic features, e.g., landscape pattern, topographic characteristics, and pedologic features, and they have generated very gratifying convergent catchment classification results [14,15,18,19,20]. These studies generally neither consider the effects of anthropogenic activities on the landscape pattern nor incorporate the landscape scale effect into catchment classification.
Here, it is hypothesized that natural and anthropogenic factors structure the landscape pattern and function across spatial scales. This study aimed to reveal the natural and anthropogenic determinants for the heterogeneity of landscape scaling relation and to identify the catchment types with spatial consistency of landscape scaling relations in an urbanizing agricultural catchment in the subtropical central China.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Jinjing river catchment (27°55′–28°4′ N,112°56′–113°30′ N, elevation of 46–452 m), located in the region of the Changsha–Zhuzhou–Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, has a population of 41,702 people (2018) and covers an area of 135 km2 (Figure 1). The catchment typifies many urbanizing agricultural landscapes in terms of geo-morphology and socio-economic dynamics in the Chinese subtropics, making it is an ideal microcosm for other catchments. The study region has a subtropical monsoon climate, a mean annual air temperature of 17.5 °C, and a mean annual precipitation of 1330 mm (1968–2018). The feature topography is low hills in the catchment, with mean slopes of 15.4%. The soil, developed from highly weathered granite parent material, is classified as Oxisol and Agrudalf. The soil depths overlying the impermeable parent materials range from 1.8 to 2.0 m.
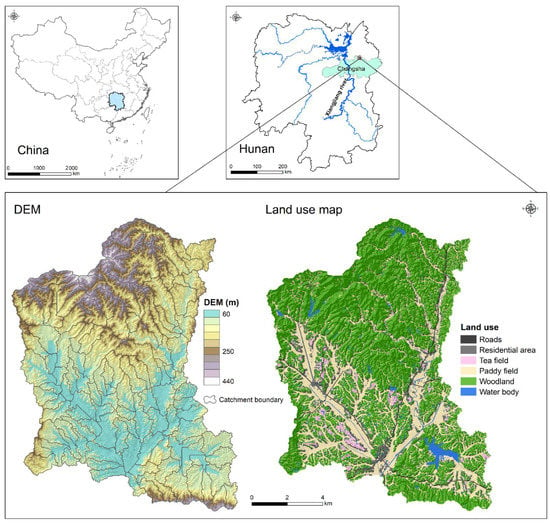
Figure 1.
Geographical location, digital elevation model (DEM), and land-use map of the Jinjing river catchment and 120 sub-catchments within. The DEM and land-use data were obtained from the Hunan Provincial Geomatics Information Center (http://www.hnpgc.com, 1 December 2021).
Forest and paddy field are the two dominant land-use types in the catchment, covering 56% and 34% of total catchment area, respectively. Forest is primarily covered with secondary Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.) and distributed on the hillsides. Paddy fields are the dominant arable land and are generally distributed in valleys and on flood plains along streams. Rice is planted twice a year from mid-April to mid-October in the studied catchment. Because rice plantation requires huge amounts of irrigation and surface drainage, many artificial reservoirs, pools, and irrigation-drainage channels were constructed in the catchment. Besides, the catchment is famous for its tea industry. Numerous tea gardens had been built after clearing up the secondary Masson pine woodland in the last two decades. The residential areas are generally distributed at the foot of hill and along streams in the catchment, and these residential areas are commonly connected by cement and asphalt roads [3,9,21].
2.2. Soil Survey and Data Preparation
The digital elevation model (DEM) of the Jinjing catchment was obtained from the Hunan Provincial Geomatics Information Center (http://www.hnpgc.com). High-resolution land-use data could reflect more-detailed multi-scale landscape features, such as single houses and small areas of arable land. Land-use data for 2015, extracted from a digital topographic map (scale 1:10,000) from the Hunan Province Geomatics Information Center (http://www.hnpgc.com), were used to study catchment landscape heterogeneity. The land-use map was validated for ensuring accuracy by a vertical photograph with a resolution of 2.1 m taken on June 2015. To reveal a detailed catchment land-use composition and configuration, the land-use data were processed into the seven following land-use/land-cover types, including woodland, paddy fields, tea fields, roads, residential areas, rivers, and lakes (Figure 1).
A soil survey was conducted in the Jinjing river catchment during 2010–2011, and 1439 soil samples were collected to determine soil chemical properties including the soil pH value, the total soil nitrogen content (TSN), and the total soil phosphorous content (TSP). The soil chemical properties were interpolated by the ordinary kriging method across the then entire catchment. Additionally, fifty bulk soil samples were collected under different land-uses and soil types within the Jinjing river catchment. Select soil physical and hydraulic parameters including soil texture (clay% and Sand%), soil bulk density (BD), soil saturated water content (Theta), and soil saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks) were determined to develop the soil pedo-transfer functions (PTFs). The detailed information for the PTFs was described in our previous study [22]. The PTFs were interpolated into the digital soil map of the entire catchment to create series maps of soil physical and hydraulic properties using the ArcGISTM 10.5 software.
2.3. Data Processing
The boundary of the Jinjing river catchment was delineated mainly according to elevation information (points and contours) (Figure 1), which was extracted from a digital topographic map and was used to calculate the digital elevation model (DEM) by using the “Topo to Raster” function in the ArcGISTM 10.5 software. Thereafter, the entire Jinjing river catchment was divided into 120 sub-catchments based on its DEM and hydrological networks and by the Hydrology Analysis extension of the ArcGISTM 10.5 software.
The average values of the selected eleven parameters, covering soil physical, hydraulic, chemical, topography, and anthropogenic factors settings, were estimated in the 120 sub-catchments (Figure 2). The soil physical and chemical settings were calculated from the series interpolated maps of soil properties. The anthropogenic setting includes the parameters of population density (PD) and the ratio of arable land to woodland (RATIO). The PD, representing the urbanization ratio in the study region, was estimated from the annual population statistics of the local government and was also corrected by a household survey in 2015. The RATIO, representing the intensity of agricultural development, was estimated based on a land-use map. The topographic setting includes the degree of relief (RELIEF) that describes the topographic characteristics and was estimated from the DEM by using Neighborhood statistics (10 × 10 m) in the spatial analysis tools of the ArcGISTM 10.5 software.
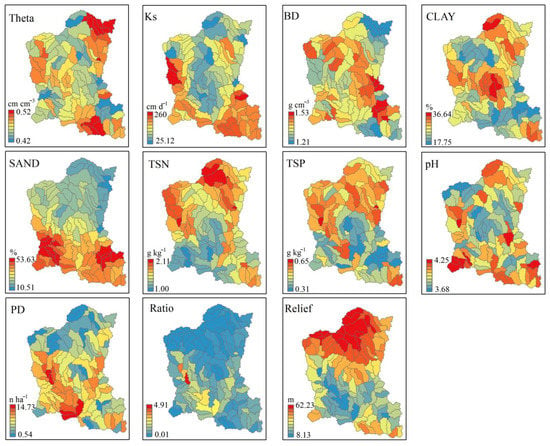
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of soil, anthropogenic, and topographic features among the 120 sub-catchments within the Jinjing river catchment. The sub-catchment features include soil saturated water content (Theta, cm cm−3), soil saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks, cm d−1), soil bulk density (BD, g cm−3), soil clay content (CLAY, %), soil sand content (SAND, %), total soil nitrogen content (TSN, g kg−1), total soil phosphorous content (TSP, g kg−1), soil pH (pH, non-dimension), population density (PD, n ha−1), ratio of arable land to woodland (Ratio, %), and relief ratio (Relief, m).
A suite of 12 commonly used landscape-level metrics was used to quantify the landscape pattern in the Jinjing river catchment and the 120 sub-catchments, and then their responses to changing grain size were investigated. The landscape-level metrics included the Edge Density (ED), the Contagion index (CONTAG), the Landscape Division Index (DIVISION), Shannon’s Evenness Index (SHEI), the Landscape shape index (LSI), the Interspersion and Juxtaposition Index (IJI), the Splitting Index (SPLIT), the Effective Mesh Size (MESH), the Landscape Shape Index (LPI), the Aggregation Index (AI), the Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION), and the Perimeter-Area Fractal Dimension (PAFRAC). Because of the large data among multiple scales, several batch ftp files, which were used in FRAGSTATS 4.2 to calculate landscape metrics [23], were built by R software (http://www.r-project.org, 14 December 2021).
2.4. Statistical Methods
Landscape metric scalograms were used to illustrate the scale effects of landscape metrics, and the grain size systematically changed from 5 m to 250 m with an increment of 5 m. That is, a new aggregated areal unit was assigned to the patch type that was the most dominant among those represented by all pixels at the next lower level. In total, the 12-landscape metrics were examined at 6050 single scales (6000 for the 120 sub-catchments and 50 for the Jinjing river catchment).
The above investigation process of scaling relations was repeatedly calculated in all 120 sub-catchments. Then, the coefficient of variation of the scaling relation for each of the landscape metrics was estimated to represent the Strength of Landscape Scale Effects (SSE) (Equation (1)), with the larger coefficient of variation valuing the stronger scale effects.
where the SSEi is the strength of landscape scale effects for the sub-catchment i; xij is the landscape metric value at spatial scale j in the sub-catchment i; n is the number of spatial scales (n = 50); and µ is the mean value of landscape metric values at spatial scales from 5 m to 250 m with an increment of 5 m.
Pearson’s correlating analysis was used to investigate the relationships between landscape scaling relations and catchment parameters. Several parameters were chosen for catchment classification based on the strength and robustness of correlation. The k-means clustering analysis was applied for catchment classification incorporating landscape scale effects. The “stats” and “factoextra” packages in R software were used to estimate and perform the k-means clustering, respectively.
3. Results
The scale effect of the landscape pattern and its spatial variating strength were quantified at catchment and sub-catchment scales, respectively. Firstly, at the catchment scale, the 12-landscape metrics exhibited different scale effects in scaling functions (Figure 3). The ED, DIVISION, LSI, SPLIT, MESH, and LPI presented a stronger scale effect with the increasing grid sizes, among which the first four and the last two metrics were well fitted by the power and logarithmic functions (R2 = 0.83–0.99, p < 0.001), respectively. In contrast, the CONTAG, SHEI, IJI, AI, COHESION, and PAFRAC demonstrated weak spatial scale effects and irregular changes with the increasing grid sizes.
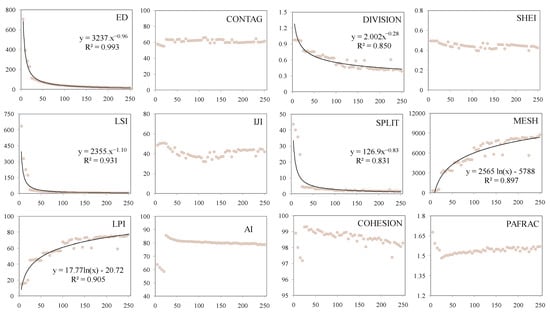
Figure 3.
Scalograms showing the effects of changing grain size (m) on the Edge Density (ED, m ha−1), Contagion index (CONTAG, %), Landscape Division Index (DIVISION, Proportion 0–1), Shannon’s Evenness Index (SHEI, non-dimension), Landscape shape index (LSI, non-dimension), Interspersion and Juxtaposition Index (IJI, %), Splitting Index (SPLIT, non-dimension), Effective Mesh Size (MESH, ha), Landscape Shape Index (LPI, non-dimension), Aggregation Index (AI, %), Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION, non-dimension), and Perimeter-Area Fractal Dimension (PAFRAC, non-dimension) in the Jinjing river catchment.
Secondly, at the sub-catchment scale, the SSE of ED, CONTAG, DIVISION, SHEI, LSI, and IJI had higher and larger spatial variations (Figure 4). The ED presented the highest SSE with a median of 95. The spatial distribution of SSE for ED, CONTAG, DIVISION, and SHEI showed spatial dependence at the sub-catchment scale, especially in the northern part of the catchment. The SSE of the above four landscape metrics even exceeded 120 in the several northern sub-catchments. Contrarily, other landscape metrics presented weaker SSE and smaller spatial diversity at the sub-catchment scale. Compared with the scale effect and its spatial variating strength of the 12-landscape metrics, ED, DIVISION, and LSI had a strong scale effect, and these scale effects also had a large spatial variation intensity.
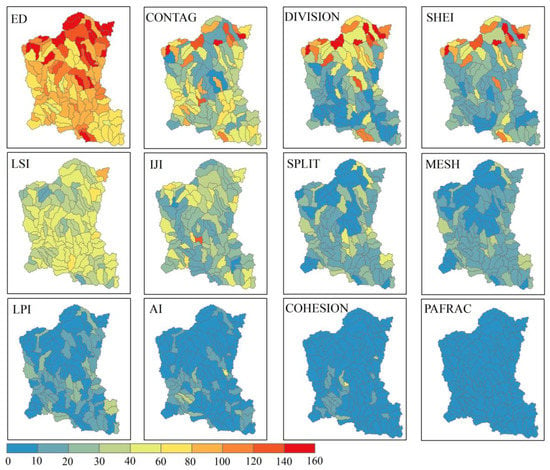
Figure 4.
Spatial diversity of landscape scaling relations reflecting by coefficient of variation of landscape metrics for grain sizes changing from 5 m to 250 m with an increment of 5 m.
The factors including Sand, PD, Relief, and Ratio presented a relatively stronger relation with SSE for most landscape metrics (Table 1). For instance, Relief significantly positively correlated to the SSE of the ED, DIVISION, and SHEI (r = 0.59–0.71, p < 0.001) and negatively correlated to the SSE of the COHESION, SPLIT, MESH, LPI, AI, and PAFRAC (r= ¬¬−0.38–−0.56, p < 0.001). The other factors such as the WP, Ks, and pH showed a weaker correlation with the SSE of few landscape metrics. Thereafter, SSE, Sand, PD, Relief, and Ratio were chosen as the potential classifying variables for catchment classification.

Table 1.
Correlations between landscape scaling relations and catchment properties.
The 120 sub-catchments were classified into four categories for the 12-landscape metrics according to the selected classifying variables (Table 2, Figure 5). The ratios of between-cluster sum of squares and the total sum of squares for the 12 classifications were 64.0–70.7%. The values of five classifying variables for categories I and IV were distributed in opposite poles. For category I, the PD, Ratio, and Sand had smaller values, while the landscape metrics (i.e., ED, CONTAG, DIVISION, and SHEI) possessed the maximum SSE. For categories II and III, the PD and Ratio had larger values, and Relief held moderate values. Maximum SSE for the landscape metrics (i.e., LSI, IJI, SPLIT, MESH, LPI, and PAFRAC) all appeared in category II.

Table 2.
Average values of sub-catchment features in the four catchment categories incorporating scaling relations.
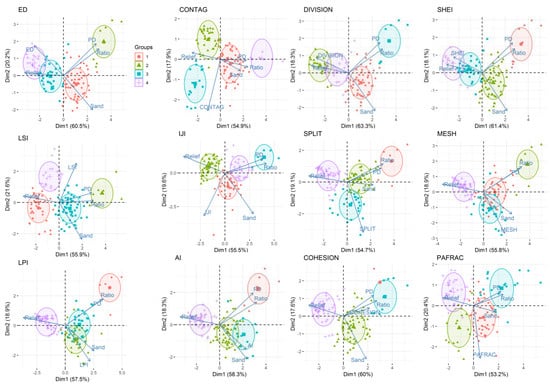
Figure 5.
Catchment classification incorporating landscape scaling relations for all the 120 sub-catchments by the k-means clustering analysis.
4. Discussion
4.1. Landscape Scaling Relations with Distinct Spatial Heterogeneity
Responses of some landscape metrics to spatial scales exhibited significant scaling functions in the Jinjing river catchment (Figure 3). The catchment landscape is a logical result of natural and anthropogenic disturbance. The ED, DIVISION, LSI, and SPLIT power-lawly decreased with increasing grain sizes, so that these landscape metrics representing area-edge, shape, aggregation of landscape patches can be readily and accurately extrapolated or interpolated across spatial scales in the catchment, although there were highly spatially distributed natural and socio-economic contexts [13]. The LPI reflects the disturbance of anthropogenic activities on landscape patterns within catchments [3], and its scaling function followed the logarithmic function. Some studies augured that the scalogram of LPI did not or poorly follow a logarithmic function [16,24]. Our inconsistent results suggested that, although general scaling responding regulations can be detected in a real landscape, some landscape metrics such as the LPI need further detection due to its responses to anthropogenic activities across various spatial scales. Beside the landscape indices above, the other six landscape metrics presented unpredictable responses to the spatial scales; in particular, the CONTAG and SHEI, quantifying the adjacency and the diversity of landscape pattern remained relatively stagnant with almost all grain sizes, showing their insensitivities to natural and anthropogenic activities across spatial scales.
The strength of scaling relations for the landscape metrics demonstrated distinguished spatial heterogeneity among the 120 sub-catchments, and it was not expectedly in accordance with the scaling relations of landscape metrics over the entire catchment. For instance, the CONTAG and SHEI had no obvious scaling relations at the catchment scale but significantly occurred at the sub-catchment scale (Figure 2 and Figure 3); the inconsistency suggested that spatial diversity and aggregation were more sensitive to an idiosyncratic landscape and were masked by internal mediating and neutralization, which could be attributed to the impacts of the number and evenness of landscape patch types and the spatial arrangement of landscape patches, as induced by coarse natural and anthropogenic processes [16]. In contrast, the scaling relation of LPI had higher sensitivity but weaker spatial heterogeneity, which verified again the aforementioned discrepancy for the LPI among different landscape through the interior landscape structure in a catchment. Meanwhile, the scaling relations of the AI, COHESION, and PAFRAC had lower sensitivity with weaker spatial heterogeneity. On the contrary, the scaling relation of ED had higher sensitivity and spatial heterogeneity, indicating there was a distinct edge effect, and scaling relations may be a reasonable and credible understanding of the mechanisms that drive edge effect occurrence and magnitude [6].
4.2. Landscape Scaling Relations Optimizing Catchment Classification
The Sand, Relief, PD, and Ratio presented strong relationships with the strength of landscape scaling relations (Table 1), suggesting effects of natural and anthropogenic processes on the structuring landscape pattern and functioning landscape evolution within sub-catchments. The Sand presented a relatively stronger relation with SSE of most landscape metrics, which was primarily due to its indirect roles in reforming landscape pattern and scaling relations through influencing soil nutrient retention and transfer [4]. The relief was correlated with the SSE of all landscape metrics. Previous studies reported that the topography impacts landscape fragmentation and isolation [10,21], and our study further reveals the initial role of topography in forming the spatial heterogeneity for landscape pattern scale effects. The Relief negatively correlated with the SSE of the ED, DIVISION, and SHEI that reflect landscape fragmentation. The primary reason was that topography promotes spatial heterogeneity of scaling relations both by creating permanent natural breaks in the landscape and through its influence on disturbance regimes and potential succession pathways [25]. Similarly, anthropogenic factors also impacted the spatial variation of the landscape scaling relation. For instance, the PD and Ratio were negatively correlated with the ED, DIVISION, and SHEI, indicating population aggregation and agricultural development weakened the landscape pattern scale effect. The PD and Ratio were closely linked to urbanization and socioeconomic development, and in turn this meant land resources were used in an orderly and reasonably manner, which introduced stable and regular landscape patches and weakened scaling relations [1,26].
Landscape scaling relations were well integrated into sub-catchment classification, suggesting that similar natural and anthropogenic processes possess spatial consistency of the landscape scaling relation of landscape features. The features of category I indicated that the sub-catchments with large relief and less anthropogenic disturbance had the relatively stronger spatial heterogeneity of landscape scaling relations for ED, CONTAG, DIVISION, and SHEI; this means more attention should be paid, when implement catchment ecological management in the category I sub-catchments. Adjacent sub-catchments were usually but not always more similar than the distant sub-catchment for category I. The results were consistent with the catchment category research that highlighted the importance of catchment structural and functional features [12]. In contrast with category I, the catchment of categories II, III, and IV with small relief and intensities of anthropogenic disturbance had lower spatial heterogeneity of the landscape scaling relation; hence, we could ignore the landscape scale effects and even upscaling management to save management resources when carrying out ecological management within. Although for landscape metrics with weaker spatial heterogeneity of landscape scaling relations, such as PAFRAC, the catchment classification was slightly inappropriate, considering that the landscapes of 120 sub-catchments under study were quite diverse in terms of composition and configuration; these results seem robust.
4.3. Ecological Implication and Future Research
Previous studies largely reported the interrelationship and mutual acting mechanisms between catchment landscape pattern and ecological and environmental issues, e.g., urbanization [1,3], hydrologic service functions [6], and agricultural non-point source pollution [4,6,7]. However, the scaling relation of the landscape pattern led to it being spatially non-stationary and produced uncertainty in the relationships between the landscape pattern and the ecological and environmental interrelationship and mechanisms [1,2,3]. If we ignore the scale effects, it may cause a failure to address these issues at a practice level. The method of incorporating landscape scale effects into catchment classification is in terms of the natural and anthropogenic determinants, defining landscape features with various strengths of scaling relations and discriminating spatial distributions of non-stationary relationships, while providing opportunities for exploring the optimal spatial scale for ecological management against single-scale regulation [1].
Our study landscapes included contrasting natural and socio-economic contexts and represented a relative wide range of landscape patterns in terms of the relative abundance and spatial distribution of landscape types; the results of spatial heterogeneity of landscape scaling relations seem robust, and the idea of incorporating scaling relations in catchment classification is well validated. The results highlighted the importance of natural and anthropogenic determinants on catchment landscape scaling relations and resulting catchment classification. However, in the present study, the landscape pattern was quantified only at the landscape level, and the measures of the landscape pattern rendered by all landscape patch types. Many catchment ecological applications require information about the composition and configuration of different landscape types that are generally detected at the class level. Therefore, before we are able to apply the scaling relations to address catchment ecological issues at the practice level, further works at the class level are needed, for instance, whether or not the class level metric has similar scaling relations and practicability in catchment classification as those observed at landscape level and whether or not the temporal scaling relations are dependent.
5. Conclusions
The results revealed that responses of landscape metrics to changing spatial scales exhibited scaling functions due to the combination of natural and anthropogenic processes at the catchment scale. The strength of scaling relations presented different spatial heterogeneity across the 120 sub-catchments and was not expectedly related to the scaling relation over the entire catchment, especially for CONTAG and SHEI. The strength of spatial heterogeneity in landscape pattern scale effects were significantly related to natural catchment and anthropogenic factors including Sand, PD, Relief, and Ratio. According to the selected four variables, landscape scale effects were well integrated into the catchment classification. Category I with maximum SSE for the landscape metrics (i.e., ED, CONTAG, DIVISION, and SHEI) had smaller values for the PD, Ratio, and Sand; category II with maximum SSE for the landscape metrics (i.e., LSI, IJI, SPLIT, MESH, LPI, and PAFRAC) possessed larger values for PD and Ratio and moderate values for Relief; category III with maximum SSE for the landscape metrics (i.e., AI and COHESION) held larger values for PD and Ratio and moderate values for Relief; category IV with lower SSE for the 12 landscape metrics had larger values for the PD, Ratio, and Sand. In terms of landscape scale effects leading to spatially non-stationary relationships and in turn challenging catchment environmental management, catchment classification incorporating landscape scaling relations could minimize uncertainty in ecological planning and provided opportunities for the applications of different scale management.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Y.P.; formal analysis, X.L.; funding acquisition, Y.P.; investigation, Y.P.; project administration, X.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Environmental Protection Scientific Research Project of Hunan Province (HBKT-2021007), the Key Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-DQC041), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41301202).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data and code presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Su, S.L.; Li, D.L.; Hu, Y.N.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y. Spatially non-stationary response of ecosystem service value changes to urbanization in Shanghai, China. Eco. Indic. 2014, 45, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, G.F.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhang, Z.H. Multi-scale analysis of relationship between landscape pattern and urban river water quality in different seasons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Shen, J.L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, R.L.; Wu, J.S. Changes in arable land in response to township urbanization in a Chinese low hilly region: Scale effects and spatial interactions. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 88, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.Y.; Song, L.F.; Li, H.; Meng, C.; Wu, J.S. Linking rice agriculture to nutrient chemical composition.; concentration and mass flux in catchment streams in subtropical central China. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 184, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Xia, N.; Jiang, P.H.; Zhong, L.S.; Pian, Y.Z.; Duan, Y.W.; Huang, Q.H.; Li, M.C. Analysis of farmland fragmentation in China Modernization Demonstration Zone since “Reform and Openness”: A case study of South Jiangsu Province. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J.X.; Turner, M.G. Importance of landscape heterogeneity in sustaining hydrologic ecosystem services in an agricultural watershed. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Hamel, P.; Sharp, R.; Kowal, V.; Wolny, S.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. Landscape configuration is the primary driver of impacts on water quality associated with agricultural expansion. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 074012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Shen, J.L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, R.L.; Wu, J.S. Multi-scaled response of groundwater nitrate contamination to integrated anthropogenic activities in a rapidly urbanizing agricultural catchment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34931–34942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.Y.; Song, L.F.; Li, H.; Ma, Q.M.; Wu, J.S. Relating land use patterns to stream nutrient levels in red soil agricultural catchments in subtropical central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10481–10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zinda, J.A.; Yang, Z.J.; Yin, M.; Ou, X.K.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Q.C. Effects of topographic attributes on landscape pattern metrics based on redundancy ordination gradient analysis. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.L.; Ma, X.Y.; Xiao, R. Agricultural landscape pattern changes in response to urbanization at ecoregional scale. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.G.; Shen, W.J.; Sun, W.Z.; Tueller, P.T. Empirical patterns of the effects of changing scale on landscape metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 761–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.G. Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landscape Ecol. 2004, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Bárdossy, A.; Zehe, E. A catchment classification scheme using local variance reduction method. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Tetzlaff, D.; Soulsby, C.; McDonnell, J.J.; Capell, R. A comparison of similarity indices for catchment classification using a cross-regional dataset. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 40, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, H.B. Sensitivity and effectiveness and of landscape metric scalograms in determining the characteristic scale of a hierarchically structured landscape. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.E. Surface metrics: Scaling relationships and downscaling behavior. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 31, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongal, H.; Sivakumar, B. Cross-entropy clustering framework for catchment classification. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, G.F.C.; Giovannini, M.R.M.; Errico, A.; Mirzaei, S.; Padulano, R.; Chirico, G.B.C.; Preti, F. Hydraulic Efficiency of Green-Blue Flood Control Scenarios for Vegetated Rivers: 1D and 2D Unsteady Simulations. Water 2021, 13, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.B.; Mohammadpour, R.; Linh, N.T.T.; Mohajane, M.; Pourjasem, A.; Sammen, S.S.; Nam, V.T. Application of soft computing to predict water quality in wetland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Fu, X.Q.; Xiao, R.L.; Wu, J.S. Landscape pattern changes at a catchment scale: A case study in the upper Jinjing river catchment in subtropical central China from 1933 to 2005. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 10, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.H. Development of Soil Hydrological Property Model and Character of Nitrogen Distribution in a Typical Subtropical Catchment. Master’s Thesis, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial pattern analysis program for categorical and continuous maps. 2012, Computer software program produced by the authors at the University of Massachusetts.; Amherst. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Saura, S.; Castro, S. Scaling functions for landscape pattern metrics derived from remotely sensed data: Are their subpixel estimates really accurate? ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2007, 62, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape ecology: The effect of pattern on process. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1989, 20, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.C.; Bennett, E.; Berhe, A.A.; Cassman, K.; DeFries, R.; Dietz, T.; Dobermann, A.; Dobson, A.; Janetos, A.; Levy, M.; et al. Anthropogenic Drivers of Ecosystem Change: An Overview. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).