Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on a Comprehensive Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Establish a comprehensive framework for grassland vulnerability assessment.
- (2)
- Analyse spatiotemporal changes in grassland vulnerability on the QTP.
- (3)
- Explore spatial autocorrelation and detect its driving factors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Framework for GVI Assessment
2.3. Data Collection and Approaches
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Classification Method
2.6. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations in VNF, VED, and VSI
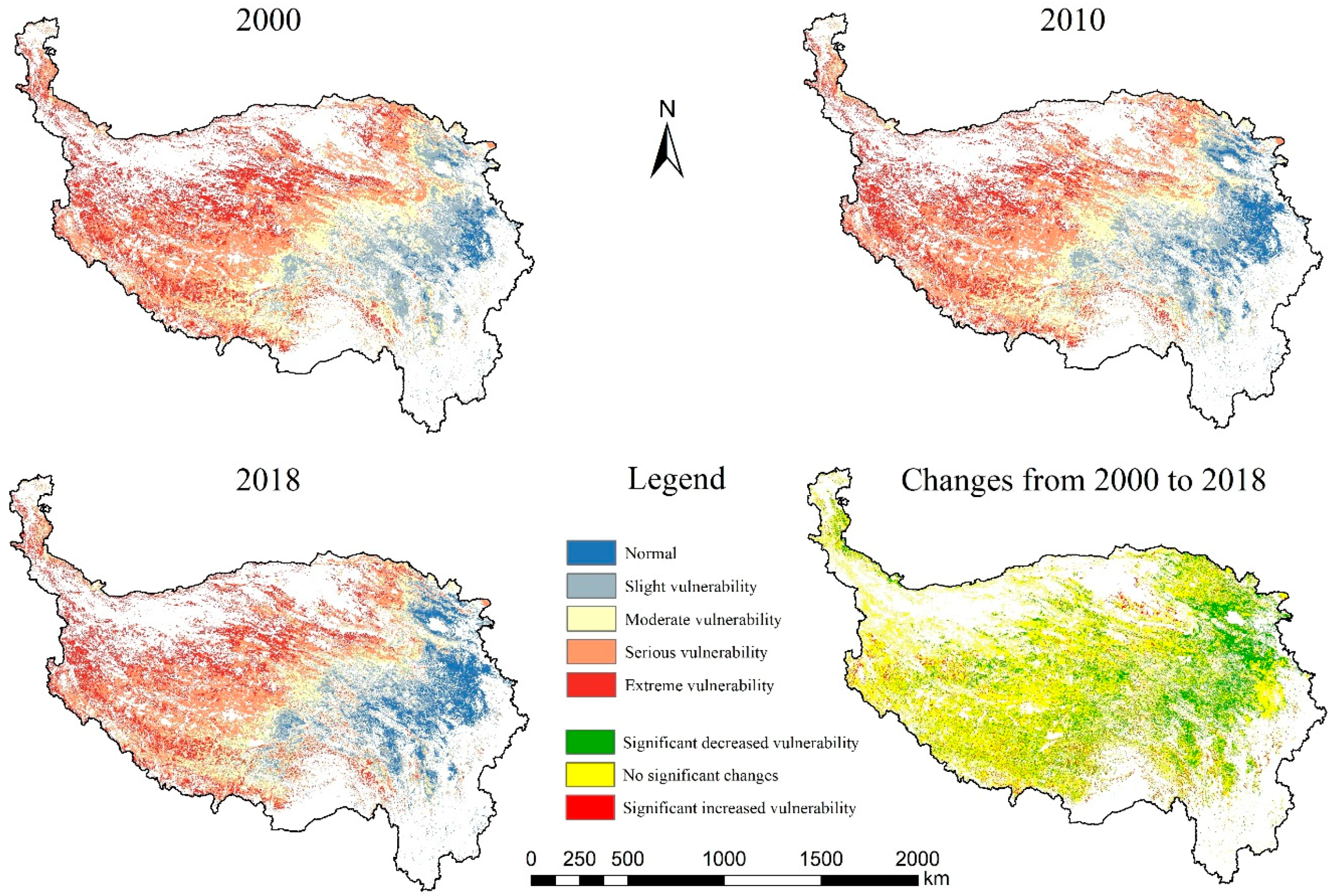
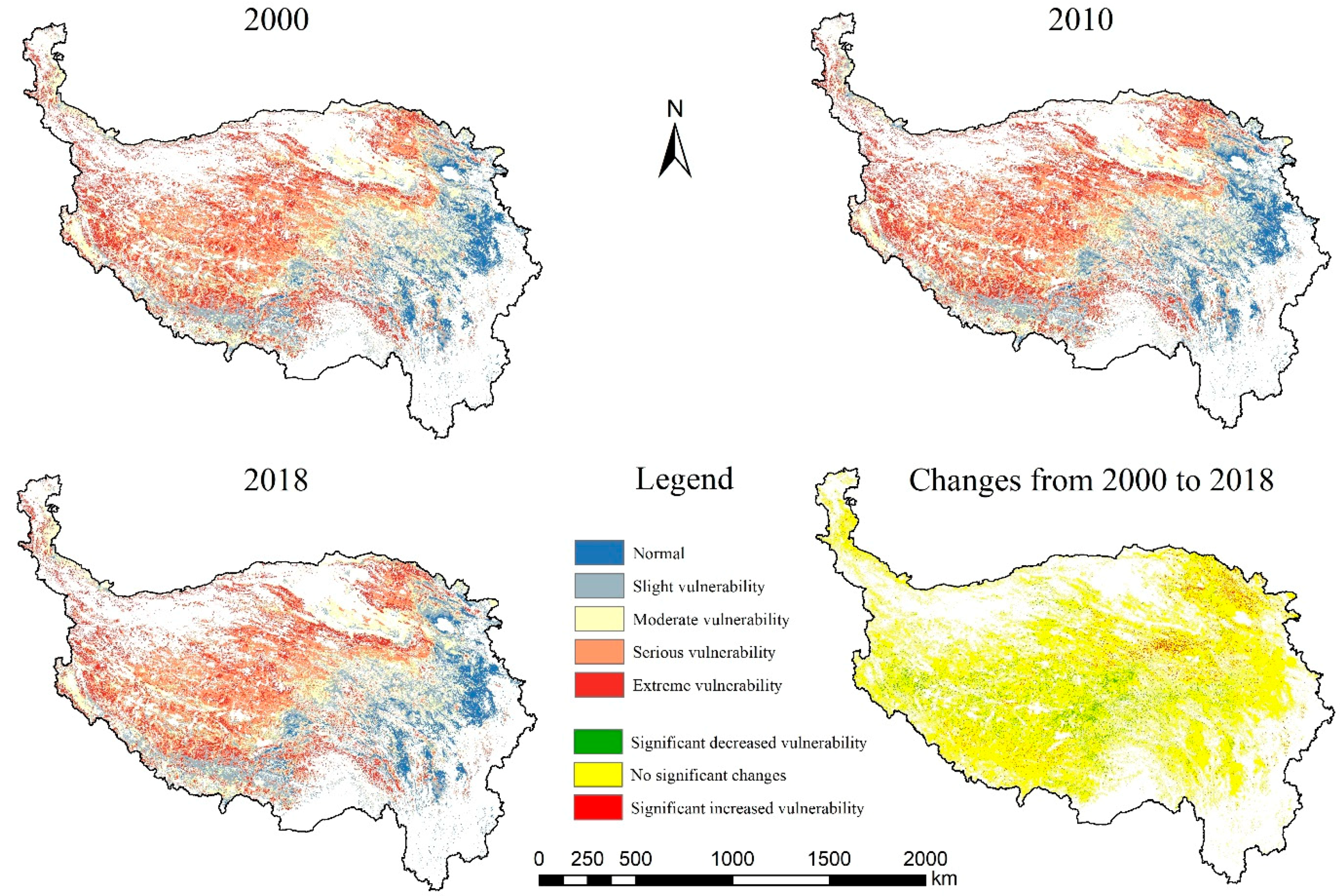
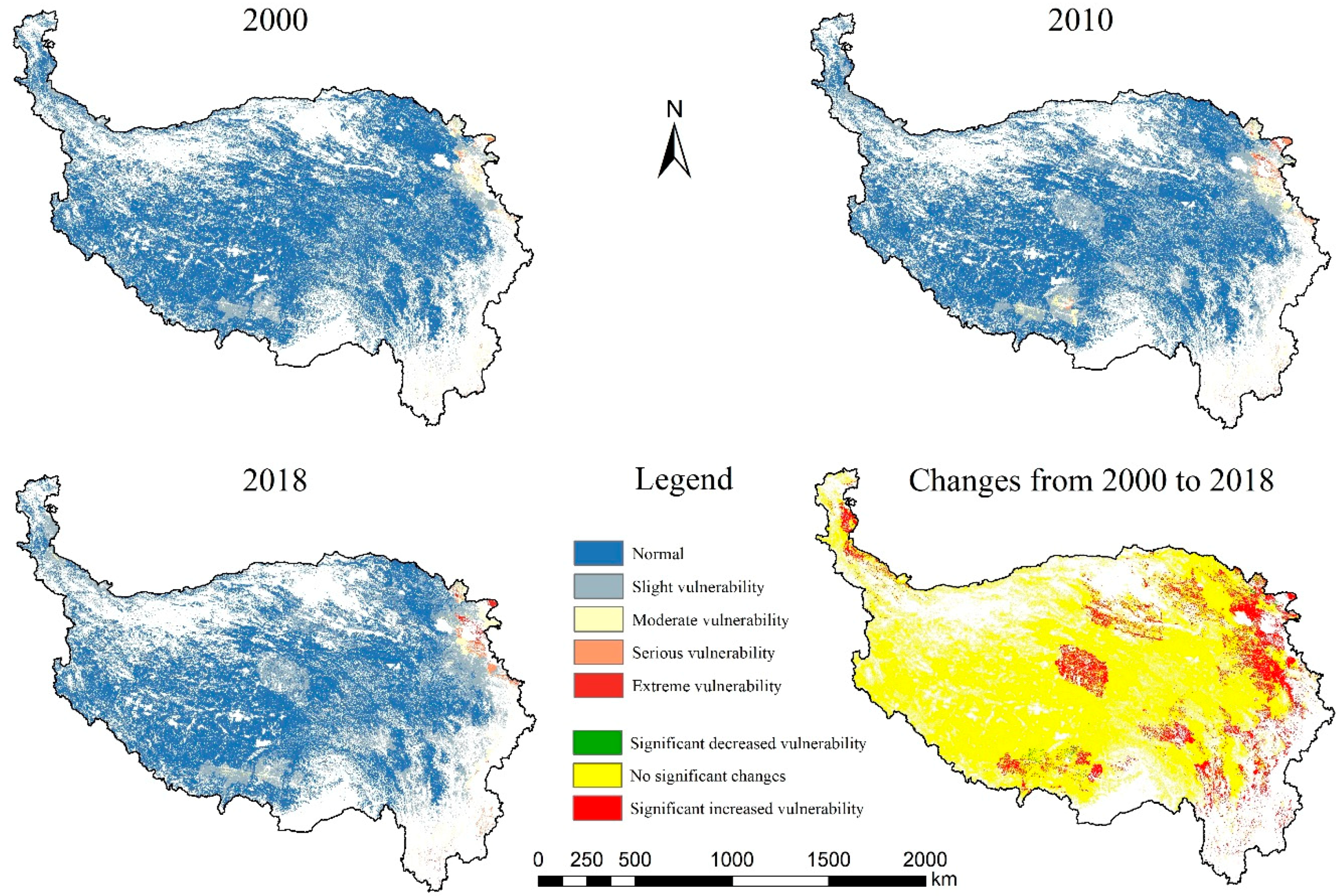
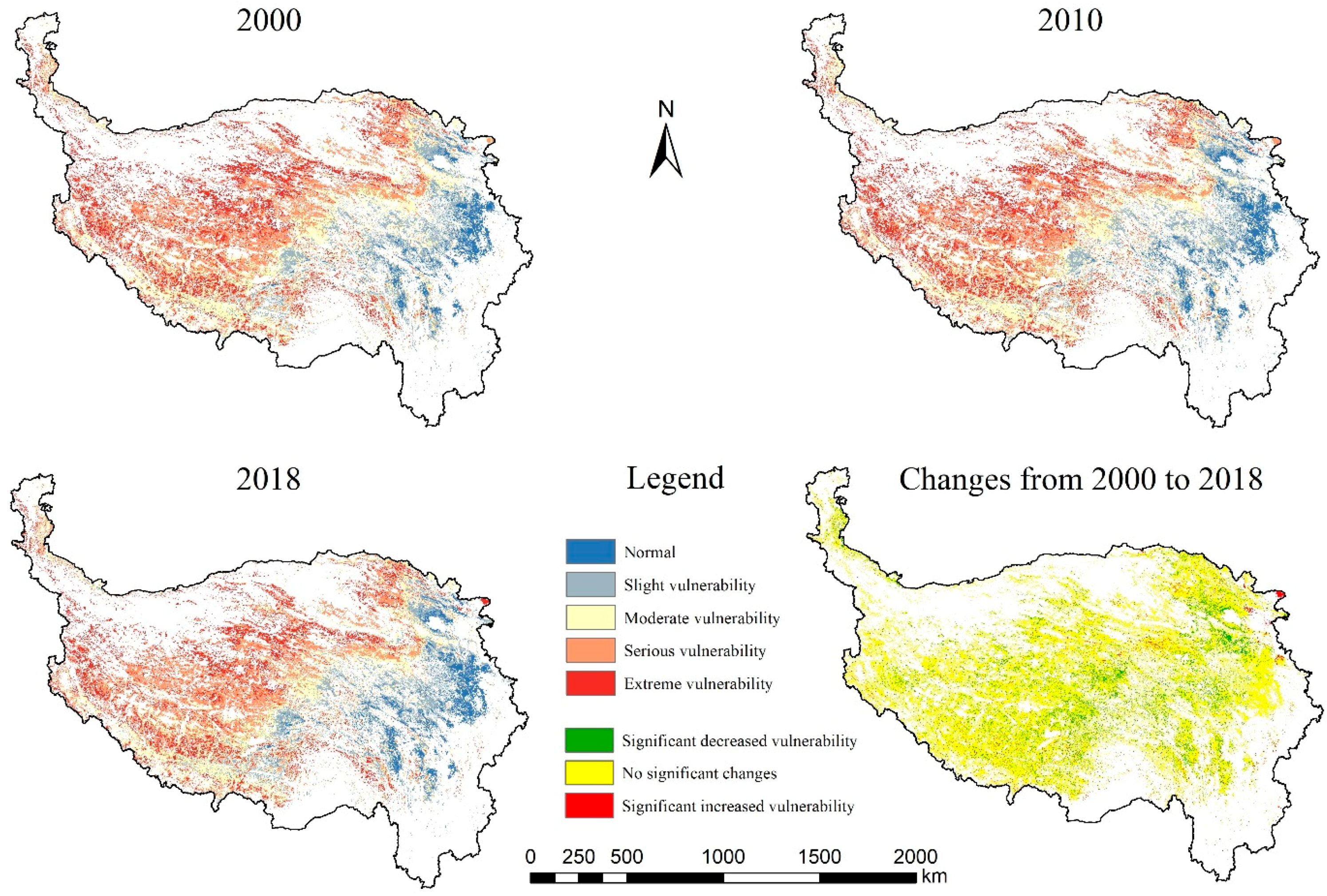
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability
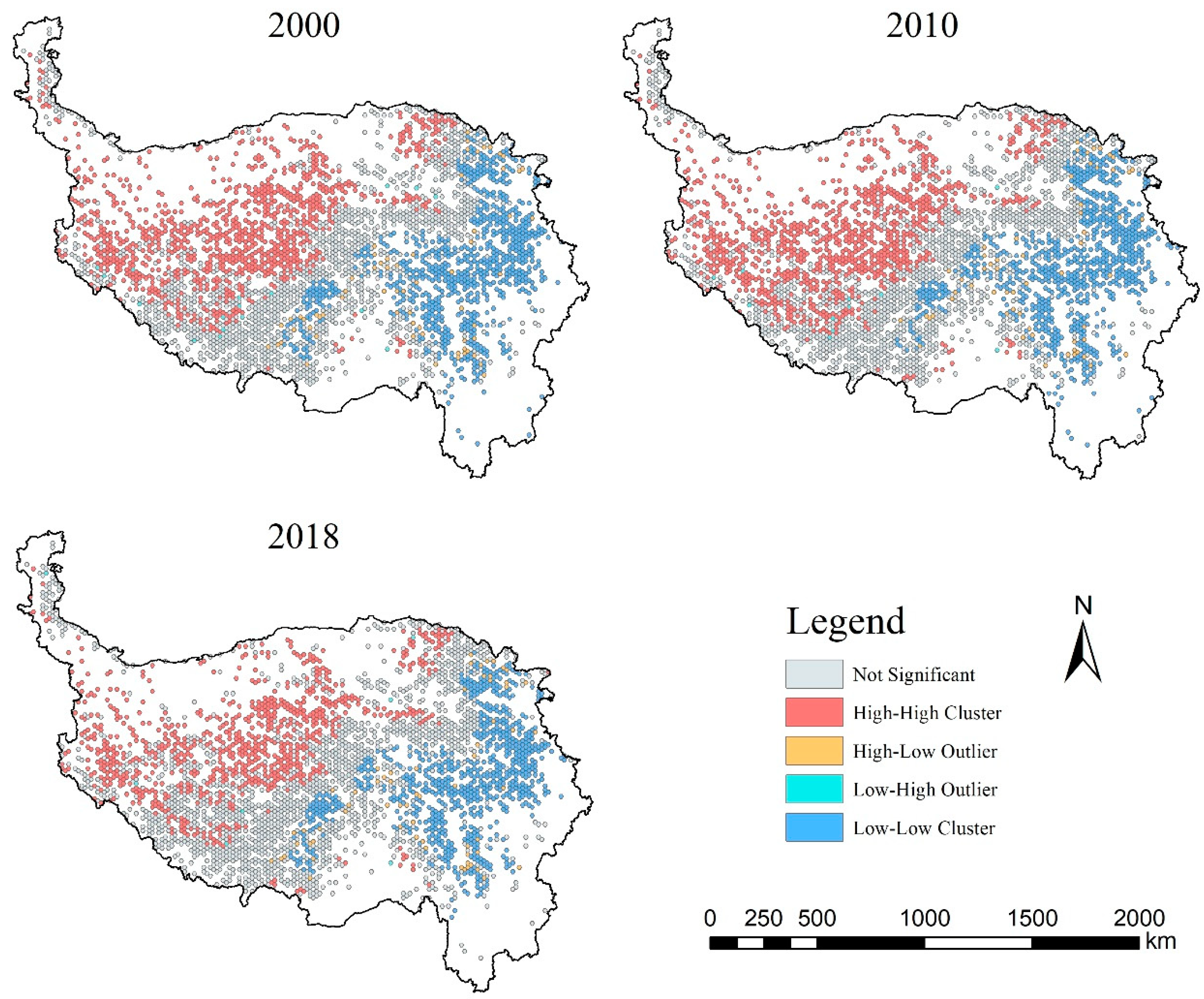
3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Characteristics of GVI
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability
4.2. Driving Factors of Grassland Vulnerability
4.3. Suggestions and Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Niu, B.; Wu, J. Assessment of the vulnerability of alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Z.H.; Ying, L.X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, H.Y.; Piao, S.L.; Wen, C.; Jiang, Y.X. The exposure, sensitivity and vulnerability of natural vegetation in China to climate thermal variability (1901–2013): An indicator-based approach. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urruty, N.; Tailliez-Lefebvre, D.; Huyghe, C. Stability, robustness, vulnerability and resilience of agricultural systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandintsetseg, B.; Boldgiv, B.; Chang, J.; Ciais, P.; Davaanyam, E.; Batbold, A.; Bat-Oyun, T.; Stenseth, N.C. Risk and vulnerability of Mongolian grasslands under climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F. Towards post-2020 global biodiversity conservation: Footprint and direction in China. Innovation 2021, 2, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, F.P. The role of grasslands in food security and climate change. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.B.; Donnelly, A. Carbon sequestration in temperate grassland ecosystems and the influence of management, climate and elevated CO2. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E. The Global 200: Priority ecoregions for global conservation. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2002, 89, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Jiang, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, F.; Su, M.; Liao, Q. Establishing an ecological vulnerability assessment indicator system for spatial recognition and management of ecologically vulnerable areas in highly urbanized regions: A case study of Shenzhen, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Song, G. Human disturbance changes based on spatiotemporal heterogeneity of regional ecological vulnerability: A case study of Qiqihaer city, northwestern Songnen Plain, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 291, 125262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanshika, D.; Shukla, R.; Gornott, C.; Joshi, P. Consistency in Vulnerability Assessments of Wheat to Climate Change—A District-Level Analysis in India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8256. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y. Ecological vulnerability assessment for ecological conservation and environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, L.; Xie, Z.; Gao, T.; Liu, L. Assessment of Ecological Vulnerability on Northern Sand Prevention Belt of China Based on the Ecological Pressure–Sensibility–Resilience Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Liu, G.H.; Huang, C.; Liu, Q.S.; Guan, X.D. Ecological Vulnerability Assessment Based on Fuzzy Analytical Method and Analytic Hierarchy Process in Yellow River Delta. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, T.; Chang, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, J. Spatial-temporal variations of ecological vulnerability in Jilin Province (China), 2000 to 2018. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Xiao, R. Effects of rapid urbanization on ecological functional vulnerability of the land system in Wuhan, China: A flow and stock perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Dong, Z.; Hu, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q. A GIS-Based Assessment of Vulnerability to Aeolian Desertification in the Source Areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.L.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.Y.; Ren, J.Z. Assessment of eco-environment vulnerability in the northeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 63, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Dossou, J.F.; Li, X.X.; Sadek, M.; Sidi Almouctar, M.; Mostafa, E. Hybrid model for ecological vulnerability assessment in Benin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Han, R.; Yu, Q.; Qi, S.; Guo, L. Spatial Heterogeneous of Ecological Vulnerability in Arid and Semi-Arid Area: A Case of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q. Effects of protection and restoration on reducing ecological vulnerability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 761, 143180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Shi, S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, B.B.; Zhou, J.J.; Li, C.H. Regional-scale assessment of environmental vulnerability in an arid inland basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Dhar, A.; Kar, A. Environmental vulnerability assessment using Grey Analytic Hierarchy Process based model. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 56, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Eladawy, A.; Yu, T.; Sha, J. A multi-dimensional vulnerability assessment of Pingtan Island (China) and Nile Delta (Egypt) using ecological Sensitivity-Resilience-Pressure (SRP) model. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 1860–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ma, C.; Huang, P.; Guo, X. Ecological vulnerability assessment based on AHP-PSR method and analysis of its single parameter sensitivity and spatial autocorrelation for ecological protection—A case of Weifang City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Weichselgartner, J. Hotspots of coastal vulnerability: A DPSIR analysis to find societal pathways and responses. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaujean, J.; Lemieux, J.M.; Dassargues, A.; Therrien, R.; Brouyère, S. Physically Based Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment Using Sensitivity Analysis Methods. Ground Water 2014, 52, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lu, Y.; Lü, D.; Wang, C. Quantifying the Variability of Forest Ecosystem Vulnerability in the Largest Water Tower Region Globally. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, X.; Guan, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Determining the contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation dynamics in agro-pastural transitional zone of northern China from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 718, 134871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yang, G.; Tian, J.; et al. The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maddalwar, S.; Nayak, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, L. Plant microbial fuel cell: Opportunities, challenges, and prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Mosbrugger, V.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Luo, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Joswiak, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Third Pole Environment (TPE). Environ. Dev. 2012, 3, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Jia, K.; Zhao, W.; Liu, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, B. Spatio-temporal changes of ecological vulnerability across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, J.; Liu, J.; Milne, R.I.; Cadotte, M.W.; Wu, Z.; Provan, J.; Zhu, G.; Gao, L.; Li, D. Protect Third Pole’s fragile ecosystem. Science 2018, 362, 1368. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Li, J.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Yao, Y.F.; Sun, B.; Ferguson, D.K.; Li, C.S.; Deng, T.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, Y.F. Bridging the knowledge gap on the evolution of the Asian monsoon during 26–16 Ma. Innovation 2021, 2, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moors, E.J.; Groot, A.; Biemans, H.; Scheltinga, C.T.V.; Stoffel, M.; Huggel, C.; Wiltshire, A.; Mathison, C.; Ridley, J.; Jacob, D.; et al. Adaptation to changing water resources in the Ganges basin, northern India. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xu, X.D.; Zhao, T.L.; Yao, T.D.; Zhang, D.Q.; Wang, N.L.; Ma, Y.M.; Ma, W.Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, S.J.; et al. Distinct impacts of vapor transport from the tropical oceans on the regional glacier retreat over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, N.F.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.T. Impact of Eastern Tibetan Plateau Glacier Melt on Land Water Storage Change across the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 05020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, H.W.; Ma, X.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, R. Relationship between vegetation phenology and snow cover changes during 2001-2018 in the Qilian Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Wu, Q.B.; Jin, H.J.; Wang, Q.F.; Huang, Y.D.; Luo, D.L.; Gao, S.H.; Jin, X.Y. Delineating the hydrological processes and hydraulic connectivities under permafrost degradation on Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Bai, W. Spatiotemporal variation in alpine grassland phenology in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1999 to 2009. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ouyang, Z. Assessment and analysis of the freeze-thaw erosion sensitivity on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2017, 39, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Dikshit, A.; Sarkar, R.; Pradhan, B.; Acharya, S.; Alamri, A.M. Spatial Landslide Risk Assessment at Phuentsholing, Bhutan. Geosciences 2020, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.L.; Chen, C.W.; Wang, Q.B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S. Fuzzy model-based assessment and monitoring of desertification using MODIS satellite imagery. Eng. Comput. 2009, 26, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Tao, W.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, P. A feasible method for the division of ecological vulnerability and its driving forces in Southern Shaanxi. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables in principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 498–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, Y.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.; Arikena, M. Assessment of spatial and temporal variation of ecological environment quality in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji Sabokbar, H.; Shadman Roodposhti, M.; Tazik, E. Landslide susceptibility mapping using geographically-weighted principal component analysis. Geomorphology 2014, 226, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhuang, D.; Wang, Y. Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Ecological Vulnerability under the Influence of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors in an Eco-Province under Construction in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Guo, L. A Long-Term Ecological Vulnerability Analysis of the Tibetan Region of Natural Conditions and Ecological Protection Programs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, B.; Su, G.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Meng, J.; Ding, Y.; Song, S.; Dai, L. Spatiotemporal analysis of ecological vulnerability in the Tibet Autonomous Region based on a pressure-state-response-management framework. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhou, L.; Wen, Y.; Chen, Y. Farmers’ adaptability to the policy of ecological protection in China—A case study in Yanchi County, China. Soc. Sci. J. 2018, 55, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, L.S.; Wang, Z. Temporal and spatial distribution of grassland coverage change in the Tibetan Plateau during 1982–2009. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhou, C.; Ding, M.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Bai, W.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, D. Spatial and temporal variability in the net primary production of alpine grassland on the Tibetan Plateau since 1982. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, D.; Nan, J.; Zheng, Z. Spatiotemporal variations of the start of thermal growing season for grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 1961–2014. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, Y.Z.; Han, L.J.; Cheng, L.H.; Lv, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Feng, X.M.; Wu, X. Shortened duration and reduced area of frozen soil in the Northern Hemisphere. Innovation 2021, 2, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Z.W.; Huang, X.T.; Li, L.H. How does grazing exclusion influence plant productivity and community structure in alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau? Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.J.; Jing, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Gao, Y.H. Short-term grazing exclusion improved topsoil conditions and plant characteristics in degraded alpine grasslands. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
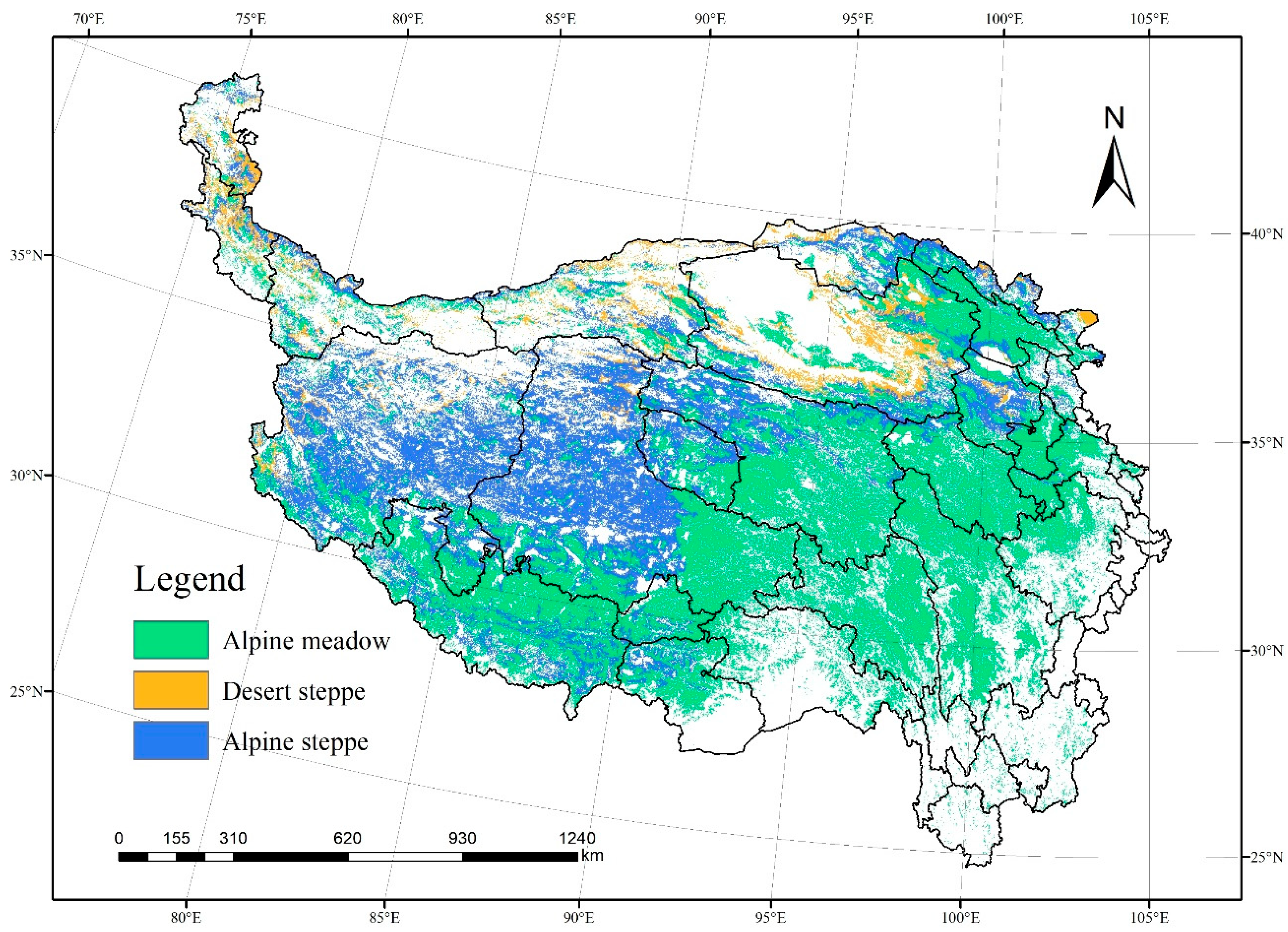
| Target Layer | Criterion Layer | Indicator | Index Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability by natural factors | Climate | Annual average temperature | negative |
| Annual average precipitation | negative | ||
| Terrain | Elevation | positive | |
| Slope | positive | ||
| Soil | Soil organic matter content | negative | |
| Vegetation | Normalized difference vegetation index | negative | |
| Vulnerability by environmental disturbances | Land desertification | positive | |
| Freeze–thaw erosion | positive | ||
| Landslide | positive | ||
| Grazing pressure | positive | ||
| Vulnerability by socioeconomic impacts | Society | Population | positive |
| Economy | Gross domestic product | positive | |
| Actual livestock | positive |
| Indicator | W1j | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2j | Wj | W2j | Wj | W2j | Wj | ||
| Annual average temperature | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| Annual average precipitation | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| Elevation | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| Slope | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| Soil organic matter content | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Normalized difference vegetation index | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.50 | 0.42 |
| Indicator | W1j | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2j | Wj | W2j | Wj | W2j | Wj | ||
| Land desertification | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.43 |
| Freeze–thaw erosion | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.31 |
| Landslide | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.18 |
| Grazing pressure | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| Indicator | W1j | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W2j | Wj | W2j | Wj | W2j | Wj | ||
| Population | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.48 |
| Gross Domestic Product | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.50 | 0.44 |
| Actual livestock | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| Vulnerability Levels | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area/104 km2 | Ratio/% | Area/104 km2 | Ratio/% | Area/104 km2 | Ratio/% | |
| Normal | 8.57 | 6.87% | 10.71 | 8.60% | 11.59 | 9.30% |
| Slight vulnerability | 19.19 | 15.40% | 19.65 | 15.77% | 20.73 | 16.63% |
| Moderate vulnerability | 27.06 | 21.72% | 26.72 | 21.44% | 26.09 | 20.94% |
| Serious vulnerability | 39.52 | 31.71% | 37.90 | 30.41% | 40.07 | 32.16% |
| Extreme vulnerability | 30.28 | 24.30% | 29.64 | 23.79% | 26.14 | 20.97% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, T.; Lü, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on a Comprehensive Framework. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094912
Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Sun S, Li T, Lü Y, Jiang W, Wu X. Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on a Comprehensive Framework. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094912
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhengyuan, Yunlong Zhang, Siqi Sun, Ting Li, Yihe Lü, Wei Jiang, and Xing Wu. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on a Comprehensive Framework" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094912
APA StyleZhao, Z., Zhang, Y., Sun, S., Li, T., Lü, Y., Jiang, W., & Wu, X. (2022). Spatiotemporal Variations in Grassland Vulnerability on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on a Comprehensive Framework. Sustainability, 14(9), 4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094912








