Environmental Fate of Trace Elements in Depositional Sediments after Flashflood Events: The Case of Mandra Town in Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
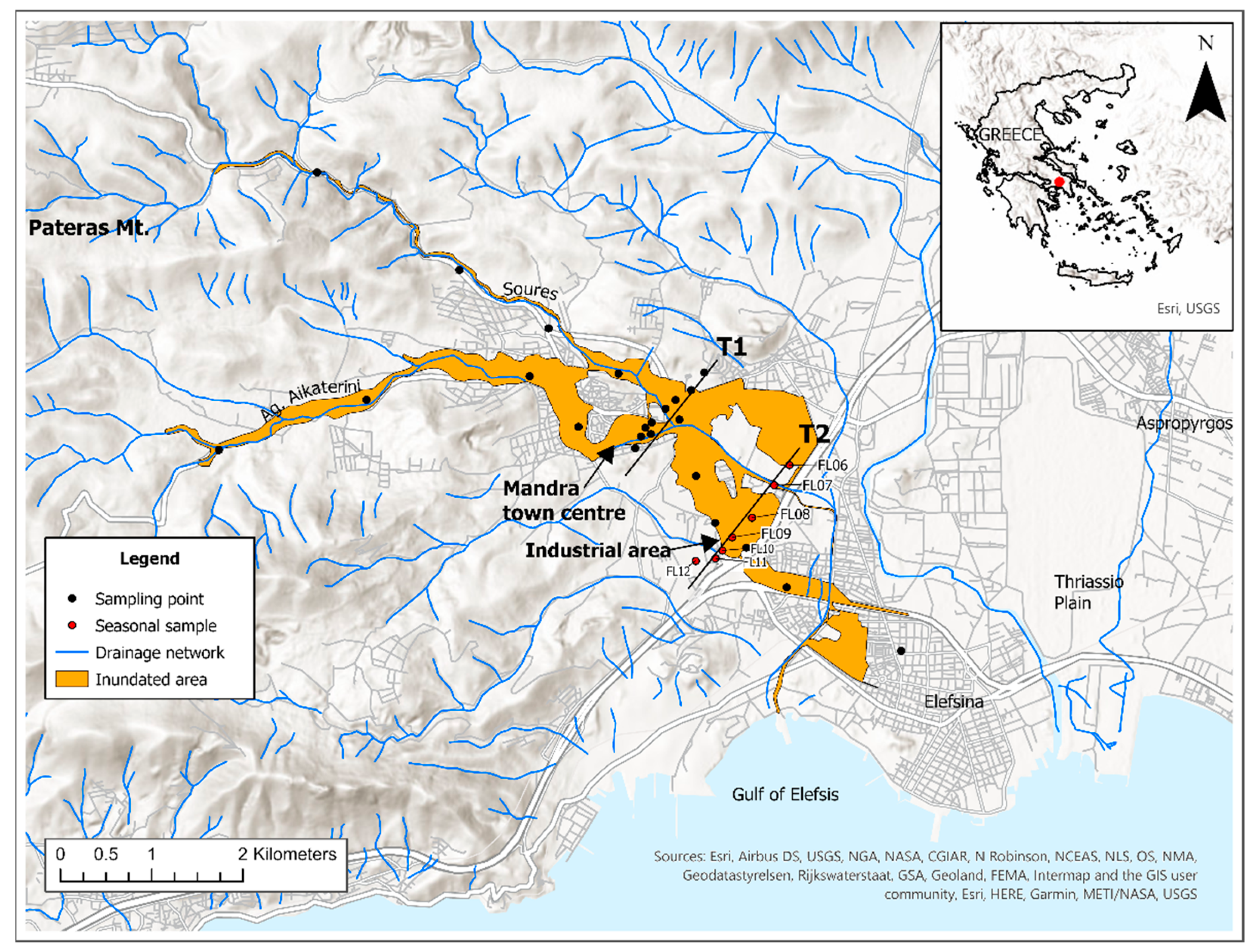
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Preparation for Analysis and Laboratory Methods
2.2.1. Determination of Physicochemical Parameters
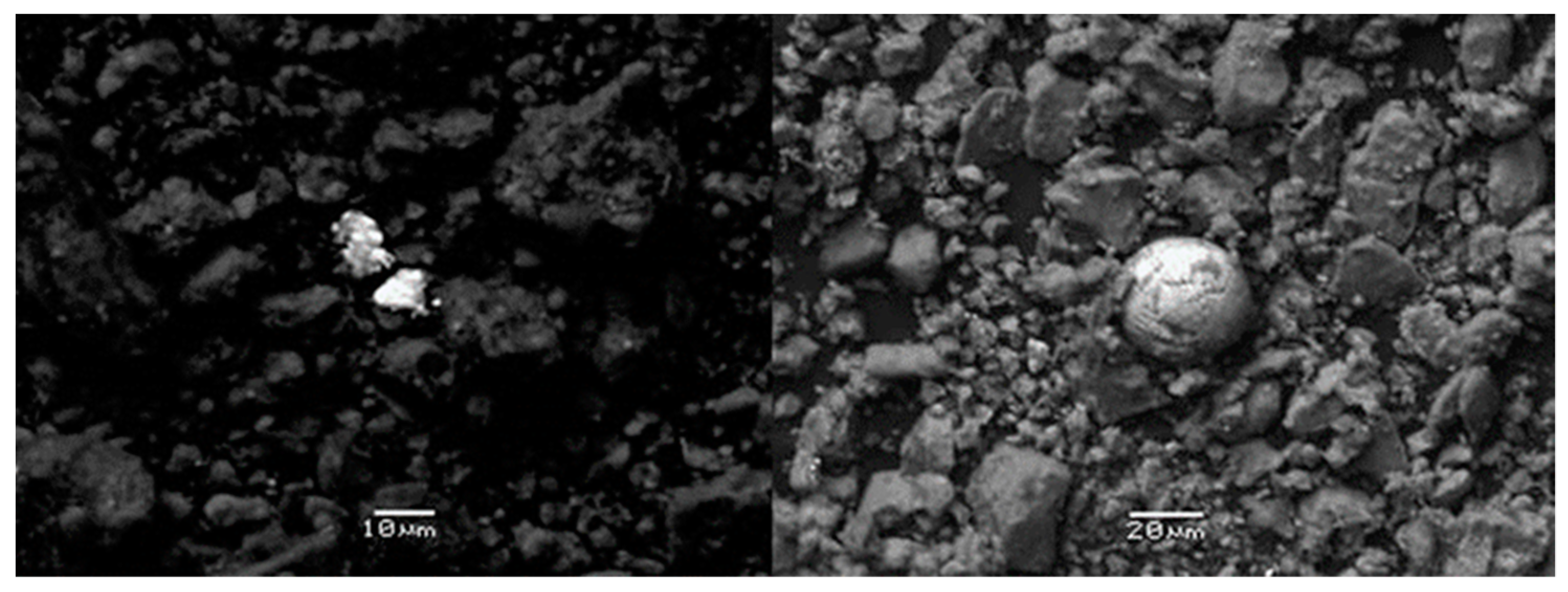
2.2.2. Mineralogical Analysis and Scanning Electron Microscopy Study
2.2.3. Chemical Analysis Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis and GIS
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics and Magnetic Susceptibility of Soils and Sediments
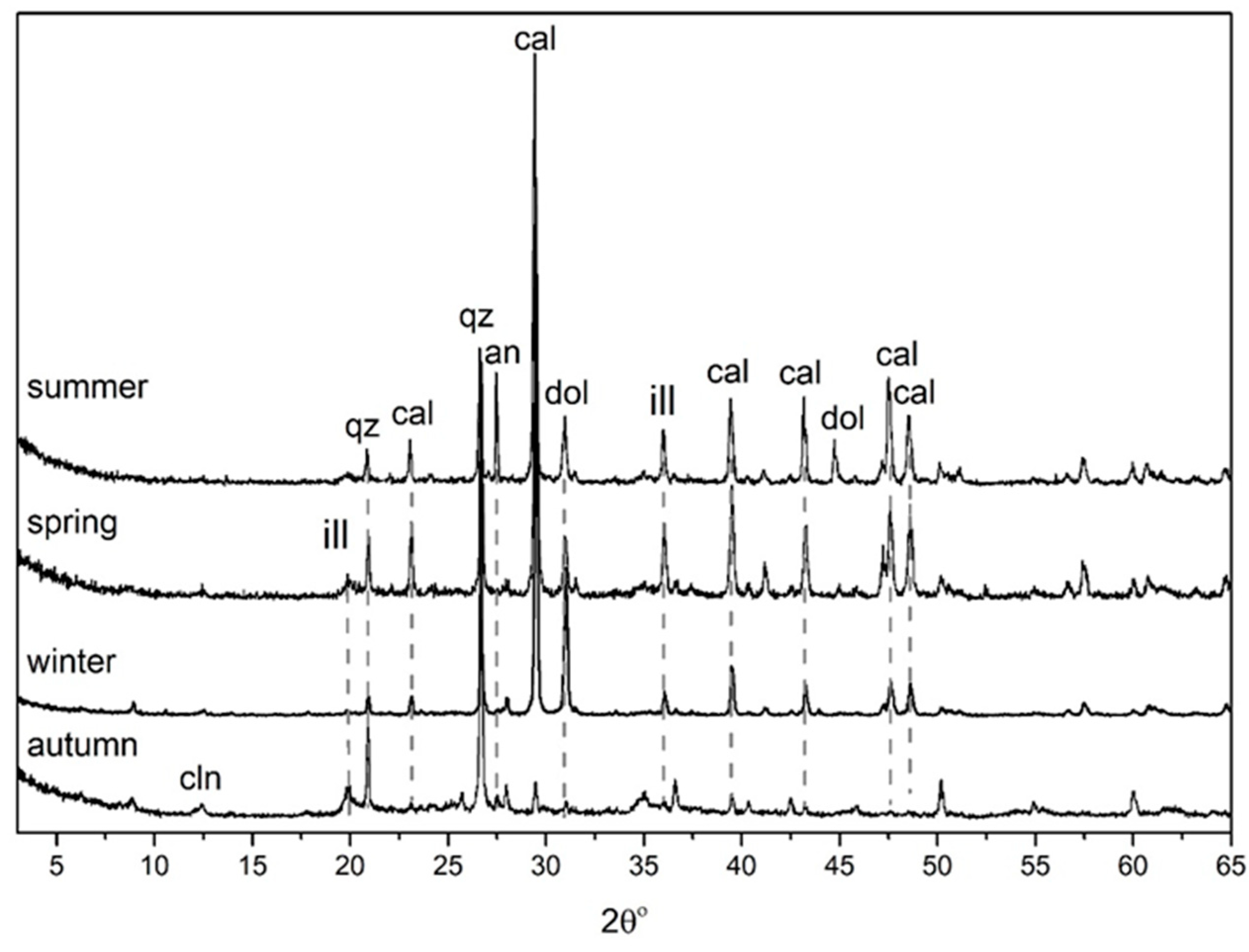
3.2. Mineralogical Composition of the Samples
3.3. Geochemical Characterization of Soil and Depositional Sediment Samples
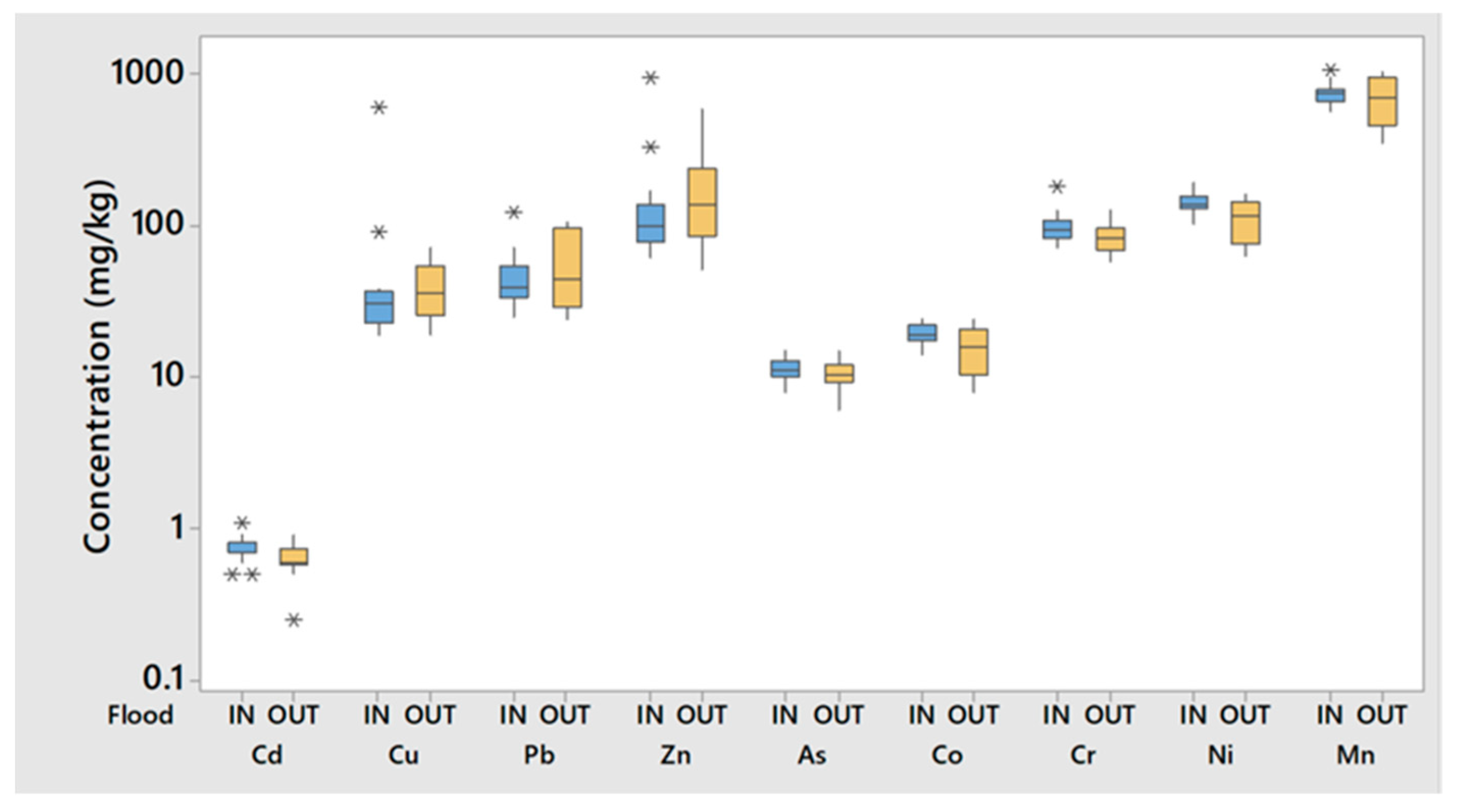
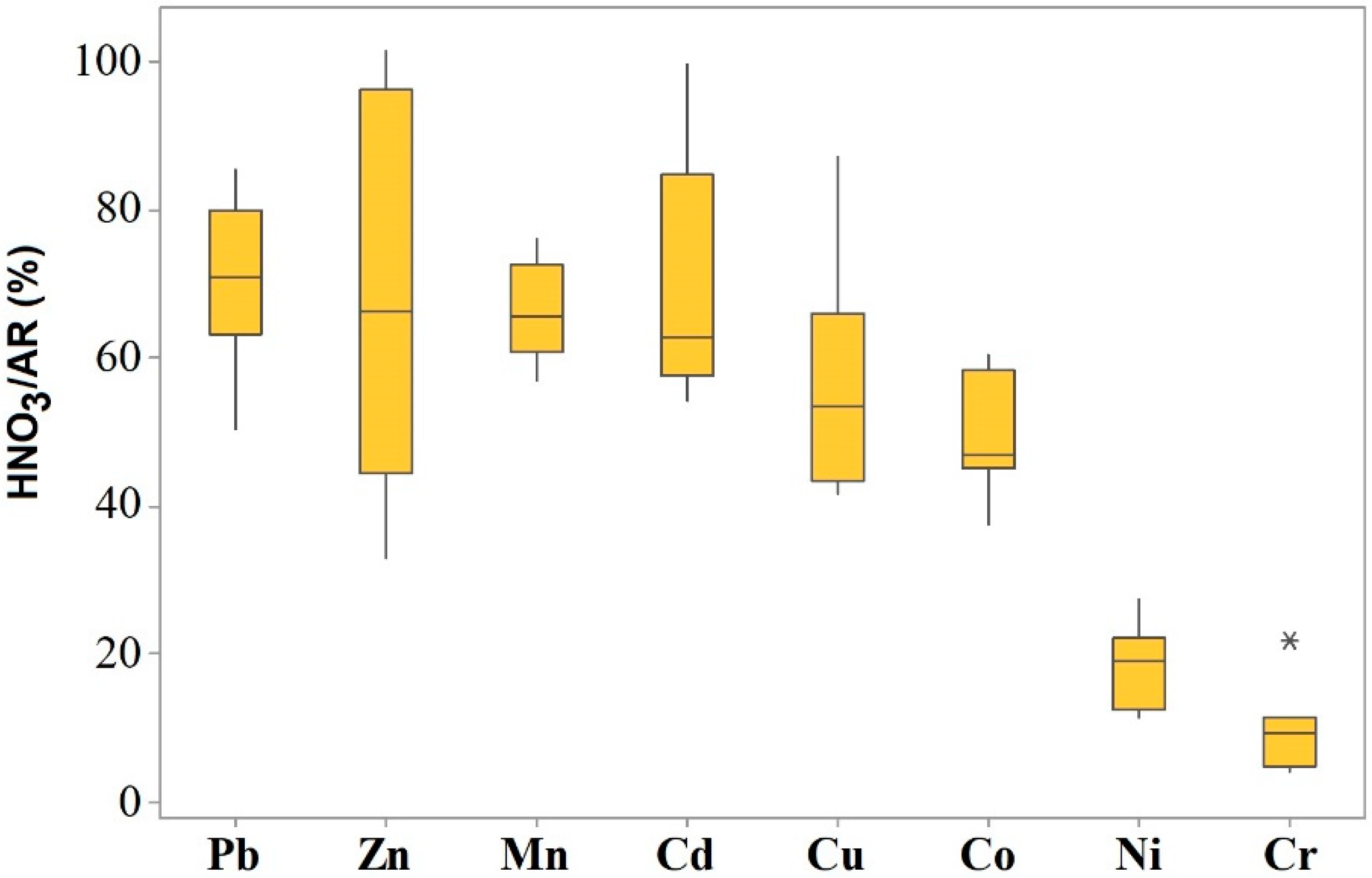
3.3.1. Aqua Regia Extractable Trace Elements
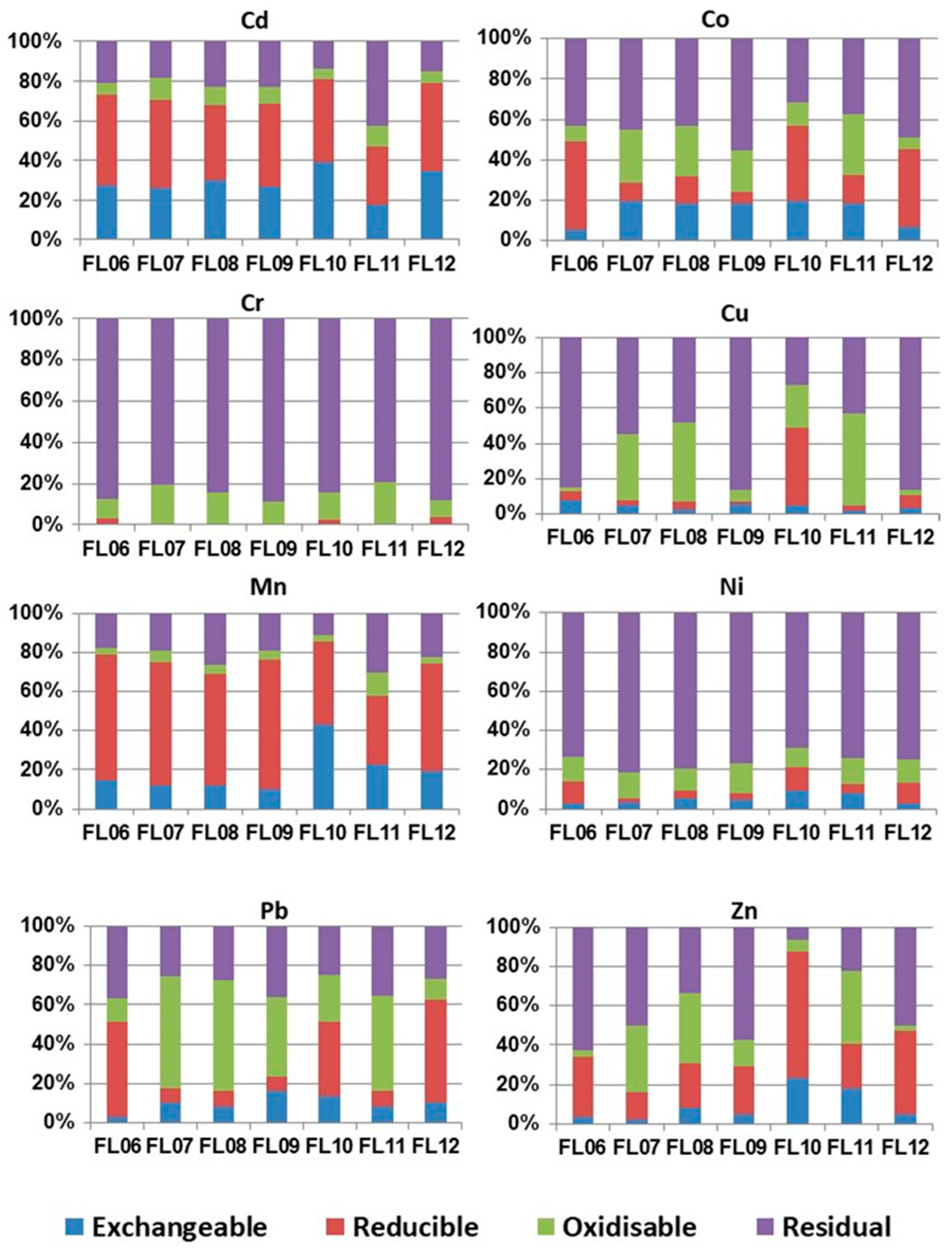
3.3.2. Sequential Extraction Results and Reactive Trace Element Concentrations
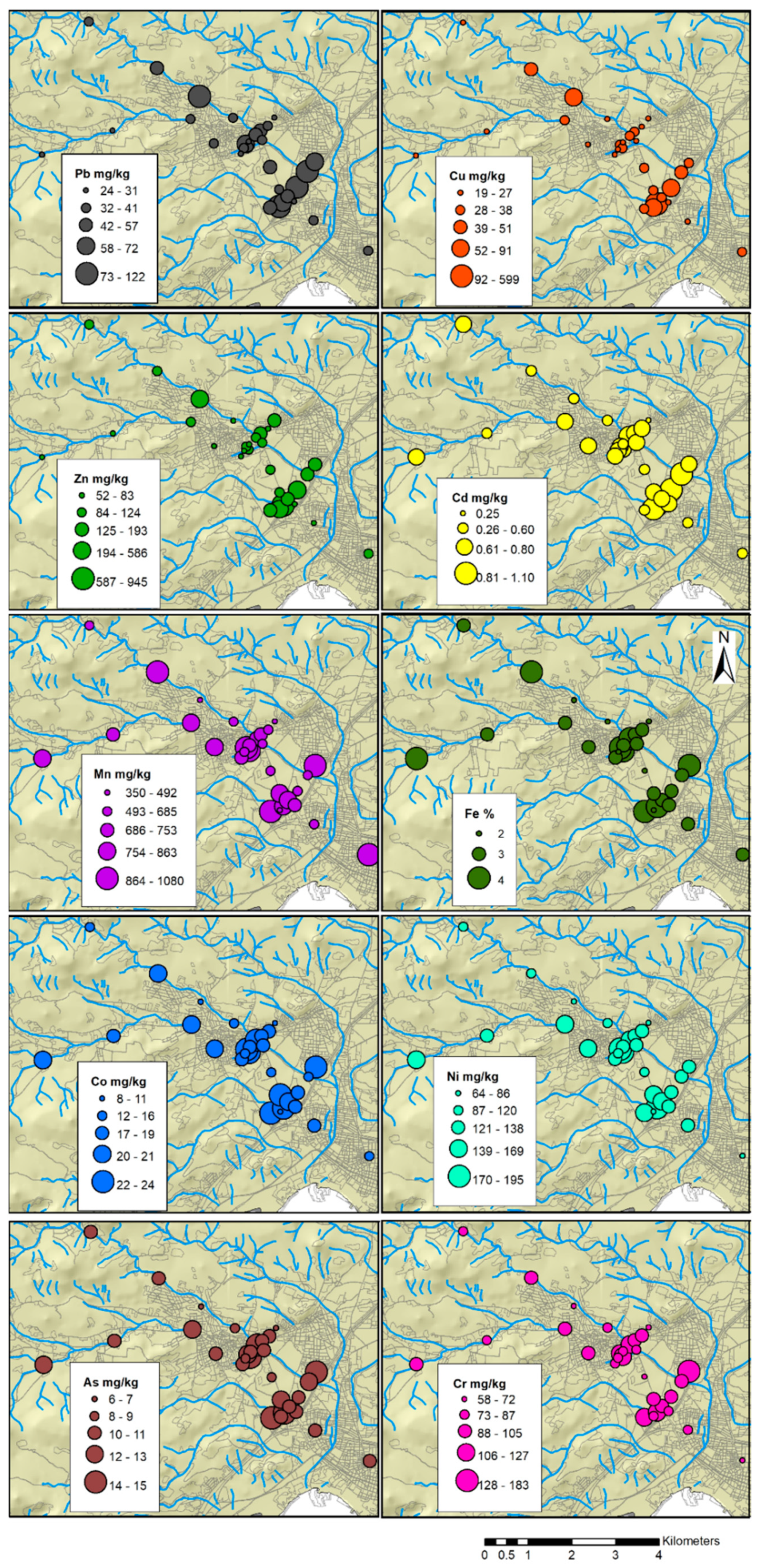
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Trace Elements and other Measured Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Natural versus Anthropogenic Sources of Trace Elements
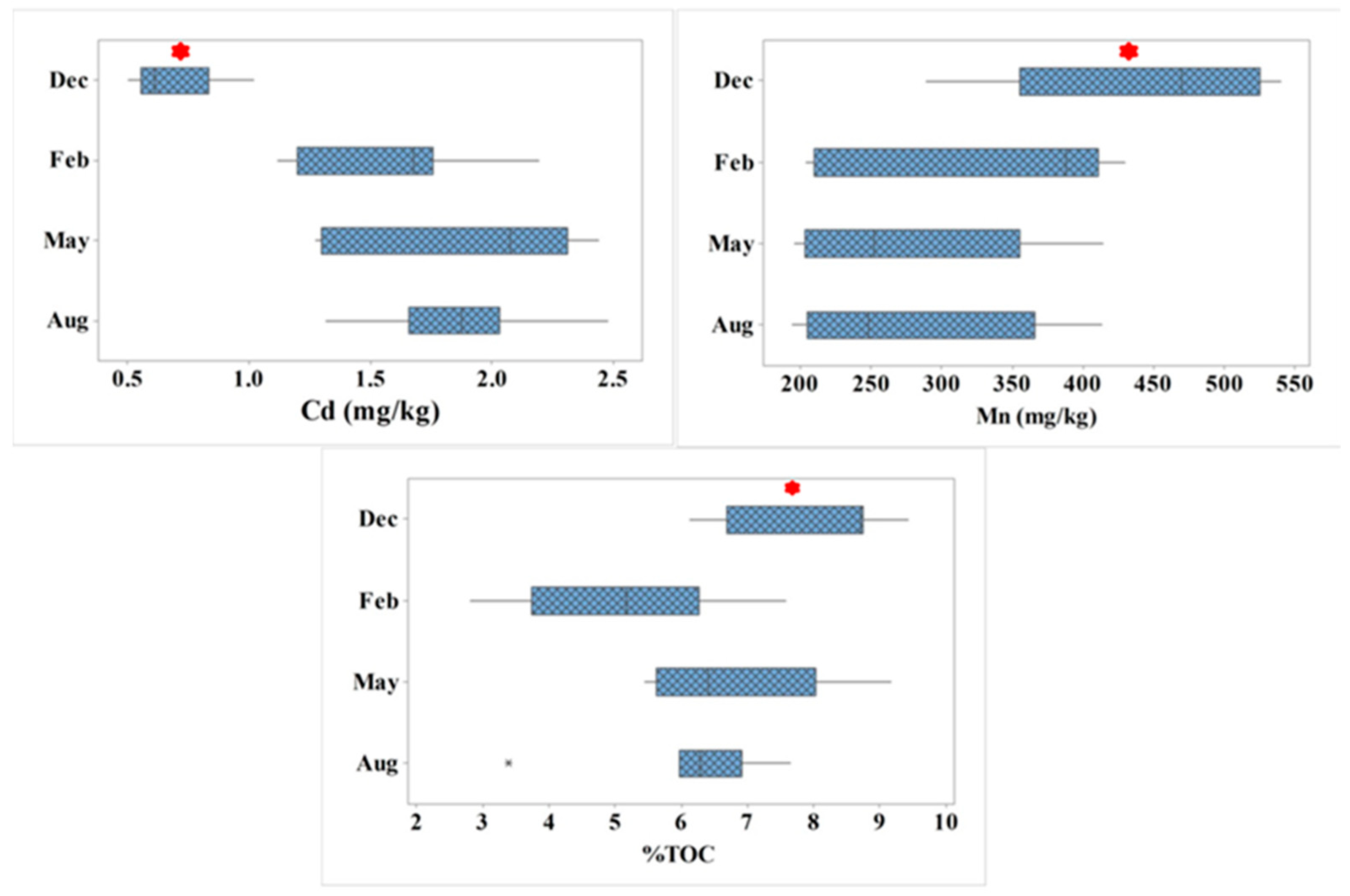
4.2. Trace Element Fractionation in Flood Sediments and Seasonal Variation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diakakis, M.; Andreadakis, E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Spyrou, N.I.; Gogou, M.E.; Deligiannakis, G.; Antoniadis, Z. An integrated approach of ground and aerial observations in flash flood disaster investigations. The case of the 2017 Mandra flash flood in Greece. Int. J. Dis. Risk Red. 2018, 33, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Kreibich, H.; Schwarze, R.; Thieken, A. Assessment of economic flood damage. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 1697–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Katsetsiadou, K.; Antoniadis, Z.; Melaki, M. Mapping and classification of direct flood impacts in the complex conditions of an urban environment. The case study of the 2014 flood in Athens, Greece. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, J.I. Major flood disasters in Europe: 1950–2005. Nat. Hazards 2007, 42, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, J.I. Normalised flood losses in Europe: 1970–2006. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C.; Llasat-Botija, M.; Prat, M.A.; Porcu, F.; Price, C.; Mugnai, A.; Yair, Y. High-impact floods and flash floods in Mediterranean countries: The FLASH preliminary database. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, M.S. Impacts of flash floods. In Coping with Flash Floods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 77, pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, C.; Aubert, D.; Durrieu de Madron, X.; Ludwig, W.; Heussner, S.; Delsaut, N.; Menniti, C.; Sotin, C.; Buscail, R. Storm-induced transfer of particulate trace metals to the deep-sea in the Gulf of Lion (NW Mediterranean Sea). Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 995–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Deligiannakis, G. Floods in Greece, a statistical and spatial approach. Nat. Hazards 2012, 62, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Deligiannakis, G.; Andreadakis, E.; Katsetsiadou, K.N.; Spyrou, N.I.; Gogou, M.E. How different surrounding environments influence the characteristics of flash flood-mortality: The case of the 2017 extreme flood in Mandra, Greece. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Wessels, M. The flood in the Odra River 1997—Impact of suspended solids on water quality. Acta Hydroch. Et Hydrobiol. 1995, 27, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkani, A.; Evelpidou, N.; Tzouxanioti, M.; Petropoulos, A.; Santangelo, N.; Hampik Maroukian, H.; Spyrou, E.; Lakidi, L. Flash Flood Susceptibility Evaluation in Human-Affected Areas Using Geomorphological Methods—The Case of 9 August 2020, Euboea, Greece. A GIS-Based Approach. GeoHazards 2021, 2, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baborowski, M.; Von Tümpling, W., Jr.; Friese, K. Behaviour of suspended particulate matter (SPM) and selected trace elements during the 2002 summer flood in the River Elbe (Germany) at Magdeburg monitoring station. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Dis. Eur. Geosci. Union 2004, 8, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfieri, L.; Burek, P.; Feyen, L.; Forzieri, G. Global warming increases the frequency of river floods in Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2247–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USGCRP. The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: A Scientific Assessment; Crimmins, A., Balbus, J., Gamble, J.L., Beard, C.B., Bell, J.E., Dodgen, D.R.J., Eisen, R.J., Fann, N., Hawkins, M.D., Hawkins, S.C., et al., Eds.; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coynel, A.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Bossy, C. Scenario of particulate trace metal and metalloid transport during a major flood event inferred from transient geochemical signals. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coynel, A.; Schäfer, J.; Dabrin, A.; Girardot, N.; Blanc, G. Groundwater contributions to metal transport in a small river affected by mining and smelting waste. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3420–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resongles, E.; Casiot, C.; Freydier, R.; Le Gall, M.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. Variation of dissolved and particulate metal(loid) (As, Cd, Pb, Sb, Tl, Zn) concentrations under varying discharge during a Mediterranean flood in a former mining watershed, the Gardon River (France). J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 158, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Grygar, T.M. A Review of Flood-Related Storage and Remobilization of Heavy Metal Pollutants in River Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Elznicová, J.; Bábek, O.; Hošek, M.; Engel, Z.; Kiss, T. Obtaining isochrones from pollution signals in a fluvial sediment record: A case study in a uranium-polluted floodplain of the Ploučnice River, Czech Republic. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, K.; Turner, L.R.; Tong, S. Floods and human health: A systematic review. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, T.J.; Hamilton, E.; Watts, M.J.; Ponting, J.; Sizmur, T. The Effect of Flooding and Drainage Duration on the Release of Trace Elements from Floodplain Soils. Environ. Tox. Chem. 2020, 39, 2124–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Shu, S.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Adams, C.; Witt, E.C. Distribution of toxic trace elements in soil/sediment in post-Katrina New Orleans and the Louisiana Delta. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrbić, B.D.; Živančev, J.; Antić, I.; Buljovčić, M. Pollution status and health risk caused by heavy elements in the flooded soil and vegetables from typical agricultural region in Vojvodina Province, Serbia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16065–16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abgottspon, F.; Bigalke, M.; Wilcke, W. Fast colloidal and dissolved release of trace elements in a carbonatic soil after experimental flooding. Geoderma 2015, 259–260, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates-Marnane, J.; Olley, J.; Burton, J.; Grinham, A. The impact of a high magnitude flood on metal pollution in a shallow subtropical estuarine embayment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, T.D.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Kikaki, A.; Chourdaki, S.; Hatzianestis, I.; Vakalas, I.; Hatiris, G.A. The impact of flash-floods on the adjacent marine environment: The case of Mandra and Nea Peramos (November 2017), Greece. J. Coast. Cons. 2020, 24, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.J.; Taylor, K.G.; Hoon, S.R. Geochemical and mineral magnetic characterisation of urban sediment particulates, Manchester, UK. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Witt, E.C.; Wang, J.; Shaver, D.K.; Summers, D.; Filali-Meknassi, Y.; Shi, H.; Luna, R.; Anderson, N. Chemical Quality of Depositional Sediments and Associated Soils in New Orleans and the Louisiana Peninsula Following Hurricane Katrina. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3437–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Kalivas, D.; Ehaliotis, C.; Gasparatos, D. Total and available heavy metal concentrations in soils of the Thriassio plain (Greece) and assessment of soil pollution indexes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6751–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounas, A.G. The Geology of the Area between Megara and Erithrai Village (Attica). Ph.D. Thesis, School of Physical Sciences, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 1971; p. 185. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos, D.G.; Economou-Eliopoulos, M. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of Fe–Ni and bauxitic-laterite deposits of Greece. Ore Geol. Rev. 2000, 16, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligiannakis, G.; Papanikolaou, D.; Roberts, G. Fault specific GIS based seismic hazard maps for the Attica region, Greece. Geomorpology 2018, 306, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argyraki, A. Garden soil and house dust as exposure media for lead uptake in the mining village of Stratoni, Greece. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10390. Soil Quality-Determination of pH. 1994. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/18454.html (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Hoogsteen, M.J.J.; Lantinga, E.A.; Bakker, E.J.; Groot, J.C.J.; Tittonell, P.A. Estimating soil organic carbon through loss on ignition: Effects of ignition conditions and structural water loss. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Oldfield, F. Environmental Magnetism; Allen and Unwin: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyoucos, G.H. A recalibration of the hydrometer method for making mechanical analysis of soils. Agron. J. 1951, 43, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.-S.; Yu, S.; Li, X.-D. Distribution, availability, and sources of trace elements in different size fractions of urban soils in Hong-Kong: Implications for assessing the risk to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauret, G.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; Henriques, B.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Pereira, M.E.; Duarte, A.C.; Romkens, P.F.A.M. Evaluation of an approach for the characterization of reactive and available pools of twenty potentially toxic elements in soils: Part I—The role of key soil properties in the variation of contaminants’ reactivity. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Copernicus Land Monitoring Service 2018. European Environment Agency (EEA). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018 (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Manly, B.F.J. Multivariate Statistical Methods, a Primer; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourliva, A.; Papadopoulou, L.; Aidona, E.; Giouri, K.; Simeonidis, K.; Vourlias, G. Characterization and geochemistry of technogenic magnetic particles (TMPs) in contaminated industrial soils: Assessing health risk via ingestion. Geoderma 2017, 295, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, R.; Álvarez-Valero, A.M.; Nieto, J.M.; Sáez, R.; Matos, J.X. Use of sequential extraction procedure for assessing the environmental impact at regional scale of the São Domingos Mine (Iberian Pyrite Belt). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3452–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, F.; Reinoso, R.; Florido, M.C.; Díaz Barrientos, E.; Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Davidson, C.M.; Madrid, L. Estimating the extractability of potentially toxic metals in urban soils: A comparison of several extracting solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnaud, S.; Mouchel, J.M.; Chebbo, G.; Thévenot, D.R. Heavy metal concentrations in dry and wet atmospheric deposits in Paris district: Comparison with urban runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 235, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moller, A.; Muller, H.W.; Abdullah, A.; Abdelgawad, G.; Utermann, J. Urban soil pollution in Damaskus, Syria: Concentrations and patterns of heavy metals in the soils of the Damascus Ghouta. Geoderma 2005, 124, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, K.; Otabbong, E.; Selinus, O. Natural and anthropogenic metal inputs in urban Uppsala, Sweden. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylali-Abanuz, G. Heavy metal contamination of surface soil around Gebze industrial area, Turkey. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaletsos, P.N.; Kalatha, S.; Godelitsas, A.; Economou-Eliopoulos, M.; Göttlicher, J.; Steininger, R. Arsenic distribution and speciation in the bauxitic Fe-Ni-laterite ore deposit of the Patitira mine, Lokris area (Greece). J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 194, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durn, G. Terra Rossa in the Mediterranean Region: Parent Materials, Composition and Origin. Geol. Croat. 2003, 56, 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Seleznev, A.A.; Yarmoshenko, I.V. Study of urban puddle sediments for understanding heavy metal pollution in an urban environment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2014, 1–2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E.; Galanos, E.; Mitsis, I. Origin, mineral speciation and geochemical baseline mapping of Ni and Cr in agricultural topsoils of Thiva valley (central Greece). J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 125, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E.; Stathopoulou, E. Availability of geogenic heavy metals in soils of Thiva town (central Greece). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9603–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyraki, A.; Kelepertzis, E.; Botsou, F.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Katsikis, I.; Trigoni, M. Environmental availability of trace elements (Pb, Cd, Zn, Cu) in soil from urban, suburban, rural and mining areas of Attica, Hellas. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 187, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.O. (Ed.) Global cadmium cycle. In Cadmium in the Environment; Wiley: New York, NY, USA; Chichest, UK; Brisbane, Australia; Toronto, ON, Canada; Singapore, 1994; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- WHO; McMichael, A.J.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.H.; Corvalán, C.F.; Ebi, K.L.; Githeko, A.K.; Scheraga, J.D. Climate Change and Human Health: Risks and Responses-SUMMARY. 2003. Available online: https://www.who.int/globalchange/environment/en/ccSCREEN.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 17 February 2022).

| Parameter | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | Standard Deviation | Median of Thriassio soil [30] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.00 | 8.03 | 7.27 | 8.36 | 0.24 | 8.0 |
| TOC (%) | 2.80 | 2.74 | 1.45 | 4.93 | 0.95 | 2.86 |
| Sand (%) | 6.29 | 4.29 | 0.57 | 21.7 | 5.8 | 50.9 |
| Silt (%) | 78.9 | 79.5 | 64.6 | 84 | 4.27 | 27.6 |
| Clay (%) | 14.9 | 13.9 | 5.93 | 23.5 | 4.82 | 21.5 |
| χ (10−6 m3/kg) | 1.99 | 1.97 | 1.09 | 3.03 | 0.39 | |
| Al (%) | 2.04 | 2 | 0.86 | 3.19 | 0.63 | |
| As (mg/kg) | 10.9 | 11 | 6 | 15 | 2.21 | |
| Ca (%) | 12.3 | 12.1 | 2.49 | 24.6 | 4.73 | |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.25 | 1.1 | 0.16 | |
| Co (mg/kg) | 18.2 | 18 | 8 | 24 | 4.17 | 24 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 93.6 | 89.5 | 58 | 183 | 24 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 53.6 | 31.5 | 19 | 599 | 104 | 37.8 |
| Fe (%) | 2.75 | 2.72 | 1.53 | 3.86 | 0.61 | 1.6 |
| Mg (%) | 1.31 | 1.23 | 0.7 | 2.53 | 0.43 | |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 739 | 742 | 350 | 1080 | 171 | 320.8 |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 133 | 134 | 64 | 195 | 32.4 | 81.1 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 49.9 | 40 | 24 | 122 | 25.8 | 111.8 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 170 | 106 | 52 | 945 | 186 | 154.6 |
| Variable | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Communality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.406 | 0.219 | −0.474 | 0.437 |
| TOC | −0.072 | −0.716 | 0.169 | 0.546 |
| Clay | 0.771 | 0.201 | 0.113 | 0.647 |
| χ | 0.444 | −0.793 | 0.039 | 0.828 |
| Cu | 0.132 | −0.112 | 0.941 | 0.916 |
| Pb | −0.190 | −0.825 | 0.288 | 0.799 |
| Zn | −0.144 | −0.427 | 0.871 | 0.961 |
| Ni | 0.863 | 0.023 | 0.112 | 0.758 |
| Co | 0.976 | −0.012 | 0.012 | 0.954 |
| Mn | 0.926 | 0.002 | −0.035 | 0.859 |
| Fe | 0.950 | −0.223 | 0.035 | 0.953 |
| As | 0.892 | −0.252 | 0.151 | 0.882 |
| Cd | 0.361 | −0.658 | 0.197 | 0.602 |
| Cr | 0.785 | −0.362 | −0.004 | 0.747 |
| Variance | 6.035 | 2.783 | 2.072 | 10.8893 |
| % Cumulative variance | 0.431 | 0.199 | 0.148 | 0.778 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kourgia, P.M.; Argyraki, A.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Botsou, F.; Kelepertzis, E.; Dassenakis, M. Environmental Fate of Trace Elements in Depositional Sediments after Flashflood Events: The Case of Mandra Town in Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042448
Kourgia PM, Argyraki A, Paraskevopoulou V, Botsou F, Kelepertzis E, Dassenakis M. Environmental Fate of Trace Elements in Depositional Sediments after Flashflood Events: The Case of Mandra Town in Greece. Sustainability. 2022; 14(4):2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042448
Chicago/Turabian StyleKourgia, Paraskevi Maria, Ariadne Argyraki, Vasiliki Paraskevopoulou, Fotini Botsou, Efstratios Kelepertzis, and Manos Dassenakis. 2022. "Environmental Fate of Trace Elements in Depositional Sediments after Flashflood Events: The Case of Mandra Town in Greece" Sustainability 14, no. 4: 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042448
APA StyleKourgia, P. M., Argyraki, A., Paraskevopoulou, V., Botsou, F., Kelepertzis, E., & Dassenakis, M. (2022). Environmental Fate of Trace Elements in Depositional Sediments after Flashflood Events: The Case of Mandra Town in Greece. Sustainability, 14(4), 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042448








