Abstract
This study demonstrates the leachate characteristics derived from bench-scale leach-bed reactors (LBRs) filled with chicken manure (CM) and zeolite. Zeolite was used to maintain the necessary porosity for the leaching process and to adsorb ammonia. Fresh water was added for leachate production and removed daily, in order to estimate the readily leachable organic and nitrogen matter of the CM. Tests were conducted at two ratios of zeolite to bed (10% and 3.5% v/v CMbed). Other operating parameters studied were the amount of water added in the LBRs, the leachate recirculation rate, and the hydraulic retention time (HRT). A control LBR with river pebbles at a similar size and ratio (10% v/v) with zeolite was also studied. Some experiments were repeated with CM, which had different characteristics. Compared to the control test, the LBR with zeolite at 10% v/v yielded leachate with less NH3 and a higher biochemical methane potential (BMP). However, free ΝH3 in the control experiment was below the inhibition threshold, proving that zeolite contributes to the higher BMP of leachate, and that this effect is not only due to NH3 adsorption.
1. Introduction
Increased and intensified chicken farming has resulted in the production of a large amount of chicken manure (CM), classified into two types: broiler CM, and egg-laying hen manure (caged layer manure). The broiler CM comes from chickens raised to produce meat and contains feces, urine, and bedding materials (wood shavings, straw, and peanut hulls), while the egg-laying manure contains excreta. In addition, both types contain feathers and wasted feed [1,2].
CM is a waste rich in organic matter and nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and is commonly used as fertilizer in the agriculture industry. However, inappropriate land application of CM without any pretreatment poses risks to the environment, due to greenhouse gas emissions and the nutrients and pathogenic microorganisms released into the surface and underground water [3]. Therefore, anaerobic digestion (AD) is a suitable technology for the management and stabilization of CM, as with other manures. Moreover, CM has a higher energy content than cow and pig manures [4]. The biogas produced from the AD process mainly consists of CH4 (50–70%) and CO2 (30–50%) and can be converted to heat and electric power, while the digestate can be used as a sustainable fertilizer [1,5]. Furthermore, the removal of the unwanted components (i.e., CO2, hydrogen sulfide, and siloxanes) from biogas enhances its calorific value, protects the combined heat and power (CHP) unit, and allows meeting the specifications of biomethane, in order to be used as a fuel in vehicles or be injected into the natural gas grid [6].
However, during AD, the organic nitrogen content of CM in the form of proteins and urea is converted into ammonia, which may result in a process inhibition, with a concomitant accumulation of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) [7]. The ammonia inhibition level is affected by several factors, such as the total ammonium nitrogen, pH, temperature, and acclimation of methanogenic biomass [8]. Therefore, a wide range of inhibitory concentrations (1.4–14 g/L) have been reported in the literature [9,10]. Many strategies have been applied to overcome ammonia inhibition, such as ammonia stripping, zeolite adsorption, membrane separation, struvite precipitation, water extraction, microbial acclimation, co-digestion, and trace element addition [1,3,11,12,13,14].
The main configurations for studying the AD process of CM substrate for biogas production include continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTR) or batch reactors [1,3,15,16]. In this case, the addition of water is necessary, to facilitate agitation and ensure solubilization of the organic matter of the CM, which consists mainly of solids. Moreover, the inorganic material (stones) trapped in the CM mass is usually accumulated in this type of reactor, reducing the operating volume and causing operational problems in agitation. A leach bed reactor (LBR) is an attractive technology for the AD of high solid wastes. LBRs can digest high-solid waste, with a low water requirement and no stirring equipment, resulting in a cost-effective and straightforward operation [17,18,19]. On the other hand, LBRs require bulking agents (i.e., straw, sawdust, or agricultural wastes) to increase their porosity, which influences the liquid distribution and permeability, while avoiding clogging and channeling problems. Another limitation is the mass transfer that can be enhanced through leachate recirculation. Recent studies by Hernández-Shek et al. [20,21] suggested that the recirculation strategy (e.g., liquid volume) should be progressively adapted to the physical evolution of the solid bed, due to the lignocellulosic fiber degradation, which affects the bed porosity. LBRs can be operated in batch mode or coupled to methanogenic reactors to perform AD [22]. The methanogenic reactor can be a CSTR or a high-rate anaerobic reactor (fixed-bed or up-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor) commonly used for the digestion of agricultural wastes [23,24], pig manure [25,26], cattle manure [27], or food waste [28]. The AD of CM in LBR has been studied by Bayrakdar et al. [13], who coupled the LBR (operated in batch mode) with a side-stream membrane for ammonia separation.
Another medium used to achieve ammonia removal to some extent is zeolite. Moreover, in the case of LBR, zeolite can be used as a bulking agent (or a part of it). Mixing inert materials such as bentonite and zeolite with ammonia-rich substrates (i.e., poultry manure and swine wastes) has been shown to significantly increase biogas production and organic matter degradation, due to adsorption of the inhibitory compounds [29,30,31,32]. In addition, zeolite serves as an ion exchanger for ammonia removal, due to the presence of Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ cations in its crystalline structure [33]. Other advantages of utilizing zeolite in AD are its resilience against high temperature and acid, and its abundance, making it economical and obtainable. However, adding high amounts of zeolite directly to an anaerobic digester can lead to toxic phenomena, due to the accumulation of heavy metals, since zeolite can adsorb metals, such as copper, cadmium, lead, and zinc [34].
Another reason for using zeolite with CM is that, after anaerobic stabilization, this mixture would be a beneficial amendment to the soil. Zeolites have been used in agriculture over the years, because of their large porosity, high cation exchange capacity, and selectivity for ammonium and potassium cations. They can control moisture content and increase the pH of acidic volcanic soils. Moreover, they can be used both as carriers of nutrients and as a medium to free nutrients. However, the primary use of zeolites in agriculture is for the capture, storage, and slow release of nitrogen, since zeolites, due to their specific selectivity for ammonium (NH4+), can reduce nitrogen losses from composts or ammonium-bearing fertilizers [35]. Therefore, the combination of LBR based systems with zeolite could present some promising advantages, both for the efficiency of the AD process itself, and for the agronomic value of the digestate.
The first step in proving the concept of a two-stage process (LBR–methanogen reactor) for treating CM was to focus on the LBR itself, uncoupled from the methanogen reactor. The leachate results from extraction (due to water percolating through the bed) and hydrolysis, to some extent (due to microorganisms contained in the CM), in the presence of zeolite. Therefore, operating parameters such as water loading, leachate recirculation rate, hydraulic retention time (HRT), and zeolite to CM bed volume ratio were tested. The leachate was assessed in terms of essential characteristics, including the biochemical methane potential (BMP). Finally, the methane production rate from the different leachates produced was estimated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chicken Manure
Chicken manure was collected from a local broiler (meat-chicken) farm housing 170,000 broilers per cycle. The annual manure production of the poultry farm is approximately 2100 tonnes. The CM was collected in plastic vessels and immediately transferred to the laboratory for analysis and storage at 4 °C. The CM collection was repeated twice, resulting in conducting the experiments using CM with different characteristics (each batch of CM is referred to as a ‘batch’). The characteristics of both CM batches used in the experiments are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Composition of chicken manure.
2.2. Zeolite
The natural zeolite used was provided by MEC Energy, Mining construction industry & trade Co (Ankara, Turkey). It consisted of 90% Clinoptilolite, 5% Feldspar, and 0–4% Cristobalite and had a particle size of 2–2.5 mm. Its chemical composition is given in Table 2. The zeolite was used after oven-drying at 105 °C for 24 h.

Table 2.
Physicochemical properties of the zeolite.
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
In this study, three identical 120-mL bench-scale LBRs (Figure 1), with an internal diameter of 3.4 cm and a bed height of 9.5 cm were operated in parallel. The waste chamber had a volume of 100 mL (CM bed volume), and the leachate collection chamber was 400 mL. The temperature was regulated at 36 ± 1 °C, by recirculating heated water in the reactor jacket. Leachate was recirculated and distributed evenly over the waste matrix to provide sufficient solid–liquid contact. Initially, an experimental set of 6 runs was performed using the first batch of CM (Table 3, R1.1–R6.1). LBRs were loaded with CM in each experimental run, using zeolite as the only bulking agent (BA) (mean diameter 2–2.5 mm). The BA/CM ratios (volume of BA to volume of CM bed) tested were 10% (R1.1–R5.1) and 3.5% v/v CM bed (R6.1). A control run (R2.1) was performed using river pebbles with a similar particle size instead of zeolite, with a BA/CM ratio of 10% v/v. Tap water was added daily at loadings of 3.40 g g−1 wet weight of CM (all runs but R4.1) and 6.79 g g−1 wet weight of CM (R4.1). The leachate produced was collected in the leachate chamber and recirculated to the top of the CM bed at different ratios (2.88 mL mL−1 CMbed.d−1 in all runs but R3.1 and 5.76 mL mL−1 CMbed.d−1 in R3.1). The total amount of leachate (in all runs but R5.1) or half of it (in R5.1) was removed and replaced with fresh tap water daily, to achieve the desired HRT (1 d in all runs but R5.1 and 2 d in R5.1, respectively). The first three runs, which produced the best results, were repeated using the CM collected some months later (batch 2). This second set of experiments is labelled as R1.2, R2.2, and R3.2 (Table 3). The solid loading was kept as similar as possible in all runs, with an average value of 12.01 ± 1.23 gr VS (CI 95% 11.52–12.50). Therefore, in all runs performed, the CM volume in LBRs was kept the same, leading to slightly different dry matter loading with respect to wet weight (ww). Each run was conducted for 6 days, since the COD extracted on the sixth day was minimum (Figure S1), and the leachates were removed and replaced with fresh tap water daily. The total quantities of COD and TAN mass extracted were estimated after measuring the total chemical oxygen demand (COD) and the total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) concentrations in each leachate portion removed. Moreover, the concentration of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) and pH were determined.
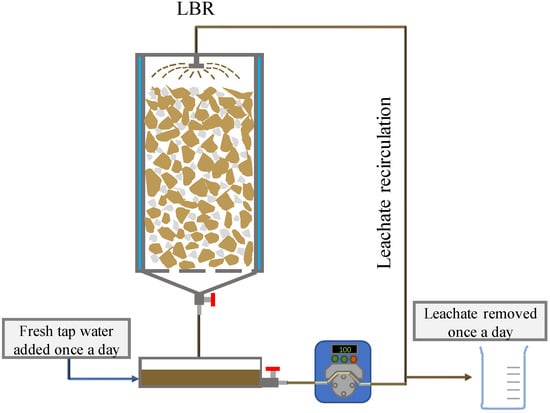
Figure 1.
Graphical presentation of the experimental setup.

Table 3.
Operating conditions of each experimental run for both sets conducted using the two different batches of CM.
Each experimental run was performed in triplicate using the three LBRs in the same conditions, to test the repeatability of the results.
2.4. Biochemical Methane Potential
In order to evaluate the biochemical methane potential (BMP) of the leachates produced from the different leaching conditions, the first portion of the leachate containing the highest organic load was separately digested in batch anaerobic serum bottles (110 mL, working volume 91 mL). All BMP tests were conducted with five or six replicates (in the case of the leachates coming from the CM-batch 1 or CM-batch2, respectively). Each bottle was inoculated with 85 mL of anaerobic sludge with a ‘highly diverse’ methanogenic community (4.7 ± 0.1 gVS L−1). The anaerobic sludge was taken from a full-scale anaerobic digester treating slaughterhouse waste. The inoculum was kept for about five days before the batch digestion test at 36 °C for degassing, as suggested by Hafner et al. [36]. The leachates removed on the first day from the three LBRs in each run were mixed and used in the BMP tests. A volume of ca. 6 mL of leachate was added into the serum bottles, to achieve an organic loading of 0.5 ± 0.1 gCOD g−1VS inoculum. A control test was run with water instead of leachate. No addition of macroelements or trace elements took place.
After leachate or water addition, degasification with N2/CO2 mixture (80/20) [36] was carried out for 1 min to obtain anaerobic conditions, and the bottles were sealed with rubber stoppers. The headspace of each bottle was connected with a NaOH (6N) displacement apparatus to trap CO2. Methane production was monitored via the volume displacement method.
2.5. Calculations
Calculations were made using Microsoft Excel software. All data collected in this work were statistically analyzed to calculate average values (Equation (1)) and standard deviations (Equation (2)).
where is the average of the measured values, SD is the standard deviation, Yi are the experimental values, and n is the number of data.
Moreover, confidence interval on the mean was computed as follows (Equation (3)):
where Z95 is the 95 confidence level.
F-test was performed to determine the homogeneity of variances, followed by a variance (t-test) method analysis, to determine the significant differences for the different operating parameters, using a confidence level of 95%.
The free ammonia (NH3-N) was calculated based on the TAN concentration, the pH and the temperature (T) expressed in K (Equation (4)), according to Allen et al. [37].
2.6. Analytical Methods
All samples collected during this study were analyzed for their concentration of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), total ammonia nitrogen (TAN), lipids, and total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), according to standard methods [38]. The pH was measured with a pH meter (HAΝΝA, HΙ 83141, Hanna instruments Hellas, Athens, Greece). The volatile fatty acid (VFAs) concentrations were measured using a gas chromatograph with a capillary FFAP column and a flame ionization detector, according to the method described by Spyridonidis et al. [39]. If there was biogas produced in the LBRs, their methane content was measured in a volume displacement apparatus connected with a CO2 trap.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Conceptualization of the Study
The scientific questions investigated in the present study relate to the effect of zeolite on the characteristics of the leachate from an LBR filled with CM. Since there are no homogeneous conditions in an LBR, repetition of the leaching experiments was a prerequisite. Moreover, the CM was a heterogeneous mixture of variable composition, as shown in Table 1. Therefore, the basic leaching experiments were repeated to assess the correlation of the results with the characteristics of the CM. Manures are a source of microorganisms and, if left under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, degradation of the organic matter of the manure will inevitably happen to some extent. Therefore, the objective of the study was to assess the characteristics of the leachate, as derived through the leaching process, without the influence of aerobic microorganisms or methanogens that would decrease the COD. Inactivation of the CM’s microorganisms through chemical or a thermal treatment was excluded, since this would influence the characteristics of the leachate. As a result, the following procedures were followed: (i) the LBRs were sparged with an air-free gas mixture to remove as much oxygen as possible, and (ii) the leachate produced was removed every day, with fresh tap water added into the LBRs to keep the hydraulic retention time (HRT) short and prevent methanogen growth. In this way, the readily releasable COD could be evaluated. The parameters considered necessary were the percentage of zeolite in the CM bed, the leachate recirculation rate, the volume of the leachate, and the HRT (Table 3). A control experiment with pebbles instead of zeolite was also set up for the basic scenario.
3.2. Effect of Different Operating Conditions on Leachate’s Characteristics
Based on the conceptualization plan described in Section 3.1, the effect of different leach-bed operating conditions on the leachate was investigated. The first batch of CM (Table 1) was initially used to test six different scenarios (Table 3). Once the six scenarios (R1.1–R6.1) were tested, the second batch of CM was used to repeat the first three scenarios (R1.2, R2.2, R3.2, Table 3). The total VS of CM loaded in each LBR was retained at the same levels in both experimental sets (Table 3). Each day, a part of the leachate was removed and replenished with tap water. The ratio of the leachate withdrawn to the total leachate within the LB resulted in the hydraulic retention time (HRT), as shown in Table 3. Measurements in all leachates that were removed daily showed a decreasing tendency of the concentrations of COD, NH3-N, and volatile fatty acids (VFAs) over time. However, in order to make comparisons, the volumes of the leachate removed daily were recorded and, based on the concentrations of COD and NH3-N, it was possible to calculate their mass and express it as a percentage of the total COD (Figure S1) and the total nitrogen (Figure S2) of the CM added in the LBRs, respectively. These parameters were correlated with the organic matter, the extraction of which into the leachate was higher, initially, and decreased as fresh water was used to replenish the withdrawn leachate. Ammonium nitrogen and volatile fatty acids are products of decomposition directly linked to the organic matter transferred into the leachate. Figure 2a shows how the different operating conditions influenced the COD transferred into the leachate. Similarly, Figure 2b depicts the ammonium nitrogen percentage in the leachate, with respect to the TKN introduced in the LBRs. Ammonium is produced via amino acid degradation, which, in the case of these short-term runs, expresses the readily releasable inorganic nitrogen from TKN.
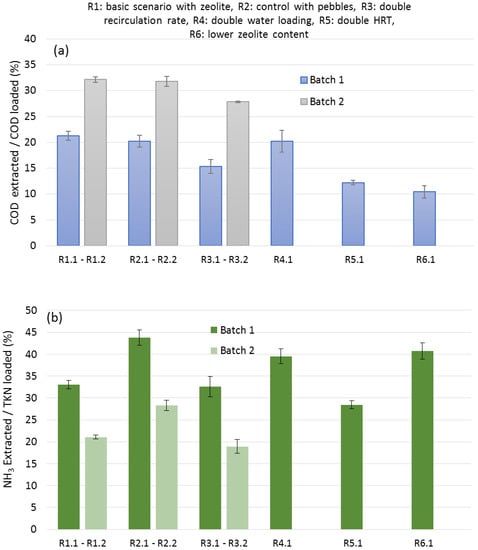
Figure 2.
(a) % COD extracted into leachate, and (b) % NH3 extracted into the leachate during each scenario tested for both CM Batches. Ri.j: Run under the ‘i’ condition with CM from the ‘j’ batch. i = 1, 2, …, 6 and j = 1, 2.
The ratio of zeolite to CM was high (10% v/v or 0.76 g gTS −1), to maintain the porosity of the CM bed. As a result, the leachate percolated easily through the CM and succeeded in transferring COD into the leachate at a percentage of 21.3 ± 0.9% (CI 95%, 20.3–22.3) in the basic scenario with the zeolite and 20.2 ± 1.1% (CI 95%, 19.0–21.5) in the control test using the first batch of CM (R1.1 and R2.1, respectively, Figure 2a). Similarly, the COD transferred summed up to 32.1 ± 4.3% (CI 95%, 26.1–338.1) and 31.8 ± 0.7% (CI 95%, 30.9–32.8) in the repetition of the tests using the second batch of CM (R1.2 and R2.2, respectively, Figure 2a).
The first two runs in each set (R1.1 and R2.1, as well as R1.2 and R2.2) were carried out with zeolite and pebbles, respectively, at the same volume ratio (10% v/v). It seems that the different materials did not influence the COD mass transfer into the leachate, even if two different batches of CM were used; the p-values for the difference between the two runs were 0.27 (using the first batch of CM) and 0.74 (using the second batch of CM), respectively. On the other hand, when zeolite was used as a bulking agent, in a ratio of 3.5% v/v CM bed in R6.1, a significantly lower amount of COD was transferred: 10.4 ± 1.2% (CI 95%, 9.1–11.8) compared to 21.3 ± 0.9% (CI 95%, 20.3–22.3) in R1.1. The p-value of R1.1 vs. R6.1 using batch1 of CM was 0.0002. This can be attributed to the lower permeability and ineffective mass transfer prevailing in the LBR, due to the lower amount of bulking agent in the sixth run. It should be noted that, even in this case, no clogging problems were recorded.
Regarding ammonia release into the leachates, Figure 2b shows that zeolite (R1.1, R1.2) contributed to the ammonium nitrogen reduction compared to pebbles (R2.1, R2.2). Specifically, 33.0 ± 1.0% (CI 95%, 31.9–34.1) and 43.8 ± 1.7% (CI 95%, 41.8–45.8) of NH3 were released in R1.1 and R2.1, respectively, when batch 1 of CM was used, resulting in a p-value of 0.0007. Similarly, in the case of the second batch of CM loaded in the LBRs (R1.2 and R2.2), the NH3 extracted in the presence of zeolite (R1.2) was 21.1 ± 0.4% (CI 95%, 20.5–21.7); that is, less than in the control (R2.2) 28.29 ± 1.2% (CI 95%, 26.6–30.0) with a p-value = 0.016. Finally, during R6.1, where 3.5% v/v of zeolite was used, more NH3 was extracted than R1.1 (p = 0.003) (Figure 2b). Therefore, the lower NH3 extracted in the leachate of R1.1 was attributed to the higher amount of zeolite than in R6.1. Moreover, it has been previously reported that adding materials such as bentonite and zeolite into ammonium-rich substrates facilitates the adsorption of inhibitory compounds such as NH3 [30,40]. In addition, achieving ammonia removal inside an AD system seems to be more practical and more straightforward than outside the digester in an additional step (e.g., through stripping).
The two-fold increase of the leachate recirculation (R3.1 and R3.2) significantly affected the COD extraction efficiency, as compared with R1.1 (p = 0.003) and R1.2 (p = 0.009), respectively. Notably, the higher recirculation rate resulted in less COD extraction (Figure 2a), although more organic matter leaching from the bed was expected. It seems that leachate recirculation favors microbial activity [41], resulting in less COD in the leachate at the end of the test. In addition, it was observed that the amount of NH3 extracted was not affected by the two-fold increase of the leachate recirculation (Figure 2b, R1.1 vs. R3.1, p = 0.80 and R1.2 vs. R3.2, p = 0.20), suggesting that the more intense recirculation did not increase the adsorption capacity of the zeolite. However, further investigation is needed to investigate the role of leachate recirculation on the LBR’s leaching pattern, as well as the distribution of the macro-, meso-, and micro-pores in the bed. Since the operation of LBRs in a batch mode results in a decrease of macropores, which are critical to the efficient percolation of the leachate, a decreased recirculation rate could be applied [21].
The higher amount of water added to produce more leachate did not contribute to extracting more COD in the leachate; the COD extracted in R4.1 (the water added was double compared to the basic experiment R1.1) was 20.2 ± 2.1% (CI 95%, 17.8–22.6) and in R1.1 was 21.3 ± 0.9% (CI 95%, 20.3–22.3), which is not statistically different at a 95% confidence level (R4.1 compared to R1.1, p = 0.46). Therefore, the water loading applied in R1.1 (5.24 g per gTS of CM; Table 3) was sufficient to extract the COD from the bed into the leachate. On the other hand, doubling the HRT (the leachate in R5.1 was left twice as long as in R1.1 before being replaced with freshwater) resulted in less COD extraction (significant difference at 95% level of confidence with p value = 0.0001). This can also be attributed to microbial activity being favored by the longer HRT, which removed part of the COD of the leachate.
With respect to NH3 extraction, the higher amount of water favored its release into the leachate: in R4.1, the ammonia extracted was 39.5 ± 1.7% (CI 95%, 37.6–41.4) compared to the ammonia extracted in R1.1, which was 33.0 ± 1.0% (CI 95%, 31.9–34.1). The difference between R4.1 and R1.1 was statistically different with p = 0.0045, meaning that the equilibrium shifted towards the leachate when the volume of water added was higher. On the other hand, the longer HRT favored the retention of the NH3 in the bed, which is evident from the comparison of the NH3 extracted from R5.1 (28.4.0 ± 0.9%; CI 95%: 27.4–29.4) with the NH3 extracted from R1.1 (33.0 ± 1.0%; CI 95%: 31.9–34.1). The difference between R5.1 and R1.1 was statistically different, with p = 0.0039; meaning that the equilibrium shifted towards the CM bed when the leachate was replaced with water at a lower rate (higher HRT).
Although it was attempted to remove the air through sparging at the beginning of the experiment, so that anaerobic conditions would prevail, aerobic conditions seemed to be unavoidable to some extent. The COD balance (COD recovered as COD in leachate and in bed after the test, per COD loaded) was incomplete, since, in all tests, the COD recovered was less than 100% (Figure 3). This cannot be attributed to methanogenesis, since no methane was detected, and the short-term experiments without inoculation of the LBRs with methanogenic biomass would not favor methane production. The air trapped in the bed matrix during the loading of the LBRs was difficult to remove, leading to loss of COD and, consequently, loss of the methane potential of the CM. Moreover, replacing the leachate with freshwater every day may have transferred oxygen, due to the replacement procedure and the dissolved oxygen in the water.
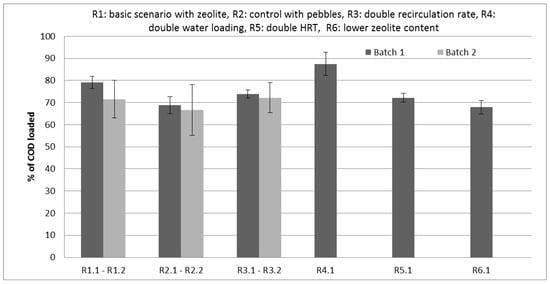
Figure 3.
COD mass balance in each scenario tested for both CM batches. Ri.j: Run under the ‘i’ condition with CM from the ‘j’ batch. i = 1, 2, …, 6 and j = 1, 2.
Comparing the results of the tests conducted with a different batch of CM, it seems that more COD and less NH3 were extracted when batch 2 was used than with batch 1 (Figure 2a,b). These differences were probably due to the different characteristics (Table 1) of the two batches, collected at different time periods. The high heterogeneity of this waste over time has been noticed by other researchers [1,13]. However, despite the heterogeneity of the CM production over time, the removal of ammonia per mass of zeolite was consistent in all tests. The ammonia removal was calculated by subtracting the ammonia contained in the leachate from the CM/zeolite mixtures from the corresponding ammonia in the leachate obtained from the CM/pebble mixtures. The mass of ammonia removed was divided by the mass of zeolite added, and it was found that the adsorbing capacity varied from 5 to 5.27 mg TAN g−1 zeolite. This capacity is one magnitude level lower than that reported in the literature [29,42]: 50 to 60 mg TAN g−1 zeolite. However, it should be considered that the leaching system studied herein has mass transfer limitations compared to the tests conducted in mixed systems.
In conclusion, the results presented herein suggest that the best leaching strategy, leading to more COD extraction, was that applied in R1.1 and R1.2, with 10% zeolite at a water loading of 5.24 g per g TS of CM, a leachate recirculation rate of 2.88 mL mL−1 CM bed d−1, and an HRT of 1 d. On the other hand, at an HRT of 2 d, more NH3 was retained in the CM bed, but the COD of the leachate was less (probably due to aerobic microbial activity). However, the latter may not be a disadvantage if the LBR is optimized to operate as an anaerobic digester and, therefore, the methanogenic activity is enhanced.
3.3. VFAs Accumulation
Figure 4 shows the profiles of the VFAs in the leachates obtained from the LBRs filled with the (a) zeolite and CM from batch 1 (R1.1), (b) pebbles and CM from batch 1 (R2.1), (c) zeolite and CM from batch 2 (R1.2), and (d) pebbles and CM from batch 2 (R2.2). In other words, the results from the tests with the zeolite are compared with those obtained with the pebbles (control) for the two batches of CM, which had different characteristics (Table 1). It seems that no correlation can be made for the VFA production. Although the VFA concentration was higher in the leachates of the LBR in the presence of zeolite (R1.1 vs. R2.1), this fact was not verified when the tests were repeated with another batch of CM (R1.2 vs. R2.2). The acetate concentration was higher in all cases, while propionate and butyrate concentrations were generally lower. Isobutyrate, valerate and isovalerate were also measured, but were detected at non-appreciable concentrations (below 0.1 g L−1; data not shown). In the runs performed with the second batch of CM, propionate and butyrate concentrations were higher on the fourth day (Figure 4c,d). These results imply that the VFA production depended on the CM used and was not affected by the presence of zeolite or pebbles. Moreover, during the leaching process, it seems that hydrolysis/acidogenesis and acetogenesis took place, while methanogenesis was not observed (no methane was detected in the gas phase). Therefore, replacing the leachate every day with water and not inoculating the LBRs did not favor methanogenesis, making it possible to interpret the results as the effect of the physicochemical process of leaching through an organic waste-zeolite (or pebble) bed and the biochemical processes of hydrolysis/acidogenesis and acetogenesis, which inevitably occur in anaerobic environments under a short HRT. The average pH (Figure 5) was lower in the runs conducted with the second batch of CM, which accords with the higher concentration of VFA noticed in the leachates. However, due to the presence of NH3 and VFA, the pH was kept at almost neutral levels (between 6 and 8)
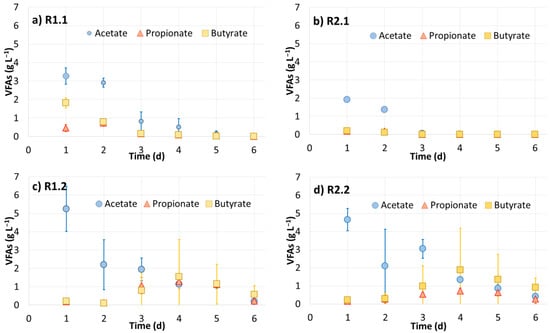
Figure 4.
VFA (acetate, propionate and butyrate) concentrations in the leachates during the 6-day operation of the LBRs. Ri.j: Run under the ‘i’ condition with CM from the ‘j’ batch. i = 1 (zeolite), 2 (pebble) and j = 1, 2.
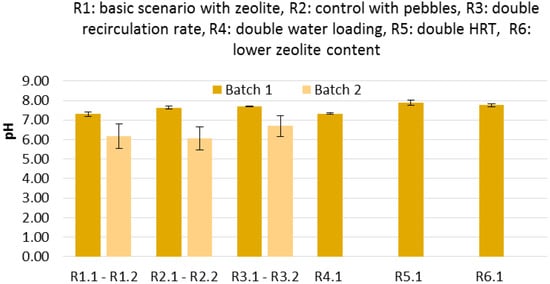
Figure 5.
Average pH in each scenario tested for both CM batches. Ri.j: Run under the ‘i’ condition with CM from the ‘j’ batch. i = 1, 2, …, 6 and j = 1, 2.
3.4. Biochemical Methane Potential
The methane potentials (LCH4 g−1 COD) of the leachates obtained from the experiments with the LBRs filled with zeolite and pebbles and with CM from different batches are shown in Figure 6. These leachates were removed from the first day of LBR operation, which had the highest organic load. The leachates coming from the CM/zeolite mixtures (R1.1 and R1.2) had higher BMP than the leachates coming from CM/pebble mixtures (R2.1 and R2.2), respectively. The leachate from the CM-batch1 with zeolite yielded 0.263 ± 0.027 LCH4 g−1 COD, while the leachate from the control test (CM-batch1 and pebbles) yielded 0.219 ± 0.008 LCH4 g−1 COD (p-value = 0.0079). In the case of the tests done with the CM coming from the second batch, the BMPs of the leachates were 0.342 ± 0.013 LCH4 g−1 COD (zeolite) and 0.319 ± 0.008 LCH4 g−1 COD (control), which are statistically different at a 95% confidence level (p-value = 0.0089). The leachate coming from the second batch of CM had a higher BMP in all cases (mixed with either zeolite or pebbles), implying that the organic matter was more biodegradable, probably indicating that the CM in batch 2 was fresher than the CM in batch1. It appears that zeolite favored the BMP of the resulting leachate. The TAN concentrations in the leachate of the first day from the CM/zeolite and CM/pebble mixtures in the case of CM-batch1 were 2.249 ± 0.098g L−1 (pH 7.10) and 2.833 ± 0.236g L−1 (pH 7.61), respectively, while in the case of CM batch 2, the NH3-N was even lower. The equivalent free ammonia concentrations were (Equation (4)) 31 and 123 mg NH3-N L−1, respectively for CM batch 1 and much lower in the case of CM batch 2. It is well known that the inhibition levels of ammonia for methanogenesis, if the methanogens have not been acclimatized, are above 3000 mg L−1 as TAN and 150 mg L−1 as free ammonia (NH3-N) [29]. Therefore, no inhibition was expected at these ammonia concentration levels; nevertheless, the statistically significant difference observed in the BMP of the leachates was attributed to the presence or absence of zeolite in both cases of CM, verifying that the zeolite favored the biodegradability of the leachates. The positive effect of zeolite has been explained by Milan et al. [43]: the properties of zeolite to (a) offer high capacity for immobilization of microorganisms, (b) facilitate the ammonia/ammonium cation equilibrium, and (c) achieve a reduction of TAN and free ammonia in the solution. Fotidis et al. [29] verified that the increase in the methane yield in bioreactors, in which the zeolite was added at high concentrations, could not only be attributed to the ammonia concentration reduction (i.e., the reduction of ammonia concentration was slight compared to the high increase in the methane yield). Moreover, in the present work, the zeolite was not transferred in the liquid leachate, nor was it present during the BMP tests, to support the argument of being an ideal support for the microorganisms’ growth. It is possible that the cations (Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+) of zeolite, exchanged for ammonium adsorption on its active sites [44], had a positive impact on the methanogens’ growth. It is also possible that other zeolite components were released in the leachates, resulting in this positive correlation with methanogenesis.
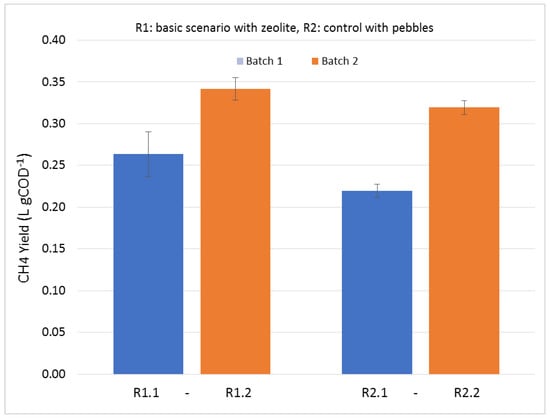
Figure 6.
Biochemical methane potential of leachates obtained from leaching through a CM/zeolite or pebble mixture. Ri.j: Run under the ‘i’ condition with CM from the ‘j’ batch. i = 1 (zeolite), 2 (pebble) and j = 1, 2.
4. Conclusions
The objective of this work was to study the effect of various operating parameters on the readily releasable COD and TAN content and the BMP of the derived leachates from lab-scale LBRs. For this reason, methanogenesis in the LBRs was not desired, and the tests performed were at low HRT, to avoid methanogen growth. The COD extracted in the leachates was not influenced by the presence of zeolite, but was affected by the ratio of bulking material (which was the zeolite) to the CM. In the case of a smaller ratio, the COD extraction was lower, probably due to poorer percolation. Although sparging with an inert gas mixture was applied to exclude the oxygen from the LBRs, aerobic conditions did prevail to some extent, since the COD at the end of the experiments was 70–90% of the initial COD. Methane was not detected, so the only microbial activity that would result in COD reduction must have been aerobic degradation, probably due to trapped air in the pores of the LBR’s bed that could not be removed through sparging. The COD detected in the leachates of the LBRs that were operated under a higher leachate recirculation rate or higher HRT was lower, probably due to the aerobic degradation being favored in these conditions. The readily releasable COD from CM varied between 20 and 30% of the inlet COD of CM. This rough estimate of the organic matter that can be easily extracted from an LBR filled with CM can help in the design of a two-stage system, where the leachate is converted to methane in a separate methanogenic bioreactor.
The amount of TAN released into the leachate was smaller in the presence of zeolite in the LBR, while it was not affected by the leachate recirculation rate. Increasing the volume of the water added in the LBRs favored TAN extraction into the leachate, while increasing the HRT favored the retention of the TAN in the bed. Despite the difference in TAN extraction due to the different characteristics of the two CMs used for leaching, the TAN removal remained consistent at 5–5.27 mg g−1 zeolite added in the LBR.
The leachates derived from the LBRs with zeolite had higher BMP (0.342 ± 0.013 or 0.263 ± 0.027 LCH4 g−1CODadded at STP conditions, depending on the CM used) compared to the control experiment. Since the free ammonia was below the inhibition limit in the leachate derived under any operational condition (even the control), the zeolite seems to favor methanogenesis in more ways than merely achieving ammonia retention or being a supporting material for methanogen growth, probably due to the components it exchanges upon NH4+ adsorption. Therefore, this interesting finding deserves further investigation, to elucidate the mechanisms of zeolite interaction within the AD process.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su14042207/s1, Figure S1: % COD extracted per day into leachate during (a) R1.1, R2.1, R3.1 for CM Batch 1, (b) R1.2, R2.2, R3.3 for CM Batch 2 and (c) R4.1, R5.1, R6.1 for CM Batch 1; Figure S2: % NH3 extracted per day into leachate during (a) R1.1, R2.1, R3.1 for CM Batch 1, (b) R1.2, R2.2, R3.3 for CM Batch 2 and (c) R4.1, R5.1, R6.1 for CM Batch 1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S.; methodology, K.S. and A.S.; conduct of experiments: A.S.; investigation, K.S. and A.S.; data curation, A.S., I.A.V.; statistical analysis: I.A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.V.; writing—review and editing, I.A.V., K.S.; visualization, A.S., I.A.V.; supervision, K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge the support of this work by the project “INVALOR” (MIS 50002495), which is implemented under the Action ‘Reinforcement of the Research and Innovation Infrastructure’, funded by the Operational Programme ‘Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation’ (NSRF 2014–2020) and co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Regional Development Fund).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to confidentiality reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Molaey, R.; Bayrakdar, A.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Çalli, B. Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: Mitigating Process Inhibition at High Ammonia Concentrations by Selenium Supplementation. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.C.; Donald, J.O. The Value and Use of Poultry Manures as Fertilizer. Available online: https://www.aces.edu/ (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Bayrakdar, A.; Molaey, R.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Sahinkaya, E.; Çalli, B. Biogas Production from Chicken Manure: Co-Digestion with Spent Poppy Straw. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujoczek, G.; Oleszkiewicz, J.; Sparling, R.; Cenkowski, S. High Solid Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 76, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hamilton, D.W.; Payne, J. Using Poultry Litter as Fertilizer. Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service. Available online: https://extension.okstate.edu/fact-sheets/print-publications/pss/using-poultry-litter-as-fertilizer-pss-2246.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Piechota, G. Removal of Siloxanes from Biogas Upgraded to Biomethane by Cryogenic Temperature Condensation System. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cao, W.; Banks, C.J.; Heaven, S.; Liu, R. Biogas Production from Undiluted Chicken Manure and Maize Silage: A Study of Ammonia Inhibition in High Solids Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamaras, S.D.; Vasileiadis, S.; Karas, P.; Angelidaki, I.; Kotsopoulos, T.A. Microbial Adaptation to High Ammonia Concentrations during Anaerobic Digestion of Manure-Based Feedstock: Biomethanation and 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, Y.; Zhadan, S.; Bochmann, G.; Salyuk, A.; Nykyforov, V. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; He, L.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Contribution of Precipitates Formed in Fermentation Liquor to the Enhanced Biogasification of Ammonia-Rich Swine Manure by Wheat-Rice-Stone Addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Maza, A.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.J. In Situ Biogas Stripping of Ammonia from a Digester Using a Gas Mixing System. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 3216–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, A.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Çalli, B. Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure by a Leach-Bed Process Coupled with Side-Stream Membrane Ammonia Separation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böjti, T.; Kovács, K.L.; Kakuk, B.; Wirth, R.; Rákhely, G.; Bagi, Z. Pretreatment of Poultry Manure for Efficient Biogas Production as Monosubstrate or Co-Fermentation with Maize Silage and Corn Stover. Anaerobe 2017, 46, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elasri, O.; Salem, M.; Ramdani, M.; Zaraali, O.; Lahbib, L. Effect of Increasing Inoculum Ratio on Energy Recovery from Chicken Manure for Better Use in Egyptian Agricultural Farms. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Pei, M.; Qiu, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qiang, H. Performance of Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure under Gradually Elevated Organic Loading Rates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cysneiros, D.; Banks, C.J.; Heaven, S.; Karatzas, K.A.G. The Effect of PH Control and “hydraulic Flush” on Hydrolysis and Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA) Production and Profile in Anaerobic Leach Bed Reactors Digesting a High Solids Content Substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikulina, N.; Uslu, S.; Lemmer, A.; Azbar, N.; Oechsner, H. Optimal Conditions for High Solid Co-Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes in a Leach-Bed Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayen, A.; Sayadi, S.; Sousbie, P.; Bernet, N.; Torrijos, M.; Escudié, R. Chicken Manure and Wheat Straw Co-Digestion in Batch Leach Bed Reactors: Optimization of the Start-up Conditions. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Shek, M.A.; Mathieux, M.; André, L.; Peultier, P.; Pauss, A.; Ribeiro, T. Quantifying Porosity Changes in Solid Biomass Waste Using a Disruptive Approach of Water Retention Curves (WRC) for Dry Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 12, 100585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Shek, M.A.; André, L.; Peultier, P.; Pauss, A.; Ribeiro, T. Immersion Effect on the Anaerobic Degradation and the Rheological Properties of Straw-Cattle Manure (SCM) at 440 L Batch Pilot Scale Reactor. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 6741–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysneiros, D.; Banks, C.J.; Heaven, S.; Karatzas, K.A.G. The Role of Phase Separation and Feed Cycle Length in Leach Beds Coupled to Methanogenic Reactors for Digestion of a Solid Substrate (Part 2): Hydrolysis, Acidification and Methanogenesis in a Two-Phase System. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7393–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.W.; Samani, Z.; Hanson, A.; Smith, G. Energy Recovery from Grass Using Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, A.S.; Murphy, J.D. Optimizing the Operation of a Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion System Digesting Grass Silage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7561–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, W. Anaerobic Mono-Digestion of Pig Manure in a Leach Bed Coupled with a Methanogenic Reactor: Effects of the Filter Media. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, W.; Huang, H. The Role of Reflux Time in a Leach Bed Reactor Coupled with a Methanogenic Reactor for Anaerobic Digestion of Pig Manure: Reactor Performance and Microbial Community. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korazbekova, K.U.; Bakhov, Z.K. Performance of Leach-Bed Reactor with Immobilization of Microorganisms in Terms of Methane Production Kinetics. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 14, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Kaur, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, S.; Varjani, S.; Wong, J.W.C. Optimization of Water Replacement during Leachate Recirculation for Two-Phase Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion System with off-Gas Diversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotidis, I.A.; Kougias, P.G.; Zaganas, I.D.; Kotsopoulos, T.A.; Martzopoulos, G.G. Inoculum and Zeolite Synergistic Effect on Anaerobic Digestion of Poultry Manure. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yu, C.; Huang, H.; Kim, M.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z. Study on a Fixed Zeolite Bioreactor for Anaerobic Digestion of Ammonium-Rich Swine Wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7064–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, D.T.N.; Dassanayake, K.B.; Sommer, S.G.; Scales, P.; Chen, D. Biogas Improvement by Adding Australian Zeolite During the Anaerobic Digestion of C:N Ratio Adjusted Swine Manure. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, B.; Liaquat, R.; Farooq, U.; Jamal, A.; Ali, M.I.; Liu, F.J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Urynowicz, M.; Huang, Z. Enhanced Biogas Production at Mesophilic and Thermophilic Temperatures from a Slaughterhouse Waste with Zeolite as Ammonia Adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, S.; Guerrero, L.; Borja, R.; Sánchez, E.; Milán, Z.; Cortés, I.; Angeles de la la Rubia, M. Application of Natural Zeolites in Anaerobic Digestion Processes: A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 58, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Vila, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Astals, S. The Role of Additives on Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, C.; Baskar, P. Zeolite and Its Potential Uses in Agriculture: A Critical Review. Agric. Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, S.D.; de Laclos, H.F.; Koch, K.; Holliger, C. Improving Inter-Laboratory Reproducibility in Measurement of Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP). Water 2020, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.; Browne, J.D.; Murphy, J.D. Evaluation of the Biomethane Yield from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Nitrogenous Substrates. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA. WEF Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Spyridonidis, A.; Skamagkis, T.; Lambropoulos, L.; Stamatelatou, K. Modeling of Anaerobic Digestion of Slaughterhouse Wastes after Thermal Treatment Using ADM1. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, N.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Improved Methane Production and Energy Recovery of Post-Hydrothermal Liquefaction Waste Water via Integration of Zeolite Adsorption and Anaerobic Digestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueurce, A.; Tomas, N.; le Roux, S.; Martinez, J.; Peu, P. Biotic and Abiotic Roles of Leachate Recirculation in Batch Mode Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kougias, P.G.; Fotidis, I.A.; Zaganas, I.D.; Kotsopoulos, T.A.; Martzopoulos, G.G. Zeolite and Swine Inoculum Effect on Poultry Manure Biomethanation. Int. Agrophysics 2013, 27, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milán, Z.; Sánchez, E.; Weiland, P.; Borja, R.; Martín, A. Ilangovan K Influence of Different Natural Zeolite Concentrations on the Anaerobic Digestion of Piggery Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, S.; Díaz, F.; Guerrero, L.; Sánchez, E.; Borja, R. Effect of Particle Size and Doses of Zeolite Addition on Anaerobic Digestion Processes of Synthetic and Piggery Wastes. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).