Impact of China’s Provincial Government Debt on Economic Growth and Sustainable Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Idea, Method and Research Data
2.1. Study Idea
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Kernel Density Estimation
2.2.2. Econometric Methodology
2.3. Research Data
- (1)
- Dependent Variables:
- (2)
- Independent Variables
- (3)
- Control Variables
3. Empirical Results
3.1. Dynamic Evolution
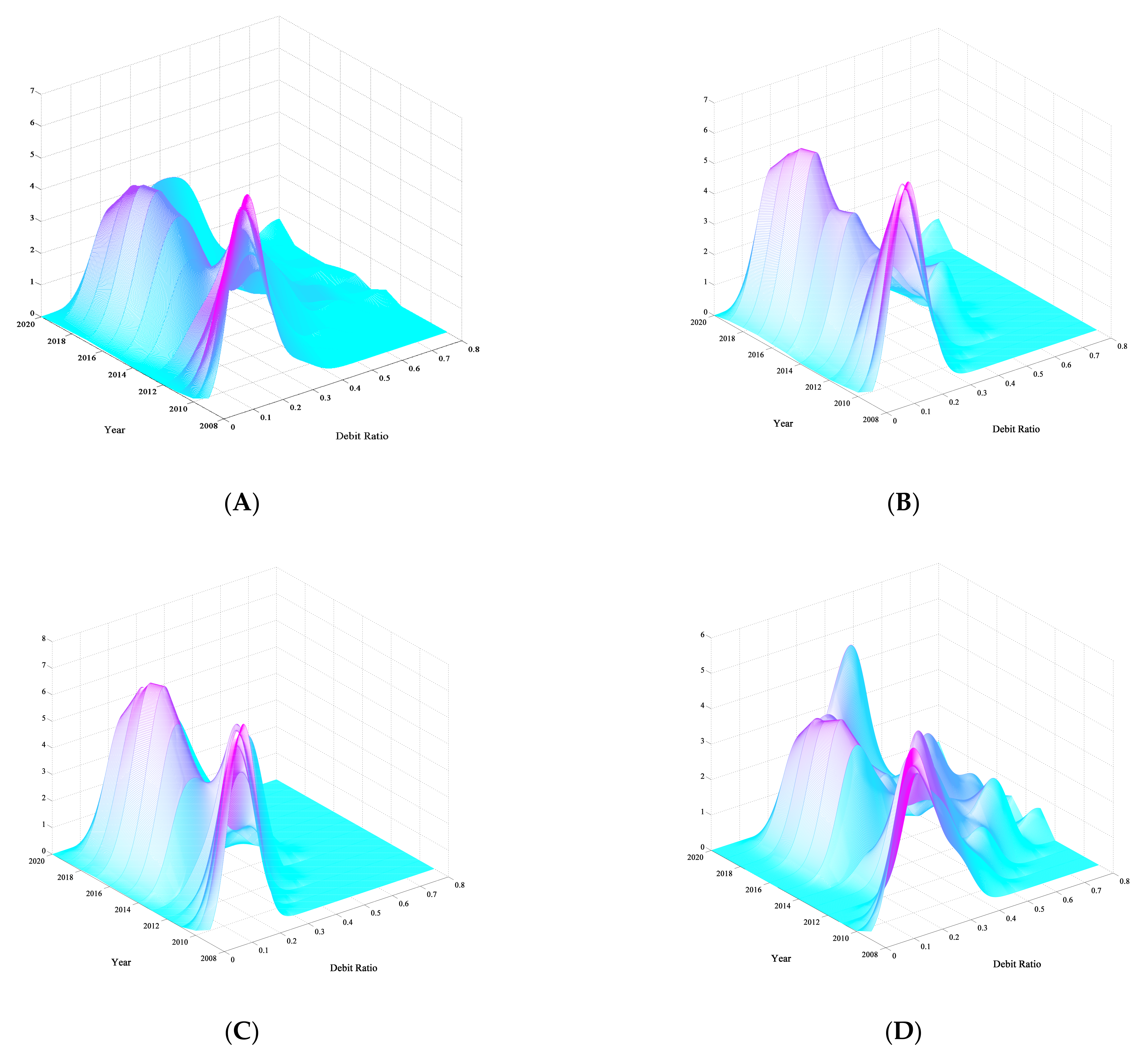
3.1.1. Temporal Evolution
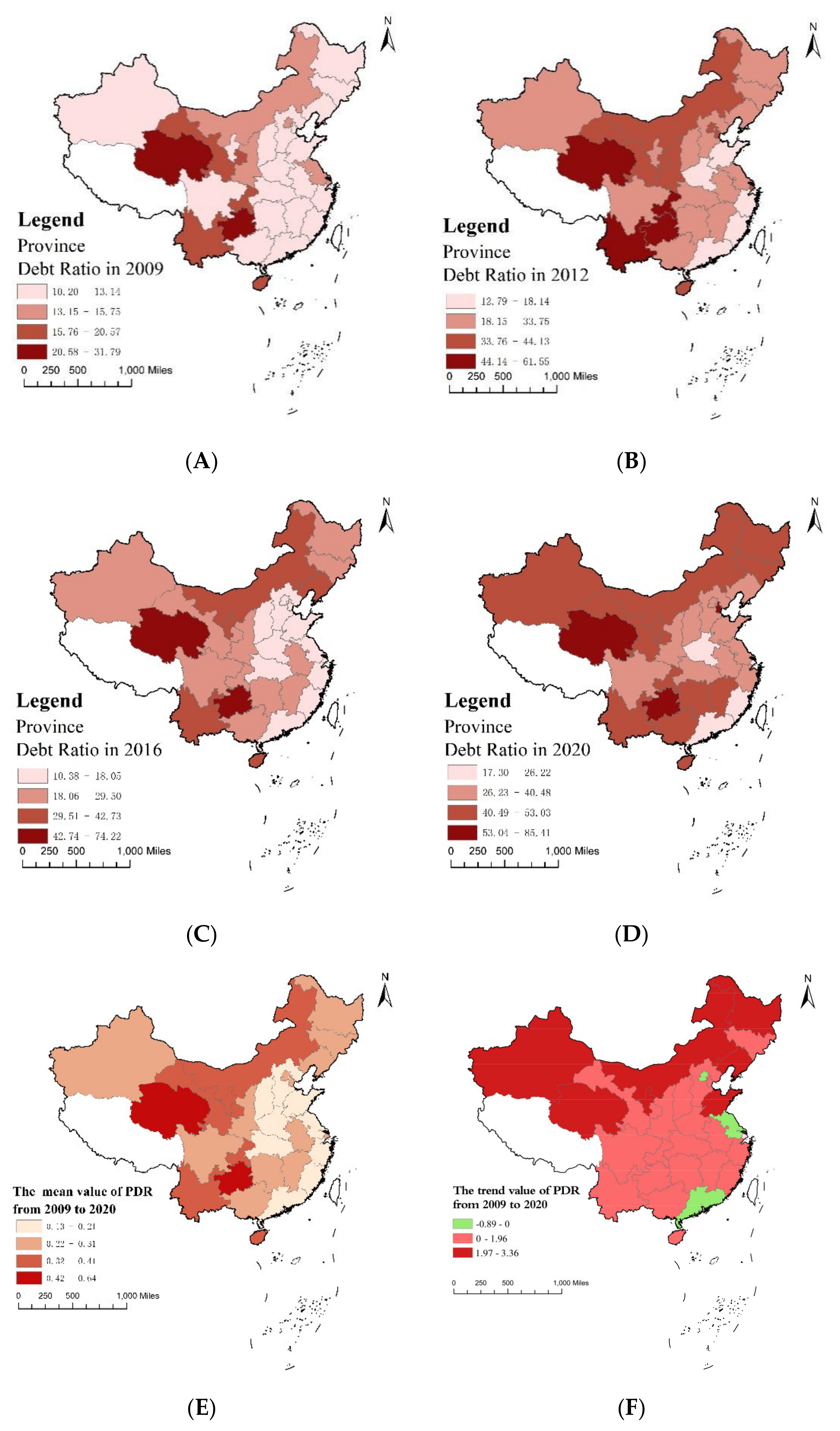
3.1.2. Spatial Evolution
3.2. Primary Finding
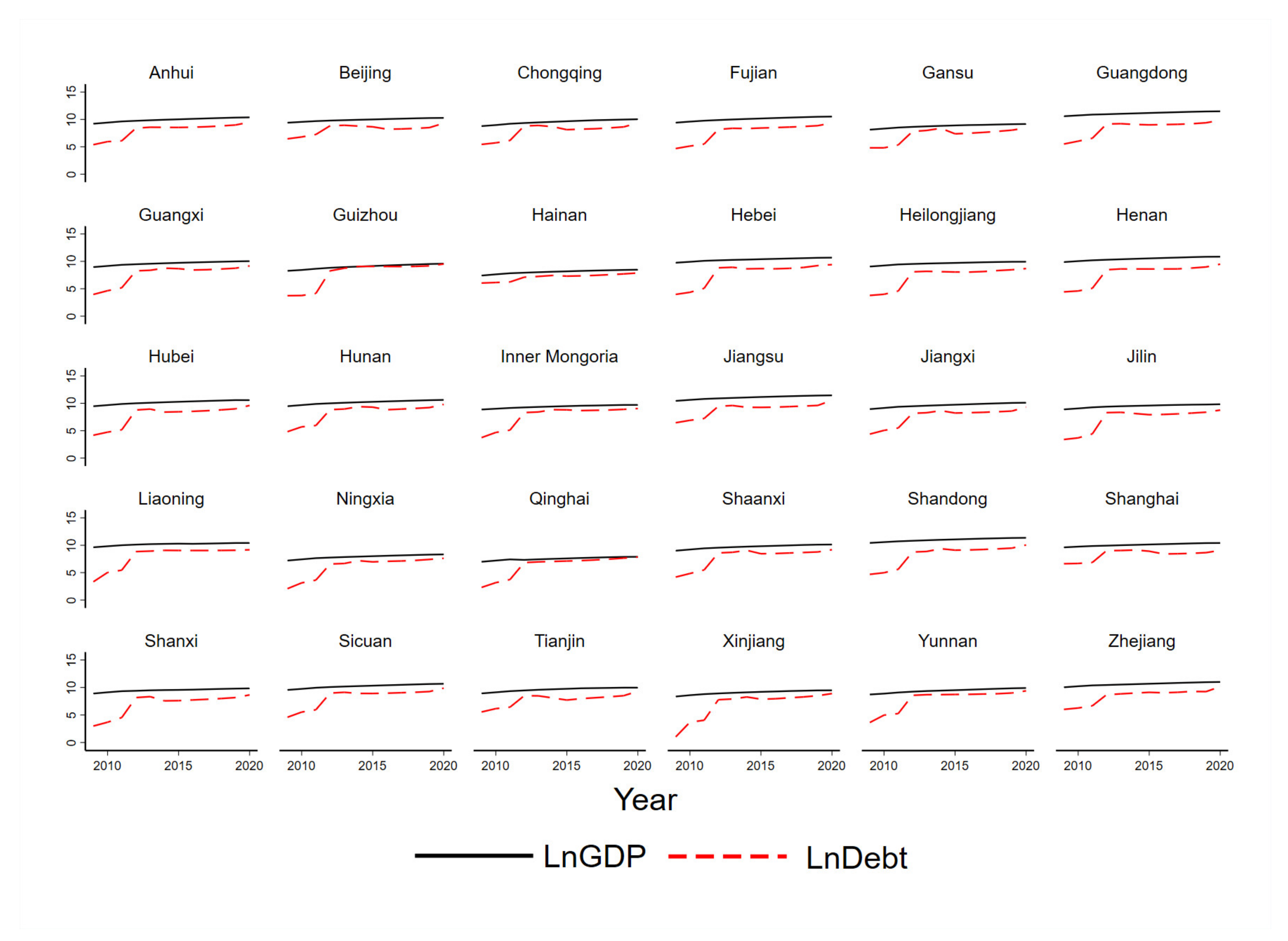
3.2.1. The Influence of Government Debt on Economic Growth
- (1)
- Benchmark regression
- (2)
- Regional variability analysis
- (3)
- Further study
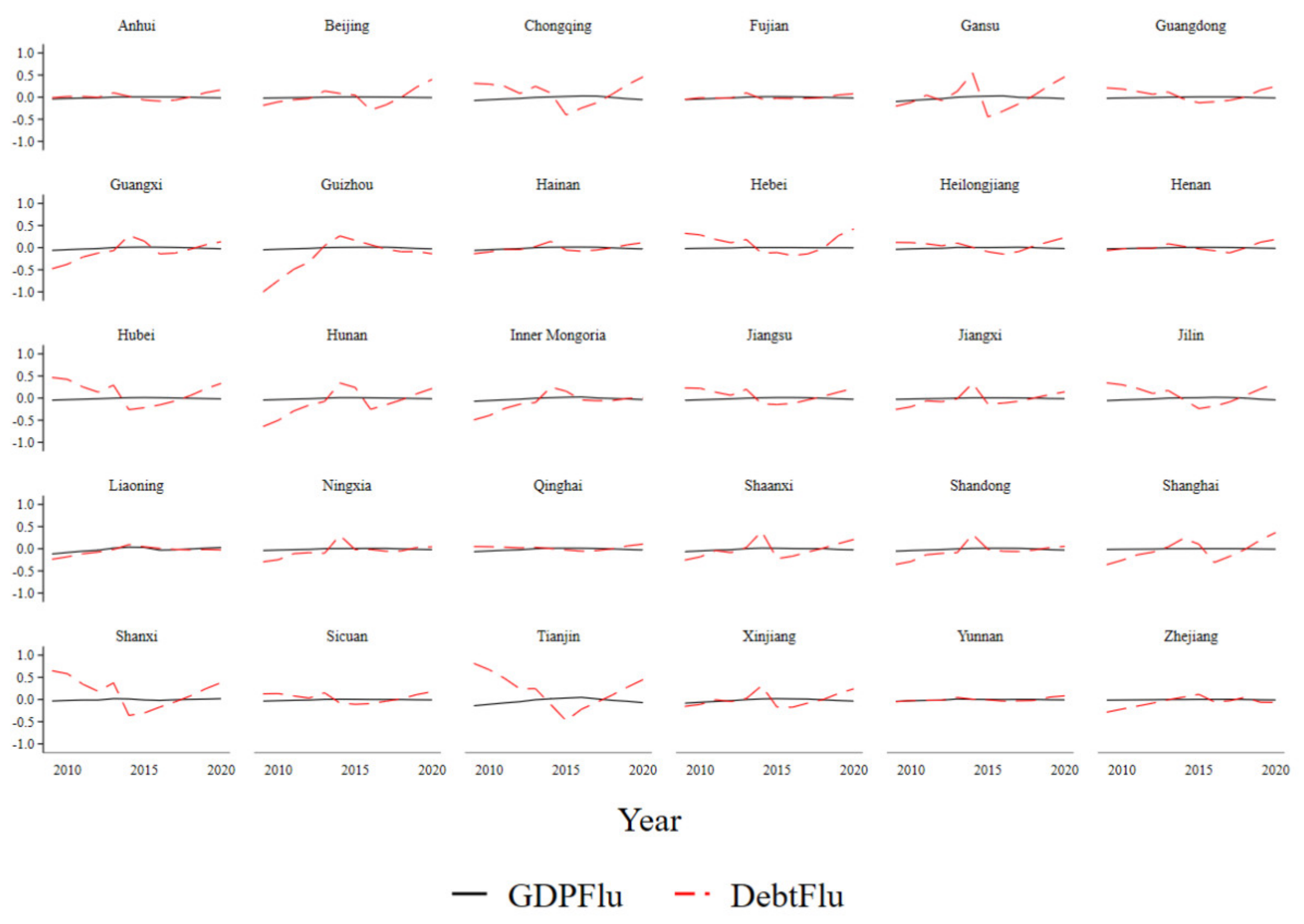
3.2.2. The Influence of Government Debt on Economic Growth Fluctuations
- (1)
- Benchmark regression
- (2)
- Regional Fluctuations analysis
- (3)
- Robustness test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions, Policy Implication and Limitations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implication
5.3. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnGDP | 360.000 | 9.715 | 0.897 | 6.986 | 11.483 |
| lnDebt | 360.000 | 7.680 | 1.770 | 1.030 | 10.567 |
| Urb | 360.000 | 56.886 | 12.642 | 29.890 | 89.600 |
| Indus | 360.000 | 46.443 | 9.872 | 28.615 | 84.880 |
| Pop | 360.000 | 5.038 | 2.710 | −1.050 | 11.470 |
| Open | 360.000 | 26.386 | 29.291 | 0.758 | 154.816 |
| Gov | 360.000 | 24.816 | 11.053 | 9.640 | 77.728 |
| Tax | 360.000 | 8.189 | 2.956 | 4.217 | 19.962 |
| Edu | 360.000 | 9.060 | 0.955 | 6.764 | 9.913 |
| GDPFlu | 360.000 | 1.5 × 10−10 | 0.013 | −0.048 | 0.049 |
| DebtFlu | 360.000 | 1.1 × 10−10 | 0.151 | −0.478 | 0.546 |
| UrbFlu | 360.000 | −1.7 × 10−10 | 0.220 | −1.002 | 0.861 |
| IndusFlu | 360.000 | 1.7 × 10−9 | 1.512 | −6.264 | 6.292 |
| PopFlu | 360.000 | −6.1 × 10−10 | 0.673 | −2.930 | 3.783 |
| OpenFlu | 360.000 | −4.8 × 10−9 | 2.494 | −10.558 | 14.479 |
| GovFlu | 360.000 | 3.1 × 10−9 | 1.254 | −4.109 | 5.331 |
| TaxFlu | 360.000 | −9.0 × 10−10 | 0.865 | −7.613 | 3.923 |
| EduFlu | 360.000 | 0.357 | 1.932 | −0.520 | 11.036 |
Appendix B
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 15.749 | 19.088 | 26.030 | 38.989 | 38.151 | 30.554 | 24.893 | 15.034 | 13.846 | 14.013 | 14.034 | 30.600 |
| Tianjin | 10.318 | 15.341 | 16.415 | 38.093 | 33.470 | 23.550 | 13.630 | 16.286 | 18.413 | 21.682 | 35.162 | 79.201 |
| Hebei | 10.923 | 15.147 | 19.964 | 25.703 | 26.420 | 19.214 | 19.754 | 17.881 | 17.103 | 20.212 | 29.079 | 33.603 |
| Shanxi | 12.815 | 18.304 | 20.496 | 29.258 | 32.992 | 15.294 | 15.863 | 17.720 | 17.221 | 17.622 | 20.626 | 32.462 |
| Inner Mongoria | 14.294 | 20.776 | 27.447 | 38.946 | 39.869 | 56.828 | 52.003 | 42.675 | 41.317 | 40.613 | 42.454 | 48.861 |
| Liaoning | 11.552 | 17.487 | 23.158 | 27.969 | 27.894 | 30.456 | 29.740 | 38.367 | 35.316 | 33.957 | 35.669 | 38.532 |
| Jilin | 10.236 | 11.384 | 20.356 | 33.753 | 32.563 | 26.067 | 19.571 | 19.455 | 20.886 | 24.610 | 37.050 | 51.776 |
| Heilongjiang | 11.537 | 13.562 | 18.337 | 23.689 | 24.667 | 22.762 | 20.857 | 20.280 | 21.325 | 25.160 | 34.884 | 43.196 |
| Shanghai | 15.103 | 18.955 | 24.917 | 40.195 | 37.980 | 38.793 | 29.031 | 15.915 | 15.323 | 15.407 | 14.997 | 22.343 |
| Jiangsu | 15.542 | 17.148 | 18.448 | 23.801 | 24.716 | 16.352 | 15.055 | 14.346 | 14.000 | 14.348 | 14.933 | 37.809 |
| Zhejiang | 11.402 | 14.714 | 17.309 | 17.064 | 18.350 | 19.887 | 21.425 | 18.051 | 17.847 | 19.208 | 16.660 | 39.773 |
| Anhui | 11.559 | 13.297 | 18.647 | 26.075 | 27.548 | 25.378 | 23.209 | 22.057 | 21.162 | 22.344 | 21.384 | 34.675 |
| Fujian | 12.655 | 13.446 | 14.170 | 18.139 | 20.037 | 17.293 | 17.678 | 17.452 | 16.913 | 16.916 | 16.591 | 26.225 |
| Jiangxi | 13.135 | 14.983 | 16.229 | 27.429 | 27.290 | 36.871 | 22.353 | 21.546 | 20.506 | 21.740 | 21.614 | 43.928 |
| Shandong | 10.967 | 11.117 | 11.814 | 12.789 | 12.869 | 19.706 | 14.379 | 14.094 | 14.030 | 14.954 | 18.472 | 31.653 |
| Henan | 11.294 | 13.286 | 15.793 | 16.059 | 17.216 | 15.992 | 14.769 | 13.757 | 12.333 | 13.616 | 14.578 | 24.028 |
| Hubei | 11.505 | 15.142 | 22.682 | 29.311 | 31.136 | 16.208 | 15.897 | 15.624 | 15.649 | 16.958 | 17.544 | 34.411 |
| Hunan | 12.867 | 18.645 | 25.863 | 31.482 | 31.425 | 44.403 | 38.140 | 21.853 | 22.166 | 23.907 | 25.595 | 43.355 |
| Guangdong | 10.884 | 12.725 | 13.997 | 16.754 | 16.264 | 12.921 | 10.956 | 10.383 | 9.846 | 10.237 | 11.098 | 17.302 |
| Guangxi | 12.030 | 17.245 | 24.569 | 30.089 | 29.960 | 40.791 | 34.872 | 25.029 | 23.714 | 26.992 | 29.799 | 43.679 |
| Hainan | 19.848 | 26.063 | 31.784 | 44.128 | 45.279 | 49.211 | 39.936 | 38.140 | 38.227 | 40.184 | 42.012 | 48.142 |
| Chongqing | 20.567 | 29.621 | 34.204 | 58.676 | 57.577 | 41.434 | 21.500 | 21.283 | 20.607 | 23.035 | 23.739 | 46.792 |
| Sicuan | 12.099 | 19.399 | 25.473 | 33.523 | 34.971 | 26.229 | 24.836 | 23.904 | 22.993 | 22.860 | 22.690 | 40.480 |
| Guizhou | 31.793 | 42.803 | 50.315 | 57.238 | 78.171 | 94.689 | 83.359 | 74.224 | 63.565 | 59.770 | 57.685 | 76.438 |
| Yunnan | 19.848 | 28.063 | 36.443 | 51.747 | 50.327 | 46.892 | 45.734 | 42.725 | 40.752 | 39.929 | 34.912 | 48.986 |
| Shaanxi | 15.442 | 19.749 | 25.814 | 38.623 | 38.313 | 50.057 | 26.154 | 25.820 | 25.126 | 24.089 | 25.325 | 37.315 |
| Gansu | 19.893 | 28.955 | 32.429 | 43.581 | 46.780 | 64.050 | 23.386 | 24.876 | 26.945 | 30.222 | 35.748 | 51.419 |
| Qinghai | 28.775 | 35.332 | 47.543 | 61.553 | 61.731 | 61.606 | 61.481 | 59.300 | 61.359 | 64.156 | 70.870 | 85.413 |
| Ningxia | 11.773 | 14.084 | 25.423 | 30.891 | 30.687 | 47.962 | 36.348 | 37.313 | 36.145 | 37.473 | 44.248 | 52.060 |
| Xinjiang | 10.196 | 16.196 | 22.601 | 31.631 | 32.523 | 42.624 | 28.241 | 29.499 | 30.932 | 32.627 | 36.570 | 53.034 |
| Whole Country | 14.553 | 19.069 | 24.289 | 33.239 | 34.239 | 35.136 | 28.168 | 25.830 | 25.186 | 26.295 | 28.867 | 43.250 |
| Eastern Region | 12.677 | 16.088 | 20.401 | 28.082 | 28.386 | 27.549 | 23.524 | 20.759 | 20.340 | 21.651 | 24.487 | 38.360 |
| Central Region | 12.431 | 15.483 | 19.711 | 26.397 | 27.103 | 26.819 | 23.331 | 20.879 | 20.400 | 21.424 | 23.537 | 36.869 |
| Western Region | 14.877 | 19.391 | 24.837 | 33.274 | 34.467 | 37.133 | 29.650 | 27.230 | 26.499 | 27.512 | 29.505 | 43.139 |
References
- Yang, H.C.; Syarifuddin, F.; Chang, C.P.; Wang, H.J. The Impact of Exchange Rate Futures Fluctuations on Macroeconomy: Evidence from Ten Trading Market. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2021, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenev, V.; Landvoigt, T.; Shultz, P.J.; Nieuwerburgh, S.V. Can Monetary Policy Create Fiscal Capacity; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozera, A.; Standar, A.; Satoła, Ł. Managing Rural Areas in the Context of the Growing Debt of Polish Local Government Units. Agriculture 2020, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, N.; Luo, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, K. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Land Marketization and Its Driving Forces for Sustainable Urban-Rural Development in Shaanxi Province in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Zou, S.; Chen, Y.; Nover, D.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y. Sustainable water management for cross-border resources: The Balkhash Lake Basin of Central Asia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 1931–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, X.; Pei, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Identifying the spatiotemporal dynamic of PM 2.5 concentrations at multiple scales using geographically and temporally weighted regression model across China during 2015–2018. Sci. Total Env. 2021, 751, 141765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Luo, P.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Huo, A.; Wang, Z. A bibliometric analysis of the research on Sponge City: Current situation and future development direction. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Duan, W.; Chen, Y. Rapidly declining surface and terrestrial water resources in Central Asia driven by socio-economic and climatic changes. Sci. Total Env. 2021, 784, 147193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumov, I.V.; Nikulina, N.L. Scenario modelling of the impact of the dynamics of public debt on the gross regional product of Russian regions. Financ. Theory Pract. 2021, 6, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yared, P. Rising Government Debt: Causes and Solutions for a Decades-Old Trend. J. Econ. Perspect. 2019, 33, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Luong, T.T. Fiscal Policy, Institutional Quality, and Public Debt: Evidence from Transition Countries. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Duan, L.; Si, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Mulder, J. Long-Term 15N Balance After Single-Dose Input of 15N-Labeled NH4+ and NO3− in a Subtropical Forest Under Reducing N Deposition. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2021, 35, 6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.E. On the mechanics of economic development. J. Monet. Econ. 1988, 22, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, M.R.; Kenneth, S.R. The EIB Project Bond Credit Enhancement Initiative to Promote Transport Investments in the European Union. Suvrem. Promet-Mod. Traffic 2015, 35, 17–20. Available online: http://worldcat.org/issn/03511898 (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Minea, A.; Parent, A. Is High Public Debt Always Harmful to Economic Growth? Reinhart and Rogoff and some complex nonlinearities. Work. Pap. 2012, 18, pp. 1–23. Available online: https://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs-00700471/document (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Wu, Y. Local Government Debt and Economic Growth in China. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2020, 18, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildreth, W.B.; Miller, G.J. Debt and the Local Economy: Problems in Benchmarking Local Government Debt Affordability. Public Budg. Financ. 2002, 22, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhao, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhou, M.; Lyu, J. Control and remediation methods for eutrophic lakes in the past 30 years. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Lustig, H.; Nieuwerburgh, S.V.; Xiaolan, M.Z. What Drives Variation in the U.S. Debt/Output Ratio? The Dogs that Didn’t Bark. In NBER Working Paper Series; National Bureau Of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w29351/w29351.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Barro, R.J. Economic Growth in a Cross Section of Countries. Q. J. Econ. 1991, 106, 407–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Hydrological Variations and Their Impacts on Vegetation in Semiarid Areas from Multiple Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coibion, O.; Gorodnichenko, Y.; Weber, M. Fiscal Policy and Households’ Inflation Expectations: Evidence from a Randomized Control Trial. In NBER Working Paper Series; National Bureau Of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w28485/w28485.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Smets, F.; Wouters, R. An Estimated Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model of the Euro Area. J. Eur. Econ. Assoc. 2003, 1, 1123–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, U.; Presbitero, A.F. Public debt and economic growth: Is there a causal effect? J. Macroecon. 2014, 41, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D. Low investment and large LDC debt in the 1980’s. Am. Econ. Rev. 1993, 83, 437–449. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/a/aea/aecrev/v83y1993i3p437-449.html (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Elmeskov, J.; Sutherland, D. Post-crisis Debt Overhang: Growth Implications Across Countries. In Proceedings of the Second International Research Conference 2012: “Monetary Policy, Sovereign Debt and Financial Stability: The New Trilemma”, Mumbai, India, 1–2 February 2012; Reserve Bank of India: Kolkata, India, 2012. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1997093 (accessed on 31 August 2012).
- Woo, J.; Kumar, M.S. Public Debt and Growth. Economica 2015, 82, 705–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattillo, C.; Poirson, H.; Ricci, L.A. External Debt and Growth. Rev. Econ. Inst. 2011, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, C.; Rother, P. The impact of Government Debt on Growth An Empirical Investigation for the Euro Area. Rev. Econ. 2011, 62, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caner, M.; Grennes, T.; Koehler-Geib, F. Finding the Tipping Point—When Sovereign Debt Turns Bad. In Policy Research Working Papers; World Bank Group: Bretton Woods, NH, USA, 2010; Available online: https://elibrary.worldbank.org/doi/abs/10.1596/1813-9450-5391 (accessed on 31 August 2010).
- Reinhart, C.; Kenneth, M.; Rogoff, S. Growth in a Time of Debt. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J. Land financing and economic growth: Evidence from Chinese counties. China Econ. Rev. 2018, 50, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Huo, A.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Nover, D. Heavy Metals in Water and Surface Sediments of the Fenghe River Basin, China: Assessment and Source Analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3072–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.; Jalles, J.T. Growth and Productivity: The role of Government Debt. International Review of Economics & Finance 2013, 25, 384–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Mu, D.; Xue, H.; Ngo-Duc, T.; Dang-Dinh, K.; Takara, K.; Schladow, G. Flood inundation assessment for the Hanoi Central Area, Vietnam under historical and extreme rainfall conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chen, J. The Role of Internally Financed Capex in Rising Chinese Corporate Debts. Comp. Econ. Stud. 2019, 61, 413–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X. China’s Sovereign Debt: A Balance-Sheet Perspective. China Econ. Rev. 2013, 31, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yao, S.; Hu, P.; Lin, Y. Optimal government investment and public debt in an economic growth model. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 45, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, W.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. Investing Like Conglomerates? When Local Governments Diversify Beyond Public Services; BIS Working Papers No 920; Bank for International Settlements: Basel, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3862686 (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Luo, P.; Mu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, W.; Mishra, B.K.; Huo, A.; Zhou, M.; Lyu, J.; Hu, M.; Duan, W.; et al. Exploring sustainable solutions for the water environment in Chinese and Southeast Asian cities. Ambio A J. Hum. Environ. 2021, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Yang, W. Does financial development influence CO2 emissions? A Chinese province-level study. Energy 2020, 200, 117523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Yu, T.; Gu, J.; Wen, H. Land assets, urban investment bonds, and local governments’ debt risk, China. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2020, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Chen, S.; Dong, Z. Economic Fluctuation, Local Government Bond Risk and Risk-Taking of City Commercial Banks. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Du, X. Holding the market under the stimulus plan: Local government financing vehicles’ land purchasing behavior in China. China Econ. Rev. 2018, 50, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, R.D.; Vaden, D. Modeled salt density for nuclear material estimation in the treatment of spent nuclear fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 404, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engwerda, J.; van Aarle, B.; Anevlavis, T. Debt stabilization games in a monetary union: What are the effects of introducing eurobonds? J. Macroecon. 2019, 59, 78–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Córdoba, G.F.; Molinari, B.; Torres, J.L. Public Debt Frontier: A Python Toolkit for Analyzing Public Debt Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Regional Economic Growth and Spillover Effects: An Analysis of China’s Pan Pearl River Delta Area. China World Econ. 2012, 20, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilscher, J.; Raviv, A.; Reis, R. Inflating Away the Public Debt? An Empirical Assessment. In NBER Working Paper Series; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w20339/w20339.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Yang, W.; Zhao, J. Study on China’s Economic Development from the Perspective of Strong Sustainability. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2020, 65, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodrick, R.J.; Prescott, E.C.; Postwar, U.S. Business Cycles: An Empirical Investigation. J. Money Credit Bank. 1997, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, J. Impact of Environmental Pollution on Health-Evidence from Cities in China. Soc. Work Public Health 2020, 35, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.C.; Tan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Shulmeister, J.; et al. Prehistoric and historic overbank floods in the Luoyang Basin along the Luohe River, middle Yellow River basin, China. Quat. Int. 2019, 521, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, D.K.; Kehoe, P.J. International Evidence on the Historical Properties of Business Cycles. Am. Econ. Rev. 1992, 82, 864–888. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, F.; Coffman, D.M.; Xia, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z. China’s Urban Construction Investment Bond: Contextualising a Financial Tool for Local Government. Land Use Policy 2020, 112, 105153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ban, L. The Green Sustainable Economic Development Model under Sustainable Use of Energy and Pollution Control. Theor. Econ. Lett. 2013, 3, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wen, J.; Deng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, C.P. Is Higher Government Efficiency Bringing about Higher Innovation. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2021, 27, 626–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Maskey, S.; Chaffe, P.L.B.; Luo, P.; He, B.; Wu, Y.; Hou, J. Recent Advancement in Remote Sensing Technology for Hydrology Analysis and Water Resources Management. Remote. Sens 2021, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, W.; Qi, X. The spatial-temporal evolution and spatial convergence of ecological total factor productivity in china. Energy Environ. 2020, 14, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yang, W. Short-run forecast and reduction mechanism of CO2 emissions: A Chinese province-level study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Saha, S.; Bhowmik, D. The Causal Nexus between Public Debt and Economic Growth, A Multivariate Time Series Analysis: Experience from a SAARC Nation. Glob. J. Hum.-Soc. Sci. Res. 2020, 20, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, W. Local government debt and regional economic growth in China. China Political Econ. 2019, 2, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Tian, Y.; Lei, A.; Boadu, F.; Ren, Z. The Effect of Local Government Debt on Regional Economic Growth in China: A Nonlinear Relationship Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeper, E.M.; Leith, C.; Liu, D. Optimal Time-Consistent Monetary, Fiscal and Debt Maturity Policy. J. Monet. Econ. 2021, 117, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z. An Empirical Study on the Impact of Foreign Strategic Investment on Banking Sustainability in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Definition | Source |
|---|---|---|
| lnGDP | Economic growth: ln(province’s real GDP) | CSY |
| GDPFlu | Economic fluctuations: province’s GDP fluctuations | Calculation |
| lnDebt | Government debt: ln(province’s government debt) | Wide Database |
| DebtFlu | Government debt fluctuations: province’s government debt fluctuations | Calculation |
| Urb | Urbanization level: number of province’s urban population/total province’s population | PSY |
| Indus | Industrial structure: province’s tertiary sector value added/province’s GDP | CSY |
| Pop | Population growth: province’s (births-deaths)/total province’s annual average | CSY |
| Open | Opening level of provinces: total imports and exports/province’s GDP | PSY |
| Gov | Public budget expenditure levels: total local general public budget expenditure/province’s GDP | PSY |
| Tax | Level of province’s tax liability: total annual province’s government tax revenue/province’s GDP | Wide Database |
| Edu | Province’s Human capital level: province’s average years of education | PSY |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnGDP | lnGDP | lnGDP | lnGDP | lnGDP | |
| L1-lnDebt | 0.024 *** | 0.020 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.023 *** | 0.016 *** |
| (6.910) | (2.640) | (4.310) | (5.500) | (4.030) | |
| L1- | / | / | / | / | −0.001 *** |
| lnDebt2 | / | / | / | / | (−3.560) |
| Urb | 0.040 *** | 0.032 *** | 0.050 *** | 0.051 *** | 0.039 *** |
| (20.020) | (8.220) | (13.470) | (19.810) | (19.550) | |
| Indus | 0.005 *** | 0.011 *** | −0.003 | 0.001 | 0.005 *** |
| (3.890) | (4.320) | (−1.340) | (0.430) | (4.010) | |
| Pop | −0.007 * | −0.006 | −0.011 | −0.006 | −0.006 * |
| (−1.790) | (−0.930) | (−1.550) | (−1.300) | (−1.670) | |
| Open | −0.003 *** | −0.002 *** | −0.012 *** | 0.001 | −0.003 *** |
| (−8.270) | (−4.410) | (−3.840) | (0.390) | (−8.440) | |
| Gov | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.007 *** | −0.001 | 0.002 |
| (1.030) | (0.370) | (2.770) | (−0.240) | (1.020) | |
| Tax | −0.015 *** | −0.016 * | −0.029 ** | −0.002 | −0.017*** |
| (−3.080) | (−1.780) | (−2.470) | (−0.280) | (−3.520) | |
| Edu | 0.164 *** | 0.208 *** | 0.104 *** | 0.095 *** | 0.151 *** |
| (10.920) | (7.330) | (3.340) | (5.440) | (10.010) | |
| Cons | 5.783 *** | 5.562 *** | 6.480 *** | 5.687 *** | 5.954 *** |
| (43.700) | (17.180) | (28.110) | (39.310) | (43.050) | |
| Province fixed effet | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effet | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| r2 | 0.955 | 0.935 | 0.961 | 0.972 | 0.957 |
| N | 330.000 | 121.000 | 88.000 | 121.000 | 330.000 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDPFlu | GDPFlu | GDPFlu | GDPFlu | |
| L1-DebtFlu | 0.009 * | 0.001 | −0.003 | 0.016 ** |
| (1.700) | (0.050) | (−0.320) | (2.120) | |
| UrbFlu | 0.004 | 0.011 ** | −0.024 *** | 0.002 |
| (1.290) | (2.460) | (−3.970) | (0.007) | |
| IndusFlu | −0.002 *** | −0.004 *** | −0.001 | −0.0002 |
| (−4.090) | (−3.680) | (−1.450) | (−0.200) | |
| PopFlu | 0.002 ** | −0.002 | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (1.990) | (−1.270) | (4.070) | (3.380) | |
| OpenFlu | −0.002 *** | −0.003 *** | −0.005 *** | −0.002 ** |
| (−7.300) | (−6.480) | (−6.200) | (−2.340) | |
| GovFlu | 0.001 | 0.001 | −0.002 * | −0.001 |
| (0.910) | (1.040) | (−1.960) | (−0.890) | |
| TaxFlu | 0.003 *** | 0.001 | 0.016 *** | 0.015 *** |
| (3.340) | (1.280) | (6.280) | (5.500) | |
| EduFlu | 0.0001 | −0.0001 | −0.003 | 0.006 |
| (0.120) | (−0.020) | (−0.410) | (0.780) | |
| Adj.r2 | 0.445 | 0.516 | 0.734 | 0.461 |
| N | 330.000 | 121.000 | 88.000 | 121.000 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDPFlu | GDPFlu | GDPFlu | GDPFlu | |
| L1-DRFlu | 0.008 * | 0.005 | −0.002 | 0.014 * |
| (1.940) | (0.830) | (−0.210) | (1.680) | |
| UrbFlu | 0.006 | 0.010 *** | −0.019 *** | 0.005 |
| (1.550) | (2.880) | (−3.910) | (0.830) | |
| IndusFlu | −0.002 ** | −0.004 * | −0.0001 | −0.0001 |
| (−2.220) | (−1.700) | (−1.430) | (−0.120) | |
| PopFlu | 0.002 | −0.002 | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (1.460) | (−1.080) | (3.130) | (2.920) | |
| OpenFlu | −0.002 *** | −0.002 *** | −0.005 *** | −0.002 *** |
| (−4.140) | (−3.710) | (−6.160) | (−4.170) | |
| GovFlu | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | −0.001 | −0.0004 |
| (0.110) | (0.630) | (−1.330) | (−0.510) | |
| TaxFlu | 0.003 ** | 0.002 *** | 0.013 ** | 0.009 *** |
| (2.480) | (2.840) | (2.280) | (2.590) | |
| EduFlu | 0.0003 *** | −0.001 | −0.010 | 0.003 |
| (5.620) | (−0.880) | (−0.880) | (0.360) | |
| Adj.r2 | 0.408 | 0.526 | 0.605 | 0.462 |
| N | 330.000 | 121.000 | 88.000 | 121.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, P.; Guo, L. Impact of China’s Provincial Government Debt on Economic Growth and Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031474
Yang W, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Deng P, Guo L. Impact of China’s Provincial Government Debt on Economic Growth and Sustainable Development. Sustainability. 2022; 14(3):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031474
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wanping, Zhenya Zhang, Yajuan Wang, Peidong Deng, and Luyao Guo. 2022. "Impact of China’s Provincial Government Debt on Economic Growth and Sustainable Development" Sustainability 14, no. 3: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031474
APA StyleYang, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Deng, P., & Guo, L. (2022). Impact of China’s Provincial Government Debt on Economic Growth and Sustainable Development. Sustainability, 14(3), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031474






