Assessment of K-Struvite Precipitation as a Means of Nutrient Recovery from Source Separated Human Urine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Analytical Procedure and Instruments
2.3. Precipitation Experiments
2.4. Equilibrium Time and Temperature
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of pH
3.2. Precipitation with Different Stoichiometry
3.3. Dissolution of Precipitate
3.4. Potassium Recovery from Human Urine
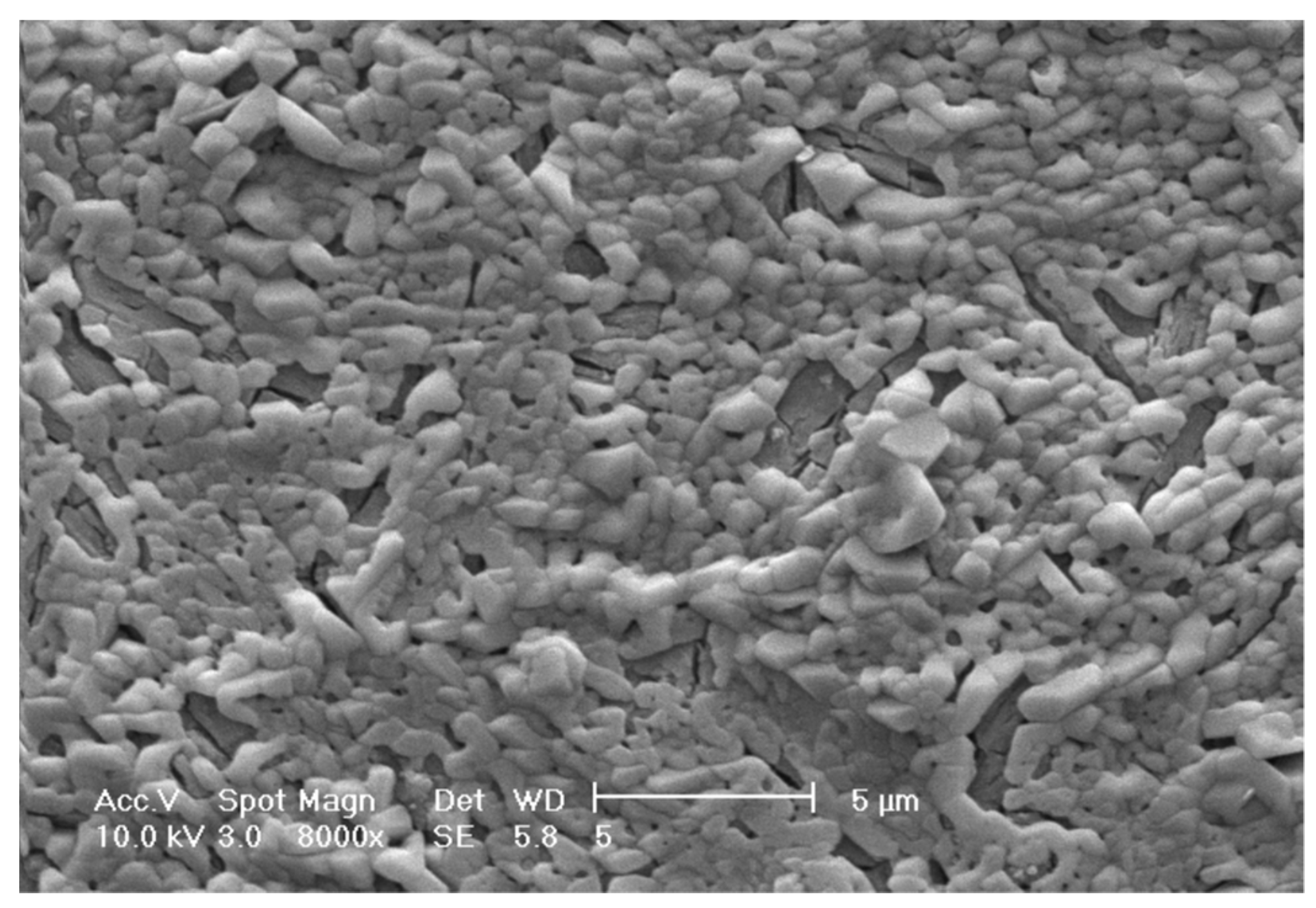
3.5. Solid Phase Analyses
4. Conclusions
- In the case of synthetic samples, K recovery efficiency was found to be dependent on initial K concentration, reaction stoichiometry, and pH.
- K recovery efficiencies reduced as the initial K concentration decreased. The lowest K recovery efficiency (7%) was obtained for initial K concentration of 390 mg K L−1 at stoichiometric dose.
- A 100% excess dose of Mg and P (K/Mg/P: 100/200/200 mM) yielded K recovery efficiency of 85% corresponding to a maximum one for synthetic samples at pH 10.02. Almost equal K recovery efficiency (87%) was obtained for synthetic human urine at pH 10.04 and 100% excess dose of Mg and P.
- In all these precipitation experiments performed using synthetically prepared samples, P and Mg were almost completely precipitated.
- As evidenced by XRD results, K-struvite did not precipitate alone, but its precipitation was accompanied by other solids, specifically Mg3(PO4)2, MgNaPO4·7H2O, and MgHPO4·7H2O.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O.; Işlek, Ç.; Erdinç, E.; Hüskalar, S.; Tatlı, M.B. Nitrogen recovery by urea hydrolysis and struvite precipitation from anthropogenic urine. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O.; Udert, K.M. Transfer into the solid phase. In Source Separation and Decentralization for Wastewater Management; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; pp. 351–365. [Google Scholar]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O.; Tatlı, B.M.; Topcuoglu, S. Nitrogen recovery by struvite precipitation from anthropogenic nutrient solution. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2006, 15, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Tünay, O.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Tatlı, M.B. Nitrogen removal and recovery from human urine by struvite precipitation. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2009, 3, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorick, D.; Macura, B.; Ahlström, M.; Grimvall, A.; Harder, R. Effectiveness of struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping for recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from anaerobic digestate: A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O.; Çetin, M.; Ölmez, T. Assessment of magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation for the treatment of leather tanning industry wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tünay, O.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Orhon, D.; Kolcak, S. Ammonia removal by magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation in industrial wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Ölmez, T.; Doğruel, S.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O. Assessment of source-based nitrogen removal alternatives in leather tanning industry wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tünay, O.; Yelmez, Z.B.; Ölmez, T.; Kabdaşlı, I. Residual COD reduction in biologically treated leather tanning effluents by advanced treatment processes. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2006, 101, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Ölmez, T.; Tünay, O. Nitrogen removal from tannery wastewater by protein recovery. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O.; Özcan, P. Application of struvite precipitation coupled with biological treatment to slaughterhouse wastewaters. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, D.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Ding, L. Recovery and removal of nutrients from swine wastewater by using a novel integrated reactor for struvite decomposition and recycling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Gurel, M.; Tunay, O. Characterization and Treatment of Textile Printing Wastewaters. Environ. Technol. 2000, 21, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Şafak, A.; Tünay, O. Bench-scale evaluation of treatment schemes incorporating struvite precipitation for young landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Pretreatment of ammonium removal from landfill leachate by chemical precipitation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaslı, I.; Tünay, O.; Öztürk, I.; Yılmaz, S.; Arıkan, O. Ammonia removal from young landfill leachate by magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation and air stripping. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, K.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M. Treatment options for nanofiltration and reverse osmosis concentrates from municipal wastewater treatment: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 2049–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Sertaç, B.; Tünay, O. Nutrient removal from human urine by chemical precipitation. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 852–856. [Google Scholar]
- Kuşcuoğlu, S. Determination of K-struvite Application Bases. Master’s Thesis, İstanbul Technical University, İstanbul, Turkey, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sertaç, B. Recovery of Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal from Source-Separated Human Urine by Chemical Precipitation. Master’s Thesis, İstanbul Technical University, İstanbul, Turkey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.I.; Weon, S.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Koopman, B. Removal of nitrogen and phosphate from wastewater by addition of bittern. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Curcio, G.M.; Molinari, R. Advances in Struvite Precipitation Technologies for Nutrients Removal and Recovery from Aqueous Waste and Wastewater. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B.; Lunn, G.; Monje, O. Struvite formation and decomposition characteristics for ammonia and phosphorus recovery: A review of magnesium-ammonia-phosphate interactions. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Qian, Y. Simultaneous removal of phosphorus and potassium from synthetic urine through the precipitation of magnesium potassium phosphate hexahydrate. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.W.; Frazier, A.W.; Gurney, E.L. Solubility products of magnesium ammonium and magnesium potassium phos-phates. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1963, 59, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luff, B.B.; Reed, R.B. Thermodynamic properties of magnesium potassium orthophosphate hexahydrate. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1980, 25, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, C.; Xie, T.; Wang, C. The precipitation of magnesium potassium phosphate hexahydrate for P and K recovery from synthetic urine. Water Res. 2015, 80, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlinger, K.N.; Young, T.M.; Schroeder, E.D. Predicting struvite formation in digestion. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O. Nutrient recovery by struvite precipitation, ion exchange and adsorption from source-separated human urine2a review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2018, 7, 106–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Qian, Y. Laboratory experiments on simultaneous removal of K and P from synthetic and real urine for nutrient recycle by crystallization of magnesium–potassium–phosphate–hexahydrate in a draft tube and baffle reactor. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, N.; Tang, S. Comparison of different K-struvite crystallization processes for simultaneous potassium and phosphate recovery from source-separated urine. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmadewanthi; Liu, J.C. Recovery of phosphate and ammonium as struvite from semiconductor wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 64, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Recovery from Sludge-Fermentation Liquid Mixture and Application of the Fermentation Liquid to Enhance Municipal Wastewater Biological Nutrient Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6164–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilsenach, J.A.; Schuurbiers, C.A.H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Phosphate and potassium recovery from source separated urine through struvite precipitation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Atalay, Z.; Tünay, O. Effect of solution composition on struvite crystallization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Sun, H.J. Crystal structure of a new phosphate compound, Mg2KNa(PO4)2·14H2O. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 2991–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, K.-N.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, C.-W.; Zheng, M. Recovery of Phosphorus and Potassium from Source-Separated Urine Using a Fluidized Bed Reactor: Optimization Operation and Mechanism Modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 3033–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
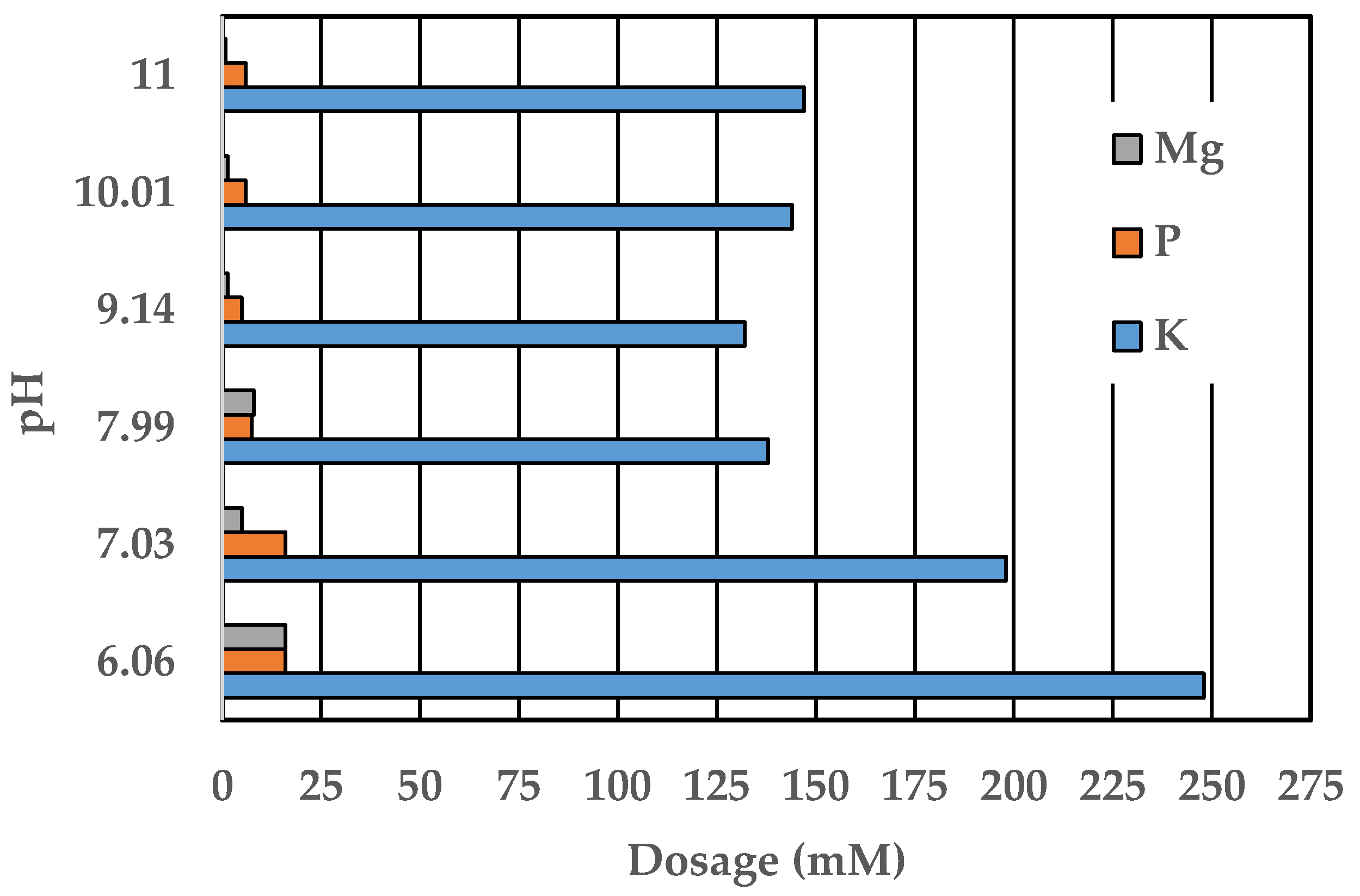
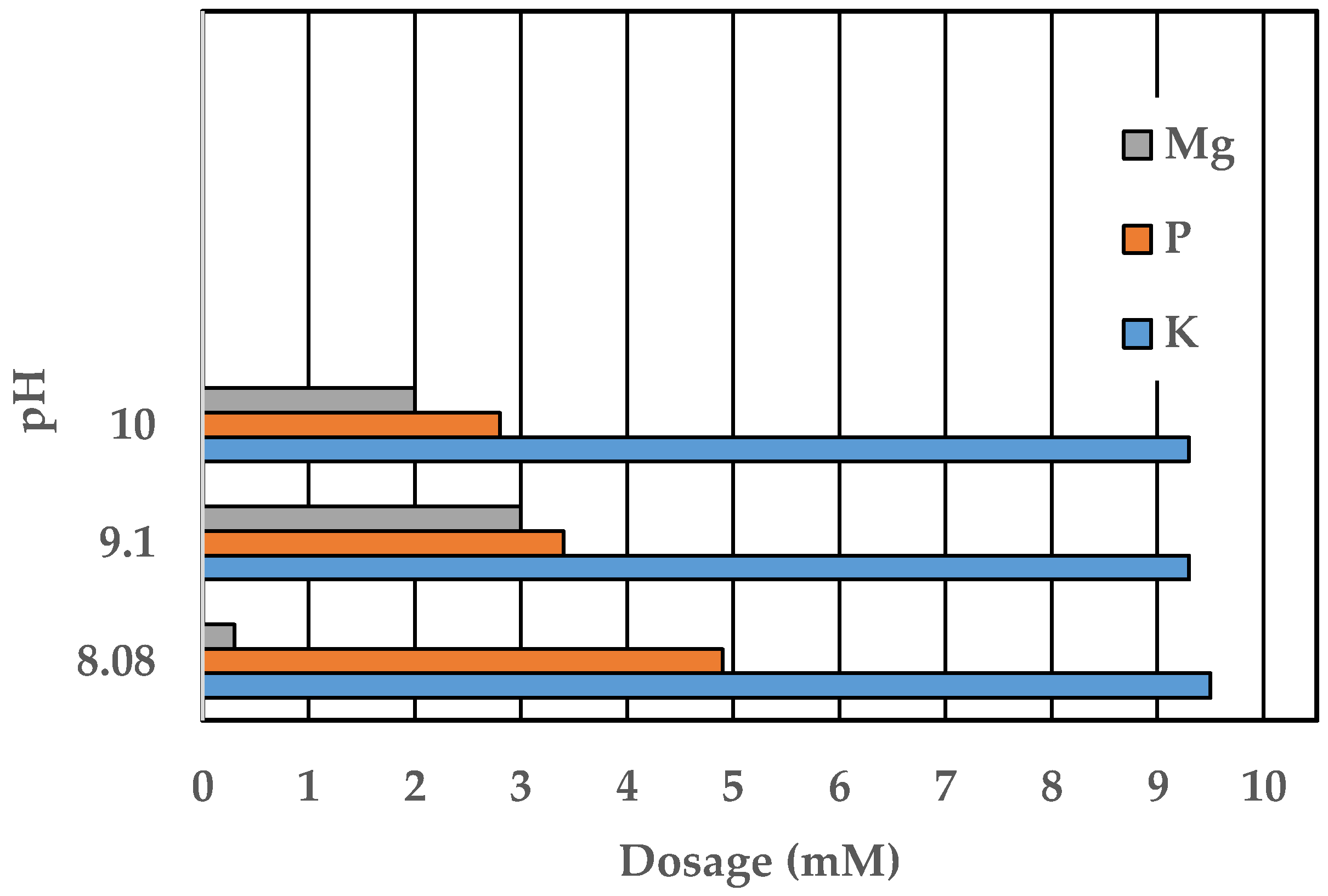



| pH | Initial (mM) | Final (mM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | P | Mg | K | P | Mg | |
| 9.03 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 75 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| 10.05 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 72 | 0.2 | 6 |
| pH | Initial (mM) | Final (mM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | P | Mg | K | P | Mg | |
| 9.02 | 180 | 150 | 150 | 121 | 1.65 | 1.6 |
| 9.02 | 180 | 125 | 125 | 112 | 2.4 | 1.3 |
| 8.99 | 250 | 187 | 187 | 190 | 2.2 | 0.9 |
| pH | Initial (mM) | Final (mM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | P | Mg | K | P | Mg | |
| 9.09 | 180 | 187.5 | 187.5 | 135 | 1.9 | 1.4 |
| 9.07 | 180 | 250 | 250 | 90 | 0.4 | 4 |
| 9.07 | 125 | 250 | 250 | 41 | 0.9 | 3 |
| 9.00 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 17 | 1.9 | 2 |
| 10.03 | 125 | 250 | 250 | 38 | 3 | 0.6 |
| 10.02 | 100 | 200 | 200 | 15 | 0.2 | 1.5 |
| 10.02 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 11 | 0.2 | 1.4 |
| 10.11 | 25 | 50 | 50 | 7 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| 10.08 | 12.5 | 25 | 25 | 6 | 1 | 1.2 |
| 10.12 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 5 | 1.9 | 1.2 |
| K | PO4 | Mg | Na | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mM | 6.5 | 19 | 19 | 7 |
| Initial (mM) | Final (mM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | K:Mg:P | K | P | Mg | K | P |
| 9.40 | 3/1/0.5 | 31.82 | 10.32 | 5.16 | 23 | 3.44 |
| 9.42 | 3/1/1 | 31.82 | 10.32 | 10.32 | 24 | 0.99 |
| 9.39 | 3/1/1.3 | 31.82 | 10.32 | 13.41 | 24 | 0.36 |
| 9.44 | 3/1/1.5 | 31.82 | 10.32 | 15.48 | 25 | 0.14 |
| 9.48 | 1/1/1 | 31.82 | 31.82 | 31.82 | 25 | 0.01 |
| 9.44 | 1/2/2 | 31.82 | 63.64 | 63.64 | 11 | 9.67 |
| 10.04 | 1/2/2 | 31.82 | 63.64 | 63.64 | 4 | 4.78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabdaşlı, I.; Kuşçuoğlu, S.; Tünay, O.; Siciliano, A. Assessment of K-Struvite Precipitation as a Means of Nutrient Recovery from Source Separated Human Urine. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031082
Kabdaşlı I, Kuşçuoğlu S, Tünay O, Siciliano A. Assessment of K-Struvite Precipitation as a Means of Nutrient Recovery from Source Separated Human Urine. Sustainability. 2022; 14(3):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031082
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabdaşlı, Işık, Sezen Kuşçuoğlu, Olcay Tünay, and Alessio Siciliano. 2022. "Assessment of K-Struvite Precipitation as a Means of Nutrient Recovery from Source Separated Human Urine" Sustainability 14, no. 3: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031082
APA StyleKabdaşlı, I., Kuşçuoğlu, S., Tünay, O., & Siciliano, A. (2022). Assessment of K-Struvite Precipitation as a Means of Nutrient Recovery from Source Separated Human Urine. Sustainability, 14(3), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031082







