Abstract
Jollibee is one of the most widely known fast food in Filipino-based restaurants in the world. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted restaurants across the world. The decrease in profit and dividend, and even closure of branches were evident. This study aimed to determine the relationships between Jollibee’s price, food quality, culture/social influence, and service quality through the SERVQUAL dimensions on customer satisfaction during the COVID-19 pandemic using the structural equation modeling (SEM) approach. A total of 303 respondents were recruited using a purposive sampling approach to answer an online survey through social media platforms. This study found that among the factors mentioned, responsiveness, reliability, and assurance dimensions yielded to be statistically insignificant to the service quality. Due to the normal attributes the staff and restaurant have, the different factors were deemed insignificant. At the same time, the service quality was observed to have the largest significant direct relationship with customer satisfaction, followed by the cultural influence, food quality, COVID-19 protocols, and pricing. It was also seen that cleanliness and appearance, empathetic staff, food quality, price, and proper implementation of COVID-19 protocol prevention would lead to high levels of satisfaction among customers in Jollibee fast-food restaurant. Moreover, cultural/social influence has played a big role seeing that the indicators represent the feeling of belongingness since childhood. This study is the first study that analyzed the factors affecting the customer satisfaction of Jollibee. Finally, this study could be used as a basis for fast-food companies and service-related industries to increase its performance by enhancing customer satisfaction worldwide.
1. Introduction
The intensifying competition in the service industry has been continuously expanding and has been a challenge for food businesses [1,2]. Every business focuses on strategies that will provide a competitive advantage over the others [1]. When it comes to strategic responses in food businesses, competitive prices, sales promotion, quality of the food, and good customer service are the key drivers for customer patronization and satisfaction, which will lead to customer loyalty [1].
Customer loyalty is also known to be linked with customer satisfaction [3]. It increases as customer satisfaction increases at a certain level [3,4]. Customer satisfaction is the customer’s reaction to the difference between what they received and what they anticipated [5]. Gerpot et al. [6] proposed that satisfaction is based on how well the services or the products fulfill customer expectations [7]. However, it is evident that customer satisfaction links with customer patronization and business profitability [8]. To which, there might be some changes that may occur in the customer’s behavior due to further developments and changes as time proceeds; such as the Internet characteristics, product attributes, conditions, and situational factors [9]. The best example of these changes is the COVID-19 pandemic which has led people to social distancing and frequent lockdowns, which have caused disruptions in the behavior of the customers [10].
Customers play a significant role in the pricing and service quality they receive [11,12]. Fair pricing and service quality promote trust and leave a branding image to customers. In addition, fair pricing and service quality fulfill customer satisfaction when well managed [11]. This is because customer satisfaction is the key to continuing the business and keeping it on surviving the similar industry [11]. However, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the behavior of consumers changed [13]. Ong et al. [13] pointed out how customers were highly anxious and would rather stay home. To which, online food delivery services have become largely significant [14]. One of the fast-food restaurants that utilized the promotion and delivery is Jollibee.
In the industry of fast-food restaurants in the Philippines, Jollibee has been the dominant market leader with over 600 outlets and over 30 stores abroad [15,16,17]. It always strives for innovative ideas and total customer experience, focusing on customers’ joy and satisfaction [18]. A report created by Beneschan [19] showed higher than 60% of Jollibee stores in the Philippines are franchised, comprising more than 218 branches. This presents the popularity of Jollibee in the country. In addition, Jollibee has been challenging the world by building their footprint across the world. Figure 1 presents the global footprint of Jollibee.
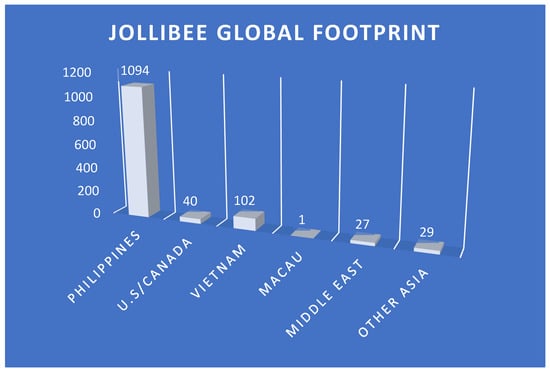
Figure 1.
Jollibee global footprint [20].
It could be seen that the majority of the branches of Jollibee are in the Philippines where they originated. Following which is Vietnam where they have 102 branches and are currently widely popularized in the United States and Canada with 40 branches. Other Asian countries including Macau have 29 and 1, respectively, and 27 in the Middle East. It could be seen that Jollibee is trying to penetrate the market through different countries with its availability [20].
With the aim to be one of the top 5 global fast-food markets [20], the sales became challenging when the COVID-19 pandemic hit [21]. Venzon [21] reported that in the February of 2020, the branch of Jollibee in China was closed due to the pandemic. In addition, Venzon [21] added that the income sales of Jollibee decreased by 14% in the same month. In April of 2020, a decrease in dividend of 62 centavos (0.0115 USD) due to the pandemic hit was reported. The report of Venzon [20] presented that valuation would lead to an increase in customer sales, and that customer loyalty would result in the restoration of the decrease in sales and value [21].
In analyzing customer satisfaction, factors such as the pricing, food quality, cultural influence, and the SERVQUAL dimensions could be utilized. The SERVQUAL dimensions have been adapted and utilized in numerous studies in different service settings, geographic locations, and cultural contexts [22]. In the UK, Nguyen et al. [23] conducted a study in fast food restaurants regarding customer satisfaction using the SERVQUAL dimensions. The study of Nguyen et al. [23] found that tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy had a significant positive effect on customer satisfaction. In Australia, a similar study was also conducted by Lee and Hing [24]. They measured the quality of restaurant operations using the SERVQUAL dimensions. However, both the study of Nguyen et al. [23] and Lee and Hing [24] only considered the SERVQUAL dimensions as a factor in determining customer satisfaction. Other factors that may influence customer satisfaction may also include the price and product quality. Moreover, these studies only used a small sampling size, which was conducted before the occurrence of the COVID-19 pandemic. Finally, in the Philippines, the effects of customer service quality and product quality on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty were studied by Altejar and Dizon [17]. The findings of the study of Altejar and Dizon [17] showed that customer service quality and product quality affect customer satisfaction, while customer satisfaction affects customer loyalty. In addition, product quality and service quality were included in the study as factors affecting customer satisfaction. Another factor that may influence customer satisfaction such as price, may also be included to have a better perspective on the economic effect of the COVID-19 pandemic [13,25]. Most of the SERVQUAL model is often utilized in service quality and application [12]. Thus, it will be interesting to investigate the model’s applicability in fast food restaurants, especially when combined with price, cultural influence, and product quality as an additional factor during the COVID-19 pandemic.
It was stated from the study by Gimeno-Arias et al. [26] that how corporate social responsibility (CSR) is one of the most significant factors affecting customer satisfaction. It was explained that when employees worked cohesively, companies would be able to achieve their goals. The practice presented among employees toward a service being provided also influenced satisfaction [26]. In line with this study, these affirmations were segregated among social and cultural influence on customer satisfaction and the SERVQUAL dimension. In addition, Bahta et al. [27] highlighted how reputation was one of the key factors affecting CSR and financial performance. It could be deduced that since Jollibee has been increasingly becoming popular, their reputation precedes them. To which, food pricing and quality could be influential factors. Overall, these factors may be considered as extended latent variables as explained in the study of Islam et al. [28] wherein reputation, trust, and satisfaction among customers influence their loyalty. Reiterating this would lead to customer loyalty and evident profitability.
As one of the rising fast-food restaurants being recognized throughout the world, the Jollibee fast-food restaurant has been challenged by the pandemic. There is therefore a need to assess the satisfaction of customers to gain the profit loss throughout the stint of the COVID-19 pandemic which may be utilized even after the pandemic. The analysis of different factors affecting customer satisfaction should be explored to better understand the behavior of consumers. This would lead to better strategies and create marketing strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic [25]. Building a sustainable business model during the COVID-19 pandemic is crucial. Ong et al. [25] explained that the need for re-planning and re-strategizing is needed to enhance profitability. The sustainable business model could then be applied even after the COVID-19 pandemic as the new normal is being adopted by consumers in the present.
To which, research questions to understand the gap and objective of this study are as follows:
1. What factors precede customer satisfaction for Jollibee fast-food restaurants in the Philippines?
2. Utilizing structural equation modeling, which factors and indicators are considered significant and insignificant?
3. How do the factors influence customer satisfaction and how can the findings contribute to the current state of Jollibee and other fast-food chains?
The study aimed to correlate the factors affecting customer satisfaction for Jollibee fast-food restaurants in the Philippines by utilizing the SERVQUAL dimensions. The tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, food quality, culture/social influence, service quality, and pricing were investigated concurrently with customer satisfaction. This study could serve as a basis for the company’s value creation and business strategy on how it could increase its number of customers by enhancing customer satisfaction. Moreover, the extended model could be applied and extended among other fast-food restaurants. Lastly, the findings of this study could be enforced by other fast-food restaurants or service-related industries for strategy planning worldwide.
The content of this research is as follows: (1) Introduction explaining the background of the study, research gap, related literature, and objectives; (2) theoretical framework and hypotheses building; (3) methodology considering participants, questionnaire, data collection, and multivariate analysis; (4) results; (5) discussion, implication, and limitation; and (6) conclusion.
2. Theoretical Framework
Figure 2 shows the theoretical framework for customers’ views of service quality with five SERVQUAL dimensions. These dimensions are tangibles (T), reliability (REL), responsiveness (RES), assurance (A), and empathy (E). Moreover, other factors such as service quality (SQ), culture/social influence (CI), COVID-19 protocols (CP), pricing (P), food quality (FQ), and customer satisfaction (C) have been investigated in the current study. These factors were hypothesized to affect customer satisfaction in Jollibee fast-food restaurants.
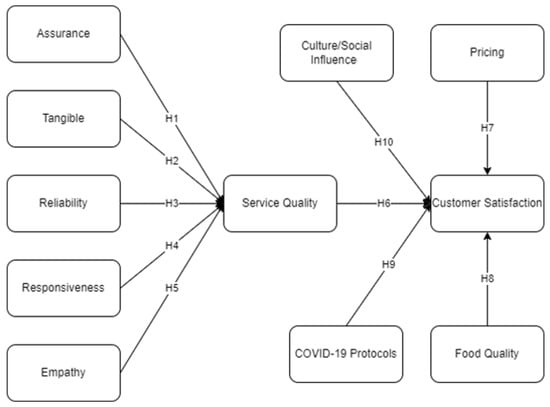
Figure 2.
Theoretical framework.
As part of the CSR, the SERVQUAL dimensions are presented to be individual factors that should be considered by service providers such as fast-food chains. It was highlighted from the study of Gimeno-Arias et al. [26] that the stakeholders such as the employees should be able to provide a thorough and reflective output by their service to enhance the satisfaction among consumers. With this, an increase in industry value will be evident. Thus, the need to assess the SERVQUAL dimensions as an effect of CSR should be considered.
Assurance refers to the staff’s knowledge, courtesy, and ability to carry trust and confidence [29]. Assurance is one of the significant dimensions of SERVQUAL, especially when customers feel uncertain about the service provided by the restaurant [30,31]. The assurance is achieved when customers entrusted their decisions regarding the waiter’s recommendations, feel confident regarding the safety of the food, and are capable of voicing their concerns and opinions without arguing or having a fear of insult [30]. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Assurance had a significant effect on service quality.
Tangibles refer to the restaurant’s physical facilities, equipment, and personnel [30,32]. It connects the restaurant’s image and embeds quality to customers [30]. Moreover, the smooth and fast transactions and suitable environment that the customers feel during the service are also part of the tangible dimension. Thus, better service is provided to customers when better tangibles are given by the organization or industry [12]. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Tangibles had a significant effect on service quality.
Reliability is the staff’s ability to provide service dependably, accurately and promptly when responding to the customer’s demand [11,31,32]. In restaurants, reliability correctness in responding to customer requests is about the preparation of the menu item, reservations, food order, and accurate billing [30]. Thus, the more the service is reliable, the better it will influence good service quality. To which, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Reliability had a significant effect on service quality.
Responsiveness refers to the ability, flexibility, and willingness of the service providers to respond to customers’ requests and concerns [11,30,33]. In addition, the responsiveness of the employees in helping the customers’ problems using services influenced customer satisfaction [34]. Thus, the more responsive the staff are in attending to the customers’ requests, the better the service quality is perceived. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Responsiveness had a significant effect on service quality.
Empathy pertains to the staff’s ability to provide care and individualized attention to the customers [11,30,35], for example, when the customers were treated as individuals when service was provided [29]. Without it, customers will be dissatisfied with the service that they received [35]. Thus, empathy hugely influences customer satisfaction [33]. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
Empathy had a significant effect on service quality.
One of the dominant factors affecting customer satisfaction is service quality [36,37,38]. Customers are the individuals who receive the products and services and evaluate its quality if it has satisfied or exceeded their needs and expectations [37,39]. In the restaurant industry, customers judge the food quality and the service quality that they had throughout their dining involvement [40]. Some studies revealed that service quality was more significant than food quality when considering dining satisfaction [30]. Moreover, the findings of the study of Yuksel and Yusel [41] found that service quality influenced customer satisfaction. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
Service quality had a significant effect on customer satisfaction.
Price is one of the significant factors affecting customer satisfaction. It is also deemed to be subsequent to service quality when considering customer satisfaction [42]. Dai [43] found that price fairness has a strong influence on customer satisfaction [43,44]. The more the product is affordable, the more it will satisfy and make the customers buy the product repetitively [45]. Therefore, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 7 (H7).
Pricing had a significant effect on customer satisfaction.
Food is one of the most critical factors of the overall dining experience [46]. Its quality captivates the customers and significantly impacts customer satisfaction [46,47,48]. In the restaurant industry, customer satisfaction is achieved by focusing on food quality [49]. In addition, Rozekhi et al. [47] found that food quality has a significant effect on customer satisfaction. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 8 (H8).
Food quality had a significant effect on customer satisfaction.
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the daily routines of the people [13,48]. Thus, the preferences and perspectives of the customers changed [25,35,50]. Around 1100 respondents from the United States (U.S) were asked if their dining behaviors have remained since November 2020 [51]. Significantly, 55% said that their breakfast behaviors changed, 51% reported that their lunch behaviors have changed, and 53% reported that their dinner behaviors changed [48]. In addition, 72% of the respondents reported that the number of the COVID-19 cases would be the basis of their decision to dine outside or not [51]. It could be posited that COVID-19 affected the habit of people since they considered this factor in their decision [52]. In addition, the study of Ong et al. [13,25] and German et al. [53] also highlighted the change in behavior of people during the COVID-19 pandemic. It was seen that with proper protocol and enhanced safety, consumers spend time and attempt to affirm the service being provided. With the danger and caution to get infected with the virus, people are more hesitant to obtain the service being offered. In relation to this study, people may be more hesitant to buy food even online due to the COVID-19 pandemic as a preventive measure [54]. Thus, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 9 (H9).
COVID-19 had a significant effect on customer satisfaction.
Culture bears a powerful influence in controlling human behavior [52]. Moreover, culture further affects the customers’ behavior about their decisions on making purchases. In addition, marketing researchers also consider this as one of the major drivers and determinants for customer behavior [13,52,55]. Moreover, marketing researchers also used cultural dimensions to measure its impact on customer behavior [13,25,35]. Hence, it was hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 10 (H10).
The cultural influence had a significant effect on customer satisfaction.
3. Methodology
3.1. Participants
A total of 303 respondents answered the survey. They were the individuals who are regularly eating or who have experienced eating at Jollibee fast food, Philippines. Through purposive sampling, an online questionnaire was utilized to collect the data due to the strict implementation of lockdowns brought by the COVID-19 pandemic. The data were collected from December 2021 until January 2022 through different social media platforms. Following the study of German et al. [53], the Yamane Taro formula as seen in equation 1 was utilized. It was suggested that with 62.6 million Filipinos at a 10% margin of error, 100 participants could be utilized. The collected data exceeded the calculated sample size during the collection period with no non-response bias. Upon the collection of data, a common method of bias analysis using the Harman’s Single Factor test was conducted. It was seen that a 36.12% result was obtained, lower than the 50% threshold [54]. Thus, the collected data were seen to be acceptable.
3.2. Questionnaire
The questionnaire utilized in this study was from studies that considered the SERVQUAL dimensions [11,12,13,14,35]. Moreover, questions used in service and retail businesses to assess the customers’ perception of service quality were also adapted for this study [56]. Prior to distribution, a validation was considered with 150 respondents. A value of 0.803 for Cronbach’s alpha was obtained, therefore, was deemed acceptable for dissemination [13,14]. The sample survey questionnaire that was utilized in this study is presented in Appendix A.
3.3. Statistical Analysis: Structural Equation Modeling
In analyzing the relationships between the service quality, food quality, and price on customer satisfaction, the structural equation modeling (SEM) was utilized. It is a data analysis technique driven by theory and is used to evaluate the prior identified hypotheses concerning the causal relations of the latent variables and observed indicators [57]. It was explained by Hair et al. [58] that how SEM is a multivariate analysis that can assess the causal relationship of factors of multiple independent variables with dependent variables. It has been widely considered in several studies that assessed service quality, intention, and customer satisfaction among service providers and related industries.
Taking for example the study of Bahta et al. [27], they assessed the performance of small and medium enterprises using partial least square SEM (PLS-SEM). It was discussed by Dash and Paul [59] that how PLS-SEM is utilized for research with theories being justified while covariance based SEM (CB-SEM), the SEM utilized in this study is utilized for research with existing frameworks. In line with this study, an established framework utilizing the SERVQUAL dimension to correlate customer satisfaction with extended latent variables was used. In addition, Ong et al. [13] presented how SEM would be a viable tool for assessing human behavior-related studies.
Figure 2 presents the SEM framework utilized in this study. A total of 45 questionnaire items were used in this study under the tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, service quality, food quality, and pricing. Moreover, a total of five items were used to assess the customers’ satisfaction. Different studies have utilized SEM in identifying customer satisfaction with SERVQUAL dimensions [13,17,22,23,24,25,28]. Thus, SEM could be utilized in assessing customer satisfaction among Jollibee consumers.
4. Results
Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics of the respondents. The majority of the respondents came from 21–26 years old (57.09%), followed by 27–33 years old (16.83%), 15–20 years old (10.20%), and the rest are older than 34 years old. Most of the respondents eat at Jollibee at least once a month (38.95%), once a week (28.71%), or twice a week (22.11). To which, most of the respondents are employed (61.06%), students (21.12%), and unemployed (11.22%) with no dependents (76.90%). Moreover, majority of the respondents have low monthly income (11,999 and below to 20,999 PhP; 228.30 USD and below to 399.55 USD) which is 54.45% and middle class (21,999–40,999 PhP; 418.57–780.09 USD) with 30.69%. Lastly, consumers would eat at Jollibee even without discounts or coupons (89.77%).

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of respondents (n = 303).
Figure 3 represents the initial SEM model of the study. From Table 2, it was found that pricing, culture/social influence, tangibles, empathy, COVID-19 protocols, overall service quality, and food quality were significant to customer satisfaction. However, responsiveness, reliability, and assurance yielded insignificant results. In addition, some of the indicators under tangibles and COVID-19 protocols, such as T5 and CP2 were observed to have low factor loadings (less than 0.05). Thus, a revised model, which is shown in Figure 4, was derived by eliminating the mentioned variables and indicators [13]. Moreover, modification indices were performed to enhance the model fit of the study [14].
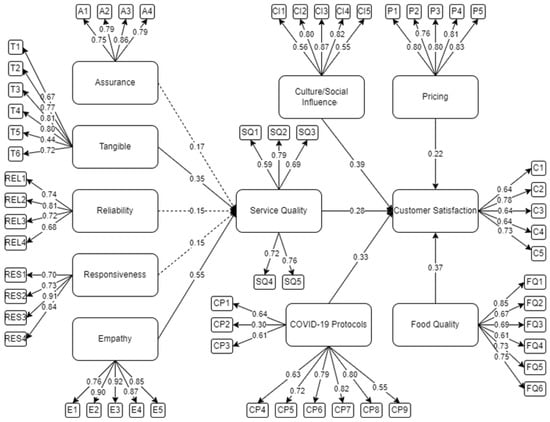
Figure 3.
Initial SEM results.

Table 2.
Relationship between the factors.
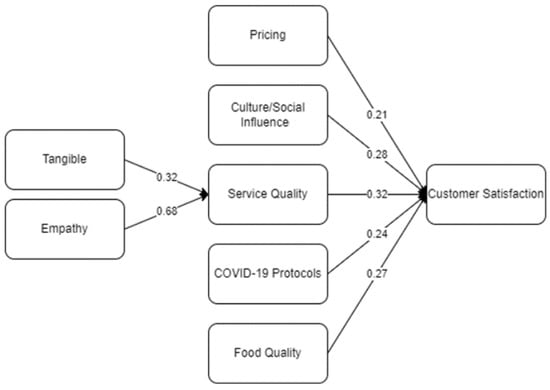
Figure 4.
Final SEM results.
Table 3 presents the model’s reliability and validity with Cronbach’s alpha (CR) values, factor loading, average extracted variance (AVE), and composite reliability (Re). In evaluating the validity of each construct, the value of the factor loading served as a basis. A good factor loading has a value greater than 0.5, which is considered significant [58]. While for the CR value and Cronbach’s value, the minimum validity required is 0.7 [60,61]. Moreover, in measuring its validity through AVE, an ideal value should be greater than 0.4 [62]. All the limits mentioned in this study have exceeded the cut-off values. In addition, a test for multicollinearity was conducted. The variance inflation factor (VIF) has presented values less than 5.00 which indicates no multicollinearity among constructs used in this study [63].

Table 3.
Construct reliability and validity.
Table 4 presents the goodness of fit measurement results for the SEM. Measures such as the GFI, AGFI, RMSEA, IFI, TLI, and CFI with their corresponding cut-off values are presented. As seen from the results, the IFI, TLI, and CFI reached the minimum cut-off as per the recommendations of Hair et al. [58] of 0.80; at the same time, the parameter estimates for the GFI and AGFI are approaching 1 [64]. In addition, the RMSEA value is less than 0.07 which indicates that the model utilized is acceptable.

Table 4.
Goodness of fit and parameter estimates.
5. Discussion
Generally, the results of this study showed that tangibles and empathy significantly affect service quality; at the same time, the service quality, COVID-19 protocols, food quality, pricing, and cultural/social influence significantly affect customer satisfaction in Jollibee Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic. Utilizing SEM, different results were seen such as the insignificant effect of responsiveness, reliability, and assurance.
Referring to Figure 4, it was found that assurance does not have a significant relationship with service quality (p-value > 0.05). These findings were contrary to the study of Almohaimmeed [65], who conducted a study about restaurant quality and customer satisfaction. From the study, it was found that assurance does have a significant positive effect on customer satisfaction [65]. In addition, it contradicts the results from the study of Tat et al. [66]; wherein it was found that assurance has the most significant positive relationship with customers’ perceived service quality. These results indicated that the staff are knowledgeable and capable of the service being provided.
It was also seen that reliability was found not to have a significant positive relationship with service quality (p-value > 0.05). Similarly, these findings were contrary to the study of Saad Andaleeb and Conway [42] where they determined that reliability has a significant impact on customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry. Qin and Prybutok [67] examined and investigated the service quality and customer satisfaction in a Chinese restaurant using enhanced SERVPERF. One of the findings in their study suggested that reliability was also a significant part of the service quality dimension, conversely, in examining the customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry [45]. However, they found that reliability has a significant but weak relationship with customer satisfaction.
Third, responsiveness was also found to have an insignificant relationship with service quality (p-value > 0.05). Interestingly, Qin and Prybutok [67] revealed that responsiveness is one of the important dimensions of service quality as opposed to the results of this study. A similar study was conducted by Namkung and Jang [68] where they examined customer satisfaction in restaurants. The findings suggested that the restaurants must give reliability, responsiveness, and assurance importance in order to produce highly satisfied customers. At the same time, Lau et al. [69] found that responsiveness was a slightly significant determinant of customer satisfaction in Chinese restaurants in Hongkong. The results of this study specifically indicate that customer assistance, shorter waiting time, and courteousness of the staff were also the contributing factors to customer satisfaction.
The three attributes, responsiveness, reliability, and assurance have been seen to be present in different branches which explains why it is not considered significant latent variables. The staff is trained and this attribute is part of the service being delivered, evident even in other countries [20]. In addition, Jollibee trains its employees to have good communication skills and be capable of responding to all the requests and concerns of the customers. This results in the insignificance of responsiveness and reliability since these attributes are part of the training and performance of the staff. Thus, with maintenance, these attributes were deemed to be normalized in Jollibee fast-food restaurants.
The tangibles dimension was found to significantly preceded service quality in Jollibee Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic (β: 0.359; p = 0.002). It was found that the indicators under this exogenous latent variable such as the virtual signs and messages to customers, staffs, uniform, store appearance, appearance of the reception area, and store hygiene were deemed to have a significant connection to customer satisfaction. These results were similar to Kincaid et al. [70], where they found that tangibles have a significant direct and indirect effect on customer behavior. Moreover, investigating the impact of service quality on customer satisfaction from different restaurants in Pakistan was conducted by Khan and Shaikh [71]. One of the results of their investigation concluded that responsiveness and tangibles were the customers’ preferred importance when choosing where to dine in a restaurant. These only indicated that customer satisfaction is influenced by virtual signs and messages in the restaurant, staff uniform, overall appearance, and hygiene.
Empathy was found to have a solid link to service quality (β: 0.676; p = 0.002). The indicators under this exogenous latent variable that was found to have a significant relationship with customer satisfaction are when staff understand the needs of the customers, when staffs apologize for the mistakes that they made, when staffs are willing to help the customers, and when staffs are courteous. Lee et al. [72] also found that among the five dimensions of the SERVQUAL dimensions, empathy was significant in preceding the customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in Korean family restaurants [73]. Similarly, in analyzing the customer loyalty to newly open cafes and restaurants in Malaysia, Moorthly et al. [74] revealed that empathy is one of the positively significant factors relating to customer loyalty. Therefore, customer satisfaction heightens staffs’ understanding of the customers’ needs, when staffs apologize for mistakes, and when staffs portray courteousness and willingness to help the customers.
The overall service quality was found to have a relationship with customer satisfaction (β: 0.319; p = 0.001) significantly. The indicators considered were the overall facility appearance, when all the services provided were done accurately, the overall responsiveness of the staffs, when the services and the requests of the customers that were provided were carefully explained, and when the staffs are competent enough to deal with the concerns of the customers. A similar study about the relationship of service quality and customer satisfaction on the repurchase intentions in restaurants was conducted by Mensah and Mensah [75]. The study found that service quality has a significant positive relationship on customer satisfaction. Qin and Prybutok [67] also posited a direct and positive relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction in fast food restaurants. Thus, customers were more satisfied when provided services were prompt, responsive, empathic, accurate, and when the overall store appearance was good.
The pricing of Jollibee Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic was also found to have a significant link with customer satisfaction (β: 0.209; p = 0.018). The indicators under this factor were the compatibility of the price to the food quality, its affordability compared to other fast-food restaurants, and the implementation of discounts, benefits of buying in a package, and the customers’ satisfaction based on its over-all pricing. These findings were similar to the results of Jawabreh et al. [76], where there is a significant link between pricing and customer satisfaction in restaurants. Similarly, the significant relationship of pricing was also consistent with the results found by Ryu and Han [77]. Thus, pricing on the menus portrays a role as one of the determinants of customer satisfaction during the pandemic. With the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the economy such as job loss, Jollibee has been a staple among Filipinos due to its price range of meals.
The food quality was also found to precede customer satisfaction significantly (β: 0.265; p = 0.004). Indicators such as the quality of its fried chicken among competitors, quality of burger among the competitors, quality of the fries among its competitors, quality of its spaghetti among its competitors, quality of sundae ice cream, and its overall food quality were deemed significant. The same result was also found by Rozekhi et al. [47] and is consistent with Kivela et al. [40] and Law et al. [78]. Thus, customers were satisfied with the quality of the foods that were mentioned under this factor. Moreover, there is a significant comparison among other fast-food restaurants. In the Philippines, most of consumers can choose from Burger King, McDonald’s, KFC, etc. With the food quality indicators, it was seen that a lot of Filipinos find the food quality in Jollibee more satisfactory than other fast-food restaurants.
The COVID-19 protocols were found to have a link in customer satisfaction (β: 0.245; p = 0.019). Because the indicators under these factors are designed positively, which would mean that the higher its beta coefficient and its factor loadings, the more it will not precede customer satisfaction. Indicators such as the social distancing, quarantines do not stop customers from buying Jollibee, the use of face masks and face shield did not also precede the customers from buying Jollibee, customers still prefer eating in Jollibee even during the pandemic, customers do also perceive that the pandemic did not affect Jollibee’s food quality, service quality, food pricing, and the total number of cases did not affect them from choosing Jollibee as their fast food preference were deemed significant. This result was opposite to what was posited by Shim et al. [9] and Sheth [10]. From their studies, customers’ behavior changes as time proceeds, especially when it is disrupted by different internal and external factors; specifically, the protocols for the pandemic. Interestingly, despite the impact of the COVID-19 on the restaurant industry, it was found in this study that the COVID-19 pandemic did not preceded the customer satisfaction, behavior, and future intentions in buying Jollibee.
Finally, the cultural/social influence of the Jollibee in the Philippines was found to have a significant relationship on customer satisfaction during the COVID-19 pandemic (β: 0.282; p = 0.001). Indicators that were significant were good tv commercials interconnected with Filipinos’ culture and values, childhood experiences that it has been established with the by Jollibee, the good memories and experiences that it has built to the customers, reminds the good Filipino tradition because of their campaigns, and Jollibee has established memories of the important people with the customers. A similar study was also conducted by Jang and Ha [79], where the influence of cultural experience emotion in restaurants was investigated. The study results deduced that cultural experience emotion is linked with the emotion and authenticity of the food and atmosphere of the restaurant. Thus, establishing good memories and experiences with the customers is one of the determinants of customer satisfaction.
Therefore, it could be deduced that cleanliness and appearance, empathetic staff, food quality, price, and proper implementation of COVID-19 protocol prevention would lead to high levels of satisfaction among customers in Jollibee fast-food restaurant. Moreover, the cultural/social influence has played a big role in that the indicators represent the feeling of belongingness since childhood. This results in an established and recognized name of Jollibee among people. The remainder of their childhood, and even homes for Filipinos living abroad could be connected here. Almendral [80] explored the feel for home upon Jollibee consumption among people living abroad. Not only were people reminded of home due to food, but also the tradition of living with families are catered in the atmosphere of Jollibee. Thus, other fast-food restaurants can capitalize on these factors to promote their own branding and establish their names by heart among consumers.
Limitations and Future Research
Despite the relevant findings and strong implications, this study still has several limitations which could be considered for extension by future research. This study only utilized online questionnaires to measure different factors affecting customer satisfaction due to the strict lockdown implemented by the COVID-19 pandemic. Interviews and thematic analysis may be done to enhance the implication of this study. Moreover, from the interview, other factors may be referred to as an extension of the framework utilized in this study. Second, the majority of the respondents in this study ranged from 21 to 26 years old, thus, limiting the broader perception of Jollibee’s customers in terms of diversity in population. Clustering of customers based on their demographics may be conducted to highlight the relevant findings. Lastly, customers’ perceptions, traditions, behavior, and culture vary across the different regions in the Philippines. This also limits the findings of this study, for the majority of the respondents were from the National Capital Region (NCR) of the Philippines. Therefore, it is recommended that the distribution of the survey and the focus of this study be conducted across branches of Jollibee Philippines for customers’ perspectives, values, and traditions to get more variety of results if any.
6. Conclusions
From the quantitative results, it was seen that tangible and empathy significantly preceded service quality. Both of these presented the highest correlation to service quality (β = 0.32 and β = 0.68), respectively. These factors preceded service quality which correlates to satisfaction the highest compared to other extended variables (β = 0.32). Following which are food quality (β = 0.27), COVID-19 protocols (β = 0.24), and pricing (β = 0.21), preceding significantly influenced customer satisfaction. It indicates that the SERVQUAL dimensions greatly affected customer satisfaction. With tangible and empathy, the visuals, such as signage and physical appearance, presented great satisfaction upon dining at Jollibee. In addition, the staff’s courteousness, amendable understanding, and willingness to help were key highlights. Moreover, it could be highlighted that cultural/social influence played a big role in attaining customer satisfaction and loyalty to Jollibee fast-food restaurants. Jollibee may still pursue its current business strategy to implement the COVID-19 protocols, for it did not affect the customers’ satisfaction and future intention to repurchase. It could be deduced that cleanliness and appearance, empathetic staff, food quality, price, and proper implementation of COVID-19 protocol prevention, would lead to high levels of satisfaction among customers in Jollibee fast-food restaurant.
Finally, Jollibee has succeeded in capturing the minds and emotions of Filipinos. Their social and cultural influence is the company’s second most potent asset in increasing customer patronization and satisfaction. Indeed, emotions, good memories, and good experiences should always be embedded in the customers’ minds whenever the services and the foods are provided to customers. The results of this study could be utilized to create strategies and food sustainability efforts through food systems management that includes the overall operational systems for Jollibee and other fast-food restaurants across the world. The theoretical framework utilized in this study did consider not only the typical SERVQUAL dimensions but also other factors such as price, food quality, COVID-19 protocol, and cultural/social influence. Thus, it could be posited that the framework can holistically measure customer satisfaction and service quality, which may be utilized by other restaurant and service-related industries worldwide.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.S.O., Y.T.P. and J.P.A.P.; methodology, A.K.S.O., Y.T.P. and J.P.A.P.; software, A.K.S.O., Y.T.P. and J.P.A.P.; validation, K.A.M., S.F.P., R.N., T.C. and T.B.; formal analysis, A.K.S.O., Y.T.P. and J.P.A.P.; investigation, A.K.S.O., Y.T.P. and J.P.A.P.; resources; J.P.A.P.; data curation, Y.T.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.S.O., Y.T.P. and J.P.A.P.; writing—review and editing, K.A.M., S.F.P., R.N., T.C. and T.B.; visualization, A.K.S.O., J.P.A.P. and Y.T.P.; supervision, Y.T.P., S.F.P. and R.N.; project administration, Y.T.P.; and funding acquisition, Y.T.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Mapua University Directed Research for Innovation and Value Enhancement (DRIVE).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by Mapua University Research Ethics Committees and Petra Christian University Research Ethics Committees (FM-RC-22-17).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study (FM-RC-22-17).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the respondents who answered our online questionnaire. We would also like to thank our friends for their contributions in the distribution of the questionnaire.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Instruments

Table A1.
Sample survey questionnaires.
Table A1.
Sample survey questionnaires.
| I. Respondent Profile | ||||||
| Gender: | ||||||
| Age: | ||||||
| ___15 to 20 years old ___21 to 26 years old | ||||||
| ___27 to 33 years old ___34 to 40 years old | ||||||
| ___41 to 46 years old ___47 to 53 years old | ||||||
| ___54 and above. | ||||||
| Number of times you eat in Jollibee: | ||||||
| ___once a week ___twice a week ___thrice a week | ||||||
| ___4 times a week and above | ||||||
| ___once a month | ||||||
| Occupation: | ||||||
| ___Student ___Employed ___Unemployed ___Other | ||||||
| Monthly Income: | ||||||
| ___₱11,999 and below ___₱12,000 to ₱20,999 | ||||||
| ___₱21,000 to ₱40,999 ___₱41,000 to ₱60,999 | ||||||
| ___₱61,000 to ₱80,999 ___₱81,000 and above | ||||||
| Discount is one of the reasons why I eat in Jollibee: | ||||||
| ___Yes ___No ___Sometimes | ||||||
| I often eat in Jollibee because I always have a discount card (senior citizen ID, PWD ID and others): | ||||||
| ___Yes ___No ___Sometimes | ||||||
| Number of Children: | ||||||
| II. Costumer assessment based on price, food quality and service quality | ||||||
| Answer the following items by marking the column that corresponds to your answer. | ||||||
| Rating Scale: | ||||||
| 5—Very satisfied | ||||||
| 4—Somewhat satisfied | ||||||
| 3—Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied | ||||||
| 2—Somewhat dissatisfied | ||||||
| 1—Very dissatisfied | ||||||
| Tangibles | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| T1. Virtual signs and messages for customers. | ||||||
| T2. Staffs’ uniform. | ||||||
| T3. Store appearance. | ||||||
| T4. Reception Appearance (counters and waiting areas). | ||||||
| T5. Accessibility to locations. | [11] | |||||
| T6. Store hygiene. | [11] | |||||
| Reliability | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| REL1. Accommodation on customers. | [12] | |||||
| REL2. Speed in serving the food orders of the customers. | [11] | |||||
| REL3. Accuracy in responding to the food orders of the customers. | [11] | |||||
| REL4. Staff returns personal belongings and other valuable items. | ||||||
| Responsiveness | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| RES1. Assistance provided by guards or other staffs upon entry. | [12] | |||||
| RES2. Queue waiting time. | ||||||
| RES3. Staffs promptly serve all customers. | [12] | |||||
| RES4. Staff courteousness. | [12] | |||||
| Assurance | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| A1. Product knowledge of the staff. | [11] | |||||
| A2. Product quality assurance. | [11] | |||||
| A3. Staff communication skill. | [11] | |||||
| A4. All customer concerns and requests were done. | [12] | |||||
| Empathy | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| E1. Staffs understand customer needs. | [12] | |||||
| E2. Staffs apologize when committing mistakes. | [12] | |||||
| E3. Staffs apologize when customer requests were not done. | [12] | |||||
| E4. Staffs willingness to help. | [12] | |||||
| E5. Staffs’ courtesy. | [12] | |||||
| Overall Service Quality | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| SQ1. Overall facility appearance. | [12] | |||||
| SQ2. All the discussed services were done accurately. | [12] | |||||
| SQ3. Overall staff responsiveness to customers. | [12] | |||||
| SQ4. All services and requests done were explained. | ||||||
| SQ5. Staff is competent in dealing with customer concerns. | ||||||
| Food Quality | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| FQ1. Quality of fried chicken among competitors. | ||||||
| FQ2. Quality of yum burger among competitors. | ||||||
| FQ3. Quality of the fries among competitors. | ||||||
| FQ4. Quality of the jolly spaghetti among competitors. | ||||||
| FQ5. Quality of the sundae among competitors. | ||||||
| FQ6. Overall food quality | ||||||
| Pricing | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| 5—Very cheap | ||||||
| 4—Somewhat cheap | ||||||
| 3—Neither costly nor cheap | ||||||
| 2—Somewhat costly | ||||||
| 1—Very Costly | ||||||
| P1. Compatibility of the price to the food quality. | ||||||
| P2. Pricing compared to other fast food restaurants. | ||||||
| P3. Affordability (5—Very affordable and 1—Very expensive). | [11] | |||||
| P4. Implementation of discount and buying package (5—Very satisfied and 1—Very dissatisfied). | [11] | |||||
| P5. Satisfaction based on overall pricing (5—Very satisfied and 1—Very dissatisfied). | ||||||
| COVID-19 Protocols | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| 5—Strongly agree | ||||||
| 4—Somewhat agree | ||||||
| 3—Neither agree nor disagree | ||||||
| 2—Somewhat disagree | ||||||
| 1—Strongly disagree | ||||||
| CP1. The social distancing has not affected my satisfaction when ordering and queuing in Jollibee. | ||||||
| CP2. It is better to eat my orders from Jollibee inside their restaurants than to take it at home. | ||||||
| CP3. Quarantines do not stop me from buying foods to Jollibee (ordering through online transactions). | ||||||
| CP4. The use of face mask and face shield didn’t stop me from queuing and ordering to Jollibee. | ||||||
| CP5. I still prefer to eat in Jollibee even if there are restaurants nearer in my location. | ||||||
| CP6. The COVID-19 pandemic didn’t affect the quality of their foods. | ||||||
| CP7. The COVID-19 pandemic didn’t affect their customer service quality. | ||||||
| CP8. The COVID-19 pandemic didn’t affect their food pricing. | ||||||
| CP9. The total number of COVID-19 cases do not affect my habit from dining inside the Jollibee. | ||||||
| Culture/Social Influence | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| CI1.I like eating Jollibee because of their good TV commercials. | ||||||
| CI2. I like eating to Jollibee because it has been with me since childhood. | ||||||
| CI3. I like eating to Jollibee because I have good memories and experiences with it. | ||||||
| CI4. I love going to Jollibee because it reminds me of the good Filipino tradition, through their influence in the commercial ads. | ||||||
| CI5. I like eating to Jollibee because it reminds me of someone. | ||||||
| Customer Satisfaction | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | References |
| C1. Satisfaction regarding the price given. | ||||||
| C2. Satisfaction regarding the overall service quality given. | ||||||
| C3. Recommend Jollibee to a friend or peer. | ||||||
| C4. Continue patronizing Jollibee’s foods and beverages. | ||||||
| C5. Overall satisfaction. | ||||||
References
- Mwangi, C.W. Strategic Responses to Competition among Large Fast Food Restaurants in Nairobi Central Business District. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Business, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Banterle, A.; Cavaliere, A.; Carraresi, L.; Stranieri, S. Food smes face increasing competition in the EU market: Marketing Management Capability is a tool for becoming a price maker. Agribusiness 2013, 30, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.T.; Chen McCain, S.-L. Transitioning loyalty programs. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 27, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, T.A.; Oliver, R.L.; MacMillan, I.C. A catastrophe model for Developing Service Satisfaction Strategies. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zineldin, M. Exploring the common ground of total relationship management (TRM) and Total Quality Management (TQM). Manag. Decis. 1999, 37, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerpott, T.J.; Rams, W.; Schindler, A. Customer retention, loyalty, and satisfaction in the German Mobile Cellular Telecommunications Market. Telecommun. Policy 2001, 25, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansemark, O.C.; Albinsson, M. Customer satisfaction and retention: The experiences of individual employees. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2004, 14, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunkoo, R.; Teeroovengadum, V.; Ringle, C.M.; Sunnassee, V. Service quality and customer satisfaction: The moderating effects of Hotel Star Rating. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 91, 102414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Eastlick, M.A.; Lotz, S.L.; Warrington, P. An online prepurchase intentions model. J. Retail. 2001, 77, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, J. Impact of COVID-19 on consumer behavior: Will the old habits return or die? J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limakrisna, N.; Ali, H. Model of customer satisfaction: Empirical study at fast food restaurants in bandung. Int. J. Bus. Commer. 2016, 5, 132–146. [Google Scholar]
- Balinado, J.R.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Young, M.N.; Persada, S.F.; Miraja, B.A.; Perwira Redi, A.A. The effect of service quality on customer satisfaction in an automotive after-sales service. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.K.; Cleofas, M.A.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Chuenyindee, T.; Young, M.N.; Diaz, J.F.; Nadlifatin, R.; Redi, A.A. Consumer behavior in clothing industry and its relationship with open innovation dynamics during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, Y.T.; Tanto, H.; Mariyanto, M.; Hanjaya, C.; Young, M.N.; Persada, S.F.; Miraja, B.A.; Redi, A.A. Factors affecting customer satisfaction and loyalty in online food delivery service during the COVID-19 pandemic: Its relation with open innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alano, C.M. Top 10 Fast-Food Restaurants. Available online: https://www.philstar.com/lifestyle/food-and-leisure/2008/07/17/73334/top-10-fast-food-restaurants (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Statista Research Department. Largest Foodservice Companies Philippines 2017, by Market Share. 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1049413/philippines-largest-foodservice-companies-by-market-share/ (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Altejar, L.; Dizon, C. Study of the Effects of Customer Service Quality and Product Quality on Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty. Coll. Bus. Adm. Major Mark. Manag. Access Address 2019, 10, m9. [Google Scholar]
- A Jolly Toast to a New Era for Jollibee BusinessMirror. Available online: https://businessmirror.com.ph/2019/11/05/a-jolly-toast-to-a-new-era-for-jollibee/ (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Beneschan, M. Analyzing Jollibee Restaurant Data. Available online: https://mikebeneschan.medium.com/analyzing-jollibee-restaurant-data-f57a24c6d942 (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Venzon, C. Can Jollibee Take a Bite Out of the Global Fast-Food Market? Available online: https://asia.nikkei.com/Spotlight/The-Big-Story/Can-Jollibee-take-a-bite-out-of-the-global-fast-food-market (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Venzon, C. Jollibee’s Quest for Global Dominance Derailed by Virus. Available online: https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Business-Spotlight/Jollibee-s-quest-for-global-dominance-derailed-by-virus (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Naik, C.K.; Gantasala, S.B.; Prabhakar, G.V. Service quality (SERVQUAL) and its effect on customer satisfaction in retailing. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. 2010, 16, 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.; Nisar, T.M.; Knox, D.; Prabhakar, G.P. Understanding customer satisfaction in the UK Quick Service Restaurant Industry. Br. Food J. 2018, 120, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Hing, N. Measuring Quality in Restaurant Operations: An application of the SERVQUAL instrument. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 1995, 14, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.K.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Picazo, K.L.; Salvador, K.A.; Miraja, B.A.; Kurata, Y.B.; Chuenyindee, T.; Nadlifatin, R.; Redi, A.A.; Young, M.N. Gym-goers preference analysis of fitness centers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A conjoint analysis approach for business sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-Arias, F.; Santos-Jaén, J.M.; Palacios-Manzano, M.; Garza-Sánchez, H.H. Using PLS-SEM to analyze the effect of CSR on corporate performance: The mediating role of human resources management and customer satisfaction. an empirical study in the Spanish food and beverage manufacturing sector. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahta, D.; Yun, J.; Islam, M.R.; Bikanyi, K.J. How does CSR enhance the financial performance of smes? the mediating role of firm reputation. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraž. 2020, 34, 1428–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Islam, R.; Pitafi, A.H.; Xiaobei, L.; Rehmani, M.; Irfan, M.; Mubarak, M.S. The impact of corporate social responsibility on customer loyalty: The mediating role of corporate reputation, customer satisfaction, and Trust. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A.; Bitner, M.J.; Gremler, D.D.; Mende, M. Services Marketing: Integrating Customer Focus across the Firm; McGraw Hill LLC: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.S.; Ariffin, H.F.; Ahmad, R. Service quality, customers’ satisfaction and the moderating effects of gender: A study of Arabic restaurants. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 224, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatolkina, N.; Gorbashko, E.; Kamynina, N.; Fedotkina, O. E-service quality from attributes to outcomes: The similarity and difference between digital and hybrid services. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. J. Mark. 1985, 49, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iberahim, H.; Mohd Taufik, N.K.; Mohd Adzmir, A.S.; Saharuddin, H. Customer satisfaction on reliability and responsiveness of self service technology for retail banking services. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 37, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandey, A.A.; Goldberg, L.; Pugh, S.D. Employee satisfaction, responsiveness, and customer satisfaction: Linkages and boundary conditions. Acad. Manag. Proc. 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuenyindee, T.; Ong, A.K.; Ramos, J.P.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Nadlifatin, R.; Kurata, Y.B.; Sittiwatethanasiri, T. Public Utility Vehicle Service Quality and customer satisfaction in the Philippines during the COVID-19 pandemic. Util. Policy 2022, 75, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joon Choi, B.; Sik Kim, H. The impact of outcome quality, Interaction Quality, and peer-to-peer quality on customer satisfaction with a Hospital Service. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2013, 23, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaja, R.; Myshketa, R.; Scalera, F. Service Quality Assessment in health care sector: The case of durres public hospital. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 235, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahari, N.; Basir, N.M.; Jangga, R. Factors of food dimension affecting customer satisfaction in family restaurants. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Business and Economic Research, Bandung, Indonesia, 12–13 March 2012; pp. 2831–2846. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.X.; Tan, K.C.; Xie, M. An integrated approach to innovative product development using Kano’s model and QFD. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2000, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivela, J.; Inbakaran, R.; Reece, J. Consumer research in the restaurant environment, part 1: A conceptual model of dining satisfaction and return patronage. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 1999, 11, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, A.; Yüksel, F. Measurement of Tourist Satisfaction with Restaurant Services: A segment-based approach. J. Vacat. Mark. 2003, 9, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad Andaleeb, S.; Conway, C. Customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry: An examination of the transaction-specific model. J. Serv. Mark. 2006, 20, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B. The Impact of Perceived Price Fairness of Dynamic Pricing on Customer Satisfaction and Behavioral Intentions: The Moderating Role of Customer Loyalty; Auburn University: Auburn, AL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, R.I.; Ghafoor, O.; Hafeez, I.; Akhtar, N.; Rehman, A.U. Factors affecting customers satisfaction in restaurants industry in Pakistan. Int. Rev. Manag. Bus. Res. 2014, 3, 869. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, A.; Johnson, M.D.; Roos, I. The effects of customer satisfaction, Relationship Commitment Dimensions, and triggers on customer retention. J. Mark. 2005, 69, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulek, J.M.; Hensley, R.L. The relative importance of food, atmosphere, and fairness of wait. Cornell Hotel. Restaur. Adm. Q. 2004, 45, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozekhi, N.A.; Hussin, S.; Siddiqe, A.S.K.A.R.; Rashid, P.D.A.; Salmi, N.S. The influence of food quality on customer satisfaction in fine dining restaurant: Case in Penang. Int. Acad. Res. J. Bus. Technol. 2016, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Peri, C. The Universe of Food Quality. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tit, A.A. The effect of service and food quality on customer satisfaction and hence customer retention. Asian Soc. Sci. 2015, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intelligence, N. Impact of Coronavirus (COVID-19) on Consumer Behavior in 2020. Available online: https://www.numerator.com/resources/blog/impact-covid-19-consumer-behavior (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Restaurant Consumers. Available online: https://www.revenuemanage.com/en/insights/the-impact-of-covid-19-on-restaurant-consumers/ (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Nayeem, T. Cultural influences on consumer behaviour. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2012, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, J.D.; Redi, A.A.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Persada, S.F.; Ong, A.K.; Young, M.N.; Nadlifatin, R. Choosing a package carrier during COVID-19 pandemic: An integration of pro-environmental planned behavior (PEPB) theory and Service Quality (SERVQUAL). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumasing, M.J.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Ong, A.K.; Nadlifatin, R. Determination of factors affecting the response efficacy of Filipinos under Typhoon Conson 2021 (jolina): An extended protection motivation theory approach. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 70, 102759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mooij, M. Global Marketing and Advertising: Understanding Cultural Paradoxes, 3rd ed.; Sage Publications Asia-Pacific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Main Page. Available online: https://is.theorizeit.org/wiki/Main_Page (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Mueller, R.O.; Hancock, G.R. Structural Equation Modeling; Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E.B. Multivariate Data Analysis, 8th ed.; Cengage: Hampshire, UK, 2019; pp. 146–157, 675–680. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, G.; Paul, J. CB-SEM vs. PLS-SEM methods for research in Social Sciences and Technology forecasting. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 173, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, K.S. The use of Cronbach’s alpha when developing and Reporting Research Instruments in science education. Res. Sci. Educ. 2017, 48, 1273–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-F. A stage model of Knowledge Management: An empirical investigation of process and effectiveness. J. Inf. Sci. 2007, 33, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, P.C.; Franses, P.H.; Hoekstra, J.C. The effect of relational constructs on customer referrals and number of services purchased from a multiservice provider: Does age of relationship matter? J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2002, 30, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuduang, N.; Ong, A.K.; Prasetyo, Y.T.; Chuenyindee, T.; Kusonwattana, P.; Limpasart, W.; Sittiwatethanasiri, T.; Gumasing, M.J.; German, J.D.; Nadlifatin, R. Factors influencing the perceived effectiveness of COVID-19 risk assessment mobile application “Morchana” in Thailand: Utaut2 approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.; Boudreau, M. Structural Equation Modeling and Regression: Guidelines for Research Practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohaimmeed, B.M. Restaurant quality and customer satisfaction. Int. Rev. Manag. Mark. 2017, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tat, H.H.; Sook-Min, S.; Ai-Chin, T.; Rasli, A.; Hamid, A.B.A. Consumers’ purchase intentions in fast food restaurants: An empirical study on undergraduate students. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2011, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Prybutok, V.R. Service quality, customer satisfaction, and behavioral intentions in fast-food restaurants. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2009, 1, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, Y.; Jang, S.C. Are highly satisfied restaurant customers really different? A quality perception perspective. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2008, 20, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.; Cheung, M.L.; Pires, G.D.; Chan, C. Customer satisfaction with sommelier services of upscale Chinese restaurants in Hong Kong. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2019, 31, 532–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, C.; Baloglu, S.; Mao, Z.; Busser, J. What really brings them back? Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 22, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.R.; Shaikh, U. Impact of service quality on customer satisfaction: Evidences from the restaurant industry in Pakistan. Manag. Mark. 2011, 9, 343–355. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Park, K.-H.; Park, D.-H.; Lee, K.A.; Kwon, Y.-J. The relative impact of service quality on service value, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty in Korean family restaurant context. Int. J. Hosp. Tour. Adm. 2005, 6, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Oriade, A.; Fallon, P. Service quality and customer satisfaction in Chinese fast food sector: A proposal for CFFRSERV. Adv. Hosp. Tour. Res. (AHTR) 2014, 2, 30–53. [Google Scholar]
- Moorthy, K.; En Chee, L.; Chuan Yi, O.; Soo Ying, O.; Yee Woen, O.; Mun Wei, T. Customer loyalty to newly opened cafés and restaurants in Malaysia. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2016, 20, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, I.; Mensah, R.D. Effects of service quality and customer satisfaction on repurchase intention in restaurants on University of Cape Coast campus. J. Tour. Herit. Serv. Mark. 2018, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jawabreh, O.; Al Jaffal, T.; Abdelrazaq, H.; Mahmoud, R. The impact of menus on the customer satisfaction in restaurants classified in Aqaba special economic zone authority (ASEZA). J. Tour. Hosp. Sport. 2018, 33, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, K.; Han, H. Influence of the quality of food, service, and physical environment on customer satisfaction and behavioral intention in quick-casual restaurants: Moderating role of perceived price. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2009, 34, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.K.Y.; Hui, Y.V.; Zhao, X. Modeling repurchase frequency and customer satisfaction for fast food outlets. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2004, 21, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.C.; Ha, J. The influence of cultural experience: Emotions in relation to authenticity at ethnic restaurants. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2015, 18, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almendral, A. Jollibee: A Taste of Home for Filipinos. Available online: https://theworld.org/stories/2012-10-26/jollibee-taste-home-filipinos (accessed on 20 March 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).