Abstract
Scientific and accurate evaluations of the high-quality development level of the manufacturing industry have important theoretical significance and reference value for the government and for decision-making departments for the formulation of corresponding incentive measures. Firstly, based on rough set theory, this paper proposes an attribute reduction method, which can help to delete redundant indexes and reduce the calculation workload. Secondly, a more scientific combination weighting method is proposed, and the calculation method of the total index in an evaluation index system is given. Finally, the HQDMI evaluation index system is constructed based on the connotations of the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Taking China as an example, the total index and sub-index of high-quality development of 30 provinces in China are calculated, the high-quality development level of the manufacturing industry in 30 provinces is clustered based on SPSS24.0, and the visualization of the clustering results is achieved by ArcGIS software. The results show that the high-quality development level of China’s manufacturing industry has regional distribution characteristics. Regions with high development levels are mainly distributed in eastern coastal areas, followed by the central development level, and those of the northeast and west are low. This study provides a theoretical application mode for the evaluation of the high-quality development level of the manufacturing industry, and it has theoretical guidance significance for promoting the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry.
1. Introduction
The manufacturing industry is the foundation of a country’s economy, the source of wealth creation and an important pillar of national prosperity. It always occupies a pivotal position in the development of the national economy [1]. Promoting the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry (HQDMI for short) is key to building a strong manufacturing country [2]. High-quality development is a new concept that was proposed in the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China in 2017, which indicates that China’s economy has changed from a high-speed growth stage to a high-quality development stage. From high-speed to high-quality development, it is a transformation process from quantitative to qualitative change. This change makes economic operation more efficient, the industrial structure more reasonable and increases the quality of the products and services provided by enterprises. It can finally realize more sustainable economic development, a greener ecological environment and more fair social distribution.
At present, the manufacturing business is currently experiencing unpredictable market shifts as a result of the enormous changes that the world economy is currently going through, including fast-shifting product demand and the regular launch of new products [3,4]. In a new era, the quantitative economic growth model characterized by factor driving is difficult to sustain, and high-quality development has gradually become the direction of economic growth. To deepen supply-side structural reform, the government must focus on the real economy and on improving the quality of the supply system [5]. The HQDMI is an important issue that needs to be tackled under the new normal. Promoting the HQDMI is of great strategic significance for achieving high-quality economic development, accelerating economic transformation and upgrading, and realizing the dream of a century-old power [6].
The high-quality development of the manufacturing industry (HQDMI for short) is a comprehensive system that includes multi-level and multi-faceted indices. The logical relationship of indices in the system is complex, and there are often some redundant indices. These redundant indices not only increase the cost of statistics and research but also weaken important indices, which can eventually lead to deviations in the evaluation results [7,8]. Therefore, it is necessary to select representative statistical indices from complicated statistical indicators to statistically characterize the HQDMI index. This index can be used to analyze how China’s provinces are clustered and to then give corresponding policy suggestions to promote the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry.
Based on the above analysis, the research objectives of this paper are as follows: (1) to build a scientific HQDMI evaluation index system; (2) to propose an attribute reduction method to reduce the calculation workload in the analysis of the evaluation index system; (3) to give a calculation method for the total HQDMI index based on the combination weighting method; and (4) taking China as an example, to analyze the development level of the HQDMI in various provinces and to propose policy implications.
The sections of this paper are organized as follows. An overview of the pertinent literature is provided in Section 2. The third section is the materials and methods section, which introduces the attribute reduction method, the combination weighting method and the index measurement. In Section 4, the HQDMI evaluation index system is built, and the total index of China’s HQDMI is calculated. Section 5 provides the analysis and discussion of the results. Section 6 contains the conclusion and policy recommendations. Finally, the appendix provides introductions of relevant charts and four weight calculation methods.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Review of Research Status
At present, systematic research on the HQDMI has gradually emerged in academic circles. Most of the domestic research on HQDMI focuses on the related theories, implementation paths, evaluation systems and factors affecting the HQDMI.
In terms of the theory and implementation path of HQDMI, Yu [9] studied the connotations, paths, and dynamic mechanisms of the HQDMI. Zhang [10] indicated the main problems of China’s HQDMI, such as internal and external environmental constraints, its unsustainable traditional development model, prominent structural contradictions on the supply side and insufficient attention to human resources. He further explored the realistic path of the HQDMI. Hu [11] promoted the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry from the aspects of promoting industrial chain upgrading, enterprise innovation, intelligent manufacturing and service-oriented manufacturing. Guo [12] elaborated on the integration development status of China’s advanced manufacturing industry and modern service industry and proposed relevant suggestions to promote the HQDMI.
In terms of the evaluation system and influencing factors of HQDMI, Huang and Zhang [13] made a statistical and comparative analysis of the evaluation dimensions and specific indicators by combing the relevant literature. Liu and Fang [14] constructed the evaluation index system of the HQDMI in the Yangtze River economic belt from six dimensions: security support, green ecology, quality brands, economic efficiency, open innovation and social contribution, and they measured the level of the HQDMI in 108 prefecture-level cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Fu and Chu [15] used the TOPSIS Evaluation Model based on the “Improved CRITICAL—Entropy Weight Method” to evaluate the HQDMI in the Yangtze River Delta from five dimensions: innovation ability, talent agglomeration, green development, quality and efficiency, and high-end industrial structure. Liu [16] constructed a manufacturing evaluation index system from four perspectives: scale development, quality and efficiency, structural optimization and sustainable development. Using Python as a tool, Chen [17] used the multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to calculate the comprehensive evaluation of the HQDMI in Shenzhen. In addition, relevant suggestions to promote HQDMI were proposed. Based on the data of the listed manufacturing companies, Meng and Zhang [18] tested the promotion effect of rising labor costs on the high-quality development of enterprises and explored the mechanism, heterogeneity and lag effect of rising labor costs. Based on the market process index and the quality competitiveness index of 31 provinces in China, using the fixed effect model, Lin [19] empirically tested the influence of the market level on product quality and the development ability of the manufacturing industry. Using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and the Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL), Lee et al. [20] examined three traditional manufacturing sectors and determined six key standards for innovative manufacturing that created a new framework for the long-term growth of traditional manufacturing sectors.
Internationally, many evaluation studies have been carried out in relevant fields, such as the quality of economic growth, the index system of performance evaluation for enterprises and the sustainability of enterprise development. Ceptureanu et al. [21] studied the impact of competitiveness on sustainable manufacturing practices of small and medium-sized enterprises in Romania’s textile industry by creating an econometric model. Abubakr et al. [22] integrated sustainable intelligent manufacturing performance by integrating sustainable manufacturing measures and discussing the current and future challenges facing the manufacturing industry. Singla et al. [23] evaluated the significance of various technology-push (TP) and demand-pull (DP) practices for India’s manufacturing industry to achieve sustainable development. Alrasheedi et al. [24] used fuzzy set theory and decision-making technology to rank and evaluate the green growth indicators of sustainable manufacturing in the manufacturing industry. Performance evaluation is an important part of the sustainable development of the manufacturing industry. Singh et al. [25] proposed a method for evaluating the sustainable development of small and medium-sized manufacturing firms. He also identified the key variables that influence the sustainability of manufacturing enterprises. He and Estebanez [26] adopted the grey fuzzy analysis method to establish an enterprise performance evaluation index system, to evaluate the cost management of micro-manufacturing enterprises based on the supply chain and to conduct an empirical analysis based on the research data of a company.
2.2. Research Gaps Based on the Literature Review
In summary, the existing research on the HQDMI may have the following three shortcomings: (1) The overall structure of the indicator system is relatively simple. Most of the existing indicator systems have a macro single-layer structure, fail to touch the end of the indicator system to the micro aspects of enterprise development and lack systematic consideration of the HQDMI. (2) Most articles mainly focus on qualitatively describing the problems and the realization path of China’s regional HQDMI. Few documents analyze the evaluation system of China’s overall HQDMI. (3) Due to insufficient attention to heterogeneity, the index system has not been given good inclusiveness and flexibility, which has reduced the possibility of governments to adapt to local conditions, guide the situation and adjust flexibly. Therefore, it is difficult to lead different regions to the path of the HQDMI with unique characteristics and distinct advantages.
2.3. Research Questions and the Intended Contributions of the Study
Based on the research gap described above, this study realizes the following research questions: (1) How can we scientifically understand and reasonably measure the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry? (2) What are the dynamic evolution trends of the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry in each province? (3) How can we scientifically judge and solve the defects and problems in the development of the manufacturing industry in various provinces and regions?
To better formulate different development policies for various regions and to further promote the high-quality development and regional coordination of the manufacturing industry, this paper aims to measure the level of high-quality development of the industry, to explore its constraints and to grasp current and future development trends.
Compared with existing research results, the biggest innovation of this paper is the scientific construction of the HQDMI index. Because the index is constructed on the basis of the attribute reduction theory of rough sets, the redundant index is eliminated. The index is selected comprehensively, and the evaluation index system that is constructed is more scientific and reasonable.
The intended contributions of this study are as follows. First of all, the index set and the indices are filtered using the rough set model, and the combination weights of the retained indicators are then creatively generated by utilizing a range of objective weighing evaluation methods. The total index of the high-quality development of the provincial manufacturing industry and the sub-indices at all levels are calculated using the linear weighting method, which is conducive to determining the main constraints of the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Secondly, 30 provinces are divided into four echelons through systematic clustering, and a visual analysis is carried out with the aid of ArcGIS software. Finally, the paper analyzes the development status of the manufacturing industry in each province. In addition, targeted policies and suggestions for the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry in each province are offered according to the research results. This study is of great significance for promoting regional coordinated development and narrowing regional differences.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Symbol Descriptions and Research Framework
This section provides an explanation of the symbols used in this study and the general research framework (Figure 1) to make it easier to understand.
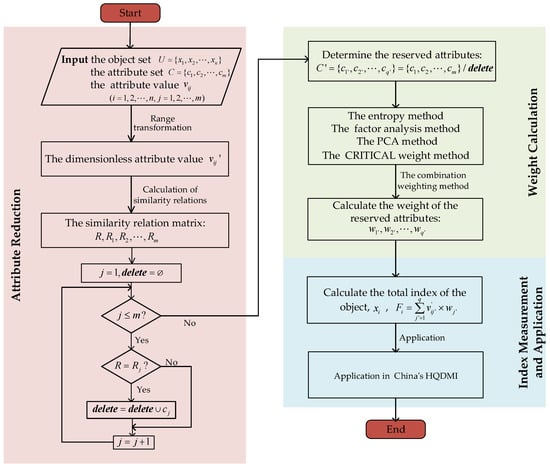
Figure 1.
Framework of the paper.
3.2. Attribute Reduction Method Based on Rough Set Theory
The real-value information system is dimensionless. The equivalence relation in the standard rough set is replaced by the similarity relation, and the index is reduced according to the classification result.
- (1)
- Rough set model
Let be an information system, and there are no decision attributes in the system, where is an object set, is an attribute set, is the range set for any and is the value range of the attribute . In other words, let be the actual value of object under the attribute ; therefore, is the range of the set . is the information function for any , .
Based on the above, a real-value attribute information system can be established. Due to the different dimensions of each attribute in the attribute set, the value range of each attribute is also different, which creates difficulty in subsequent research. We adopt the method of range transformation to eliminate the dimension between each attribute; therefore, all attribute values are in the range of 0–1.
If the attribute is a cost index, the attribute value is transformed as follows:
If the attribute is a benefit index, the attribute value is transformed as follows:
The attribute value matrix after range transformation is as follows:
- (2)
- Calculation of similarity relations
We regard each attribute value of an object in the dimensionless information system as a set. For any two objects and ,, if the Hamming distance of the two sets is not greater than a given value (as shown in Equation (4)), the two objects have a similar relationship, so we record it as . However, if there is no similar relationship between the two objects (i.e., Equation (4) does not hold), we record it as .
where is the similarity between object and object . Index reduction is determined by similarity. As becomes larger, the classification accuracy becomes higher. However, the classification accuracy is lower [27,28].
Based on the above statement, we have the similarity relation matrix:
Next, attribute reduction is performed based on the similarity relation matrix.
- (3)
- Attribute reduction
Attribute reduction deletes unimportant attributes while ensuring that the classification ability of the knowledge base remains unchanged. If the similarity relation matrix that is calculated according to all attributes is the same as the one that is calculated after deleting an attribute, the attribute is redundant; otherwise, the attribute is necessary.
For any attribute , if is removed from the attribute set , Equation (4) changes to . In this case, the similarity relation matrix is referred to as . When the similarity relation matrix , the attribute does not affect the classification ability of the system, so it is a redundant attribute. Otherwise, the attribute is not redundant and should be preserved.
We assume that the set of all redundant attributes is and that the remaining attributes have not been deleted, so the reserved attribute set is referred to as . Attribute reduction is achieved, and is the set of attributes after reduction.
3.3. Combination Weighting Method
The weight of an index is an important part of an evaluation system. It represents the importance of the index to the entire evaluation system. Reasonable weighting of the evaluation index is related to the accuracy of the final evaluation result [29]. There are many methods for multi-index weighting in academia, which can be summarized in two categories: the subjective weighting method and the objective weighting method. In the subjective weighting method, the evaluator decides the weight of the index according to the degree of importance that he or she attaches to the index, which possesses definite subjectivity. The objective weighting method determines the weight of the index according to the amount of information provided by each index and does not involve people’s subjective intentions. Because an evaluation system is very complex, involving a wide range, wide content and large data statistics, it may be difficult to make subjective judgments on the importance of each of the two indices. In addition, it even has an impact on the consistency of hierarchical single sorting and total sorting, failing consistency tests.
Common weight calculation methods are the entropy method, the factor analysis method, principal component analysis (PCA) and the CRITICAL weight method. Many scholars have described the above methods in detail [30,31,32,33]. Each of the four weighting methods has its advantages and disadvantages (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Advantages and disadvantages of four types of weighting methods.
The weighting method combined with the four objective weighting methods is more accurate and comprehensive, and it can avoid any errors caused by any single method. Therefore, we propose the combined weighting method as follows:
For any attribute , we suppose that the attribute ’s weights calculated by the four methods (the entropy method, factor analysis method, PCA method and CRITICAL method; see Appendix B for an introduction to the four types of weighting methods) are respectively. Therefore, the combined weight is as follows:
3.4. Index Measurement
Based on the reduced attribute set and the dimensionless attribute value calculated in Section 3.1, as well as the combined attribute weight calculated in Section 3.2, the total index of object can be obtained as follows:
where is the dimensionless value of object under index , and is the weight of the index . is between 0–1, and it represents the final level of the object .
4. Evaluation Index System Construction and Index Calculation of the HQDMI
The evaluation index system of the HQDMI is an important bridge and link that connects the theoretical connotations and policy practices of the HQDMI [34]. At present, China is still in an important period of strategic opportunities for development. Facing the increasingly complex international situation, research on the HQDMI undoubtedly has a great practical demand for promoting the rise in China’s manufacturing power. Therefore, it is necessary to build a set of scientific and effective evaluation index systems of the HQDMI to analyze the current situation, internal differences and main shortcomings of China’s HQDMI and to propose policy suggestions to accelerate the realization of the HQDMI. These are of great significance to realizing the rise in China’s manufacturing power.
After clarifying the research objectives, the main work of this section is as follows: First, the source and pretreatment method of the data used in this paper are introduced in Section 4.1. Second, a seven-dimensional HQDMI evaluation index system is built in Section 4.2. In addition, nine redundant attributes are identified and removed according to the attribute reduction method proposed in Section 3.2. Next, in Section 4.3, the weights of the reserved attributes are calculated by using the combination weighting method. Finally, the total index of China’s HQDMI from 2011 to 2019 is calculated in Section 4.4.
4.1. Data Sources
This paper takes 30 provinces (municipalities and autonomous regions directly under the Central Government) as the research objects (excluding Tibet, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan) to estimate China’s HQDMI. The original data come from the “China Statistical Yearbook”, statistical yearbooks of various provinces and regions, the “China Environmental Statistical Yearbook”, the “China High-tech Industry Statistical Yearbook”, “China Energy Statistical Yearbook”, the China Science and Technology Statistical Yearbook, the China Trade and Foreign Economic Statistics Yearbook, the National Science and Technology Expenditures Statistical Bulletin, etc. The data are reliable, accurate and standardized, and the time range is 2011–2019.
To obtain more realistic data, missing statistical data are generated by the mathematical calculation method, the GM (1, 1) prediction method, the interpolation method, the expert estimation method and other methods. To eliminate the price impact, this article converts the time series data calculated at the current year’s price into the actual value of the 2011 constant price correction. In addition, because the amount of foreign direct investment in the statistical data is in U.S. dollars, it is first converted into RMB units at the average exchange rate of the year during data processing, and then the price effect is eliminated through the deflator method to obtain the actual value of the year. All price index adjustments are based on 2011, and the price index comes from statistical yearbooks of various provinces in China.
4.2. Pre-Selection of HQDMI Indices
The evaluation system of the HQDMI involves a wide range of aspects and contents. When selecting indices, we should not only ensure the systematicness and scientificity of the system, but we should also consider the principles of comprehensiveness, adaptability and measurability. According to the characteristics, ideas and concepts of the HQDMI, and referring to the high-frequency indices proposed in [35,36,37,38,39,40,41], the evaluation system of China’s HQDMI is finally constructed. To ensure the availability and operability of original data [34], the unavailable indices are deleted. Combined with relevant literature reviews and investigations, the evaluation index of the HQDMI is pre-selected. The evaluation system for the HQDMI includes seven subsystems: innovation development, economic benefit, quality benefit, structural optimization, opening up, social contribution and green ecology. Innovation development is the first and leading position of the new development concepts, and it is the engine of the HQDMI. An economic benefit is the basis of the HQDMI. Quality benefit reflects the effectiveness of the HQDMI. Structural optimization is the key to the HQDMI. Opening up is an important path for the HQDMI. Social contribution is the fundamental purpose of the HQDMI because sharing development is an essential requirement of socialism with Chinese characteristics. Green ecology is an inherent requirement of the HQDMI. In this paper, the similarity is selected as 0.6, and the reduction set of attributes can be obtained by using the attribute reduction method in Section 3.1. The results show that there are nine redundant indices in the pre-selection of HQDMI indices, which will be deleted from the system in future research. Finally, the index reduction results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Index set of HQDMI.
4.3. Index Weight Solution
Since the HQDMI evaluation system is a very complex systematic project that involves a wide range, wide content and large data statistics, it may be difficult to make subjective judgments on the importance of each of the two indices. Therefore, we use the combination weighting method in Section 3.3 to calculate the weight of each index. The combination weight results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Weight of evaluation index for HQDMI.
4.4. HQDMI Index Calculation
In this study, the objects are 30 provinces in China (excluding Tibet, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan), the attributes are the evaluation indices and the attribute values are specific values of evaluation indices. According to the evaluation index system of the HQDMI and the calculation methods introduced in Section 3.4, the average value of the total HQDMI index and of each sub-index from 2011 to 2019 are calculated and obtained, as shown in Table A1.
In order to further analyze the trend of the HQDMI in each province from 2011 to 2019, the general index trend chart of the HQDMI in the 30 provinces of China from 2011 to 2019 is drawn, as shown in Figure 2.
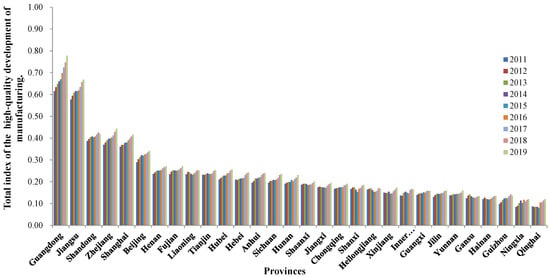
Figure 2.
Total index of HQDMI in 30 provinces of China from 2011 to 2019.
It can be seen from Figure 2 that there are obvious differences in the development level of the manufacturing industry among different regions in China. For a long time, there has been a serious imbalance in the development of China’s manufacturing industry at the regional level, which is mainly reflected in the high level of industrial development in the eastern coastal areas. In particular, the levels of the HQDMI in Guangdong and Jiangsu lead the country, and their growth rates are also higher than those of other provinces, whereas the industrial development of the vast central and western regions is relatively lagging. In eastern coastal provinces and cities, natural resources are relatively low, but there are good technical conditions, superior locations, rich human resources and a high level of industrial development. Therefore, in order to promote the HQDMI in China, we should not only adhere to the principle of overall consideration, but we should also give full attention to regional characteristics to achieve differentiated development. Moreover, we should adhere to the development path of regional integration, focus on strengthening regional cooperation, promote the overall improvement of the ability of the HQDMI in China and finally realize China’s entry into the ranks of manufacturing powers.
5. Analysis and Discussion of Results
5.1. Analysis of Results
To analyze the grade type of the total index of the HQDMI, this paper uses SPSS 24.0 software to cluster the evaluation results of the average value of the total HQDMI index in 30 provinces of China. Clustering is the process of combining the study objects’ tighter relationships into categories, focusing on the composition of parts inside and between categories and clarifying categorization boundaries.
Figure 3 shows that the 30 provinces are split into several subcategories, and they are finally grouped into a single category. In order to better study the commonness of the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry in each province, this paper sets the distance between categories as 2 for the threshold (dotted line in Figure 3) in combination with the distribution of provinces on the clustering pedigree map. The 30 provinces are divided into four categories. To explore the geographical distribution of these four kinds of provinces more intuitively, this paper uses ARCGIS software for visualization, as shown in Figure 4.
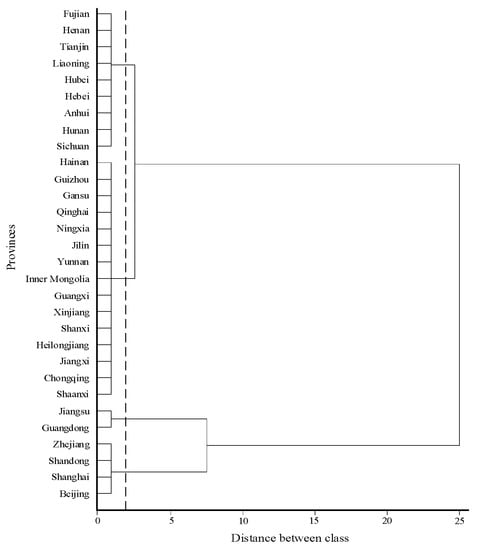
Figure 3.
Clustering pedigree of HQDMI in China.
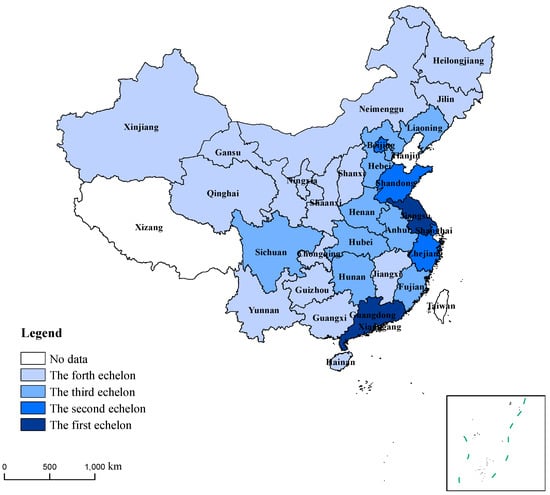
Figure 4.
Classification of HQDMI in China.
It can be seen from Figure 4 that the total index of the HQDMI can be divided into four echelons: the first echelon includes Guangdong and Jiangsu; the second echelon includes Shandong, Zhejiang, Shanghai and Beijing; the third echelon includes Henan, Fujian, Liaoning, Tianjin, Hubei, Hebei, Anhui, Sichuan and Hunan; and the fourth echelon includes Shaanxi, Jiangxi, Chongqing, Shanxi, Heilongjiang, Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Jilin, Yunnan, Gansu, Hainan, Guizhou, Ningxia and Qinghai.
Overall, China’s HQDMI at this stage has the characteristic of regional imbalance, which shows a decreasing trend in the east coast, the middle, the northeast and the west. In contrast, the level of the HQDMI in most western provinces is at the bottom compared with the rest of the country, and 10 of the 15 provinces in the fourth echelon come from the western region. The total index of the HQDMI in Guangdong is 7.12 times that of Qinghai Province. The regional gap in the HQDMI is obvious. It is worth noting that, in terms of green ecology, there is a small development gap among provinces in China (Figure 5h), indicating that, under the concept of green development in the new era of China, local governments have a strong awareness of environmental protection, and all provinces in China take green ecology as an internal requirement for the HQDMI.
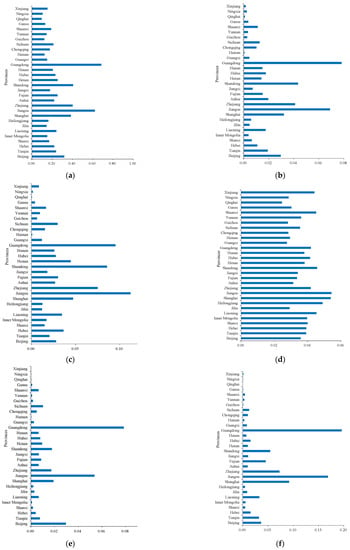
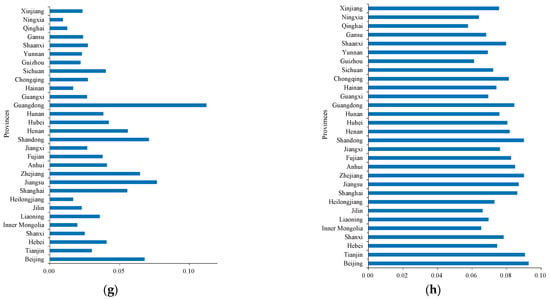
Figure 5.
The average of the sub-system indices of HQDMI in 30 provinces of China from 2011 to 2019. (a) The average of the total index of HQDMI; (b) The average of the innovation development index; (c) The average of the economic benefit index; (d) The average of the quality benefit index; (e) The average of the structural optimization index; (f) The average of the opening up index; (g) The average of the social contribution index; (h) The average of the green ecological index.
In order to make a more comprehensive and in-depth analysis of the HQDMI in various regions of China, this paper further combines the calculation results of each subsystem index, and it compares and analyzes the innovation development, economic benefit, quality benefit, structure optimization, opening up, social contribution and the average value of green ecosystem sub-index of 30 provinces in China from 2011 to 2019, as shown in Figure 5.
(1) Guangdong Province and Jiangsu Province, which are located in the first echelon of HQDMI in China, are in the top two in terms of innovation development, economic benefit, structural optimization, opening up and social contribution. It shows that Guangdong and Jiangsu are in the leading position in the process of promoting the HQDMI. After reforming and opening up, Guangdong has appeared at the forefront of reform and opening up and has become a window to introduce western economy, culture, science and technology. Since 1989, Guangdong’s GDP has continuously ranked first in the country, becoming the largest economic province in China, accounting for 12.5% of China’s total economy, and the comprehensive competitiveness of Guangdong’s economy ranks first in the country. As the birthplace of modern national industry, Jiangsu has always been an important town of economic development. The comprehensive competitiveness of Jiangsu Province’s economy ranks first in the country, and its scale of actual use of foreign capital ranks first in the country. In order to speed up the construction of an advanced manufacturing base with international competitiveness, Jiangsu Province has greatly developed strategic emerging industries and high-tech industries. New industries, new formats and new models have strong momentum in their development.
(2) Shandong, Zhejiang, Shanghai and Beijing rank third to sixth in the second echelon of the country. Except for Beijing, the capital of China, these provinces belong to the eastern coastal areas with strong economic development, financial strength and innovation ability. Shandong, a large Eastern Economic Province, is the third largest in China in terms of innovation development index, economic benefit score and social contribution index due to active kinetic energy conversion. Zhejiang and Shanghai are located in the Yangtze River Delta. The Yangtze River Delta economic zone is one of the regions with the most active economic development, the highest degree of openness and the strongest innovation ability in China. It plays an important strategic role in the overall situation of national modernization and the all-around opening pattern. As the capital, Beijing has good development in innovation and development, industrial structure optimization, social contribution and (especially) green ecology. Therefore, Beijing has advantages in pollution control and energy conservation.
(3) In the third echelon, Henan, Fujian, Liaoning, Tianjin, Hubei, Hebei, Anhui, Sichuan and Hunan rank seventh to fifteenth in China. Henan, Hubei, Anhui and Hunan belong to the central region. After the 18th CPC National Congress, Henan actively promoted strategic emerging industries by vigorously developing high-tech industries and advanced manufacturing industries, and the industry continued to move forward to the middle and high end. Hubei is one of the old industrial bases in China, with a solid foundation for industrial development. The equipment manufacturing industry is an important pillar industry in Hubei. Anhui Province is adjacent to the Yangtze River Delta economic circle. In recent years, although the government has introduced Anhui Province into the Yangtze River Delta, its main function is to receive heavy industry and other high-polluting enterprises from the Yangtze River Delta. There are also a series of problems in the quality, efficiency and opening up in Anhui Province. The characteristics of a heavy chemical industry and resource-based industry in Hunan Province are relatively prominent. The proportion of traditional heavy chemical industries, such as the chemical industry, the iron and steel industry and the metallurgy and nonferrous metals industry, is relatively high. The total number of high-tech manufacturing industries and strategic emerging industries is still small. The driving capacity of industrial economic growth needs to be strengthened, and the industrial structure should be further optimized. Standing at a new historical starting point, the central provinces should seize new historical opportunities in China in the new period; adhere to opening up both at home and abroad; gradually form an all-around, multi-level and wide-ranging opening pattern; build an inland-open highland; and accelerate the realization of the rise of the Central Plains. As a coastal province, Fujian’s economy lags behind many coastal cities. In terms of its industrial structure, Fujian is dominated by the light industry, and there are few strategic emerging industries and high-tech industries. Fujian has problems in terms of quality and efficiency, as well as in terms of innovation, development and social contribution. Liaoning Province had a higher level of industrial development in the early days of the founding of the People’s Republic of China compared with other provinces. However, with the continuous development of the social economy and the innovation and reform of science and technology, Liaoning Province failed to change the development concept and development mode in time, and the transformation of the industrial development mode was not complete, which led to its slow development. Therefore, some deficiencies emerged in the optimization of its industrial structure. In addition, compared with other provinces, Liaoning also has obvious deficiencies in social contribution and green ecology. In the future, Liaoning needs to further strengthen its social livelihood, environmental governance and supervision. Tianjin and Hebei belong to the Beijing Tianjin Hebei region. The Beijing Tianjin Hebei region is located in the heart of the Bohai Sea in Northeast Asia. It is the largest and most dynamic region in northern China. Compared with Hebei Province, Tianjin ranks higher in innovation and development, structural optimization, opening up and green ecology, and Hebei Province is undertaking the transfer of traditional manufacturing industries from Beijing to Tianjin and will inevitably bring about environmental pollution and a waste of resources. As a part of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, Hebei Province should give full attention to the complementary role of industrial institutions, optimize and upgrade its industries and promote the regional economic integration development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. It is worth noting that Hebei has some shortcomings in green ecology. Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei should strengthen their top-level design, clarify their functional focus and industrial division, and pay close attention to the function of the Bohai Rim region’s cooperation and development coordination mechanism. Sichuan Province ranks in the middle of the total index of the HQDMI, but it is lower than the national average in five aspects: innovation and development, quality and efficiency, structural optimization, opening up and green ecology. The core of Sichuan’s sustainable development is still to seek the innovative and coordinated development of the economy and environment. Therefore, Sichuan should continue to improve its innovation ability, optimize its industrial structure and strengthen the implementation of industrial policies on environmental protection.
(4) The fourth tier includes Shaanxi, Jiangxi, Chongqing, Shanxi, Heilongjiang, Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Jilin, Yunnan, Gansu, Hainan, Guizhou, Ningxia and Qinghai, ranking 16th to 30th in China. Shaanxi Province has a good development foundation and comparative advantages in transportation, power transmission, transformation equipment, national defense and the military industry, but the proportion of high-tech strategic emerging industries, private enterprises and civil–military integration products is small. In addition, Shaanxi Province ranks last in the opening-up sub-index among the six central provinces. In recent years, Jiangxi Province has developed a distinctive industrial system which is driven by semiconductor lighting, mobile intelligent terminals, and digital audio-visual products, but there are still many problems in innovation and development, in quality and in social benefits. Chongqing’s manufacturing industry is based on electronic manufacturing, the material industry, equipment manufacturing, the energy industry, automobile manufacturing and other industries. Although the scale of the manufacturing industry has increased, the traditional manufacturing industry is still in a state of overcapacity due to the bottleneck. Therefore, based on the development of the traditional manufacturing industry, Chongqing should speed up the development of the modern manufacturing industry and promote the development of its manufacturing industry with the sustained and rapid development of the high-tech industry and the strategic emerging industry. Shanxi Province, as a big coal province in China, had a rapid development speed in the last century. However, due to the depletion of resources and the change in development concept in recent years, Shanxi Province has slow development and ranks at the bottom of the six central provinces in terms of innovation and development, economic benefits, structural optimization and social contribution. As a traditional big province of the equipment manufacturing industry, Heilongjiang Province’s equipment manufacturing industry is still on a large scale, but the technical content and added value are low. The ability of independent R&D and design are weak and there is more imported equipment, but its abilities of digestion, absorption and re-innovation are insufficient. Its structural optimization and opening up rank last among the three northeast provinces. Xinjiang covers an area of 1.66 million square kilometers, ranking first in China. It is rich in natural resources. The development level of its manufacturing industry is of great significance. At present, the oil processing industry is the pillar of Xinjiang’s industry, but it is also a high-consumption and high-pollution industry. Therefore, we should deepen the structure of industry and products, extend the industrial chain of the petroleum industry, increase the proportion of refined petroleum products and downstream products and increase resource development products, thus enhancing the added value of products and making efficient use of resources. At present, the development of Inner Mongolia’s manufacturing industry is far from forming an industrial pattern of coordinated development with scientific and technological innovation, modern finance and human resources, and the industrial layout is scattered and does not gather. There are problems such as weak innovation supportability, the slow transformation of the manufacturing industry and the slow follow-up of emerging industries. Guangxi is dominated by traditional manufacturing enterprises such as the non-metallic mineral products industry, the wood processing industry, the agricultural and sideline food processing industry, the chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing industry and the automobile manufacturing industry, and medium and high-tech industries with high added value are at a disadvantage in the competition. In addition, the growth rate of Guangxi’s industrial added value has also declined in recent years, and there are obvious shortcomings in its innovation ability and opening up. Therefore, Guangxi should take advantage of the development of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao; take the initiative to undertake industrial transfer; focus on the introduction of capital, technology and talents; and speed up its development. The early industrial development of Jilin Province was dominated by the automobile industry and the petrochemical industry. At present, the manufacturing of transportation equipment, chemical raw materials and chemical products are its main pillar industries. However, in the current structural adjustment, the difficult transition and the impact of the population exodus have contributed to it ranking last among the three eastern provinces in terms of innovation and development, economic benefits and quality benefits. Yunnan Province is faced with the dual pressure of transformation and upgrading as well as improving the quality of development. There are a series of problems, such as insufficient accumulation, the slow development of emerging industries and the difficult transformation of new and old kinetic energy. Yunnan should take advantage of favorable geographical conditions and the institutional arrangement of the free trade area to actively participate in and strengthen economic and trade exchanges and scientific and technological cooperation between China and the ASEAN Free Trade Area, thus making it an important window for cooperation and exchange between China and ASEAN. After its long-term development, Gansu has gradually formed a manufacturing development pattern focusing on Petrochemical General equipment, electronics and electrical equipment, new energy equipment, high-end CNC machine tools and agricultural machinery and equipment. For a long time, comprehensive competitiveness has needed to be improved for the following reasons: (1) slow industrial transformation and upgrading; (2) insufficient manufacturing industry agglomeration; (3) low-level industrial intelligence; (4) the lack of a complete industrial chain, supply chain and value chain system; (5) the independent innovation ability of manufacturing enterprises is not strong; and (6) the “industry–university research” close collaborative development mechanism has not yet been formed. The economy is relatively backward, and the industrial structure is not perfect. Therefore, the development level of the manufacturing industry is not high, and there are obvious deficiencies in innovation development, economic benefit and social contribution. Hainan should make use of its advantages and rely on the Hainan free trade port to vigorously develop tourism, the modern service industry and the high-tech industry. Affected by multiple factors, the development level of the manufacturing industry in Guizhou is very backward, and it has not reached the middle stage of industrialization. There is a long way to go to promote the manufacturing industry in Guizhou Province to reach the national average level. Ningxia ranks lower in innovation and development, economic benefits, quality benefits, structural optimization, opening up and (especially) social contribution, which ranks at the bottom of the country. Ningxia should actively support the development of characteristic and advantageous industries and policies according to its resource endowment and comparative advantages. Qinghai Province is located in Qinghai Tibet Plateau, the interior of China, and is far away from the sea. It has only a small industry, resources are not over-exploited and environmental pollution is not serious. Qinghai Province should adhere to the comprehensive development and utilization of superior resources and the cultivation of a characteristic economy as the main direction of developing high-tech industry. It is also necessary to increase the development of key technologies and major projects and to strive to form a diversified development pattern for the manufacturing industry.
5.2. Discussion
The scientific significance of constructing the HQDMI evaluation index system is reflected in the following aspects: (1) It offers a quantitative research methodology for the scientific evaluation of the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. (2) It provides a unified evaluation system for the evaluation of manufacturing development. (3) It gives the government and manufacturing enterprises a basis for making decisions to create effective measures. (4) It provides technical support for government managers to formulate incentive policies. (5) It offers theoretical support for enterprise transformation and upgrading. (6) It is crucial in directing the manufacturing industry’s high-quality growth. In addition, this paper takes China, a typical representative of developing countries, as an example to objectively evaluate the development level of China’s manufacturing industry. The research findings can not only offer crucial policy recommendations for China’s manufacturing industry development, industrial structure adjustment and industrial economic growth, but they can also serve as a valuable source of information and a benchmark for other developing nations that are formulating their own manufacturing industry development, industrial structure adjustments and industrial economic policies.
Taking China as an example, four aspects, i.e., innovation and development, economic benefits, structural optimization and opening up, deserve special attention in the process of promoting the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry.
In terms of innovation and development, most provinces in China have weak innovation capacity, so they need to continue to increase R&D investment, break through technical barriers and enhance the core competitiveness of enterprises. For a long time, China’s manufacturing industry has rapidly expanded its industrial scale by introducing technology while ignoring scientific and technological innovation. China’s original achievements must be highly valued.
In terms of economic benefits, compared with manufacturing powers such as the United States and Germany, the brand building of China’s manufacturing industry is still lagging behind. There are many low-end products along with low market awareness, low added value and weak competitiveness, which lead to low economic benefits.
In terms of structural optimization, due to the weak independent R&D and innovation capacity of China’s manufacturing industry, its manufacturing industry structure is mainly low-end and traditional, and the development level of the high-tech manufacturing industry with high added value and high-tech content is relatively low. Therefore, China’s manufacturing industry should develop in directions that are high-end, intelligent, green, integrated and service oriented.
In terms of opening up, due to lateral policies, coastal areas have taken the lead in adopting opening up policies and have actively introduced foreign capital, technology, management, advanced equipment, etc.; therefore, the development level of the manufacturing industry in the region has rapidly improved. However, the northwest and southwest regions, due to geographical conditions, are far less open to the outside world than coastal areas. Therefore, northwest and southwest regions should improve their systems in a way that is conducive to opening up and that is compatible with international trade and investment rules, thus creating a good international economic and trade environment for the development of their manufacturing industries.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions
This paper proposes a general methodology system of “attribute reduction–weight calculation– index calculation”, which is simple and more scientific and can provide a theoretical basis for the construction of an evaluation index system. Based on the methodology system, a scientific evaluation index system of the HQDMI was constructed from the perspective of innovation, economy, quality, structural optimization, openness, social contribution and green ecology. Taking China as an example, the total index of the HQDMI and the average of each subsystem index in China’s 30 provinces from 2011 to 2019 were calculated. This study examines the weaknesses of the HQDMI development in China’s 30 provinces in depth and offers a dynamic trend and policy recommendations for the industry’s high-level development. Conclusions and specific policy recommendations are as follows:
The results show that there are obvious differences in the level of the HQDMI in different regions in China, showing a decreasing trend in the eastern coastal, central, northeastern and western regions. This paper divides the provinces into four echelons according to the total index of the HQDMI. Among them, the manufacturing industries in the Pearl River Delta and Yangtze River Delta are at the forefront of the country in terms of innovation development, economic benefit, quality benefit, structural optimization, opening up and social contribution. These regions have strong innovation abilities, and their governments have more funds and human resources to invest in energy conservation and environmental protection. However, in some remote areas with fragile environments, it is not suitable to over-exploit resources, and conditions for developing the manufacturing industry are poor. Moreover, the total index of the HQDMI in the central region and the northeast region has a large gap compared with the eastern coastal provinces. Most of the central and northeast provinces are dominated by heavy industries, which cause environmental pollution. In addition, the local governments lack systematic measures to deal with pollutants, so the sub-index of green ecology in the central and northeast provinces is low.
6.2. Recommendations
According to the results, this study proposes the following policy recommendations to improve the HQDMI:
(1) Enhance the spatial balance of development. We should break the institutional barriers encountered in the flow of production factors, eliminate regional market barriers, promote the free flow of production factors and improve the spatial allocation efficiency of production factors. Moreover, a regional transmission mechanism for the HQDMI between the eastern coastal areas and the central areas should be established to promote the common development of developed and underdeveloped areas.
(2) Focus on limited resources to break through technical bottlenecks and account for industrial weaknesses. The enthusiasm and creativity of local governments should be fully utilized in the system and mechanism reform. We should make better use of high-quality capital, technology and human resources at home and abroad, and we should enhance the ability to drive innovation. The government should drive development by innovation, strengthen forward-looking applied basic research, lead cutting-edge technological innovation and provide long-term and stable support for basic research and original research.
(3) Accelerate the development of advantageous industrial clusters. With the increasing support of advantageous industries for economic growth, we should promote the clustered development of advantageous industries and vigorously develop the advanced manufacturing industry. We should focus on the development of intelligent equipment and intelligent products, promote the intelligent production process, cultivate new production methods and comprehensively improve the intelligent level of enterprise R&D.
(4) Strengthen the brand construction of product quality. We should improve product quality control technology, improve product quality management mechanisms, lay a solid foundation for quality development, optimize the quality development environment and strive to achieve a substantial improvement in the quality of the manufacturing industry. Moreover, we should promote the quality revolution of Chinese products and services, and we should continue to cultivate and carry the craftsman spirit of continuing to improve and pursue excellence. Through the spirit of craftsmanship, technical workers are encouraged to continuously improve the process and technology of manufacturing enterprises, thus continuously improving the quality and reputation of manufacturing products and services.
(5) Intensify reform and opening up, and coordinate domestic development and opening up. To promote the HQDMI, we must unblock the domestic cycle, link the domestic and international double cycles, and utilize both the home and international markets and resources to the fullest extent possible. Based on the strategic location advantages of the “Belt and Road”, domestic and foreign production factor resources and the HQDMI of the province should be realized in-depth and with precision; therefore, industries and enterprises with competitive advantages can expand overseas markets. We should introduce superior overseas enterprises that can account for shortcomings; therefore, the two markets and resources can be deeply complementary in the HQDMI of the province.
(6) Increase the ability of income distribution policy adjustment. We should adhere to the principle of distribution according to work, increase the labor remuneration of workers (especially front-line workers) and improve the working environment of enterprise workers. We should improve the order and fairness of the market, improve the system and mechanism of distribution according to factors and strive to achieve equality of opportunity. We should raise the level of residents’ labor income and property income and expand the proportion of middle-income groups. Moroever, we should standardize the order of income distribution, establish personal income and property information systems and strengthen the protection of citizens’ legitimate property rights and interests.
(7) Regard protecting the ecological environment as an inherent requirement of the HQDMI. It is necessary to formulate, improve and implement relevant laws, regulations and standards for the protection of the ecological environment, and we should protect the ecological environment with a stable system and mechanism. We should formulate and implement public policies to promote ecological environment protection, and we should guide government departments, enterprises, individuals and other subjects to actively participate in ecological environment protection through policies. We should strengthen the construction of environmental infrastructure, provide environmental public goods, increase the supply of high-quality ecological products and meet the needs of the people for high-quality ecological products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S. and J.S.; methodology, Y.S.; software, M.Z.; validation, Y.S., J.S. and M.Z.; formal analysis, Y.S.; investigation, Y.S.; resources, Y.S.; data curation, Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.S.; visualization, Y.S.; supervision, Y.S.; project administration, Y.S.; funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 71371172.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Description
| Symbol | Symbol Description |
| The object set | |
| The attribute set | |
| There is a similar relationship between object . | |
| There is no similar relationship between object . | |
| The similarity relation matrix based on the attribute set | |
| The similarity relation matrix based on the attribute set | |
| The redundant attributes set | |
| The reserved attribute set | |
| The combined weight of the attribute | |
| The total index of object |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The average of the total HQDMI index and one of each sub-index in 30 provinces of China from 2011 to 2019.
Table A1.
The average of the total HQDMI index and one of each sub-index in 30 provinces of China from 2011 to 2019.
| Ranking | Total Index of HQDMI | Index of HQDMI Subsystem | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovative Development | Economic Benefit | Quality Benefit | Structural Optimization | Opening Up | Social Contribution | Green Ecology | ||||||||||
| 1 | Guangdong | 0.6861 | Guangdong | 0.0782 | Jiangsu | 0.1122 | Jiangsu | 0.0542 | Guangdong | 0.0785 | Guangdong | 0.1957 | Guangdong | 0.1122 | Beijing | 0.0927 |
| 2 | Jiangsu | 0.6213 | Jiangsu | 0.0689 | Guangdong | 0.0952 | Shanghai | 0.0538 | Jiangsu | 0.0538 | Jiangsu | 0.1685 | Jiangsu | 0.0767 | Tianjin | 0.0906 |
| 3 | Shandong | 0.4078 | Shandong | 0.0434 | Shandong | 0.0856 | Heilongjiang | 0.0489 | Beijing | 0.0296 | Shanghai | 0.0918 | Shandong | 0.0710 | Zhejiang | 0.0900 |
| 4 | Zhejiang | 0.4026 | Zhejiang | 0.0410 | Zhejiang | 0.0751 | Shandong | 0.0456 | Shanghai | 0.0191 | Zhejiang | 0.0728 | Beijing | 0.0679 | Shandong | 0.0899 |
| 5 | Shanghai | 0.3857 | Shanghai | 0.0321 | Shanghai | 0.0472 | Liaoning | 0.0453 | Shandong | 0.0178 | Shandong | 0.0544 | Zhejiang | 0.0647 | Jiangsu | 0.0870 |
| 6 | Beijing | 0.3199 | Beijing | 0.0296 | Henan | 0.0445 | Shaanxi | 0.0451 | Zhejiang | 0.0172 | Fujian | 0.0455 | Henan | 0.0559 | Shanghai | 0.0861 |
| 7 | Henan | 0.2539 | Anhui | 0.0196 | Hebei | 0.0363 | Xinjiang | 0.0440 | Sichuan | 0.0102 | Beijing | 0.0363 | Shanghai | 0.0555 | Anhui | 0.0848 |
| 8 | Fujian | 0.2532 | Tianjin | 0.0192 | Liaoning | 0.0346 | Guangdong | 0.0419 | Henan | 0.0095 | Liaoning | 0.0329 | Hubei | 0.0423 | Guangdong | 0.0844 |
| 9 | Liaoning | 0.2422 | Hubei | 0.0176 | Fujian | 0.0301 | Zhejiang | 0.0419 | Fujian | 0.0087 | Tianjin | 0.0322 | Anhui | 0.0409 | Fujian | 0.0825 |
| 10 | Tianjin | 0.2390 | Liaoning | 0.0175 | Sichuan | 0.0296 | Hubei | 0.0414 | Hubei | 0.0078 | Hubei | 0.0154 | Hebei | 0.0407 | Henan | 0.0817 |
| 11 | Hubei | 0.2326 | Fujian | 0.0151 | Beijing | 0.0279 | Shanxi | 0.0399 | Tianjin | 0.0076 | Hebei | 0.0154 | Sichuan | 0.0401 | Chongqing | 0.0812 |
| 12 | Hebei | 0.2210 | Hunan | 0.0150 | Hubei | 0.0276 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0397 | Jiangxi | 0.0066 | Sichuan | 0.0127 | Hunan | 0.0383 | Hubei | 0.0804 |
| 13 | Anhui | 0.2198 | Henan | 0.0141 | Anhui | 0.0268 | Hebei | 0.0392 | Liaoning | 0.0065 | Jiangxi | 0.0108 | Fujian | 0.0378 | Shaanxi | 0.0796 |
| 14 | Sichuan | 0.2129 | Sichuan | 0.0127 | Hunan | 0.0260 | Tianjin | 0.0391 | Anhui | 0.0065 | Henan | 0.0101 | Liaoning | 0.0358 | Shanxi | 0.0782 |
| 15 | Hunan | 0.2066 | Shaanxi | 0.0112 | Tianjin | 0.0204 | Henan | 0.0382 | Shaanxi | 0.0065 | Chongqing | 0.0100 | Tianjin | 0.0301 | Jiangxi | 0.0761 |
| 16 | Shaanxi | 0.1903 | Hebei | 0.0109 | Jiangxi | 0.0180 | Hunan | 0.0380 | Hunan | 0.0065 | Anhui | 0.0098 | Shaanxi | 0.0272 | Hunan | 0.0757 |
| 17 | Jiangxi | 0.1795 | Chongqing | 0.0101 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0170 | Yunnan | 0.0360 | Chongqing | 0.0048 | Jilin | 0.0086 | Chongqing | 0.0272 | Xinjiang | 0.0756 |
| 18 | Chongqing | 0.1771 | Jiangxi | 0.0071 | Shaanxi | 0.0165 | Beijing | 0.0358 | Hebei | 0.0041 | Guangxi | 0.0082 | Jiangxi | 0.0268 | Hebei | 0.0745 |
| 19 | Shanxi | 0.1710 | Shanxi | 0.0064 | Chongqing | 0.0153 | Sichuan | 0.0354 | Jilin | 0.0029 | Hunan | 0.0072 | Guangxi | 0.0267 | Hainan | 0.0740 |
| 20 | Heilongjiang | 0.1634 | Heilongjiang | 0.0058 | Shanxi | 0.0148 | Jiangxi | 0.0340 | Guangxi | 0.0025 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0055 | Shanxi | 0.0250 | Heilongjiang | 0.0729 |
| 21 | Xinjiang | 0.1543 | Jilin | 0.0046 | Heilongjiang | 0.0125 | Fujian | 0.0336 | Heilongjiang | 0.0020 | Shanxi | 0.0049 | Gansu | 0.0238 | Sichuan | 0.0722 |
| 22 | Inner Mongolia | 0.1519 | Guangxi | 0.0045 | Jilin | 0.0120 | Anhui | 0.0314 | Guizhou | 0.0017 | Heilongjiang | 0.0045 | Xinjiang | 0.0234 | Liaoning | 0.0695 |
| 23 | Guangxi | 0.1506 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0039 | Guangxi | 0.0118 | Gansu | 0.0302 | Shanxi | 0.0017 | Shaanxi | 0.0042 | Yunnan | 0.0230 | Guangxi | 0.0694 |
| 24 | Jilin | 0.1463 | Gansu | 0.0036 | Yunnan | 0.0096 | Hainan | 0.0294 | Gansu | 0.0011 | Hainan | 0.0032 | Jilin | 0.0229 | Yunnan | 0.0690 |
| 25 | Yunnan | 0.1452 | Yunnan | 0.0034 | Xinjiang | 0.0084 | Jilin | 0.0291 | Yunnan | 0.0010 | Yunnan | 0.0031 | Guizhou | 0.0220 | Gansu | 0.0681 |
| 26 | Gansu | 0.1316 | Guizhou | 0.0028 | Guizhou | 0.0064 | Ningxia | 0.0286 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0009 | Xinjiang | 0.0012 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0197 | Jilin | 0.0661 |
| 27 | Hainan | 0.1251 | Ningxia | 0.0024 | Gansu | 0.0040 | Chongqing | 0.0284 | Hainan | 0.0003 | Guizhou | 0.0009 | Hainan | 0.0168 | Inner Mongolia | 0.0652 |
| 28 | Guizhou | 0.1229 | Xinjiang | 0.0016 | Ningxia | 0.0015 | Guizhou | 0.0281 | Qinghai | 0.0003 | Gansu | 0.0007 | Heilongjiang | 0.0167 | Ningxia | 0.0639 |
| 29 | Ningxia | 0.1064 | Qinghai | 0.0008 | Hainan | 0.0009 | Guangxi | 0.0275 | Ningxia | 0.0002 | Ningxia | 0.0005 | Qinghai | 0.0125 | Guizhou | 0.0611 |
| 30 | Qinghai | 0.0963 | Hainan | 0.0005 | Qinghai | 0.0005 | Qinghai | 0.0246 | Xinjiang | 0.0001 | Qinghai | 0.0000 | Ningxia | 0.0094 | Qinghai | 0.0576 |
Appendix B
This section mainly introduces the steps of using the entropy weight method, principal component analysis, factor analysis and the CRITICAL method to calculate the index weight.
- (1)
- The steps to calculate the index weight by the entropy weight method are as follows [30,31]:
We assume that there are objects, namely , and indices, namely . is the observation value of object at index . It is assumed that all indices are “benefit oriented” (if not, they can be transformed to become benefit oriented through standardization). For a normalized decision matrix , let
The information entropy value of the index is:
When , we specify = 0; therefore, .
The coefficient of the variation degree of each index can be calculated as
We calculate the weight of each index as:
- (2)
- The introduction to principal component analysis is as follows [32]:
We assume that there are objects and indices. is the observation value of the object at the index ; therefore, we have the following matrix:
In matrix , the th column vector is . We use vectors for linear combination, and the combination coefficient satisfies the following formula:
The coefficient in Equation (A5) is determined by the following principles:
- (a)
- and , i.e., and are not related.
- (b)
- is the index with the largest variance in , followed by , i.e.:
The comprehensive index determined above is called the first principal component, the second principal component, …, and the principal component of the original index. The variance contribution rate of each principal component is regarded as the weight of the principal component, namely:
In Equation (A7), are the characteristic roots of the covariance matrix of the matrix .
- (3)
- The introduction of the factor analysis method is as follows [33]:
- (1)
- Here, we standardize the original data. We assume that there are objects and indices and that is the observation value of object at index ; therefore, we can standardize the existing data :where ,
- (2)
- We then calculate the correlation matrix of indices :where
- (3)
- We then find the eigenvector matrix and eigenvalue () of the correlation matrix .
- (4)
- We can take eigenvalues and eigenvectors according to the requirements of variance contribution , and use these eigenvalues and eigenvectors to establish the initial factor load matrix.
- (5)
- We can establish the factor model:where are common factors, and is a special factor.
- (6)
- The initial factor load matrix is rotated to obtain a new ideal factor load matrix:
- (7)
- We can express the factors as linear combinations of variables:The regression coefficient is solved by the least square solution:
- (8)
- We then determine the weight of each index. The weight of index is , where is the contribution rate. is the standardized weight of index .
- (4)
- The introduction to the CRITICAL method is as follows:We can calculate the amount of information contained in each index:where is the standard deviation of the th index, is the quantitative value of the conflict between the th index and other indices and is the correlation coefficient between indices and .The weight of the index is:
References
- Peng, S.T.; Li, P.F. Evaluation of quality of China’s manufacturing and its improvement path. Stud. Social. Chin. Charact. 2018, 5, 34–40+54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.W. Theoretical mechanism and evaluation analysis of high–quality development of manufacturing industry. Mod. Manag. 2020, 40, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Peron, M.; Sgarbossa, F.; Strandhagen, J.O. Decision support model for implementing assistive technologies in assembly activities: A case study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 60, 1341–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, M.; Fragapane, G.; Sgarbossa, F.; Kay, M. Digital Facility Layout Planning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.S.; Shi, X.A.; Liu, J. 40 years of manufacturing in China: Intelligentization process and outlook. China Soft Sci. 2019, 1, 1–9+30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J.; Yu, D.H.; Chen, H.Q.; Li, Y. Comprehensive Measurement, Spatiotemporal Evolution, and Spatial Correlation Analysis of High-Quality Development in the Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhu, J.F. The performance evaluation in logistics service supply chain based on fuzzy–rough sets. Syst. Eng. 2007, 7, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.X.; Qiu, G.F.; Wu, W.Z. A general approach to attribute reduction in rough set theory. Sci. China Ser. F Inf. Sci. 2007, 50, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.H. Research on the connotation, path and dynamic mechanism of high–quality development of manufacturing industry. Rev. Ind. Econ. 2020, 1, 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y. The basic logic and practical path of the high–quality development of China’s manufacturing industry. Theory Explor. 2020, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C. Drive by innovation to build high quality growth of China’s manufacturing industry—Based on the review of the development of the manufacturing industry in the past 70 years. Econ. Rev. J. 2019, 10, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.X. Integration of advanced manufacturing industry and modern service industry to promote high quality development of manufacturing industry. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 19, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.C.; Zhang, S.Q. Research review on the evaluation index system of high-quality development in China’s manufacturing industry. Stat. Decis. 2021, 37, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Fang, Z.Y. Evaluation and analysis of high–quality development of manufacturing industry in city clusters of Yangtze River economic belt. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.Z.; Chu, L.P. Research on the evaluation of high–quality development of manufacturing industry from the perspective of integration of the Yangtze River delta–TOPSIS evaluation model based on improved CRITICAL–entropy weight method. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2020, 39, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Gu, Y. Construction and analysis of manufacturing power evaluation system. Strategy Study CAE 2015, 17, 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Research on evaluation and strategy of high–quality development of Shenzhen manufacturing industry-multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method based on python. J. Univ. South China (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 21, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.Y.; Zhang, G.S. The influence of rising labor cost on the high-quality development of enterprises. Inq. Econ. Issues 2021, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.Y. Marketization and high–quality development of manufacturing industry an empirical analysis based on China’s provincial panel data. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 20, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Z.Y.; Chu, M.T.; Chen, S.S.; Tsai, C.H. Identifying Comprehensive Key Criteria of Sustainable Development for Traditional Manufacturing in Taiwan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceptureanu, E.G.; Ceptureanu, S.I.; Bologa, R.; Bologa, R. Impact of Competitive Capabilities on Sustainable Manufacturing Applications in Romanian SMEs from the Textile Industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakr, M.; Abbas, A.T.; Tomaz, I.; Soliman, M.S.; Luqman, M. Sustainable and Smart Manufacturing: An Integrated Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.; Ahuja, I.S.; Sethi, A.P.S. Technology push and demand pull practices for achieving sustainable development in manufacturing industries. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 240–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrasheedi, M.; Mardani, A.; Mishra, A.R.; Streimikiene, D.; Liao, H.C.; Al-nefaie, A.H. Evaluating the green growth indicators to achieve sustainable development: A novel extended interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy-combined compromise solution approach. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 29, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Olugu, E.U.; Musa, S.N.; Mahat, A.B. Fuzzy-based sustainability evaluation method for manufacturing SMEs using balanced scorecard framework. J. Intell. Manuf. 2018, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.N.; Estebanez, R.P. Construction and Analysis of Performance Evaluation Index System for Chinese Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Based on Fuzzy Hierarchical Analysis Model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2020, 1230786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Geng, H.; Wang, W.T. Index reduction of industrial technological innovation capability evaluation based on rough set method. Prices Mon. 2008, 12, 34–35+41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y. Construction and demonstration of evaluation index system for high quality development of manufacturing industry: A case study of central China take as an example. Technol. Econ. Guide 2020, 28, 167–169. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.J.; Yang, Y.Q. Health status evaluation of aero-engines based on combination weighting method and unascertained measure model. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2020, 29, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S. The KPI design method of performance assessment of hydraulic engineering construction enterprise based on entropy method. J. Shandong Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 2020, 50, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J. Research on China’s renewable energy quota distribution based on factor analysis and entropy method. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2020, 40, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.L.; Gao, T.B.; Wang, S.E. Evaluation of urbanization level using principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Ind. Eng. J. 2008, 3, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.J.; He, Y.H.; Huang, R.Q.; Ju, N.P. Weights of slope stability evaluation indexes based on factor analysis method. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2015, 50, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. Theoretical interpretation and measurement methods of high–quality development in China. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2020, 37, 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.G.; Cao, L. Construction and measurement of manufacturing enterprises high-quality development evaluation system—Based on the data of 1881 listed companies from 2015 to 2018. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2020, 37, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J. Research on evaluation index system of high-quality development of state-owned enterprises. Account. Financ. 2020, 4, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Xiong, X. Evaluation and transformation suggestions on industrial competitiveness of different cities in Hunan province. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.W. Research on the evaluation of high-quality development of manufacturing industry in the central region of chain: Analysis based on the data from 2007 to 2018. Econ. Probl. 2020, 9, 85–91+117. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Huang, C.; Wu, C.Q. The temporal and spatial pattern evolution of industrial high-quality development index in the Yangtze River economic belt. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Qiao, B.H. Thoughts on constructing the high-quality development index system of manufacturing industry. Ind. Econ. Rev. 2018, 5, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Xiao, H.; Liao, S. Study on evaluation of continuous innovation ability of high-end equipment manufacturing enterprises based on MC-ZF-HD-DS. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2015, 24, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).