Adoption of Sustainability Innovations and Environmental Opinion Leadership: A Way to Foster Environmental Sustainability through Diffusion of Innovation Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
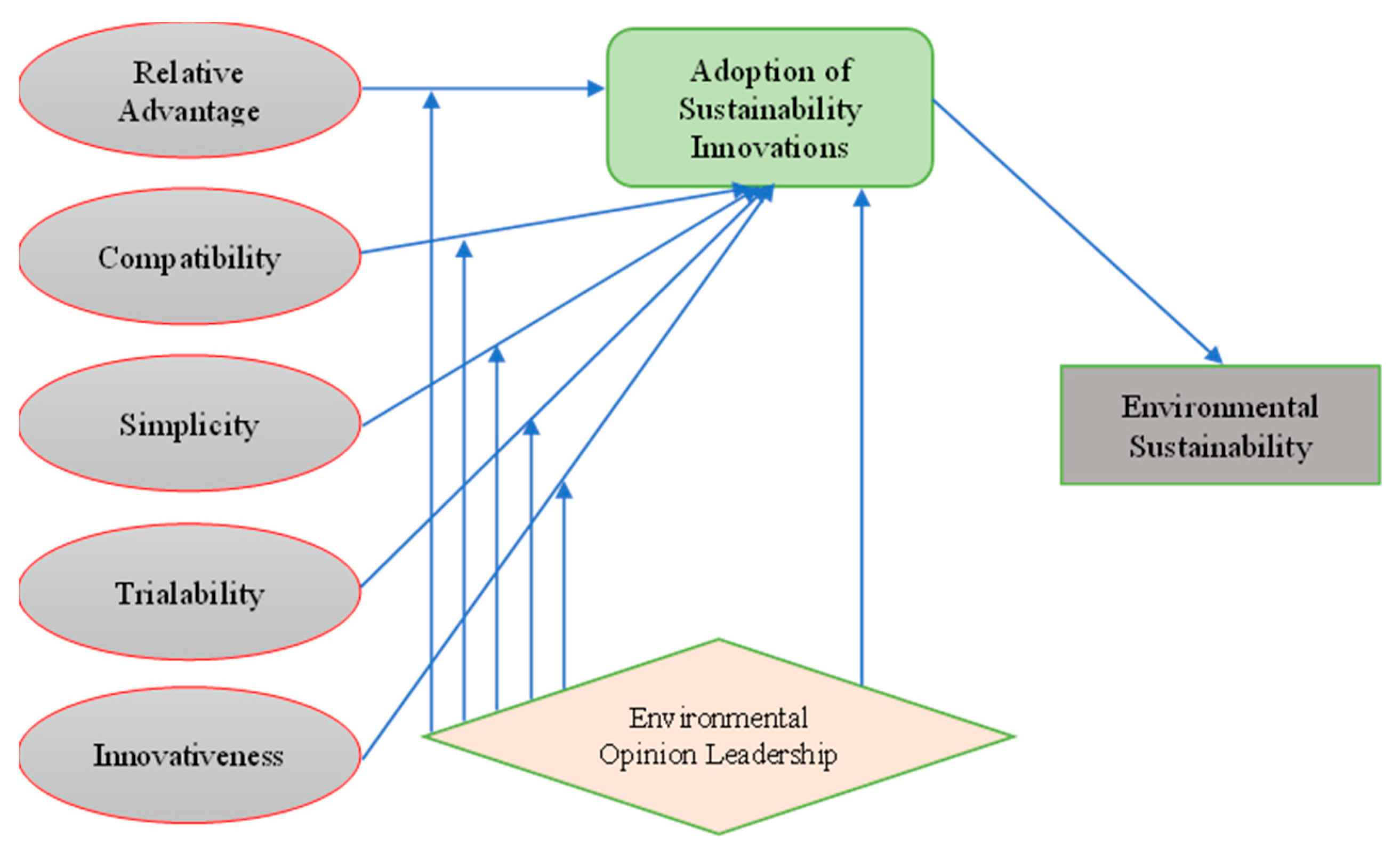
2. Literature Review
3. Research Methodology
4. Results
4.1. Convergent Validity
4.2. Discriminant Validity
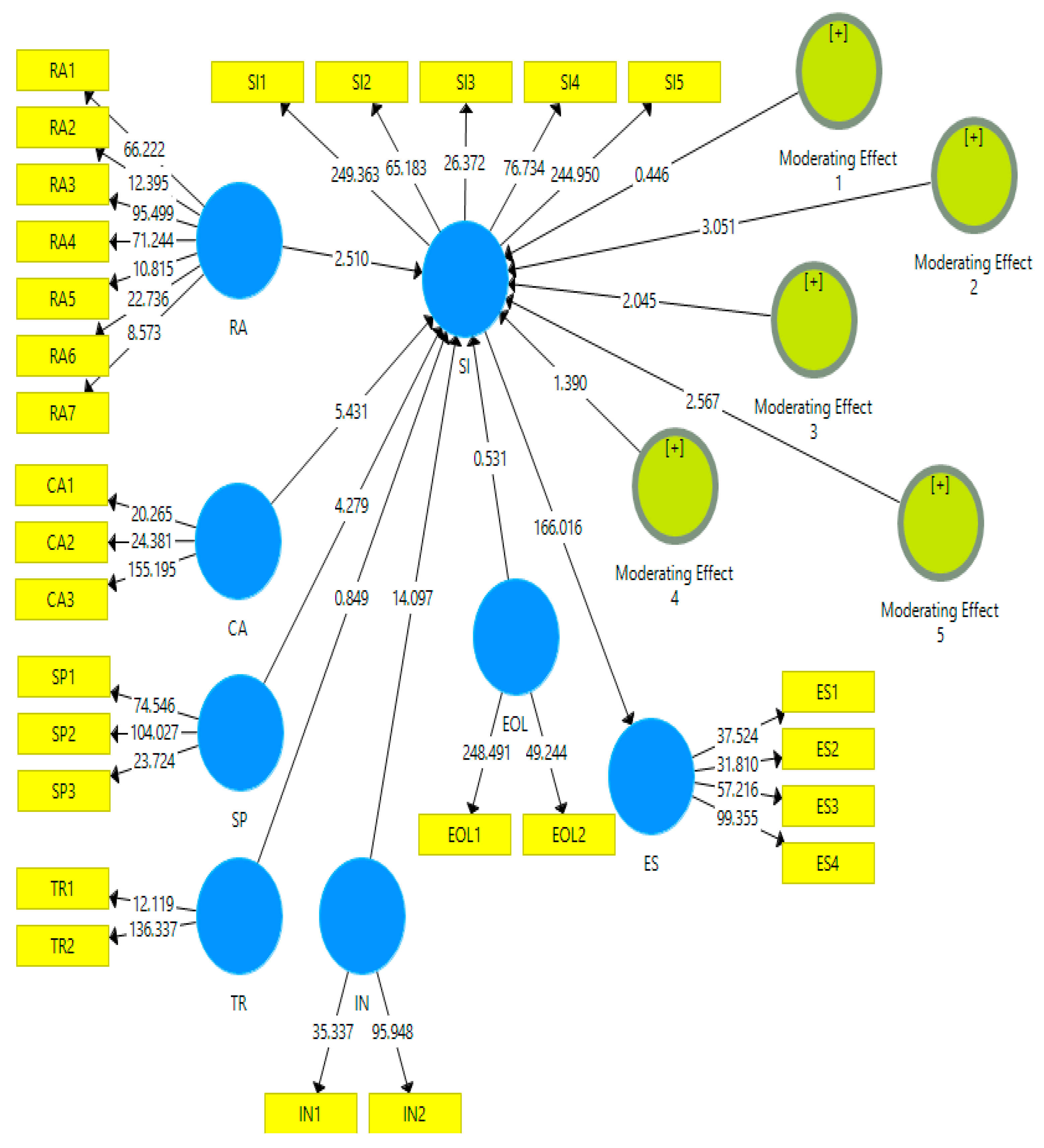
4.3. Direct Effect Results—PLS
4.4. Moderating Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Implications
6.2. Practical Implications
6.3. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danish, M.S.S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Stepanova, D.; Mikhaylov, A.; Grilli, M.L.; Khosravy, M.; Khosravy, T. A systematic review of metal oxide applications for energy and environmental sustainability. Metals 2020, 10, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gaur, V.K.; Gupta, S.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Gnansounou, E.; You, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Wong, J.W. Trends in mitigation of industrial waste: Global health hazards, environmental implications and waste derived economy for environmental sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Cherian, J.; Ahmad, N.; Scholz, M.; Samad, S. Conceptualizing the Role of Target-Specific Environmental Transformational Leadership between Corporate Social Responsibility and Pro-Environmental Behaviors of Hospital Employees. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakarakos, G.; Dounis, A. Intelligent management of distributed energy resources for increased resilience and environmental sustainability of hospitals. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.H.; McManus, C.; Lee, J.A. Analyzing the adoption of radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules using the diffusion of innovations theory: Understanding where we are in the United States? Ultrasonography 2022, 41, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, A.L.; Dentzman, K.; Wardropper, C.B. Using diffusion of innovations theory to understand agricultural producer perspectives on cover cropping in the inland Pacific Northwest, USA. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2021, 36, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, I. Detailed review of Rogers’ diffusion of innovations theory and educational technology-related studies based on Rogers’ theory. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. TOJET 2006, 5, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Talebian, A.; Mishra, S. Predicting the adoption of connected autonomous vehicles: A new approach based on the theory of diffusion of innovations. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 95, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carino, S.; Porter, J.; Pour, S.M.; Collins, J. Environmental sustainability of hospital foodservices across the food supply chain: A systematic review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 825–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koytcheva, M.K.; Sauerwein, L.K.; Webb, T.L.; Baumgarn, S.A.; Skeels, S.A.; Duncan, C.G. A systematic review of environmental sustainability in veterinary practice. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2021, 44, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Ahmad, M.; Mukeshimana, M.C. Solar energy development in Pakistan: Barriers and policy recommendations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ullah, Z.; Mahmood, A.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Vega-Muñoz, A.; Han, H.; Scholz, M. Corporate social responsibility at the micro-level as a “new organizational value” for sustainability: Are females more aligned towards it? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, J. Diffusion of innovation theory. Can. J. Nurs. Inform. 2011, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Smerecnik, K.R.; Andersen, P.A. The diffusion of environmental sustainability innovations in North American hotels and ski resorts. J. Sustain. Tour. 2011, 19, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, J.P. A review and critique of Rogers’ diffusion of innovation theory as it applies to organizations. Organ. Dev. J. 2003, 21, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Dearing, J.W.; Cox, J.G. Diffusion of innovations theory, principles, and practice. Health Aff. 2018, 37, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junnonyang, E. Integrating TAM, perceived risk, trust, relative advantage, government support, social influence and user satisfaction as predictors of mobile government adoption behavior in Thailand. Int. J. Ebusiness Egovernment Stud. 2021, 13, 159–178. [Google Scholar]
- Sin, K.Y.; Osman, A.; Salahuddin, S.N.; Abdullah, S.; Lim, Y.J.; Sim, C.L. Relative advantage and competitive pressure towards implementation of e-commerce: Overview of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 35, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawless, M.W.; Fisher, R.J. Sources of durable competitive advantage in new products. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. Int. Publ. Prod. Dev. Manag. Assoc. 1990, 7, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainty, A.R.; Bagilhole, B.M.; Neale, R.H. The compatibility of construction companies’ human resource development policies with employee career expectations. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2000, 7, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee Mashhadi, A.H.; Emadzadeh, A.; Hosseini, M. Assessing the compatibility of the Radiology Technology Curriculum with Professional Requirements: Viewpoints of Radiology Technology Employee in Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. Future Med. Educ. J. 2019, 9, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinsky, E.A. Defining who is an employee after AB 5: Trading uniformity and simplicity for expanded coverage. Cath. UL Rev. 2021, 70, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bongers, I.; Stikkelbroek, Y.; Bachrach, N. Alarming Situation Amongst Mental Health Care Employees; Mental Health Issues with Possible Resignation as a Consequence. TSG. 2022. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/med/35789616 (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Cillo, V.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; Ardito, L.; Del Giudice, M. Understanding sustainable innovation: A systematic literature review. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Haghgoo, I.; Davidavičienė, V.; Meidutė-Kavaliauskienė, I. Customer loyalty in mobile banking: Evaluation of perceived risk, relative advantages, and usability factors. Eng. Econ. 2021, 32, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Yin, C. The Distinction between the Absolute and Relative Advantages of Cultural Capital: Different Conceptualizations, Different Consequences. Sociology 2021, 55, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.; de Gennaro, G.; Romano, M.; Battini, L.; Aragona, M.; Corfini, M.; Del Prato, S.; Bertolotto, A. Early vs. standard screening and treatment of gestational diabetes in high-risk women—An attempt to determine relative advantages and disadvantages. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuil, D.A.; Datta, D.K. Effects of firm-specific and country-specific advantages on relative acquisition size in service sector cross-border acquisitions: An empirical examination. J. Int. Manag. 2019, 25, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Ha, V.D.; Dang, T.T.N. The Impact of Human Resource Management Activities on the Compatibility and Work Results. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2020, 7, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.K.; Brower, R. Job satisfaction among federal employees: The role of employee interaction with work environment. Public Pers. Manag. 2019, 48, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppuge, R.H.; Gregar, A. Employees’ organizational preferences: A study on family businesses. Econ. Sociol. 2018, 11, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebetci, Ö. Enhancing end-user satisfaction through technology compatibility: An assessment on health information system. Health Policy Technol. 2018, 7, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryja, C.; Satzger, G. Digital nudging to overcome cognitive resistance in innovation adoption decisions. Serv. Ind. J. 2018, 39, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, G.; Garlapati, D.; Agrawal, U.; Prasuna, R.G.; Mathimani, T.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biological approaches practised using genetically engineered microbes for a sustainable environment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 405, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerg-Bretzke, L.; Limbrecht-Ecklundt, K.; Walter, S.; Spohrs, J.; Beschoner, P. Correlations of the “work–family conflict” with occupational stress—A cross-sectional study among university employees. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skačkauskienė, I.; Vestertė, J. Service modularisation compatibility to organisational objectives. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Contemporary Issues in Business, Management and Economics Engineering, Vilnius, Lithuania, 13–14 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Giedraiti, A.; Stašys, R. Improvement of teamwork compatibility: The example of an industrial enterprise. Forum Sci. Oeconomia 2019, 7, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, D.; Moraes, C. Voluntary simplicity: An exploration of market interactions. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2009, 33, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thamagasorn, M.; Pharino, C. An analysis of food waste from a flight catering business for sustainable food waste management: A case study of halal food production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, J.R.; García-Cortijo, M.C.; Pinilla, V.; Castillo-Valero, J.S. The business model and sustainability in the Spanish wine sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 330, 129810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Tao, W.; Shin, N.; Kim, K.-S. An empirical study of customers’ perceptions of security and trust in e-payment systems. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2010, 9, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshtaria, T.; Matin, A.; Mercan, M.; Datuashvili, D. The impact of customers’ purchasing patterns on their showrooming and webrooming behaviour: An empirical evidence from the Georgian retail sector. Int. J. Electron. Mark. Retail. 2021, 12, 394–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulfraz, M.B.; Sufyan, M.; Mustak, M.; Salminen, J.; Srivastava, D.K. Understanding the impact of online customers’ shopping experience on online impulsive buying: A study on two leading E-commerce platforms. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 68, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. Consumer behavior and environmental sustainability in tourism and hospitality: A review of theories, concepts, and latest research. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Kwon, J. The role of trait and emotion in cruise customers’ impulsive buying behavior: An empirical study. J. Strateg. Mark. 2022, 30, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqshbandi, M.M.; Tabche, I.; Choudhary, N. Managing open innovation: The roles of empowering leadership and employee involvement climate. Manag. Decis. 2018, 57, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Pascual, L.; Galende, J. Ambidextrous Relationships and Social Capability as Employee Well-Being: The Secret Sauce for Research and Development and Sustainable Innovation Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.U.; Aslam, F.; Maitlo, Q.U. Impact of employee’s resilience on organizational resilience: Mediating role of compassion. J. Innov. Sustain. RISUS 2020, 11, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, M.M.A.K.; Moniruzzaman; Dey, M.; Alam, E.; Uddin, A. Strengthening the Trialability for the Intention to Use of mHealth Apps Amidst Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchetchik, A.; Zvi, L.I.; Kaplan, S.; Blass, V. The joint effects of driving hedonism and trialability on the choice between internal combustion engine, hybrid, and electric vehicles. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 151, 119815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMujaini, H.; Hilmia, M.F.; Abudaqa, A.; Alzahmi, R. Corporate foresight organizational learning and performance: The moderating role of digital transformation and mediating role of innovativeness in SMEs. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2021, 5, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E. Customer participation and the trade-off between new product innovativeness and speed to market. J. Mark. 2008, 72, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.Y.; Hamilton, R.T. Socioemotional wealth and the innovativeness of family SMEs in the United Arab Emirates. J. Small Bus. Entrep. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncoro, W.; Suriani, W.O. Achieving sustainable competitive advantage through product innovation and market driving. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2018, 23, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluyinka, S.; Endozo, A.N.; Cusipag, M.N. Integrating Trialability and Compatibility with UTAUT to Assess Canvas Usage During COVID-19 Quarantine Period. Asia-Pac. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2021, 21, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Oluyinka, S.; Cusipag, M. Trialability and purposefulness: Their role towards Google classroom acceptance following educational policy. Acta Inform. Pragensia 2021, 10, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.; Li, G.; Jiao, H.; Addo, F.; Jawahar, I.M. Career sustainability during manufacturing innovation: A review, a conceptual framework and future research agenda. Career Dev. Int. 2019, 24, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Jiang, C.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Hao, Y. Corporate Social Responsibility and High-quality Development: Do Green Innovation, Environmental Investment and Corporate Governance Matter? Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2022, 58, 3191–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hamid, S.N.b.A.; Aziz, A.B.; Ul Hameed, W. The contributing factors towards e-logistic customer satisfaction: A mediating role of information Technology. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2019, 7, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer-Davis, S. The relationship between technology stress and leadership style: An empirical investigation. J. Bus. Educ. Leadersh. 2018, 8, 48–65. [Google Scholar]
- Erosa, V.E. Online Money Flows: Exploring the Nature of the Relation of Technology’s New Creature to Money Supply—A Suggested Conceptual Framework and Research Propositions. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2018, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, L.; Chang, B.-G. The affecting factors of circular economy information and its impact on corporate economic sustainability-Evidence from China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S. Assessing the moderating effect of subjective norm on luxury purchase intention: A study of Gen Y consumers in India. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2020, 48, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; McGinley, S.; Choi, H.-M.; Agmapisarn, C. Hotels’ environmental leadership and employees’ organizational citizenship behavior. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 87, 102375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurzel, R.K.; Liefferink, D.; Di Lullo, M. The European Council, the Council and the Member States: Changing environmental leadership dynamics in the European Union. In The Future of European Union Environmental Politics and Policy; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 62–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Asante, D.; Zhang, J.; Cao, M. The effects of environmental factors on low-carbon innovation strategy: A study of the executive environmental leadership in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Carleton, E. Uncovering How and When Environmental Leadership Affects Employees’ Voluntary Pro-environmental Behavior. J. Leadersh. Organ. Stud. 2017, 25, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cabarcos, M.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, P.; Quiñoá-Piñeiro, L.M. An approach to employees’ job performance through work environmental variables and leadership behaviours. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 140, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Shahbaz, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Sinha, A. Clean energy consumption, economic growth, and environmental sustainability: What is the role of economic policy uncertainty? Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Cao, S.; Wei, Y.; Dilly, O.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Koenig, H.; Tscherning, K.; Helming, K. Comparison of sustainability issues in two sensitive areas of China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2009, 12, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampantamit, T.; Ho, L.; Lachat, C.; Sutummawong, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Goethals, P. Aquaculture Production and Its Environmental Sustainability in Thailand: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Sánchez, I.; Hussain, N.; Khan, S.; Martínez-Ferrero, J. Assurance of corporate social responsibility reports: Examining the role of internal and external corporate governance mechanisms. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021, 29, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; van Oers, L.; Tukker, A.; van der Voet, E. Assessing the future environmental impacts of copper production in China: Implications of the energy transition. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, P.; Schwebel, D.C.; Hu, G. Assessing the use of media reporting recommendations by the World Health Organization in suicide news published in the most influential media sources in China, 2003–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guy, J.H.; Deakin, G.B.; Edwards, A.M.; Miller, C.; Pyne, D. Adaptation to hot environmental conditions: An exploration of the performance basis, procedures and future directions to optimise opportunities for elite athletes. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.P.; Syrou, N.F. Workplace safety and occupational health job risks hazards in public health sector in Greece. Eur. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 6, em0118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellstrom, T.; Friel, S.; Dixon, J.; Corvalan, C.; Rehfuess, E.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Gore, F.; Bartram, J. Urban environmental health hazards and health equity. J. Urban Health 2007, 84, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Usman, M.; Anwar, S.; Yaseen, M.R.; Makhdum, M.S.A.; Kousar, R.; Jahanger, A. Unveiling the dynamic relationship between agriculture value addition, energy utilization, tourism and environmental degradation in South Asia. J. Public Aff. 2021, e2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Turning food waste to energy and resources towards a great environmental and economic sustainability: An innovative integrated biological approach. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwah-Amoah, J. Stepping up and stepping out of COVID-19: New challenges for environmental sustainability policies in the global airline industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 123000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soflaei, F.; Shokouhian, M.; Zhu, W. Socio-environmental sustainability in traditional courtyard houses of Iran and China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prybutok, V.; Zhang, X.; Ryan, S.D. Evaluating leadership, IT quality, and net benefits in an e-government environment. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.H.; Malhotra, A.; Segars, A.H. Knowledge management: An organizational capabilities perspective. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2001, 18, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skordoulis, M.; Ntanos, S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Arabatzis, G.; Galatsidas, S.; Chalikias, M. Environmental innovation, open innovation dynamics and competitive advantage of medium and large-sized firms. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, T. Do environmental subsidies spur environmental innovation? Empirical evidence from Chinese listed firms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 173, 121123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaghaany, M.; Kbelah, S.; Almagtome, A. Value relevance of sustainability reporting under an accounting information system: Evidence from the tourism industry. Afr. J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 2019, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Skordoulis, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Ntanos, S.; Galatsidas, S.; Arabatzis, G.; Chalikias, M.; Kalantonis, P. The Mediating Role of Firm Strategy in the Relationship between Green Entrepreneurship, Green Innovation, and Competitive Advantage: The Case of Medium and Large-Sized Firms in Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hua, N. Transcending the COVID-19 crisis: Business resilience and innovation of the restaurant industry in China. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 49, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholphirul, P.; Rukumnuaykit, P.; Charoenrat, T.; Kwanyou, A.; Srijamdee, K. Service marketing strategies and performances of tourism and hospitality enterprises: Implications from a small border province in Thailand. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2021, 34, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasombat, T.; Pumipatyothin, P.; Napathorn, C. Understanding Employability in Changing Labor Market Contexts: The Case of an Emerging Market Economy of Thailand. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ullah, K.; Khan, A. The impact of green HRM on green creativity: Mediating role of pro-environmental behaviors and moderating role of ethical leadership style. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2021, 33, 3789–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X. How responsible leadership motivates employees to engage in organizational citizenship behavior for the environment: A double-mediation model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
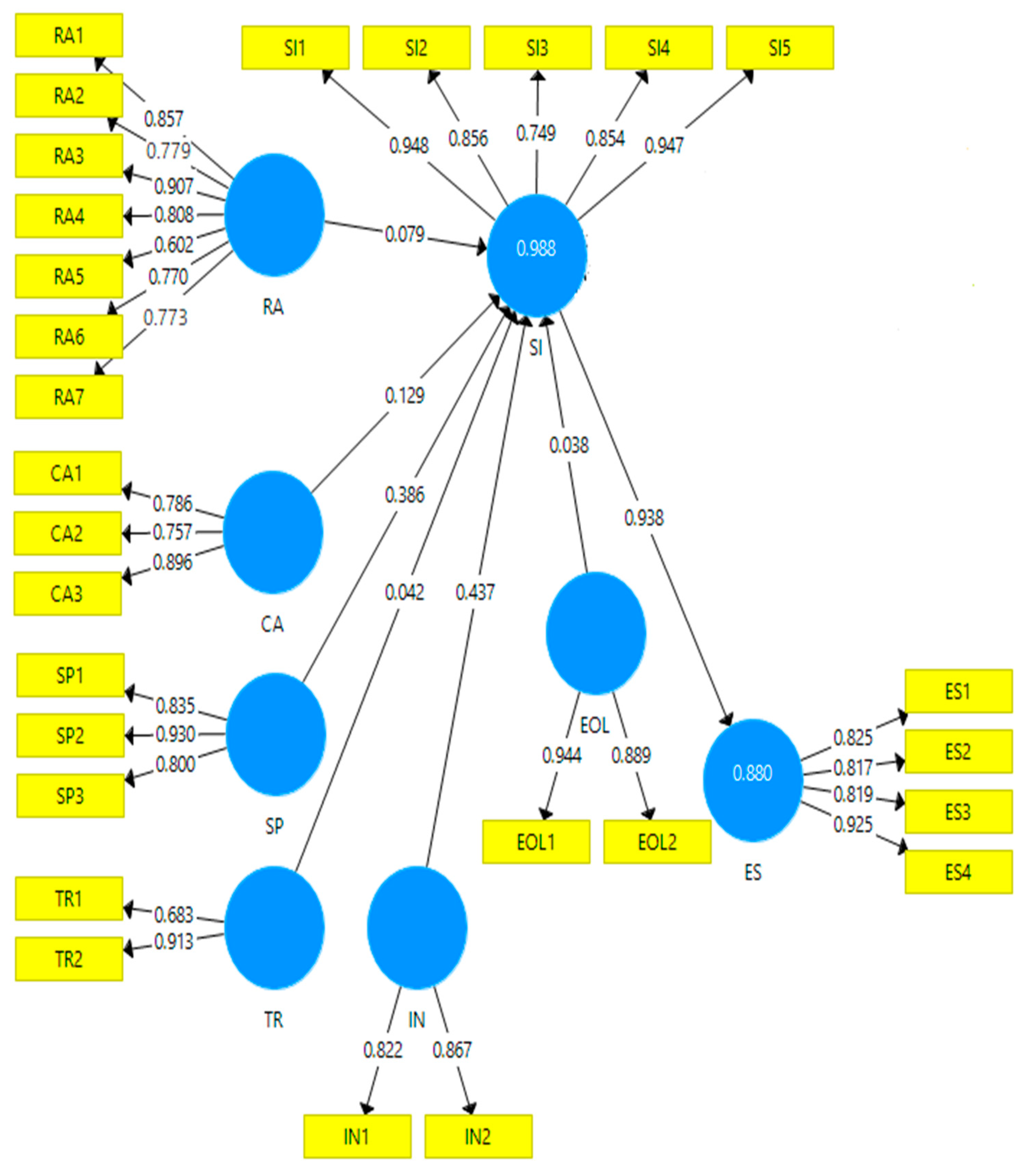



| Variables | Items | Factor Loadings | Alpha | CR | AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | CA1 | Working a sustainably fits with the way I work. | 0.786 | 0.781 | 0.855 | 0.665 |
| CA2 | Working a sustainably fits with my practice preferences. | 0.757 | ||||
| CA3 | Working a sustainably fits with my service needs. | 0.896 | ||||
| Environmental Opinion Leadership | EOL1 | Our hospital is likely to be consulted by other hospitals in our industry about sustainability innovations. | 0.944 | 0.815 | 0.913 | 0.840 |
| EOL2 | Our hospital is considered by other hospitals to be a reliable source of information on environmental sustainability. | 0.889 | ||||
| Environmental Sustainability | ES1 | Creation of an environmental committee. | 0.825 | 0.869 | 0.910 | 0.718 |
| ES2 | Creation of an environmental impact assessment report. | 0.817 | ||||
| ES3 | Creation of a detailed program to reduce environmental impacts. | 0.819 | ||||
| ES4 | The hiring of external consultants to advise on environmental policies or programs. | 0.925 | ||||
| Innovativeness | IN1 | Our hospital often embraces new ideas. | 0.822 | 0.789 | 0.833 | 0.714 |
| IN2 | Our hospital will often adopt new practices and products before other resorts in our industry. | 0.867 | ||||
| Relative Advantage | RA1 | Relative advantage will add significant value and market advantage to our hospital’s profile and services. | 0.857 | 0.853 | 0.884 | 0.532 |
| RA2 | Relative advantage will increase customer satisfaction. | 0.779 | ||||
| RA3 | Relative advantage will increase employee satisfaction, retention, and productivity. | 0.907 | ||||
| RA4 | Relative advantage is well matched to our current procedures. | 0.808 | ||||
| RA5 | Relative advantage is compatible with our existing employee practices. | 0.602 | ||||
| RA6 | Relative advantage requires too much technical expertise. | 0.770 | ||||
| RA7 | Relative advantage is much too complex to implement at this time. | 0.773 | ||||
| Adoption of Sustainability Innovations | SI1 | Energy saver control system in guest rooms. | 0.948 | 0.921 | 0.941 | 0.763 |
| SI2 | The keycard control system in guest rooms that shuts off power when the card is removed. | 0.856 | ||||
| SI3 | Using energy-saving light bulbs in guest rooms. | 0.749 | ||||
| SI4 | Recycling containers in rooms. | 0.854 | ||||
| SI5 | Strategically reducing the number of cleaning chemicals to use. | 0.947 | ||||
| Simplicity | SP1 | Simplicity will be a simple and easy process. | 0.835 | 0.817 | 0.892 | 0.734 |
| SP2 | Simplicity will be easily attainable because of our expansive knowledge about environmental sustainability. | 0.930 | ||||
| SP3 | Simplicity will require minimal resources. | 0.800 | ||||
| Trialability | TR1 | Before adopting a sustainability innovation, our resort would need to test the adoption on a smaller scale. | 0.683 | 0.871 | 0.784 | 0.756 |
| TR2 | Having time to try sustainability innovations would motivate our resort to adopt those innovations. | 0.913 |
| CA | EOL | ES | IN | RA | SI | SP | TR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | ||||||||
| EOL | 0.852 | |||||||
| ES | 0.885 | 0.814 | ||||||
| IN | 0.884 | 0.756 | 0.722 | |||||
| RA | 0.789 | 0.738 | 0.715 | 0.739 | ||||
| SI | 0.831 | 0.763 | 0.749 | 0.758 | 0.781 | |||
| SP | 0.735 | 0.715 | 0.792 | 0.727 | 0.698 | 0.783 | ||
| TR | 0.740 | 0.811 | 0.879 | 0.814 | 0.873 | 0.764 | 0.697 |
| Direct Relationship | Original Sample | Standard Deviation | T Statistics | p Values | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1. RA -> SI | 0.079 | 0.031 | 2.510 | 0.012 | Significant |
| H2. CA -> SI | 0.129 | 0.024 | 5.431 | 0.000 | Significant |
| H3. SP -> SI | 0.386 | 0.090 | 4.279 | 0.000 | Significant |
| H4. TR -> SI | 0.042 | 0.050 | 0.849 | 0.396 | Insignificant |
| H5. IN -> SI | 0.437 | 0.031 | 14.097 | 0.000 | Significant |
| H6. SI -> ES | 0.938 | 0.006 | 166.016 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Direct Relationship | Original Sample | Standard Deviation | T Statistics | p Values | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H7. Moderating Effect 1 -> SI | 0.056 | 0.125 | 0.446 | 0.655 | Insignificant |
| H8. Moderating Effect 2 -> SI | 0.197 | 0.064 | 3.051 | 0.002 | Significant |
| H9. Moderating Effect 3 -> SI | 0.160 | 0.078 | 2.045 | 0.041 | Significant |
| H10. Moderating Effect 4 -> SI | 0.043 | 0.031 | 1.390 | 0.165 | Insignificant |
| H11. Moderating Effect 5 -> SI | 0.189 | 0.074 | 2.567 | 0.011 | Significant |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.J.; Ul Hameed, W.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, A.A.; Tariq, M.A.U.R.; Ahmed, S. Adoption of Sustainability Innovations and Environmental Opinion Leadership: A Way to Foster Environmental Sustainability through Diffusion of Innovation Theory. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14547. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114547
Khan AJ, Ul Hameed W, Iqbal J, Shah AA, Tariq MAUR, Ahmed S. Adoption of Sustainability Innovations and Environmental Opinion Leadership: A Way to Foster Environmental Sustainability through Diffusion of Innovation Theory. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):14547. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114547
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Ali Junaid, Waseem Ul Hameed, Jawad Iqbal, Ashfaq Ahmad Shah, Muhammad Atiq Ur Rehman Tariq, and Saira Ahmed. 2022. "Adoption of Sustainability Innovations and Environmental Opinion Leadership: A Way to Foster Environmental Sustainability through Diffusion of Innovation Theory" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 14547. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114547
APA StyleKhan, A. J., Ul Hameed, W., Iqbal, J., Shah, A. A., Tariq, M. A. U. R., & Ahmed, S. (2022). Adoption of Sustainability Innovations and Environmental Opinion Leadership: A Way to Foster Environmental Sustainability through Diffusion of Innovation Theory. Sustainability, 14(21), 14547. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114547








