Satellite-Based Discrimination of Urban Dynamics-Induced Local Bias from Day/Night Temperature Trends across the Nile Delta, Egypt: A Basis for Climate Change Impacts Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets Description and Analysis Procedure
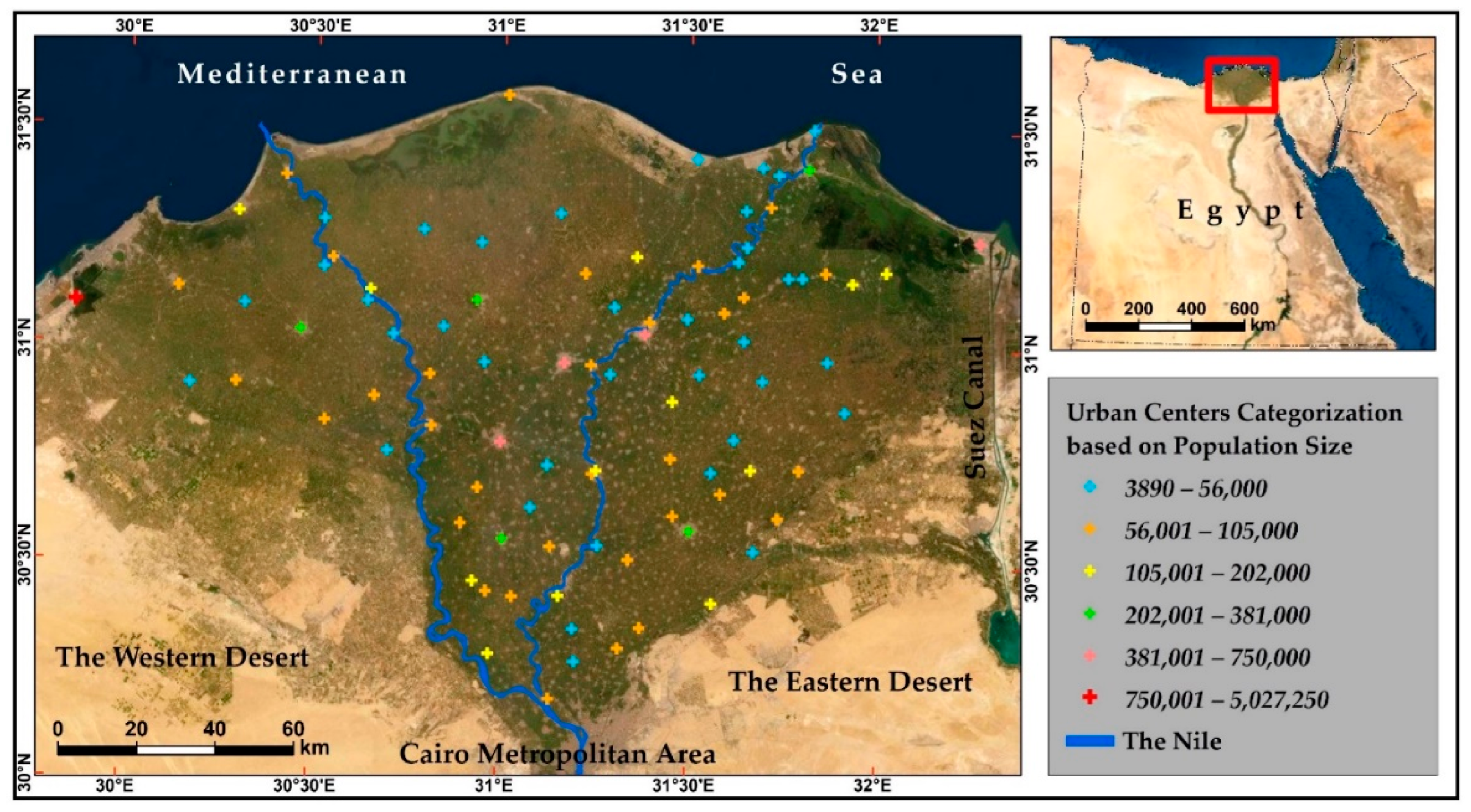
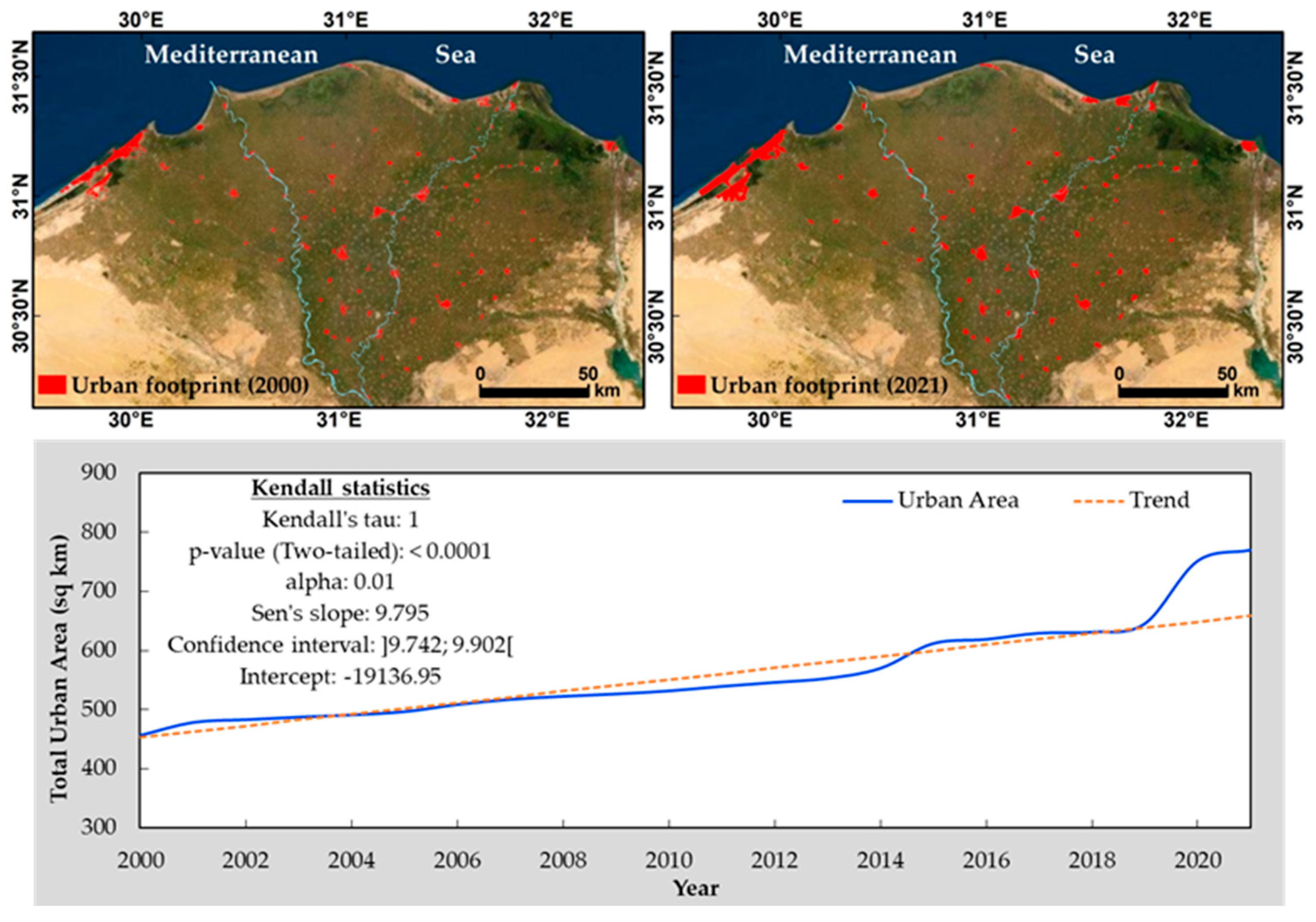
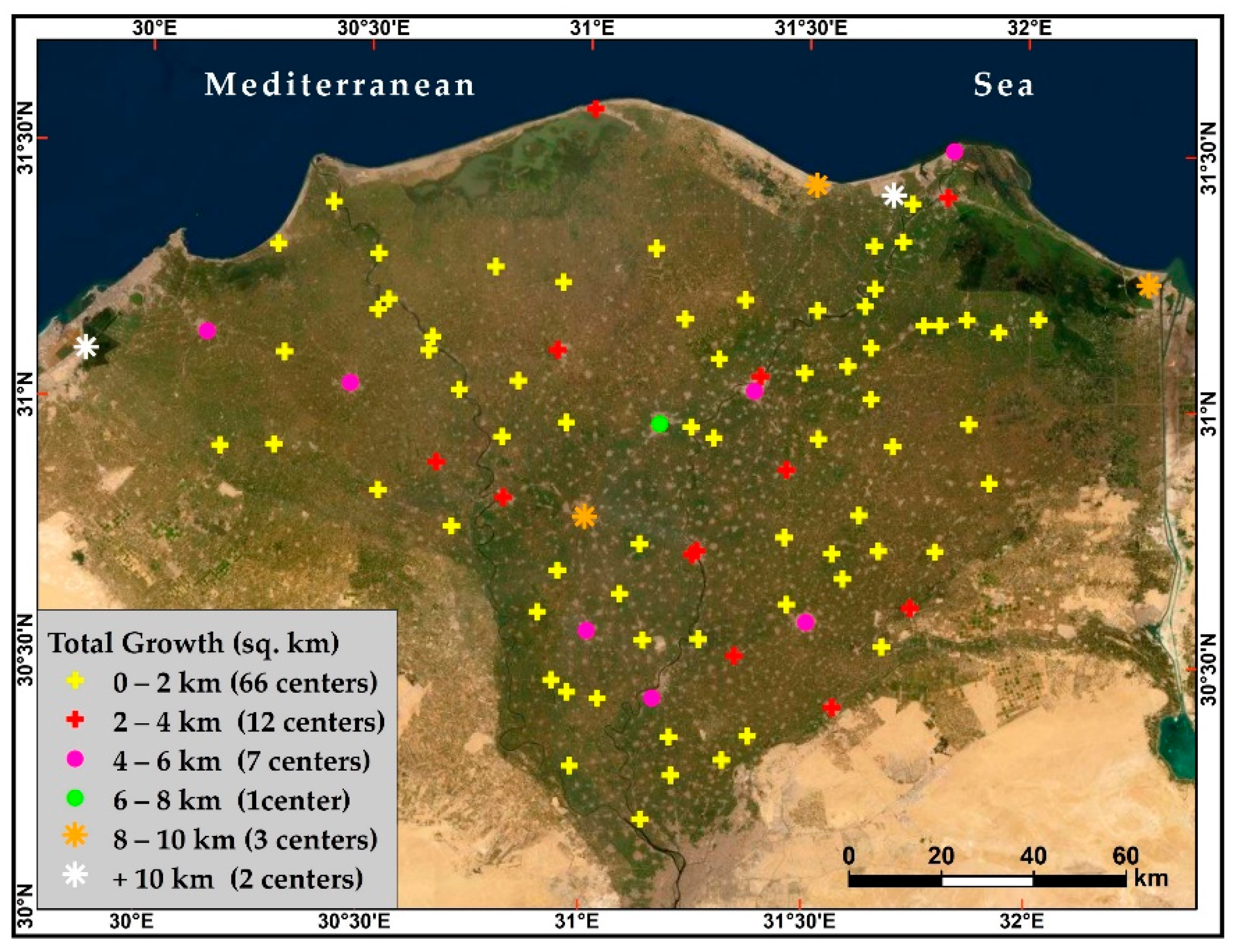
2.2.1. Urban Dynamics Data and Mapping
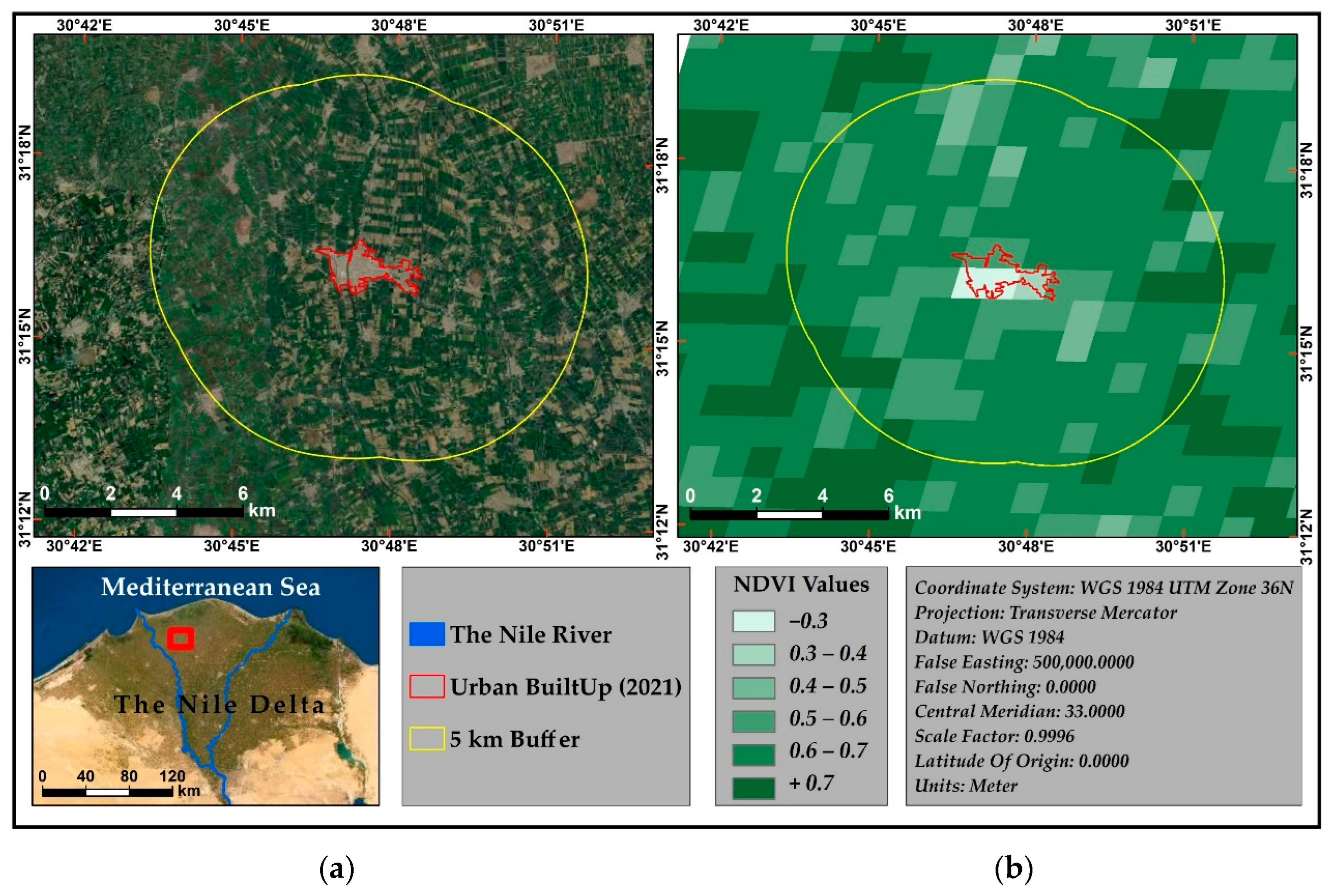
2.2.2. Vegetation Indices and Urban–Rural Distinction
2.2.3. LST Time-Series Construction
2.2.4. Trend Analysis
2.2.5. Local–Regional Warmings Separation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Urban Dynamics in the Overall Nile Delta
3.2. Day/Night and Urban/Rural LST Trends and the Nexus with Urban Dynamics
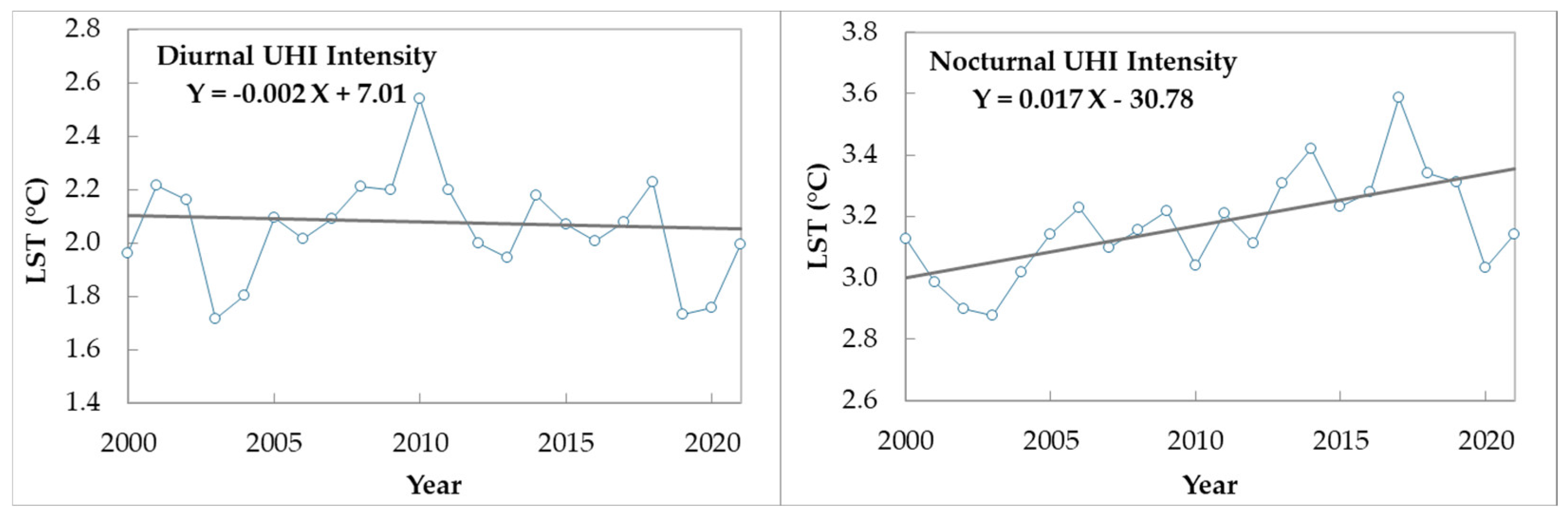
3.3. Urban Bias Estimation and Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, D.J.; Warne, A.G. Nile Delta in its Destruction Phase. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 794–825. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4298835 (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Fishar, M.R. Nile Delta (Egypt). In The Wetland Book: II: Distribution, Description, and Conservation; Finlayson, C.M., Milton, G.R., Prentice, R.C., Davidson, N.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1251–1260. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change: The IPCC Impacts Assessment. Canberra. 1990. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/ipcc_far_wg_II_full_report.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 1995: Impacts, Adaptations and Mitigation of Climate Change: Scientific-Technical Analyses. Cambridge. 1995. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/ipcc_sar_wg_II_full_report.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Cambridge. 2022. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/downloads/report/IPCC_AR6_WGII_FinalDraft_FullReport.pdf. (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. The Regional Impact of Climate Change: An Assessment of Vulnerability. Cambridge. 1997. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2020/11/The-Regional-Impact.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Cambridge. 2001. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/WGII_TAR_full_report-2.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Cambridge. 2007. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/ar4_wg2_full_report.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge. 2014. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/WGIIAR5-PartA_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge. 2014. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/WGIIAR5-Chap21_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2022).
- FAO. Climate Change and Food Security: Risks and Responses. Rome. 2015. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i5188e/I5188E.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Ammann, P.; Dietler, D.; Winkler, M.S. Health impact assessment and climate change: A scoping review. J. Clim. Chang Health 2021, 3, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Erazo, C.P.; Álvarez-García, J.; Río-Rama, M.D.L.C.D.; Durán-Sánchez, A. Scientific Mapping on the Impact of Climate Change on Cultural and Natural Heritage: A Systematic Scientometric Analysis. Land 2021, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.; Darby, S. Evaluating sustainable adaptation strategies for vulnerable mega-deltas using system dynamics modelling: Rice agriculture in the Mekong Delta’s An Giang Province, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, S.; Brondizio, E.; Renaud, F.G.; Hetrick, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Matthews, Z.; Tessler, Z.; Tejedor, A.; Sebesvari, Z.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; et al. Population dynamics, delta vulnerability and environmental change: Comparison of the Mekong, Ganges–Brahmaputra and Amazon delta regions. Sustain. Sci. 2016, 11, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazcarro, I.; Arto, I.; Hazra, S.; Bhattacharya, R.N.; Adjei, P.O.-W.; Ofori-Danson, P.K.; Asenso, J.K.; Amponsah, S.K.; Khondker, B.; Raihan, S.; et al. Biophysical and Socioeconomic State and Links of Deltaic Areas Vulnerable to Climate Change: Volta (Ghana), Mahanadi (India) and Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (India and Bangladesh). Sustainability 2018, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arto, I.; García-Muros, X.; Cazcarro, I.; González-Eguino, M.; Markandya, A.; Hazra, S. The socioeconomic future of deltas in a changing environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 648, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nahry, A.H.; Doluschitz, R. Climate change and its impacts on the coastal zone of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutaleb, K.A.A.; Mohammed, A.H.E.-S.; Ahmed, M.H.M. Climate Change Impacts, Vulnerabilities and Adaption Measures for Egypt’s Nile Delta. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 2, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, H.S.; Bello, A.R.S.; Alotaibi, B.M.; Aldosri, F.O.; Straquadine, G.S. Climate Change Adaptation in the Delta Nile Region of Egypt: Implications for Agricultural Extension. Sustainability 2019, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, D.M. Climate Change, Agriculture and Rural Communities’ Vulnerability in the Nile Delta BT—Climate Change Impacts on Agriculture and Food Security in Egypt: Land and Water Resources—Smart Farming—Livestock, Fishery, and Aquaculture; Omran, E.-S.E., Negm, A.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 525–576. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Ma, T.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Mapping urban dynamics (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia using consistent nighttime light data from DMSP and VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, S.; Song, C. A global dataset of annual urban extents (1992–2020) from harmonized nighttime lights. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasisith, S. Detecting Urban Sprawl in the Middle Nile Delta Region to Assess the Effects on Egypt’s Agriculture; Central European University: Budapest, Hungary, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, T.M.; Blackburn, G.A.; Whyatt, J.D.; Atkinson, P.M. Dramatic Loss of Agricultural Land Due to Urban Expansion Threatens Food Security in the Nile Delta, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qian, F.; Song, D.-X.; Zheng, K.-J. Research on Urban Heat-Island Effect. Procedia Eng. 2016, 169, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, C.R.; Teodoro, A.C.; Gonçalves, A. Study of the Urban Heat Island (UHI) Using Remote Sensing Data/Techniques: A Systematic Review. Environments 2021, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Cardinali, M.; Gambelli, A.M.; Filipponi, M.; Castellani, B.; Nicolini, A. Outdoor thermal comfort improvements due to innovative solar awning solutions: An experimental campaign. Energy Build. 2020, 225, 110341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Jones, P.D. Urban Bias in Area-averaged Surface Air Temperature Trends. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1989, 70, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, Z. Identifying and Correcting Urban Bias for Regional Surface Air Temperature Series of North China over Period of 196Q_2000. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 743–753. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Huang, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, G.; Yang, Y. A New Method for Correcting Urbanization-Induced Bias in Surface Air Temperature Observations: Insights From Comparative Site-Relocation Data. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 625418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janis, M.J. Observation-Time-Dependent Biases and Departures for Daily Minimum and Maximum Air Temperatures. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 588–603. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/26184999 (accessed on 20 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Vose, R.S.; Williams, C.N.; Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R.; Easterling, D.R. An evaluation of the time of observation bias adjustment in the U.S. Historical Climatology Network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, R.; Jones, P.D.; Hiebl, J.; Frank, D.; Brunetti, M.; Maugeri, M. The early instrumental warm-bias: A solution for long central European temperature series 1760–2007. Clim. Chang. 2010, 101, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienst, M.; Lindén, J.; Engström, E.; Esper, J. Removing the relocation bias from the 155-year Haparanda temperature record in Northern Europe: Removing the relocation bias from a 155-year temperature record. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4015–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, G.; Gavin, J.; Karl, T.R. Urban Warming. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Diaz, H.F.; Kukla, G. Urbanization: Its Detection and Effect in the United States Climate Record. J. Clim. 1988, 1, 1099–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Kelly, P.M.; Goodess, C.M.; Karl, T. The Effect of Urban Warming on the Northern Hemisphere Temperature Average. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 285–290. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/26195817 (accessed on 1 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, H.E. The Climate of Towns. Man’s Role in Changing the Face of the Earth; Hutchinson: London, UK, 1956; pp. 584–603. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, A.; Guo, J.; Liu, X. Urbanization Effects on Observed Surface Air Temperature Trends in North China. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Z.-W. Urbanization-related warming in local temperature records: A review. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2015, 9, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázdil, R.; Budíková, M. An urban bias in air temperature fluctuations at the Klementinum, Prague, The Czech Republic. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4211–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jung, H.-S.; Nam, K.-Y.; Kwon, W.-T. Adjusting urban bias in the regional mean surface temperature series of South Korea, 1968–1999. Int. J. Clim. 2003, 23, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portman, D.A. Identifying and Correcting Urban Bias in Regional Time Series: Surface Temperature in China’s Northern Plains. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.C. Assessment of Urban Versus Rural In Situ Surface Temperatures in the Contiguous United States: No Difference Found. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2941–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalo, J.A.; Matsumoto, J.; Takahashi, H.G.; Ii, M.Q.V.; Olaguera, L.M.P.; Ren, G.; Cinco, T.A. The effect of urbanization on temperature indices in the Philippines. Int. J. Clim. 2021, 42, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ren, G.; Qin, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zhai, T.; Tysa, S.K.; Xue, X.; Yang, G.; Sun, X. Urbanization Effects on Estimates of Global Trends in Mean and Extreme Air Temperature. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 1923–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperson, D.L.; Davis, J.M.; Bloomfield, P.; Karl, T.R.; McNab, A.L.; Gallo, K.P. Estimating the Urban Bias of Surface Shelter Temperatures Using Upper-Air and Satellite Data. Part I: Development of Models Predicting Surface Shelter Temperatures. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperson, D.L.; Davis, J.M.; Bloomfield, P.; Karl, T.R.; McNab, A.L.; Gallo, K.P. Estimating the Urban Bias of Surface Shelter Temperatures Using Upper-Air and Satellite Data. Part II: Estimation of the Urban Bias. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.E. Urban heat island effects on estimates of observed climate change. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2009, 1, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Guo-Yu, R.E.N. Correcting urban bias for surface air temperature series of Beijing Station over time period 1915–2012. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 2197–2207. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tett, S.F.B.; Yan, Z. Correcting urban bias in large-scale temperature records in China, 1980-2009. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, R.; Van De Vyver, H. Estimating urban heat island effects on near-surface air temperature records of Uccle (Brussels, Belgium): An observational and modeling study. Adv. Sci. Res. 2011, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, R.; Young, P.J.; Blair, G.S.; Cai, X.-M.; Chapman, L. Urbanisation’s contribution to climate warming in Great Britain. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Board on Atmospheric Sciences and Climate; Committee on Scientific Accomplishments of Earth Observations from Space. Earth Observations from Space: The First 50 Years of Scientific Achievements; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Li, G.; Cao, C. Development of environmental monitoring satellite systems in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.-W. Earth observation big data for climate change research. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2015, 6, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.; Onoda, M. Satellite Earth Observations in Environmental Problem-Solving BT—Satellite Earth Observations and Their Impact on Society and Policy; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Andries, A.; Murphy, R.J.; Morse, S.; Lynch, J. Earth Observation for Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification within Environmental Land Management Policy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzui, A.E.; Abdelkader, A.; Pătru-Stupariu, I. Analysing urban dynamics using multi-temporal satellite images in the case of a mountain area, Sinaia (Romania). Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, Y. Remote Sensing of Urban Dynamics. In Landscape and Land Capacity; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2020; pp. 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, G.; Mainali, K.P.; Mishra, N.B. Analyzing the dynamics of urbanization in Delhi National Capital Region in India using satellite image time-series analysis. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2021, 49, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, M.; Cao, C.; Singh, R.P.; Chen, W.; Ju, H. Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes and Their Influence on the Ecosystem in Chengdu City, China during the Period of 1992–2018. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twisa, S.; Buchroithner, M.F. Land-Use and Land-Cover (LULC) Change Detection in Wami River Basin, Tanzania. Land 2019, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inalpulat, M.; Genc, L. Quantification of LULC Changes and Urbanization Effects on Agriculture Using Historical Landsat Data in North-West Anatolia, Turkey. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 3999–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Dech, S. (Eds.) Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing: Sensors, Methods, Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Li, Z.-L. Quantitative Remote Sensing in Thermal Infrared: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q.; Larson, R.C. Satellite Remote Sensing of Urban Heat Islands: Current Practice and Prospects BT—Geo-Spatial Technologies in Urban Environments; Jensen, R.R., Gatrell, J.D., McLean, D.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 91–111. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Zhang, P.; Wolfe, R.E.; Bounoua, L. Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect across biomes in the continental USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulibdeh, A. Analysis of urban heat island characteristics and mitigation strategies for eight arid and semi-arid gulf region cities. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.; Uchihama, D.; Ochi, S.; Yasuoka, Y. Assessment with satellite data of the urban heat island effects in Asian mega cities. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y. The footprint of urban heat island effect in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfîcă, L.; Ichim, P.; Apostol, L.; Ursu, A. The extent and intensity of the urban heat island in Iași city, Romania. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2017, 134, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhao, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, L. Determining the Boundary and Probability of Surface Urban Heat Island Footprint Based on a Logistic Model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, X.; Tang, Q. The footprint of urban heat island effect in 302 Chinese cities: Temporal trends and associated factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 655, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, C.-E.; Yang, Y.-J. Influence of urbanization on the thermal environment of meteorological station: Satellite-observed evidence. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2015, 6, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Gao, Z.; Ning, G.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, M. Modulations of surface thermal environment and agricultural activity on intraseasonal variations of summer diurnal temperature range in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudelsee, M. Trend analysis of climate time series: A review of methods. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 190, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, L.; Luo, M. Effects of urbanization on the decrease in sunshine duration over eastern China. Urban Clim. 2019, 28, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Jung, D.; Choung, Y.-J. Development of a Multiple Linear Regression Model for Meteorological Drought Index Estimation Based on Landsat Satellite Imagery. Water 2020, 12, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Pal, S.C.; Sattar, A.; Singh, S.K.; Das, B.; Chakrabortty, R.; Mohammad, P. Trend of extreme rainfall events using suitable Global Circulation Model to combat the water logging condition in Kolkata Metropolitan Area. Urban Clim. 2020, 32, 100599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, S.; Luo, M. Urbanization effects on high-frequency temperature variability over South China. Urban Clim. 2022, 42, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Theil, H. A Rank-Invariant Method of Linear and Polynomial Regression Analysis. In Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie Wetenschappen, Series A Mathematical Sciences, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 1950; pp. 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipel, K.W.; McLeod, A.I. (Eds.) Chapter 23 Nonparametric Tests for Trend Detection. In Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 45, pp. 853–938. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Yu, H.; Kan, G.; He, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, M.; Wang, G. Re-evaluation of the Power of the Mann-Kendall Test for Detecting Monotonic Trends in Hydrometeorological Time Series. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wagan, B. Precipitation Trends over Time Using Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho Tests in Swat River Basin, Pakistan. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, T.; Gough, W.A. Characterization and estimation of urban heat island at Toronto: Impact of the choice of rural sites. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2011, 108, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervenkov, H.; Slavov, K. Theil–Sen estimator vs. Ordinary least squares—Trend analysis for selected ETCCDI climate indices. Comptes Rendus Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2019, 72, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redeker, C.; Kantoush, S.A. The Nile Delta: Urbanizing on Diminishing Resources. Built Environ. 2014, 40, 201–212. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/43296887 (accessed on 25 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Fiske, M.; Stein, T.; Gamal, M.; El Araby, H.; Madani, A.; Mehanee, S.; Becker, R. Monitoring the urbanization of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Ambio 1999, 28. Available online: https://www.ostgov/biblio/942608 (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Shalaby, A.; Moghanm, F.S. Assessment of urban sprawl on agricultural soil of northern Nile Delta of Egypt using RS and GIS. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagouz, M.; Abou-Shleel, S.; Belal, A.; El-Mohandes, M. Detection of land use/cover change in Egyptian Nile Delta using remote sensing. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, H.A.; Brazel, A.J.; Balling, R.C. Analysis of the Kuwait city urban heat island. Int. J. Clim. 1990, 10, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.L.; Saleem, A.; Sadr, R. Recent warming trend in the coastal region of Qatar. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 128, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Islam, M.N.; Jones, P.D. Urbanization effects on the air temperature rise in Saudi Arabia. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benas, N.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Cartalis, C. Trends of urban surface temperature and heat island characteristics in the Mediterranean. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2016, 130, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.; Kushwaha, G.; Nikam, B.; Srivastav, S.; Shelar, A.; Kumar, P. Analysing the day/night seasonal and annual changes and trends in land surface temperature and surface urban heat island intensity (SUHII) for Indian cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hove, L.W.A.; Jacobs, C.M.J.; Heusinkveld, B.G.; Elbers, J.A.; van Driel, B.L.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Temporal and spatial variability of urban heat island and thermal comfort within the Rotterdam agglomeration. Build. Environ. 2015, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeong, S.-J. Shifting the urban heat island clock in a megacity: A case study of Hong Kong. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 13, 014014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, W.; Ismael, H. Assessment of constructing canopy urban heat island temperatures from thermal images: An integrated multi-scale approach. Sci. Afr. 2020, 10, e00607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlow, E. Regarding Some Pitfalls in Urban Heat Island Studies Using Remote Sensing Technology. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Horton, B.; Jones, P.D.; Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R.; Parker, D.E.; Salinger, M.J.; Razuvayev, V.; Plummer, N.; Jamason, P.; et al. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science 1997, 277, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Groisman, P.Y.; Coughlan, M.; Plummer, N.; Wang, W.-C.; Karl, T.R. Assessment of urbanization effects in time series of surface air temperature over land. Nature 1990, 347, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D.E. Large-scale warming is not urban. Nature 2004, 432, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, D.E. A Demonstration That Large-Scale Warming Is Not Urban. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2882–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, C.; Rohde, R.; Muller, R.A.; Wurtele, J.; Curry, J.; Groom, D.; Jacobsen, R.; Perlmutter, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Mosher, S. SInfluence of Urban Heating on the Global Temperature Land Average using Rural Sites Identified from MODIS Classifications. Geoinform. Geostat. Overv. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.C.; Gallo, K.P.; Lawrimore, J.; Owen, T.W.; Huang, A.; McKittrick, D.A. Global rural temperature trends. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, C. Impacts of Spatial Configuration of Land Surface Features on Land Surface Temperature across Urban Agglomerations, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
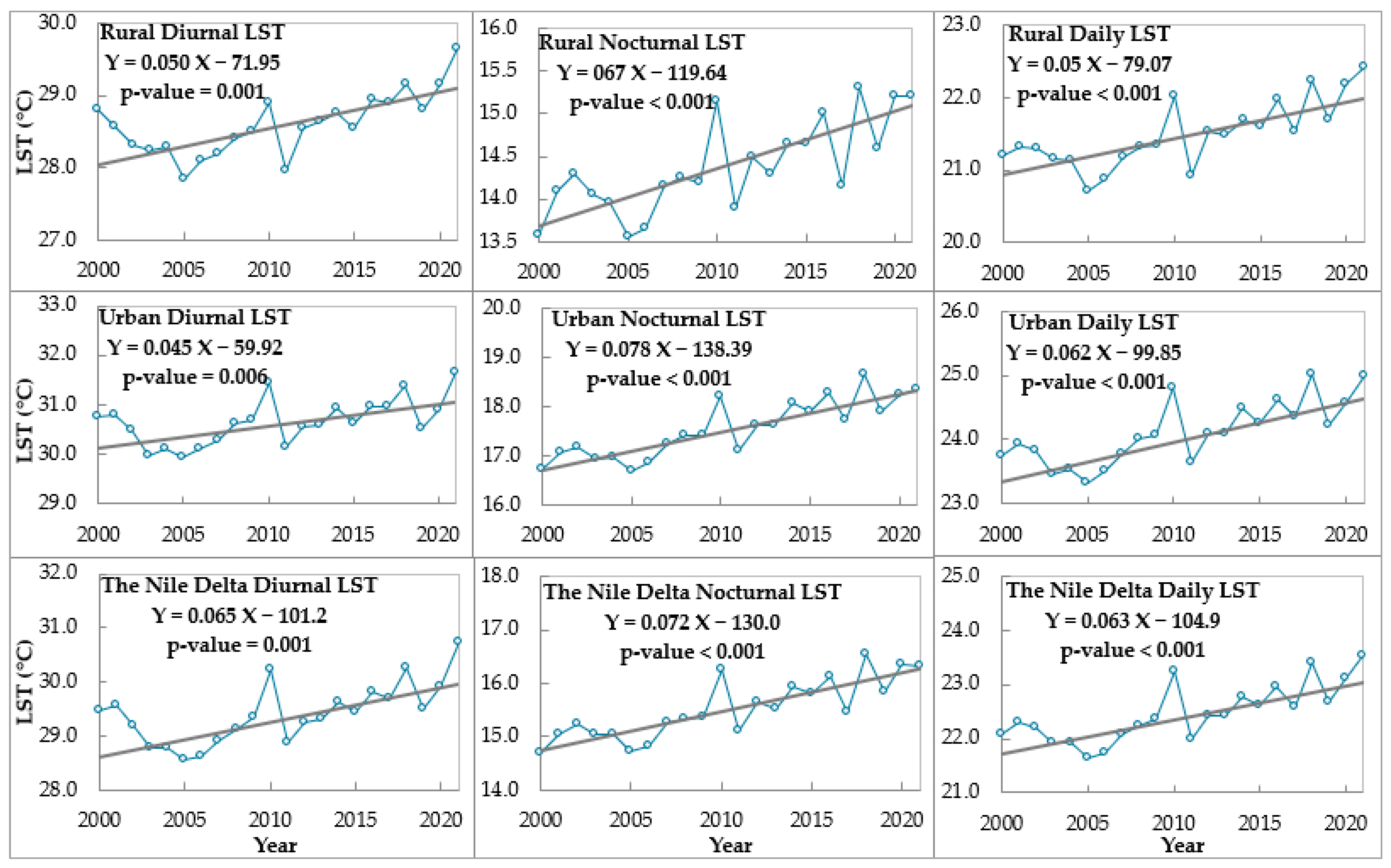
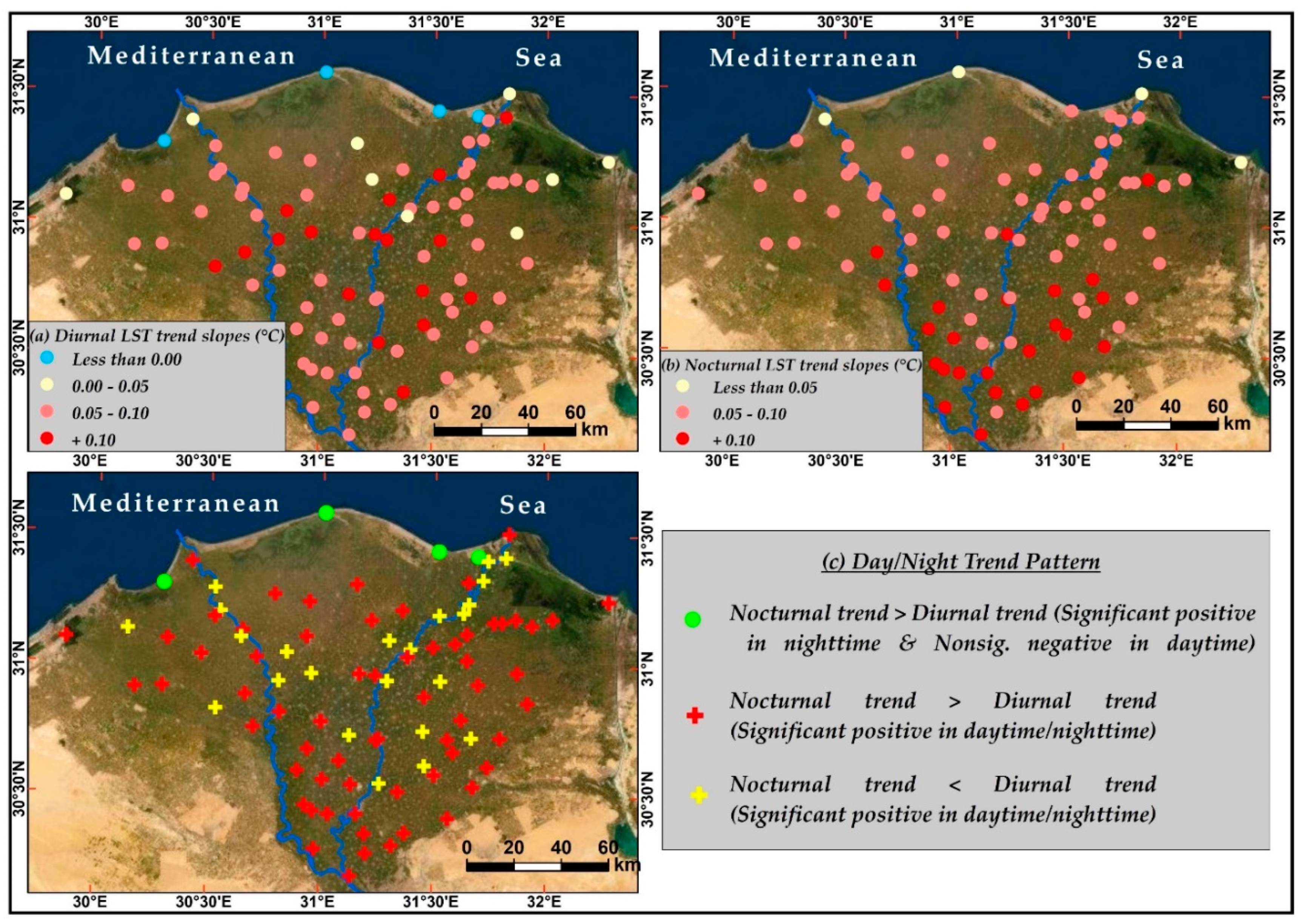
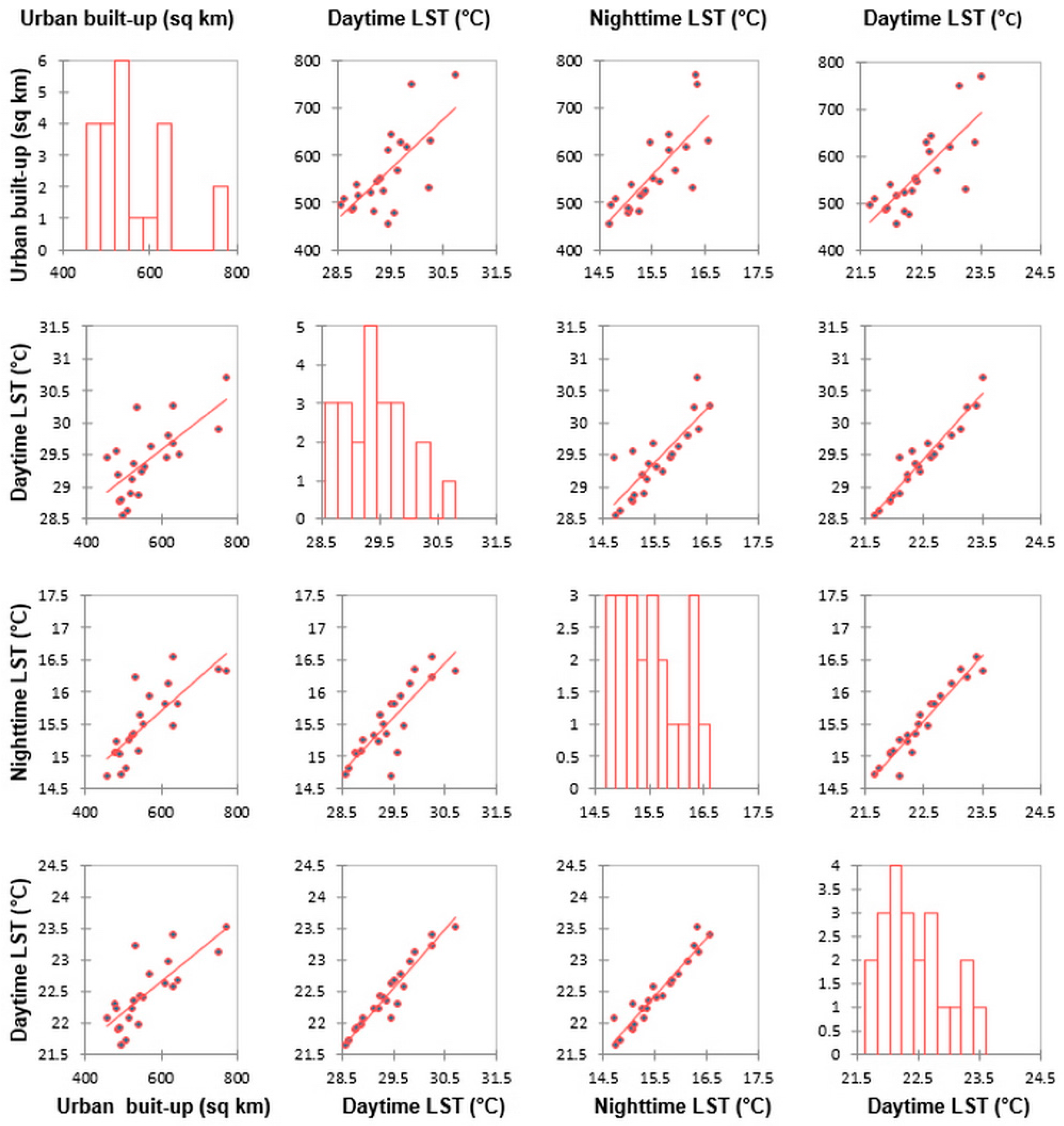
| Statistics | Item | Rural LST (°C) | Urban LST (°C) | The Nile Delta LST (°C) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Night | Daily | Day | Night | Daily | Day | Night | Daily | ||
| Descriptive | Obs. | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Min. | 27.9 (2005) | 13.5 (2000/5) | 20.7 (2005) | 29.9 (2005) | 16.7 (2000/5) | 23.3 (2005) | 28.6 (2005) | 14.7 (2000/5) | 21.6 (2005) | |
| Max. | 29.7 (2021) | 15.3 (2018) | 22.4 (2021) | 31.6 (2021) | 18.6 (2018) | 25.0 (2018/21) | 30.7 (2021) | 16.5 (2018) | 23.5 (2021) | |
| Mean | 28.6 | 14.4 | 21.5 | 30.7 | 17.6 | 24.1 | 29.4 | 15.5 | 22.5 | |
| Std. dev. | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | |
| Trend | K. tau | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.62 |
| S | 116.0 | 131.0 | 139.0 | 99.0 | 161.0 | 143.0 | 117.0 | 157.0 | 143.0 | |
| Var(S) | 1254.7 | 1255.7 | 1255.7 | 1257.7 | 1257.7 | 1257.7 | 1257.7 | 1257.7 | 1257.7 | |
| p-value | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.006 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| alpha | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Sen Slope | 0.050 | 0.067 | 0.050 | 0.045 | 0.078 | 0.062 | 0.065 | 0.072 | 0.063 | |
| Intercept | −71.95 | −119.64 | −79.07 | −59.92 | −138.39 | −99.85 | −101.2 | −130.0 | −104.9 | |
| Year | Observed Urban LST (°C) | Observed Rural LST (°C) | Calculated UHI Intensity/Bias (°C) | Corrected LST (°C) for Trend | Corrected LST (°C) for Trend/UHI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Night | Day | Night | Day | Night | Day | Night | Day | Night | |
| 2000 | 30.77 | 16.71 | 28.81 | 13.59 | 1.96 | 3.13 | 30.77 | 16.71 | 28.81 | 13.59 |
| 2001 | 30.78 | 17.07 | 28.56 | 14.09 | 2.22 | 2.99 | 30.78 | 17.06 | 28.56 | 14.07 |
| 2002 | 30.47 | 17.18 | 28.31 | 14.28 | 2.16 | 2.90 | 30.48 | 17.15 | 28.32 | 14.25 |
| 2003 | 29.96 | 16.93 | 28.25 | 14.05 | 1.71 | 2.88 | 29.97 | 16.88 | 28.26 | 14.00 |
| 2004 | 30.10 | 16.97 | 28.30 | 13.95 | 1.80 | 3.02 | 30.11 | 16.90 | 28.31 | 13.88 |
| 2005 | 29.94 | 16.69 | 27.85 | 13.55 | 2.09 | 3.14 | 29.95 | 16.61 | 27.86 | 13.47 |
| 2006 | 30.11 | 16.88 | 28.10 | 13.65 | 2.01 | 3.23 | 30.13 | 16.78 | 28.11 | 13.55 |
| 2007 | 30.29 | 17.25 | 28.20 | 14.15 | 2.09 | 3.10 | 30.31 | 17.13 | 28.22 | 14.03 |
| 2008 | 30.61 | 17.41 | 28.40 | 14.25 | 2.21 | 3.16 | 30.63 | 17.27 | 28.42 | 14.11 |
| 2009 | 30.70 | 17.42 | 28.50 | 14.20 | 2.20 | 3.22 | 30.72 | 17.27 | 28.52 | 14.05 |
| 2010 | 31.44 | 18.19 | 28.90 | 15.15 | 2.54 | 3.04 | 31.47 | 18.02 | 28.92 | 14.98 |
| 2011 | 30.15 | 17.11 | 27.95 | 13.90 | 2.20 | 3.21 | 30.17 | 16.93 | 27.98 | 13.71 |
| 2012 | 30.55 | 17.61 | 28.55 | 14.50 | 2.00 | 3.11 | 30.58 | 17.41 | 28.58 | 14.30 |
| 2013 | 30.60 | 17.61 | 28.65 | 14.30 | 1.95 | 3.31 | 30.63 | 17.39 | 28.68 | 14.08 |
| 2014 | 30.93 | 18.07 | 28.75 | 14.65 | 2.18 | 3.42 | 30.96 | 17.83 | 28.78 | 14.41 |
| 2015 | 30.62 | 17.88 | 28.55 | 14.65 | 2.07 | 3.23 | 30.65 | 17.63 | 28.59 | 14.40 |
| 2016 | 30.96 | 18.28 | 28.95 | 15.00 | 2.01 | 3.28 | 31.00 | 18.01 | 28.99 | 14.73 |
| 2017 | 30.98 | 17.74 | 28.90 | 14.15 | 2.08 | 3.59 | 31.02 | 17.45 | 28.94 | 13.86 |
| 2018 | 31.38 | 18.64 | 29.15 | 15.30 | 2.23 | 3.34 | 31.42 | 18.34 | 29.19 | 15.00 |
| 2019 | 30.53 | 17.91 | 28.80 | 14.60 | 1.73 | 3.31 | 30.58 | 17.59 | 28.85 | 14.28 |
| 2020 | 30.91 | 18.23 | 29.15 | 15.20 | 1.76 | 3.03 | 30.96 | 17.89 | 29.20 | 14.86 |
| 2021 | 31.65 | 18.34 | 29.65 | 15.20 | 2.00 | 3.14 | 31.70 | 17.99 | 29.70 | 14.85 |
| Yearly Trend | 0.045 | 0.078 | 0.05 | 0.067 | −0.002 | 0.017 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Total Trend | 0.945 | 1.638 | 1.05 | 1.407 | −0.042 | 0.357 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, W.; Hamdi, I. Satellite-Based Discrimination of Urban Dynamics-Induced Local Bias from Day/Night Temperature Trends across the Nile Delta, Egypt: A Basis for Climate Change Impacts Assessment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114510
Abbas W, Hamdi I. Satellite-Based Discrimination of Urban Dynamics-Induced Local Bias from Day/Night Temperature Trends across the Nile Delta, Egypt: A Basis for Climate Change Impacts Assessment. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):14510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114510
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Waleed, and Islam Hamdi. 2022. "Satellite-Based Discrimination of Urban Dynamics-Induced Local Bias from Day/Night Temperature Trends across the Nile Delta, Egypt: A Basis for Climate Change Impacts Assessment" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 14510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114510
APA StyleAbbas, W., & Hamdi, I. (2022). Satellite-Based Discrimination of Urban Dynamics-Induced Local Bias from Day/Night Temperature Trends across the Nile Delta, Egypt: A Basis for Climate Change Impacts Assessment. Sustainability, 14(21), 14510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114510







