Impacts of Reduced Inequalities on Quality Education: Examining the Relationship between Regional Sustainability and Higher Education
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Links between Regional Development and Higher Education
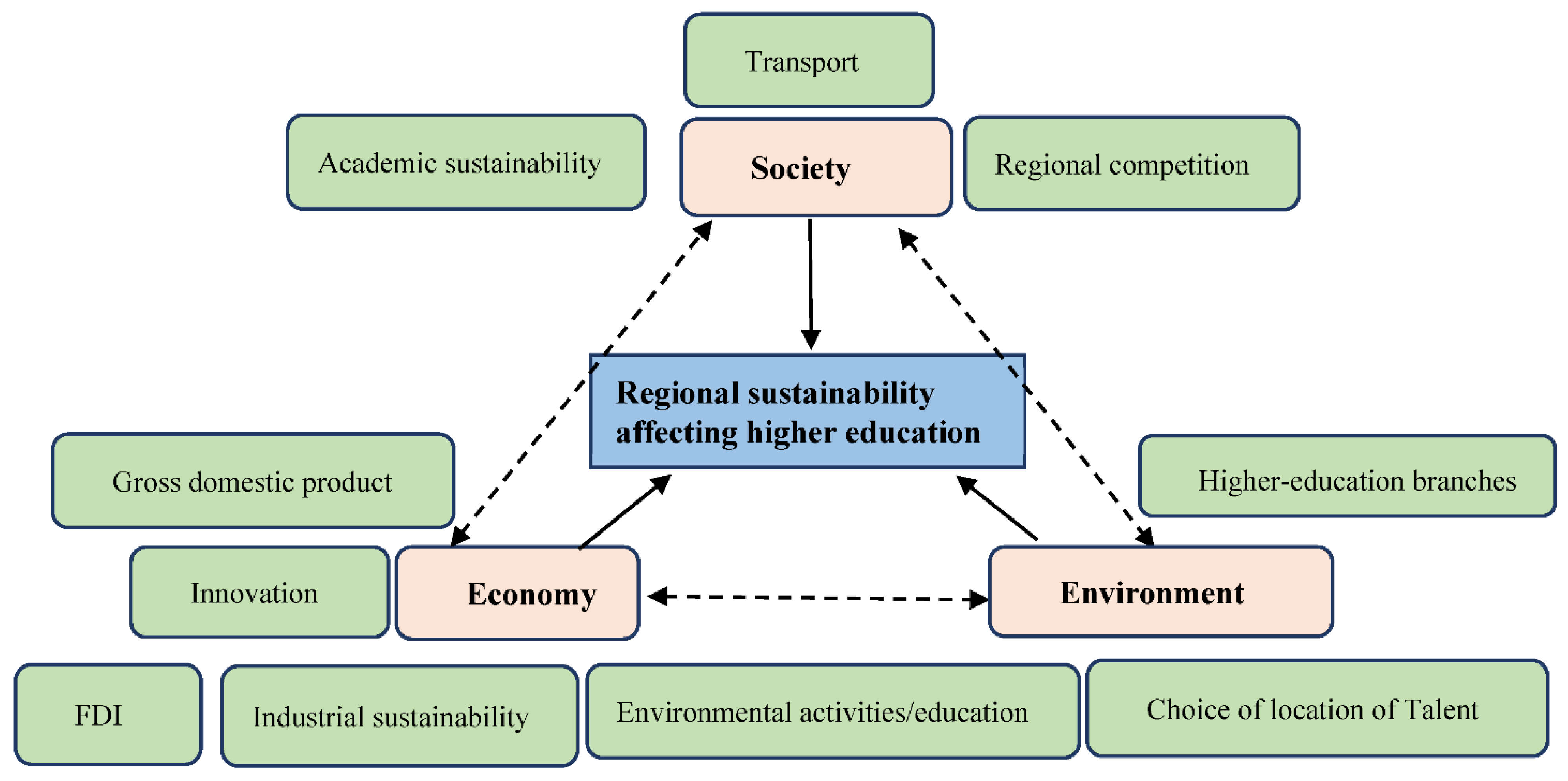
2.2. How Regional Sustainability Affects Higher Education from Economic, Social, and Environmental Perspectives
3. Data and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Fixed-Effects Model Results
4.2. Controlling for Endogeneity
5. Conclusions, Limitations, and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerf, M.E. Sustainable Development Goal Integration, Interdependence, and Implementation: The Environment–Economic–Health Nexus and Universal Health Coverage. Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1900021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, A.; Janetschek, H.; Malerba, D. Translating Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interdependencies into Policy Advice. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.; Woo, M.; Wang, F. Megaregions and Regional Sustainability. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2016, 20, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Fu, Y.; Shen, H.; Liu, F. Using Ranked Weights and Shannon Entropy to Modify Regional Sustainable Society Index. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindsted, T. Regional Planning, Sustainability Goals and the Mitch-Match Between Educational Practice and Climate, Energy and Business Plans. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wu, D.; Fu, X.; Deng, H.; Wu, G. Regional-Scale Analysis on the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats in Sustainable Development of Shangri-La County. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2015, 22, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, F.; Lou, E. Building Information Modelling, Lean and Sustainability: An Integration Framework to Promote Performance Improvements in the Construction Industry. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Cheng, S.; Shen, L. A Shangri-La Strategy for Sustainable Development and its Practice in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2000, 22, 83–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peer, V.; Penker, M. Higher Education Institutions and Regional Development: A Meta-Analysis. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2016, 39, 228–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbo, P.; Benneworth, P. Understanding the Regional Contribution of Higher Education Institutions; OECD Publishing Working Papers No 9; OECD: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, L.H.T.; Li, V.J. The Role of Higher Education in China’s Inclusive Urbanization. Cities 2017, 60, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisher, B.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Kim, S. Economic Transition, Higher Education and Worker Productivity in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2011, 94, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, G. The Rising Significance of Education for Health? Soc. Forces 2007, 85, 1621–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Radinger-Peer, V.; Pflitsch, G. The Role of Higher Education Institutions in Regional Transition Paths Towards Sustainability. Rev. Reg. Res. 2017, 37, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, C.K.; Bisaillon, V.; Webster, A.; Amor, B. Integration of Sustainable Devel1opment in Higher Education—A Regional Initiative in Quebec (Canada). J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, S. The Expansion of Higher Education in Turkey: Access, Equality and Regional Returns to Education. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2017, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.C.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y. Research Collaboration across Higher Education Systems: Maturity, Language Use, and Regional Differences. Stud. High. Educ. 2013, 38, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruss, G.; McGrath, S.; Petersen, I.; Gastrow, M. Higher Education and Economic Development: The Importance of Building Technological Capabilities. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2015, 43, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G. China’s Higher Education Development and Development Strategies. J. Shanghai Univ. Financ. Econ. 2002, 3, 41–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Marginson, S. Public/Private in Higher Education: A Synthesis of Economic and Political Approaches. Stud. High. Educ. 2018, 43, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, O. The silver bullet? Assessing the role of education for sustainability. Soc. Forces 2020, 99, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lin, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, M.; Ye, H.; Kong, L. Towards Sustainable Urban Communities: A Composite Spatial Accessibility Assessment for Residential Suitability Based on Network Big Data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januškaitė, V.; Užienė, L. Intellectual Capital as a Factor of Sustainable Regional Competitiveness. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.; Alfonso, T.S.; Cardenas, M.L. Systematic Review of Integrated Sustainable Transportation Models for Electric Passenger Vehicle Diffusion. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2513. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, D.; Cao, K.; Xu, J. The Impacts of Transportation Sustainability on Higher Education in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Luo, S. Higher Education Input, Technological Innovation, and Economic Growth in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira; Aurora, A.C.; Queirós Anabela, S.S. Economic Growth, Human Capital and Structural Change: A Dynamic Panel Data Analysis. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, H.C.G.; Torjesen, S.; Ennals, R. Higher Education in a Sustainability Society; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.F.; Wall, T.; Salvia, L.A.; Frankenberger, F.; Hindley, A.; Mifsud, M.; Brandli, L.; Will, M. Trends in Scientific Publishing on Sustainability in Higher Education. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Vieira, L.; Raposo, L. Distance and Academic Performance in Higher Education. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2018, 13, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Research on the Planning Strategies Oriented to Knowledge City; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Atherton, A.; Giurco, D. Campus Sustainability: Climate Change, Transport and Paper Reduction. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2011, 12, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, J. Regional competition and the distribution of floating population in China. Popul. Res. 2010, 34, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z. Changing Patterns of the Floating Population in China, 2000–2010. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2014, 40, 695–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K. Campus Sustainability in Chinese Higher Education Institutions: Focuses, Motivations and Challenges. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2015, 16, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Mackinnon, G.J. Econometric Theory and Methods; Russell: Frisco, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; He, C. The Rising Labor Costs and Spatial Restructure of Chinese Manufacturing. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T. Regional Industrial Growth: Evidence from Chinese Industries. Reg. Sci. Reg. Econ. 2004, 34, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Gabriel, S. Labor Migration, Human Capital Agglomeration and Regional Development in China. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2012, 42, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Pan, Y. Human Capital, Housing Prices, and Regional Economic Development: Will “Vying for Talent” Through Policy Succeed? Cities 2020, 98, 102577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.M.; Peraita, C.; Serrano, L.; Soler, Á. Higher Education Institutions, Economic Growth and GDP Per Capita in European Union Countries. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2018, 26, 1616–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. Research on Problems and Strategies in the Development of Independent Colleges in Universities; Hohai University: Nanjing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S. Role of Higher Education Sector in Changing Service Sector Innovation System. World J. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 9, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Y. Analysis of the Correlation Between the Adjustment and Upgrade of Human Capital and Industrial Structure in China’s Higher Education. Mod. Educ. Manag. 2016, 3, 25–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Melo, P.C.; Graham, D.J. Transport-Induced Agglomeration Effects: Evidence for US Metropolitan Areas. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2018, 10, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Ding, Y. Chinese universities’ land value needs an accurate assessment: On the basis of the land evaluation of 24 universities in Beijing. Price Theory Pract. 2016, 8, 21–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H. Optimum Choice of site for university new campus. Educ. Econom. 2010, 1, 14–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.R. Conceptualizing Tourism Transport: Inequality and Externality Issues. J. Transp. Geogr. 1999, 7, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Rassenfosse, D.G.; Jensen, P.; Marginson, S. The Determinants of Quality National Higher Education System. J. High. Educ. Policy Manag. 2013, 35, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canhoto, A.; Quinton, S.; Jackson, P.; Dibb, S. The Co-Production of Value in Digital, University–Industry R&D Collaborative Projects. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2016, 56, 86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannelongue, G.; Gonzalez-Benito, J.; Quiroz, I. Environmental Management and Labour Productivity: The Moderating Role of Capital Intensity. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, M.; Zoboli, R. Environmental Efficiency and Labor Productivity: Trade-off or Joint Dynamics? A Theoretical Investigation and Empirical Evidence from Italy using NAMEA. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friman, H. New Trends in the Higher Education: Renewable Energy at the Faculty of Electrical Engineering. Energy Procedia 2017, 115, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.D.; Leydesdorff, L. Publish or Patent: Bibliometric Evidence for Empirical Trade-Offs in National Funding Strategies. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; Guermat, C.; Brodi, L. National Innovation and Knowledge Performance: The Role of Higher Education Teaching and Training. Stud. High. Educ. 2015, 40, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Kajikawa, Y. Assessing the Industrial Opportunity of Academic Research with Patent Relatedness: A Case Study on Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2015, 90, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C. Transport Development, Regional Concentration and Economic Growth. Reg. Stud. 2013, 50, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, A. Agglomeration Effects in Europe. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2002, 46, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y. High-Level Talent Flow and its Influence on Regional Unbalanced Development in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 91, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z. The Scale of Higher Education and Urbanization. Comp. Educ. Study 2001, 9, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Tao, J.; Wang, S. FDI, Technology Spillovers and Green Innovation in China: Analysis Based on Data Envelopment Analysis. Ann. Oper. Res. 2015, 228, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.C. Regional Difference and Threshold Effects of FDI Technology Spillovers. World Econ. 2007, 9, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, A.; Colea, M.A.; Fredriksson, P.G. Institutionalized Pollution Havens. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1239–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, S. An Indicator Approach to Industrial Sustainability Assessment: The Case of China’s Capital Economic Circle. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Patton, D.; Kenney, M. Building Global-Class Universities: Assessing the Impact of the 985 Project. Res. Policy 2013, 42, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Tian, L.; Zhang, W. Research on the Development Efficiency of Regional High-End Talent in China: A Complex Network Approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zang, F. Spatial-Temporal Pattern Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment Based on Land Use/Land Cover Change in Baishuijiang National Nature Reserve in Gansu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S. Relevant Issues of Clean Energy Development in China. Energy Technol. Econ. 2011, 23, 20–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Hong, J.; Ni, D.; He, R. A Spatiotemporal Investigation of Energy-Driven Factors in China: A Region-Based Structural Decomposition Analysis. Energy 2020, 207, 118249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quatraro, F.; Scandura, A. Academic Inventors and the Antecedents of Green Technologies. A Regional Analysis of Italian Patent Data. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 156, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, W.; Cheng, P.; Li, Z. The Impact of the Digital Economy on Enterprise Sustainable Development and Its Spatial-Temporal Evolution: An Empirical Analysis Based on Urban Panel Data in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H. Digital Rural Construction and Farmers’ Income Growth: Theoretical Mechanism and Micro Experience Based on Data from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Glascock, J.L.; Lu-Andrews, R. An Investigation into Real Estate Investment and Economic Growth in China: A Dynamic Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2016, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J. Coupling Coordination between Marine S&T Innovation and the High-Quality Development of the Marine Economy: A Case Study of China’s Coastal Provinces. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, J.A. Specification Tests in Econometrics. Econornetrica 1978, 46, 1251–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J.M. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach; South-Western Cengage Learning: Mason, IA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]

| Independent Variables | Definition | Sources | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic sustainability | Economic growth | GDP | Regions’ GDP (trillions of yuan). | Provinces’ statistical yearbooks |
| Technology absorptive capacity | FDI | Percentage of FDI to GDP at province level (millions of yuan). | Provinces’ statistical yearbooks | |
| Industrial sustainability | CLP | China’s and provinces’ statistical yearbooks; China’s Industrial Statistics Yearbook | ||
| Social sustainability | Transport development | Traff | Percentage of highway length to population with higher education in each region (km). | Provinces’ statistical yearbooks |
| Academic sustainability | R&D | Percentage of R&D investment in higher education to GDP at province level. | Provinces’ statistical yearbooks | |
| Urbanisation level | Urban | Percentage of regional population to total population at province level. | Provinces’ statistical yearbooks | |
| Environmental sustainability | Environmental development | Environ | Percentage of landscaping area to total land area at province level (hectares). | Provinces’ statistical yearbooks |
| Renewable energy utilisation | REI | Percentage of output value of new energy industry to GDP at province level (millions of yuan). | Industrial and commercial bureau database | |
| Green patent authorisation | GP | Proportion of GP authorisation by higher education to the total number of authorised patents. | State Intellectual Property Office database; Provinces’ statistical yearbooks |
| Constant | Economic Sustainability | Social Sustainability | Environmental Sustainability | Adjusted R2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | FDI | CLP | Traff | R&D | Urban | Environ | REI | GP | |||
| National level | −3.524 ** | 0.402 ** | 0.992 | 4.360 *** | 0.094 ** | 0.177 | 0.058 | 0.027 ** | 0.794 ** | −0.84 | 0.657 |
| Eastern China | −3.074 * | 0.536 * | 1.480 ** | 0.363 ** | 0.100 *** | 0.175 *** | 1.305 *** | 0.744 *** | −0.576 | −0.129 * | 0.713 |
| Middle China | 1.928 | 5.084 *** | 0.145 * | 0.761 ** | −0.186 | −0.327 * | −5.333 | 0.174 * | 0.424 * | 0.219 *** | 0.612 |
| Western China | 3.9 ** | 0.186 ** | 0.046 *** | 5.115 | 0.743 *** | 8.527 ** | 0.088 * | 0.542 *** | −5.807 | −3.962 ** | 0.589 |
| Constant | Economic Sustainability | Social Sustainability | Environmental Sustainability | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | FDI | CLP | Traff | R&D | Urban | Environ | REI | GP | ||
| National level | −1.198 * | 1.227 ** | 1.562 * | −0.39 | 0.314 *** | 0.591 * | 0.09 * | 0.848 ** | −0.928 | −0.447 |
| Eastern China | 1.376 ** | 0.06 ** | 1.509 * | 0.413 *** | 2.407 * | 0.736 *** | −1.91 | 0.803 *** | −0.296 * | −0.137* * |
| Middle China | 2.148 * | 0.622 | 1.558 ** | 0.579 ** | −0.361 * | −0.765 * | −1.549 ** | 0.633 * | −0.324 | 0.288 *** |
| Western China | 2.248 *** | 0.459 ** | 0.948 | 0.331 * | 1.116 *** | −0.102 | 0.524 ** | 0.653 *** | −0.059 * | 0.662 |
| Adjusted R2 | Sargan’s Test | Significance in First Stage | Wu–Hausman Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| National level | 0.675 | 1 | 0.000 *** | 0.005 *** |
| Eastern China | 0.725 | 1 | 0.002 ** | 0.012 *** |
| Central China | 0.699 | 1 | 0.011 ** | 0.007 *** |
| Western China | 0.701 | 1 | 0.000 *** | 0.013 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Zhu, X.; Cao, M. Impacts of Reduced Inequalities on Quality Education: Examining the Relationship between Regional Sustainability and Higher Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114112
Liu T, Zhu X, Cao M. Impacts of Reduced Inequalities on Quality Education: Examining the Relationship between Regional Sustainability and Higher Education. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):14112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114112
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tingting, Xiaoxian Zhu, and Mengqiu Cao. 2022. "Impacts of Reduced Inequalities on Quality Education: Examining the Relationship between Regional Sustainability and Higher Education" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 14112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114112
APA StyleLiu, T., Zhu, X., & Cao, M. (2022). Impacts of Reduced Inequalities on Quality Education: Examining the Relationship between Regional Sustainability and Higher Education. Sustainability, 14(21), 14112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114112







