Sustainability Perspectives in Organizational and Workplace Learning Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Reflections on Sustainability in Organization and Workplace Learning Studies
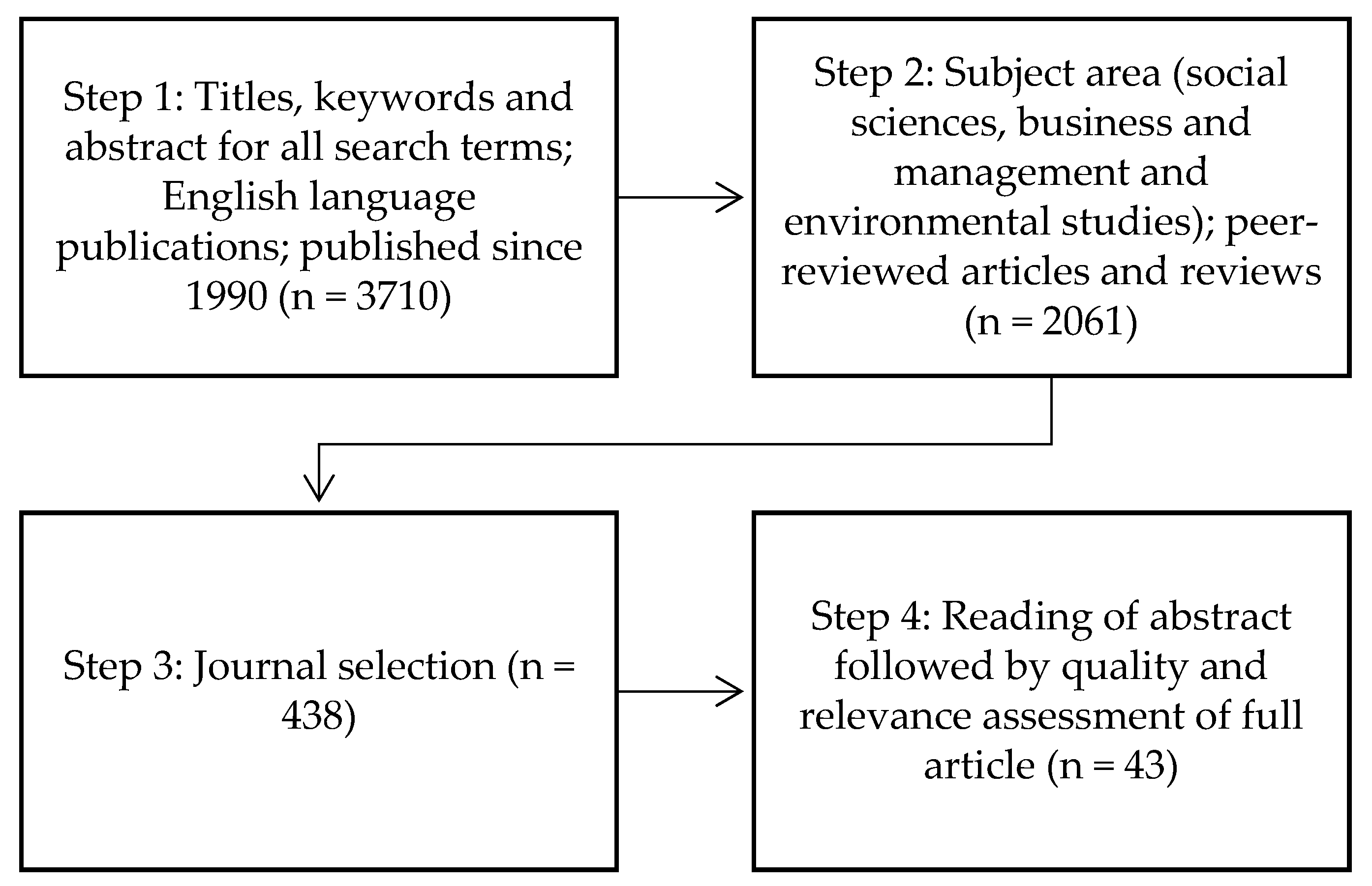
3. Methods
3.1. Eligibility Criteria
3.2. Quality Assessment
3.3. Analytical Strategy
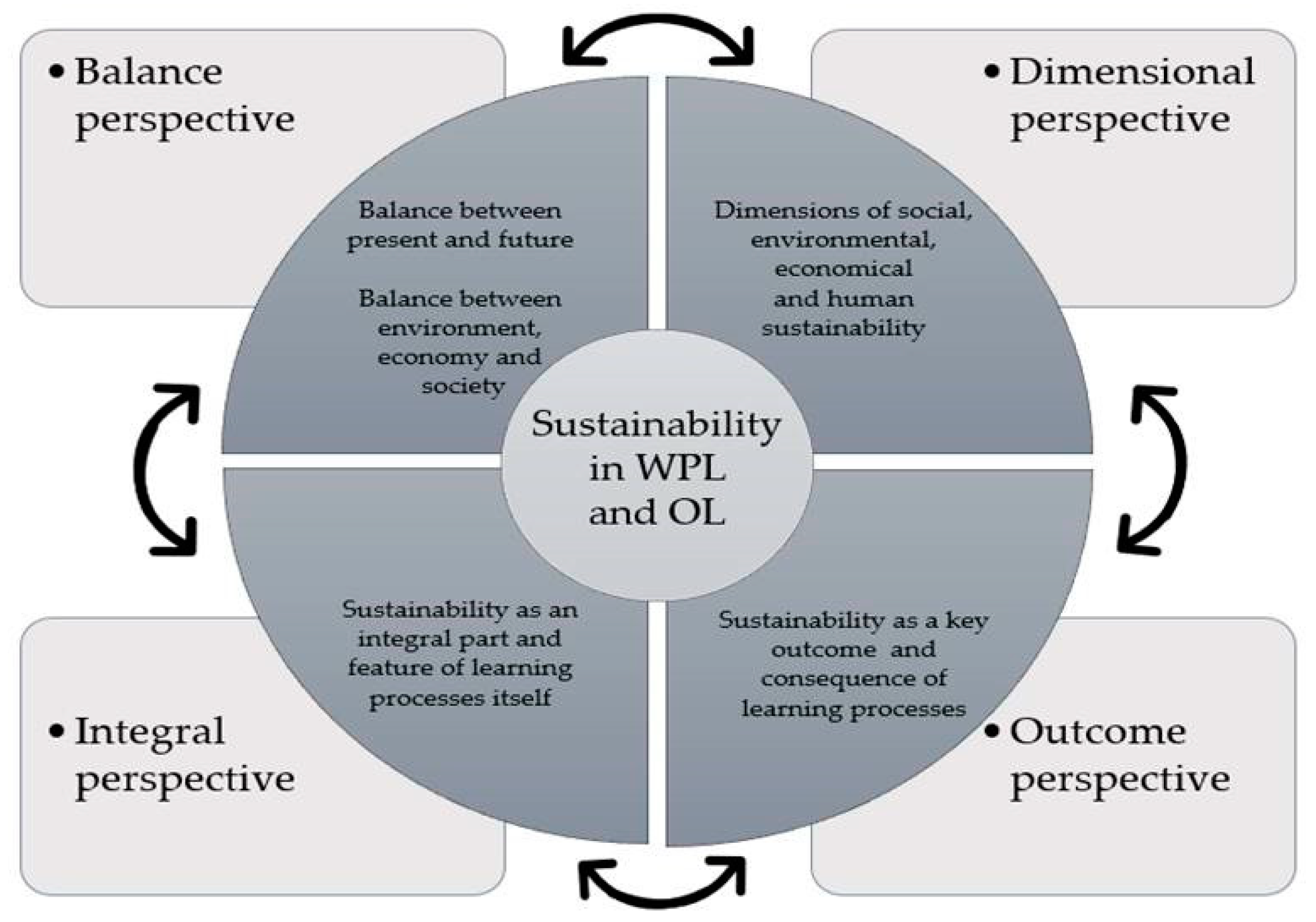
4. Results
4.1. Balance Perspective
4.2. Dimensional Perspective
4.3. Integral Perspective
4.4. Outcome Perspective
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wals, A.E.J.; Schwarzin, L. Fostering organizational sustainability through dialogical interaction. Learn. Organ. 2012, 19, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. About the Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Benn, S.; Edwards, M.; Angus-Leppan, T. Organizational Learning and the Sustainability Community of Practice: The Role of Boundary Objects. Organ. Environ. 2013, 26, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, T. Developing organizational practices of ecological sustainability: A learning perspective. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2007, 28, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarestky, J.; Collins, J.C. Supporting the United Nations’ 2030 sustainable development goals: A call for international HRD action. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 2017, 20, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, M.; Cennamo, C.; Neumann, K. Beyond what and why: Understanding organizational evolution towards sustainable enterprise models. Organ. Environ. 2013, 26, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmetty, S.; Collin, K. Throwaway knowledge, useful skills or a source for wellbeing? Outlining sustainability of workplace learning situations. Int. J. Lifelong Educ. 2020, 39, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heizmann, H.; Liu, H. Becoming green, becoming leaders: Identity narratives in sustainability leadership development. Manag. Learn. 2018, 49, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.; Thorpe, R.; Coleman, C. Reviewing Management Learning: The field and the journal. Manag. Learn. 2020, 51, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully-Russ, E. Human resource development and sustainability: Beyond sustainable organizations. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 2012, 15, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torraco, R.J.; Lundgren, H. What HRD is doing—What HRD should be doing: The case for transforming HRD. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2020, 19, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerman, J.W.; Rao, M.B.; Vanka, S.; Gupta, M. Sustainable human resource management and the triple bottom line: Multi-stakeholder strategies, concepts, and engagement. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2020, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkjaer, B. Taking stock of “Organizational Learning”: Looking back and moving forward. Manag. Learn. 2021, 53, 582–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, U.; Thomassen, M.L. Sustainable organizational learning and corporate entrepreneurship: A conceptual model of sustainability practices in organizations. J. Workplace Learn. 2021, 33, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova-Nowak, I.V.; Cseh, M. The Meaning of Organizational Learning:A Meta-Paradigm Perspective. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2015, 14, 299–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterby-Smith, M.; Lyles, M.A. The Evolving Field of Organizational Learning and Knowledge Management; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brandi, U.; Elkjaer, B. Organisational learning viewed from a social learning perspective. In Handbook of Organizational Learning and Knowledge Management; Easterby-Smith, M., Lyles, M.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alerasoul, S.A.; Afeltra, G.; Hakala, H.; Minelli, E.; Strozzi, F. Organisational learning, learning organisation, and learning orientation: An integrative review and framework. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2022, 32, 100854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkjaer, B.; Lotz, M.M.; Nickelsen, N.C.M. Current Practices in Workplace and Organizational Learning: Revisiting the Classics and Advancing Knowledge; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cuel, R. A journey of learning organization in social science: Interview with Silvia Gherardi. Learn. Organ. 2020, 27, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, J.G. Exploration and Exploitation in Organizational Learning. Organ. Sci. 1991, 2, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.M.; Pilar Pérez Santana, M. Building ambidexterity: The role of human resource practices in the performance of firms from Spain. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2012, 51, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.C.; Snell, S.A. Intellectual capital architectures and ambidextrous learning: A framework for human resource management. J. Manag. Stud. 2009, 46, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyris, C.; Schön, D. Organizational Learning II: Theory, Method, and Practice; Addison Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Argyris, C. A life full of learning. Organ. Stud. 2003, 24, 1178–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, H.; Bang, A.; Justice, S.B.; Marsick, V.J.; Poell, R.F.; Yorks, L.; Clark, M.; Sung, S.Y. Conceptualizing reflection in experience-based workplace learning. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 2017, 20, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argote, L.; Miron-Spektor, E. Organizational learning: From experience to knowledge. Organ. Sci. 2011, 22, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Han, S.J.; Lee, J.; Sunalai, S.; Yoon, S.W. Integrative Literature Review on Informal Learning: Antecedents, Conceptualizations, and Future Directions. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2018, 17, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, E.W. Organizational learning and the learning organization: A dichotomy between descriptive and prescriptive research. Hum. Relat. 1997, 50, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örtenblad, A. What does “learning organization” mean? Learn. Organ. 2018, 25, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Demystifying Literature Reviews: What I Have Learned From an Expert? Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2019, 18, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapuji, H.; Crossan, M. From questions to answers: Reviewing organizational learning research. Manag. Learn. 2004, 35, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierly, P.E.; Hämäläinen, T. Organizational learning and strategy. Scand. J. Manag. 1995, 11, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.; Rosenthal, A. Exploring learning organizations: Enacting mental models—The power of the Rosenthal stage. J. Workplace Learn. 1997, 9, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.C.; O’Kane, P.; Mazumdar, B.; McCracken, M. Performance Management: A Scoping Review of the Literature and an Agenda for Future Research. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2018, 18, 47–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, B. Our common future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Boström, M.; Andersson, E.; Berg, M.; Gustafsson, K.; Gustavsson, E.; Hysing, E.; Lidskog, R.; Löfmarck, E.; Ojala, M.; Olsson, J. Conditions for transformative learning for sustainable development: A theoretical review and approach. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, V.C.; Hrivnak, M.W.; Valcea, S.; Mahoney, C.B.; LaWong, D. A comprehensive three-dimensional sustainability measure: The ‘missing P’of ‘people’–a vital stakeholder in sustainable development. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2018, 25, 772–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.; Pye, A.; Correia, F. Boundary objects, power, and learning: The matter of developing sustainable practice in organizations. Manag. Learn. 2017, 48, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. Towards the sustainable corporation: Win-win-win business strategies for sustainable development. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1994, 36, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnesson, K.; Albinsson, G. Reflecting talks: A pedagogical model in the learning organization. Reflective Pract. 2019, 20, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, M.; van Eijnatten, F.M. Socially sustainable work organizations: Conceptual contributions and worldviews. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2011, 28, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Siebenhüner, B. Policy instruments for sustainability-oriented organizational learning. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2007, 16, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A.; Sharicz, C. The shift needed for sustainability. Learn. Organ. Int. J. 2011, 18, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, S.; Martin, A. Learning and change for sustainability reconsidered: A role for boundary objects. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2010, 9, 397–412. [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick, T.; Bierema, L. Corporate social responsibility: Issues for human resource development professionals. Int. J. Train. Dev. 2008, 12, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, D. Insights into triple bottom line integration from a learning organization perspective. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2006, 12, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratton, A. The role of talent development in environmentally sustainable hospitality. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. 2018, 10, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, M.; Frieling, E. Bureaucratic boundaries for collective learning in industrial work. J. Workplace Learn. 2007, 19, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.E.; Figueiredo, M.D. Practicing sustainability for responsible business in supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, E.; Evans, K.; Kersh, N. The challenge of establishing sustainable workplace ‘Skills for Life’provision in the UK: Organisational ‘strategies’ and individual ‘tactics’. J. Educ. Work 2014, 27, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.M.; Torphy, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Masuda, Y.J.; Fisher, J.R.; Galey, S.; Burford, K.; Frank, K.A.; Montambault, J.R. How different forms of social capital created through project team assignments influence employee adoption of sustainability practices. Organ. Environ. 2019, 34, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, J.M.; Sinclair, A.J. Stoking the dialogue on the domains of transformative learning theory: Insights from research with faith-based organizations in Kenya. Adult Educ. Q. 2016, 66, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluye, P.; Potvin, L.; Denis, J.-L. Making public health programs last: Conceptualizing sustainability. Eval. Program Plan. 2004, 27, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upstill-Goddard, J.; Glass, J.; Dainty, A.; Nicholson, I. Implementing sustainability in small and medium-sized construction firms. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2016, 23, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton-Short, L.; Cseh, M. Changing Cities, Changing Culture. Adv. Dev. Hum. Resour. 2015, 17, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kola-Olusanya, A. Embedding environmental sustainability competencies in human capital training and development. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2013, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C. Greening HRD: Conceptualizing the triple bottom line for HRD practice, teaching, and research. Adv. Dev. Hum. Resour. 2015, 17, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedchayanon, N.; Chorkaew, S. The sufficiency economy and people-centered development. Eur. J. Train. Dev. 2014, 38, 822–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, C.; Lam, C.F.; Spreitzer, G.M. It’s the little things that matter: An examination of knowledge workers’ energy management. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2011, 25, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ergene, S.; Banerjee, S.B.; Hoffman, A. (Un) Sustainability and Organization Studies: Towards a Radical Engagement. Organ. Stud. 2020, 42, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.B. Embedding sustainability across the organization: A critical perspective. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2011, 10, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manring, S.L. Creating and managing interorganizational learning networks to achieve sustainable ecosystem management. Organ. Environ. 2007, 20, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crona, B.I.; Parker, J.N. Learning in support of governance: Theories, methods, and a framework to assess how bridging organizations contribute to adaptive resource governance. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Porter, T. Sustainability, complexity and learning: Insights from complex systems approaches. Learn. Organ. 2011, 18, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perey, R.; Benn, S. Organising for ecological repair: Reconstructing land management practice. Organ. Environ. 2015, 28, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wals, A.E.J. Learning our way to sustainability. J. Educ. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 5, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, R. A process-philosophical understanding of organizational learning as “wayfinding”: Process, practices and sensitivity to environmental affordances. Learn. Organ. 2017, 24, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, M.; van Eijnatten, F.M.; Balkin, D.B. Crafting sustainable work: Development of personal resources. J. Organ. Change Manag. 2010, 23, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossan, M.M.; Lane, H.W.; White, R.E. An organizational learning framework: From intuition to institution. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1999, 24, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, A.M. Leadership’s influence on innovation and sustainability: A review of the literature and implications for HRD. Eur. J. Train. Dev. 2014, 38, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenhüner, B.; Arnold, M. Organizational learning to manage sustainable development. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2007, 16, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Boulet, M. Transformations? Skilled change agents influencing organisational sustainability culture. Aust. J. Environ. Educ. 2016, 32, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, P.M.; Lichtenstein, B.B.; Kaeufer, K.; Bradbury, H.; Carroll, J.S. Collaborating for systemic change. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2007, 48, 44. [Google Scholar]
- de Paiva Duarte, F. Sustainability learning challenges in a Brazilian government organization. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2017, 25, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, H.M.; Talwar, A. How Do Corporations Embed Sustainability Across the Organization? Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2010, 9, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitleton-Kelly, E. A complexity theory approach to sustainability: A longitudinal study in two London NHS hospitals. Learn. Organ. 2011, 18, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prugsamatz, R. Factors that influence organization learning sustainability in non-profit organizations. Learn. Organ. 2010, 17, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.G. An integrative metatheory for organisational learning and sustainability in turbulent times. Learn. Organ. 2009, 16, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Promote Sustained, Inclusive and Sustainable Economic Growth, Full and Productive Employment and Decent Work for All. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal8 (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Collin, K. Connecting work and learning: Design engineers’ learning at work. J. Workplace Learn. 2006, 18, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, U.; Iannone, R.L. Approaches to learning in the context of work–workplace learning and human resources. J. Workplace Learn. 2021, 33, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, G.; Gherardi, S.; Verzelloni, L. Through the practice lens: Where is the bandwagon of practice-based studies heading? Manag. Learn. 2010, 41, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuti, A.; Giancaspro, M.L. People make the difference: An explorative study on the relationship between organizational practices, employees’ resources, and organizational behavior enhancing the psychology of sustainability and sustainable development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, P.; Kira, M.; Shani, A.B.R. Organizational development for social sustainability in work systems. In Research in Organizational Change and Development; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Conigliaro, P. Between Social Sustainability and Subjective Well-being: The Role of Decent Work. Soc. Indic. Res. 2021, 157, 139–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, K.; Söderlund, J. The HR quadriad: A framework for the analysis of HRM in project-based organizations. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2011, 22, 2202–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierema, L.L. HRD research and practice after ‘The Great COVID-19 Pause’: The time is now for bold, critical, research. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 2020, 23, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, P.; Forslin, J.; Shani, A.B. Creating Sustainable Work Systems: Emerging Perspectives and Practice; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer, J. Building sustainable organizations: The human factor. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2010, 24, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandi, U.; Collin, K.; Lemmetty, S. Sustainability Perspectives in Organizational and Workplace Learning Studies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13101. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013101
Brandi U, Collin K, Lemmetty S. Sustainability Perspectives in Organizational and Workplace Learning Studies. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13101. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013101
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandi, Ulrik, Kaija Collin, and Soila Lemmetty. 2022. "Sustainability Perspectives in Organizational and Workplace Learning Studies" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13101. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013101
APA StyleBrandi, U., Collin, K., & Lemmetty, S. (2022). Sustainability Perspectives in Organizational and Workplace Learning Studies. Sustainability, 14(20), 13101. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013101






