Abstract
The coevolution of mycorrhizae with plants represents a major evolutionary adaptation to the land environment. As a bioinoculant, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) play a beneficial role in sustainable agriculture by symbiotically associating with many crop plants. In this review, we primarily focus on the nutritional and non-nutritional functionality of AMF in soil and plant productivity. AMF maintain soil quality and health via three aspects: soil structure, plant physiology, and ecological interactions. These lead plants to increase their functionality, further growth, and productivity. The formation of soil aggregates via glomalin production maintains the soil structure. Physiologically, AMF change nutrient acquisition and thereby increase soil fertility and productivity. Biotic (pathogens and weed plants) and abiotic (salinity, drought, extreme temperature, soil pH, and heavy metals) stress alleviation is also achieved via altering a plant’s physiological status. By serving as a biocontrol agent, AMF negatively interact with plant pathogens. As a result of beneficial interactions with other rhizosphere microorganisms and above-ground organisms, AMF induce a synergistic effect on plant performance. Moreover, they are also involved in land restoration and seedling establishment. The collective effect of all these functions positively influences overall plant performance and productivity.
1. Introduction
After the “Green Revolution”, farmers were quick to conduct high-input farming practices involving synthetic inorganic fertilizers and agrochemicals that intensify the production processes necessary to fulfill the global food demand but without considering the impact of agrochemicals on natural ecosystem functionality. Soil quality degradation and disturbance to natural ecosystem functionality are evident and therefore threaten environmental sustainability; furthermore, they could be a warning for future food security [1,2]. To alleviate this issue, the establishment of sustainable agriculture is a better alternative. The core objective of sustainable agriculture is to conduct all farming practices using environmentally friendly approaches [1,3].
As part of sustainable agriculture, organic farming and regenerative agriculture depend on applying beneficial microorganisms. For the elimination of the negative impact on crop production, the application of bacteria has been well documented, but research based on the application of fungi is more limited [4,5]. With respect to farming, factors such as climate, soil health, and water availability, are some of the significant environmental determinants of plant viability, functionality, and productivity [1,6]. More interestingly, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) can address these ecological determinants and plant physiological events by symbiotically associating with the plants. This is because mycorrhizae coevolved with plants from 400 million years ago and acquired evolutionary adaptions related to plants and to the terrestrial environment [7,8]. Furthermore, this coevolution enhanced the ability of mycorrhizae to diminish biotic and abiotic stresses, and other ecosystem issues that plants encounter.
In this review, we discuss the nutritional and non-nutritional functionality of AMF as beneficial microorganisms in agricultural sustainability [9]. AMF induce morphological, biochemical, and physiological alterations, including changes at the gene expression level in the plant to intensify plant productivity [10,11]. Most approaches discussed herein are based on their ability to enhance plant nutrient and water uptake by means of fungal mycelium extension. In mycorrhizal application approaches, lower levels of disturbance to agricultural fields help mycorrhizae provide better mycelium and maintain the common underground networks (CMN) that connect individual plants [12,13,14].
2. Background of Mycorrhizal Fungi Symbiosis
Mycorrhizae are involved in the association between fungi in different taxonomic groups with most species of plants to form a mutualistic symbiosis, although plants of some families, such as the Brassicaceae, Cyperaceae, Juncaceae, Urticaceae, and Chenopodiaceae, inhibit mycorrhizal colonization [15,16]. Colonization variation in plant roots has divided mycorrhizae, which are mainly classified into two categories: Endomycorrhizae (Phylum Glomeromycota) and Ectomycorrhizae (Phyla: Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, and Mucoromycota). Endomycorrhizae are further divided into arbuscular, orchid, and ericoid types [17,18,19]. Arbutoid considers ectendomtcorrhizae because they have both ericoid and ectomycorrhizae features. Generally, mycorrhizal fungi depend on their host plants for 20% of carbon, and some other plants parasitically (fully) depend on monotropoid mycorrhizae fungi for carbon [20,21]. With respect to abundance, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonize a huge number of plant species (80–90%), and only 10% of plants form ectomycorrhizae. Both types play a significant role in sustainable agriculture and forestry [22].
The symbiotic interaction is formed via a sequence of chemical signals exchanged between the plant and the fungus, and the essential genetic determinants of the plant identify the mycorrhizae as a beneficial organism [23,24]. In the pre-symbiotic stage, plant roots produce strigolactones, which lead to fungal spore germination [25], and meanwhile, mycorrhizae produce “Myc-factors” (lipo-chitooligosaccharides and chitooligosaccharides) [26], thereby initiating the symbiosis. Subsequently, the internalization of arbuscular mycorrhizae occurs via the formation of hypophodia, and then, arbuscules and vesicles. In parallel with this, ectomycorrhizae form the mantle and Hartig net intercellularly interface with the roots of the host [15,27]. The best known and most prominent ectomycorrhizae form symbiotic relationships with temperate forest plant species (mostly trees) and endomycorrhizae of the same with cultivated crops. The fungus proceeds in its significant role either through plant metabolic modification or by increasing the plant root absorption area via the development of fine fungal hyphae if the plant is in normal or stressful environmental conditions [22].
3. Factors Affecting the Functional Effect of AMF in the Agricultural Field
AMF have a wide distribution among plants and form different colonization patterns and exhibit considerable diversity in terms of host plants, climate, latitude, C:N:P ratio in soil, soil types, soil acidity, and rhizosphere and above-ground organisms [28,29].
Host specificity and variation in colonization percentage can be identified within the genotypes of the same species [30]. For instance, AMF colonization variation was identified in the roots of different sexes in dioecious plants [31]. Even with the photosynthetic behavior of plants (e.g., C3 and C4 plants), the contribution of AMF to drought resistance is different. Due to specific physiological mechanisms in C4 plants, the latter have formed better adaptation to drought conditions when compared to C3 plants and are less subject to severe damages. Therefore, C3 plants take more advantage of AMF symbiosis when the plant is in a drought condition [32]. In a no-till crop rotation system, different underground AMF relationships give the next cultivated crop an additional advantage by minimizing the buildup of the pest population, enhancing soil health, forming the shared mycorrhizal network, and so on [30].
The colonization variations of AMF in Schizachyrium scoparium (Michx.) Nash plant are related to the differences in latitude. Variables, such as pH, N:P ratio in soil, annual temperature, and growing season length, vary with latitude. The results have shown that colonization percentage is negatively correlated with latitude [28]. Carrenho et al. [33] reported that clay soil forms lower AMF colonization than sandy soil in maize, peanut, and sorghum because of the higher nutrient concentration, higher suberin deposition on plant epidermal cells, and lower space between the soil particles in clay soil that reduce AMF colonization in plants. Rising temperatures have been shown to decrease AMF colonization and positively affect the level of biomass in upland prairie with Mediterranean temperature gradients in the Pacific Northwest [34].
4. Improvement of Soil Quality and Health
Soil quality depends on the physical and chemical properties, and the diversity, distribution, and activity of the soil biota [35,36,37]. Soil health refers to the ability of the soil to function as a living ecosystem. Soil health is governed by soil quality and thus influences human health via enhancing crop quality. As a beneficial biological tool, AMF maintains soil quality and health by influencing three main factors: soil structure, plant physiology, and ecological interactions (Figure 1) [38,39].
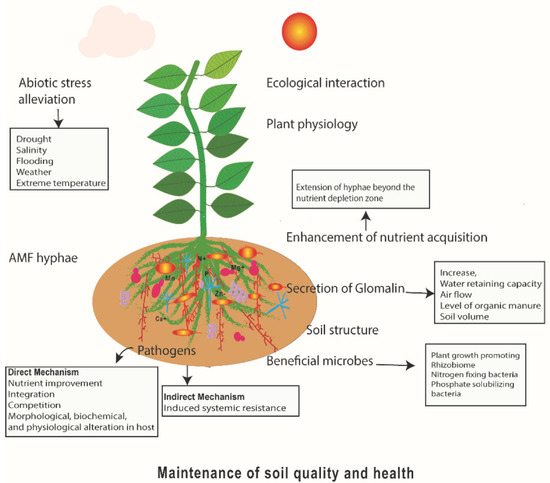
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of maintaining soil quality and health by AMF to enhance plant productivity.
Maintaining the soil structure is one of the important processes in agriculture. AMF form water-stable soil micro-aggregates by secreting hydrophobic glycoprotein, glomalin, which acts as a long-term binding agent [40]. AMF deposit glomalin between the outer hyphal walls and adjacent soil particles to form micro-aggregates and further macro-aggregates, thus forming the backbone for soil aggregation [35,41]. This facilitates an increase in water-retaining capacity, airflow, soil volume, and level of organic matter. In agricultural lands, to take more advantage of the maintenance these aggregates provide, lower disturbance and no-till fields are required [42]. AMF maintain both positive and negative ecological interactions in the rhizosphere. AMF contact positively with beneficial microorganisms, including phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB), nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Negatively, mycorrhizae interact to suppress both disease-causing soil-borne pathogens and pests [43,44]. AMF identify the pathogens via chitin-related compounds, i.e., chito-oligosaccharides (COs), and lipo-chito-oligosaccharides (LCOs), and also, plants produce microbe-specific molecular patterns in their receptor complexes. In the beginning, all chitin-related molecules are identified by the LysM–RLK complex. By combining this complex with other proteins, microbe identification is achieved.
4.1. Maintenance of Plant Physiology
4.1.1. Stimulation of Soil Fertility by Enhancing Nutrient Acquisition
In general, AMF affect nutrient acquisition from the soil and enhance growth, biomass, and finally, plant productivity [45]. AMF are obligate biotrophs and depend on 20% of fixed carbon in their host [46]. However, due to their nutrient uptake capability, mycorrhizal fungi have become the main part of sustainable agriculture. This is because fungal hyphae can grow beyond the nutrition depletion zone where plant roots cannot reach and absorb the nutrients from an area of 25 cm in the soil [47] and thus cause different hydraulic redistribution patterns in plants. As a result of changes in environmental parameters, nutrient availability, and symbiotic relationships, plants alter their morphology up to the molecular level. In mycorrhizal plants, the root architecture is changed by forming recognizable lateral root branches, root hairs, and a distinctive apex [48]. The modifications of cell division and differentiation in the root are changed due to molecular mechanisms. Non-mycorrhizal plants uptake nutrients directly from the soil via nutrient transporters located in the root hairs and the epidermis [49]. In AMF symbiosis, at first, nutrient uptake occurs through extraradical mycelium transporters to the intraradical mycelium and then further transfers to the plant cell via mycorrhizae-inducible transporters located in the peri-arbuscular membrane (Figure 2) [50]. The nutrient uptake efficiency is correlated to the level of hyphae distribution and colonization [51].
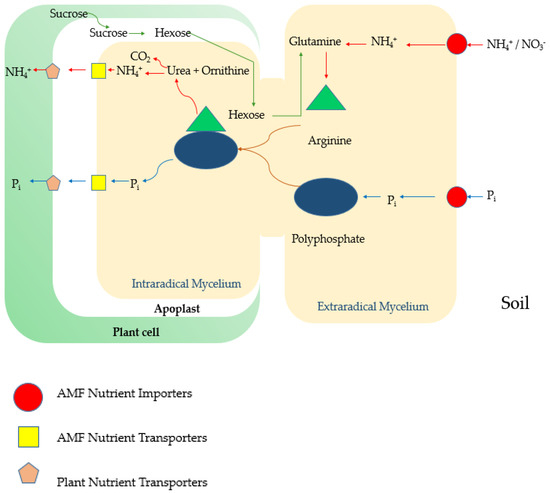
Figure 2.
Schematic presentation of the nutrient transport pathways: direct root pathway and mycorrhizal pathway from soil to plant cell.
Plants form different types of plant nutrient transporters for direct pathways and mycorrhizal-induced nutrient uptake pathways [52]. For example, rice plants use OsPT2 and OsPT6 for direct pathways and OsPT11 for the mycorrhizal-induced pathway. After AMF colonize the plant, this downregulates the gene that is coded for plant nutrient transporters involved in the direct nutrient uptake pathway. Nevertheless, nutrient transporters located in mycorrhizal membranes are also species specific. As an example, Glomus versiforme forms GvPT, and G. intraradices forms GiPT as a Pi transporter [53,54].
In the phosphorus transport process, Pi is absorbed in the form of negatively charged polyphosphate granules by phosphate importers located in the extraradical mycelium (ERM) [55]. In nitrogen uptake, nitrogen importers take nitrogen in the forms of NH4+ and NO3− and then convert these into glutamines, and further, positively charged arginine is formed [56]. Then, negatively charged polyphosphate granules and positively charged arginine form a complex and are transported to the intraradical mycelium (IRM). In the IRM, arginine is broken down to form the urea and the ornithine. Afterward, the ammonia and the hydrolyzed urea products are transported into plant cells via the symbiotic interface. With the help of arginine, polyphosphate granules are also transported to the IRM, and furthermore, the latter releases Pi to the symbiotic interface (Figure 2). The molecular mechanisms involved in some of these events are still unclear [57]. Scientists have shown that, in a faba bean/wheat intercropping system, AMF symbiosis enhanced root length, density, and biomass in the pure stand wheat system and increased the uptake of P and micronutrients, such as Fe and Zn. Interestingly, wheat intercropping with faba bean increased the P uptake into the wheat plant. AMF do not influence the P uptake in faba beans, either in a pure or intercropping system [58].
The combination of these features with pathogen biocontrol capability (discussed in Section 4.2.2) leads mycorrhizae to act as a better biofertilizer in agriculture. Therefore, the application of a mycorrhizal inoculum reduces the utilization of agrochemicals, including fertilizer and pesticides.
4.1.2. Abiotic Stress Alleviation
AMF respond to both biotic and abiotic stresses that plants encounter. Plant pathogens act as a biotic stress, which was discussed in Section 4.2.2. Abiotic stresses, such as drought, salinity, flooding, heavy metals, and extreme temperature, may cause an adverse effect on plant physiology and thus, ultimately, plant productivity [59]. Due to these conditions, both plant and AMF communities undergo changes in their composition [60]. Because both organisms are subjected to these stresses independently, AMF are reduced in abundance and diversity. Changing their diversity may lead to the formation of a more resistant species community, and AMF provide the feedback effect to repair the plant species’ diversity and productivity [47].
Increasing the salinity causes a decrease in water absorption in plants because of osmotic changes. In plants under saline stress, AMF employ several morphological, biochemical, and physiological strategies to overcome the condition by enhancing water uptake. Morphologically, AMF enhance water and nutrient uptake by induction of root volume via expanding the root length, the projected area, and the surface [61,62]. The alteration of biochemical pathways in plants thus leads the latter to make changes in their physiology. To balance the ion concentrations of Na+ and Cl−, AMF facilitate the absorption of more nutrient ions (NO3−, PO43−, Ca2+, and Mg2+) from the soil solution to plants and thus increase plant growth and productivity while maintaining the salinity stress. Meanwhile, AMF induce the production of osmoregulators (proline, amides, glycine betaines, polyamines, sugar, and mannitol) [60] and balance ionic homeostasis [61,63] to maintain the water level in the plant. Upreti et al. [64,65] showed that AMF maintained the salinity stress in grape (Vitis vinifera L.) plants via the induction of morpho-physiological responses, including K+:Na+ ratio, phosphorus, accumulation of spermidine, polyamines-spermine, and abscisic acid [64].
Several studies have demonstrated that the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is higher when plants are under salinity stress, and this causes damage to biomolecules, such as lipids, proteins, and DNA. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi neutralize the damage by enhancing the activity of the antioxidant enzymes present in plants [61]. The colonization of AMF with Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. produced resistance against salinity stress by improvement of the plant biomass and rapid recycling of the reduced antioxidants ascorbate and glutathione. In this experiment, Rhizophagus irregularis acted more on pigeon pea plants than Funneliformis mosseae [66]. Not only the water uptake but salinity stress decreased the rate of photosynthesis by reduction in the photosynthetic enzymes and chlorophylls. This is because chlorophyll biosynthesis depends on the presence of Mg2+ ions. The process of AMF enhancing Mg2+ ions was already mentioned above. Apart from this, AMF upregulate the chloroplast genes (RppsbA and RppsbD) expression of the PSII system [63,67]. With respect to salinity, similar mechanisms involving AMF induce resistance to the extreme temperature (cold or heat) and flooding conditions, equally enhancing water and nutrient uptake, accumulation of osmolytes, production of antioxidants, osmotic adjustment, and improvement of photosynthesis [63].
Low levels of heavy metals are required for various aspects of the functionality of plants, including enzymatic reactions and oxidoreduction. However, high concentrations of heavy metals can be toxic to plants and cause a disturbance in plant physiology and productivity. Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Zn, Cu, and Co) can be accumulated in agricultural soil due to anthropogenic activities, including the long-term application of commercial fertilizers and biocides, sewage treatments, mining, and atmospheric deposition [68]. The application of AMF exhibits a positive effect on plant productivity by the remediation of heavy metals in contaminated soil [63,69] via two mechanisms. First, similar to nutrient absorption, the hyphae can deliver heavy metals to the host, resulting in the accumulation of metals in host plants. This can be followed by the phytoextraction process, and those heavy metal accumulated plants can be harvested and destroyed in the field [70]. Second, the hyphae can bind to the metal elements and thus decrease the bioavailability of elements to the host plant [63,70]. To test this, bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil was tested by using native plants and an AMF inoculum. For the combination of the plant Caragana korshinskii and the AMF Funneliformis geosporus, a 73.81% degradation rate was noted after 2 months in 0–5000 mg/kg of petroleum-contaminated soil [71]. A sunflower plant inoculated with Rhizophagus intraradices accumulated 23% more Cd than the non-inoculated plant, and Cd was primarily accumulated in plant roots, and a reduction in plant growth was observed in the non-inoculated plant [72]. To withstand drought stress, mycorrhizae form an array of reactions that are discussed in more detail in Section 5.
4.2. Ecological Interactions
4.2.1. Beneficial Ecological Interactions
To double agricultural production, the ability of mycorrhizae to create synergistic interactions with other beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms, such as the plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs), nitrogen fixation bacteria, and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, is of considerable importance [73,74]. The application of the consortium of AMF and Azotobacter chroococcum to a wheat cultivation system had a greater influence on plant yield than the application of pure AMF alone. This is because Azotobactor provides a better complement to wheat–AMF interaction via nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, and phytohormone production [74]. Using the consortium of rhizobia, PGPRs, and AMF improved the growth parameters: shoot and root dry weight, leaf number, sugar, and protein content in wheat and faba bean plants. This consortium was more effective than the use of individual microorganisms or a combination of PGPRs and rhizobia [73]. Many species of Bacillus (e.g., B. pumilus, B. subtilis, B. megaterium, and B. licheniformis) also interact with AMF and confer a benefit relating to pathogen biocontrol, stress alleviation, and nutrient acquisition in different plant systems [75]. In Acacia gerrardii plants under salt stress, B. subtilis displayed a better performance in plant productivity than AMF when they were added as a single inoculant. However, their synergistic effect facilitated enhanced plant growth more than the use of Bacillus subtilis alone because B. subtilis alleviates the adverse effect of salt on AMF functionality [76]. The integration of AMF and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) increased plant growth and tuber inulin content in the economically important plant Helianthus tuberosus L. In this process, first, PSB produced organic acids, such as citric, formic, lactic, and succinic acid, to reduce the soil pH and then converted insoluble phosphorus into bioavailable orthophosphate. The AMF increased the uptake process of orthophosphate into plant roots and increased the yield of single-inoculated plants [77]. Other than microorganisms, AMF interact with above-ground insect herbivores and influence plant productivity. As an example, Sitobion avenae interacting with an AMF–barley plant system increased the grain N:P ratio and the abundancy of the AMF family Gigasporaceae [78].
4.2.2. Pathogen Biocontrol
A large number of pathogens, including above-ground and soil-borne organisms, cause adverse biotic stress on plant viability and functionality, and this results in a substantial yield loss in the cultivated fields. Like other beneficial microorganisms, mycorrhizae have the ability to biocontrol pathogens by acting as a priming system in pathogen resistance.
AMF identify the pathogens via chitin-related compounds, i.e., chito-oligosaccharides (COs) and lipo-chito-oligosaccharides (LCOs). Plants also produce microbe-specific molecular patterns on their receptor complexes. In the beginning, all chitin-related molecules are identified by the LysM–RLK complex. By combining this complex with other proteins, microbe identification is achieved. Along with that, mycorrhizae confer plant pathogen resistance via direct and indirect mechanisms. Indirectly, the AMF can trigger the induced systemic resistance (ISR) of plants. With that, the plants change their gene expression level, lignification incensement, and hormone levels [79,80], thus increasing pathogen resistance. Rice plants inoculated with Rhizophagus intraradices increased pathogen resistance by regulating the expression of host plant genes (OsNPR1, OsJAmyb, OsEREBP, and OsAP2) and triggering the ISR. In addition, signal transduction genes and the gene for calcium-mediated signaling in leaves are also upregulated in the absence of any pathogens [81].
As direct mechanisms, AMF are involved in plant nutrient improvement, integration with other beneficial organisms, direct competition, morphological, biochemical, and physiological alteration of plants for pathogen biocontrol (Figure 1). By creating a competition for space, infection sites, and nutrients for the pathogen, and photosynthesis, the AMF control plant invasion by pathogens [38]. For example, AMF competed with the major plant pathogenic nematode, Meloidogyne incognita, for the colonization in root nodules of the plant Prunus perscisa and inhibited gall formation [70]. Additionally, the formation of the underground common mycorrhizal network (CMN) that connects individual plants influences biocontrol by enhancing the available bioactive zone for plants [82,83]. Interestingly, AMF can act as an early warning system for herbivore attacks via exchanging signals among plants. When a plant is attacked by the aphids, they cause changes in plant volatiles, such as methyl salicylate, and share the message of aphid attack with the neighboring plants via a common mycorrhizal network [70].
The bioprotective potential of AMF depends on the collective effect of more than one independent mechanism, as was discussed above.
5. Drought Resistance
With the limitation of the available water content in the soil, both morphological and molecular changes occur in plant cells. Accordingly, drought-stressed plants increase the production of ethylene, and this ultimately promotes leaf senescence. Meanwhile, a reduction in chlorophyll content leads to inhibition of the photosynthetic rate. The accumulation of toxic free radicals induces changes in cell-membrane-like integrity, cell size, protein conformation, and lipid peroxidation, and it finally leads to cell death. All these changes collectively lead to decreasing plant productivity. Against these changes, plants also adapt themselves to manage the drought stress by making changes in plant transcriptome and proteome by means of regulation of gene expressions [84,85].
By providing support to the natural plant-mediated resistance, mycorrhizal fungi also help fix plant productivity when plants are under drought conditions. Mainly AMF-colonized plants maintain greater chlorophyll content and photosynthetic capacity if the plants are in water-stressed conditions. Under severe drought conditions, AMF-inoculated Zea mays L. plants significantly increased the photosynthetic pigments by 38.05% for total chlorophyll and 89.80% for carotenoids when compared to the control treatment [86]. Nevertheless, for both drought and salinity stresses [67], AMF make changes in their stress-related plant hormones [ABA, Strigolactones, and Jasmonic acid (JA)]. The elevation of JA causes increases in the shoot carbohydrate level, and furthermore, causes a variation in the root osmotic potential. On the other hand, as a solution for the drought, mycorrhizal fungi improve the plant water status as a result of changes in stomatal conductance, membrane conductivity, and hydraulic conductivity. Membrane conductivity is changed by increasing the upregulation of genes related to aquaporin synthesis and thus increasing the absorption of water by plants. Increasing hydraulic conductivity is achieved via penetration of the mycorrhizal hyphae through small soil pores where root hairs are accessible. The formation of stable soil aggregates via the production of glomalin by AMF also supports this process [85].
As another major event, AMF trigger the production of plant molecules that make them resistant to drought. According to this process, AMF upregulate the gene expression of the molecules, such as metallothioneins and polyamines, which counteract the cell damage. To balance the osmotic potential, increases in the production of osmolytes, such as proline, sugar, and glycine betaine, are also achieved by AMF [86]. AMF facilitate the maintenance of low oxidative damage resulting from underwater deficits either by decreasing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) via increasing water absorption through the hyphae or by the production of the antioxidants superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and catalase. AMF reduced the accumulation of malondialdehyde and soluble protein in plants and increased the activity of superoxide dismutase and catalase [85]. The inoculation of a C3 plant, Leymus chinensis, with an indigenous AMF caused a reduction in malondialdehyde level by 66% and 32% at light to moderate drought, whereas AMF treatment had no impact on malondialdehyde content under extreme drought [32].
6. Land Restoration
In general, mycorrhizae have positive effects on plants by maintaining all factors that are related to plant growth [87] and influencing the community structure through community assembly and succession. Consequently, AMF have been applied to the restoration of ecosystems [88,89,90,91].
In central Asia, ephemeral plants supply higher fodder for livestock and play a role in reducing the occurrence of sandstorms. Overutilization of ephemeral plants causes a disturbance to desert vegetation [90]. As a solution to the slowing rate of natural restoration, the inoculation with AMF has been found to speed up the total cover, community productivity, and biodiversity of ephemeral plants over a three-year study period [92]. Long-term mining activities cause an adverse effect on soil and vegetation biodiversity. Observations have shown that the introduction of AMF leads to mine restoration and plant re-establishment, mainly by improving mineral acquisition and maintaining ecosystem stability and functioning [93,94]. Proper maintenance of coastal dunes is required because of their ecological role in the protection of coastal areas from sea activities. The introduction of AMF restores the dune by improving the soil conditions and plant growth in this area. Tivane et al. [95] reported that the application of AMF increased the growth of the dune plant Canavalia rosea and was involved in the rehabilitation of the dune [95]. Desertification proceeds mainly due to a disturbance of the natural ecosystem. The re-establishment of natural plant–microbe interactions may have the potential of triggering the restoration of natural plant cover. Scientists have determined that the interaction of indigenous AMF with rhizobial nitrogen-fixing bacteria enhanced soil fertility and improved Anthyllis plant performance in the desertified semiarid ecosystem in southeastern Spain [96].
7. Mycorrhizae Improve Seed Germination and Seedling Establishment
Dormancy is one of the major barriers to seed germination. When seeds are inoculated with mycorrhizae, this helps break down dormancy by avoiding environmental stresses (heat, salinity, and drought) [97]. The establishment of mycorrhizae with plant seedlings confers wider root arrangement via hyphal development and further influences growth by increasing the root length, diameter, surface area, biomass, and shoot growth [98]. Meanwhile, it increases the photosynthesis rate, N, P, and K content, and finally enhances the seedlings’ resistance to environmental stresses, including pathogens [29,99].
During the seed germination stage, mycorrhizae begin to infect basal cells in the embryo. Then, the embryo obtains its carbon, water, and nutrients by digestion of hyphal coils that are formed in those basal cells [100]. This condition is called initial mycoheterotrophy [101]. In this process, the seeds produce protocorm, and further seedlings are formed. Seedlings give rise to the formation of the root; thereafter, fungi colonize in the root’s cortical cells and facilitate the nutrient acquisition from the substrate by the roots. To take more advantage, the selection of the most suitable mycorrhizal isolates for seed germination is required [101,102].
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi play a major role in plant viability, growth, productivity, and finally, yield, by alleviation of all stresses and other ecosystem constituents that plants encounter. As a successful bioinoculant in sustainable agriculture, AMF maintain higher food production with the preservation of the ecological system without disturbing the environmental sustainability. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi may interact synergistically with each other and the host plants.
With the help of molecular biotechnology, mycorrhizal functionality can be enhanced through gene manipulation. The consortium of AMF with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) enhances Pi uptake more than the application of AMF alone. This is because the involvement of PSB supplies a greater amount of bioavailable orthophosphate for the absorption process of the fungus. PSB first produces the organic acids to decrease the soil pH, and this leads to the conversion of insoluble phosphorous to orthophosphate. The incorporation of genes that code for the phosphate solubilization process in PSB into the AMF genome confers a benefit to the Pi uptake process of AMF. Normally, AMF uptake P in the form of orthophosphate. In this case, it would be possible to introduce engineered AMF to secrete organic acid when the fungus counteracts with the roots. AMF are obligate biotrophs that limit colonization under waterlogged anoxic conditions. For this reason, researchers are not interested in selecting an aquatic plant as a host to examine AMF symbiosis. Moreover, more than 75% of the rice is cultivated under wetland waterlogging conditions, and this limits AMF root colonization. The construction of genetically engineered AMF with resistance to anaerobic conditions is very important for the global food security. Most research work has been directed toward AMF and their interactions with below-ground inhabitants. As such, more investigations are required on the interaction among AMF and above-ground inhabitants and whether they benefit or reduce mycorrhizal colonization and functionality.
Mycorrhizal behavior highly depends on ecosystem fluctuations. The application of AMF to agricultural lands causes a variation in their abundance, colonization, and functionality. To optimize the productivity of AMF application in sustainable agriculture, the production of customized fungal inoculants by exploration of all field parameters and selection of plants with the highest AMF colonization potential are much more important. Furthermore, AMF biofertilization technology would be affordable for farmers, including those in developing countries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C.K. and N.Y.; validation, R.K., S.C.K. and N.Y.; investigation, R.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.K., S.C.K., S.T., M.C.A.G., N.S., S.L.S. and N.Y.; writing—review and editing, R.K., S.C.K., S.T., M.C.A.G., N.S., S.A., Z.S.S., S.L.S. and N.Y.; visualization, S.C.K. and N.Y.; supervision, S.C.K., S.T. and N.Y.; project administration, N.Y.; funding acquisition, N.S., S.C.K. and S.L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by Chiang Mai University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Faculty of Applied Sciences, Rajarata University of Sri Lanka, and Chiang Mai University, Thailand.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Velten, S.; Leventon, J.; Jager, N.; Newig, J. What is sustainable agriculture? A systematic review. Sustainability 2015, 7, 7833–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirkell, T.J.; Charters, M.D.; Elliott, A.J.; Sait, S.M.; Field, K.J. Are mycorrhizal fungi our sustainable saviours? considerations for achieving food security. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Pandey, V.C.; Singh, D.P. Efficient soil microorganisms: A new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessey, J.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 2003, 255, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, M.S. Can science and technology feed the world in 2025? Field Crop Res. 2007, 104, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wezel, A.; Bellon, S.; Doré, T.; Francis, C.; Vallod, D.; David, C. Agroecology as a science, a movement or a practice. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianinazzi-pearson, V. Plant cell responses to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Getting to the roots of the symbiosis. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erik, V.; Van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Rilling, M.C.; Toby, K.E. Mycorrhizal fungal establishment in agricultural soils: Factors determining inoculation success. New Phytol. 2012, 197, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, S.F.; Wagg, C.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. An underground revolution: Biodiversity and soil ecological engineering for agricultural sustainability. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendahl, S. Communities, populations and individuals of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, T.; Hempel, S.; Powell, J.R.; Barto, E.K.; Rillig, M.C. Compositional divergence and convergence in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. Ecology 2012, 93, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, K.; Rich, M.K.; Kyozuka, J. An ancestral function of strigolactones as symbiotic rhizosphere signals. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Zobel, M. How mycorrhizal associations drive plant population and community biology. Science. 2020, 367, 6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toju, H.; Sato, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Kadowaki, K.; Tanabe, A.S.; Yazawa, S. How are plant and fungal communities linked to each other in belowground ecosystems?A massively parallel pyrosequencing analysis of the association specificity of root-associated fungi and their host plants. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 3112–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram Singh, S.; Singh, U.; Chaubey, A.; Bhat, M.I. Mycorrhizal fungi for sustainable agriculture a review. Agric. Rev. 2010, 31, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lekberg, Y.; Rosendahl, S.; Olsson, P.A. The fungal perspective of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization in ‘nonmycorrhizal’ plants. New Phytol. 2014, 4, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Rabara, R.C.; Negi, S. AMF: The future prospect for sustainable agriculture. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 102, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfante, P. The future has roots in the past: The ideas and scientists that shaped mycorrhizal research. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeron-Santiago, I.A.S.; Martinez-Trujillo, M.; Valdez-Alarcon, J.J.; Pedraza-Santos, M.E.; Santoyo, G.; Pozo, M.J.; Chavez-Barcenas, A.T. An updated review on the modulation of carbon partitioning and allocation in arbuscular mycorrhizal plants. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharachary, C.; Kunwar, I.K.; Mukerji, K.G. Some Aspects of Monotropoid Mycorrhizae. In Techniques in Mycorrhizal Studies; Mukerji, K.G., Manoharachary, C., Chamola, B.P., Eds.; Springer: Dorgrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Soka, G. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and ecosystem processes: Prospects for future research in tropical soils. Open J. Ecol. 2014, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Khan, M.Y.; Waqas, M.R.; Binyamin, R.; Akhtar, S.; Zahir, Z.A. Arbuscular Mycorrhizas: An Overview. In Arbuscular Mycorrhizas and Stress Tolerance of Plants; Wu, Q.S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–327. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, T.M.; Barrios-Masias, F.H.; Carlisle, E.A.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Jackson, L.E. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizae on tomato yield, nutrient uptake, water relations, and soil carbon dynamics under deficit irrigation in field conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, E. Mycorrhizal symbiosis modulates the rhizosphere microbiota to promote rhizobia-legume symbiosis. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besserer, A.; Puech-Pagès, V.; Kiefer, P.; Gomez-Roldan, V.; Jauneau, A.; Roy, S.; Portais, J.C.; Roux, C.; Bécard, G.; Séjalon-Delmas, N. Strigolactones Stimulate arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by activating mitochondria. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Suseela, V. Unraveling arbuscular mycorrhiza-induced changes in plant primary and secondary metabolome. Metabolites 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, C.; Jung, E.; Kothe, E. Hartig net formation of Tricholoma vaccinum spruce ectomycorrhizal in hydroponic culture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2015, 22, 19394–19399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frater, P.N. Factors Affecting Mycorrhizal Colonization in Schizachyrium scoparium. Master’s Thesis, lowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sulistiona, W. The role of mycorrhizae on seedling and early growth of sugarcane. In Mycorrhizal Fungi—Utilization in Agriculture and Forestry; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ellouze, W.; Navarro-Borrell, A.; Taheri, A.E.; Klabi, R.; Dai, M.; Kabir, Z.; Hamel, C. Management of the Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis in Sustainable Crop Production. In Mycorrhizal Fungi: Use in Sustainable Agriculture and Land Restoration; Solaiman, Z.M., Abbott, L.K., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 89–118. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, S. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and maternal plant sex on seed germination and early plant establishment. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, B.; Chai, H.; Yang, X.; Song, W.; Li, S.; Lu, A.; Zhang, T.; Sun, W. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate drought stress in C3 (Leymus chinensis) and C4 (Hemarthria altissima) grasses via altering antioxidant enzyme activities and photosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrenho, R.; Trufem, S.F.B.; Bononi, V.L.R.; Silva, E.S. The effect of different soil properties on arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of peanuts, sorghum and maize. Acta Bot. Bras. 2007, 21, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.E. Climate Change Effects on Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Prairie Plants along a Mediterranean Climate Gradient; University of Oregon: Eugene, OR, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, P.; Gianinazzi, S.; Perotto, S.; Turnau, K.; Barea, J. The contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sustainable maintenace of plant health and soil fertility. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, R.R.; Harale, P.; Kurhe, A. Studies on soil quality paramenters in relations to cropping patterns, micronutrients and pH from Goagalgaon are in Ahmednagar district of Maharashta, India. Int. J. Multidiscip. Curr. Res. 2020, 6, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Bunemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.M. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi: Potential Soil Health Indicators. In Soil Health; Giri, B., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Fall, A.F.; Nakabonge, G.; Ssekandi, J.; Founoune-Mboup, H.; Apori, S.O.; Ndiaye, A.; Badji, A.; Ngom, K. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil fertility: Contribution in the improvement of physical, chemical and biological properties of the soil. Front. Fungal Biol. 2022, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifheit, E.F.; Veresoglou, S.D.; Lehmann, A.; Morris, E.K.; Rillig, M.C. Multiple factors influence the role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soil aggregation—A meta-analysis. Plant Soil. 2014, 374, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and glomalin play a crucial role in soil aggregate stability in Pb—Contaminated soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bone, F.; Rubio, R.; Morales, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil aggregation. J. Soil Sc. Plant Nutr. 2008, 8, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjundappa, A.; Bagyaraj, D.J.; Saxena, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Chakdar, H. Interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Bacillus spp. in soil enhancing growth of crop plants. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, D.J.; Firestone, M.K.; Nuccio, E.; Hodge, A. Interactions between an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and a soil microbial community mediated litter decomposition. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Hardan, A.N. Importance of mycorrhizae in crop productivity. In Mitigating Environmental Stresses for Agricultural Sustainability in Egypt; Awaad, H., Abu-hashim, M., Negm, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 471–484. [Google Scholar]
- Ingraffia, R.; Amato, G.; Frenda, A.S.; Giambalvo, D. Impacts of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nutrient uptake, N2 fixation, N transfer, and growth in a wheat/faba bean intercropping system. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0213672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.C.; Gehring, C.A. Mycorrhizas: Symbiotic Mediators of Rhizosphere and Ecosystem Processes. In The Rhizosphere; Cardon, Z.G., Whitbeck, J.L., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2007; pp. 73–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Dalpe, Y.; Fang, C.; Dube, C.; Khanizadeh, S. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on biomass and root morphology of selected strawberry cultivars under salt stress. Botany 2011, 89, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bücking, H.; Liepold, E.; Ambilwade, P. The role of the mycorrhizal symbiosis in nutrient uptake of plants and the regulatory mechanisms underlying these transport processes. In Plant Science; Dhal, N.K., Sahu, S.C., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Volume 4, pp. 108–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ortas, I.; Rafique, M. The Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake by Arbuscular Mycorrhizae. In Mycorrhiza—Nutrient Uptake, Biocontrol, Ecorestoration, 4th ed.; Varma, A., Prasad, R., Tuteja, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guo, C.; Chen, Z.; He, J.; Zou, Y. Mycorrhizal inoculation modulates root morphology and root phytohormone responses in trifoliate orange under drought stress. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2016, 28, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issam, A.; Ghadraoui, O.E.; Serbouti, S.; Ahamad, H.; Mansouri, I.; Kamari, F.E.; Taroq, A.; Ousaaid, D.; Squalli, W.; Farah, A. The mechanisms of absorption and nutrients transport in plants: A review. Trop. J. Nat Prod. Res. 2022, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.E.; Gianinazzi-pearson, V.; Koide, R.; Cairney, J.W.G. Nutrient transporters in mycorrhizas: Structure, physiology and consequences for efficiency of the symbiosis. Plant Soil 1994, 159, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K. A meta-analysis of mycorrhizal responses to nitrogen, phosphorus, and atmospheric CO2 in field studies. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobae, Y. Dynamic phosphate uptake in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots under field conditions. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajulu, M.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Jin, H.; Abubaker, J.; Douds, D.D.; Allen, J.W.; Bucking, H.; Lammers, P.J.; Shachar-Hill, Y. Nitrogen transfer in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature 2005, 435, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, J.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, N.; Wang, E. Nutrient exchange and regulation in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekarana, M. Meta-analytical approach on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation efficiency on plant growth and nutrient uptake. Agriculture 2020, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, B.; Ciura, J.; Szymanska, R.; Kruk, J. Improving photosynthesis, plant productivity and abiotic stress tolerance—Current trends and future perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 231, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C. Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelin, H.; Devi, T.S.; Gupta, S.; Kapoor, R. Mitigation of salinity stress in plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Current understanding and new challenges. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Mahatma, M.K.; Thirumalaisamy, P.P.; Meena, H.N.; Bhaduri, D.; Arora, S.; Panwar, J. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) for Sustainable Soil and Plant Health in Salt-Affected Soils. In Bioremediation of Salt Affected Soils: An Indian Perspective; Arora, S., Singh, A.K., Singh, Y.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Diagne, N.; Ngom, M.; Djighaly, P.I.; Fall, D.; Hocher, V.; Svistoonoff, S. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant growth and performance: Importance in biotic and abiotic stressed regulation. Diversity 2020, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, K.K.; Bhatt, R.M.; Panneerselvam, P.; Varalakshmi, L.R. Morpho-physiological responses of grape rootstock “Dogridge” to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation under salinity stress. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2016, 16, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastogeer, K.M.G.; Zahan, M.I.; Tahjib-Ul-Arif, M.; Akter, M.A.; Okazaki, S. Plant salinity tolerance conferred by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and associated mechanisms: A meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 588550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Garg, N. High Effectiveness of Rhizophagus irregularis is linked to superior modulation of antioxidant defence mechanisms in Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. genotypes grown under salinity stress. Mycorrhiza 2017, 27, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, A.; Rathore, P.; Ramteke, P.W.; Ramakrishna, W.; Reddy, M.S.; Pecoraro, L. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their synergistic interactions to counteract the negative effects of saline soil on agriculture: Key macromolecules and mechanisms. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-tamayo, A.I.; Zuleta-Patino, D.M.; Rios-osorio, L.A. Role of mycorrhiza-forming fungi in the bioremediation of agricultural soils contaminated with heavy metals: A systematic review. Rev. Hechos. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, M.; Kamran, M.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, H.; Yang, G.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Anastopoulos, L.; et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-induced mitigation of heavy metal phytotoxicity in metal contaminated soils: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Arato, M.; Borghi, L.; Nouri, E.; Reinhardt, D. Beneficial services of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi—From ecology to application. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, e1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.Q.; Qu, M.M.; Li, J.; Li, C. Bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil by plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in northern Shaanxi. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2016, 25, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- De Andrade, S.A.L.; De Silveira, A.P.D.; Jorge, R.A.; De Abreu, M.F. Cadmium accumulation in sunflower plants influenced by mycorrhiza. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2008, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raklami, A.; Bechtaoui, N.; Tahiri, A.I.; Anli, M.; Meddich, A.; Oufdou, K. Use of rhizobacteria and mycorrhizae consortium in the open field as a strategy for improving crop nutrition, productivity and soil fertility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, e1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Behl, R.K.; Singh, K.P.; Jain, P.; Narula, N. Performance and gene effects for wheat yield under inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi and Azotobacter chroococcum. Plant Soil Environ. 2004, 50, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurrahman, M.; Somenahally, A.; Gentry, T. Interactions of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi with hyphosphere microbial communities in a saline soil: Impacts on phosphorus availability and alkaline phosphatase gene abundance. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, A.; Abd-Allah, E.F.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Wirth, S.; Egamberdieva, D. The interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and endophytic bacteria enhances plant growth of Acacia gerrardii under salt stress. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, e1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacoon, S.; Jogloy, S.; Riddech, N.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Kuyper, T.W.; Boonlue, S. Interaction between phosphate solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth promotion and Tuber inulin content of Helianthus tuberosus L. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, T.D.J.; Miranda, J.P.; Ferrari, J.; Hartley, S.E.; Hodge, A. Aphids influence soil fungal communities in conventional agricultural systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, e895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouteden, N.; Waele, D.D.; Panis, B.; Vos, C.M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for the biocontrol of plant-parasitic nematodes: A review of mechanisms involved. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, e1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahat, M.M.; Sijim, K.; Othman, R. Mycorrhizal fungi as a biocontrol agent. Plant Pathol. J. 2010, 9, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Campos-Soriano, L.; García-Martínez, J.; Segundo, B.S. The arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis promotes the systemic induction of regulatory defence-related genes in rice leaves and confers resistance to pathogen infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Cameron, D.D.; Phoenix, G.K. Using AMF inoculation to improve the nutritional status of Prunella vulgaris plants in green roof substrate during establishment. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mar Alguacil, M.; Torrecillas, E.; Lozano, Z.; Roldán, A. Evidence of differences between the communities of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonizing galls and roots of Prunus persica infected by the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8656–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Nasir, F.; Jiang, S.; Mingsen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H. Mechanistic insights into arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-mediated drought stress tolerance in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goicoechea, N. Mycorrhizal Fungi as Bioprotectors of Crops Against Verticillium wilt—A hypothetical scenario under changing environmental conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folli-Pereira, M.d.S.; Garlet, J.; Bertolazi, A.A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their potential applications for sustainable agriculture, Agriculturally Important Fungi for Sustainable Agriculture. In Perspective for Diversity and Crop Productivity; Yadav, A.N., Mishra, S., Kour, D., Yadav, N., Kumar, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, H.; Ahanger, M.A.; Su, Y.; Lei, Y.; Mustafa, N.S.A.; Ahmad, P.; Zhang, L. Improved drought tolerance by AMF inoculation in maize (Zea mays) involves physiological and biochemical implications. Plants 2019, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.; Feng, G. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can accelerate the restoration of degraded spring grassland in central Asia. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 65, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuab, R.; Lone, R.; Ahmad, J.; Reshi, Z.A. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi: A Potential Tool for Restoration of Degraded Land. In Mycorrhiza-Nutrient Uptake, Biocontrol, Ecorestoration; Varma, A., Prasad, R., Tuteja, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 415–434. [Google Scholar]
- De Moura, M.A.; Oki, Y.; Arantes-Garcia, L.; Cornelissen, T.; Nunes, Y.R.F.; Fernandes, G.W. Mycorrhiza fungi application as a successful tool for worldwide mine land restoration: Current state of knowledge and the way forward. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 178, e106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayudyningsih, R.; Sari, R.; Mangopang, A.D. Isolation of indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) to support revegetation on the nickel post-mining land. Earth. Environ. Sci. 2019, 308, 012038. [Google Scholar]
- Asmelash, F.; Bekele, T.; Birhane, E. The potential role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the restoration of degraded lands. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, e1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. Occurrence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mining-impacted sites and their contribution to ecological restoration: Mechanisms and applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1901–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunatre, R.; Fonvielle, N.; Spiegelberger, T.; Buisson, E.; Dutoit, T. Recovery of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi root colonization after severe anthropogenic disturbance: Four species assessed in old-growth Mediterranean grassland. Folia Geobot. 2016, 51, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmim, A.T.; Íris, V.; Sónia, V.G.; Rui, O.; Célia, M.M.; Orlando, A.Q. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) promote the growth of the pioneer dune plant of coastal areas. African J. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 14, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, N.; Perez-Solis, E.; Azcón-Aguilar, C.; Jeffries, P.; Barea, J.M. Management of indigenous plant-microbe symbioses aids restoration of desertified ecosystems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinkellner, S.; Lendzemo, V.; Langer, I.; Schweiger, P.; Khaosaad, T.; Toussaint, J.; Vierheilig, H. Flavonoids and strigolactones in root exudates as signals in symbiotic and pathogenic plant fungus interaction. Molecules 2007, 12, 1290–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellouze, W.; Hamel, C.; Cruz, A.F.; Ishii, T.; Gan, Y.; Bouzid, S.; St-Arnaud, M. Phytochemicals and spore germination: At the root of AMF host preference? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 60, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiuxiu, S.; Yansu, L.; Xianchang, Y.; Chaoxing, H. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculums on cucumber seedlings. Adv. Plants Agric. 2019, 9, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Heijden, M.G.A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as support system for seedling establishment in grassland. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.C.; Luo, Y.; Jacquemyn, H. Co-cultures of mycorrhizal fungi do not increase germination and seedling development in the epiphytic orchid Dendrobium nobile. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, e571426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, S.A. Influence of mycorrhizal fungi on seed germination and growth in terrestrial and epiphytic orchids. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).