Evaluating the Evolution of Soil Erosion under Catchment Farmland Abandonment Using Lakeshore Sediment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
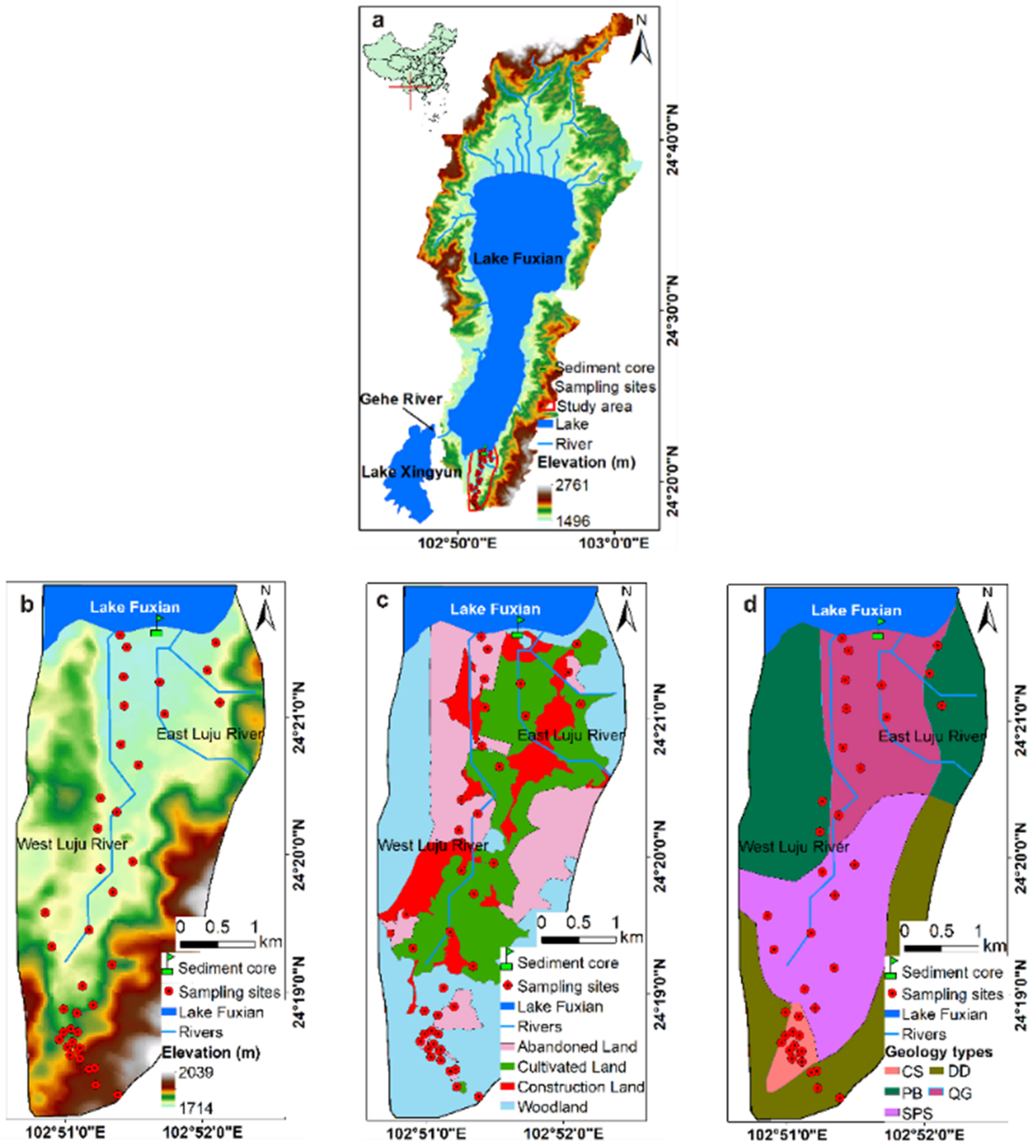
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Pre-Treatment
2.3.2. Gamma Counting
2.3.3. Particle Size Analyses
2.3.4. Measurement of Oxides and Minor Elements
2.4. Sediment Dating
2.5. Sediment Source Apportionment
3. Results
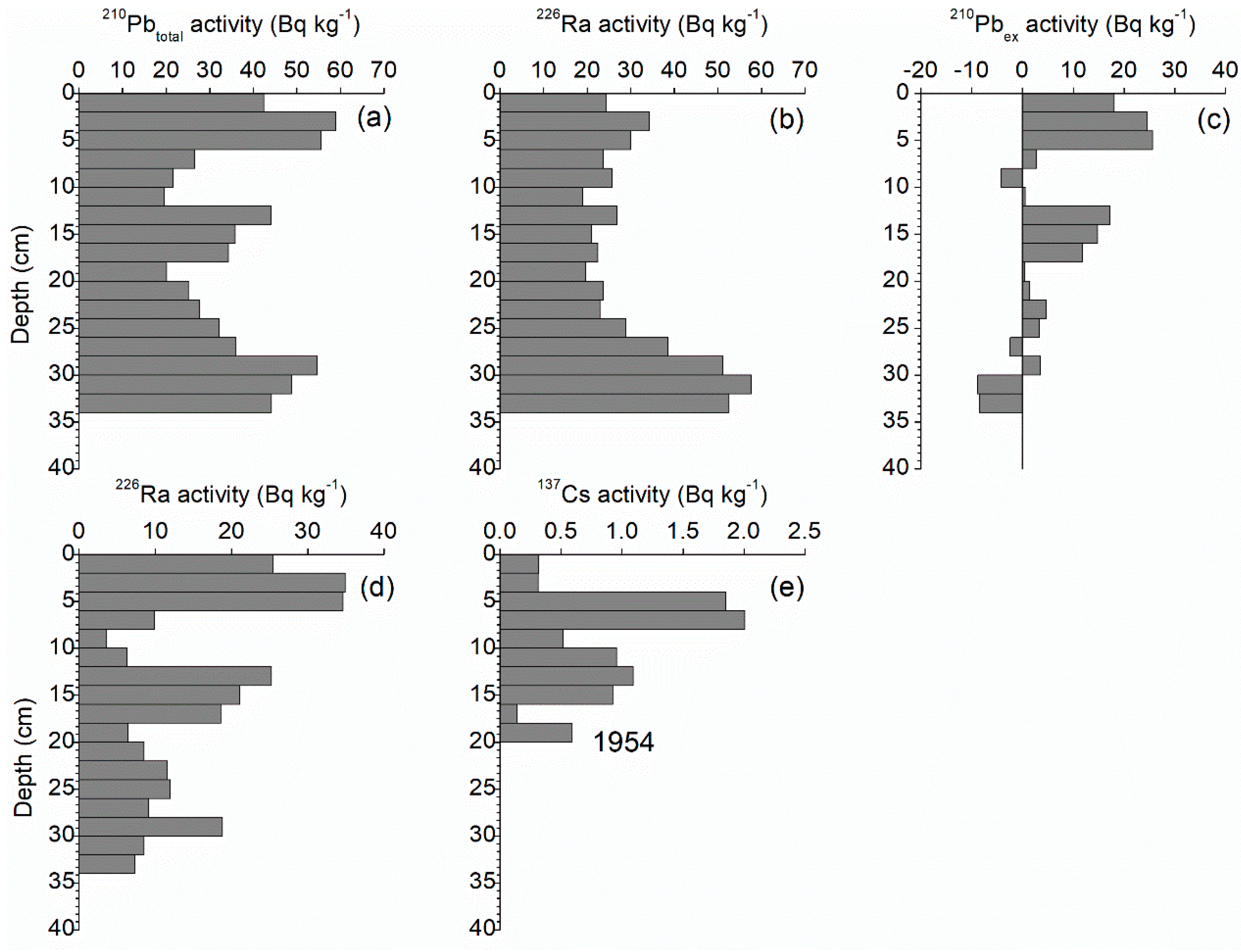
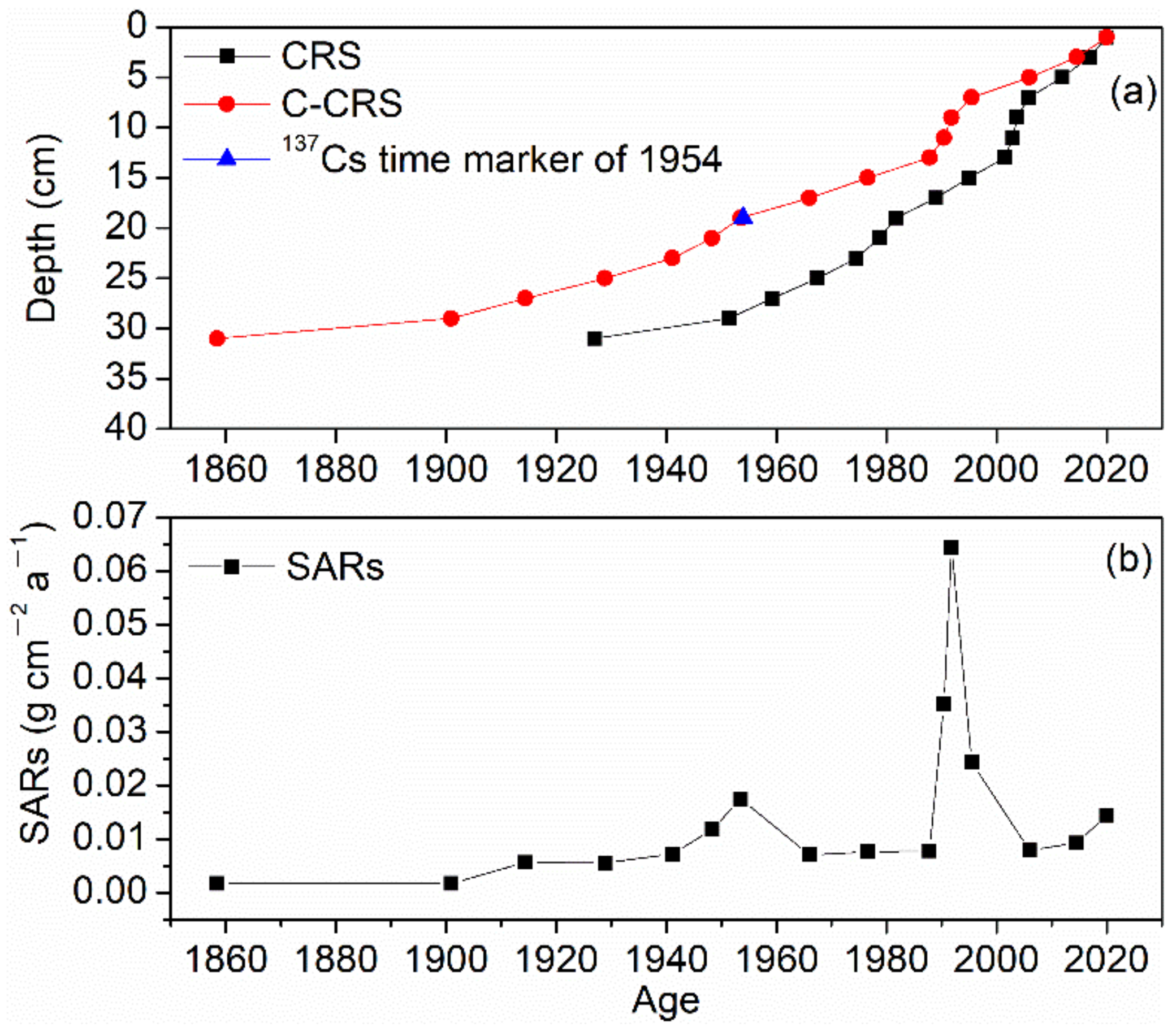
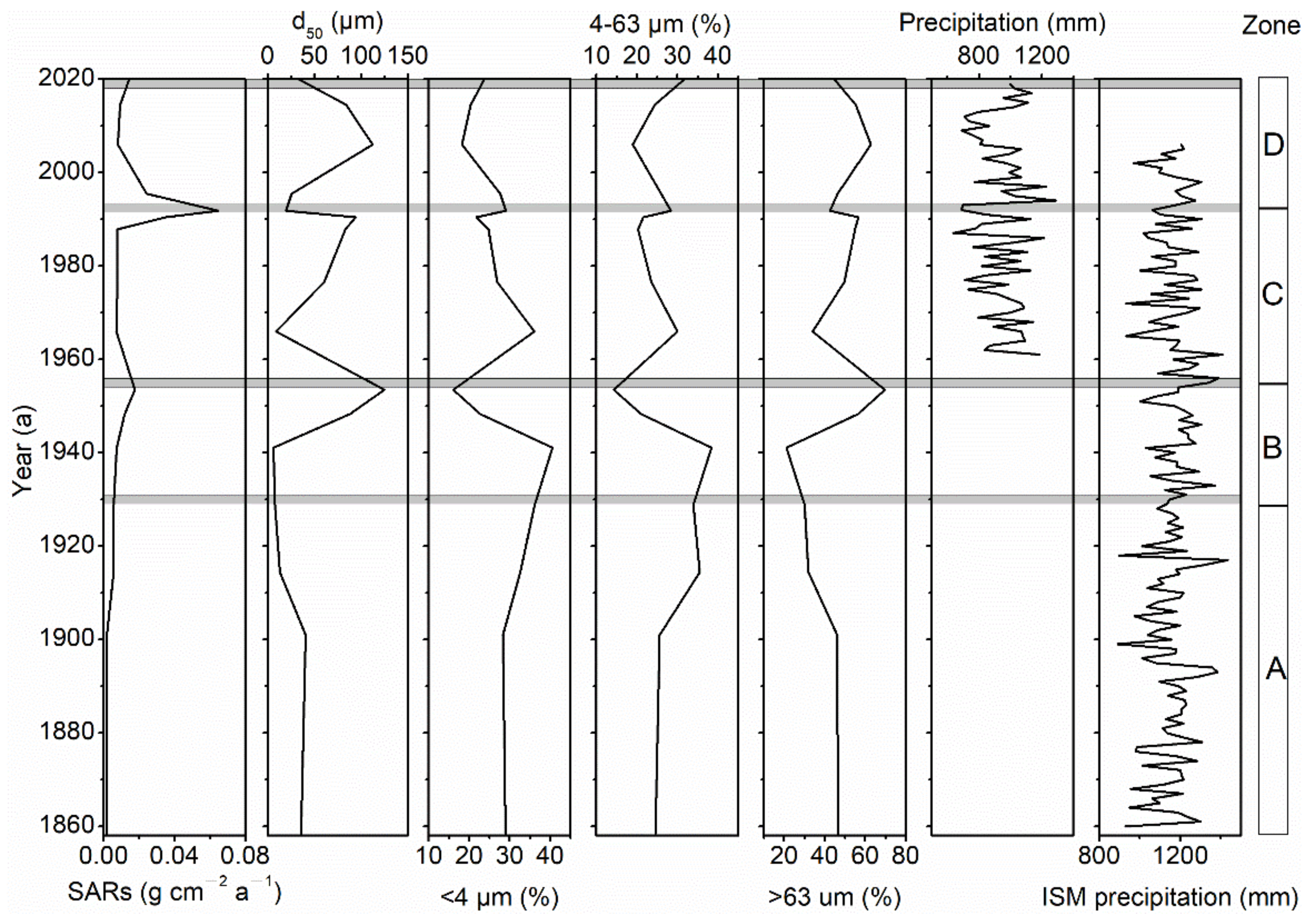
3.1. Sediment Chronology and Accumulation Rates
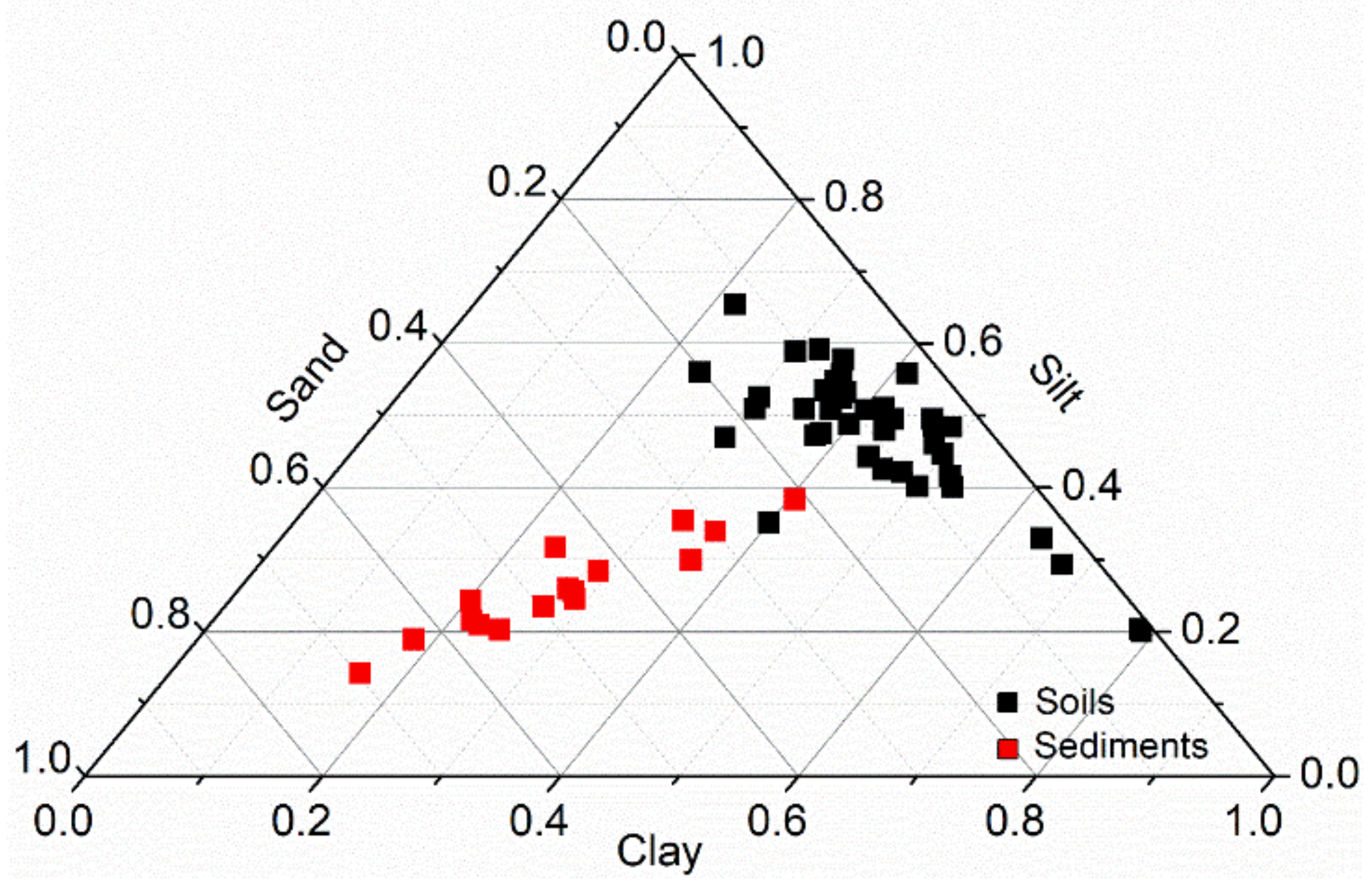
3.2. Particle Size in Catchment Soils and Lakeshore Sediment
3.3. Selection of Optimum Fingerprinting Properties
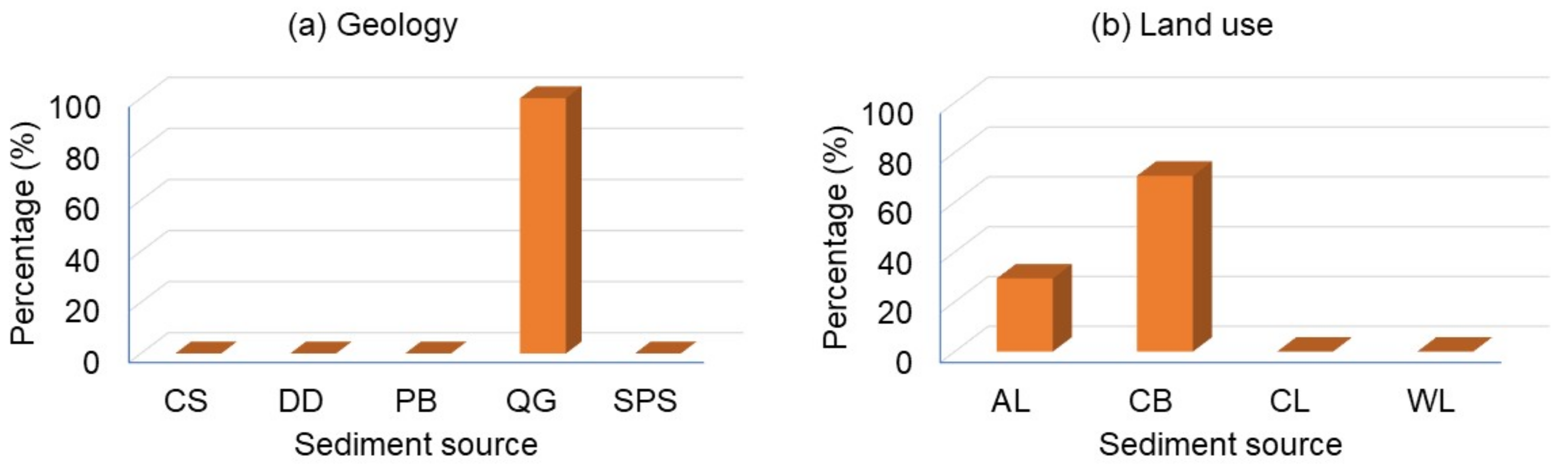
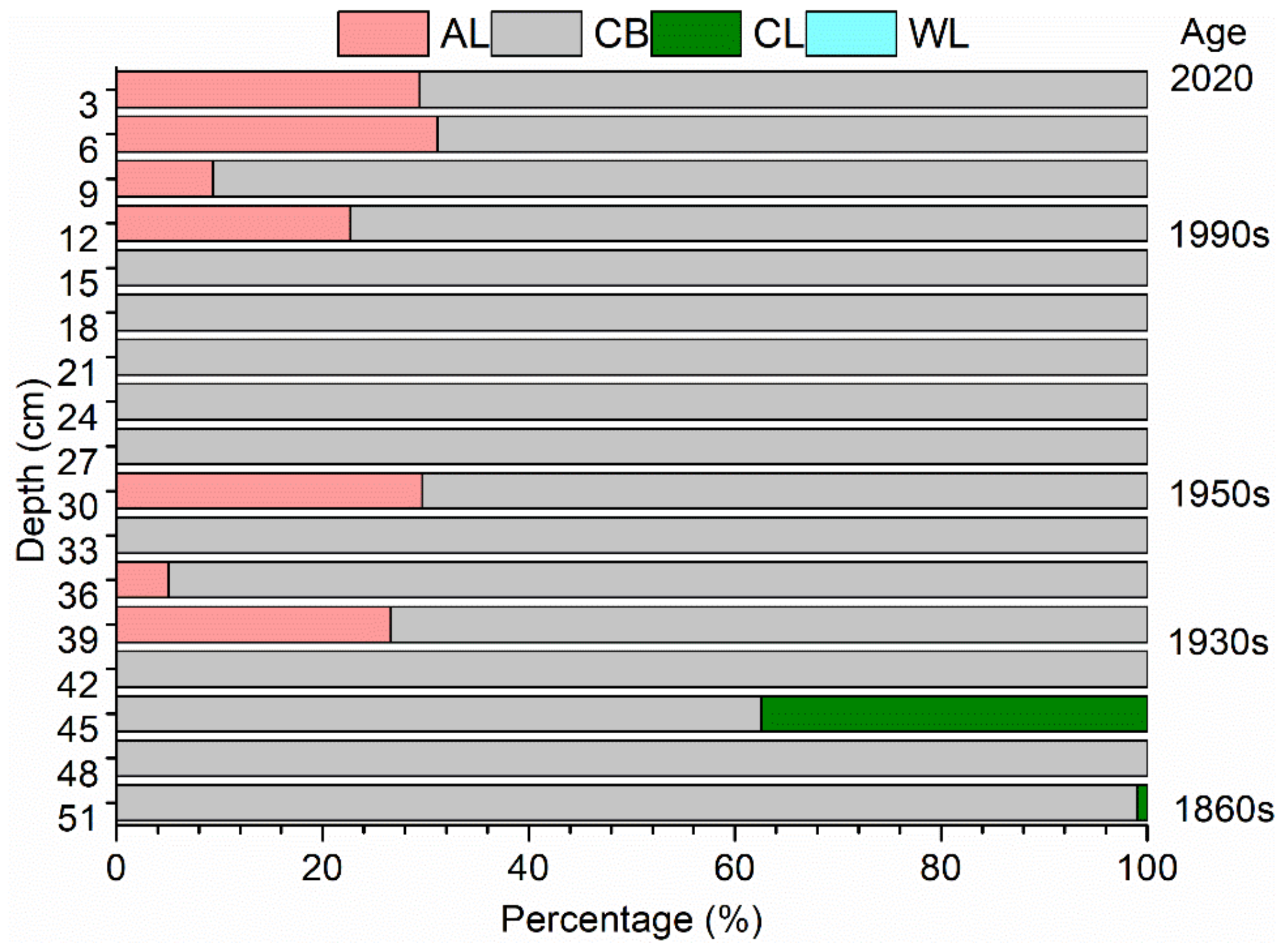
3.4. Spatiotemporal Sediment Source Apportionment
3.5. Results of Uncertainty in Sediment Fingerprinting
4. Discussion
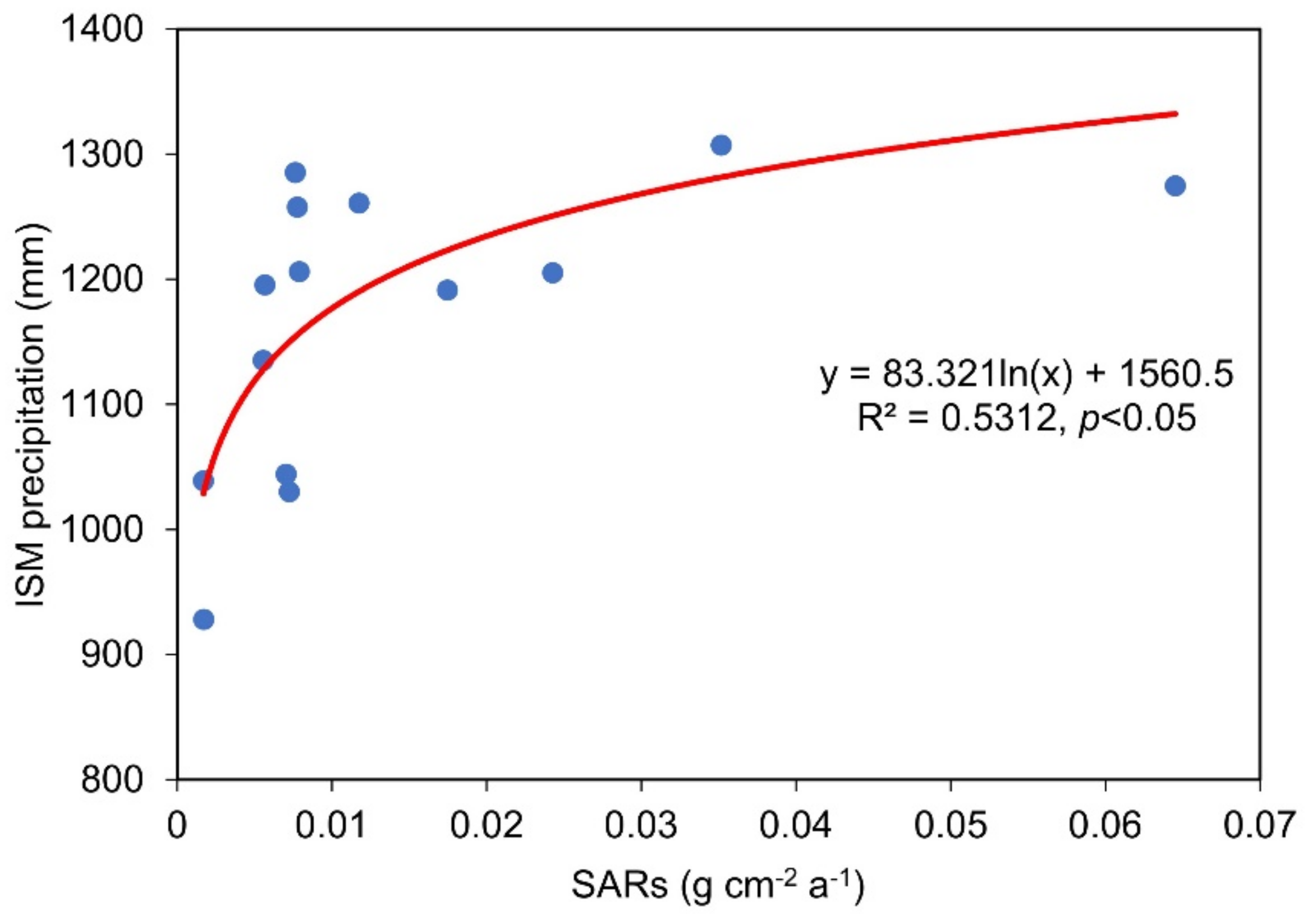
4.1. Responding of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors to Changing of SARs
4.2. Interpreting of Spatiotemporal Source Apportionment in Geology and Land Use
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphrey, O.S.; Osano, O.; Aura, C.M.; Marriott, A.L.; Dowell, S.M.; Blake, W.H.; Watts, M.J. Evaluating spatio-temporal soil erosion dynamics in the Winam Gulf catchment, Kenya for enhanced decision making in the land-lake interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 151975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenle, A.A.; Boillat, S.; Speranza, C.I. Key dimensions of land users’ perceptions of land degradation and sustainable land management in Niger State, Nigeria. Environ. Chall. 2022, 8, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena-González, J.; Lozano-Parra, J.; Alfonso-Torreño, A.; Lozano-Fondón, C.; Abdennour, M.A.; Cerdà, A.; Pulido-Fernández, M. Soil erosion in Mediterranean chestnut tree plantations at risk due to climate change and land abandonmentl. Cent. Eur. For. J. 2020, 66, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Niedda, M.; Pirastru, M.; Castellini, M.; Giadrossich, F. Simulating the hydrological response of a closed catchment-lake system to recent climate and land-use changes in semi-arid Mediterranean environment. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, E.A.; Swaffield, S.; Moore, K. Agricultural land use management responses to a cap and trade regime for water quality in Lake Taupo catchment, New Zealand. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.J.; Leng, M.J.; Osburn, C.L.; Fritz, S.C.; Law, A.C.; McGowan, S. A landscape perspective of Holocene organic carbon cycling in coastal SW Greenland lake-catchments. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 202, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.; Allcock, S.L.; Barnett, H.; Mather, A.; Eastwood, W.J.; Jones, M.; Primmer, N.; Yiğitbașıoğlu, H.; Vannière, B. Cause-and-effect in Mediterranean erosion: The role of humans and climate upon Holocene sediment flux into a central Anatolian lake catchment. Geomorphology 2019, 331, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabit, L.; Benmansour, M.; Abril, J.M.; Walling, D.E.; Meusburger, K.; Iurian, A.R.; Bernard, C.; Tarján, S.; Owens, P.N.; Blake, W.H.; et al. Fallout 210Pb as a soil and sediment tracer in catchment sediment budget investigations: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, M.; Solomon, H.; Ndakidemi, P.; Blake, W.H. Pinpointing areas of increased soil erosion risk following land cover change in the Lake Manyara catchment, Tanzania. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.M.; Sahoo, P.K.; Guimarães, J.T.F.; Leite, A.S.; Salomão, G.N.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Júniora, W.N.; Dall’Agnol, R. Multivariate statistics and geochemical approaches for understanding source-sink relationship—a case study from close-basin lakes in Southeast Amazon. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2020, 99, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitch, J.L.; Phillips, J.; Peukert, S.; Taylor, A.; Blake, W.H. Understanding the geomorphic consequences of enhanced overland flow in mixed agricultural systems: Sediment fingerprinting demonstrates the need for integrated upstream and downstream thinking. J. Soils Sediment. 2019, 19, 3319–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. Tracing suspended sediment sources in catchments and river systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 344, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Walling, D.E.; Grenfell, S.E.; Smith, P. Tracing sediment loss from eroding farm tracks using a geochemical fingerprinting procedure combining local and genetic algorithm optimisation. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5461–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. The evolution of sediment source fingerprinting investigations in fluvial systems. J. Soil. Sediment. 2013, 13, 1658–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.G.; Blake, W.H. Sediment fingerprinting in agricultural catchments: A critical re-examination of source discrimination and data corrections. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, J.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Thompson, A.M. Apportionment of suspended sediment sources in an agricultural watershed using sediment fingerprinting. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.L.; Walling, D.E.; Leeks, G.J.L. Source type ascription for fluvial suspended sediment based on a quantitative composite fingerprinting technique. Catena 1997, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.N.; Hancock, G.J.; Bartley, R.; Hawdon, A.A.; Keen, R.J. Using sediment tracing to assess processes and spatial patterns of erosion in grazed rangelands, Burdekin River basin, Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 180, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, O.; Laceby, J.P.; Huon, S.; Lefèvre, I.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O.; Ribolzi, O. Combining multiple fallout radionuclides (137Cs, 7Be, 210Pbxs) to investigate temporal sediment source dynamics in tropical, ephemeral riverine systems. J. Soil. Sediment. 2015, 16, 1130–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, W.H.; Ficken, K.J.; Taylor, P.; Russell, M.A.; Walling, D.E. Tracing crop-specific sediment sources in agricultural catchments. Geomorphology 2012, 139–140, 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; McChesney, D.; Walling, D.E.; Haley, S.M.; Smith, P. Sediment source tracing in a lowland agricultural catchment in southern England using a modified procedure combining statistical analysis and numerical modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddadchi, A.; Ryder, D.S.; Evrard, O.; Olley, J. Sediment fingerprinting in fluvial systems: Review of tracers, sediment sources and mixing models. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2013, 28, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, F.; Fang, N.; Shi, Z. Sediment source analysis using the fingerprinting method in a small catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Soil. Sediment. 2016, 16, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowntree, K.M.; van der Waal, B.W.; Pulley, S. Magnetic susceptibility as a simple tracer for fluvial sediment source ascription during storm events. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 194, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhayay, H.R.; Bodé, S.; Griepentrog, M.; Huygens, D.; Bajracharya, R.M.; Blake, W.H.; Dercon, G.; Mabit, L.; Gibbs, M.; Semmens, B.X.; et al. Methodological perspectives on the application of compound-specific stable isotope fingerprinting for sediment source apportionment. J. Soil. Sediment. 2017, 16, 1537–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Fingerprinting sediment sources in the water-wind erosion crisscross region on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma 2019, 337, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenleyside, C.; Tucker, G.M. Farmland Abandonment in the EU: An Assessment of Trends and Prospects; WWF and IEEP: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Estel, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Alcántara, C.; Levers, C.; Prishchepov, A.; Hostert, P. Mapping farmland abandonment and recultivation across Europe using MODIS NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Taleshi, M.S.; Moeinaddini, M.; Riyahi Bakhtiari, A.; Feiznia, S.; Squizzato, S.; Bourliva, A. A one-year monitoring of spatiotemporal variations of PM2.5-bound PAHs in Tehran, Iran: Source apportionment, local and regional sources origins and source-specific cancer risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 115883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirami, C.; Brotons, L.; Burfield, I.; Fonderflick, J.; Martin, J.-L. Is land abandonment having an impact on biodiversity? A meta-analytical approach to bird distribution changes in the north-western Mediterranean. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, F.J.; Kucharz, M.; Jobda, M.; Donald, P.F. Impacts of agricultural intensification and abandonment on farmland birds in Poland following EU accession. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 168, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysse-Lainé, A.; Perrin, C. How can alternative farmland management styles favour local food supply? A case study in the Larzac (France). Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shen, Q.; Zang, D.; Li, H.; Sow, Y. Study on the impact of environmental pollution on farmland abandonment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 1458–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Oh, Y.G.; Yoo, S.H.; Suh, K. Vulnerability assessment of rural aging community for abandoned farmlands in South Korea. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilin, R.; Lindborg, R.; Stenseke, M.; Pereira, H.M.; Llausàs, A.; Slätmo, E.; Cerqueira, Y.; Navarro, L.; Rodrigues, P.; Reichelt, N.; et al. Analysing how drivers of agricultural land abandonment affect biodiversity and cultural landscapes using case studies from Scandinavia, Iberia and Oceania. Land Use Policy 2014, 36, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Pedroso, R.; Lautenbach, S.; Vicens, R. Farmland abandonment in Rio de Janeiro: Underlying and contributory causes of an announced development. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, P.B.; Ziervogel, G.; Hoffman, M.T.; New, M.G. Transition from subsistence grazing to nature-based recreation: A nuanced view of land abandonment in a mountain social-ecological system, southwestern Cape, South Africa. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Arnáez, J.; Pascual, N.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Errea, M.P.; Lana-Renault, N. Space–time process and drivers of land abandonment in Europe. Catena 2017, 149, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Cao, G.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S. An estimation of the extent of cropland abandonment in mountainous regions of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voicu, M.F.; Shaw, C.; Kurz, W.A.; Huffman, T.; Liu, J.; Fellows, M. Carbon dynamics on agricultural land reverting to woody land in Ontario, Canada. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, N.R.; Watanabe, T. Abandonment of Agricultural Land and Its Consequences: A Case Study in the Sikles Area, Gandaki Basin, Nepal Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 2006, 26, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Rai, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Khanal, N.R.; Koirala, H.L.; Nepal, P. Farmland abandonment and its determinants in the different ecological villages of the Koshi river basin, central Himalayas: Synergy of high-resolution remote sensing and social surveys. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirpke, U.; Zoderer, B.M.; Tappeiner, U.; Tasser, E. Effects of past landscape changes on aesthetic landscape values in the European Alps. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 212, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolecka, N.; Kozak, J.; Kaim, D.; Dobosz, M.; Ostafin, K.; Ostapowicz, K.; Wężyk, P.; Price, B. Understanding farmland abandonment in the Polish Carpathians. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 88, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, M.; Bouniol, J.; Fonte, S.J.; Kessler, A. How rural out-migrations drive changes to farm and land management: A case study from the rural Andes. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Akasaka, T.; Yabuhara, Y.; Nakamura, F. Influence of farmland abandonment on the species composition of wetland ground beetles in Kushiro, Japan. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 249, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J.; Nishikori, M.; Toyoshi, M.; Feuer, H.N. The contribution of land exchange institutions and markets in countering farmland abandonment in Japan. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilonis, I.; Szlavecz, K.; Pouyat, R.; Whigham, D.; Xia, L. Historical land use and stand age effects on forest soil properties in the Mid-Atlantic US. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 370, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Xu, X. The spatial distribution of farmland abandonment and its influential factors at the township level: A case study in the mountainous area of China. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Bai, P.; Liu, C. Estimation of reservoir evaporation losses for China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Sun, L. Drivers of cropland abandonment in mountainous areas: A household decision model on farming scale in Southwest China. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Study on the abandonment of sloping farmland in Fengjie County, Three Gorges Reservoir Area, a mountainous area in China. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Green, S.M.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Wen, X.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Quine, T.A. Nitrogen functional gene activity in soil profiles under progressive vegetative recovery after abandonment of agriculture at the Puding Karst Critical Zone Observatory, SW China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, G.; Li, G.; Zhou, D.; Luo, Y. Spatial pattern and mechanisms of farmland abandonment in Agricultural and Pastoral Areas of Qingzang Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Jin, B.X.; Zhou, J.S.; Wang, J.L.; Peng, S.Y. Analysis of the spatiotemporal land-use/land-cover change and its driving forces in Fuxian Lake watershed, 1974 to 2014. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, B. A century of change in sediment accumulation and trophic status in Lake Fuxian, a deep plateau lake of Southwestern China. J. Soils Sediment. 2018, 18, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, L. Influence of spatial variation in land-use patterns and topography on water quality of the rivers inflowing to Fuxian Lake, a large deep lake in the plateau of southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.F.; Zhen, X.M.; Zhou, L.M.; Wang, N.; Wang, H. Comprehensive analysis of the soil erosion in Fuxian Lake basin based on DEM. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 16, 76–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.C.; Wang, J.L.; Li, S.H.; Zhou, J.S.; Jin, B.X. Remote sensing monitoring of soil erosion in Fuxian Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 23, 65–70, 76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- NIGLAS. Lake Fuxian; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- World Reference Base for Soil Resource. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Appleby, P.G. Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments, Basin Analysis, Coring, and Chronological Techniques; Last, W.M., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 171–203. [Google Scholar]
- Imboden, D.M.; Stiller, M. The influence of radon diffusion on the 210Pb distribution in sediments. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Walling, D.E. Using 210Pb measurements to estimate sedimentation rates on river floodplains. J. Environ. Radioact. 2012, 103, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C. 210Pb sediment radiochronology: An integrated formulation and classification of dating models. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 82, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.L.; Walling, D.E. Selecting fingerprint properties for discriminating potential suspended sediment sources in river basins. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 218–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Owens, P.N.; Leeks, G.J.L. Fingerprinting suspend sediment sources in the catchment of the River Ouse, Yorkshire, UK. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 955–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.L.; Walling, D.E.; Webb, L.; King, P. Apportioning catchment scale sediment sources using a modified composite fingerprinting technique incorporating property weightings and prior information. Geoderma 2010, 155, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motha, J.A.; Wallbrink, P.J.; Hairsine, P.B.; Grayson, R.B. Determining the sources of suspended sediment in a forested catchment in southeastern Australia. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, F.; Magand, O.; Chapron, E.; Bertrand, S.; Boës, X.; Charlet, F.; Mélières, M.A. Radionuclide dating (210Pb, 137Cs, 241Am) of recent lake sediments in a highly active geodynamic setting (Lakes Puyehue and Icalma—Chilean Lake District). Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; McHenry, J.R. Application of radioactive fallout caesium-137 for mearuring soil erosion and sediment accumulation rates and patterns: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1990, 19, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Walling, D.E. Rates of overbank sedimentation on the floodplains of British lowland rivers documented using fallout 137Cs. Geogr. Ann. 1996, 78, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wren, D.G.; Taylor, J.M.; Rigby, J.R.; Locke, M.A.; Yasarer, L.M.W. Short term sediment accumulation rates reveal seasonal time lags between sediment delivery and deposition in an oxbow lake. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 281, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobkov, M.; Belkina, N.; Kovalevski, V.; Zobkova, M.; Efremova, T.; Galakhina, N. Microplastic abundance and accumulation behavior in Lake Onego sediments: A journey from the river mouth to pelagic waters of the large boreal lake. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaske, S.N.; Pathak, K.; Dash, S.S.; Nayak, D.B. Assessment and management of soil erosion in the hilltop mining dominated catchment using GIS integrated RUSLE model. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sontakke, N.A.; Singh, N.; Singh, H.N. Instrumental period rainfall series of the Indian region (AD 1813—2005): Revised reconstruction, update and analysis. Holocene 2008, 18, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Blake, W.H.; Taylor, A.; Kitch, J.; Millward, G. Evaluating the effectiveness of soil conservation at the basin scale using floodplain sedimentary archives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F. A Study on Rural Land Institution Historical Change in China. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Zeng, H.; Ma, L. Geochemical evidence of human impacts on deep Lake Fuxian, southwest China. Limnologica 2014, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Kung, J.K. The shaping of an institutional choice: Weather shocks, the Great Leap Famine, and agricultural decollectivization in China. Explor. Econ. Hist. 2014, 54, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithold, E.L.; Blair, N.E.; Wegmann, K.W. Source-to-sink sedimentary systems and global carbon burial: A river runs through it. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 153, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wei, Y.; Bao, Q.; Sun, H.; Yan, H. The sensitivity of the carbon sink by coupled carbonate weathering to climate and land-use changes: Sediment records of the biological carbon pump effect in Fuxian Lake, Yunnan, China, during the past century. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, C.; Bao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Sun, H.; Yan, H. Recent environmental changes in the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau inferred from organic geochemical records from the sediments of Fuxian Lake. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2021, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Gong, Z.; Du, Y. Evolution characteristics and simulation prediction of forest and grass landscape fragmentation based on the “Grain for Green” projects on the Loess Plateau, P.R. China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Assessing effects of the Returning Farmland to Forest Program on vegetation cover changes at multiple spatial scales: The case of northwest Yunnan, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Yang, B.; Huang, C. Comparison of spatiotemporal carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus burial in two plateau lacustrine sediments: Implication for N and P control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 9904–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y. The effect of China’s agricultural tax abolition on rural families’ incomes and production. China Econ. Rev. 2014, 29, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Meng, F.; Prishchepov, A.V. How is urbanization shaping agricultural land-use? Unraveling the nexus between farmland abandonment and urbanization in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 214, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Yang, Y.W. Measurement of factors behind the decline of the agricultural labour share in total labour force of China (1990–2030). Chin. J. Popul. Sci. 2012, 4, 13–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bucała-Hrabia, A. Long-term impact of socio-economic changes on agricultural land use in the Polish Carpathians. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.D.; Futter, M.N.; Moldan, F.; Valinia, S.; Frogbrook, Z.; Kothawala, D.N. Variability in organic carbon reactivity across lake residence time and trophic gradients. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.A.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Farmland marginalization in the mountainous areas: Characteristics, influencing factors and policy implications. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, P.; Kiczko, A.; Kardel, I. Large-scale assessment of spatial variability in stream power distribution: An indicator of channel erosion and deposition potential. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, D.; Beaufoy, G.; Brouwer, F.; Selby, A.; Guiheneuf, P.Y.; Manterola, J.J. Farming at the Margins: Abandonment or Redeployment of Agricultural Land in Europe; Institute for European Environmental Policy Agricultural Economics Research Institute: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, M.; Murgia, L.; Ledda, L.; Deligios, P.A.; Sirigu, A.; Chessa, F.; Pazzona, A. Solar radiation distribution inside a greenhouse with south-oriented photovoltaic roofs and effects on crop productivity. Appl. Energy 2014, 133, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

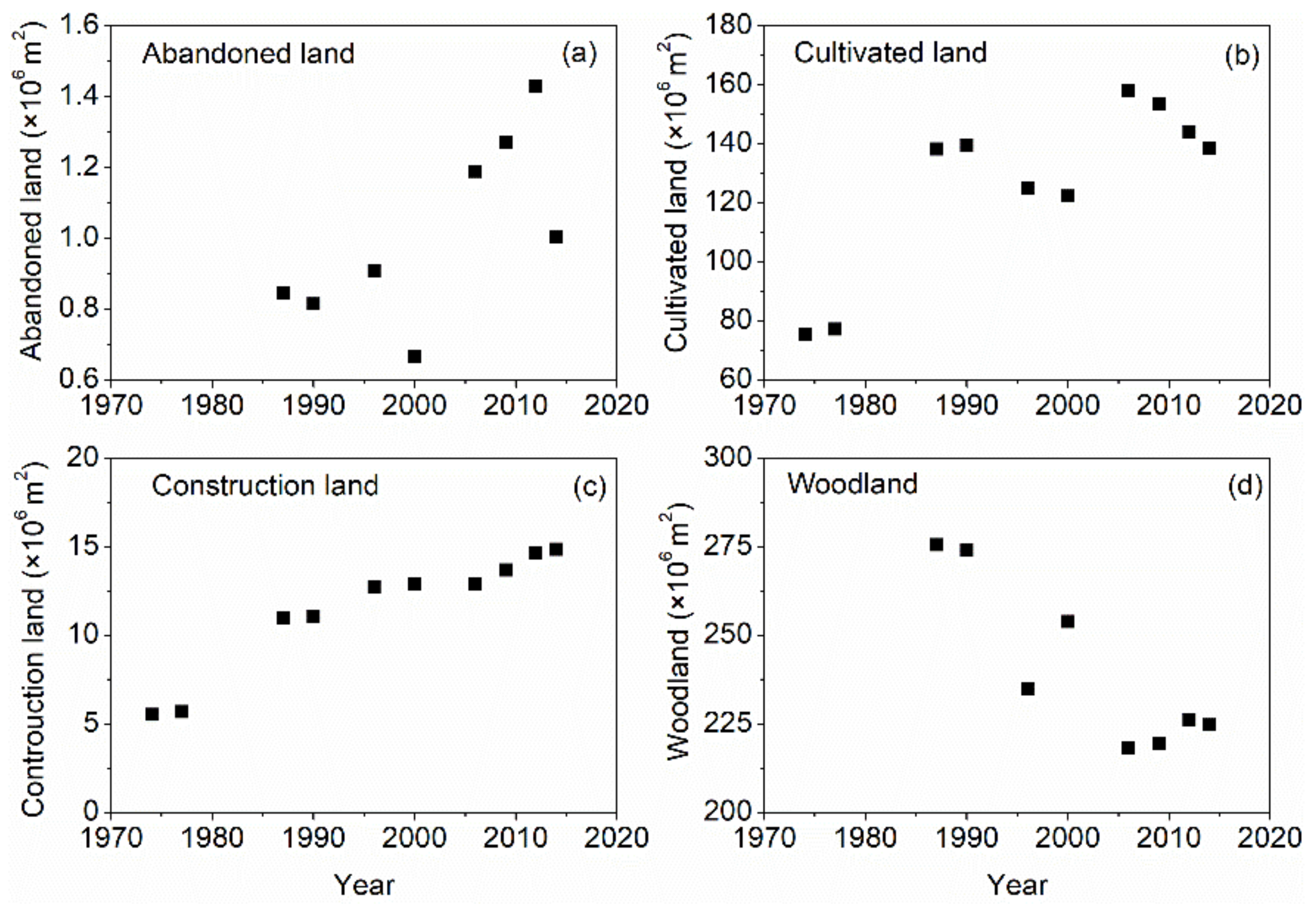
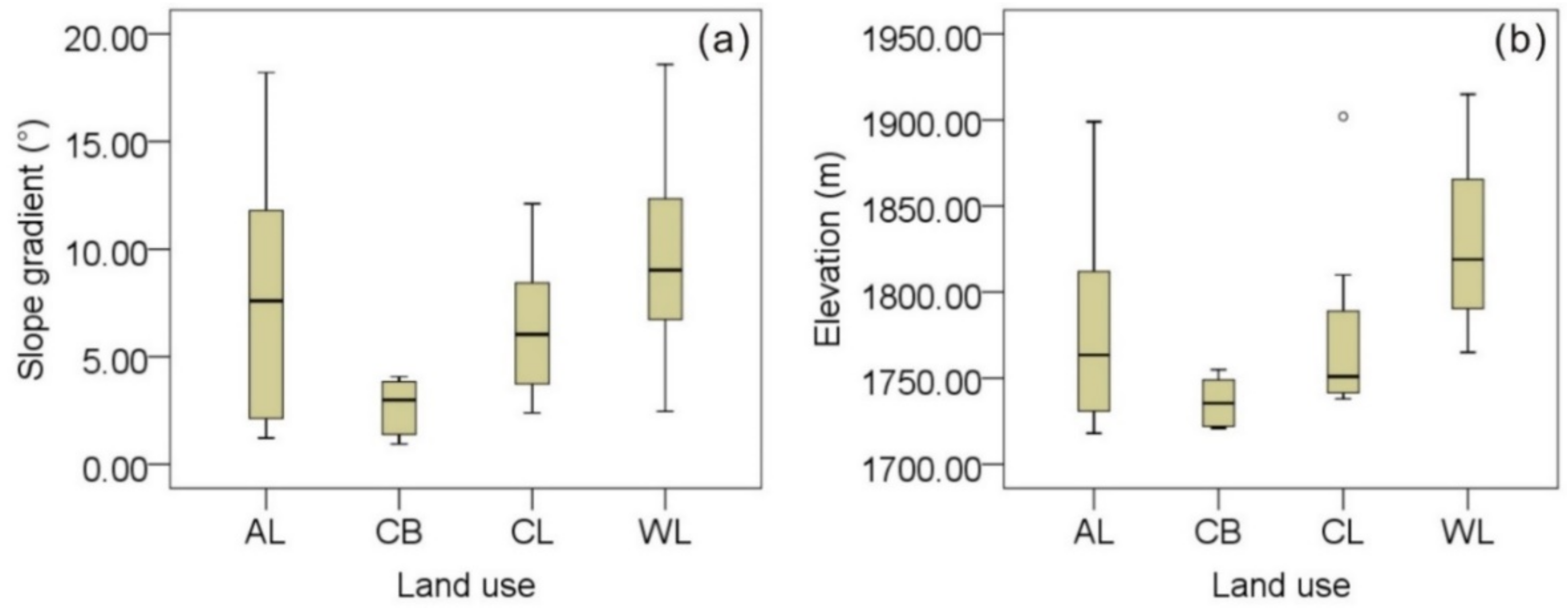
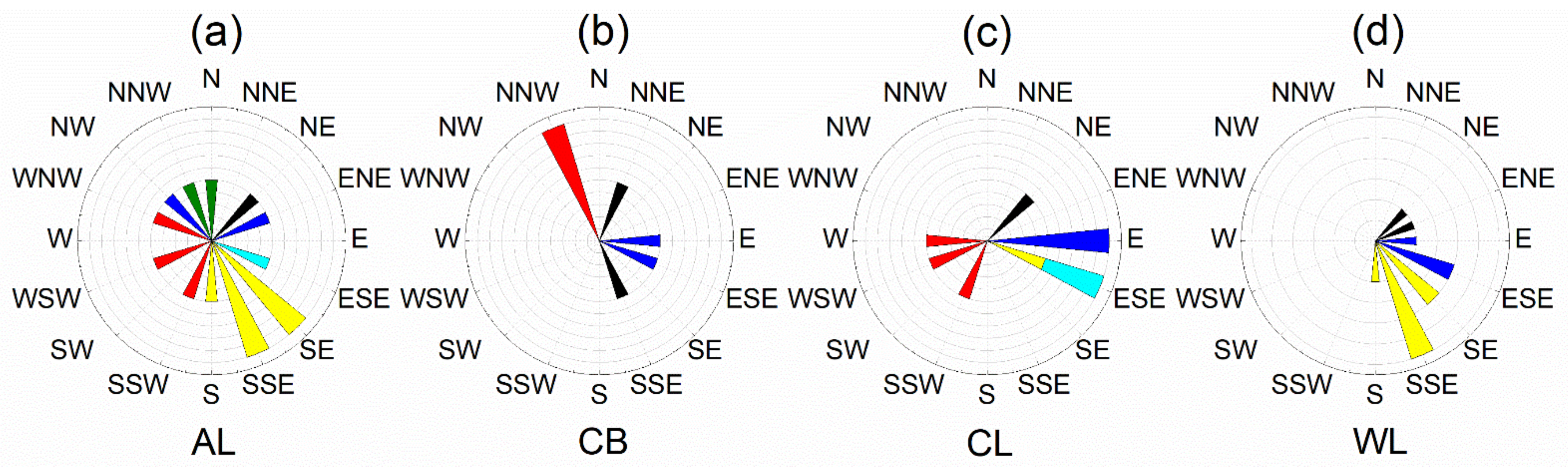
| Property | Source Samples | Sediment Samples | Sediment Mean Inside a | Sediment Samples Inside b | H-Value of Land Use (Geology) | p-Value of Land Use (Geology) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mix | Max | Mean | Mix | Max | |||||
| Na2O | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.52 | 0.29 | 0.65 | P | |||
| MgO | 2.40 | 0.84 | 7.46 | 3.53 | 2.50 | 4.23 | P | P | 8.641 (13.625) | 0.029 * (0.004 *) |
| Al2O3 | 19.48 | 11.18 | 27.66 | 10.99 | 9.37 | 14.47 | ||||
| SiO2 | 44.26 | 33.15 | 64.54 | 53.67 | 40.19 | 57.96 | P | P | 7.121 (10.237) | 0.064 (0.030 *) |
| K2O | 2.36 | 1.10 | 4.19 | 2.24 | 1.62 | 2.43 | P | P | 0.802 (5.983) | 0.857 (0.204) |
| CaO | 4.17 | 0.31 | 15.63 | 8.51 | 6.87 | 14.76 | P | P | 7.618 (10.715) | 0.050 * (0.023 *) |
| Fe2O3 | 11.93 | 4.49 | 19.02 | 6.27 | 4.94 | 9.86 | P | P | 4.753 (8.765) | 0.192 (0.064) |
| P | 2274.19 | 765.00 | 6801.90 | 1653.22 | 677.80 | 5087.90 | P | |||
| S | 404.24 | 135.60 | 648.00 | 296.56 | 164.30 | 673.20 | P | |||
| Ti | 13,800.17 | 4138.90 | 28,260.20 | 9373.46 | 7583.50 | 14,985.50 | P | P | 1.412 (6.794) | 0.721 (0.147) |
| V | 273.46 | 116.20 | 451.30 | 149.45 | 111.00 | 272.30 | P | |||
| Cr | 145.78 | 72.50 | 263.50 | 122.84 | 85.20 | 195.10 | P | P | 4.436 (3.294) | 0.220 (0.527) |
| Mn | 978.95 | 289.20 | 2192.90 | 1084.03 | 746.80 | 1782.50 | P | P | 2.052 (1.353) | 0.578 (0.865) |
| Co | 30.13 | 6.60 | 65.60 | 19.95 | 9.10 | 49.40 | P | P | 2.130 (2.709) | 0.561(0.625) |
| Ni | 74.17 | 30.90 | 117.50 | 31.45 | 20.90 | 56.90 | P | |||
| Cu | 105.46 | 25.70 | 233.60 | 54.88 | 37.50 | 100.00 | P | P | 1.026 (10.796) | 0.805 (0.022 *) |
| Zn | 173.87 | 61.60 | 307.50 | 196.64 | 158.30 | 233.30 | P | P | 5.867 (10.300) | 0.116 (0.029 *) |
| Ga | 24.76 | 10.50 | 37.60 | 12.87 | 9.50 | 18.00 | P | |||
| As | 22.34 | 7.20 | 42.60 | 12.51 | 8.40 | 20.60 | P | P | 10.381 (7.568) | 0.012 * (0.108) |
| Br | 3.23 | 0.80 | 7.40 | 1.55 | 0.70 | 2.70 | P | |||
| Rb | 117.75 | 65.50 | 190.70 | 83.58 | 66.40 | 90.90 | P | P | 1.992 (14.909) | 0.591 (0.002 *) |
| Sr | 65.83 | 35.90 | 151.60 | 70.89 | 60.70 | 104.20 | P | P | 18.558 (24.576) | 0.000 * (0.000 *) |
| Y | 47.01 | 20.00 | 83.60 | 32.86 | 27.00 | 41.60 | P | P | 0.766 (1.225) | 0.864 (0.886) |
| Zr | 329.85 | 112.10 | 500.30 | 524.21 | 336.00 | 669.30 | P | |||
| Nb | 30.21 | 7.10 | 53.40 | 19.89 | 16.90 | 23.70 | P | P | 3.217 (9.599) | 0.370 (0.041 *) |
| Mo | 2.20 | 0.10 | 5.20 | 1.49 | 0.40 | 2.40 | P | P | 1.855 (8.922) | 0.620 (0.059) |
| Ba | 260.12 | 77.10 | 492.10 | 387.78 | 257.30 | 455.60 | P | P | 14.412 (15.165) | 0.001 * (0.001 *) |
| La | 57.67 | 34.10 | 86.30 | 50.91 | 44.80 | 66.30 | P | P | 1.726 (2.156) | 0.651 (0.727) |
| Ce | 119.45 | 56.40 | 160.70 | 90.93 | 77.40 | 121.60 | P | P | 4.206 (4.716) | 0.242 (0.325) |
| Hf | 8.40 | 3.20 | 12.20 | 13.29 | 8.10 | 17.80 | P | |||
| Pb | 61.01 | 24.00 | 234.60 | 65.48 | 55.50 | 74.90 | P | P | 4.421 (18.701) | 0.222 (0.000 *) |
| Th | 13.63 | 5.30 | 24.80 | 8.42 | 5.60 | 10.60 | P | P | 13.532 (21.206) | 0.002 * (0.000 *) |
| CO3 | 13.33 | 8.26 | 18.43 | 12.85 | 11.08 | 15.74 | P | P | 1.036 (6.926) | 0.804 (0.138) |
| Sources Types | Step | Fingerprint Property Selected | Wilks’ Lambda | Cumulative Source Type Samples Classified Correctly (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land use | 1 | As | 0.420 | 83.7 |
| 2 | Sr | 0.749 | 100.0 | |
| Geology | 1 | CaO | 0.126 | 78.4 |
| 2 | Rb | 0.506 | 93.7 | |
| 3 | Sr | 0.804 | 99.9 | |
| 4 | Th | 0.996 | 100.0 |
| <4 μm | 4–63 μm | >63 μm | As | Sr | CaO | Rb | Th | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <4 μm | 1 | 0.036 | −0.723 ** | 0.663 ** | −0.360 ** | −0.320 * | 0.294 * | 0.648 ** |
| 4–63 μm | 1 | −0.716 ** | 0.195 | 0.092 | −0.271 * | 0.495 ** | 0.126 | |
| >63 μm | 1 | −0.597 ** | 0.188 | 0.410 ** | −0.547 ** | −0.540 ** | ||
| As | 1 | 0.093 | −0.431 ** | 0.377 ** | 0.583 ** | |||
| Sr | 1 | 0.143 | −0.299 * | −0.456 ** | ||||
| CaO | 1 | −0.479 ** | −0.548 ** | |||||
| Rb | 1 | 0.736 ** | ||||||
| Th | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Kitch, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H. Evaluating the Evolution of Soil Erosion under Catchment Farmland Abandonment Using Lakeshore Sediment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912241
Wang X, Zhao Z, Han X, Liu J, Kitch J, Liu Y, Yang H. Evaluating the Evolution of Soil Erosion under Catchment Farmland Abandonment Using Lakeshore Sediment. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912241
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaolei, Zihan Zhao, Ximou Han, Jinliang Liu, Jessica Kitch, Yongmei Liu, and Hao Yang. 2022. "Evaluating the Evolution of Soil Erosion under Catchment Farmland Abandonment Using Lakeshore Sediment" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912241
APA StyleWang, X., Zhao, Z., Han, X., Liu, J., Kitch, J., Liu, Y., & Yang, H. (2022). Evaluating the Evolution of Soil Erosion under Catchment Farmland Abandonment Using Lakeshore Sediment. Sustainability, 14(19), 12241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912241






