Arsenic Adsorption and Desorption in Various Aqueous Media in the Nearshore Zone and Influencing Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics Experiments
2.3.2. Isothermal Adsorption Experiments
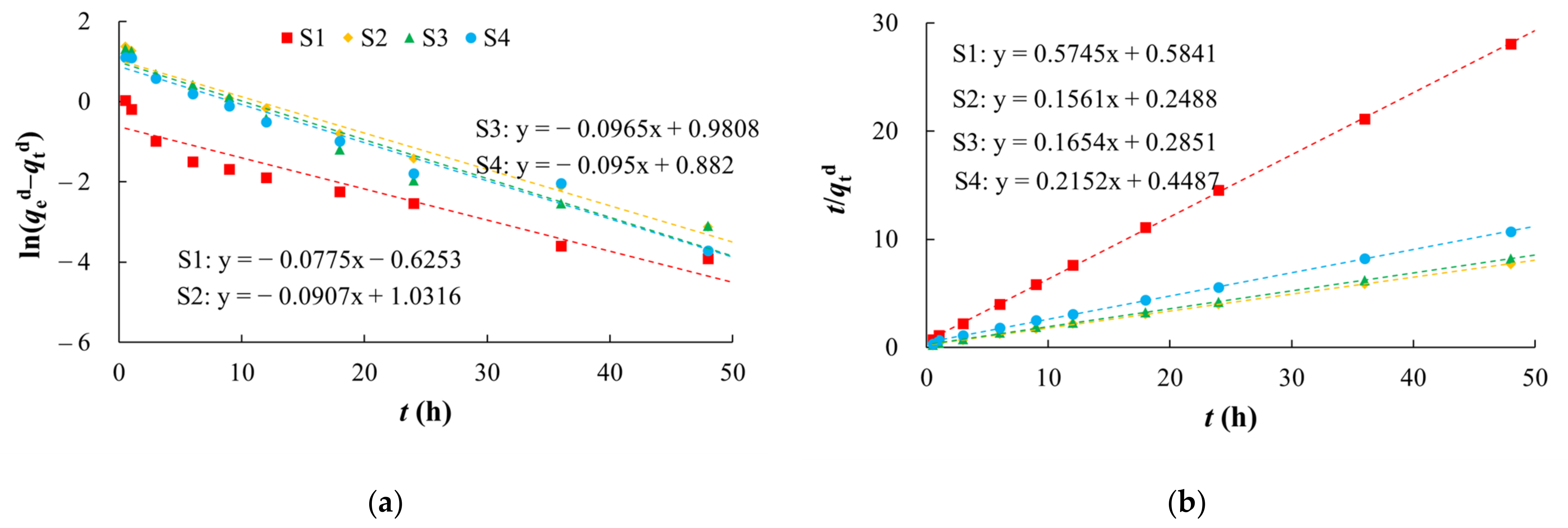
2.3.3. Desorption Kinetics Experiments
2.3.4. Desorption Thermodynamics Experiments
2.3.5. Experiments to Investigate the Factors Influencing Arsenic Adsorption and Desorption
2.3.6. Water Sample Testing
2.4. Models and Calculations
2.4.1. Adsorption Capacity and Adsorption Ratio
2.4.2. Kinetic Model
2.4.3. Isothermal Adsorption Model
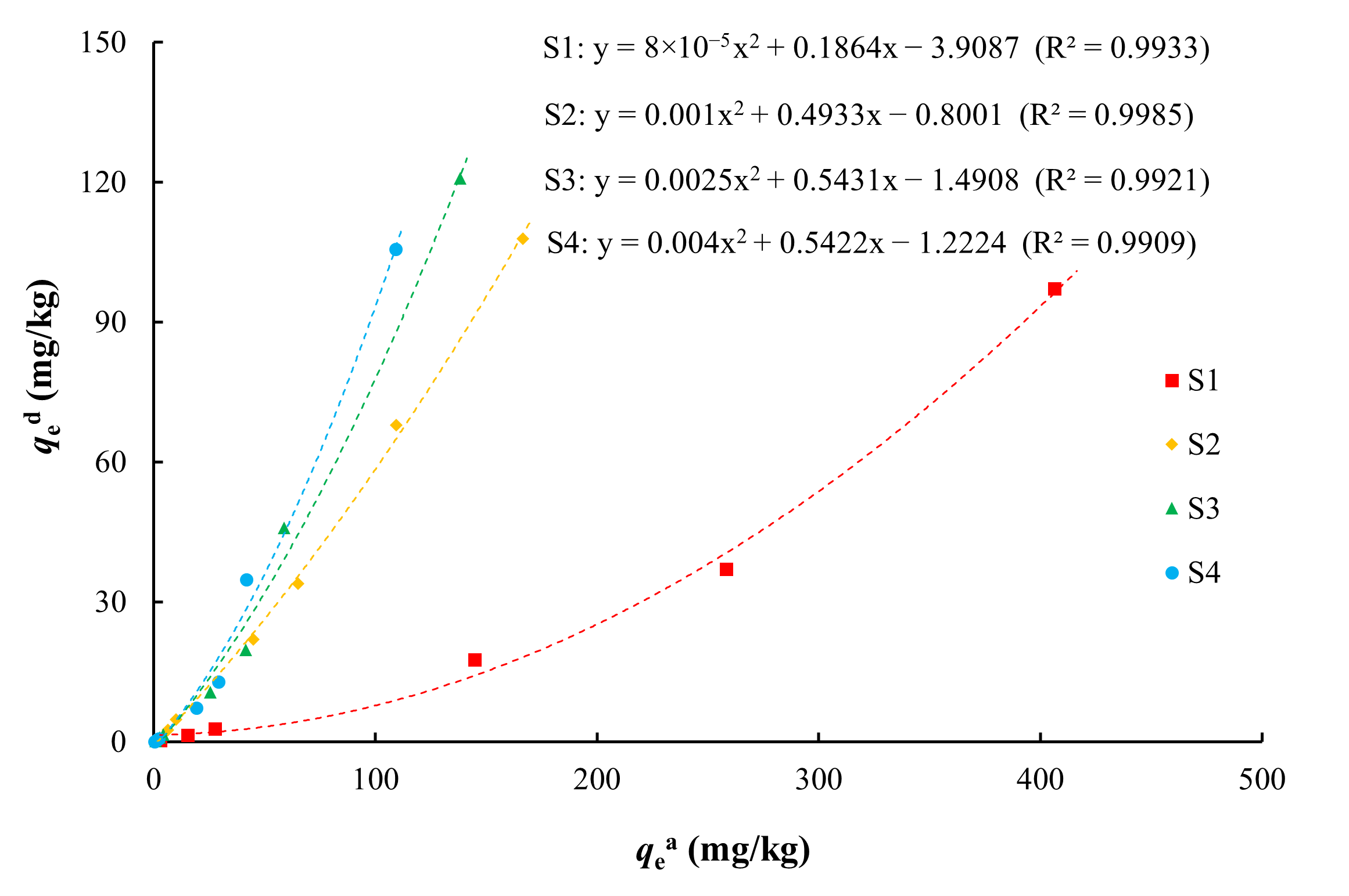
2.4.4. Desorption Capacity and Desorption Ratio
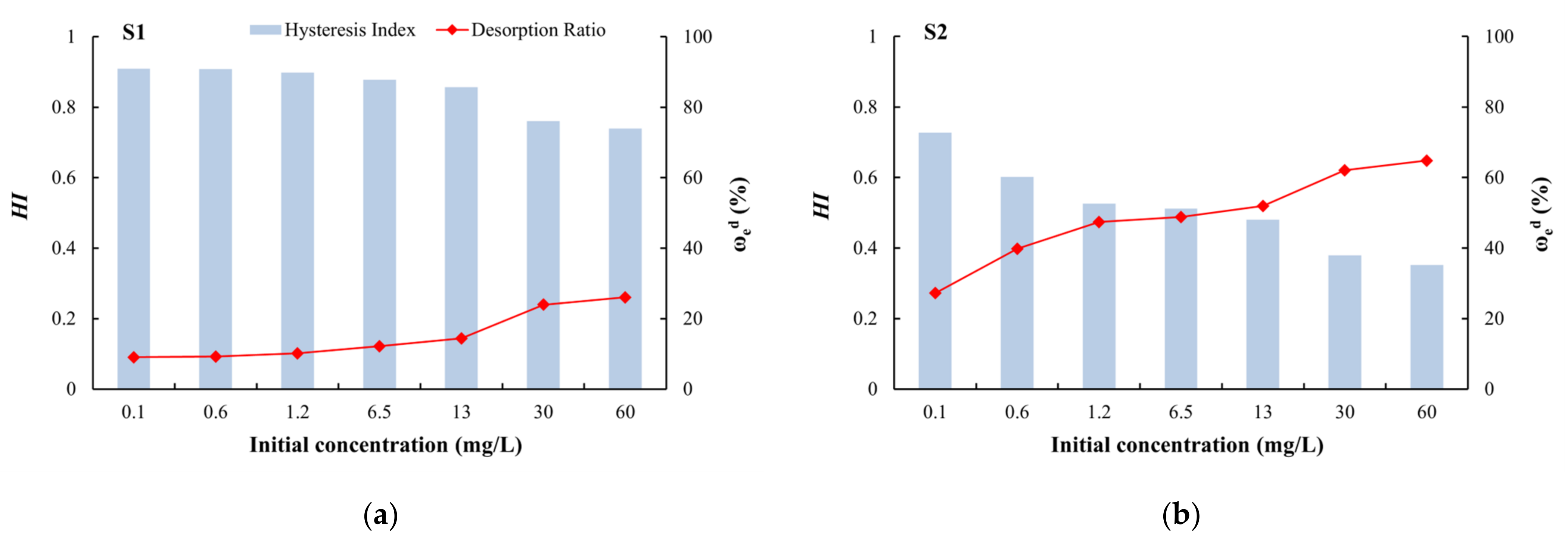
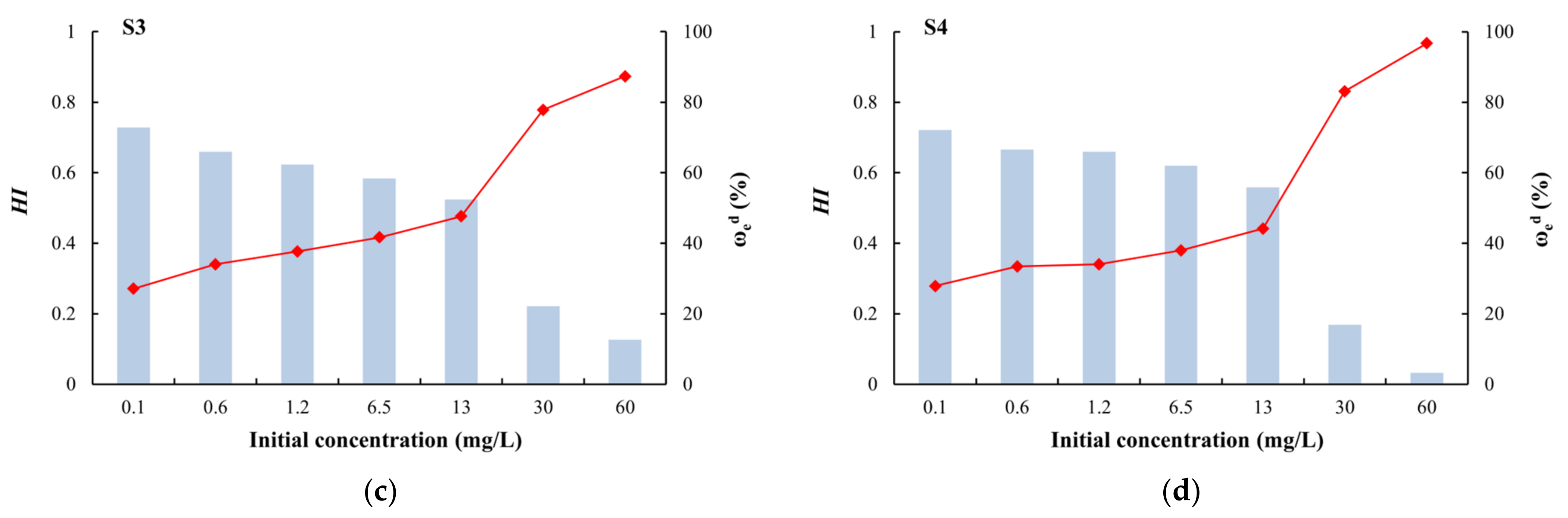
2.4.5. Hysteresis Index (HI)
3. Results and Discussion
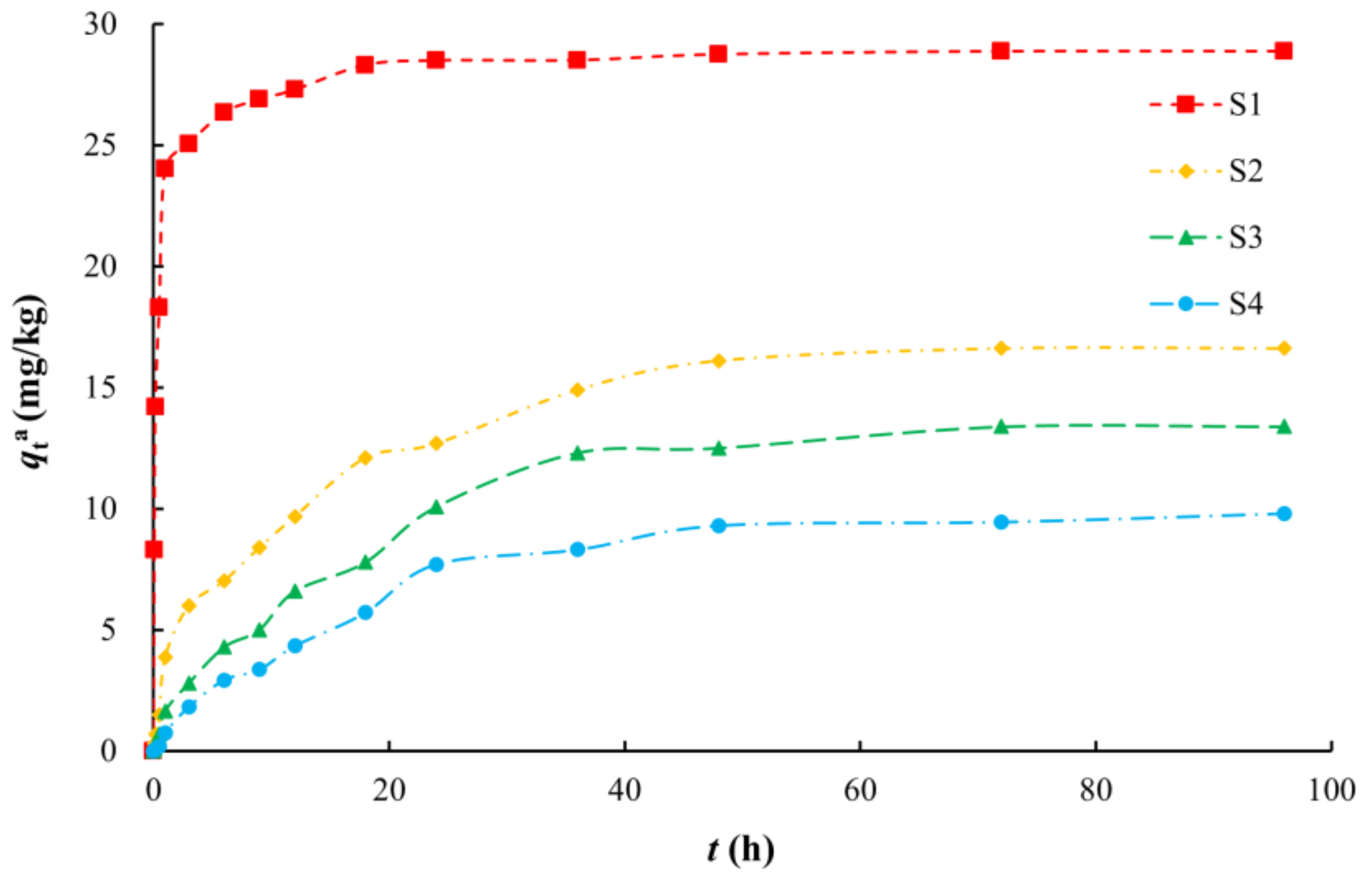
3.1. Adsorption Kinetics Characteristics
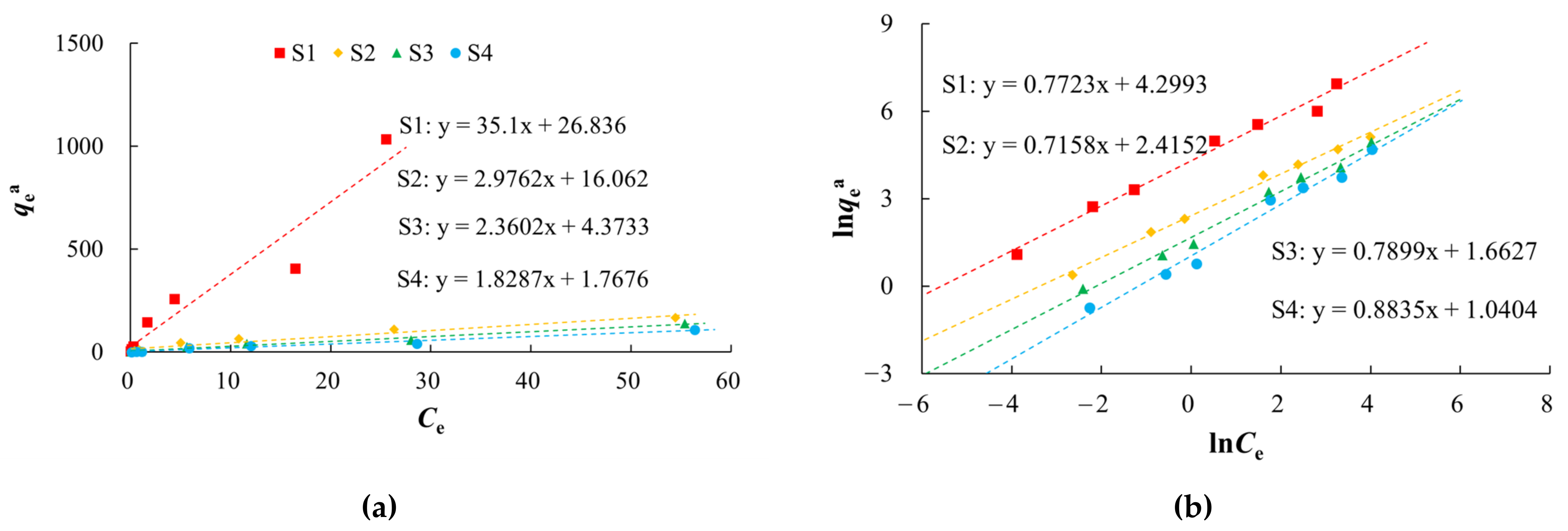
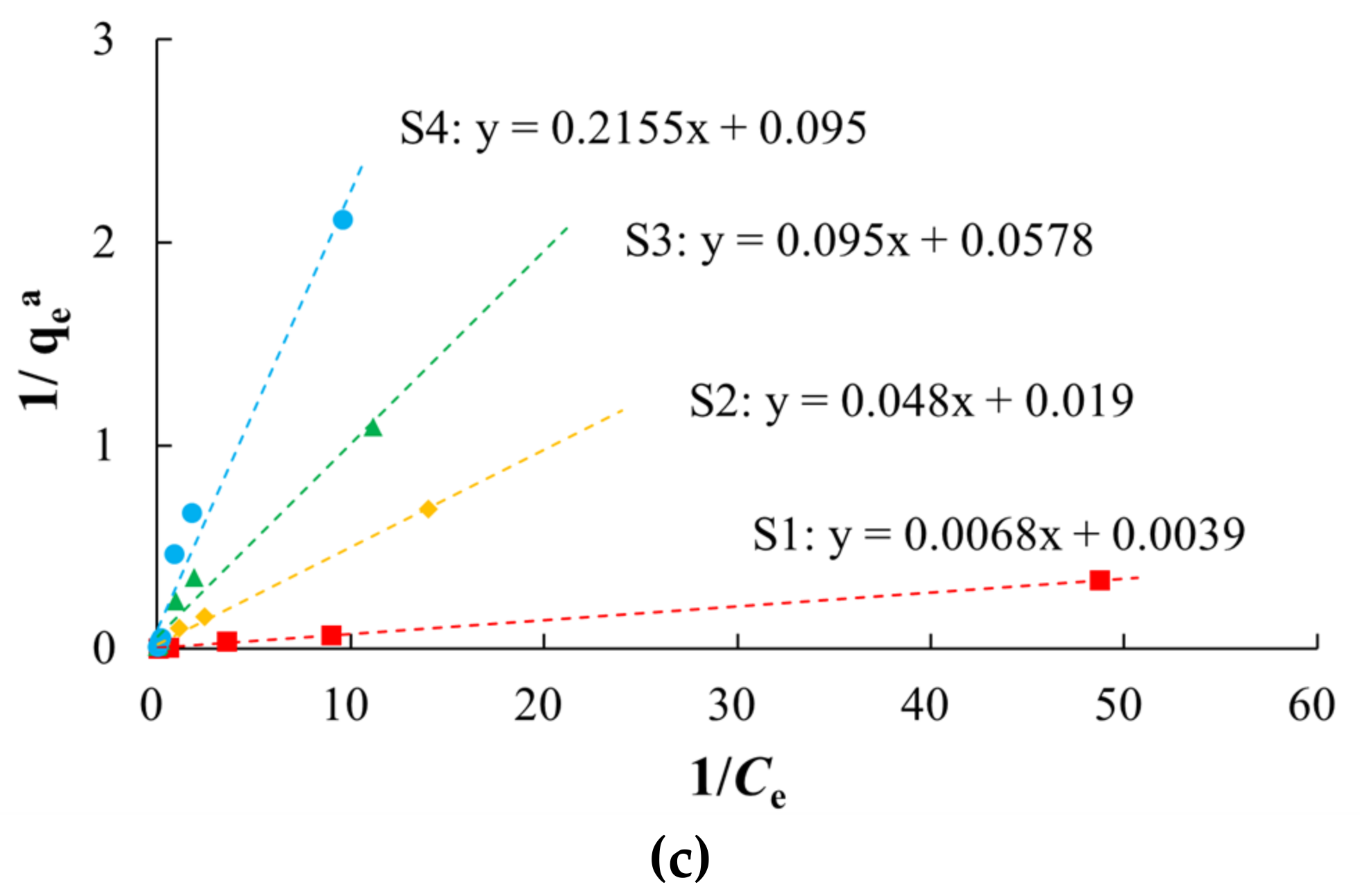
3.2. Isothermal Adsorption Characteristics
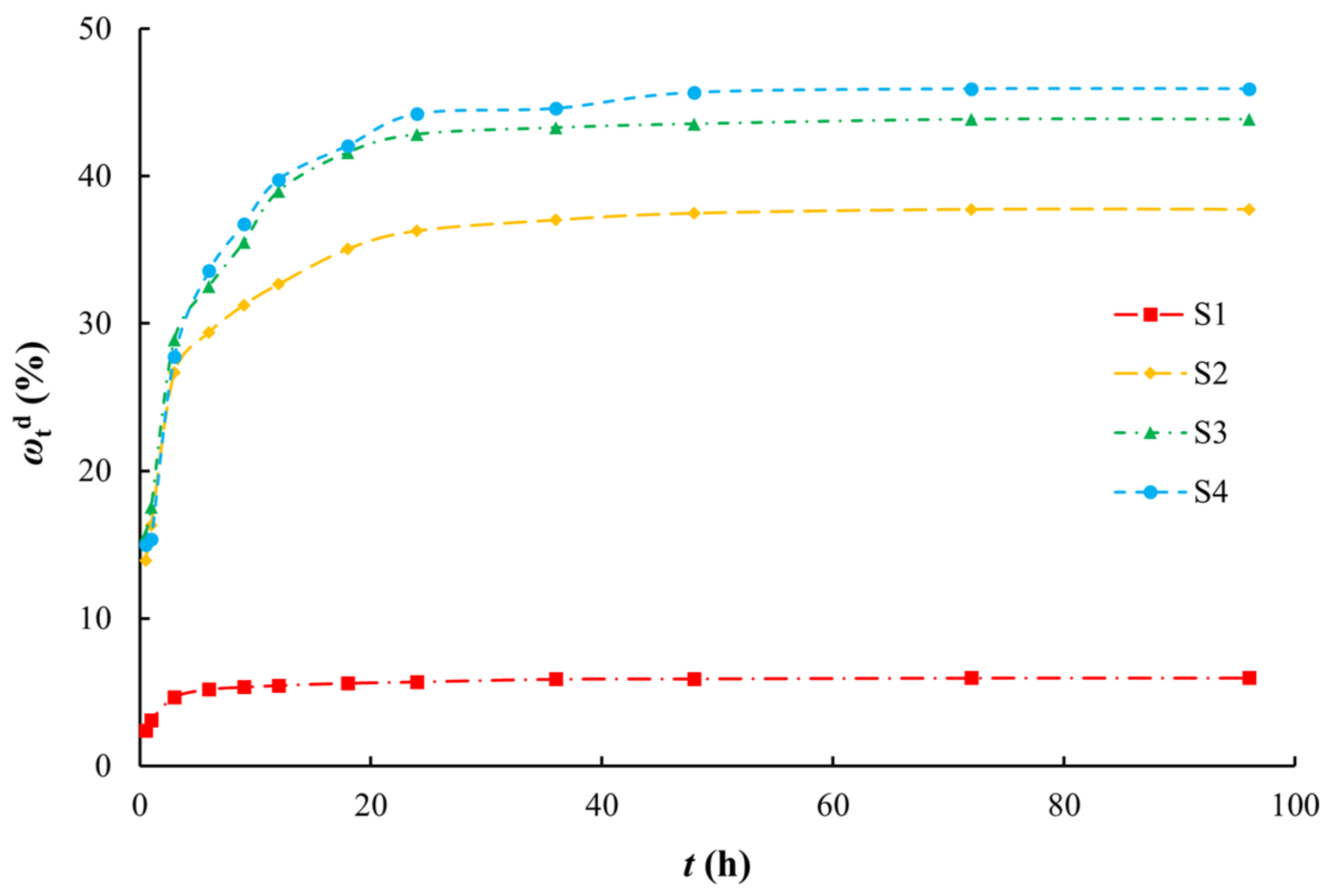
3.3. Desorption Characteristics and the Relationship with Adsorption
3.4. Factors Influencing Adsorption and Desorption
3.4.1. pH
3.4.2. Temperature
3.4.3. Carbonate
3.4.4. Ionic Strength
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, S.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C. Hydrochemical evolution of pore water in riverbed sedimentation zone during riverbank infiltration. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2021, 70, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zuo, R.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Riverbank filtration in China: A review and perspective. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufenkji, N.; Ryan, J.N.; Elimelech, M. The promise of bank filtration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 422A–428A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, G. Water supply safety of riverbank filtration wells under the impact of surface water-groundwater interaction: Evidence from long-term field pumping tests. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhu, P.; Xu, W.; Su, X. Evaluation of the influence of river bank infiltration on groundwater in an inland alluvial fan using spectral analysis and environmental tracers. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomčić, D.; Hajdin, B.; Stevanović, Z.; Bajić, D.; Hajdin, K. Groundwater management by riverbank filtration and an infiltration channel: The case of Obrenovac, Serbia. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.W.; Fuller, C.C. Effect of enhanced manganese oxidation in the hyporheic zone on basin-scale geochemical mass balance. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Du, Q.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Jinsheng, W. The impact of well drawdowns on the mixing process of river water and groundwater and water quality in a riverside well field, Northeast China. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Lu, S.; Yuan, W.; Woo, N.C.; Dai, Z.; Dong, W.; Du, S.; Zhang, X. Redox zonation for different groundwater flow paths during bank filtration: A case study at Liao River, Shenyang, northeastern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1573–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.H.; Lopipero, P.A.; Bates, M.N.; Steinmaus, C.M. Arsenic epidemiology and drinking water standards. Science 2002, 296, 2145–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Wei, M.; Ren, X.; Wang, D. Poor groundwater quality and high potential health risks in the Datong Basin, northern China: Research from published data. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 791–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarathilaka, P.; Seneweera, S.; Meharg, A.; Bundschuh, J. Arsenic speciation dynamics in paddy rice soil-water environment: Sources, physico-chemical, and biological factors—A review. Water Res. 2018, 140, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.S.M.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C.S. Arsenic and human health effects: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, P.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Elumalai, V. Groundwater Arsenic and Fluoride and Associated Arsenicosis and Fluorosis in China: Occurrence, Distribution and Management. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 713–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Ahmed, K.M.; Whitehead, P.G. A review of arsenic and its impacts in groundwater of the Ganges–Brahmaputra—Meghna delta, Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Rasool, A.; Junaid, M.; Zhang, H. A comprehensive review on current status, mechanism, and possible sources of arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global perspective with prominence of Pakistan scenario. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 2020, 368, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, I.; Prommer, H.; Berg, M.; Siade, A.J.; Sun, J.; Kipfer, R. The river—Groundwater interface as a hotspot for arsenic release. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R.; Dong, Z.; Shahid, M.; Arshad, M. Unraveling Health Risk and Speciation of Arsenic from Groundwater in Rural Areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12371–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.V.; Bringas, E.; Yadav, G.D.; Rathod, V.K.; Ortiz, I.; Marathe, K.V. Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: A review of current technologies for contaminants removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 162, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. Arsenic(III) and Arsenic(V) Removal from Water Sources by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs): A Mini Review of Recent Developments. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; van Geen, A. Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Guo, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, M. Environmental biogeochemistry of high arsenic geothermal fluids. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Su, X.; Yu, K.; Sun, C. Microbial Community Structure of Arsenic-Bearing Groundwater Environment in the Riverbank Filtration Zone. Water 2022, 14, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wen, D.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Guo, Q. A review of high arsenic groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: Distribution, characteristics and geochemical processes. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 41, 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y. Enhancement of arsenic adsorption during mineral transformation from siderite to goethite: Mechanism and application. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S. Competitive Adsorption of Arsenate and Arsenite on Oxides and Clay Minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirbahman, A.; Kent, D.B.; Curtis, G.P.; Davis, J.A. Kinetics of sorption and abiotic oxidation of arsenic(III) by aquifer materials. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu, S.; Breeze, D.; Saada, A.; Baranger, P. The Influence of pH, Electrolyte Type, and Surface Coating on Arsenic(V) Adsorption onto Kaolinites. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ofner, J.; Kappler, A. Formation of binary and ternary colloids and dissolved complexes of organic matter, Fe and As. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4479–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Hering, J.G. Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: Implications for arsenic mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.R.; Turner, R.; Hall, G. Anomalous arsenic concentrations in groundwaters of an island community, Bowen Island, British Columbia. Environ. Geochem. Health 1998, 20, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, Y. Effect of sulfide on As(III) and As(V) sequestration by ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y. Biogeochemistry of Iron Enrichment in Groundwater: An Indicator of Environmental Pollution and Its Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, T.; Subacz, J.L.; Phillippi, J.M.; Barnett, M.O. Effects of dissolved carbonate on arsenic adsorption and mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7875–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, L.; Chakraborty, S.; Appelo, C.; Roman-Ross, G.; Nath, B.; Ansari, A.; Lanson, M.; Chatterjee, D.; Mallik, S.B. Chemodynamics of an arsenic ‘‘hotspot’’ in a West Bengal aquifer: A field and reactive transport modeling study. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1273–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Ren, Y.; Wei, C. Removal of arsenite from water by synthetic siderite: Behaviors and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.; Banerjee, D.; Hudson-Edwards, K.; Mishra, R.; Purohit, R.; Ravenscroft, P.; Cronin, A.; Howarth, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Talukder, T.; et al. Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: The example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1255–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, H.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Xiu, W.; Zhao, B. Molecular Evidence of Arsenic Mobility Linked to Biodegradable Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7280–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbitz, K.; Wennrich, R. Mobilization of heavy metals and arsenic in polluted wetland soils and its dependence on dissolved organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 209, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Su, X.; Feng, X.; Sun, C. Sources and influencing factors of arsenic in nearshore zone during river water infiltration. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 29, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W. Biogeochemical Process of Fe and Mn during River Bank Infiltration Affected by Groundwater Exploiting. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Feng, X.; Su, X. Geochemical characteristics of arsenic in groundwater during riverbank filtration: A case study of Liao River, Northeast China. Water Supply 2020, 20, 3288–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. Biogeochemical Process of Arsenic in Groundwater and Its Simulation Affected by Groundwater Exploitation in Riverside. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Lu, S.; Gao, R.; Su, D.; Yuan, W.; Dai, Z.; Papavasilopoulos, E.N. Groundwater flow path determination during riverbank filtration affected by groundwater exploitation: A case study of Liao River, Northeast China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Weber, W.J. A Distributed Reactivity Model for Sorption by Soils and Sediments. 10. Relationships between Desorption, Hysteresis, and the Chemical Characteristics of Organic Domains. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2562–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Weber, W.J. A Distributed Reactivity Model for Sorption by Soils and Sediments. 11. Slow Concentration-Dependent Sorption Rates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3549–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Park, J.; Chun, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, I.-C.; Kim, K.S. Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron-reduced graphite oxide modified composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; Sletten, R.S.; Wenzel, W.W. Sequentially Extracted Arsenic from Different Size Fractions of Contaminated Soils. Water Air Soil Poll. 2000, 124, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunhikrishnan, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Müller, K.; Laurenson, S.; Naidu, R.; Kim, W.-I. The Influence of Wastewater Irrigation on the Transformation and Bioavailability of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil. Adv. Agron. 2012, 115, 215–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qishlaqi, A.; Moore, F. Statistical Analysis of Accumulation and Sources of Heavy Metals Occurrence in Agricultural Soils of Khoshk River Banks, Shiraz, Iran. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2007, 2, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Anawar, H.M.; Akai, J.; Komaki, K.; Terao, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Safiullah, S.; Kato, K. Geochemical occurrence of arsenic in groundwater of Bangladesh: Sources and mobilization processes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 77, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakour, H.; Lin, T.-F. Experimental determination and modeling of arsenic complexation with humic and fulvic acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, U.; Fobian, A. Pollution of two soils by arsenic, chromium and copper, Denmark. Geoderma 1991, 49, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Xing, B. Mechanisms of slow sorption of organic chemicals to natural particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Lamshöft, M.; Zühlke, S.; Spiteller, M. Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; McGinley, P.M.; Katz, L.E. A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 1. Conceptual basis and equilibrium assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, E.; Laird, D.A.; Koskinen, W.C.; Dowdy, R.H. Atrazine desorption from smectites. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.C.; Davis, J.A.; Waychunas, G.A. Surface chemistry of ferrihydrite: Part 2. Kinetics of arsenate adsorption and coprecipitation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossl, P.R.; Eick, M.; Sparks, D.L.; Goldberg, S.; Ainsworth, C.C. Arsenate and chromate retention mechanisms on goethite. 2. Kinetic evaluation using a pressure-jump relaxation technique. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Puls, R.W. Adsorption, desorption and oxidation of arsenic affected by clay minerals and aging process. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Mucci, A. Acid base reactions, phosphate and arsenate complexation, and their competitive adsorption at the surface of goethite in 0.7 M NaCl solution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2361–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.; Johnston, C.T. Mechanisms of Arsenic Adsorption on Amorphous Oxides Evaluated Using Macroscopic Measurements, Vibrational Spectroscopy, and Surface Complexation Modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 234, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Demopoulos, G.P. Infrared spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction characterization of the nature of adsorbed arsenate on ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, A.; Dimirkou, A. Phosphate Adsorption on Hematite, Kaolinite, and Kaolinite-Hematite (k-h) Systems As Described by a Constant Capacitance Model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 192, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Raven, K.P.; Loeppert, R.H. Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on ferrihydrite: Surface charge reduction and net OH- release stoichiometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaghebeur, M.; Rate, A.; Rengel, Z.; Hinz, C. Desorption kinetics of arsenate from kaolinite as influenced by pH. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, D.P.; Johnson, B.B.; Wells, J.D. Modeling the Effect of Temperature on Adsorption of Lead(II) and Zinc(II) onto Goethite at Constant pH. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 184, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Benedí, J.; Bolado, S.; Cancillo, I.; Calvo, C.; García-Sinovas, D. Adsorption–Desorption of Arsenate in Three Spanish Soils. Vadose Zone J. 2005, 4, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Nriagu, J.; Haack, S. Carbonate Ions and Arsenic Dissolution by Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Van Der Weiden, M.J.J.; Tournassat, C.; Charlet, L. Surface Complexation of Ferrous Iron and Carbonate on Ferrihydrite and the Mobilization of Arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3096–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; De Cristofaro, A.; Violante, A. Effect of pH, phosphate and oxalate on the adsorption/desorption of arsenate on/from goethite. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peryea, F.J. Phosphate Starter Fertilizer Temporarily Enhances Soil Arsenic Uptake by Apple Trees Grown under Field Conditions. HortScience 1998, 33, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B. A critique of diffuse double layer models applied to colloid and surface chemistry. Clays Clay Miner. 1997, 45, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Mishra, D.; Chaudhury, G.R.; Das, R.P. Arsenic adsorption mechanism on clay minerals and its dependence on temperature. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample ID | Lithology | Sampling Depth (m) | The Weight Percentage of Different Particle Sizes (%) | SSA (m2/g) | TOC (g/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.063 mm | 0.063–0.15 mm | 0.15–0.25 mm | 0.25–0.5 mm | 0.5–2 mm | >2 mm | |||||
| S1 | Silty clay | 1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36.2 | 12.2 |
| S2 | Fine sand | 3 | 2.24 | 26.42 | 36.11 | 17.72 | 9.98 | 7.53 | 6.6 | 4.1 |
| S3 | Medium sand | 5 | 0.56 | 6.47 | 18.99 | 59.11 | 9.18 | 5.69 | 5.1 | 2.5 |
| S4 | Coarse sand with gravel | 7 | 0.16 | 2.46 | 13.44 | 22.37 | 15.53 | 46.04 | 3.7 | 0.6 |
| Sample ID | Pseudo First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (h−1) | qe (mg/kg) | R2 | k2 (L·mg−1·h−1) | qe (mg/kg) | R2 | |
| S1 | 0.0749 | 3.87 | 0.9274 | 0.0669 | 28.99 | 0.9999 |
| S2 | 0.0644 | 14.50 | 0.9795 | 0.0068 | 18.12 | 0.9776 |
| S3 | 0.0600 | 13.40 | 0.9717 | 0.0037 | 16.67 | 0.9479 |
| S4 | 0.0597 | 10.32 | 0.9803 | 0.0035 | 13.25 | 0.9579 |
| Sample ID | Henry Model | Freundlich Model | Langmuir Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kh (L/kg) | R2 | Kf (mg(1−1/n)L1/nkg−1) | n | R2 | Kl (L/mg) | qm (mg/kg) | R2 | |
| S1 | 35.1 | 0.9239 | 73.6482 | 1.2948 | 0.9854 | 0.5735 | 256.4103 | 0.9991 |
| S2 | 2.9762 | 0.9449 | 11.1920 | 1.3970 | 0.9933 | 0.3958 | 52.6316 | 0.9959 |
| S3 | 2.3602 | 0.9772 | 5.2735 | 1.2660 | 0.9892 | 0.6084 | 17.3010 | 0.9695 |
| S4 | 1.8287 | 0.9720 | 2.8303 | 1.1319 | 0.9819 | 0.4413 | 10.5152 | 0.9713 |
| Sample ID | Pseudo First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (h−1) | qe (mg/kg) | R2 | k2 (L·mg−1·h−1) | qe (mg/kg) | R2 | |
| S1 | 0.0775 | 0.5351 | 0.9048 | 0.5651 | 1.7406 | 0.9998 |
| S2 | 0.0907 | 2.8056 | 0.9738 | 0.0979 | 6.4061 | 0.9994 |
| S3 | 0.0965 | 2.6666 | 0.9447 | 0.0960 | 6.0459 | 0.9992 |
| S4 | 0.0950 | 2.4157 | 0.9677 | 0.1032 | 4.6468 | 0.9992 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.; Yang, Y.; Su, X.; Yu, K.; Wang, X. Arsenic Adsorption and Desorption in Various Aqueous Media in the Nearshore Zone and Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710935
Lu S, Yang Y, Su X, Yu K, Wang X. Arsenic Adsorption and Desorption in Various Aqueous Media in the Nearshore Zone and Influencing Factors. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710935
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Shuai, Yimeng Yang, Xiaosi Su, Kaining Yu, and Xinzhou Wang. 2022. "Arsenic Adsorption and Desorption in Various Aqueous Media in the Nearshore Zone and Influencing Factors" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710935
APA StyleLu, S., Yang, Y., Su, X., Yu, K., & Wang, X. (2022). Arsenic Adsorption and Desorption in Various Aqueous Media in the Nearshore Zone and Influencing Factors. Sustainability, 14(17), 10935. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710935







