Evaluating the Sustainable Development of the Semiconductor Industry Using BWM and Fuzzy TOPSIS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Establish a comprehensive framework to evaluate sustainable development performance.
- Determine the weights of evaluation criteria using BWM, which overcomes the shortcomings of AHP.
- Incorporate the concept of aspiration level to optimize the fuzzy TOPSIS technique.
- Investigate the sustainable development of the semiconductor industry based on four dimensions of sustainable value creation (i.e., economy, environment, society, and innovation).
2. Literature Review
2.1. Environmental Dimension
2.2. Economic Dimension
2.3. Social Dimension
2.4. Innovation Dimension
3. Methods
3.1. Best Worst Method
3.2. Basic Concepts in Fuzzy Set Theory
- (i)
- Addition of two sets of triangular fuzzy numbers:
- (ii)
- Subtraction of two sets of triangular fuzzy numbers:
- (iii)
- Multiplication of two sets of triangular fuzzy numbers:
- (iv)
- Division of two sets of triangular fuzzy numbers:
3.3. Fuzzy Modified TOPSIS-AL Technique
4. Results
4.1. Obtaining the Weights of Criteria through BWM
4.2. Sustainable Development Performance of the Semiconductor Industry
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Fang, M.; Jin, F.; Wu, C.; Chen, H. Multi-attribute decision making based on stochastic DEA cross-efficiency with ordinal variable and its application to evaluation of banks’ sustainable development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, P.; Guo, S. Assessing the eco-efficiency of a circular economy system in China’s coal mining areas: Emergy and data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Lin, S.-W.; Lu, W.-M. Dynamic eco-efficiency evaluation of the semiconductor industry: A sustainable development perspective. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.T.; Lee, H.C. Taiwan’s renewable energy strategy and energy-intensive industrial policy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Ryu, Y. Performance Assessment of the semiconductor industry: Measured by DEA environmental assessment. Energies 2020, 13, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.M.; Vermeulen, W.J.; Simboli, A.; Raggi, A. Sustainability assessment in circular inter-firm networks: An integrated framework of industrial ecology and circular supply chain management approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.R.; Ali, S.M.; Paul, S.K.; Munim, Z.H. Measuring sustainability performance using an integrated model. Measurement 2021, 184, 109931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, M.M.; Khan, M.; Hussain, M.; Helo, P. Conceptualizing and incorporating social sustainability in the business world. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’amato, D.; Korhonen, J. Integrating the green economy, circular economy and bioeconomy in a strategic sustainability framework. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 188, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-M.; Kireeva, N.; Timoshin, A.; Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Kamyab, H. A multi-criteria framework for designing of stand-alone and grid-connected photovoltaic, wind, battery clean energy system considering reliability and economic assessment. Energy 2021, 224, 120154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkel, I.; Rabinowitz, G. Modeling cost benefit analysis of inspection in a production line. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Chung, H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, C. The Impact of Technological Capability on Financial Performance in the Semiconductor Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, H.; Shan, J.; Cai, J. Innovation efficiency of semiconductor industry in China: A new framework based on generalized three-stage DEA analysis. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2019, 66, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Lin, S.-W.; Lu, W.-M. Sustainability assessment of Taiwan’s semiconductor industry: A new hybrid model using combined analytic hierarchy process and two-stage additive network data envelopment analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavurmaci, M.; Üstün, A.K. Assessment of groundwater quality using DEA and AHP: A case study in the Sereflikochisar region in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kengpol, A.; Tuammee, S. The development of a decision support framework for a quantitative risk assessment in multimodal green logistics: An empirical study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 54, 1020–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Meng, F.; Xiong, B. Interval cross efficiency for fully ranking decision making units using DEA/AHP approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 271, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chul Park, S.; Lee, J.H. Supplier selection and stepwise benchmarking: A new hybrid model using DEA and AHP based on cluster Analysis. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2017, 69, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Dirong, X.; Lin, H.; Lei, W. Economic Feasibility Analysis for Renewable Energy Project Using an Integrated TFN–AHP–DEA Approach on the Basis of Consumer Utility. Energies 2017, 10, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otay, İ.; Oztaysi, B.; Cevik Onar, S.; Kahraman, C. Multi-expert performance evaluation of healthcare institutions using an integrated intuitionistic fuzzy AHP&DEA methodology. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 133, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-W.; Liou, J.J.H.; Wang, H.-S.; Tsai, Y.-S. An integrated model for solving problems in green supplier selection and order allocation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-W.; Lo, H.-W.; Chen, K.-Y.; Liou, J.J. A novel FMEA model based on rough BWM and rough TOPSIS-AL for risk assessment. Mathematics 2019, 7, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.P.; Talib, N.A.; Kowang, T.O. Development of Sustainability Framework Based on the Theory of Resource Based View. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2018, 8, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatheshwara, K.; Vinodh, S. Sustainable electronics product design and manufacturing: State of art review. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2021, 14, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, A.; Agrawal, R.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S. Developing A sustainability framework for Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 2021, 98, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesios, C.; De, D.; Moursellas, A.; Dey, P.K.; Evangelinos, K. Sustainability performance analysis of small and medium sized enterprises: Criteria, methods and framework. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 75, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Planelles, J.; Segarra-Oña, M.; Peiro-Signes, A. Building a Theoretical Framework for Corporate Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani Mavi, R.; Saen, R.F.; Goh, M. Joint analysis of eco-efficiency and eco-innovation with common weights in two-stage network DEA: A big data approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 144, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J.; Kothadiya, O.; Tavasszy, L.; Kroesen, M. Quality assessment of airline baggage handling systems using SERVQUAL and BWM. Tour. Manag. 2018, 66, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, H.; Alizadeh, A.; Amini, M. A new approach based on BWM and MULTIMOORA methods for calculating semi-human development index: An application for provinces of Iran. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 70, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stević, Ž.; Pamučar, D.; Subotić, M.; Antuchevičiene, J.; Zavadskas, E.K. The location selection for roundabout construction using Rough BWM-Rough WASPAS approach based on a new Rough Hamy aggregator. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Hashemi-Tabatabaei, M.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Keshavarz-Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.; Banaitis, A. A new fuzzy BWM approach for evaluating and selecting a sustainable supplier in supply chain management. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2021, 28, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, C.P.; Sharma, A. Sustainable outsourcing partner selection and evaluation using an integrated BWM–VIKOR framework. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 1529–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method: Some properties and a linear model. Omega 2016, 64, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf. Sci. 1975, 8, 199–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. Effects of the entropy weight on TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazancoglu, I.; Sagnak, M.; Kumar Mangla, S.; Kazancoglu, Y. Circular economy and the policy: A framework for improving the corporate environmental management in supply chains. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Luthra, S.; Joshi, S.; Kumar, A. Developing a framework for enhancing survivability of sustainable supply chains during and post-COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022, 25, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami-Marbini, A.; Agrell, P.J.; Tavana, M.; Khoshnevis, P. A flexible cross-efficiency fuzzy data envelopment analysis model for sustainable sourcing. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2761–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T. A modified TOPSIS with a different ranking index. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimension | Criteria | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental (D1) | Clean energy use (A11) | Whether a company can build a wafer-fabrication plant that achieves clean production. Effective power saving is achieved by implementing energy-efficiency measures. The development of energy-efficient semiconductor technology can help customers produce more energy-efficient products. | [5,23,24] |
| Recycling/renewable capacity (A12) | Whether a company can establish recycling technologies to share with suppliers. Through joint investment in the development of recycling and reuse, companies can achieve their sustainability goals of manufacturing environmentally friendly products of high quality. | [9,25,26,27] | |
| Green resource integration (A13) | Whether a company can promote sustainable supply chain management. Companies can establish a supplier risk management matrix and necessitate their suppliers to propose and implement green manufacturing goals. | [6,7] | |
| Pollution-discharge treatment (A14) | Whether a firm is actively implementing environmental-protection policies to reduce pollution discharge and thus improve their energy-use efficiency. Pollution discharge from the semiconductor industry, especially wafer cleaning and cooling, can have a serious impact on the environment. | [5,26,27] | |
| Economic (D2) | Firm size (A21) | A firm’s capitalization, employees, market share, and management. | [7,9,10] |
| Financial strength (A22) | A firm’s assets and liabilities, income statement, and cash flows shown in its financial statements. | [9,24] | |
| Material cost/selling price (A23) | A firm’s profitability as it includes all direct and indirect fixed and variable costs such as materials, labor, equipment, plant, operations, and marketing, and net/gross profit. | [10,24,27] | |
| Social (D3) | Partner complementarity (A31) | Whether the different resources, capabilities, and technologies owned by all stakeholders in the semiconductor industry can be integrated and managed to enhance competitiveness. | [8,9,25] |
| Corporate brand image (A32) | The firm’s value as it refers to society’s perception. | [8,24] | |
| CRM capability (A33) | A firm can provide to meet customer needs. | [8,9,25,27] | |
| Innovation (D4) | Core technical patent (A41) | Patents not only come from a firm’s own R&D but can also be obtained by various means, such as the purchase of patents and technology licensing. | [5,6,7] |
| Product life cycle (A 42) | The timeline over which a semiconductor product goes through a series of stages, including introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. | [5,24,26] | |
| R&D capability (A43) | Whether a firm, based on R&D, possesses advanced technologies and knowledge, clearly understands market needs, and owns product-innovation capabilities. | [6,7,26] |
| Linguistic Variable | Code |
|---|---|
| Equally important | 1 |
| Moderately more important | 3 |
| Strongly more important | 5 |
| Very strongly more important | 7 |
| Extremely more important | 9 |
| Intermediate values | 2, 4, 6, 8 |
| Linguistic Variable | Code | Fuzzy Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Very poor | VP | (0, 1, 2) |
| Poor | P | (2, 3, 4) |
| Fair | F | (4, 5, 6) |
| Good | G | (6, 7, 8) |
| Very good | VG | (8, 9, 10) |
| Expertise | Expert Composition | Number of Experts |
|---|---|---|
| Practical Experience (years) | 5–10 11–20 21–30 | 1 5 2 |
| Field | Vice President Project Manager Engineer | 3 2 3 |
| Expert No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best | D3 | D1 | D1 | D1 | D1 | D3 | D3 | D1 |
| Worst | D4 | D3 | D3 | D4 | D4 | D4 | D4 | D2 |
| Expert No. | Best | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| 2 | D1 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 5 |
| 3 | D1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| 4 | D1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| 5 | D1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 7 |
| 6 | D3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| 7 | D3 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| 8 | D1 | 1 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| Expert No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worst | D4 | D3 | D3 | D4 | D4 | D4 | D4 | D2 |
| D1 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| D2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
| D3 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| D4 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Expert No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0.360 | 0.423 | 0.418 | 0.448 | 0.401 | 0.290 | 0.336 | 0.425 |
| D2 | 0.176 | 0.203 | 0.186 | 0.172 | 0.200 | 0.232 | 0.185 | 0.135 |
| D3 | 0.339 | 0.168 | 0.176 | 0.253 | 0.278 | 0.341 | 0.335 | 0.213 |
| D4 | 0.125 | 0.206 | 0.219 | 0.126 | 0.122 | 0.137 | 0.144 | 0.227 |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waggregation | 0.3862 | 0.1910 | 0.2578 | 0.1650 |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A11 | (4.875, 5.875, 6.875) | (5.250, 6.250, 7.125) | (1.250, 2.000, 3.000) | (4.875, 5.875, 6.875) |
| A12 | (5.000, 6.000, 7.000) | (4.250, 5.250, 6.250) | (4.750, 5.750, 6.750) | (4.750, 5.750, 8.250) |
| A13 | (5.500, 6.500, 7.500) | (6.375, 7.375, 8.375) | (1.875, 2.750, 3.750) | (4.875, 5.875, 6.875) |
| A14 | (6.000, 7.000, 7.875) | (5.625, 6.625, 7.625) | (1.750, 2.625, 3.625) | (5.500, 6.500, 7.500) |
| A21 | (2.250, 3.000, 4.000) | (2.750, 3.750, 4.750) | (2.750, 3.750, 4.750) | (3.250, 4.250, 5.250) |
| A22 | (3.125, 4.000, 5.000) | (3.250, 4.250, 5.250) | (2.125, 3.125, 4.125) | (3.375, 4.375, 5.375) |
| A23 | (3.25, 4.000, 5.000) | (3.250, 4.250, 5.250) | (3.500, 4.500, 5.500) | (3.750, 4.750, 5.750) |
| A31 | (3.375, 4.250, 5.250) | (3.875, 4.750, 5.750) | (3.125, 4.000, 5.000) | (2.750, 3.750, 4.750) |
| A32 | (4.625, 5.625, 6.500) | (3.500, 4.500, 5.500) | (4.125, 5.125, 6.125) | (3.625, 4.625, 5.500) |
| A33 | (4.000, 5.000, 6.000) | (3.000, 4.000, 5.000) | (3.000, 4.000, 5.000) | (2.875, 3.875, 4.875) |
| A41 | (4.375, 5.375, 6.375) | (3.375, 4.375, 5.375) | (3.750, 4.750, 5.750) | (3.000, 4.000, 5.000) |
| A42 | (3.875, 4.750, 5.750) | (3.000, 3.875, 4.875) | (3.625, 4.625, 5.625) | (2.500, 3.500, 4.500) |
| A43 | (5.250, 6.250, 7.125) | (4.250, 5.250, 6.250) | (2.750, 3.750, 4.750) | (3.125, 4.125, 5.125) |
| Aspiration level | (10, 10, 10) | (10, 10, 10) | (10, 10, 10) | (10, 10, 10) |
| Worst level | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A11 | (0.488, 0.588, 0.688) | (0.525, 0.625, 0.713) | (0.125, 0.200, 0.300) | (0.488, 0.588, 0.688) |
| A12 | (0.500, 0.600, 0.700) | (0.388, 0.488, 0.588) | (0.338, 0.425, 0.525) | (0.625, 0.725, 0.825) |
| A13 | (0.550, 0.650, 0.750) | (0.638, 0.738, 0.838) | (0.188, 0.275, 0.375) | (0.488, 0.588, 0.688) |
| A14 | (0.600, 0.700, 0.788) | (0.563, 0.663, 0.763) | (0.175, 0.263, 0.363) | (0.550, 0.650, 0.750) |
| A21 | (0.225, 0.300, 0.400) | (0.275, 0.375, 0.475) | (0.275, 0.375, 0.475) | (0.325, 0.425, 0.525) |
| A22 | (0.313, 0.400, 0.500) | (0.325, 0.425, 0.525) | (0.213, 0.313, 0.413) | (0.338, 0.438, 0.538) |
| A23 | (0.325, 0.400, 0.500) | (0.325, 0.425, 0.525) | (0.350, 0.450, 0.550) | (0.375, 0.475, 0.575) |
| A31 | (0.338, 0.425, 0.525) | (0.388, 0.475, 0.575) | (0.313, 0.400, 0.500) | (0.275, 0.375, 0.475) |
| A32 | (0.463, 0.563, 0.650) | (0.350, 0.450, 0.550) | (0.413, 0.513, 0.613) | (0.363, 0.463, 0.550) |
| A33 | (0.400, 0.500, 0.600) | (0.300, 0.400, 0.500) | (0.300, 0.400, 0.500) | (0.288, 0.388, 0.488) |
| A41 | (0.438, 0.538, 0.638) | (0.338, 0.438, 0.538) | (0.375, 0.475, 0.575) | (0.300, 0.400, 0.500) |
| A42 | (0.388, 0.475, 0.575) | (0.300, 0.388, 0.488) | (0.363, 0.463, 0.563) | (0.250, 0.350, 0.450) |
| A43 | (0.525, 0.625, 0.713) | (0.425, 0.525, 0.625 | (0.275, 0.375, 0.475) | (0.313, 0.413, 0.513) |
| Aspiration level | (1, 1, 1) | (1, 1, 1) | (1, 1, 1) | (1, 1, 1) |
| Worst level | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A11 | (0.109, 0.131, 0.153) | (0.155, 0.185, 0.211) | (0.024, 0.039, 0.059) | (0.139, 0.168, 0.197) |
| A12 | (0.111, 0.134, 0.156) | (0.115, 0.144, 0.174) | (0.066, 0.083, 0.103) | (0.179, 0.207, 0.236) |
| A13 | (0.123, 0.145, 0.167) | (0.189, 0.218, 0.248) | (0.037, 0.054, 0.073) | (0.139, 0.168, 0.197) |
| A14 | (0.134, 0.156, 0.175) | (0.166, 0.196, 0.226) | (0.034, 0.051, 0.071) | (0.157, 0.186, 0.214) |
| A21 | (0.050, 0.067, 0.089) | (0.081, 0.111, 0.140) | (0.054, 0.073, 0.093) | (0.093, 0.122, 0.150) |
| A22 | (0.070, 0.089, 0.111) | (0.096, 0.126, 0.155) | (0.042, 0.061, 0.081) | (0.096, 0.125, 0.154) |
| A23 | (0.072, 0.089, 0.111) | (0.096, 0.126, 0.155) | (0.068, 0.088, 0.108) | (0.107, 0.136, 0.164) |
| A31 | (0.075, 0.095, 0.117) | (0.115, 0.140, 0.170) | (0.061, 0.078, 0.098) | (0.079, 0.107, 0.136) |
| A32 | (0.103, 0.125, 0.145) | (0.104, 0.133, 0.163) | (0.081, 0.100, 0.120) | (0.104, 0.132, 0.157) |
| A33 | (0.089, 0.111, 0.134) | (0.089, 0.118, 0.148) | (0.059, 0.078, 0.098) | (0.082, 0.111, 0.139) |
| A41 | (0.097, 0.120, 0.142) | (0.100, 0.129, 0.159) | (0.073, 0.093, 0.112) | (0.086, 0.114, 0.143) |
| A42 | (0.086, 0.106, 0.128) | (0.089, 0.115, 0.144) | (0.071, 0.090, 0.110) | (0.071, 0.100, 0.129) |
| A43 | (0.117, 0.139, 0.159) | (0.126, 0.155, 0.185) | (0.054, 0.073, 0.093) | (0.089, 0.118, 0.147) |
| Aspiration level | (0.223, 0.223, 0.223) | (0.071, 0.071, 0.071) | (0.031, 0.031, 0.031) | (0.066, 0.066, 0.066) |
| Worst level | (0.000, 0.000, 0.000) | (0.000, 0.000, 0.000) | (0.000, 0.000, 0.000) | (0.000, 0.000, 0.000) |
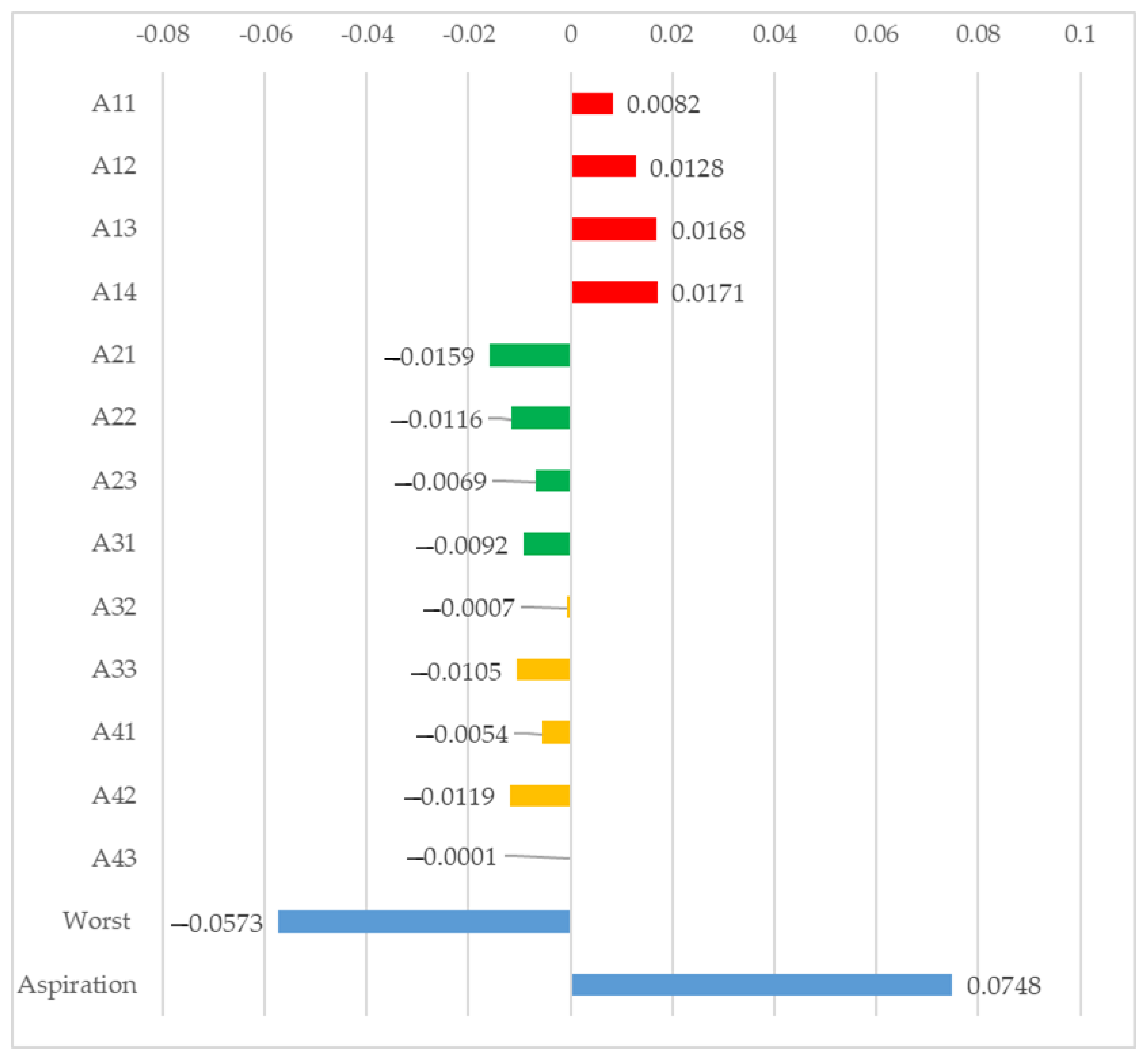
| di+ | di− | CCi | Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A11 | 0.245 | 0.238 | 0.008 | 4 |
| A12 | 0.226 | 0.251 | 0.013 | 3 |
| A13 | 0.217 | 0.269 | 0.017 | 2 |
| A14 | 0.215 | 0.269 | 0.017 | 1 |
| A21 | 0.318 | 0.147 | −0.016 | 13 |
| A22 | 0.303 | 0.162 | −0.012 | 11 |
| A23 | 0.286 | 0.177 | −0.007 | 8 |
| A31 | 0.295 | 0.169 | −0.009 | 9 |
| A32 | 0.265 | 0.199 | −0.001 | 6 |
| A33 | 0.299 | 0.165 | −0.011 | 10 |
| A41 | 0.282 | 0.183 | −0.005 | 7 |
| A42 | 0.305 | 0.161 | −0.012 | 12 |
| A43 | 0.267 | 0.204 | 0.000 | 5 |
| Aspiration level | 0 | 1 | 0.075 | |
| Worst level | 1 | 0 | −0.057 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, S.-P.; Tsai, J.-F. Evaluating the Sustainable Development of the Semiconductor Industry Using BWM and Fuzzy TOPSIS. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710693
Shen S-P, Tsai J-F. Evaluating the Sustainable Development of the Semiconductor Industry Using BWM and Fuzzy TOPSIS. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710693
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Shih-Ping, and Jung-Fa Tsai. 2022. "Evaluating the Sustainable Development of the Semiconductor Industry Using BWM and Fuzzy TOPSIS" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710693
APA StyleShen, S.-P., & Tsai, J.-F. (2022). Evaluating the Sustainable Development of the Semiconductor Industry Using BWM and Fuzzy TOPSIS. Sustainability, 14(17), 10693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710693





