A Sustainable Cold Mix Asphalt Mixture Comprising Paper Sludge Ash and Cement Kiln Dust
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials Properties and Testing Method
2.1. Materials
- (a)
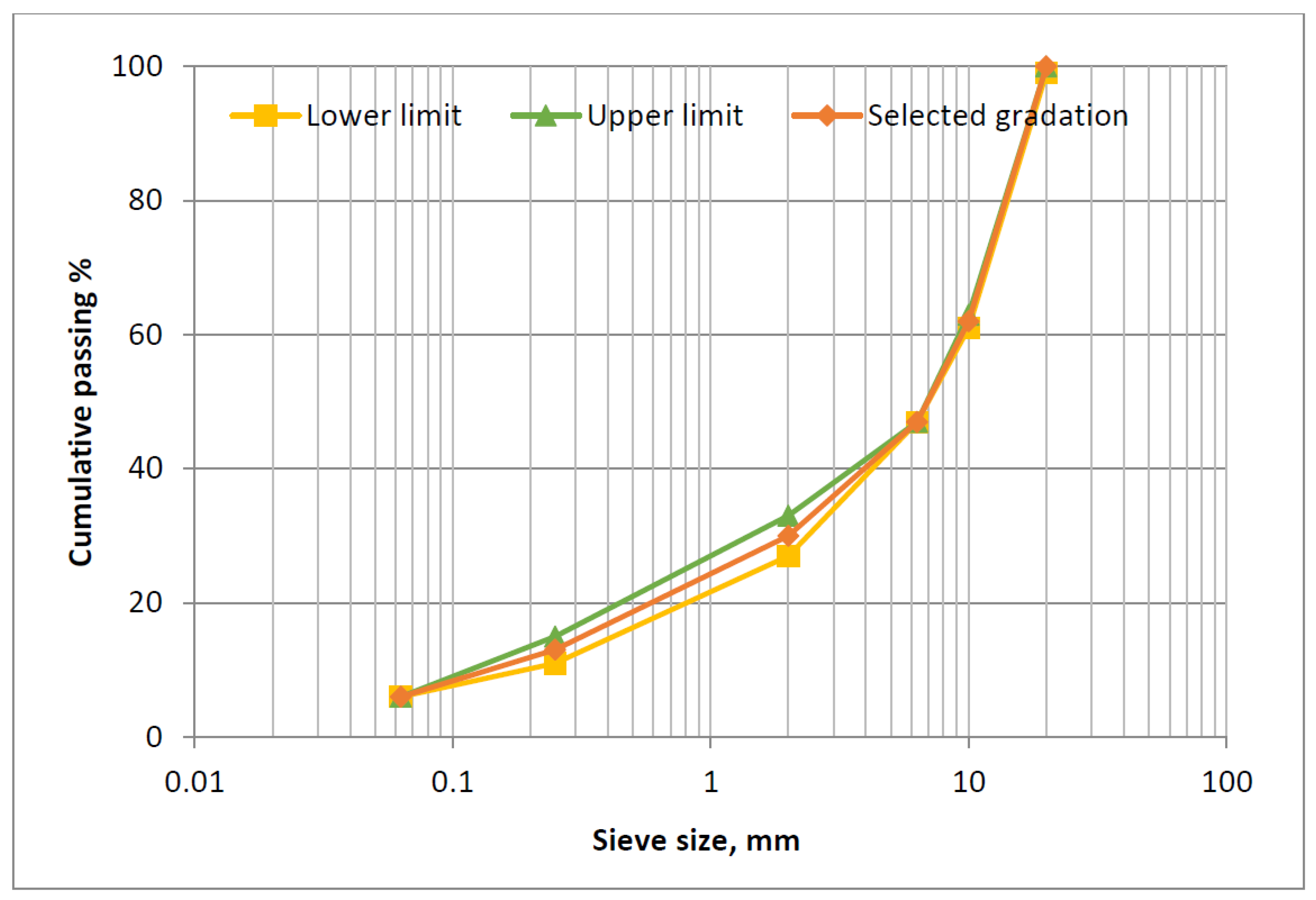
- Aggregate
- (b) Bitumen emulsion and bitumen
- (c) Fillers
2.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of Fillers
2.3. Sample Preparation and Conditioning
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Indirect Tensile Stiffness Modulus (ITSM)
2.4.2. Resistance to Permanent Deformation
2.4.3. Resistance to Fatigue (Four-Point Bending Test)
3. Results and Discussion
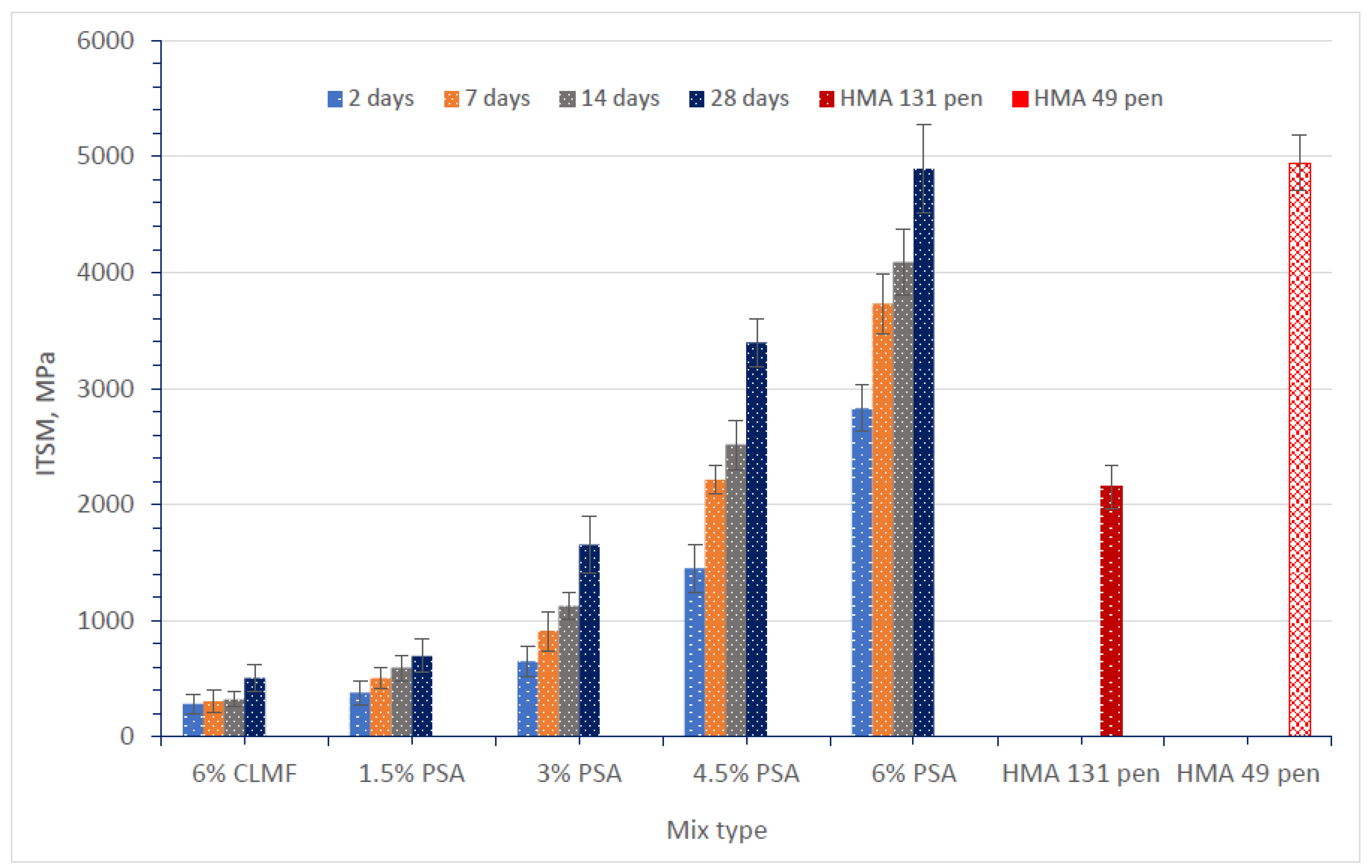
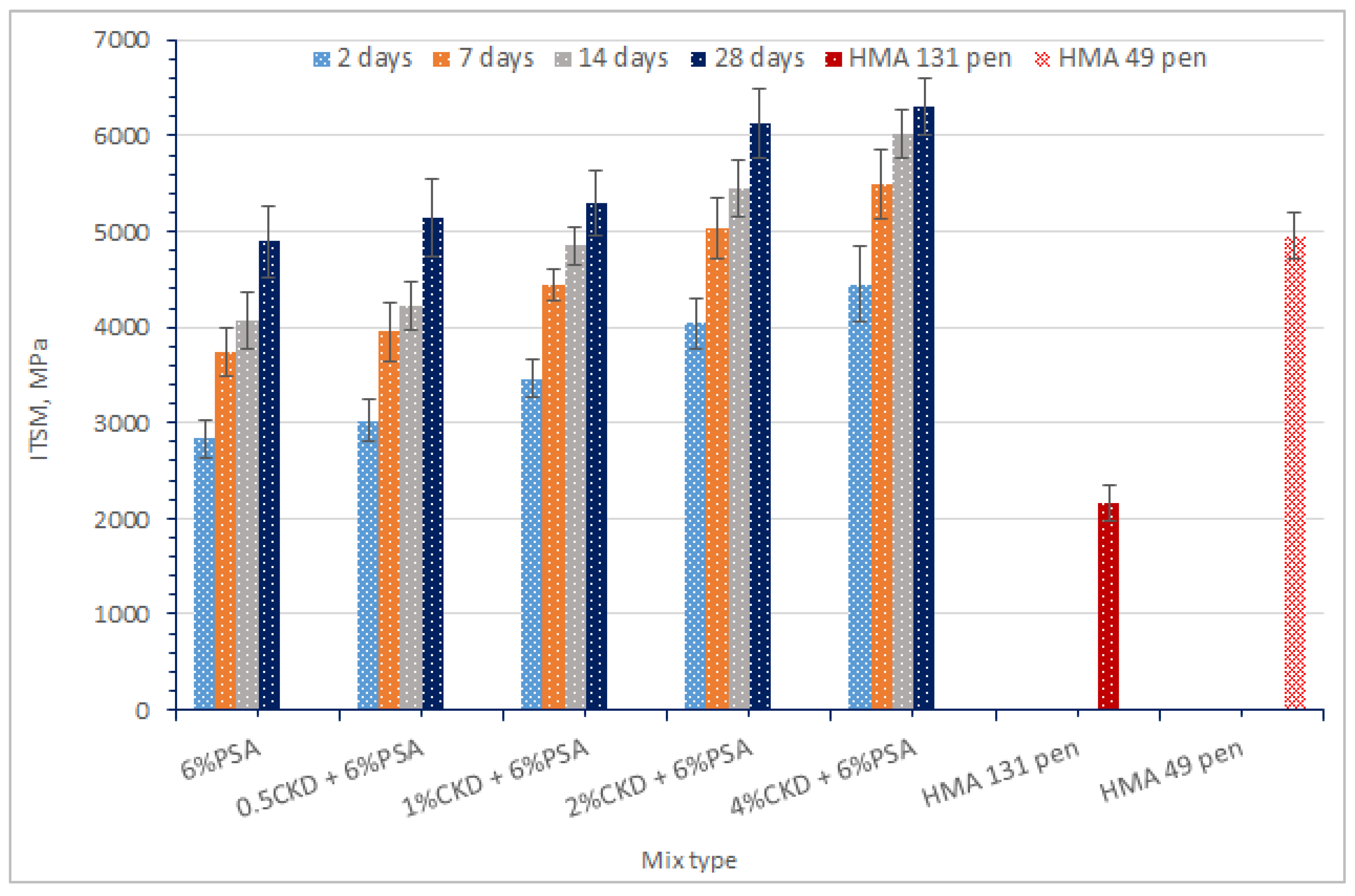
3.1. Influence of Replacing the Traditional Mineral Filler with PSA
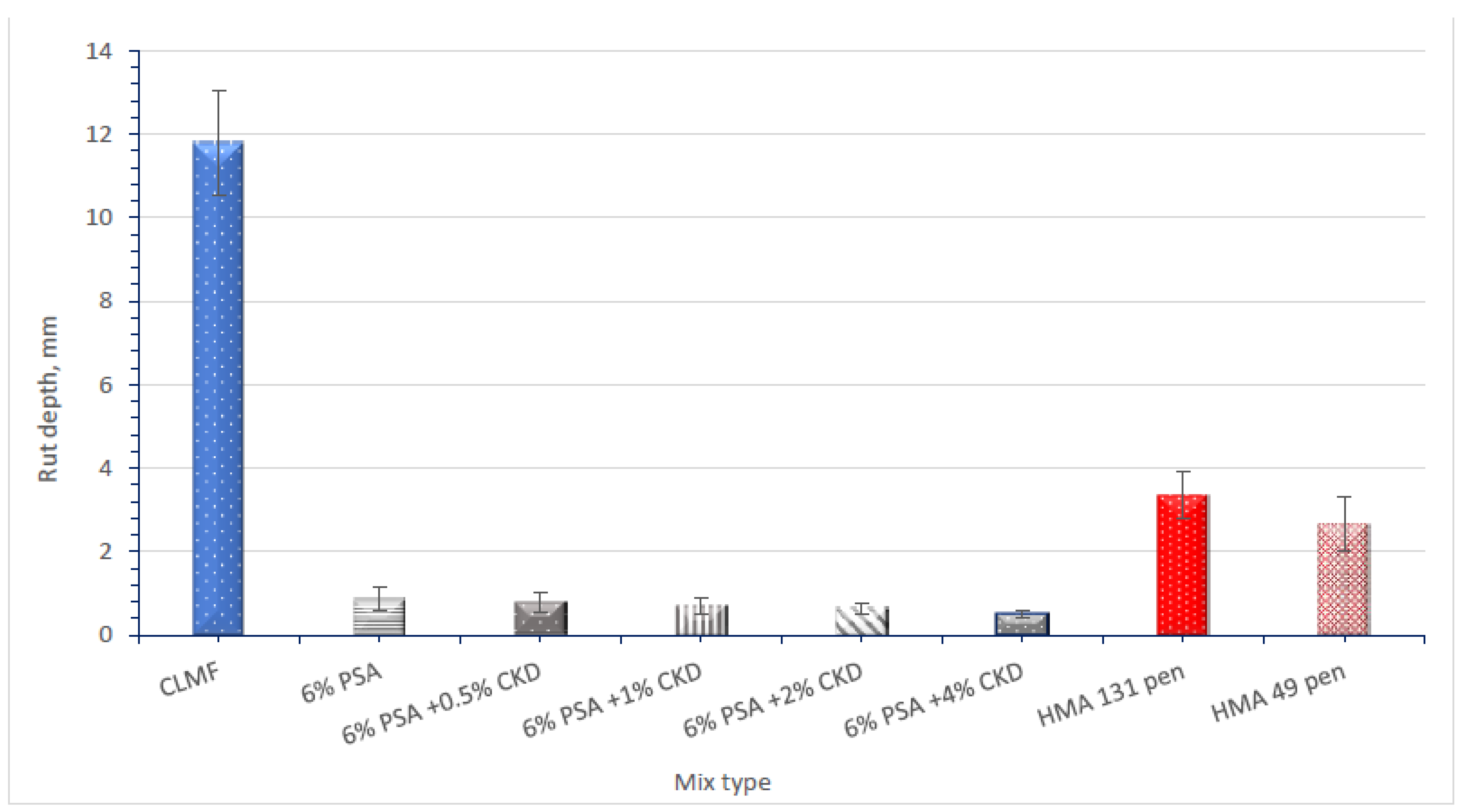
3.2. Wheel Track Test Results at 45 °C
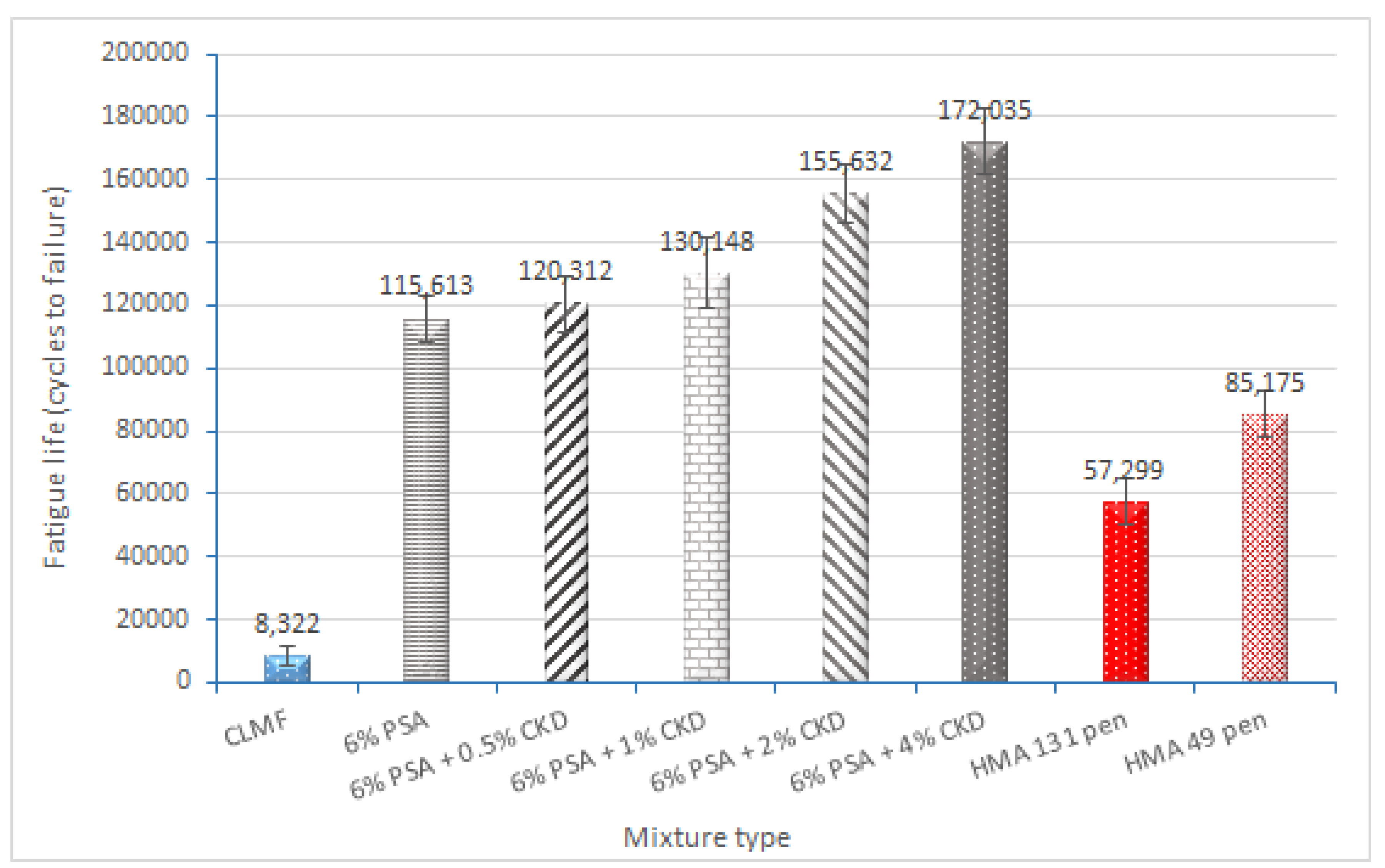
3.3. Resistance to Fatigue Results
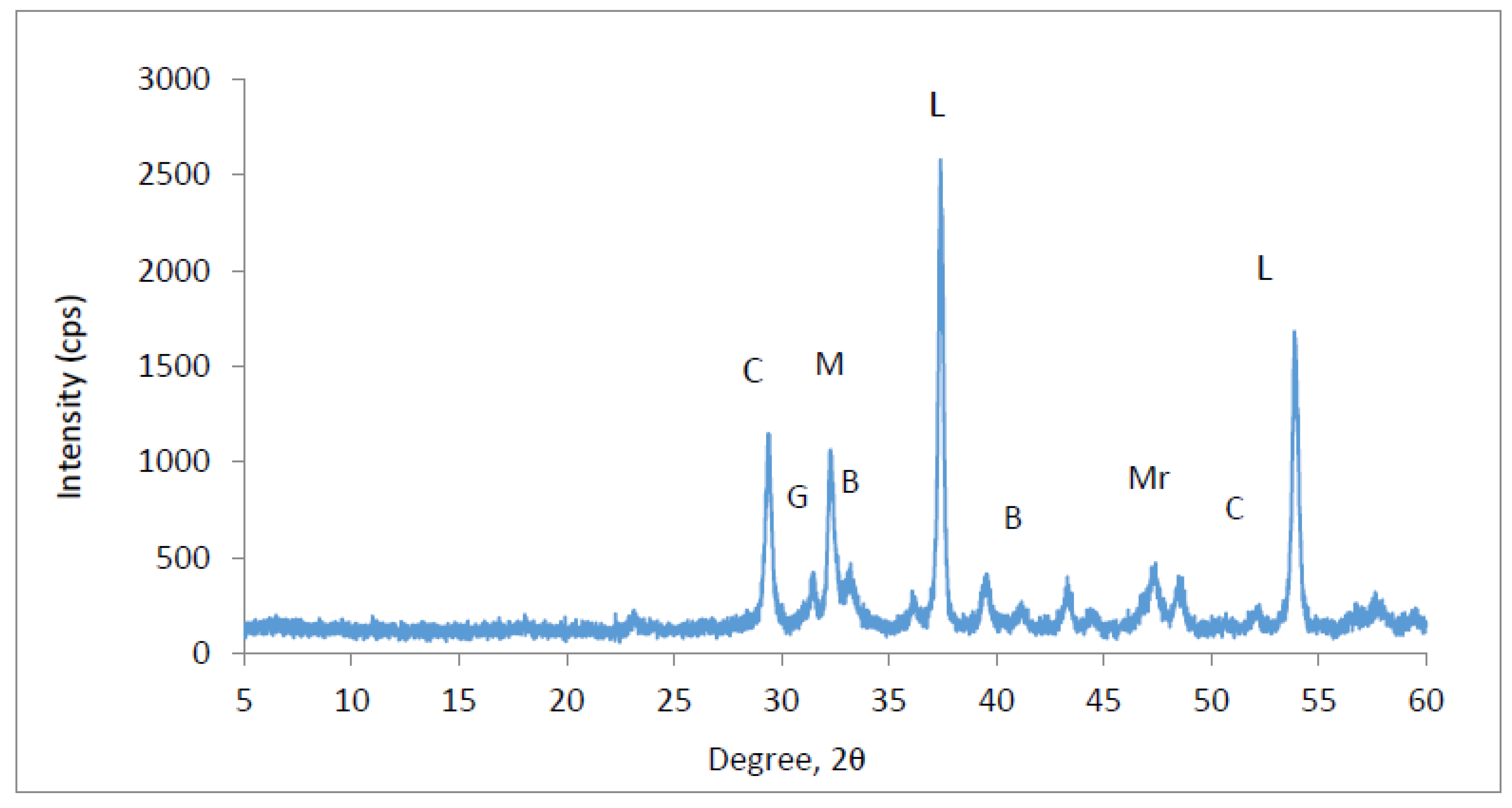
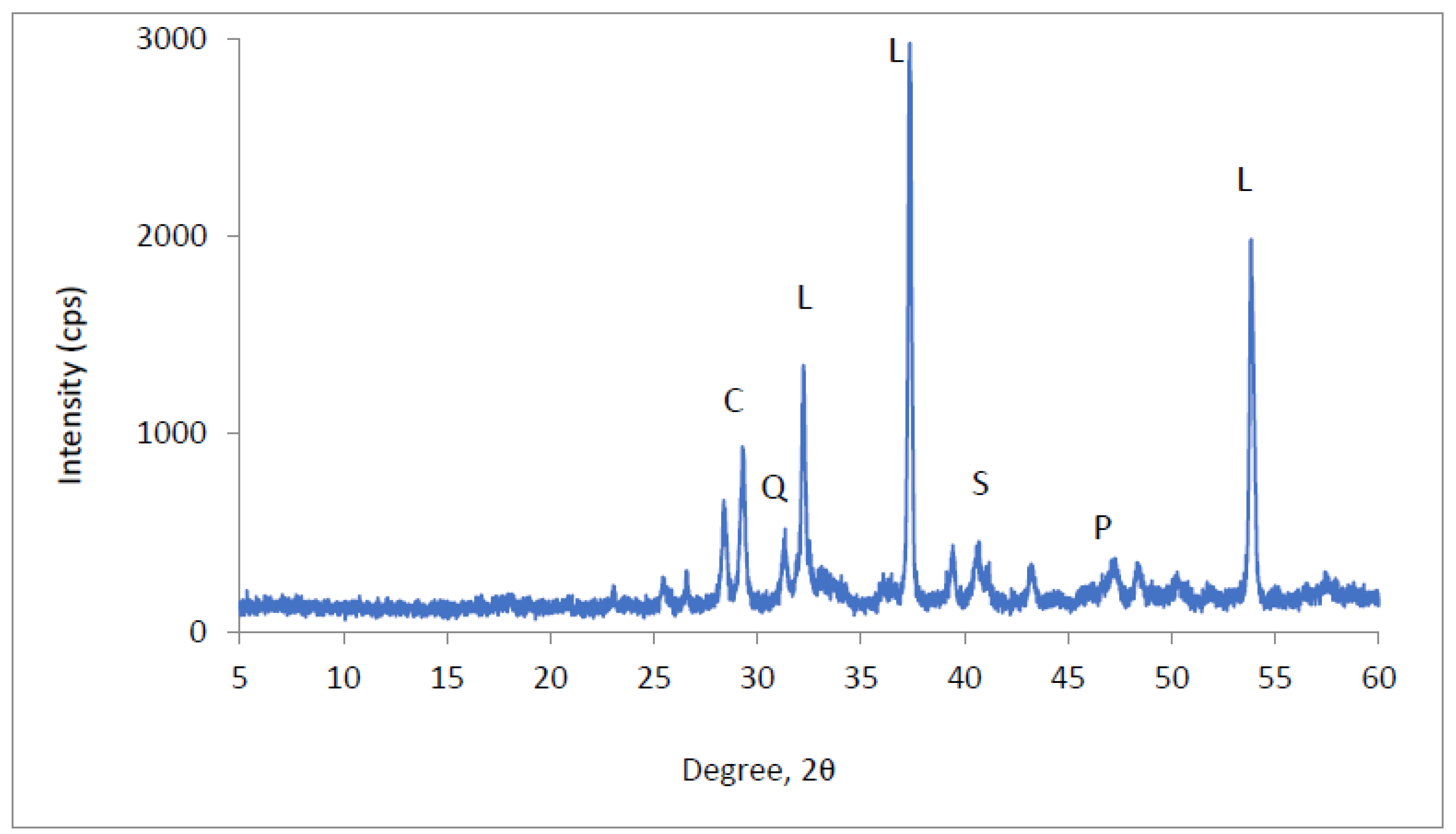
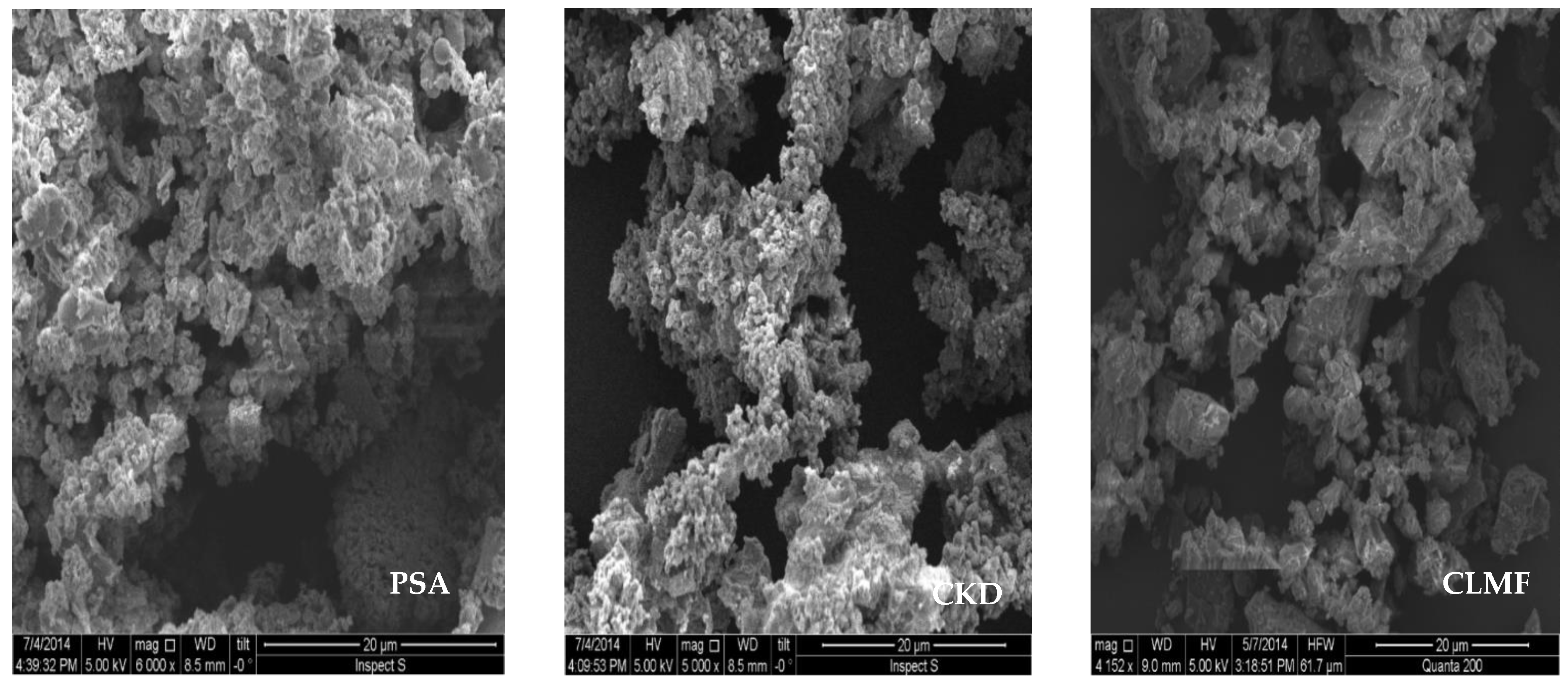
3.4. SEM Observation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- PSA and CKD behave as secondary binding materials in CBEM binder course mixes, where hydration is essential to activate the CaO.
- (2)
- PSA and CKD tend to accelerate the emulsion’s breaking and coalescence. The results have shown that combining high alkali material with a high calcium hydroxide filler PSA, improves the performance of PSA significantly.
- (3)
- After 10,000 cycles at 45 °C, CBEM with CLMF performed poorly in wheel track testing, while CBEM containing PSA and CKD showed an improved performance in terms of permanent deformation. At 45 °C, these mixtures form a cohesive dense microstructure by forming hydration products, meaning that they were more resistant to rutting. As a result, this mix is appropriate for usage in hot areas and on heavily trafficked highways.
- (4)
- The addition of PSA and CKD to CBEM improves fatigue performance considerably. In comparison to conventional CBEM with CMLF and CBEM with PSA and CKD, as well as both grades of hot asphalt concrete, it had a longer fatigue life in four-point bending tests at strains of 150 microstrain. This enhancement can be linked to the newly produced mixture’s cohesive and better interlocking integral microstructure, as well as the production of a rich binding paste in the hydration products.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Busaltan, S.; Al Nageim, H.; Atherton, W.; Sharples, G. Mechanical properties of an upgrading cold-mix asphalt using waste materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahed, T.; Dulaimi, A.; Shanbara, H.K.; Al Nageim, H.J.S. The impact of cement kiln dust and cement on cold mix asphalt characteristics at different climate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Shanbara, H.K.; Al-Rifaie, A.J.C.; Materials, B. The mechanical evaluation of cold asphalt emulsion mixtures using a new cementitious material comprising ground-granulated blast-furnace slag and a calcium carbide residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Wang, Y.; Leng, Z.; Zhong, J. Influence of ternary blended cementitious fillers in a cold mix asphalt mixture. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, D. Cold Asphalt Materials for Use in the Structural Layers of Roads; Project Report 75; Transport Research Laboratory: Berkshire, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, P. Evaluation, Prediction and Enhancement of HAUCphalt-A Cold Mix Asphalt Technology; University of Ulster: Belfast, Northern Ireland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, X. Reduction of moisture susceptibility of cold asphalt mixture with Portland cement and bentonite nanoclay additives. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Schito, G.; Cui, Q. VOC emissions from asphalt pavement and health risks to construction workers. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Asphalt mixtures emission and energy consumption: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.d.C.; Moreno, F.; Martínez-Echevarría, M.J.; Martínez, G.; Vázquez, J.M. Comparative analysis of emissions from the manufacture and use of hot and half-warm mix asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autelitano, F.; Bianchi, F.; Giuliani, F. Airborne emissions of asphalt/wax blends for warm mix asphalt production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autelitano, F.; Giuliani, F. Analytical assessment of asphalt odor patterns in hot mix asphalt production. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Singh, B. Cold mix asphalt: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.S.; Chandrappa, A.K.; Sahoo, U.C. Design and performance of cold mix asphalt—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.I.; Mohammed, M.K.; Thom, N.; Parry, T. Characterisation of high-performance cold bitumen emulsion mixtures for surface courses. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.A.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Nemaa, Z.K.; Abo Almaali, Y.; Saghafi, B.; Al-Kafaji, M.; Al-Jawad, O.; Al-Yasari, R. Evaluating the cracking performance indices of half-warm mix asphalt comprising waste glass. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Hanz, A.; Bahia, H. Measuring moisture susceptibility of cold mix asphalt with a modified boiling test based on digital imaging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Wei, C. Long-term performance and microstructure of asphalt emulsion cold recycled mixture with different gradations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.A.; Al-Busaltan, S.F.; Almuhanna, R.R. Characterize cold bituminous emulsion mixtures incorporated ordinary portland cement filler for local surface layer. J. Univ. Babylon 2018, 26, 247–263. [Google Scholar]
- Al Nageim, H.; Al-Busaltan, S.F.; Atherton, W.; Sharples, G. A comparative study for improving the mechanical properties of cold bituminous emulsion mixtures with cement and waste materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, S.S.; Huang, W. Experimental study of cement-asphalt emulsion composite. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Lura, P.; Partl, M.N.; Jerjen, I. Influence of cement content and environmental humidity on asphalt emulsion and cement composites performance. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 1275–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.K.; Kalla, P.; Jethoo, A.S.; Agrawal, R.; Singh, H. Sustainable use of waste in flexible pavement: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.C.; Martínez, G.; Baena, L.; Moreno, F. Warm mix asphalt: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 24, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Sadique, M. The development of a novel, microwave assisted, half-warm mixed asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraldo, E.; Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Mariani, E. Effect of reinforced fibers on stiffness of recycled asphalt half-warm emulsion mixes. In Sustainability, Eco-Efficiency, and Conservation in Transportation Infrastructure Asset Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.E.; Zamhari, K.A.; Hainin, M.R.; Oluwasola, E.A.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Hassan, N.A. High temperature characteristics of warm mix asphalt mixtures with nanoclay and chemical warm mix asphalt modified binders. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 122, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.J.C.; Materials, B. Mechanical properties and reaction characteristics of asphalt emulsion mixture with activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Assessment the performance of cold bituminous emulsion mixtures with cement and supplementary cementitious material for binder course mixture. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Li, H.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Q. Properties of cold mix asphalt mixtures with reclaimed granular aggregate from crushed PCC pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalan, A.A.; Al-Sahaf, N.A.; Al-Hdabi, A. Investigation of binder course cold asphalt emulsion mixture properties containing cement and GGBS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering Technologies, Najaf, Iraq, 23–24 April 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012014. [Google Scholar]
- Shanbara, H.K.; Dulaimi, A.; Al-Mansoori, T.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Herez, M.; Sadique, M.; Abdel-Wahed, T. The future of eco-friendly cold mix asphalt. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Veropalumbo, R.; Oreto, C.; Biancardo, S.A.; Abbondati, F.; Viscione, N.J.C. Verifying the mechanical performance of cold and hot asphalt mastics containing jet grouting waste as a filler. Coatings 2021, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoori Kadhim, M.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Dulaimi, A.; Sadique, M.; Al Nageim, H.; Al-Kafaji, M.; Al-Yasari, R. Developing a sustainable, post treated, half warm mix asphalt for structural surface layer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaimi, A.; Al Nageim, H.; Ruddock, F.; Seton, L. Microanalysis of alkali-activated binary blended cementitious filler in a novel cold binder course mixture. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Lyon, France, 17–21 April 2016; pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Malaiskiene, J.; Kizinievic, O.; Kizinievic, V.; Boris, R.J.C.; Materials, B. The impact of primary sludge from paper industry on the properties of hardened cement paste and mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloochi, H.; Aponte, D.; Barra, M. Waste paper ash as a hydraulic road binder: Hydration, mechanical and leaching considerations. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, R.; Rajor, A. Use of cement kiln dust in cement concrete and its leachate characteristics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 61, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Rehman, S.; Al-Amoudi, O. Literature review on cement kiln dust usage in soil and waste stabilization and experimental investigation. Int. J. Res. Rev. Appl. Sci. 2011, 7, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Merzah, S.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Al Nageim, H. Investigating the feasibility of using cement Kiln dust in cold bituminous emulsion asphalt. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Civil Engineering, Architecture and Urban Development, Tehran, Iran, 27–29 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Read, J.; Whiteoak, D. The Shell Bitumen Handbook, 5th ed.; Shell Bitumen: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardization. BS EN 13108: Part 1. Bituminous Mixtures Materials Specification-Asphalt Concrete; British Standard Institution: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaids, A. Construction and performance of dense cold bitumen mixtures as strengthening over layer and surface layer. In Proceedings of the 1st European Symposium on Performance and Durability of Bituminous Materials, London, UK, March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Shah, S.P. Hydration and properties of novel blended cements based on cement kiln dust and blast furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Singh, K.L. Accelerated curing potential of cold mix asphalt using silica fume and hydrated lime as filler. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asphalt Institute. Asphalt Cold Mix Manual, Manual Series No.14 (MS-14), 3rd ed.; Asphalt Institute: Lexington, KY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Serfass, J.-P.; Poirier, J.-E.; Henrat, J.-P.; Carbonneau, X. Influence of curing on cold mix mechanical performance. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, K.J. Mix Design Considerations for Cold and Half-Warm Bituminous Mixes with Emphasis of Foamed Bitumen. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardization. BS EN 12697: Part 26. Bituminous Mixtures-Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt-Stiffness; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y. Performance evaluation of asphalt modified with steel slag powder and waste tire rubber compounds. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standardization. BS EN 12697: Part 22. Bituminous Mixtures-Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt-Wheel Tracking Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardization. PD 6691: Guidance on the Use of BS EN 13108 Bituminous Mixtures–Material Specifications; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thanaya, I. Improving the performance of cold bituminous emulsion mixtures (CBEMs) incorporating waste materials. In Performance of Bituminous and Hydraulic Materials in Pavements; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.F.; Needham, D. A study of cement modified bitumen emulsion mixtures. In Proceedings of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists (AAPT), Reno, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sadique, M.; Al-Nageim, H. Hydration kinetics of a low carbon cementitious material produced by physico-chemical activation of high calcium fly ash. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2012, 10, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaunsali, P.; Peethamparan, S. Evolution of strength, microstructure and mineralogical composition of a CKD–GGBFS binder. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, M.; Coakley, E. The influence of physico-chemical properties of fly ash and CKD on strength generation of high-volume fly ash concrete. Adv. Cem. Res. 2016, 28, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone filler | PD, Mg/m3 | 2.57 |
| Fine aggregate | BPD, Mg/m3 | 2.54 |
| APD, Mg/m3 | 2.65 | |
| WA, % | 1.7 | |
| Coarse aggregate | BPD, Mg/m3 | 2.62 |
| APD, Mg/m3 | 2.67 | |
| WA, % | 0.8 |
| Description | (C 60 B 5) Bitumen Emulsion |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Black to dark brown liquid |
| Type | Cationic |
| Bitumen content | 60% |
| Base bitumen | 100/150 pen |
| Base bitumen, 1/10 mm | 147 pen |
| Softening point, °C | 40.5 |
| Relative density at 15 °C, g/mL | 1.05 |
| Boiling point, °C | 100 |
| Bituminous Binder 49 | Bituminous Binder 131 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Property | Value | Property | Value |
| Appearance | Black | Appearance | Black |
| Density at 25 °C | 1.02 | Density at 25 °C | 1.05 |
| Softening point, °C | 51.5 | Softening point, °C | 43.5 |
| Penetration at 25 °C | 49 | Penetration at 25 °C | 131 |
| Filer Type | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | Fe2O3 | SO3 | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSA | 70.276 | 24.671 | 2.209 | 2.721 | 0 | 0.342 | 0.335 | 1.811 |
| CKD | 59.319 | 20.192 | 0.882 | 1.287 | 1.551 | 3.852 | 4.88 | 2.177 |
| CLMF | 76.36 | 16.703 | 0 | 0.981 | 0 | 0.096 | 0.348 | 2.258 |
| Item | Range |
|---|---|
| Specimen temperature conditioning | 4 h before testing |
| Rise time | 124 ± 4 ms |
| Specimen thickness mm | 63 ± 3 |
| Transient peak horizontal deformation | 5 μm |
| Specimen diameter mm | 100 ± 3 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.35 |
| Loading time | 3–300 s |
| No. of conditioning plus | 5 |
| No. of test plus | 5 |
| Test temperature °C | 20 ± 0.5 |
| Compaction Marshall | 50 × 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulaimi, A.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Kadhim, M.A.; Al-Khafaji, R.; Sadique, M.; Al Nageim, H.; Ibrahem, R.K.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Pawłowski, W.; Mahdi, J.M. A Sustainable Cold Mix Asphalt Mixture Comprising Paper Sludge Ash and Cement Kiln Dust. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610253
Dulaimi A, Al-Busaltan S, Kadhim MA, Al-Khafaji R, Sadique M, Al Nageim H, Ibrahem RK, Awrejcewicz J, Pawłowski W, Mahdi JM. A Sustainable Cold Mix Asphalt Mixture Comprising Paper Sludge Ash and Cement Kiln Dust. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):10253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610253
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulaimi, Anmar, Shakir Al-Busaltan, Mustafa Amoori Kadhim, Ruqayah Al-Khafaji, Monower Sadique, Hassan Al Nageim, Raed Khalid Ibrahem, Jan Awrejcewicz, Witold Pawłowski, and Jasim M. Mahdi. 2022. "A Sustainable Cold Mix Asphalt Mixture Comprising Paper Sludge Ash and Cement Kiln Dust" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 10253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610253
APA StyleDulaimi, A., Al-Busaltan, S., Kadhim, M. A., Al-Khafaji, R., Sadique, M., Al Nageim, H., Ibrahem, R. K., Awrejcewicz, J., Pawłowski, W., & Mahdi, J. M. (2022). A Sustainable Cold Mix Asphalt Mixture Comprising Paper Sludge Ash and Cement Kiln Dust. Sustainability, 14(16), 10253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610253










