Dynamic Interdependence between Anglers and Fishes in Spatially Coupled Inland Fisheries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
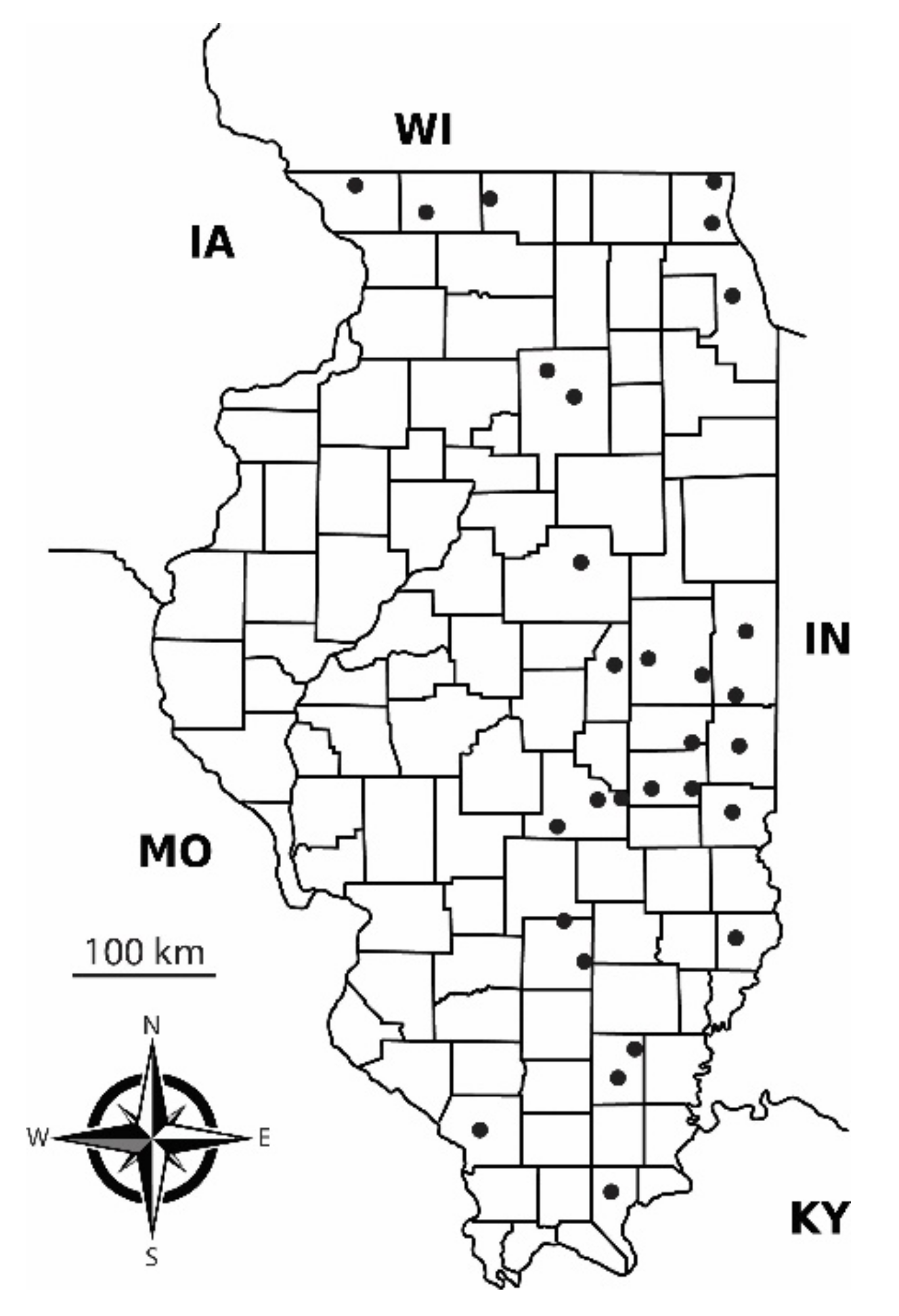
2.1. Characteristics of the Angling Landscape
2.2. Fish Abundance
2.3. Model Development and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Recreational Angling Landscape
3.2. Model Estimation and Interpretation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooke, S.J.; Cowx, I.G. The role of recreational fishing in global fish crises. BioScience 2004, 54, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Cooke, S.J. Recreational fisheries: Socioeconomic importance, conservation issues and management challenges. In Recreational Hunting, Conservation and Rural Livelihoods: Science and Practice; Dickson, B., Hutton, J., Adams, W.A., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher, K.; Westlund, L.; Hoshino, E.; Mills, D.; Willmann, R.; de Graaf, G.; Brummett, R. Hidden Harvest: The Global Contribution of Capture Fisheries; Report No.66469-GLB; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10986/11873 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Arlinghaus, R.; Tillner, R.; Bork, M. Explaining participation rates in recreational fishing across industrialized countries. Fish. Manage. Ecol. 2015, 22, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcomme, R.L.; Cowx, I.G.; Coates, D.; Béné, C.; Funge-Smith, S.; Halls, A.; Lorenzen, K. Inland capture fisheries. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2010, 365, 2881–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, J.R.; Sullivan, M.; Cox, S.; Lester, N.P.; Walters, C.J.; Parkinson, E.A.; Shuter, B.J. Canada’s recreational fisheries: The invisible collapse? Fisheries 2002, 27, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; Abell, R.; Hogan, Z.E.B.; Revenga, C.; Taylor, B.W.; Welcomme, R.L.; Winemiller, K. Overfishing of inland waters. BioScience 2005, 55, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Cowx, I.G. Contrasting recreational and commercial fishing: Searching for common issues to promote unified conservation of fisheries resources and aquatic environments. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 128, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embke, H.S.; Rypel, A.L.; Carpenter, S.R.; Sass, G.G.; Ogle, D.; Cichosz, T.; Hennessy, J.; Essington, T.E.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Production dynamics reveal hidden overharvest of inland recreational fisheries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24676–24681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Population Division. The World’s Cities in 2016—Data Booklet ST/ESA/SER.A/392; UN: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, S.J.; Murchie, K.J. Status of aboriginal, commercial and recreational inland fisheries in North America: Past, present and future. Fish. Manage. Ecol. 2015, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Abbott, J.K.; Fenichel, E.P.; Carpenter, S.R.; Hunt, L.M.; Alós, J.; Klefoth, T.; Cooke, S.J.; Hilborn, R.; Jensen, O.P.; et al. Governing the recreational dimension of global fisheries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5209–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of the Interior; US Fish and Wildlife Service; US Department of Commerce; US Census Bureau. National Survey of Fishing, Hunting, and Wildlife-Associated Recreation; FHW/11-NAT (RV); Fish & Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Youn, S.J.; Taylor, W.W.; Lynch, A.J.; Cowx, I.G.; Beard, T.D., Jr.; Bartley, D.; Wu, F. Inland capture fishery contributions to global food security and threats to their future. Global Food Secur. 2014, 3, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Cooke, S.J.; Deines, A.M.; Bower, S.D.; Bunnell, D.B.; Cowx, I.G.; Rogers, M.W. The social, economic, and environmental importance of inland fish and fisheries. Environ. Rev. 2016, 242, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Twardek, W.M.; Lennox, R.J.; Zolderdo, A.J.; Bower, S.D.; Gutowsky, L.F.; Beard, D. The nexus of fun and nutrition: Recreational fishing is also about food. Fish Fish. 2018, 192, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R. Overcoming human obstacles to conservation of recreational fishery resources, with emphasis on central Europe. Environ. Conserv. 2006, 33, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Taylor, W.W. Complexity of coupled human and natural systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, E.A.; Post, J.R.; Cox, S.P. Linking the dynamics of harvest effort to recruitment dynamics in a multistock, spatially structured fishery. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Brock, W. Spatial complexity, resilience, and policy diversity: Fishing on lake-rich landscapes. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.R. Resilient recreational fisheries or prone to collapse? A decade of research on the science and management of recreational fisheries. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2013, 20, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.M.; Sutton, S.G.; Arlinghaus, R. Illustrating the critical role of human dimensions research for understanding and managing recreational fisheries within a social-ecological system framework. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2013, 20, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, S.; Beardmore, B.; Haider, W.; Dieckmann, U.; Arlinghaus, R. Ecological, angler, and spatial heterogeneity drive social and ecological outcomes in an integrated landscape model of freshwater recreational fisheries. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2019, 27, 170–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.M.; Arlinghaus, R.; Lester, N.; Kushneriuk, R. The effects of regional angling effort, angler behavior, and harvesting efficiency on landscape patterns of overfishing. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2555–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, H.G.; Allen, M.S.; Camp, E.V.; Cole, N.; Hunt, L.M.; Matthias, B.; Arlinghaus, R. Understanding and managing social-ecological feedbacks in spatially structured recreational fisheries: The overlooked behavioral dimension. Fisheries 2016, 419, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardmore, B.; Haider, W.; Hunt, L.M.; Arlinghaus, R. The importance of trip context for determining primary angler motivations: Are more specialized anglers more catch-oriented than previously believed? N. Am J. Fish. Manag. 2011, 31, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Alós, J.; Beardmore, B.; Daedlow, K.; Dorow, M.; Fujitani, M.; Johnston, F. Understanding and managing freshwater recreational fisheries as complex adaptive social-ecological systems. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2017, 251, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.R.; Persson, L.; Parkinson, E.V.; Kooten, T.V. Angler numerical response across landscapes and the collapse of freshwater fisheries. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurin, J.B.; Borer, E.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Anderson, K.; Blanchette, C.A.; Broitman, B.; Halpern, B.S. A cross-ecosystem comparison of the strength of trophic cascades. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, E.T.; Halpern, B.S.; Seabloom, E.W. Asymmetry in community regulation: Effects of predators and productivity. Ecology 2006, 87, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.F.; Baxter, C.V.; Marcarelli, A.M.; Wipfli, M.S. Effects of experimentally added salmon subsidies on resident fishes via direct and indirect pathways. Ecosphere 2016, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of the Interior; US Fish and Wildlife Service; US Department of Commerce; US Census Bureau. 2006 National Survey of Fishing, Hunting, and Wildlife-Associated Recreation—Illinois; FHW/06-IL; Fish & Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Stein, J.A.; Illyes, R.F.; Miller-Ishmael, L.; Carroll, B.; McNamara, T.; Claussen, J.; Philipp, D.P. Database Management and Analysis of Fisheries in Illinois; INHS Center for Aquatic Ecology 20041; Illinois Natural History Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 1–154. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2142/10467 (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Stein, J.A.; Illyes, R.F.; McNamara, T.; Miller-Ishmael, L.; Carroll, B.; Claussen, J.; Philipp, D.P. Database Management and Analysis of Fisheries in Illinois; Technical Report CAEC 2005 6; Illinois Natural History Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 2005; pp. 1–166. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2142/10436 (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Stein, J.A.; Illyes, R.F.; McNamara, T.; Miller-Ishmael, L.; Carroll, B.; Claussen, J.; Philipp, D.P. Database management and analysis of Fisheries in Illinois; Technical Report CAEC 2006 2; Illinois Natural History Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 2006; pp. 1–130. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2142/10090 (accessed on 4 August 2019).
- Papenfuss, J.T.; Phelps, N.; Fulton, D.; Venturelli, P.A. Smartphones reveal angler behavior: A case study of a popular mobile fishing application in Alberta, Canada. Fisheries 2015, 40, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, E.V.; Ahrens, R.N.; Crandall, C.; Lorenzen, K. Angler travel distances: Implications for spatial approaches to marine recreational fisheries governance. Mar. Policy 2018, 87, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, M.J.; Stein, J.; Oplinger, R.W.; Aday, D.D.; Hoxmeier, J.W.; Claussen, J.E.; Philipp, D.P.; Wahl, D.H. Quality Management of Bluegill: Factors Affecting Population Size Structure; Aquatic Ecology Technical Report; Illinois Natural History Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 2007; Volume 17, pp. 1–160. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, J.B. Structural Equation Modeling and Natural Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 1–365. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.R.; Chizinski, C.J.; Pope, K.L. Reservoir area of influence and implications for fisheries management. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2015, 35, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, D.L.; Sager, C. Managing hybrid bluegill fisheries: Estimating and predicting the effects of young anglers. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2004, 44, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Siepker, M.J.; Ostrand, K.G.; Cooke, S.J.; Philipp, D.P.; Wahl, D.H. A review of the effects of catch-and-release angling on black bass, Micropterus spp.: Implications for conservation and management of populations. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.; Philipp, D.P. (Eds.) Centrarchid Fishes: Diversity, Biology and Conservation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–560. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, B.; Holling, C.S.; Carpenter, S.; Kinzig, A. Resilience, adaptability and transformability in social-ecological systems. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 92, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennacchioli, D.; Coscia, M.; Rinzivillo, S.; Giannotti, F.; Pedreschi, D. The retail market as a complex system. EPJ Data Sci. 2014, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardmore, B.; Haider, W.; Hunt, L.M.; Arlinghaus, R. Evaluating the ability of specialization indicators to explain fishing preferences. Leisure Sci. 2013, 35, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.B.; Hartter, J.; Boag, A.E.; Jain, M.; Stevens, K.; Ann Nicholas, K.; Liu, J. Top 40 questions in coupled human and natural systems CHANS research. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 222, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, P.C. Experimental analysis of a reduced daily bluegill limit in Minnesota. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2005, 25, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, L.M.; Longoni, M.; LeBlanc, C.L.; Wali, A. Anglers’ appraisals of the risks of eating sport-caught fish from industrial areas: Lessons from Chicago’s Calumet region. Res. Human Ecol. 2008, 15, 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, F.D.; Arlinghaus, R.; Dieckmann, U. Diversity and complexity of angler behaviour drive socially optimal input and output regulations in a bioeconomic recreational-fisheries model. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 1507–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenichel, E.P.; Abbott, J.K.; Huang, B. Modelling angler behaviour as a part of the management system: Synthesizing a multi-disciplinary literature. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Cooke, S.J.; Lyman, J.; Policansky, D.; Schwab, A.; Suski, C.; Thorstad, E.B. Understanding the complexity of catch-and-release in recreational fishing: An integrative synthesis of global knowledge from historical, ethical, social, and biological perspectives. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2007, 15, 75–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Volume I: Comprehensive Tables; ST/ESA/SER.A/399; UN: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, S.P.; Beard, T.D.; Walters, C. Harvest control in open-access sport fisheries: Hot rod or asleep at the reel? Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 70, 749–761. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, S.; Arlinghaus, R.; Dieckmann, U. Foraging on spatially distributed resources with sub-optimal movement, imperfect information, and travelling costs: Departures from the ideal free distribution. Oikos 2010, 119, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Landres, P.B.; Morgan, P.; Swanson, F.J. Overview of the use of natural variability concepts in managing ecological systems. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- MEA. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Global Assessment Reports; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, C.; Ovando, D.; Clavelle, T.; Strauss, C.K.; Hilborn, R.; Melnychuk, M.C.; Branch, T.A.; Gaines, S.D.; Szuwalski, C.S.; Cabral, R.B.; et al. Global fishery prospects under contrasting management regimes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5125–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, R.I.; Forman, R.T.; Kareiva, P.; Neugarten, R.; Salzer, D.; Fisher, J. Urban effects, distance, and protected areas in an urbanizing world. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2009, 93, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
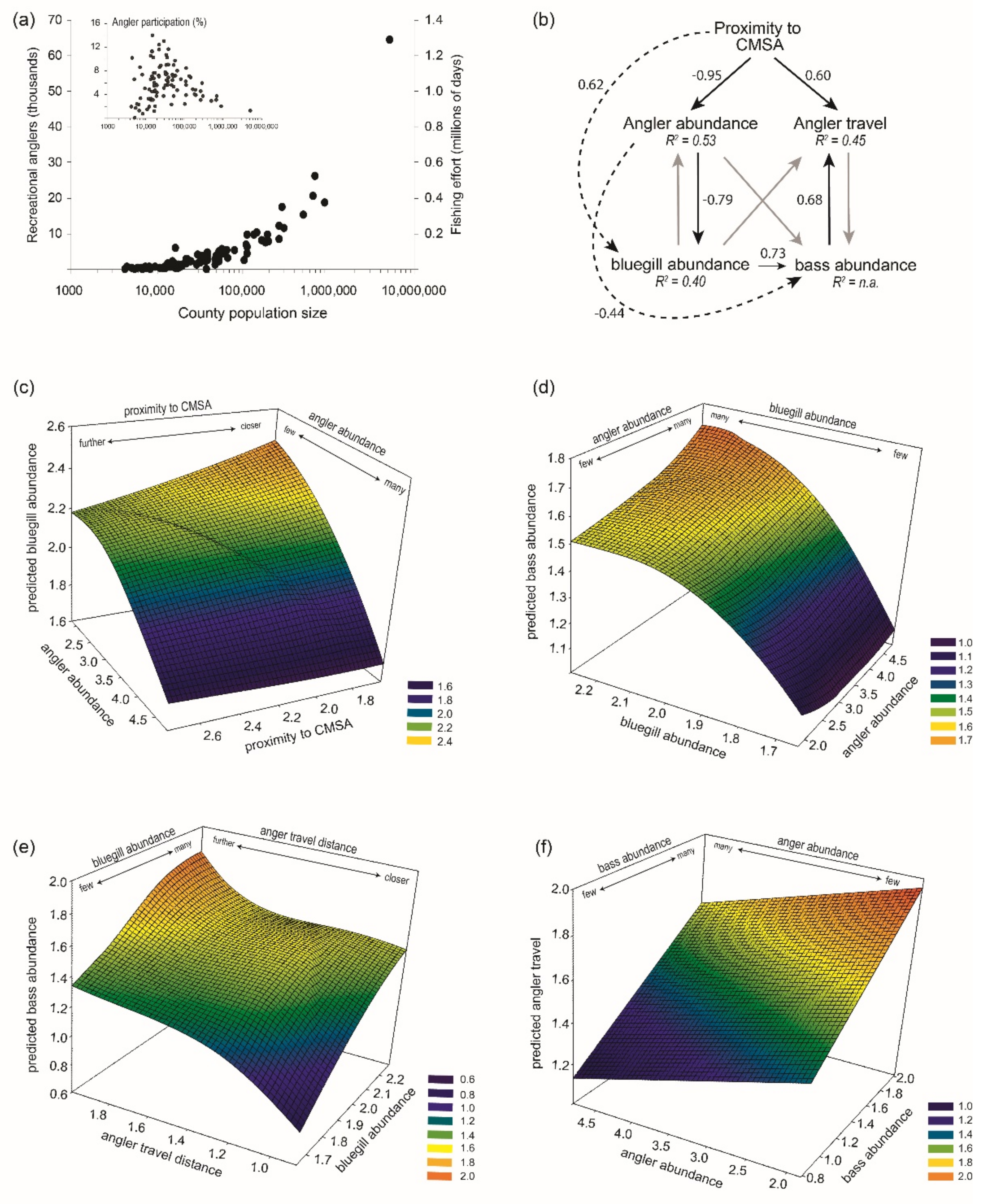
| Response | β | R.W. | S.E. | C.R. | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angler abundance | Proximity | −0.95 | −2.29 | 0.48 | −4.70 | <0.001 |
| Angler travel | Proximity | 0.60 | 0.51 | 0.17 | 3.11 | 0.002 |
| bluegill | Angler abund. | −0.79 | −0.21 | 0.05 | −4.32 | <0.001 |
| bass | bluegill | 0.73 | 0.95 | 0.49 | 1.95 | 0.050 |
| bass | Angler travel | −0.37 | −0.36 | 0.58 | −0.62 | 0.536 |
| Angler travel | bass | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.34 | 2.05 | 0.041 |
| bass | Angler abund. | 0.18 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.95 | 0.340 |
| Angler abundance | bluegill | 0.16 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 0.63 | 0.530 |
| Angler travel | bluegill | −0.33 | −0.44 | 0.39 | −1.14 | 0.250 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collins, S.F.; Diana, M.J.; Wahl, D.H. Dynamic Interdependence between Anglers and Fishes in Spatially Coupled Inland Fisheries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610218
Collins SF, Diana MJ, Wahl DH. Dynamic Interdependence between Anglers and Fishes in Spatially Coupled Inland Fisheries. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):10218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610218
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollins, Scott F., Matthew J. Diana, and David H. Wahl. 2022. "Dynamic Interdependence between Anglers and Fishes in Spatially Coupled Inland Fisheries" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 10218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610218
APA StyleCollins, S. F., Diana, M. J., & Wahl, D. H. (2022). Dynamic Interdependence between Anglers and Fishes in Spatially Coupled Inland Fisheries. Sustainability, 14(16), 10218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610218





