Abstract
Water pollution from intensive livestock husbandry is a persistent social-ecological problem. Since remedies require attention to the slurry–water nexus among practitioners, the agricultural press is a strategic entry point for agenda setting. Systematic content analysis can provide insights into how farming practices and sustainability issues are communicated, which may influence farmers’ attention to the issue and to potential solutions. To address this question, we present a semantic network analysis of three specialized farming magazines in Germany and analyze their coverage of the slurry–water nexus, in particular relationships of actors and issues and co-occurrence with political events. We used text mining methods in order to analyze a text corpus consisting of 4227 online articles published between 2010 and 2020. Results show that one fifth of all slurry-themed articles contained water-related content. We found a shift over time from dominantly management-oriented content towards a politicized debate with more actors and stronger semantic relationships with water protection constructed as an insulated stand-alone issue. This is accompanied by a shift from thematic reporting to episodic reporting focused on environmental legislation and compliance management. This implies less attention to innovations for water-conserving slurry management. Despite its shortcomings, episodic coverage may open up windows of opportunity to improve communication by experts and policy makers.
1. Introduction
Nutrient surpluses from agricultural land use are a major source of ground- and surface water pollution []. Thirty years after the EU Nitrates Directive went into force, nitrate levels in groundwater are still well above the specified target levels in many areas of the European Union (EU), with particularly high levels in regions with intensive livestock production [,]. A portion of 75% of excess nitrogen in the European Union, which contributes to the degradation of agricultural landscapes, ecosystems, and environmental resources, originates from livestock farming [].
The linkages between nitrogen use and nitrate contamination are generally well understood [] but difficult to measure and predict due to variation in natural and farm processes []. Nitrate pollution is not merely a result of biophysical processes, but of complex social-ecological interlinkages where causal relationships need to be understood to enable effective countermeasures []. We use the term “slurry–water nexus” to denote the mutual relations between farm animal excrements and hydrological issues that may be constructed by farmers who do not necessarily presuppose a one-sided negative relation between slurry and water.
In this context, the agricultural press is an important factor since its issue coverage may both affect and reflect farmers’ awareness and attitudes towards livestock farming and water management [].
The objective of this article is to use a text mining approach to analyze specialized farming magazines in Germany in order to gain insights into the development of media coverage of the slurry–water nexus. We are especially interested in the dynamics of network agenda setting by tracking the magazines’ coverage of the slurry–water nexus. Insights into how the relationship between agricultural practice and environmental issues, in particular water resources, is communicated can point to strategic entry points for policy communication, eventually contributing to potentially more sustainable farming practices. However, our ambition was not to identify or assess how agricultural media influenced farmers’ actual behavior.
The theoretical background for our analysis is media agenda-setting theory [,,], a comprehensive framework that aims to uncover different media strategies that may affect—in our case—agricultural and environmental policy-making []. The basic assumption of a positive relationship between the intensity of media coverage of an issue and its perceived importance among members of the audience has been validated by numerous studies [,].
Three different levels of agenda setting can be analytically distinguished: first, through the choice of issues and actors referred to [], second, by highlighting specific attributes of actors or issues [], and third, through connections made between issues, attributes and actors []. Guo and McCombs [] refer to these relationships as “network agenda setting”. Third-level or network agenda setting implies the assumption that all elements of first and second-level agenda setting are mutually related.
Analyzing all three levels of agenda setting with regard to the slurry–water nexus helps to gain a deeper understanding of how media reflect discourses within the farmers’ community. Changes in discourse over time may indicate shifts in farmers’ awareness of this nexus.
So far, research on agenda setting related to agriculture and the environment in the agricultural press has rarely used text-mining methods. However, such an approach is important to tackle the increasing number of farm media publications. Farming magazines often publish large numbers of articles with unstructured and varying text formats. This makes their systematic analysis challenging. Copyright issues and pay walls constitute additional barriers to both quantitative and qualitative analyses. Recent changes in European and German copyright law, however, require publishers to make their publications available for quantitative analysis, such as text mining, while qualitative content analyses still require approval [].
Analysis of farming magazines accounts for a particularity that sets these specialized publications apart from other types of media. Farmers are familiar with the topics discussed in farm magazines and can refer to personal experience and interpersonal discussion as alternative sources []. Hence, second and third-level agenda setting is likely more relevant than first-level agenda setting. With this article, we aim to contribute to a more systematic understanding of agenda setting in this particular media environment in Germany by examining coverage of the slurry–water nexus between 2010 and 2020, a period of intense public debate about the country’s lackluster implementation of the European Nitrates Directive.
Specifically, this paper aims to address the following research questions (RQ):
RQ 1: How does the representation of issues and attributes related to the slurry–water nexus change over time?
RQ 2: Which relationships between issues and actors are presented and how do they change over time?
RQ 3: Was coverage of the slurry–water nexus related to specific events?
RQ 1 concerns first- and second-level agenda setting, while RQ 2 addresses third-level or network agenda setting. The network structure is shaped by the frequency of links between the elements of agenda setting in media coverage []. If, for example, the issues of slurry and water frequently appear together in media reports, the recipients are likely to perceive these topics as being connected. RQ 3 links the findings to earlier studies which found that reporting in news media, including coverage of environmental issues such as water or climate change, was primarily driven by specific events and represented them within associative networks [,,].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Text Mining
Text mining is a process through which unstructured textual data are retrieved, transformed into a structured format, and analyzed semantically []. Computer-assisted extraction and analysis of information from large amounts of data allow to find patterns that could not be detected by analyzing small samples. Advanced statistical methods are combined to algorithms that are able to discover statistical characteristics of large text corpora. Computer-assisted content analysis techniques reach from basic word counts to supervised and unsupervised machine learning methods which enable a wide array of data exploration from word frequencies to in-depth discourse analysis []. Text mining has become an established method for analyzing various kinds of text for economic, administrative and research purposes [,]. While manual content analysis of large samples would be costly [] text mining, particularly in longitudinal studies, can help to discover shifts in content patterns by capturing developments in word usage and discourse elements over time []. Finally, text mining enables “[b]oosting the empirical credence of analysis” by analyzing large samples rather than “picking cherries” [], i.e., limiting analysis to sub-samples that might not be representative for the text corpus as a whole.
Advanced algorithms for the processing of natural language have been developed by computer scientists and adopted in different academic disciplines. In the social sciences and humanities, e.g., in linguistics, history, or media studies, automated text analysis is a relatively recent field []. Print media studies have used text mining methods to investigate, for example, the construction of terrorism in newspapers [] or the framing of refugees [], discourses of democracy [], or agenda setting related to elections []. Regarding environmental issues in news media, previous text mining studies have analyzed climate change discourses [,] as well as the presentation of environmental threats, such as drought [] or nitrogen pollution []. Altaweel and Bone [], Hori [] and Murphy, et al. [] have examined the coverage of water issues in regional and national newspapers.
Two literature reviews on the application of automated text analysis for food science and nutrition [] and for agriculture [] have shown major efforts to use algorithmic approaches as decision-support tools in agriculture and food processing. Mostly scientific journals are used as a database for research on, for example, extreme weather events in agriculture [], mountain livestock farming [], impacts of environmental and poverty-related factors on sustainable agriculture [], or food security [].
With regard to agriculture, text mining studies have investigated reporting on agricultural biotechnology [], on land use change [], on farm-management decision making [], and on the agri-food sector in German nationwide newspapers [], reporting on COVID-19 and agriculture in Bangladesh [], and the framing of global soybean expansion in EU print media and diverse other sources [].
In this article, we combine three text-mining methods to investigate network agenda setting in the three specialized farming magazines: frequency analysis, semantic network analysis, and concordance analysis which are specified in Section 2.5. Figure 1 illustrates the typical methodological phases of a text mining analysis, which are described in more detail in the following sections.
Figure 1.
Methodological phases in a text mining analysis, source: authors’ diagram.
2.2. Selection of Magazines and Collection of Data
The three most influential specialized farming magazines in Germany were selected for this analysis (top agrar, DLG-Mitteilungen, agrarheute). top agrar has the highest circulation with around 100,000 sold copies, followed by agrarheute with around 40,000 copies and DLG-Mitteilungen with around 19,000 copies distributed. Furthermore, the online editions of top agrar and agrarheute achieve 5,000,000 and 3,000,000 visits per month, respectively, while DLG-Mitteilungen has no online edition [,,]. All three magazines provide specialist information and convey agricultural knowledge for practitioners.
While top agrar and agrarheute cover a broad spectrum of thematic categories, including reports and news about events, politics, society, markets, and trends, DLG-Mitteilungen focuses on reports about production, management, and technology. According to their published media data, all three magazines are particularly read by farm managers, who often operate larger farms [,,].
2.3. Data Extraction and Creation of Text Corpus
In a second step, we extracted the data and created the corpus using the statistical environment R []. top agrar and agrarheute provide an online portal with both freely accessible content and content with costs. Articles are available in html format while articles in DLG-Mitteilungen are available as a pdf that can be downloaded by subscribers.
We applied two different procedures in order to access the articles. We automatically crawled and extracted the html data matching the search term “Gülle” (slurry) from top agrar and agrarheute with the R package rvest [] and the pdf documents from DLG-Mitteilungen with readtext [] and rtika []. There is no one-to-one translation of the German term “Gülle” into English. “Gülle” denotes a mixture of urine and feces with a negligible share of cropped straw addition, and is best represented by the term “liquid slurry”. For greater readability, we use the term “slurry”.
After data extraction, we created the text corpus []. It contains all articles published in the three magazines between 2010 and 2020 that include the term “Gülle”. The text search yielded a total of 4227 articles (2770 from top agrar, 1185 from agrarheute, and 272 from DLG-Mitteilungen), comprising altogether 1,183,027 words. The word share is 56% for top agrar, 21% for agrarheute, and 23% for DLG-Mitteilungen.
2.4. Text Preprocessing
As a preparatory step for the analysis, the text corpus was cleaned and the text was preprocessed. We removed punctuation, numbers, and Unicode symbols, and transformed all words to lower cases to converge similar words with different capitalization using the tm package []. The text was then lemmatized, i.e., word inflections were reduced to their lexical base forms in order to transform all occurrences of the same word stem into one standardized form. We created a separate list to include lemmatizations of specific words that were not included in the original list and to synchronize abbreviations with their corresponding terms (e.g., WFD = Water Framework Directive).
Given our focus on the slurry–water nexus, we were particularly interested in the relation of slurry and water and therefore searched for the terms water, waterbody, waterbodies, groundwater, surface water, river, rivers, brook, brooks, lake, lakes, and drinking water within the text corpus. The selected terms were integrated in a dictionary under the term water resources in order to make the analysis more targeted.
We removed a set of pre-defined and self-defined stopwords (i.e., words that are meaningless for the analysis) []. Furthermore, we removed the search term “Gülle” because it appears in every document and would therefore dominate the results. We then statistically identified multi-word units (collocations) that appear together significantly more often than to be expected statistically, and transformed them into single-word units []. For example, “European” and “Union” were merged into “European Union”. Finally, we created document-term matrices and word lists for each year of analysis which display the frequency counts for all terms that occur in the text corpus.
2.5. Analysis of the Text Corpus
The analysis of the cleaned and prepared text corpus comprised three steps. First, we applied frequency analysis in order to explore how often a topic was covered in a defined period of time []. We analyzed how reporting on water and slurry developed over time and whether disruptions and shifts occurred. A high number of occurrences in a certain time period indicates that the key term received particular attention while, vice versa, few occurrences suggest low levels of attention. Because the number of articles per year was not evenly distributed, the absolute frequency may deliver skewed results. Therefore, we calculated the relative frequency, i.e., the occurrences of the term water resources in relation to the overall number of words in the text corpus per year. Since the number of articles issued varied across years, relative frequency is more suitable than absolute frequency as an indicator for the importance given to water-related topics.
Second, we applied semantic network analysis to identify relationships between certain words or concepts []. A semantic concept is a coherent idea that arises when context is added to words. For example, the word “farmer” belongs to the concept “agriculture”, as well as specifications such as “arable farmer” or “livestock farmer”. A semantic network is a graphic representation of major semantic structures and latent patterns of meaning []. Identification of semantic networks in different sub-corpora over time allows to discover persistent, changing, newly evolving, or vanishing issues [].
We reconstructed semantic networks for the key term “water resources” and co-occurring terms for each year separately to track changes in agenda setting and to investigate the “dynamics of meaning” over time []. Our main interest was to investigate the context of meaning of water resources rather than to identify general themes covered in the magazines [,]. Thus, we used all documents that were found to relate to water resources.
We analyzed which terms occurred together with the key term more often than coincidentally, using log-likelihood as a measure of deviation from random conjoint co-occurrence []. Each network structure consists of a key term in the center and co-occurring terms associated with it. Co-occurring terms of first order (“roots”) and second order (“leaves”) were identified []. Leaves provide semantic specification to the roots and allow to determine the meanings of words within their semantic context. For more condensed results, all words with a frequency lower than 10 were removed. We chose 13 co-occurring root terms, each accompanied by 13 leaves connected by links (“edges”). The number of terms was selected after a preliminary evaluation of alternative counts. As a result, 13 root terms and leave terms turned out to be readily interpretable and to reveal meaningful patterns. The networks were visualized with the igraph package for R [].
Finally, to validate the interpretations of the semantic networks, we conducted a concordance analysis. Concordance analysis extracts examples for the contexts in which the key term occurred. The examination of the immediate relations provides evidence of meaningful representation []. Concordances are often presented in the form of keywords in context (KWICs). KWICs list the keyword within a limited excerpt of text along with the preceding and following words []. We retrieved the key term “water resources” together with five preceding and five following words for all sentences within which the key term occurred. An example would be: “[…] larger amounts of slurry got into the rivers, because the exact application rate is difficult […]” (German: “[…] gelangen größere Güllemengen in die Flüsse, weil die exakte Ausbringmenge schwer […]“).
3. Results
3.1. Frequency Analysis
Around one fifth (21%) of all 4227 articles reported on water in relation to slurry. Figure 2 shows the relative frequency (see Section 2.5) of the key term “water resources” and the search term “slurry” throughout the investigation period. The relative frequency indicates the ratio of the search term to the total number of words in the text corpus in each year. Since the number of articles issued varied across years, relative frequency is more suitable than absolute frequency as an indicator for the importance given to water-related topics.
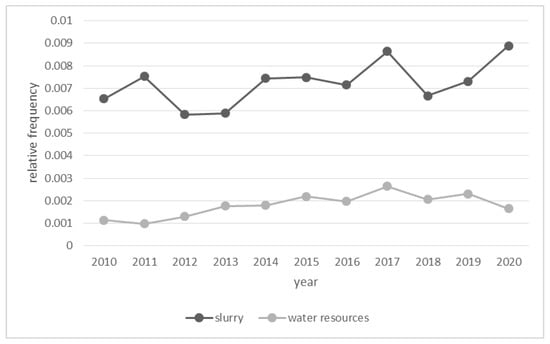
Figure 2.
Relative annual frequency of the terms “slurry” and “water resources” (occurrences in relation to total number of words, excluding stopwords), source: authors’ analysis.
“Slurry” occurs between three and eight times as often as “water resources”, which is the key term for the inclusion of an article into the analysis. The relative frequency of the key term “water resources” generally increased over time, with two peaks in 2017 and 2019, indicating elevated levels of attention. Despite a decline to an eight-year low, the value for 2020 was still twice as high as for 2011, the lowest value.
3.2. Semantic Network Analysis
We determined the roots and leaves that co-occurred with the key term “water resources” for each year. While the roots point to the overall direction of each year’s agenda, the leaves serve as their descriptors. The relations between the key term and the roots and leaves indicate which issues and actors were covered (or omitted) as well as which attributes were associated and moved to the foreground. For example, in 2015 the key term water resources was most closely related to the root term nitrate (Table 1). Nitrate was, in turn, connected to leaves such as ammonia, soil, trend or fertilization. In 2020, nitrate as a root term was related to leaves such as pollute, fertilizer ordinance, fertilization, or designation.

Table 1.
Root terms identified for the investigation period 2010–2020 in order of significance of co-occurrence with the key term “water resources”, source: authors’ analysis.
Table 1 shows the 13 roots for each year. Table A1 in Appendix A provides the relations of roots and leaves for the year 2015 as an example. The relations of key term, root terms, and leave terms are visualized as semantic networks as shown in Figure 3.
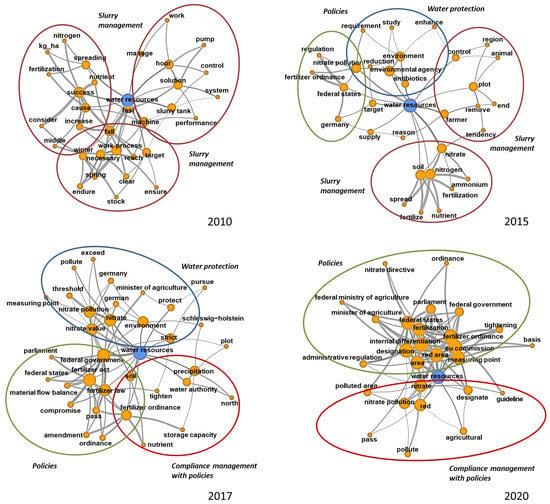
Figure 3.
Semantic networks of selected years. The figure shows the key term (water resources, blue nodes), root terms, and leave terms (orange nodes) as well as their links (black lines). The size of the nodes indicates their degree of connection, the edge width indicates the significance of co-occurrence. Terms with less than two links (edges) were removed for greater clarity. Source: authors’ visualization.
A total of 28 of the 95 different root terms found across all semantic networks (see Table 1) appeared more than once during the investigation period, i.e., in at least two years. These 28 terms were used to trace shifts in patterns of meaning. The use context of most recurring root terms changed during the investigation period, although not for all of them (e.g., winter, spreading, plot). Use contexts mostly shifted from farm management to political concepts, in some cases fundamentally. This is indicated by terms such as nitrate, measure, area, pollute, nitrate pollution, environment, nitrate value, protection, which correspond to the terminology in legislative texts related to water resource management.
Eight recurring terms appeared as roots only in the first half of the investigation period (between 2010 and 2014). These were mostly associated with farm management (target, necessary, winter, nitrogen, spread(ing)), but also with regulatory issues (netherlands, control, means). From 2014 onwards, numerous environment-related terms appeared, i.e., pollute, nitrate pollution, nitrate value, environment, protection, and in 2017, the term fertilizer ordinance entered the semantic networks. Several political terms appeared only in 2019, related to the latest amendment of the fertilizer ordinance (red area, fertilization, measuring point, eu commission).
Building on these general descriptions of the data, we now turn to our research questions. We analyzed the magazines’ agenda setting by comparing the issues, attributes, and actors that appear together in the semantic networks during the investigation period as well as their relation to potentially relevant events.
- RQ 1: How does the representation of issues and attributes change over time?
The use context of representations of water resources was explored by identifying co-occurrences as well as concordances of terms. The analysis shows that the concepts in the semantic networks changed over time, indicating shifts in agenda setting. More specifically, representations of water resources co-occurred with different terms in the text corpus in different time periods.
Figure 3 shows the semantic networks for the first and the last year of the investigation period as well as 2015 and 2017, two peak years indicating changes in agenda setting. The key term and the co-occurring roots and leaves are shown as nodes that are connected by edges. The edge width represents the weight value, i.e., the significance of the co-occurrence. The size of the nodes represents their degree of connectivity. Nodes with less than two edges have been removed for greater clarity.
The clusters—terms surrounded by the same oval line in Figure 3—correspond to the category of issues in media agenda-setting theory and can be used to detect themes. Our analysis identified four themes: i. slurry management; ii. water protection; iii. policies; and iv. compliance management related to policies. The “slurry management” theme is linked to technical aspects related to the collection, application, storage, and processing of slurry. The “water protection” theme covers the status and protection of water resources in relation to agriculture. The “policies” theme refers to the content and implications of agriculture-related policies. The “compliance management” theme relates to questions how slurry management could be adapted to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
In 2010, the slurry management theme (colored brown in Figure 3) was in the foreground. In 2015, the water protection (colored blue) and policies (colored green) themes found their way onto the agenda, and in 2017, also compliance management (colored red). In 2020, the focus of reporting was on policies and compliance management.
The density of interconnections between the terms increased during the investigation period (see Figure 3). This suggests that the discussion focused on a small number of issues that were intensively covered and connected. In the first half of the investigation period, diverse issues were reported with a focus on slurry management while in the second half, concentration on the fertilizer legislation led to a narrowing range of issues, accompanied by a broadening of actors mentioned.
In the earlier years of the investigation period, the root terms related to the slurry–water nexus suggest a predominance of farm-management issues, as indicated by terms such as target, slurry tank, spreading, work process, or manage. In 2010, relations between the key term water resources and the root terms were weak, indicating little coverage of water resources. All clusters in the semantic network of 2010 (presented in Figure 3) deal with slurry management. For example, DLG-Mitteilungen (2010) wrote: “This includes, especially in the northeastern German lowlands, targeted drainage management that retains not only the nutrients but also the water necessary for high yields.” (1). The German original text of the translations are presented in Appendix B. The numbers in brackets refer to the corresponding German sentences in Appendix B.
Farm-management issues became less frequent over time apart from an uptick in 2018. In the second half of the investigation period coverage focused increasingly on political issues. The semantic networks show a shift towards the political dimension of the slurry-water nexus (Figure 3, years 2017 and 2020). In 2017, for example, the root term nitrate was strongly connected with the root term federal government with leaves such as fertilizer law, Bundestag (Federal Parliament) or states, whereas in 2015, nitrate was exclusively related to slurry management. The semantic network contains clusters focusing on policy issues, slurry management related to policies and water protection issues. This can be recognized by the frequent mentioning of regulations, such as the Fertilizer Ordinance, detailed content on the implementation of regulations, such as red areas where particularly strict regulations apply, as well as the naming of political actors. The concordance analysis confirms this result, for example a statement about “areas where the nitrate limits in groundwater are still significantly exceeded and where further action is required” (2) (top agrar, 2019). With the new Fertilizer Ordinance in 2017, the political debate reached its peak, as indicated by the very high number of concordances, for example: “Last week, the federal and state governments were able to agree on legal certainty on the issue of water protection in areas classified as critical, where nitrate contamination in groundwater is particularly high” (3) (agrarheute 2017).
In 2018, a broader range of issues gained attention, for example: “This would allow the residues to be used economically, but also to relieve oversaturated waters and soil in areas with intensive livestock farming” (4), as top agrar reported, referring to a research project. Episodic reporting had a greater significance in the farm magazines in 2018. It was partly connected to public discourse, e.g., debates on climate change. top agrar, for example, wrote about the purchase of biochar by farmers who, for the promise “of fertile soil that can store more water in times of climate change, […] accept high costs” (5) (top agrar 2018). In the visualization of the 2020 network, the nodes show a stronger connectivity and cluster formation around the key term. More frequent mentioning of legal institutions than before and a strong focus on policymaking left practical management issues behind. The relative frequency of representations of water resources decreased and the semantic network indicates a growing engagement with the implementation of the requirements of the Fertilizer Ordinance.
Pitching their coverage at the interface of farm management and political issues, the magazines reported on ways how farm management could be most efficiently adapted to legal guidelines evenly across all years of observation, for example how to deal with retention periods for the spreading of slurry. Root terms such as comply or obey are indicative of compliance issues, e.g., “the soil must thaw during the day and the distances of the edges from ditches and watercourses must be obeyed” (6) (agrarheute 2013).
Reporting on water protection as an independent issue is an important part of the semantic networks of 2014 and 2015 and was particularly bound to other protection topics, such as environmental and animal protection. Water protection issues on the agenda are indicated by root terms such as nitrate pollution or environment. The semantic network of 2015 displays a particularly strong relationship between water resources and the root term nitrate. While the cluster around this term was still dedicated to the issue of slurry management in 2015, the use context shifted towards water protection and policies during the following years. Another cluster—centered around the root term antibiotics—illustrates a focus on water protection, which had been triggered by several official reports on the role of agriculture in water pollution. In 2014, top agrar quoted a statement by the environmental NGO BUND: “Protecting groundwater against pollution from industrial agriculture is therefore a command of reason” (7) (top agrar 2014). Although the water protection issue never disappeared from the agenda, its salience dropped in the following years. Still, in 2017, for example, the Green Party called for a “realistic” Material Flow Balance Ordinance “[t]o protect people and the environment. Because our groundwater and soils do not forget the sins of a misguided agricultural policy” (8) (top agrar 2017).
- RQ 2: Which relationships between issues and actors are presented and how do they change over time?
In the next step, we identified which actors were mentioned together with the issues. Altogether, 24 different actors and actor groups appeared in the semantic networks of the investigation period. We counted the actors once per semantic network and year and assigned them to levels of operation (individual/farm, state/Länder, national/federal, EU). In 2015, 2017, 2019, and 2020, actors or groups were even identified as roots, indicating a particularly important role in the coverage of the slurry–water nexus in these years. In 2015, these actors were farmers and the German Environment Agency, in 2017 the German government and water authorities, and in 2019 and 2020 the European Commission.
The semantic networks show how the co-occurrence of actor groups and issues developed over time. The number of different mentioned actors decreased between 2010 and 2012 before increasing continuously until 2020. The most frequent actors in the semantic networks were Federal government institutions at the national level. They first appeared in 2014 and then gained in importance at the expense of government institutions at the state (Länder) level, particularly the ministry of agriculture of Lower Saxony. Lower Saxony, together with North Rhine-Westphalia, is the state with the highest-density livestock regions as well as slurry imports from the Netherlands, which together leads to high slurry surpluses in many locations and consequently nitrate leaching and water pollution. Agricultural actors (= farm level) were elements of the networks just as often. EU-level institutions were found in almost every year. In 2017 and 2018, consumers and society at large were mentioned, reflecting the relevance of protection issues in the semantic networks of these two years. A water authority was part of a semantic network in 2017 only.
Table 2 shows at which levels actors appeared together with the main issues in each year. Issues without co-occurrence of actors were not included in the table. This exclusion applied entirely to slurry management issues. Slurry management was significantly related to actors in 2010 only. Issues of farm management related to the slurry-water nexus were associated with actors at farm and state level. Water protection as well as recommendations for adapting slurry management practices to legal requirements included actors at all levels. Policy issues were linked to actors at state, federal, and EU level.

Table 2.
Issues and actors co-occurring in the analyzed agricultural press during the investigation period, source: authors’ analysis.
The farm management issues, which prevailed in the semantic networks between 2010 and 2013, were connected to agricultural actors and state governments. Issues of slurry management related to policies were covered throughout these four years, particularly at the farm level, but, depending on the policy discussed, also the state, federal, and EU level.
During 2014/15, issues of water protection, connected with environmental concerns, emerged in the coverage. However, they were not a continuous part of the semantic networks, but appeared occasionally in relation to the environment, animal welfare, and consumer preferences in 2017 and 2018. This strand of coverage focused on the federal and the farm level. Water protection was the only issue that was also related to the society level. From 2017 onward, political issues gained in salience and the political pressure emanating from the EU Nitrate Directive and the Fertilizer Ordinance was reflected in the dominant salience of government actors.
- RQ 3: Was coverage of the slurry–water nexus related to specific events?
We now relate the results of the semantic network analysis to the sequence of major events, connected to the slurry–water nexus during the investigation period (as compiled in Table A2 in Appendix A). Events related to the slurry–water nexus were identified through searching the word lists as well as studying literature and documents of governmental and non-governmental institutions. We included regulatory and legislative activities and policy events such as major reports, studies and court decisions. Figure 4 shows the events with potential relevance for the slurry-water nexus during the investigation period in connection to the relative frequency of the term water resources.
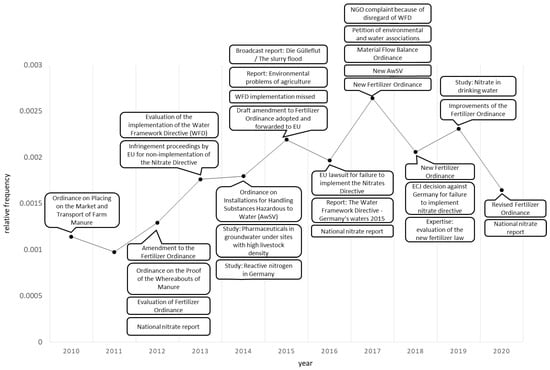
Figure 4.
Potential events with respect to the slurry–water nexus and relative frequency of the key term water resources, source: authors’ analysis and visualization.
Between 2010 and 2020, a remarkable number of new or revised regulations addressed or affected the slurry–water nexus (Figure 4). Of particular relevance were the amendments of the Fertilizer Ordinance and the Nitrate Directive, the implementation of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the adoption of the Ordinance on Installations for Handling Substances Hazardous to Water (Verordnung über Anlagen zum Umgang mit wassergefährdenden Stoffen, AwSV) which affected liquid manure, slurry, and leachate installations in agriculture. The Fertilizer Ordinance served to implement the EU Nitrate Directive in Germany.
The AwSV was discussed in relation to protecting water bodies through safe storage of slurry when it was adopted in 2014. Coverage of the WFD was low throughout the study period despite significant events: in 2013, the implementation of the management plans was evaluated; in 2015, the European Commission determined that Germany had missed the binding WFD goals; and in 2017, the environmental NGOs NABU and BUND submitted a complaint to the EU Commission for Germany’s failure to comply with the Directive.
Only the Fertilizer Ordinance was widely and increasingly covered by the three farming magazines, often in connection with the EU Nitrate Directive. In June 2012, an amendment of the Fertilizer Ordinance went into force. However, a connection to water resources was barely made in that year’s coverage and the Ordinance appeared in the semantic network only once, namely in relation to the impact of its revision on farming practice. More intense coverage of the Fertilizer Ordinance in later years was triggered by a sequence of event. In 2013, the European Union initiated infringement proceedings against Germany for failure to comply with the Nitrate Directive. In 2015, a draft amendment to the Fertilizer Ordinance was adopted and forwarded to the EU in December. In 2016, the EU sued Germany for its inadequate implementation of the Nitrate Directive. In 2017, the new Fertilizer Ordinance went into force. In 2018, the European Court of Justice ruled that Germany’s old Fertilizer Ordinance had been insufficient and demanded the new fertilizer legislation to be implemented in accordance with the requirements of the Nitrate Directive. Another revision of the Fertilizer Ordinance went into force in 2018, improvements had to be made in 2019 and the most recent version went into force in 2020/2021.
Attention to water protection issues in the text corpus peaked in 2014 and 2015, when reporting covered the problematization of farm impacts on water by various organizations, which was often scrutinized by the magazines. The main concerns are reflected in the semantic network for 2015. Three publications shaped public discourse and were critically discussed in the farm press: the study “Antibiotics and antiparasitics in groundwater under sites with high livestock density” by the German Environment Agency, the report “Environmental problems of agriculture” by the German Advisory Council on the Environment (SRU), and a report by the public television broadcaster WDR which connected slurry to water pollution and mass animal husbandry.
For the period starting in 2016, we found that coverage was more often linked to political issues. In 2017, the two amended ordinances, the AwSV and the Fertilizer Ordinance, had their highest relative frequency during the investigation period and the semantic networks indicate an intensive discussion on both (see the terms ordinance and fertilizer ordinance in Figure 3). From 2018 onward, the struggle over the rules of the new Fertilizer Ordinance is reflected in the semantic networks, but less so the ruling over Germany’s failure to implement the EU Nitrate Directive. Reporting on the new ordinance was linked to animal welfare and societal preferences for environmental and nature protection in 2018 only. Once the new Fertilizer Ordinance came into force, issues around political pressure and implementing the new regulation into agricultural practice came to the foreground. The linkages between these issues in the semantic network are strong, indicating that they were strongly related to each other and to the new Fertilizer Ordinance.
4. Discussion
4.1. Three Phases of Agenda Setting
The aim of our analysis was to understand agenda setting related to the slurry–water nexus in specialized farming magazines in Germany. Our research questions were guided by the distinction between three levels of agenda setting. First, by setting concrete thematic priorities, the media influence how the audience perceives the importance of an issue []. Second, media influence the audience’s perceptions by highlighting certain positive or negative attributes of issues or persons []. Third, media coverage makes connections made between issues, attributes and actors, creating a semantic network [].
The results of our analysis show a general increase in the coverage of water resources in relation to slurry in the three the farming magazines between 2010 and 2020. However, after a steady rise, mentions of water resources peaked in 2017 and dropped from 2018 onward. This could be caused by fewer triggering events or less dedication by editors to cover the slurry–water nexus. In any case, the relative frequency of the issue never fell below the level of the earlier years of the investigation period, indicating a continued place on the agenda.
The analysis revealed two major shifts in issues, actors, and attributes, which allow us to distinguish three distinct phases in the investigation period:
- From 2010 to 2013, thematic reporting set the agenda and issues of farm management and compliance management were at the foreground. These issues were mainly connected to the farm level and to institutions at state level, and occasionally to institutions at EU level.
- Between 2014 and 2016, water and environmental protection issues appeared in the semantic networks, reflecting the public discourse on ecologically sustainable agriculture, and were occasionally resumed in the following years. The magazines increasingly discussed specific events, indicating a turn towards episodic reporting. Policies became a concurrent issue. Connections to actors at the farm level recede, while links to national and European institutions, not least the German Environment Agency, increase.
- Finally, from 2017 onward we found a shift in coverage towards political issues with regard to the slurry–water nexus which was related to tightening legislation with potentially far-reaching consequences for farming practice. The strength of the edges and the degree of interconnection of the concepts in the semantic networks (see Figure 3) show an intensification of episodic reporting that focused on two pieces of regulation: the EU Nitrate Directive and the German Fertilizer Ordinance. The appropriateness of the amendments was questioned and their implementation was extensively discussed. In 2019 and 2020, coverage of a revised version of the fertilizer ordinance focused on the new regulatory aspects rather than on water resources. Management issues were crowded out by politics and compliance issues. Moreover, we found little coverage of innovations for enhancing the slurry–water nexus. With the increasing focus on policy and regulation the diversity of issues on the magazines’ agendas decreased while the number and range of actors mentioned increased, reflecting broader involvement beyond the traditional farm sector.
The shifts were accompanied by changes in concepts presented and thus in the use context of the slurry–water nexus. While in the earlier years, often technological terminology dominated, environment-related vocabulary co-occurred with water resources in the later years, indicating a link to environmental discourses in the broader public. From 2014 onward, the slurry–water nexus is regularly connected to environmental and animal protection. However, the discussion of water protection as an issue independent of politics lost salience when fewer high-level studies were published. This finding resonates with the studies by Sweeney and Hollifield [] and Abrams and Meyers [] who found that issue choice in specialized farming magazines was oriented towards national newspapers which reflect broader public discourse. Interestingly, public discourse was often reflected through the lens of agricultural insiders, e.g., an interview with the German conservative politicians and agricultural officials Johannes Röring and Franz-Josef Holzenkamp in 2015: “Many consumers demand the highest standards, but have been unwilling to pay for them. In doing so, they overlook the fact that farmers have continuously developed animal welfare and environmental protection over the past decades. This process is continuing, partly because societal attitudes and expectations are changing. Agriculture must continue to respond to this” (9).
The shifts in the weight of actors in the semantic networks from the farm and the state level to the federal and the EU level, and from farm practitioners to government institutions, could be explained by power indexing, i.e., the observation that the (frequency of) appearance of actors in the media depends on how relevant and powerful they are perceived by the content makers []. The shift in the types of actors in the semantic networks indicates a politicization of the slurry–water nexus, as does the broadening range of actors. Politicization denotes a process where an issue gains public salience and more actors invest resources to influence the agenda, often but not necessarily leading to stronger polarization []. Such a process is clearly reflected in our data. In the years with increased coverage of water protection issues, non-agricultural actors were cited rather than representatives of the farming community. This was particularly the case when reports by public institutions and general media on environmental damage caused by agriculture, and particularly by intensive animal husbandry, were covered in the magazines. Politicization can also explain the low presence of actors from the water sector in the semantic networks—a regional water authority appears in the semantic network only once (in 2017)—since these public bodies have little interest in being seen as partisan.
Our finding that coverage increasingly focused on the discussion of political and public events as well as on compliance contrasts with previous studies which found that reporting of specialized farming magazines with regard to, e.g., climate change [] or sustainable agriculture [], primarily addressed farm-management issues. Again, the concept of politicization offers an explanation, since our data reflect a rising influence of non-agricultural actors, the increasing preference of society for environmental services, and calls for more stringent implementation of EU policies. At the same time, coverage of political and public events allows news outlets to constantly offer new content, which is particularly important for magazines that maintain online editions, such as top agrar and agrarheute. Separate examination of the three magazines showed slightly higher coverage of farm management issues by DLG-Mitteilungen. The difference in the ratio of farm management and policy issues between top agrar and agrarheute on the one hand and DLG-Mitteilungen on the other hand suggests a relationship between news format and choice of issues.
However, coverage of events in relation to the slurry–water nexus was selective. Particularly, events related to the Fertilizer Ordinance and, later, the Nitrate Directive were extensively discussed and drove the focus on political issues from 2017 onwards. In contrast, the WFD gained little attention, although farmers are important stakeholders for its successful implementation []. This might be explained by the WFD’s lower news value, in particular with regard to relevance and cultural meaningfulness to the readership, continuity of reporting, and degree of affectedness []. While regulation of fertilization is immediately relevant to farm practice and business, participation in stakeholder dialogues at the level of water bodies is far removed from most farmers’ everyday lives.
4.2. Implications for Policy and Practice
After thirty years of EU water legislation, slurry management practice and policymaking in Europe are still insufficient for the adequate protection of water resources. Reports by the European Environment Agency [] and the European Court of Auditors [] show that emissions from agriculture are responsible for nitrate concentrations in water bodies far above the legal threshold values in most EU countries, including Germany.
We expected that continuous coverage of the slurry–water nexus could help to increase farmers’ awareness of relationships between slurry and water and of the interactions between different agricultural practices and the quality and quantity of water resources. Effects of news media on the audience’s awareness and perception of a topic have long been well established in research on media agenda setting [].
Our findings confirm the assumption that in the context of the slurry–water nexus, manifold actors compete for attention and struggle for discursive dominance. The coverage of water-related issues in the farm press reflected these struggles and thereby communicated a range of economic and practical, public, and political aspects to agricultural practitioners. Over time, agenda setting went through different phases, separated by distinct shifts, during which the farming magazines connected the slurry-water nexus to different issues and actor groups. Our results show that coverage of the issue was increasingly driven by political and communicative events, which reflects a broader trend of politicization of farm management practices and a high level of polarization around agro-environmental policy issues.
The intensive reporting on policies and policy implementation from 2017 onwards suggests that coverage of compliance management to meet regulatory requirements partly crowded out slurry management issues. Innovations for water-conserving slurry management received little coverage although public policies aimed to promote technological modernization and investments. Those technologies that were discussed mostly represented minor adjustments to current practice rather than more far-reaching innovations. Hence, politicization has not served to open up the debate on slurry management practices in the professional arenas analyzed in this paper. Hence, if continuous coverage of the slurry–water nexus did increase farmers’ issue awareness as expected, the issue framing found in our analysis suggests that audience attention was probably strongly guided towards politicization rather than just towards problem solutions.
The results suggest that policy makers could use text mining methods for continuous tracking of topic, issue, and actor salience and to evaluate communication strategies with a view to improving issue awareness and desired associations [,].
4.3. Methodological Reflections and Recommendations for Future Research
Our study contributes to previous research in several ways.
First, it extends research on agricultural media coverage of environmental issues. Taking the slurry–water nexus in Germany as an example, we expected coverage of the relation between farm management and environmental resources to become stronger over time. Yet, our results show that the specialized farming magazines turned their attention towards the design and implementation of policies for water protection at the expense of relations between farming practice and environmental resources.
Furthermore, we found evidence that between 2010 and 2020, specialized farming magazines increasingly turned from thematic to episodic reporting. This probably reflects both politicization processes in farm policy [] and the need for media outlets with online activities, such as top agrar and agrarheute, to produce more content. By analyzing a large number of articles over a period of ten years with text mining methods, we extended prior research on agricultural media and set the basis for future studies of specialized farm magazines. The results of this analysis can, for example, serve as a starting point for a qualitative analysis of specific research questions on the slurry–water nexus, cf. [].
In view of the turn of the agricultural press towards online formats, systematic analysis of news values could provide more insights into newly evolving modes of reporting of specialized farming magazines and comparison with general media. Our study is repeatable since the magazines’ databases can be accessed through university and non-university libraries free of charge. The study design is transferable to other study contexts and other countries.
Second, the study contributes to the application of agenda-setting theory to the analysis of agricultural publications. With examining all three levels of agenda setting by means of semantic network analysis, we were able to discover patterns of relationships and their change over time in a large and unstructured text corpus. We created the foundation for deeper analysis and assessment of the relevance of issue agenda setting, reference to actors and events as well as relationships in agenda setting by specialized farming magazines and other media outlets. Since previous survey studies found a relationship between media agenda setting and public behavior [,], our results could be used in further studies to investigate to what extent content in agricultural media has influenced farmers’ behavior.
Third, by analyzing semantic networks, we found shifts in concepts as well as in use contexts from rather technological to more environment-related terminology. Further, more detailed content analysis would allow to examine how the agricultural press produce meaning with regard to the slurry–water nexus. A comparative application of the text mining approach to other types of media could contribute to understanding semantic patterns in the co-construction of environmental issues in agriculture more broadly.
5. Conclusions
From our analysis we draw four key conclusions.
First, our analysis reveals a shift from thematic to episodic coverage of the slurry–water nexus in specialized farm media in Germany that was accompanied by a shift in issues from farm management to politics and regulatory compliance and a shift in actors from agricultural-sector insiders at the farm and the state level to a broader range of political actors at the national and EU level. This shift likely reflects both an increased need of online media outlets to create fresh content and a broader politicization of farm management practices and their environmental effects. It also reflects the news value (relevance, continuity, and degree of affectedness) of environmental regulations for an audience of farmers faced with tightening implementation rules and more administrative work.
Second, the coverage since 2017 was strongly oriented towards compliance management to meet legal requirements, with little discussion of innovations for enhancing the slurry–water nexus. Hence, news value dynamics and politicization might work as mutually reinforcing mechanisms that crowd out more long-term deliberation on farm development in the face of environmental and climate change (and their strong implications for the management of water resources).
Third, our results partly contrast with previous research that found specialized farming magazines to focus on thematic reporting and instead show a trend towards more episodic coverage. Therefore, if we understand events as windows of opportunity for communication on the slurry–water nexus, the findings demonstrate the difficulty of linking political events to long-term issues rather than short-term issues with high news value.
Finally, text mining in general and semantic network analysis in particular proved to be suitable methods to extract and process information about agenda setting in the agricultural press and to reveal issues and actors, patterns of relationships and use contexts, and their development over time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.-N. and S.U.; methodology, A.A.-N.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.-N.; writing—review and editing, A.A.-N., S.U., J.Z. and P.H.F.; visualization, A.A.-N.; supervision, S.U., J.Z. and P.H.F.; project administration, S.U. and J.Z.; funding acquisition, S.U. and J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) for the junior research group BioKum (031B0751).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data were obtained from top agrar, agrarheute, and DLG-Mitteilungen and are available at https://www.topagrar.com/, https://www.agrarheute.com/, and https://www.dlg-mitteilungen.de/ upon subscription (accessed on 15 June 2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Michael Fiebig for his assistance in data preparation. Authors would also thank the R Core Team and the developers of the open-source packages used for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Example of roots and leaves of the key term water resources for the year 2015.
Table A1.
Example of roots and leaves of the key term water resources for the year 2015.
| Root Terms | Leave Terms |
|---|---|
| water resources | nitrate, nitrate pollution, control, farmer, soil, federated state, supply, environment, environmental agency, nitrogen, plot, aim, antibiotics |
| nitrate | water resources, ammonia, retard, soil, trend, sharp, nitrogen fertilizer, spread, fertilization, active ingredient, nitrate value, nitrification inhibitor |
| nitrate pollution | fertilizer ordinance, threaten, requirement, federal agricultural ministry, consider, area, federated state, regulation, criticism, compost, measure, environmental agency |
| control | cheap, surveillance, number, actually, region, approve, quantity, compliance, animal, kg, strong, reinforce |
| farmer | water resources, consultant, drive, reason, reasonable, thank, pay, last, remove, cow, calculate, end |
| soil | fertilization, nitrogen, fertilize, tolerate, spread, success, design, total nitrogen, nutrient, mineral fertilizer, plantation, fertilizer |
| federated state | federal government, regulation, fertilizer ordinance, schmidt, country opening clause, state, limitation, reduction, germany, planned, political, new_fertilizer_ordinance |
| supply | chance, impossible, abroad, retract, export, germany, base, reduce, evaluation, reason, total, decade |
| environment | environmental agency, water resources, improvement, reduction, sustainable, study, requirement, concentration, view, meat, cause, reinforce |
| environmental agency | current, water resources, antibiotics, nitrate pollution, study, german_farmers_association, agriculture, stipulate, entitle, cooperation, demand, duty |
| nitrogen | fertilize, phosphorus, nitrogen demand, ammonium, spread, soil, nitrogen fertilization, mineral, nitrogen application, nitrate, nutrient, ha |
| plot | manage, silage corn, end, hectare, trend, eastern germany, grassland, region, cost, remove, ceiling, animal |
| aim | ecological, federated state, point, germany, criticize, small, reduction, water resources, next, case, pay, claim |
| antibiotics | environmental agency, water resources, high quality, risk, partial, income, consistent, together, veterinarian, nature conservation, food, profit |

Table A2.
Key events and policies with potential influence on the thematization of the slurry-water-nexus.
Table A2.
Key events and policies with potential influence on the thematization of the slurry-water-nexus.
| Year | Event | Detailed Description/Content |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Ordinance on the Placing on the Market and Transport of Farm Manure (Verordnung über das Inverkehrbringen und Befördern von Wirtschaftsdünger) | Farmers have to record and report on the delivery, transport, and reception of farm manure. This impacts on water resources indirectly, as slurry cannot “get lost” due to the record-keeping obligation. |
| 2012 | Amendment to the Fertilizer Ordinance | The Fertilizer Ordinance was implemented in 1996 and first revised in 2008. |
| Ordinance on the Proof of the Whereabouts of Farm Manure (Verordnung über den Nachweis des Verbleibs von Wirtschaftsdünger) | All nutrient flows of farm manure and substances containing farm manure as a raw material have to be monitored. Thus, the danger of discharge of substances hazardous to water through slurry is reduced. | |
| Report of the Federal Government/Länder Working Group on the Evaluation of the Fertilizer Ordinance | Representatives from federal and state ministries as well as experts from federal and state institutions evaluated the implementation and effectiveness of the existing regulations of the Fertilizer Ordinance. Based on the identified need for improvement, the Working Group has developed implementation options for the amendment of the ordinance. | |
| National nitrate report | Every four years, EU member states are obliged to report on the implementation of the Nitrates Directive to the European Commission. | |
| 2013 | Infringement proceedings initiated by the EU against Germany for non-implementation of the Nitrate Directive | |
| Evaluation of the implementation of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) | ||
| 2014 | Ordinance on Installations for Handling Substances Hazardous to Water (AwSV) passed—includes liquid manure, slurry, leachate installations (Verordnung über Anlagen zum Umgang mit wassergefährdenden Stoffen AwSV) | Installations in the agricultural sector that serve for storage or filling of, among others, liquid manure, slurry, and leachate must be built in such a way that substances hazardous to water cannot escape and leaks can be identified quickly. |
| Federal Environment Agency (UBA) study on pharmaceuticals in groundwater under sites with high livestock density [] | Evaluation of accumulation of residues and metabolites in the groundwater under agricultural land. | |
| Study by the Federal Environment Agency (UBA): Reactive nitrogen in Germany [] | Examination of causes and effects of reactive nitrogen formation and possible measures for improvement. | |
| 2015 | Draft amendment to Fertilizer Ordinance adopted and forwarded to EU | |
| WFD implementation missed | ||
| Expert council for environmental issues (SRU) report: Environmental problems of agriculture | Evaluation of effects of CAP reforms on natural resources. | |
| TV report (WDR): The slurry flood—danger for our drinking water? (Die Gülleflut—Gefahr für unser Trinkwasser?) | TV report about excessive slurry accumulation and its relations to water pollution and mass animal husbandry. | |
| 2016 | EU lawsuit against Germany for failure to implement the Nitrates Directive | |
| Report: The Water Framework Directive—Germany’s waters 2015 [] | Report on the evaluation of the effects of the WFD in the management period 2009–2015. | |
| National Nitrate Report | See above (2012) | |
| 2017 | New Fertilizer Ordinance | See above (2010) |
| New AwSV | See above (2014) | |
| Material Flow Balance Ordinance (Stoffstrombilanzverordnung—StoffBilV) | The ordinance aims to ensure the sustainable and resource-efficient handling of nutrients on farm in order to reduce leakage into the environment. | |
| Petition of environmental and water associations | NGOs demand action against mass animal husbandry, antibiotics, and water pollution. | |
| Environmental organizations file complaint with EU Commission because of disregard of WFD by Germany | ||
| 2018 | ECJ rules that Germany has failed to implement EU Nitrate Directive | |
| New Fertilizer Ordinance | ||
| Expertise on the evaluation of the German fertilizer law of 2017 | Report on the evaluation of the 2017 fertilizer law with regard to water protection on behalf of BDEW (German Association of Energy and Water Industries). | |
| 2019 | Improvements of the Fertilizer Ordinance | The EU demanded improvements to meet the requirements of the Nitrate Directive. |
| NGO study: Nitrate in drinking water | Study of BUND (Federation for Environmental and Nature Protection) on the nitrate pollution caused by agriculture. | |
| 2020 | New Fertilizer Ordinance | See above (2010) |
| National nitrate report | See above (2012) |
Appendix B. Translations of the Citations
- (1)
- “Hierzu zählt insbesondere im nordostdeutschen Tiefland ein gezieltes Dränmanagement, das nicht nur die Nährstoffe, sondern auch das für hohe Ertragsleistungen notwendige Wasser in der Fläche zurückhält”.
- (2)
- “… nach wie vor Gebiete, in denen die Nitratgrenzwerte im Grundwasser deutlich überschritten werden und weitergehender Handlungsbedarf besteht”.
- (3)
- “Vergangene Woche konnten sich Bund und Länder auf Rechtssicherheit bei dem Punkt Gewässerschutz in als kritisch eingestuften Gebiete verständigen, in denen die Nitratbelastung im Grundwasser besonders hoch liegt”.
- (4)
- “Damit könnten die Rückstände wirtschaftlich genutzt, aber auch übersättigte Gewässer und Boden in Gegenden mit intensiver Tierhaltung entlastet werden”.
- (5)
- “… eines fruchtbaren Bodens, der in Zeiten des Klimawandels mehr Wasser speichern kann, nehmen sie hohe Kosten in Kauf”.
- (6)
- “Der Boden muß tagsüber auftauen und die Randabstände zu Gräben und Wasserläufen müssen eingehalten werden”.
- (7)
- “Der Schutz des Grundwassers vor Belastungen aus der Agrarindustrie sei daher ein Gebot der Vernunft”.
- (8)
- “Zum Schutz der Menschen und der Umwelt. Denn unser Grundwasser und unsere Böden vergessen die Sünden einer fehlgeleiteten Agrarpolitik nicht”.
- (9)
- “Viele Verbraucher fordern höchste Standards, sind aber bisher wenig bereit, dafür zu zahlen. Dabei übersehen sie, dass die Landwirte in den vergangenen Jahrzehnten den Tier- und Umweltschutz kontinuierlich weiterentwickelt haben. Dieser Prozess setzt sich fort, auch weil sich die gesellschaftlichen Einstellungen und Erwartungen verändern. Darauf muss die Landwirtschaft weiterhin reagieren. Wir müssen die heiklen Punkte wie Antibiotika, Nitrat im Trinkwasser, nicht-kurative Eingriffe und Verlust der Artenvielfalt konsequent anpacken. Dabei werden wir uns an der ein oder anderen Stelle ändern müssen”.
References
- Evans, A.E.V.; Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Qadir, M.; Boelee, E.; Ippolito, A. Agricultural water pollution: Key knowledge gaps and research needs. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 36, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W.; van Grinsven, H.; Grizzetti, B.; Bouraoui, F.; Powlson, D.S.; Sutton, M.A.; Bleeker, A.; Reis, S. The European nitrogen problem in a global perspective. In The European Nitrogen Assessment: Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives; Sutton, M.A., Howard, C.M., Erisman, J.W., Billen, G., Bleeker, A., Grennfelt, P., Van Grinsven, H., Grizzetti, B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 9–31. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Water and Agriculture: Towards Sustainable Solutions; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Brink, C.; van Grinsven, H. Costs and benefits of nitrogen in the environment. In The European Nitrogen Assessment: Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives; Sutton, M.A., Howard, C.M., Erisman, J.W., Billen, G., Bleeker, A., Grennfelt, P., Van Grinsven, H., Grizzetti, B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 513–540. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, J.E.; Trnka, M.; Kersebaum, K.C.; Skjelvåg, A.O.; Seguin, B.; Peltonen-Sainio, P.; Rossi, F.; Kozyra, J.; Micale, F. Impacts and adaptation of European crop production systems to climate change. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersebaum, K.C.; Matzdorf, B.; Kiesel, J.; Piorr, A.; Steidl, J. Model-based evaluation of agri-environmental measures in the Federal State of Brandenburg (Germany) concerning N pollution of groundwater and surface water. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Bunker, I.; Uthes, S.; Zscheischler, J. The Potential of Bioeconomic Innovations to Contribute to a Social-Ecological Transformation: A Case Study in the Livestock System. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2021, 34, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, N.A.; Jarvis, R.M.; Reed, M.S.; Cooper, J. Framing of sustainable agricultural practices by the farming press and its effect on adoption. Agric. Hum. Values 2021, 38, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; McCombs, M. Network agenda setting: A third level of media effects. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Communication Association, Boston, MA, USA, 27–31 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McCombs, M.; Llamas, J.P.; Lopez-Escobar, E.; Rey, F. Candidate Images in Spanish Elections: Second-Level Agenda-Setting Effects. J. Mass Commun. Q. 1997, 74, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCombs, M.E.; Shaw, D.L. The Agenda-Setting Function of Mass Media. Public Opin. Q. 1972, 36, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.; Babbitt, C. Exploring the politics of pork: Industrial hog farming and the role of local newspaper coverage in state agenda setting. Great Plains Res. 2014, 24, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.; Rogers, E. Agenda-Setting Research: Where Has It Been, Where Is It Going? Commun. Yearb. 1988, 11, 555–594. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Zhou, S. Theoretical and methodological trends of agenda-setting theory: A thematic analysis of the last four decades of research. Agenda Setting J. 2017, 1, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheufele, D.A. Agenda-Setting, Priming, and Framing Revisited: Another Look at Cognitive Effects of Political Communication. Mass Commun. Soc. 2000, 3, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMBF. Urheberrecht in der Wissenschaft. ein Überblick für Forschung, Lehre und Bibliotheken; Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung: Berlin, Germany, 2020; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Ader, C.R. A Longitudinal Study of Agenda Setting for the Issue of Environmental Pollution. J. Mass Commun. Q. 1995, 72, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. The Application of Social Network Analysis in Agenda Setting Research: A Methodological Exploration. J. Broadcasting Electron. Media 2012, 56, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaweel, M.; Bone, C. Applying content analysis for investigating the reporting of water issues. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, D.; Barkemeyer, R. Media coverage of sustainable development issues—Attention cycles or punctuated equilibrium? Sustain. Dev. 2012, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wei, Y.; Western, A.; Skinner, D.; Lyle, C. Evolution of newspaper coverage of water issues in Australia during 1843–2011. AMBIO 2015, 44, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, A.J.; Wadsworth, R.A.; Fisher, P.F. Using semantics to clarify the conceptual confusion between land cover and land use: The example of ‘forest’. J. Land Use Sci. 2008, 3, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, G. Opening up to Big Data: Computer-Assisted Analysis of Textual Data in Social Sciences. Forum Qual. Soc. Res. 2013, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, A.; Cortez, P.; Rita, P.; Moro, S. Research trends on Big Data in Marketing: A text mining and topic modeling based literature analysis. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2018, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.P.; Zhang, C.-Y. Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: A survey on Big Data. Inf. Sci. 2014, 275, 314–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler-Holland, J.; Schumacher, K.; Fichtner, W. Topic Modeling Uncovers Shifts in Media Framing of the German Renewable Energy Act. Patterns 2021, 2, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stulpe, A.; Lemke, M. Blended Reading. Theoretische und praktische Dimensionen der Analyse von Text und sozialer Wirklichkeit im Zeitalter der Digitalisierung. In Text Mining in den Sozialwissenschaften: Grundlagen und Anwendungen Zwischen Qualitativer und Quantitativer Diskursanalyse; Lemke, M., Wiedemann, G., Eds.; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2016; pp. 17–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mautner, G. Mining Large Corpora for Social Information: The Case of Elderly. Lang. Soc. 2007, 36, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.M.; Fagerjord, A. Digital Humanities: Knowledge and Critique in a Digital Age; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Atteveldt, W. Semantic Network Analysis: Techniques for Extracting, Representing, and Querying Media Content; BookSurge: Charleston, SC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielatos, C.; Baker, P. Fleeing, Sneaking, Flooding: A Corpus Analysis of Discursive Constructions of Refugees and Asylum Seekers in the UK Press, 1996–2005. J. Engl. Linguist. 2008, 36, 5–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, G. Text Mining for Qualitative Data Analysis in the Social Sciences: A Study on Democratic Discourse in Germany; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barkemeyer, R.; Figge, F.; Hoepner, A.; Holt, D.; Kraak, J.M.; Yu, P.-S. Media coverage of climate change: An international comparison. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2017, 35, 1029–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, J. Reporting on climate change: A computational analysis of U.S. newspapers and sources of bias, 1997–2017. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2020, 61, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, M.M.; Kuhlicke, C.; Marx, A. Near-real-time drought impact assessment: A text mining approach on the 2018/19 drought in Germany. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040a9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zottola, A.; Atanasova, D.; Cardwell, E.; Forrester, J.; Stevens, C. Framing nitrogen pollution in the British press: 1984–2018. Discourse Commun. 2020, 14, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, S. An exploratory analysis of the text mining of news articles about “water and society”. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2015, 168, 501–508. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, C.; Klotz, A.C.; Kreiner, G.E. Blue skies and black boxes: The promise (and practice) of grounded theory in human resource management research. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2017, 27, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Yang, P.; Feng, H. Utilization of text mining as a big data analysis tool for food science and nutrition. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 875–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, B.; Roche, M. A survey of the applications of text mining for agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 163, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogato, A.; Meggio, F.; Migliorati, M.D.A.; Marinello, F. Extreme weather events in agriculture: A systematic review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, A.; Contiero, B.; Schneider, M.K.; Arsenos, G.; Bernués, A.; Dovc, P.; Gauly, M.; Holand, Ø.; Martin, B.; Morgan-Davies, C.; et al. Topics and trends in Mountain Livestock Farming research: A text mining approach. Animal 2021, 15, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Shuai, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Shuai, J. Modelling environment and poverty factors for sustainable agriculture in the Three Gorges Reservoir Regions of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3940–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.W.; Brown, M.E.; Niles, M.T.; ElQadi, M.M. Text mining the food security literature reveals substantial spatial bias and thematic broadening over time. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, C.E. Localized Debates of Agricultural Biotechnology in Community Newspapers: A Quantitative Content Analysis of Media Frames and Sources. Sci. Commun. 2007, 28, 314–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaweel, M.R.; Alessa, L.N.; Kliskey, A.D.; Bone, C.E. Monitoring Land Use: Capturing Change through an Information Fusion Approach. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1182–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.T.; Rodriguez, L.F.; Diesner, J.; Lin, T. Improving farm management optimization: Application of text data analysis and semantic networks. In Proceedings of the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual International Meeting 2015, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26–29 July 2015; pp. 3040–3049. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, M.; Böhm, J.; Spiller, A. Die Agrar- und Ernährungswirtschaft in der Öffentlichkeit—Eine Analyse der deutschen Qualitätspresse auf Basis der Framing-Theorie. J. Socio-Econ. Agric. 2011, 4, 59–83. [Google Scholar]
- Moriom Khatun, M.; Siddik, M.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Khaled, S. Content analysis of COVID-19 and agriculture news in Bangladesh using topic modeling algorithm. Curr. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 21, 296–314. [Google Scholar]
- Mempel, F.; Corbera, E. Framing the frontier—Tracing issues related to soybean expansion in transnational public spheres. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2021, 69, 102308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwirtschaftsverlag GmbH. Top Agrar. Media-Daten 2020; Landwirtschaftsverlag GmbH: Münster, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag. Agrarheute Mediadaten 2020; Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- DLG-Verlag. DLG-Mitteilungen Media-Daten 2020; DLG-Verlag GmbH: Frankfurt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Rvest: Easily harvest (scrape) web pages. R Package Version 0.3 2016, 2, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, K.; Obeng, A. Readtext: Import and Handling for Plan and Formatted Text Files. R Package Version 0.76. 2020. Available online: https://readtext.quanteda.io/index.html (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Goodman, S. Rtika. 2020. Available online: https://docs.ropensci.org/rtika/ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Benoit, K.; Watanabe, K.; Wang, H.; Nulty, P.; Obeng, A.; Müller, S.; Matsuo, A. Quanteda: An R package for the quantitative analysis of textual data. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinerer, I.; Hornik, K.; Meyer, D. Text Mining Infrastructure in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, M. German Stopwords. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/solariz/german_stopwords/blob/master/german_stopwords_plain.txt (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Dzudzek, I.; Glasze, G.; Mattissek, A. Verfahren der lexikometrischen Analyse von Textkorpora. In Handbuch Diskurs und Raum; Glasze, G., Mattissek, A., Eds.; Transcript: Bielefeld, Germany, 2009; pp. 233–260. [Google Scholar]
- Doerfel, M.L. What constitutes semantic network analysis? A comparison of research and methodologies. Connections 1998, 21, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Glasze, G. Vorschläge zur Operationalisierung der Diskurstheorie von Laclau und Mouffe in einer Triangulation von lexikometrischen und interpretativen Methoden. Forum Qual. Soz. 2007, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, G.; Gerhard; Quasthoff, U.; Uwe; Wittig; Thomas. Text Mining: Wissensrohstoff Text: Konzepte, Algorithmen, Ergebnisse; W3L: Herdecke, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Niekler, A. Automatisierte Verfahren für die Themenanalyse Nachrichtenorientierter Textquellen; Herbert von Halem Verlag: Cologne, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann, G.; Niekler, A. Hands-on: A Five Day Text Mining Course for Humanists and Social Scientists in R. 2017. Available online: https://freesoft.dev/program/101287767 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Lemke, M. Kookkurrenzanalyse. ePol Text Mining Verfahren (eTMV), 2/5 Serie “Atomenergiediskurs”. 2014. Available online: https://www.epol-projekt.de/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/eTMV_2_ML.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJournal Complex Syst. 2005, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanowitsch, A. Corpus Linguistics: A Guide to the Methodology; Language Science Press: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Stone, G. The Powerful Role of Interpersonal Communication in Agenda Setting. Mass Commun. Soc. 2003, 6, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, S.; Hollifield, C. Influence of agricultural trade publications on the news agendas of national newspapers and news magazines. J. Appl. Commun. 2000, 84, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, K.M.; Meyers, C.A. Conversations with gatekeepers: An exploratory study of agricultural publication editors’ decisions to publish risk coverage. J. Appl. Commun. 2010, 94, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.L. Toward a Theory of Press-State Relations in the United States. J. Commun. 1990, 40, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feindt, P.H.; Schwindenhammer, S.; Tosun, J. Politicization, Depoliticization and Policy Change: A Comparative Theoretical Perspective on Agri-food Policy. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. Pract. 2021, 23, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, S.P.; Bentlage, B.; Weiner, R.; Babin, N.; Bulla, B.R.; Fagan, K.; Haigh, T.; Carlton, J.S.; Prokopy, L.S. National print media vs. agricultural trade publications: Communicating the 2012 Midwestern US drought. Clim. Chang. 2020, 161, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Court of Auditors. Sustainable Water Use in Agriculture: CAP Funds More Likely to Promote Greater Rather Than More Efficient Water Use; European Court of Auditors: Luxembourg, 2021; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Galtung, J.; Ruge, M.H. The Structure of Foreign News: The Presentation of the Congo, Cuba and Cyprus Crises in Four Norwegian Newspapers. J. Peace Res. 1965, 2, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtin, P.; Khabirova, E.; Kuzminov, I.; Thurner, T. The future of food production–a text-mining approach. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2020, 32, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umweltbundesamt. Antibiotika und Antiparasitika im Grundwasser unter Standorten Mit Hoher Viehbesatzdichte; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Umweltbundesamt. Reaktiver Stickstoff in Deutschland. Ursachen, Wirkungen, Maßnahmen; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- BMUB; UBA. Die Wasserrahmenrichtlinie—Deutschlands Gewässer 2015; Umweltbundesamt: Bonn, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).