Selenium Application Decreases the Enrichment and Human Exposure Risk of Cadmium in the Leaf of Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) Planted in Uncontaminated Purple Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil
2.2. Planting and Harvesting
2.3. Se Addition
2.4. Analysis Method
2.5. Calculation
2.6. Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic of Pb, Cd, and Se in the Jute Leaf
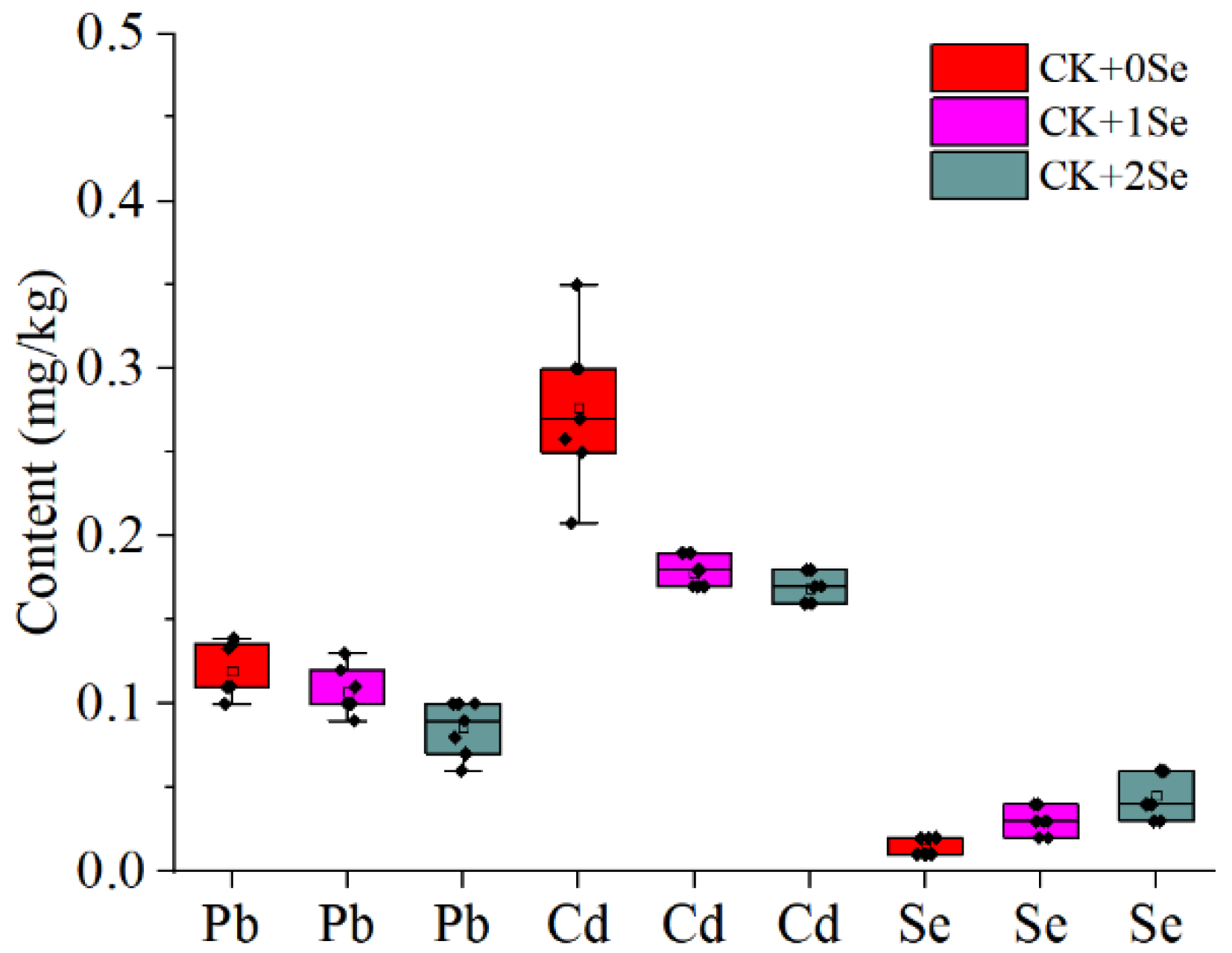
3.2. Pb, Cd, and Se across Seven Harvest
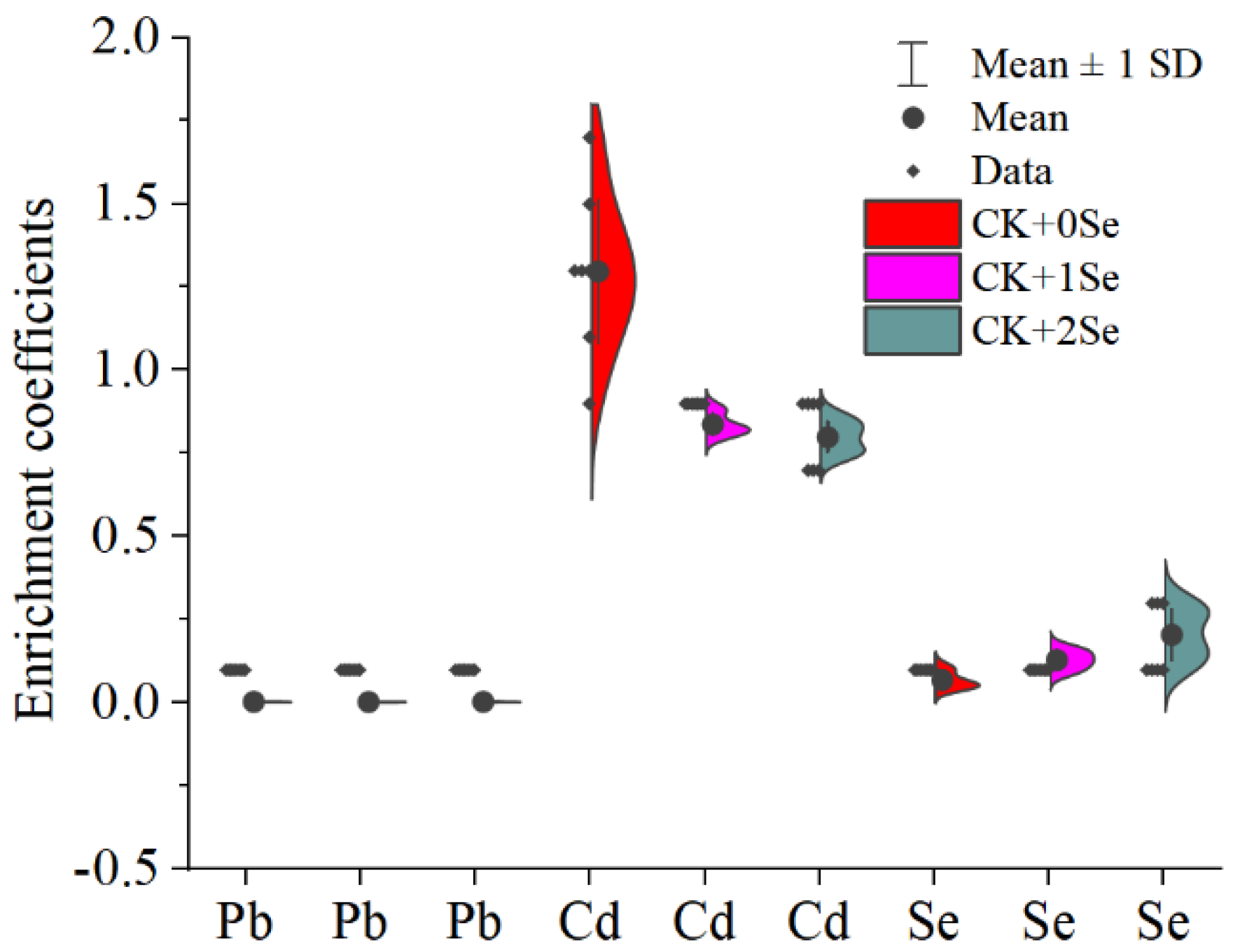
3.3. Enrichment Coefficient of Pb, Cd, and Se
3.4. Exposure Risk of Pb and Cd Enrichment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oladoye, P.O.; Olowe, O.M.; Asemoloye, M.D. Phytoremediation technology and food security impacts of heavy metal contaminated soils: A review of literature. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y. Technologies for removing heavy metal from contaminated soils on farmland: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolak, A.; Sarzyńska, M.; Szpyrka, E.; Stawarczyk, K. Sources of soil pollution by heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.A.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H.N. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadi, M.; el Kouali, M.E.K.; Talbi, M.; Ainane, T. Phytoremediation Review: Bioavailability of heavy metals and the role of bioaccumulative plants in the remediation of contaminated soils. J. Anal. Sci. Appl. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shmaefsky, B.R. Principles of phytoremediation. In Phytoremediation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilescu, M. Enhancing phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Rensing, C.; Ding, Y. Application of inorganic selenium to reduce accumulation and toxicity of heavy metals (metalloids) in plants: The main mechanisms, concerns, and risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J. Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Rensing, C.; Wu, Z.; et al. Underlying mechanisms responsible for restriction of uptake and translocation of heavy metals (metalloids) by selenium via root application in plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T.J.F.B. Selenium transformation and selenium-rich foods. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon-Smits, E.A. On the ecology of selenium accumulation in plants. Plants 2019, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Ning, Z.; Kwon, S.Y.; Li, M.-L.; Tack, F.M.; Kwon, E.E.; Rinklebe, J.; Yin, R. The beneficial and hazardous effects of selenium on the health of the soil-plant-human system: An overview. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndlovu, J.; Afolayan, A. Nutritional analysis of the South African wild vegetable Corchorus olitorius L. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2008, 7, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.M. Biochemistry, medicinal and food values of jute (Corchorus capsularis L. and C. olitorius L.) leaf: A review. Int. J. Enhanc. Res. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2013, 2, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Irshad, S.; Shafiq, F.; Iqbal, M.; Alharbi, B.M.; Alnusaire, T.S. Jute: A potential candidate for phytoremediation of metals—A review. Plants 2020, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, D.A.; Slima, D.F. Heavy metal accumulation by Corchorus olitorius L. irrigated with wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14996–15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, F.; Wang, X.; Saleem, M.H.; Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Saleem Malik, I.; Munir, M.; Mahpara, S.; Mehmood, N.; Ahmad, T. Risk assessment of heavy metals in basmati rice: Implications for public health. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, N.; Heidari, K.; Meshkinian, A.; Kamani, H.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Conti, G.O. Non-carcinogenic risk assessment of exposure to heavy metals in underground water resources in Saraven, Iran: Spatial distribution, monte-carlo simulation, sensitive analysis. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; He, Y.; Ma, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. Study on the current status and trend of food consumption among Chinese population. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2005, 26, 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, H. Cadmium accumulation and pollution risks to human health based on Monte-Carlo model of soil and vegetable-using vegetable field in Tianjin suburbs as example. China Environ. Sci. 2008, 28, 634–639. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Li, H. Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: Influence of different forms of selenium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Norton, G.J.; Duan, G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of selenium fertilization on the accumulation of cadmium and lead in rice plants. Plant Soil 2014, 384, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Cai, M.; Jia, W.; Zhao, X. Selenium reduces cadmium accumulation in seed by increasing cadmium retention in root of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 158, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Li, F. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake into rice suspension cells by regulating the expression of lignin synthesis and cadmium-related genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Rinklebe, J.; Tsang, D.C.; Tack, F.M.; Abbasi, G.H.; Hussain, A.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Lee, B.C. Effects of selenium on the uptake of toxic trace elements by crop plants: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 2531–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul-Soud, M.; Abd-Elrahman, S.H. Foliar selenium application to improve the tolerance of eggplant grown under salt stress conditions. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2016, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manion, L.K.; Kopsell, D.E.; Kopsell, D.A.; Sams, C.E.; Rhykerd, R.L. Selenium fertilization influences biomass, elemental accumulations, and phytochemical concentrations in watercress. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Catron, B.; Chan, Q.; Hu, Q.; Caruso, J.A. Identification of selenium compounds using HPLC-ICPMS and nano-ESI-MS in selenium-enriched rice via foliar application. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2009, 24, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chang, C.; Fei, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, G.; Lei, J. Cadmium accumulation in edible flowering cabbages in the Pearl River Delta, China: Critical soil factors and enrichment models. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Classification | OM g/kg | TN g/kg | TP % | TK g/kg | NH4+-N% | NO3−-N % | pH | Pb mg/kg | Cd mg/kg | Se mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purple soil | 9.95 | 0.64 | 0.0569 | 18.4 | 0.30 | 0.064 | 5.63 | 24.4 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
| Items | Elements | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK + 0Se | CK + 1Se | CK + 2Se | ||
| IRi | 0.082 | 0.082 | 0.082 | |
| CDI | Pb | 0.00014 | 0.00013 | 0.00010 |
| Cd | 0.00033 | 0.00021 | 0.00020 | |
| Se | 0.00002 | 0.00003 | 0.00006 | |
| HQ | Pb | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.10 |
| Cd | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.20 | |
| Se | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Tao, L.; Li, X.; Xiong, C.; Yang, X.; Nie, Q.; Lin, J. Selenium Application Decreases the Enrichment and Human Exposure Risk of Cadmium in the Leaf of Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) Planted in Uncontaminated Purple Soil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9535. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159535
Liu D, Tao L, Li X, Xiong C, Yang X, Nie Q, Lin J. Selenium Application Decreases the Enrichment and Human Exposure Risk of Cadmium in the Leaf of Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) Planted in Uncontaminated Purple Soil. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9535. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159535
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dan, Lei Tao, Xiang Li, Chunmei Xiong, Xiaoxia Yang, Qingyu Nie, and Junjie Lin. 2022. "Selenium Application Decreases the Enrichment and Human Exposure Risk of Cadmium in the Leaf of Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) Planted in Uncontaminated Purple Soil" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9535. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159535
APA StyleLiu, D., Tao, L., Li, X., Xiong, C., Yang, X., Nie, Q., & Lin, J. (2022). Selenium Application Decreases the Enrichment and Human Exposure Risk of Cadmium in the Leaf of Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) Planted in Uncontaminated Purple Soil. Sustainability, 14(15), 9535. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159535







