Study on Comparing the Performance of Fully Automated Container Terminals during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
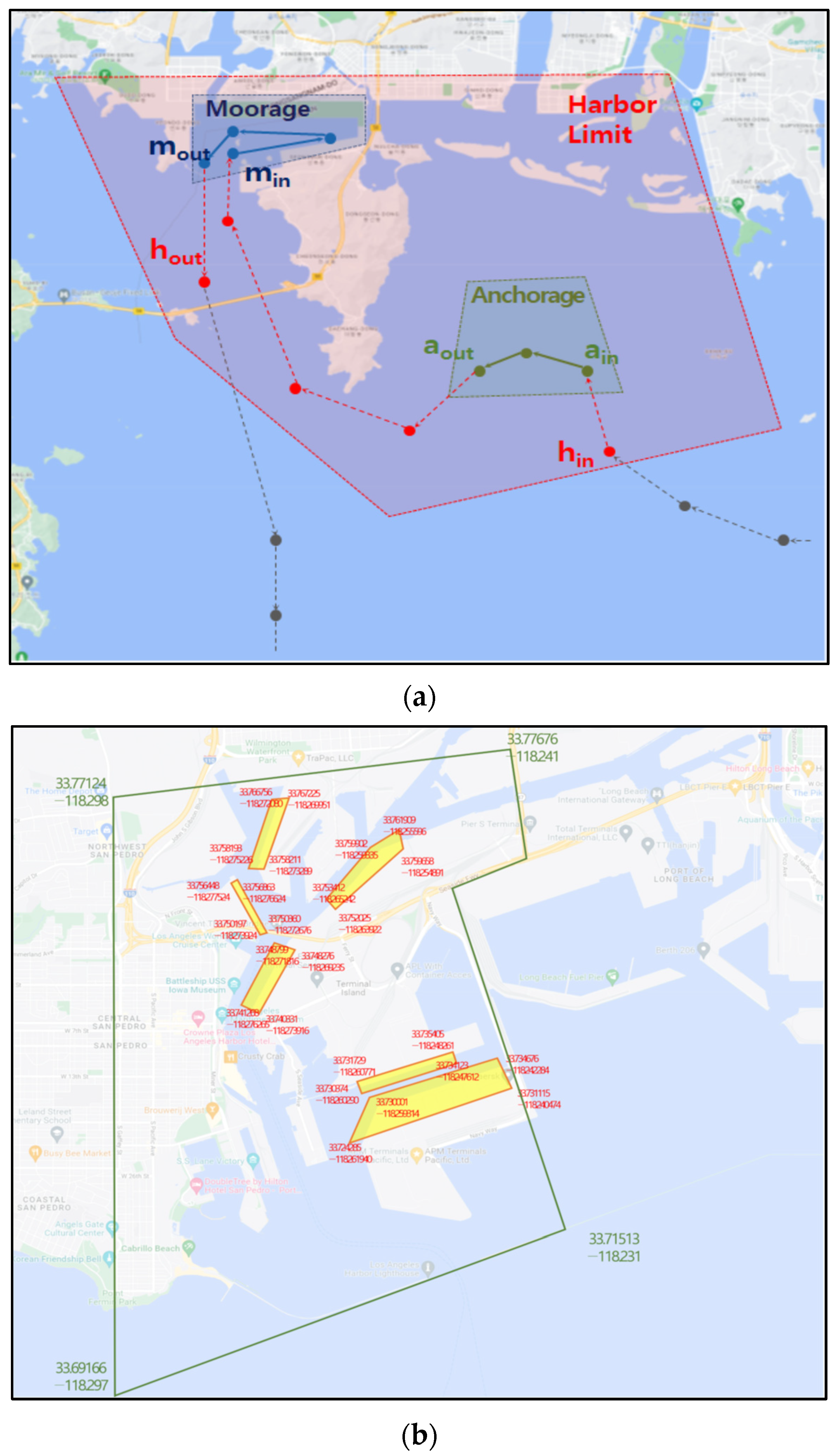
3.1. Analysis Targets
3.2. Performance Factors
3.3. Analysis Methods
3.3.1. Throughput
3.3.2. Berthing Times and Number of Ship Arrivals
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magableh, G.M. Supply chains and the COVID-19 pandemic: A comprehensive framework. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2021, 18, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, D.; Wang, H.; Yu, M. Risk assessment of port congestion risk during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Review of Maritime Transport; The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Notteboom, T.E.; Haralambides, H.E. Port management and governance in a post-COVID-19 era: Quo vadis? Marit. Econ. Logist. 2020, 22, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. The Container Port Performance Index 2020: A Comparable Assessment of Container Port Performance; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA; IHS Markit: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mankowska, M.; Plucinski, M.; Kotowska, I.; Filina-Dawidowicz, L. Seaports during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The terminal operators’ tactical responses to disruptions in maritime supply chains. Energies 2021, 14, 4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. OECD Economic Outlook; OECD: Paris, France, 2021; Volume 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X.; Tan, C. Yard operations and management in automated container terminals: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, W.K.; Rahman, N.; Hanafiah, R.; Hamid, S. The global trends of automated container terminal: A systematic literature review. Marit. Bus. Rev. 2020, 6, 206–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Gailus, S.; Liu, L.; Ni, L. The Future of Automated Ports. McKinsey & Company. 2018. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/travel-logistics-and-infrastructure/our-insights/the-future-of-automated-ports# (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Verschuur, J.; Koks, E.E.; Hall, J.W. Observed impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on global trade. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021, 4, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoush, A.; Ballini, F.; Olcer, A. Ports, maritime transport, and industry: The immediate impact of COVID-19 and the way forward. Marit. Technol. Res. 2022, 4, 250092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, K.; Haralambides, H. Global trends in maritime and port economics: The COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2021, 23, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notteboom, T.; Pallis, T. A Survey-based Analysis of the Impact of COVID-19 on World Ports; IAPH: Tokyo, Japan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cengiz, H.; Turan, E. Business impact of Covid-19 pandemic on global maritime industry. J. Nav. Sci. Eng. 2021, 17, 43–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, H.; Hanaoka, S.; Kawasaki, T. The cruise industry and the COVID-19 outbreak. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2020, 5, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Shi, J. The effect of COVID-19 pandemic on port performance: Evidence from China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 209, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarksons. Shipping Intelligence Network. 2021. Available online: https://sin.clarksons.net/ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Sea-Intelligence. Global Liner Performance (GLP) Report; Sea-Intelligence: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Economic Bulletin. European Central Bank. 2021. Available online: https://www.ecb.europa.eu/pub/economic-bulletin/focus/2021/html/ecb.ebbox202103_01~8ecbf2b17c.en.html#:~:text=The%20sharp%20rebound%20in%20global,generally%2C%20in%20higher%20input%20prices (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Thumbe, N.; Ranjan, J.; Ritanjali, M. Impact of COVID-19 on the Indian seaport transportation and maritime supply chain. Transp. Policy 2021, 110, 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Notteboom, T.E.; Pallis, T.; Rodrigue, J. Disruptions and resilience in global container shipping and ports: The COVID-19 pandemic versus the 2008–2009 financial crisis. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2021, 23, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, J.; Notteboom, T. Automation in Container Port System and Management, Transportation Research Board. In TR News; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; Volume 334, pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; An, Y. Financial analysis of automated container terminal capacity from the perspective of terminal operating company. J. Marine Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Ha, W. Evaluation of Handling Systems for Container Terminals. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2001, 127, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mileski, J.P.; Zeng, Q. Alignments between strategic content and process structure: The case of container terminal service process automation. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2017, 21, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisha, T.; Ouhimmou, M.; Paquet, M.; Montecinos, J. Developing the seaport container terminal layout to enhance efficiency of the intermodal transportation system and port operations–case of the Port of Montreal. Marit. Policy Manag. 2021, 49, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Su, X.; Li, G.; Jin, X.; Yu, M. A simulation based meta-heuristic approach for the inbound container housekeeping problem in the automated container terminals. Marit. Policy Manag. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chang, D.; Shi, X.; Yuan, J.; Gao, Y. Analysis and design of typical automated container terminals layout considering carbon emissions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, D.; Letrouit, L.; Montes, C.P. The container transport system during Covid-19: An analysis through the prism of complex networks. Transp. Policy 2022, 11, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, G.; Han, P.; Osen, O.; Zhang, H. Impacts of COVID-19 on ship behaviours in port area: An AIS data-based pattern recognition approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 1–12. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9706415 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Orive, A.C.; Santiago, J.; Corral, M.; Gonzalez-Cancelas, N. Strategic Analysis of the Automation of Container Port Terminals through BOT (Business Observation Tool). Logistics 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drewry Maritime Research. Global Container Terminal Operators Annual Review and Forecast 2020/21; Drewry Maritime Research: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Drewry Maritime Research. Global Container Terminal Operators, Annual Review and Forecast 2021/22; Drewry Maritime Research: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardo, M.; Paolo, B.; Dimitris, Z.; Giannis, S.; Stefano, M.; Peter, K.; Sandro, C. COVID-19 impact on global maritime mobility. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18039. [Google Scholar]
- Drewry Maritime Research. Ship Operating Cost Annual Review and Forecast 2018/2019; Drewry Maritime Research: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Category | Fully Automated | Non-Fully Automated | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Port | Terminal | Port | Terminal | |
| Port | Rotterdam | RWG, APMT | Rotterdam | ECT Delta, Euromax |
| LA/LB | LBCT, TraPac | LA/LB | TTI(Pier T), SSA(Pier A), APMT | |
| Qingdao | QQCTN | Qingdao | QQCT, QQCTU | |
| Shanghai | Yangshan Port Phase 4 | Shanghai | Yangshan Port Phases 1–2, Phase 3 | |
| Total | 6 terminals | 9 terminals | ||
| Category | Port | Terminal | Throughput (1000 TEU) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | Change (%) | |||
| Fully Automated | Rotterdam | RWG | 1921 | 2228 | 15.98 |
| APMT | 2323 | 2421 | 4.22 | ||
| LA/LB | LBCT | 1159 | 1911 | 64.88 | |
| Trapac | 790 | 1075 | 36.08 | ||
| Qingdao | QQCTN | 1286 | 1690 | 31.42 | |
| Shanghai | Yangshan Phase 4 | 3271 | 4204 | 28.52 | |
| Average | 1792 | 2255 | 30.18 | ||
| Non-fully Automated | Rotterdam | ECT Delta | 5300 | 5100 | −3.77 |
| Euromax | 2793 | 2455 | −12.1 | ||
| LA/LB | TTI (Pier T) | 2100 | 2400 | 14.29 | |
| SSA (Pier A) | 875 | 812 | −7.2 | ||
| APMT | 2564 | 2284 | −10.92 | ||
| Qingdao | QQCT | 8926 | 9103 | 1.98 | |
| QQCTU | 6348 | 6782 | 6.84 | ||
| Shanghai | Yangshan Phases 1, 2 | 8936 | 8672 | −2.95 | |
| Yangshan Phase 3 | 7601 | 7346 | −3.35 | ||
| Average | 5049 | 4995 | −1.91 | ||
| Mann–Whitney U test | U = 2.00, p = 0.0016 (p < 0.05) | ||||
| Category | Port | Terminal | Berthing Time (Hour) | Moving and Waiting Time (Hour) | Total Time in Port (Hour) | Number of Ship Arrivals (Ships) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | Change (%) | 2019 | 2020 | Change (%) | 2019 | 2020 | Change (%) | 2019 | 2020 | Change (%) | |||
| Fully Automated | Rotterdam | RWG | 10.91 | 12.84 | 17.64 | 50.33 | 49.69 | −1.27 | 61.24 | 62.53 | 2.11 | 1979 | 2037 | 2.93 |
| APMT | 12.78 | 12.88 | 0.76 | 33.27 | 35.8 | 7.60 | 46.05 | 48.68 | 5.71 | 1239 | 1080 | −12.83 | ||
| LA/LB | LBCT | 80.69 | 78.11 | −3.19 | 6.98 | 8.45 | 21.06 | 87.67 | 86.56 | −1.27 | 106 | 125 | 17.92 | |
| Trapac | 87.34 | 94.35 | 8.03 | 9.52 | 5.26 | −44.75 | 96.86 | 99.61 | 2.84 | 75 | 100 | 33.33 | ||
| Qingdao | QQCTN | 16.23 | 16.95 | 4.47 | 2.83 | 2.46 | −13.07 | 19.06 | 19.41 | 1.84 | 297 | 494 | 66.33 | |
| Shanghai | Yangshan Phase 4 | 21.65 | 21.62 | −0.16 | 1.69 | 2.37 | 40.24 | 23.34 | 23.99 | 2.78 | 827 | 1018 | 23.10 | |
| Average | 38.27 | 39.46 | 4.59 | 17.44 | 17.34 | −0.56 | 55.70 | 56.80 | 1.96 | 754 | 809 | 21.80 | ||
| Non-fully Automated | Rotterdam | ECT Delta | 16.27 | 18.72 | 15.04 | 36.24 | 35.65 | −1.63 | 52.51 | 54.37 | 3.54 | 3936 | 3631 | −7.75 |
| Euromax | 12.97 | 12.60 | −2.88 | 46.68 | 49.65 | 6.36 | 59.65 | 62.25 | 4.36 | 2040 | 1879 | −7.89 | ||
| LA/LB | TTI (Pier T) | 57.13 | 74.01 | 29.55 | 1.28 | 3.14 | 145.31 | 58.41 | 77.15 | 32.08 | 301 | 255 | −15.28 | |
| SSA (Pier A) | 32.17 | 35.00 | 8.79 | 6.01 | 10.99 | 82.86 | 38.18 | 45.99 | 20.46 | 245 | 297 | 21.22 | ||
| APMT | 72.07 | 107.10 | 48.59 | 3.41 | 1.89 | −44.57 | 75.48 | 108.99 | 44.40 | 232 | 199 | −14.22 | ||
| Qingdao | QQCT | 14.08 | 15.41 | 9.46 | 2.25 | 1.76 | −21.78 | 16.33 | 17.17 | 5.14 | 3146 | 3217 | 2.26 | |
| QQCTU | 17.41 | 17.94 | 3.06 | 2.5 | 3.24 | 29.60 | 19.91 | 21.18 | 6.38 | 1948 | 2148 | 10.27 | ||
| Shanghai | Yangshan Phases 1, 2 | 17.98 | 21.64 | 20.35 | 1.3 | 2.82 | 116.92 | 19.28 | 24.46 | 26.87 | 1847 | 1707 | −7.58 | |
| Yangshan Phase 3 | 17.97 | 20.50 | 14.09 | 1.23 | 1.87 | 52.03 | 19.2 | 22.37 | 16.51 | 1495 | 1368 | −8.49 | ||
| Average | 28.67 | 35.88 | 16.23 | 11.21 | 12.33 | 10.02 | 39.88 | 48.21 | 20.89 | 1688 | 1633 | −3.05 | ||
| Mann–Whitney U test | U = 12.00, p = 0.0879 * | U = 18.00, p = 0.3277 | U = 3.00, p = 0.0028 ** | U = 10.00, p = 0.0496 ** | ||||||||||
| Category | Average Ship Size (TEU) | Ship Operating Cost ($/Day) | Ship Operating Cost per Ship during Average Berthing Times ($) | Total Annual Ship Operating Cost ($1000) | Change ($1000, %) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Fully Automated | 6262 | 6636 | 25,344 | 25,780 | 40,410 | 42,385 | 30,463 | 34,290 | 3827 | 12.6 |
| Non-fully Automated | 6831 | 6944 | 25,987 | 26,180 | 31,046 | 39,138 | 52,399 | 63,930 | 11,532 | 22.0 |
| Category | Total Handling Charge Income ($1 Million) | Change ($1 Million, %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Fully Automated | 1934 | 2435 | 501 | 25.9% |
| Non-fully Automated | 5865 | 5732 | −133 | −2.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.; Kim, G.; Kang, M. Study on Comparing the Performance of Fully Automated Container Terminals during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159415
Kim B, Kim G, Kang M. Study on Comparing the Performance of Fully Automated Container Terminals during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159415
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Bokyung, Geunsub Kim, and Moohong Kang. 2022. "Study on Comparing the Performance of Fully Automated Container Terminals during the COVID-19 Pandemic" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159415
APA StyleKim, B., Kim, G., & Kang, M. (2022). Study on Comparing the Performance of Fully Automated Container Terminals during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability, 14(15), 9415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159415






