Energy-Efficient Mobile Agent Protocol for Secure IoT Sustainable Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- i.
- It offers a mobile agent-based collaborative routing solution that exploits fitness functions and selects the most optimal nodes for data aggregation services.
- ii.
- The probability of the nodes for data routing is increased and it trains the proposed protocol using experiences to reduce its communication overheads.
- iii.
- Mutual trust offers an authentic method using security tokens, and nodes are confident in sending their data to the mobile agents.
- iv.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate the significant improvement of the proposed protocol for computing and resources management.
2. Related Work
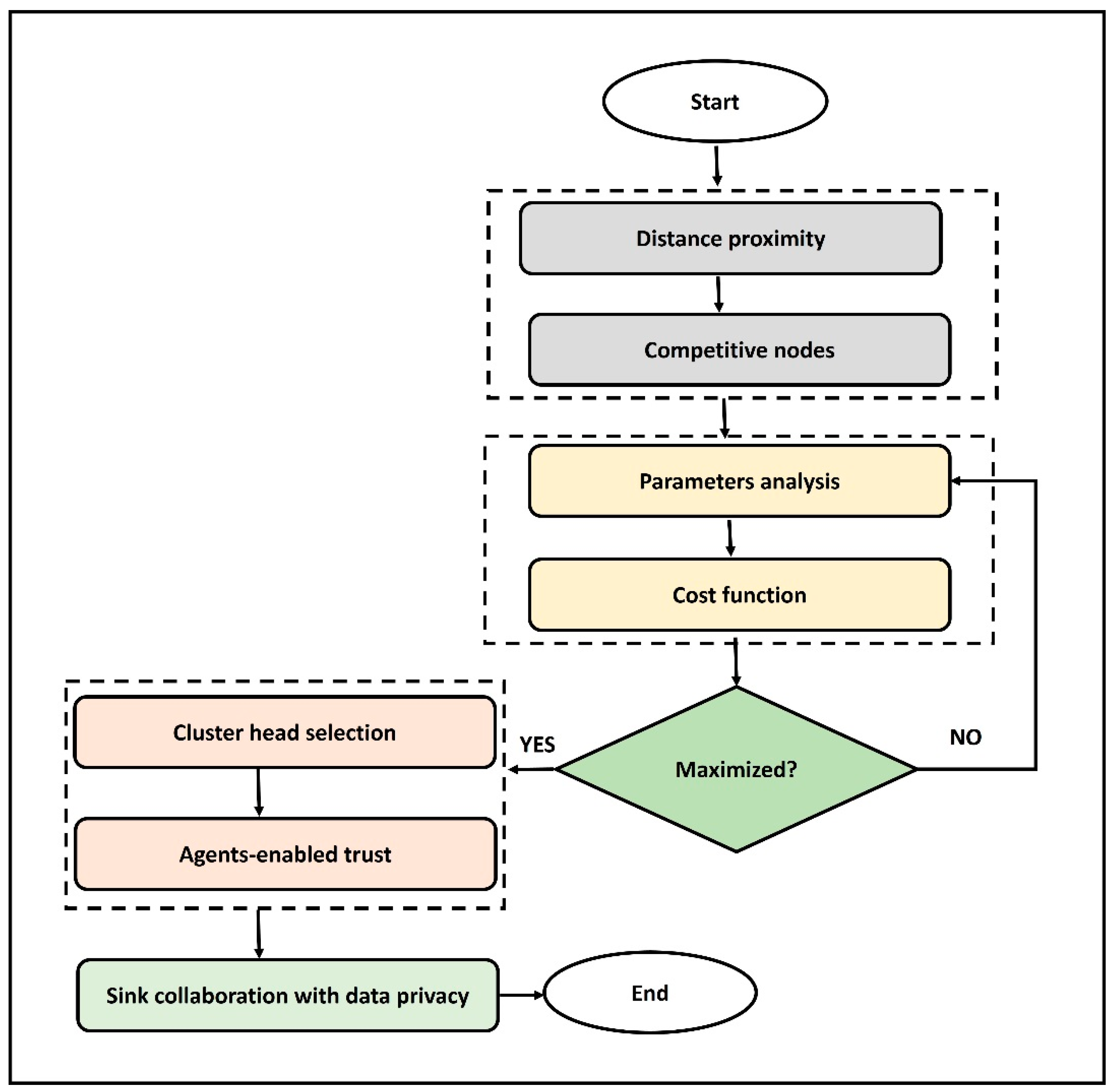
3. Proposed Energy-Efficient Mobile Secured Agent Protocol
3.1. Mobile Agent-Based Optimal Routing
3.2. Mutual Trust with Authentication and Privacy
4. Simulations
4.1. Security Analysis of Proposed Protocol
4.2. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, N.; Altamimi, M.; Haseeb, K.; Siraj, M. Secure and Sustainable Predictive Framework for IoT-Based Multimedia Services Using Machine Learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.-N.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain for Internet of Things: A survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 8076–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, W.H. Current research on Internet of Things (IoT) security: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2019, 148, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Fortino, G.; Messina, F.; Rosaci, D.; Sarne, G.M.L. Using blockchain in a reputation-based model for grouping agents in the Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2019, 67, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadori, H.Q.; Zukarnain, Z.A.; Hanapi, Z.M.; Subramaniam, S. FuMAM: Fuzzy-based mobile agent migration approach for data gathering in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 15643–15652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chaurasiya, V.K. A strategy for elimination of data redundancy in internet of things (IoT) based wireless sensor network (wsn). IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 13, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Said, G.; Sher, M.; Ning, H. Fog-assisted secure healthcare data aggregation scheme in IoT-enabled WSN. Peer-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Haseeb, K.; Saba, T.; Lloret, J.; Tariq, U. Secured Big Data Analytics for Decision-Oriented Medical System Using Internet of Things. Electronics 2021, 10, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Zatar, W. Agent based routing approach to support structural health monitoring-informed, intelligent transportation system. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetis, I.E.; Gavalas, D.; Pantziou, G.E.; Konstantopoulos, C. Mobile agents-based data aggregation in WSNs: Benchmarking itinerary planning approaches. Wirel. Netw. 2018, 24, 2111–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.-N.; Wong, R.C.-W.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Vasilakos, A.V. Big data analytics for large-scale wireless networks: Challenges and opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, Y.-G.; He, P. A comprehensive survey on the reliability of mobile wireless sensor networks: Taxonomy, challenges, and future directions. Inf. Fusion 2018, 44, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, S.A.; Farajzadeh, K.; Rezazadeh, J.; Farahbakhsh, R.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Dehkordi, M.A. Survey on data aggregation techniques in IoT sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 2020, 26, 1243–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Gain, S. Mitigating hot spot problem in wireless sensor networks using political optimizer based unequal clustering technique. J. Cybersecur. Inf. Manag. 2021, 8, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younan, M.; Khattab, S.; Bahgat, R. From the wireless sensor networks (WSNs) to the Web of Things (WoT): An overview. J. Intell. Syst. Int. Things 2021, 4, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Bai, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xue, N.; Ren, J. A multiobjective single bus corridor scheduling using machine learning-based predictive models. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, M.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Jeon, G. Edge computing-based person detection system for top view surveillance: Using CenterNet with transfer learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 107, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Huang, H. A novel reinforcement learning-based hyper-heuristic for heterogeneous vehicle routing problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 156, 107252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Nayyar, A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A. Fog computing: From architecture to edge computing and big data processing. J. Supercomput. 2019, 75, 2070–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.; Kumar, N.; Khurana, M.; Kumar, A.; Barnawi, A. Storage as a service in Fog computing: A systematic review. J. Syst. Archit. 2021, 116, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, M.; Wu, W.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Jeon, G. Computation offloading algorithm for arbitrarily divisible applications in mobile edge computing environments: An OCR case. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Din, S.; Ahmad, A.; Paul, A.; Jeon, G. Software-Defined Internet of Things to Analyze Big Data in Smart Cities, in Edge Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Iqbal, J.; Talha, M.; Arshad, M.; Diyan, M.; Han, K. Big data processing using internet of software defined things in smart cities. Int. J. Parallel Progr. 2020, 48, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K. Improving the security and authentication of the cloud with iot using hybrid optimization based quantum hash function. J. Intell. Syst. Internet Things 2021, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.P.; Amgoth, T.; Annavarapu, C.S.R. Machine learning algorithms for wireless sensor networks: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, J.; Wei, Z.; You, I. A deep reinforcement learning based approach for energy-efficient channel allocation in satellite internet of things. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62197–62206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. A deep-learning-based smart healthcare system for patient’s discomfort detection at the edge of Internet of Things. IEEE Int. Things J. 2021, 8, 10318–10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.U.; Yaqoob, I.; Tran, N.H.; Kazmi, S.A.; Dang, T.N.; Hong, C.S. Edge computing enabled smart cities: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Int. Things J. 2020, 7, 10200–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Ansari, N. EdgeIoT: Mobile edge computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. Energy-efficient fair cooperation fog computing in mobile edge networks for smart city. IEEE Int. Things J. 2019, 6, 7543–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Revenue-optimal task scheduling and resource management for IoT batch jobs in mobile edge computing. Peer-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 1776–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.; Manfroi, D.; Deitos, E.; Cegoni, J.; Castilhos, R.; Rochol, J.; Pignaton, E.; Kunst, R. An IoT-based smart cities infrastructure architecture applied to a waste management scenario. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2019, 87, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghebleh, B.; Wakil, K.; Navimipour, N.J. A comprehensive study on the trust management techniques in the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 9326–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fissaoui, M.; Beni-Hssane, A.; Saadi, M. Multi-mobile agent itinerary planning-based energy and fault aware data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellami, B.; Hakiri, A.; Ben Yahia, S.; Berthou, P. Energy-aware task scheduling and offloading using deep reinforcement learning in SDN-enabled IoT network. Comput. Netw. 2022, 210, 108957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaglio, C.; Pace, P.; Aloi, G.; Liotta, A.; Fortino, G. Lightweight reinforcement learning for energy efficient communications in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29355–29364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Rathore, S.; Jeong, Y.-S.; Park, J.H. SoftEdgeNet: SDN based energy-efficient distributed network architecture for edge computing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Han, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, Y. An energy efficient and QoS aware routing algorithm based on data classification for industrial wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 46495–46504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsboui, T.; Qin, Y.; Hill, R.; Al-Aqrabi, H. Enabling distributed intelligence for the Internet of Things with IOTA and mobile agents. Computing 2020, 102, 1345–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Derakhshan, F.; Karimipour, H.; Aghdasi, H.S. An efficient route planning model for mobile agents on the internet of things using Markov decision process. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2020, 98, 102053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennan, S.; Balasubramaniyam, S.; Luhach, A.K.; Ramasubbareddy, S.; Chilamkurti, N.; Nam, Y. Energy and delay aware data aggregation in routing protocol for Internet of Things. Sensors 2019, 19, 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masdari, M.; Özdemir, S. Towards coverage-aware fuzzy logic-based faulty node detection in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 111, 581–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Distance between nodes | |
| Preset threshold | |
| Set of cluster heads | |
| Optimized function | |
| Commutative value | |
| Lost packets | |
| Residual energy | |
| Error level | |
| Agent’s distance | |
| Delay rate | |
| t | Time interval |
| Encryption | |
| Data messages | |
| xor | |
| Session key | |
| New session key | |
| Random numbers |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nodes | 20–100 |
| Sink nodes | 2 |
| Field dimension | 200 m × 200 m |
| Initial energy | 2–5j |
| Transmission range | 5 m |
| Packet size | 32 bytes |
| Time intervals | 2000 s |
| Number of simulations | 10 |
| Mobile agents | 5 |
| Malicious devices | 2–10 |
| Attack | Proposed Countermeasures |
|---|---|
| Replay attack | Time stamp, pseudorandom |
| Token security | Encrypted with a session key |
| Data privacy | Xor between data blocks and new session key |
| Mutual trust | Exchange of security tokens |
| Non-verifiable trust | System authentication error |
| Security for session key | Encryption layer using public key |
| Route failure | Resend security token |
| Data modification | Digital hash |
| Erroneous data packets | Timely detection of faulty nodes/links |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elhoseny, M.; Siraj, M.; Haseeb, K.; Nawaz, M.; Altamimi, M.; Alghamdi, M.I. Energy-Efficient Mobile Agent Protocol for Secure IoT Sustainable Applications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148960
Elhoseny M, Siraj M, Haseeb K, Nawaz M, Altamimi M, Alghamdi MI. Energy-Efficient Mobile Agent Protocol for Secure IoT Sustainable Applications. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148960
Chicago/Turabian StyleElhoseny, Mohamed, Mohammad Siraj, Khalid Haseeb, Muhammad Nawaz, Majid Altamimi, and Mohammed I. Alghamdi. 2022. "Energy-Efficient Mobile Agent Protocol for Secure IoT Sustainable Applications" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148960
APA StyleElhoseny, M., Siraj, M., Haseeb, K., Nawaz, M., Altamimi, M., & Alghamdi, M. I. (2022). Energy-Efficient Mobile Agent Protocol for Secure IoT Sustainable Applications. Sustainability, 14(14), 8960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148960









