Establishing an Intelligent Emotion Analysis System for Long-Term Care Application Based on LabVIEW
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
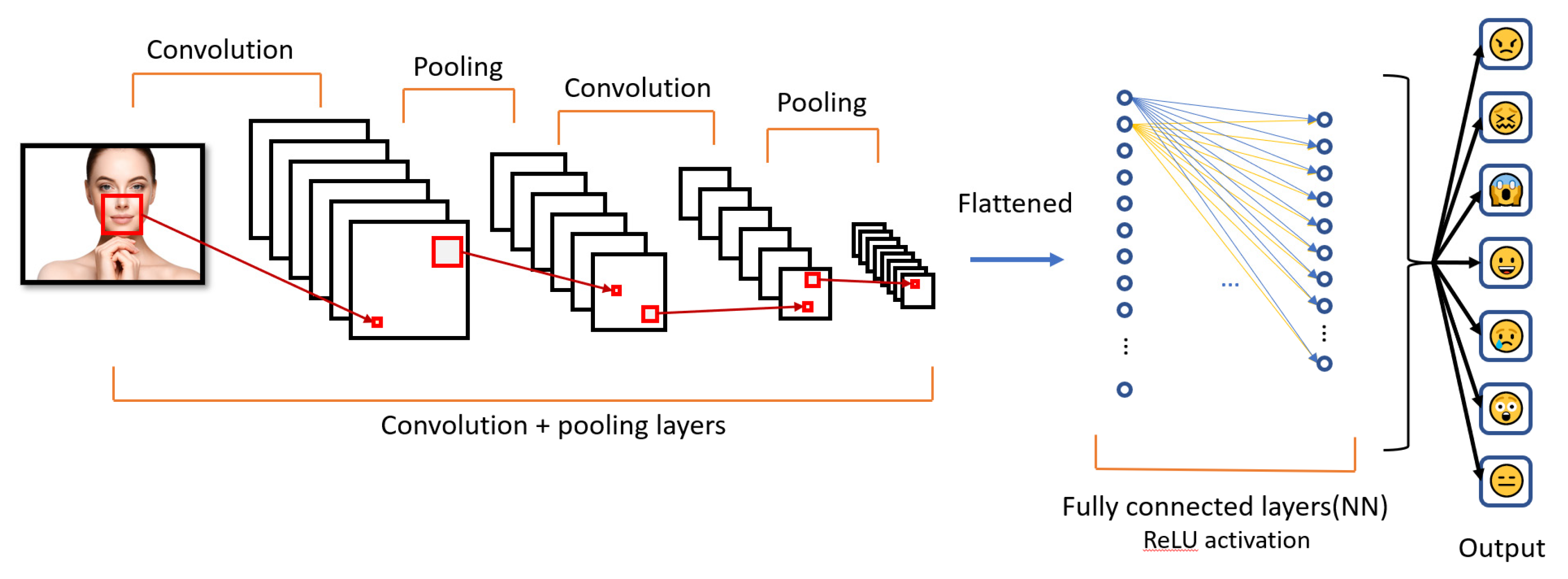
3. System Structure
- happy: the cheek muscles rise, the corners of the mouth rise, the corners of the mouth pull back, the eyebrows are flat, and the eyes become smaller;
- sadness: upper eyelid drooping, dilated pupils, corners of the mouth pulling down, cheeks pulling down, eyebrows locked deeply;
- anger: enlarged nostrils, enlarged eyes;
- disgust: raise your nose and raise your mouth;
- fear: the middle of the eyebrows is crowded together;
- surprise: the mouth is slightly open, the pupils are dilated, and the eyebrows are raised;
- contempt: The corners of the lips tighten and lift only one side of the face, and one eyebrow rises;
4. Main Results
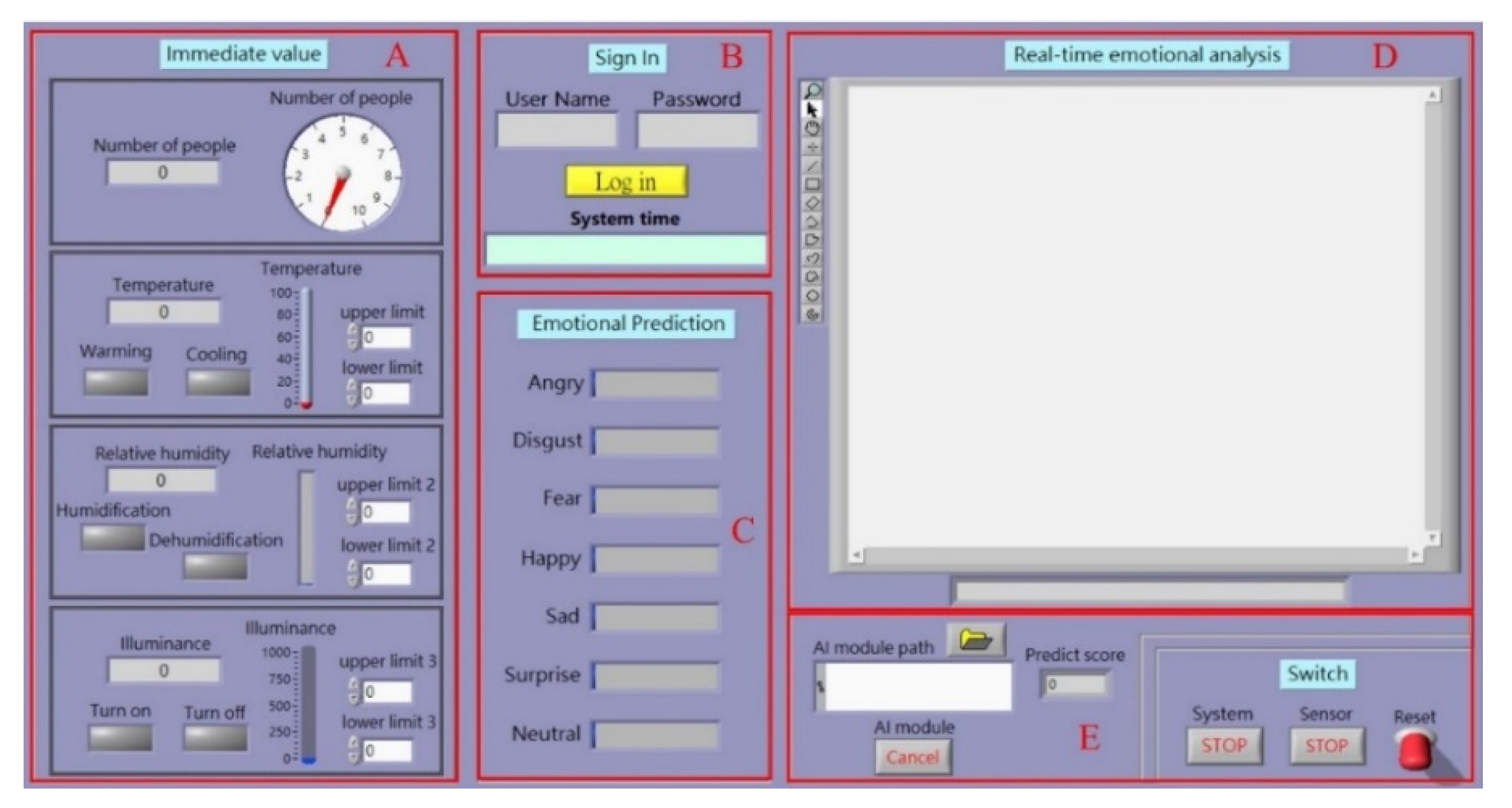
4.1. Environmental Monitoring
4.2. Sign-in Function
4.3. Sentiment Prediction
4.4. Facial Expression Image Monitoring
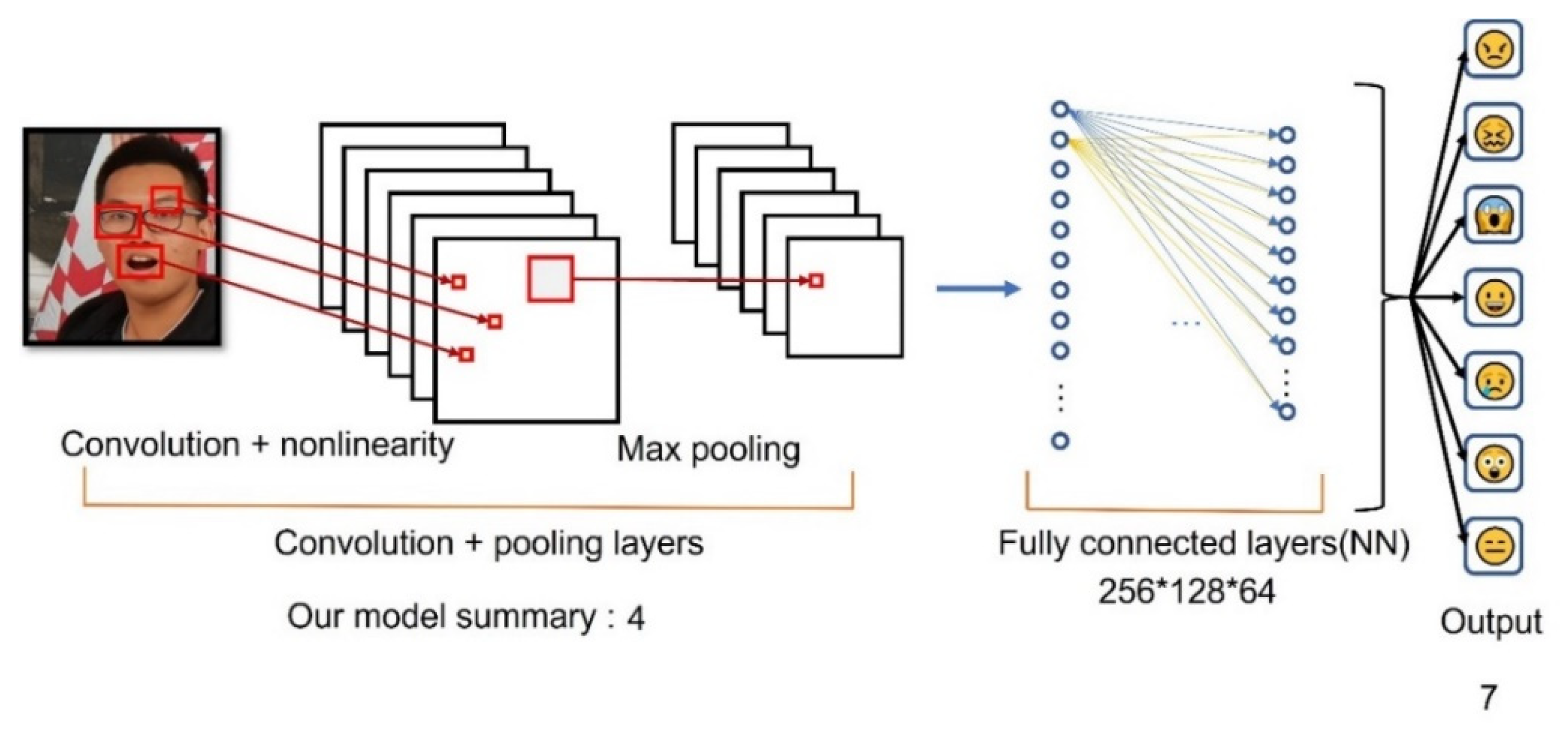
4.5. Model Construction and Methods

| Actual (Positive) | Actual (Negative) | |
|---|---|---|
| Predict (Positive) | TP | FP |
| Predict (Negative) | FN | TN |
5. Conclusions
- There may be more appropriate hyperparameter configurations such as convolutional and fully connected layers, or better depth models may be used to obtain better accuracy.
- The amplification of the data volume of the data set, the amount of data in some categories is not sufficient, resulting in the low accuracy of the identification of the category.
- Due to national laws and treaty restrictions, more personal identity and health information cannot be added to the research materials, and cannot be disclosed, and the conclusion of the research is easy to be questioned.
- The device can use cams with higher resolution and autofocus functions to improve the efficiency of detection and identification, and in the future, it can even obtain more information according to portable electronic devices to achieve a smarter system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Economic Affairs. 2021/2022 Industrial Technology White Paper; Taiwan Institute of Economic Res: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2021; Available online: https://reurl.cc/NAxmGm (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Industrial Technology Research Institute & Nan Shan Life Insurance Company. Taiwan’s Long-Term Care Industry White Paper; Institute of Industrial Technology International Strategy Development Institute of Industrial Technology: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2021; Available online: https://reurl.cc/55WN17 (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- CommonWealth Magazine. The Average Life Expectancy of Taiwanese Rural Residents Is 7 Years Shorter than That of Urban Residents! How Can 5G Bridge This Gap? Taipei City, Taiwan. 2021. Available online: https://reurl.cc/6ZORvd (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Lepage, P.; Létourneau, D.; Hamel, M.; Briere, S.; Corriveau, H.; Tousignant, M.; Michaud, F. Telehomecare telecommunication framework—From remote patient monitoring to video visits and robot telepresence. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 3269–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K.; Shibata, T.; Saito, T.; Tanie, K. Psychological and social effects of robot assisted activity to elderly people who stay at a health service facility for the aged. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; Volume 3, pp. 3996–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baños, R.M.; Etchemendy, E.; Castilla, D.; García-Palacios, A.; Quero, S.; Botella, C. Positive mood induction procedures for virtual environments designed for elderly people. Interact. Comput. 2012, 24, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Perez, J.; Lohse, M.; Evers, V. Robots to motivate elderly people: Present and future challenges. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE RO-MAN, Gyeongju, Korea, 26–29 August 2013; pp. 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahara, L.; Musa, P.; Wibowo, E.P.; Karim, I.; Musa, S.B. The Facial Emotion Recognition (FER-2013) Dataset for Prediction System of Micro-Expressions Face Using the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Algorithm based Raspberry Pi. In Proceedings of the 2020 Fifth International Conference on Informatics and Computing (ICIC), Gorontalo, Indonesia, 3–4 November 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Erhan, D.; Carrier, P.L.; Courville, A.; Mirza, M.; Hamner, B.; Cukierski, W.; Tang, Y.; Thaler, D.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Challenges in representation learning: A report on three machine learning contests. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Daegu, Korea, 3–7 November 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ecman, P. Micro Expressions. 2017. Available online: https://www.slideserve.com/tyrell/microexpressions (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Lee, P.L.; Wang, C.L. Emotional Management for the Elderly. J. Crisis Manag. 2012, 9, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.W.; Chiou, S.F.; Pan, M.L.; Wu, H.H.; Jiang, J.R.; Lu, Y.D. The Development of an Intelligent Long-Term Care Services System That Integrates Innovative Information and Communication Technologies. J. Nurs. Res. 2017, 64, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sharma, A.; Shabaz, M. Research on digital media animation control technology based on recurrent neural network using speech technology. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022, 13, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. Brain MRI analysis for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using an ensemble system of deep convolutional neural networks. Brain Inform. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, T.; Zhuang, X. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (2019) Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multi-modality 3D convolutional neural network. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Thibeau-Sutre, E.; Diaz-Melo, M.; Samper-González, J.; Routier, A.; Bottani, S.; Dormont, D.; Durrleman, S.; Burgos, N.; Colliot, O. Initiative ADN (2020) Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: Overview and reproducible evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.T.; Ryu, S.; Qureshi, M.N.I.; Choi, M.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, B. 3D-deep learning based automatic diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease with joint MMSE prediction using resting-state fMRI. Neuroinformatics 2020, 18, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poongodi, M.; Sharma, A.; Hamdi, M.; Maode, M.; Chilamkurti, N. Smart healthcare in smart cities: Wireless patient monitoring system using IoT. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 12230–12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, G.K.; Kaur, S.; Gaba, G.S.; Kansal, L.; Sharma, A.; Dhiman, G. COVID-19: Role of robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning during pandemic. Curr. Med. Imaging 2021, 18, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, L.; Sharma, A.; Dhiman, G.; Vimal, S. The Application of Convolutional Neural Network Model in Diagnosis and Nursing of MR Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2022, 14, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, M.S.; Srikanth, L.; Naidu, V.P.S. Design and development of LabVIEW based environmental test chamber controller. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, 15–16 December 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wati, D.A.R.; Abadianto, D. Design of face detection and recognition system for smart home security application. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International conferences on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 1–2 November 2017; pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.-C.; Huang, W.-T.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, T.-Y. Establishing an AI Model on Data Sensing and Prediction for Smart Home Environment Control Based on LabVIEW. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 7572818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, T.; Bae, H.B.; Lee, Y.; Jang, S.; Lee, S. Deep-Learning-Based Stress Recognition with Spatial-Temporal Facial Information. Sensors 2021, 21, 7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Gao, M.; Liu, R.; Mao, J. MIFAD-net: Multi-layer interactive feature fusion network with angular distance loss for face emotion recognition. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maithri, M.; Raghavendra, U.; Gudigar, A.; Samanth, J.; Barua, P.D.; Murugappan, M.; Chakole, Y.; Acharya, U.R. Automated Emotion Recognition: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, D.; Zafeiriou, S.P. Exploiting multi-cnn features in cnn-rnn based dimensional emotion recognition on the omg in-the-wild dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2021, 12, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.; Singh, J. A Deep Learning Approach for Real Time Facial Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th International Conference on System Modeling & Advancement in Research Trends (SMART), Moradabad, India, 10–11 December 2021; pp. 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-X.; Zhang, X.-X.; Guo, L.-X.; Ding, Z.-W.; Zhang, L.-L.; Wei, S.-Y.; Fan, R.; Ma, Y.-Z. An intelligent old-age home endowment monitoring system based on Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing (PIC), Nanjing, China, 15–17 December 2017; pp. 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuheir, M.; Albaseer, A.; Baccour, E.; Erbad, A.; Abdallah, M.; Hamdi, M. Emotion recognition for healthcare surveillance systems using neural networks: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Harbin City, China, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, S. Emotion Recognition of the Elderly Living Alone Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), Penghu, Taiwan, 15–17 September 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Schuller, B. EmoBed: Strengthening monomodal emotion recognition via training with crossmodal emotion embeddings. Proc. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 12, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vithanawasam, T.M.W.; Madhusanka, B.G.D.A. Face and upper-body emotion recognition using service robot’s eyes in a domestic environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Research Conference on Smart Computing and Systems Engineering (SCSE), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 28 March 2019; pp. 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Yuan, T.; Al-Nabhan, N. Emotion-aware and intelligent internet of medical things toward emotion recognition during COVID-19 pandemic. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 16002–16013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.; Douglas-Cowie, E.; Tsapatsoulis, N.; Votsis, G.; Kollias, S.; Fellenz, W.; Taylor, J.G. Emotion recognition in human-computer interaction. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2001, 18, 32–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, G.; Hong, X.; Zheng, W.; Pietikäinen, M. Spontaneous facial micro-expression analysis using spatiotemporal completed local quantized patterns. Neurocomputing 2016, 175, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S.J.; Zhao, G.; Piteikainen, M. Facial micro-expression recognition using spatiotemporal local binary pattern with integral projection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S.J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Feng, X.; Pietikäinen, M. Discriminative spatiotemporal local binary pattern with revisited integral projection for spontaneous facial micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, J.K.; Yan, W.J.; Wang, S.J.; Zhao, G.; Fu, X. A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 7, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zheng, W.; Xin, M.; Yan, J. Integrating facial expression and body gesture in videos for emotion recognition. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2014, 97, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, H.; Ma, T. Feature extraction and facial expression recognition based on bezier curve. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Xi’an, China, 11–13 September 2014; pp. 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, D.; Hebbar, R.; Vinod, P.V.; Harsheetha, M.P.; Jyothi, L.; Madhu, S.H. CNN based technique for systematic classification of field photographs. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Design Innovations for 3Cs Compute Communicate Control (ICDI3C), Bangalore, India, 25–28 April 2018; pp. 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O.; Yang, L. Cellular neural networks: Theory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1988, 35, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springenberg, J.T.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T.; Riedmiller, M. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations ICLR 2015—Workshop Track Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Shi, H.; Zurada, J.M. Cellular neural networks with transient chaos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2007, 54, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, C.; Huang, L. Invariance principle and complete stability for cellular neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2006, 53, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Micro-Expression | Validation Data | Training Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Classification) | Elder | Others | Total | Elder | Others | Others |
| happy | 345 | 1248 | 1593 | 2315 | 6784 | 9099 |
| anger | 244 | 976 | 1220 | 1042 | 4253 | 5295 |
| sadness | 287 | 881 | 1168 | 2151 | 5382 | 7533 |
| fear | 193 | 829 | 1022 | 1097 | 4721 | 5818 |
| disgust | 43 | 153 | 196 | 282 | 805 | 1087 |
| surprise | 218 | 716 | 934 | 1126 | 3686 | 4812 |
| contempt | 284 | 996 | 1280 | 1972 | 5819 | 7791 |
| 1614 | 5799 | 7413 | 9985 | 31,450 | 41,435 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, K.-C.; Huang, W.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Ho, W.-S. Establishing an Intelligent Emotion Analysis System for Long-Term Care Application Based on LabVIEW. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148932
Yao K-C, Huang W-T, Chen T-Y, Wu C-C, Ho W-S. Establishing an Intelligent Emotion Analysis System for Long-Term Care Application Based on LabVIEW. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148932
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Kai-Chao, Wei-Tzer Huang, Teng-Yu Chen, Cheng-Chun Wu, and Wei-Sho Ho. 2022. "Establishing an Intelligent Emotion Analysis System for Long-Term Care Application Based on LabVIEW" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148932
APA StyleYao, K.-C., Huang, W.-T., Chen, T.-Y., Wu, C.-C., & Ho, W.-S. (2022). Establishing an Intelligent Emotion Analysis System for Long-Term Care Application Based on LabVIEW. Sustainability, 14(14), 8932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148932







