Occurrence, Comparison and Priority Identification of Antibiotics in Surface Water and Sediment in Urbanized River: A Case Study of Suzhou Creek in Shanghai
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
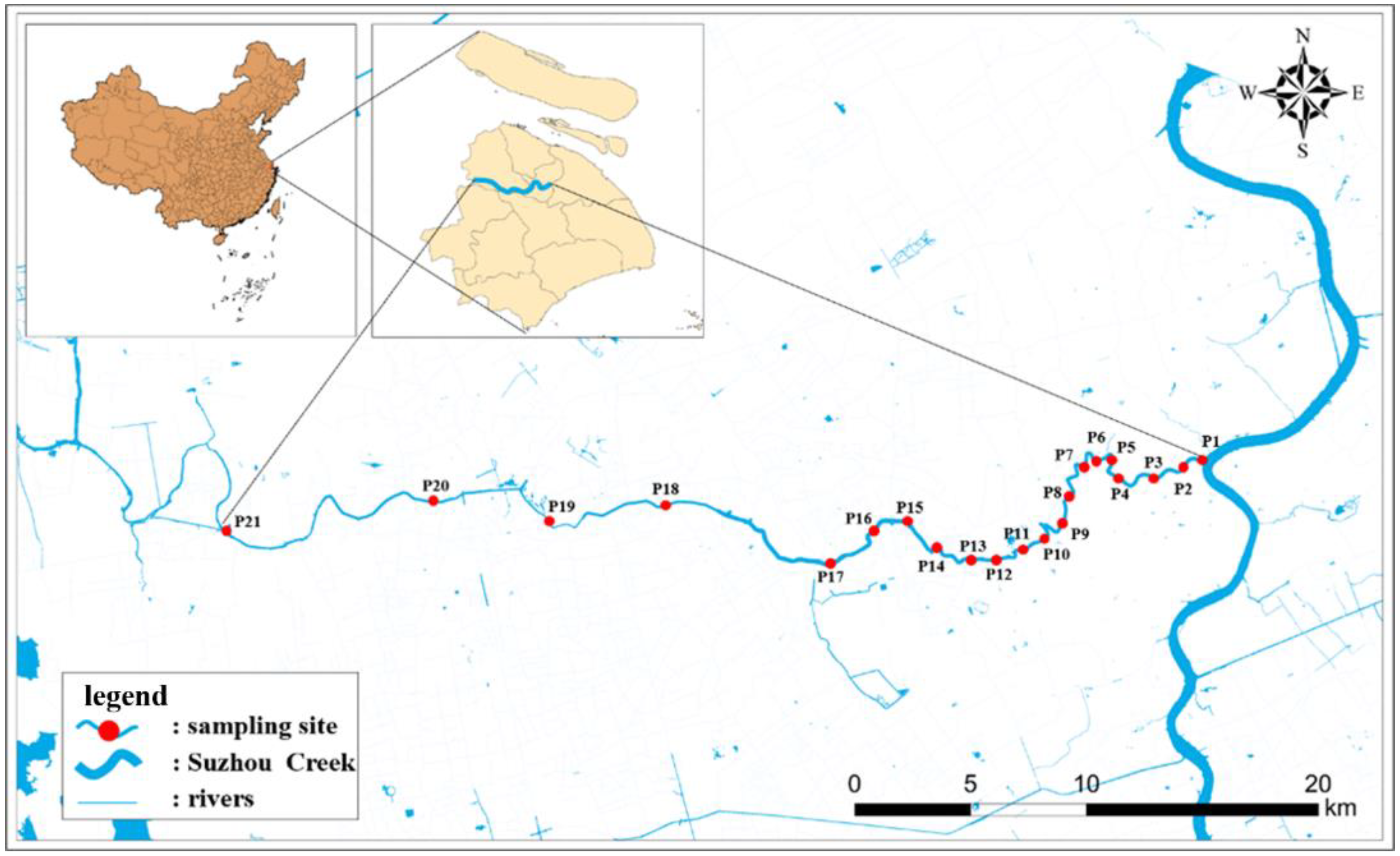
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Sample Pretreatment
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Quality Analysis and Control
2.6. Pseudo Distribution Coefficient
2.7. Environmental Risk Assessment
2.8. Priority Antibiotics Screening Method
- (1)
- High frequency of detection (>80%)
- (2)
- Strong positive correlation with total antibiotic concentration (SUM) (p < 0.05) or high concentration antibiotics
- (3)
- Significant risk of acute or chronic toxicity to aquatic organisms (RQ > 0.01)
- (4)
- Detection frequency is over 30% in sediment
3. Results and Discussion
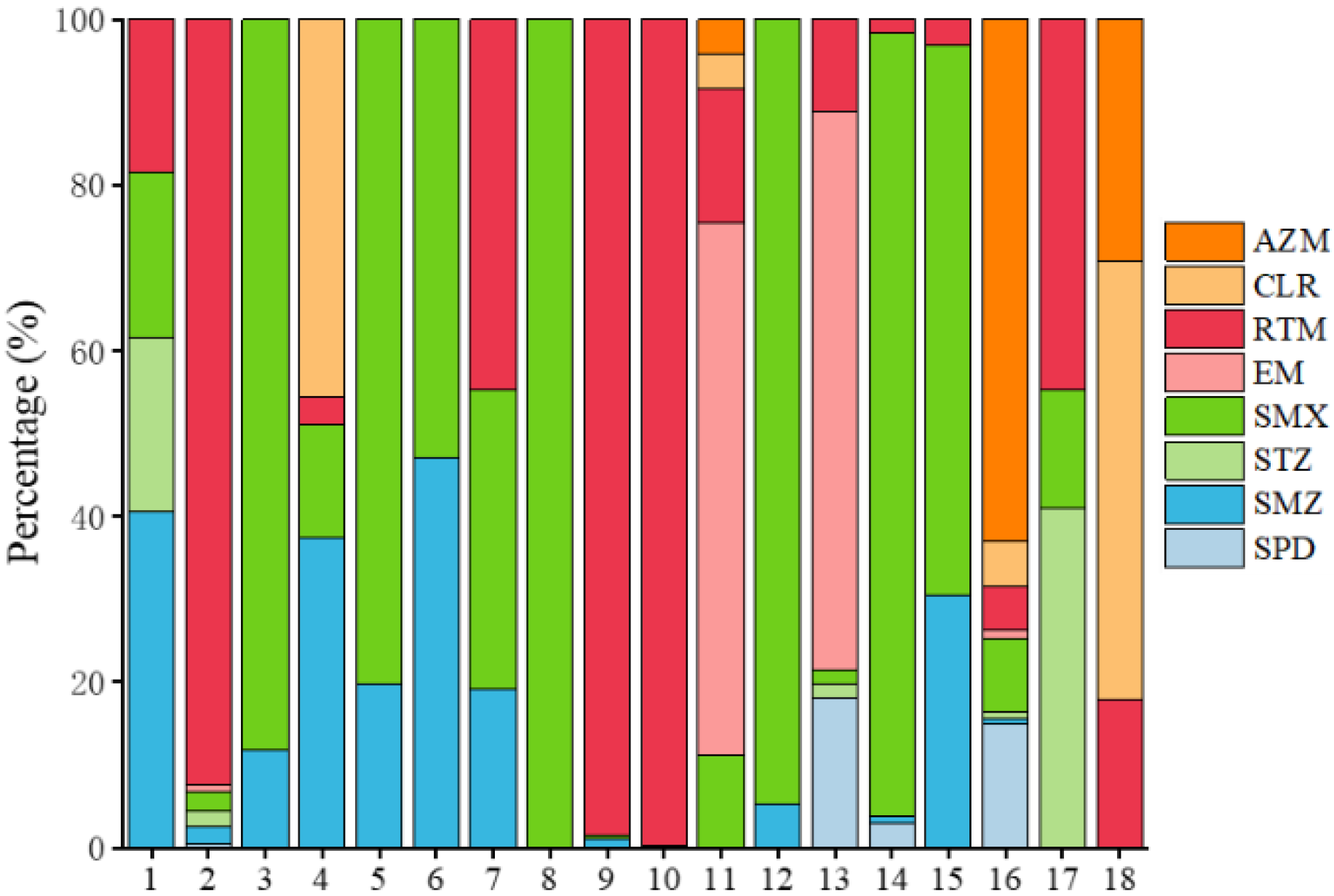
3.1. Occurrence of Selected Antibiotics
3.1.1. Antibiotics in Surface Water
3.1.2. Antibiotics in Sediment
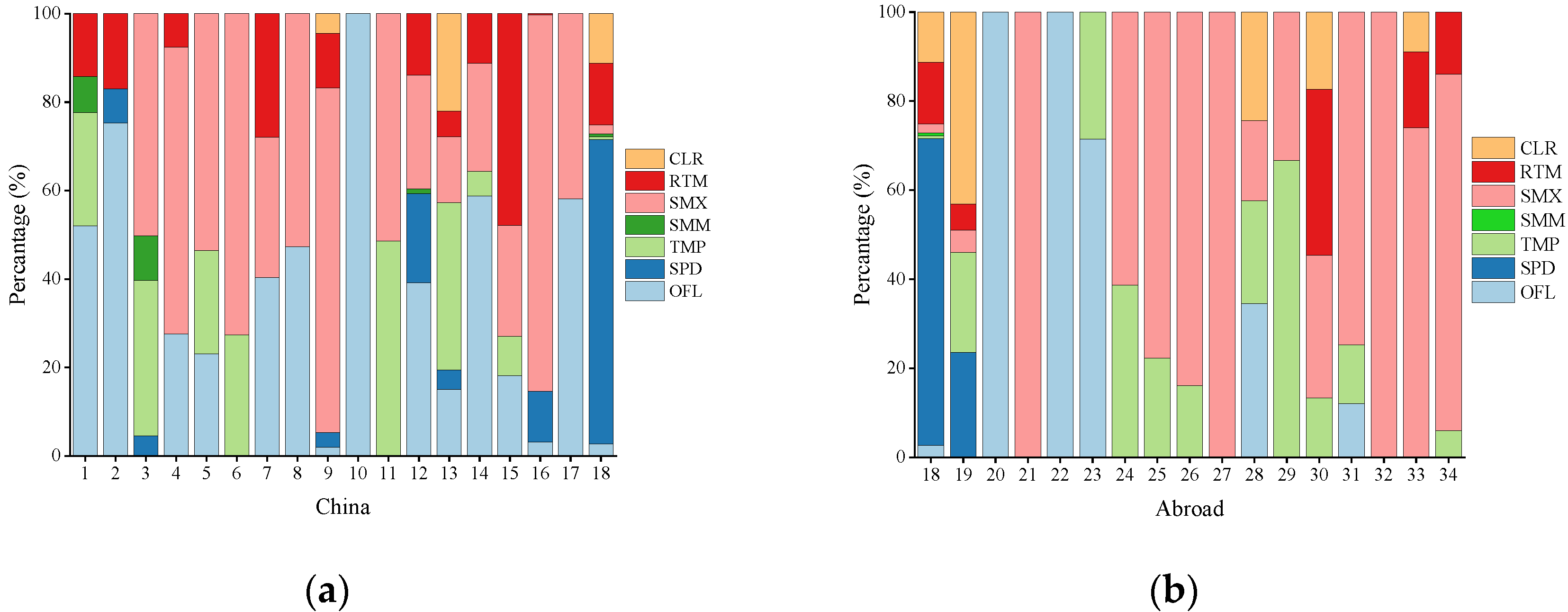
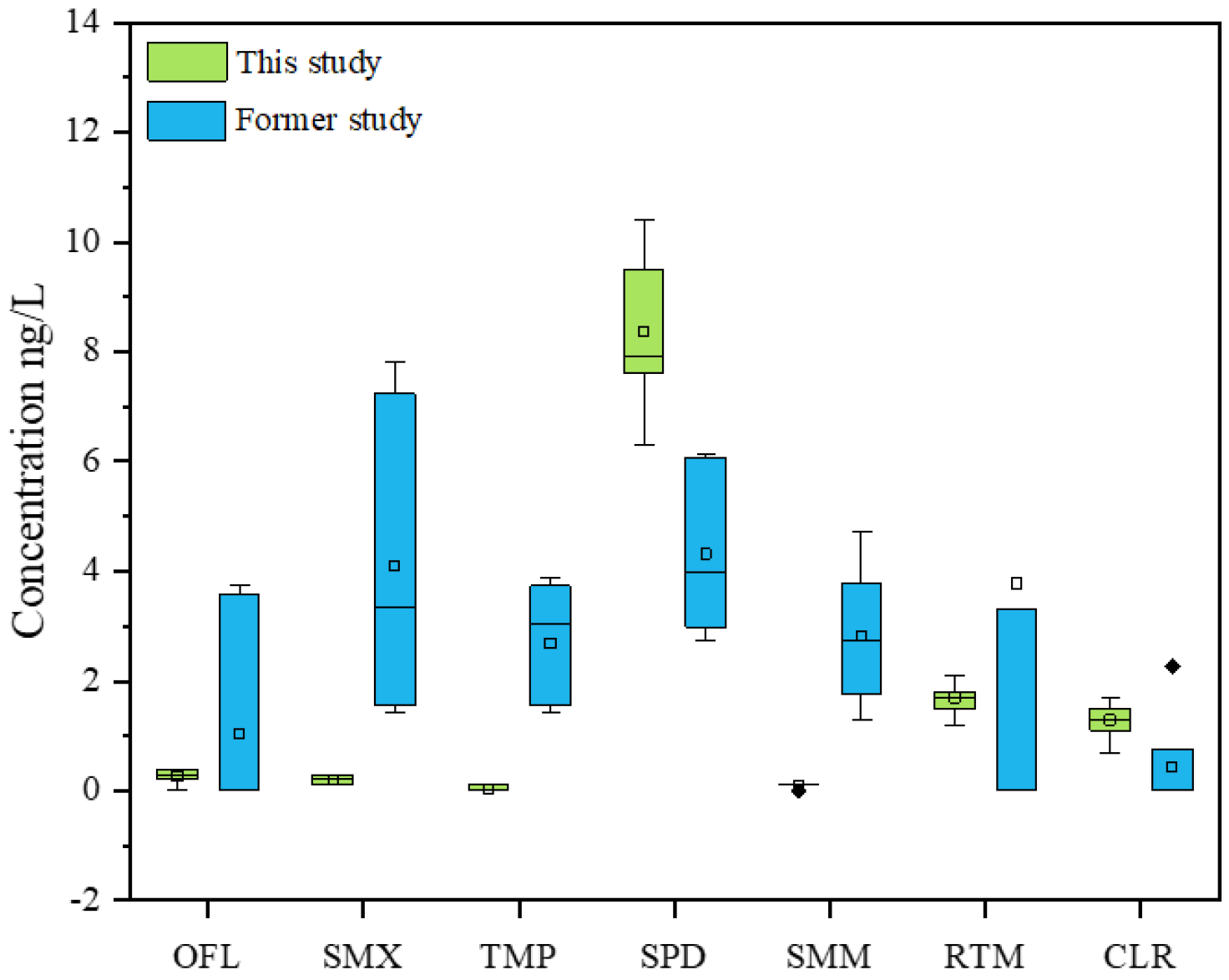
3.1.3. Comparison of Antibiotics in Different Studies
3.2. Correlation Analysis and Pseudo Distribution Coefficient
3.2.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis
3.2.2. Pseudo Distribution Coefficient
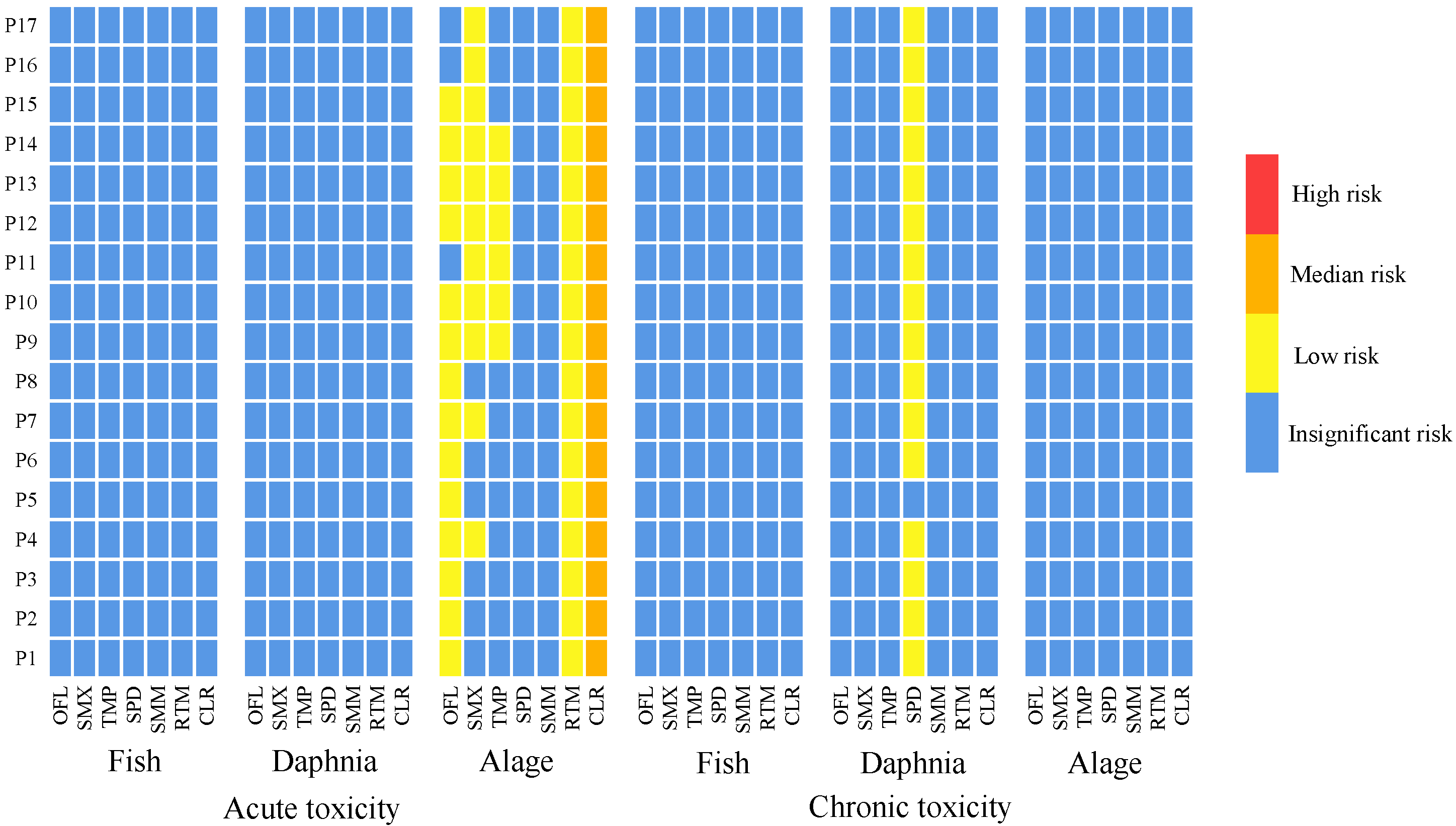
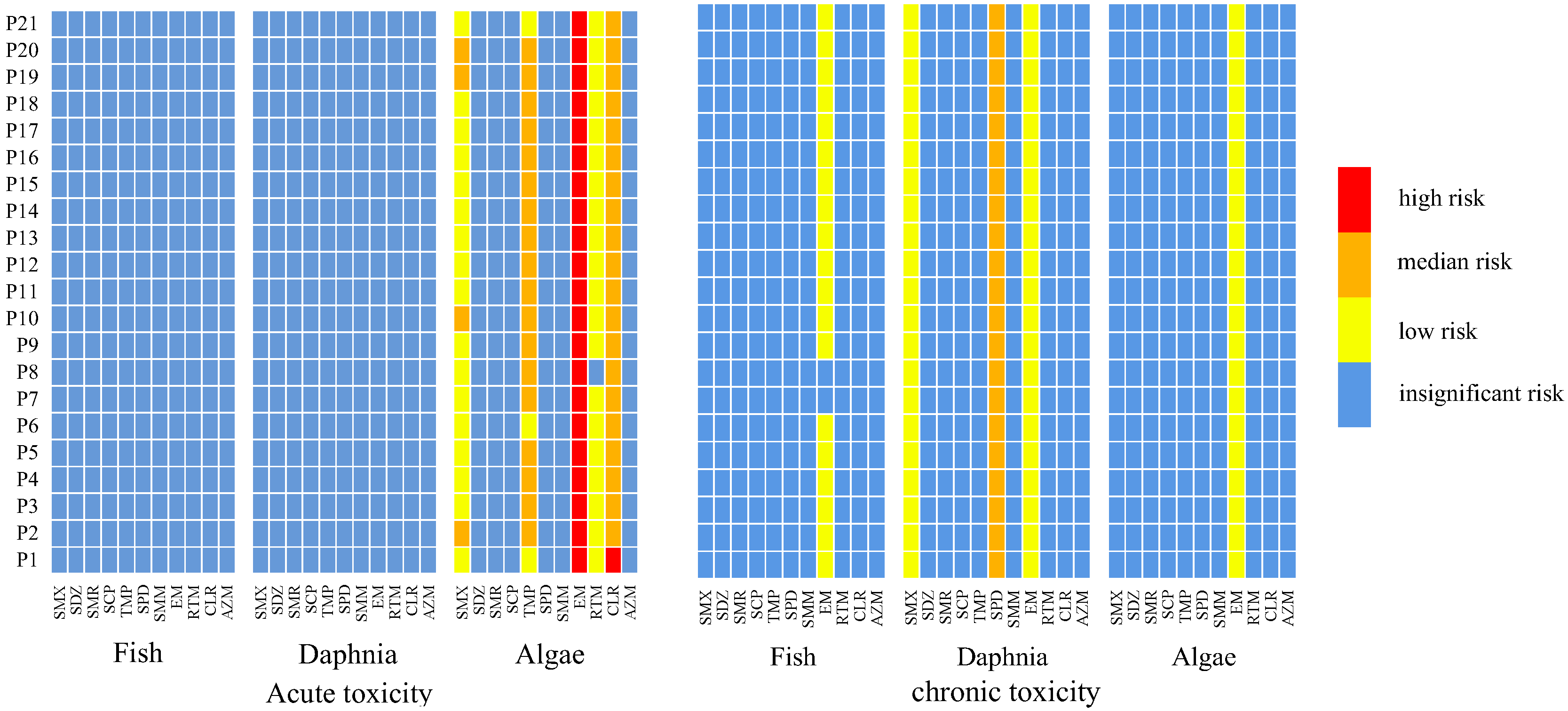
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
3.4. Identification of the Priority Antibiotics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gould, I.M.; MacKenzie, F.M.; Struelens, M.J.; Meer, J.M.W.V.D. Towards a European strategy for controlling antibiotic resistance Nijmegen, Holland August 29–31, 1999. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.-Q. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review–Part I. Chemosphere 2008, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.J.; Smith, S.G.; Kolpin, D.W.; Zaugg, S.D.; Buxton, H.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Esposito, K.; Stinson, B. Pharmaceutical Formulation Facilities as Sources of Opioids and Other Pharmaceuticals to Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4910–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Jingfeng, G.; Yuwei, W.; Wanjun, D.; Jie, L.; Yi, Z.; Haoran, Z.; Mingyan, Z. The removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes and inhibition of the horizontal gene transfer by contrastive research on sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron activating peroxymonosulfate or peroxydisulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126866. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.J.; Yu, K.F.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.H.; Pan, C.G.; Huang, X.Y. Antibiotics in coral reef fishes from the South China Sea: Occurrence, distribution, bioaccumulation, and dietary exposure risk to human. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanu, D.; Styrishave, B.; Darko, G.; Weisser, J.J.; Abaidoo, R.C. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in water and lettuce in Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, N.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Fang, H.; Fu, C.W.; Tang, C.X.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Antibiotics in Drinking Water in Shanghai and Their Contribution to Antibiotic Exposure of School Children. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, A.P.; Kumar, S.; Giri, B.S.; Kim, K.-H. Antibiotic resistance in major rivers in the world: A systematic review on occurrence, emergence, and management strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1484–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairigo, P.; Ngumba, E.; Sundberg, L.-R.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Occurrence of antibiotics and risk of antibiotic resistance evolution in selected Kenyan wastewaters, surface waters and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boger, B.; Surek, M.; Vilhena, R.D.; Fachi, M.M.; Junkert, A.M.; Santos, J.; Domingos, E.L.; Cobre, A.D.; Momade, D.R.; Pontarolo, R. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria in subtropical urban rivers in Brazil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Labadie, P.; Alliot, F.; Teil, M.J.; Blanchard, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence of antibiotics in rural catchments. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, N.A.; Schmitt, H.; Van der Zaan, B.; Gerritsen, H.W.; Zuidema, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Prevalence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a wastewater effluent-receiving river in the Netherlands. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Hain, E.; Timm, A.; Tarnowski, M.; Blaney, L. Occurrence of antibiotics, estrogenic hormones, and UV-filters in water, sediment, and oyster tissue from the Chesapeake Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, Q.M.; Wan, J.Q.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Fan, H.M. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in multifunctional reservoirs in Dongguan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13565–13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.F.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.R.; Wang, X.L.; Song, C.; Wang, S.G. Distribution, combined pollution and risk assessment of antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding the Yellow Sea, North China. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Chaemfa, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Song, M.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Y. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological-health risks of selected antibiotics in coastal waters along the coastline of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.H.; Que, C.J.; Xu, G.; Sun, Y.F.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Sun, R.; Tang, L. Occurrence, fate and interrelation of selected antibiotics in sewage treatment plants and their receiving surface water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.J.; Li, N.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotic distribution, risk assessment, and microbial diversity in river water and sediment in Hong Kong. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2191–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Guo, C.; Wang, D.; Du, P.; Luo, Y.; Wan, J.; Meng, W. Distribution, sources and composition of antibiotics in sediment, overlying water and pore water from Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.H.; Shi, Y.L.; Li, W.H.; Liu, J.M.; Cai, Y.Q. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in urban soil in Beijing and Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11360–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, G.; Hilgert, S.; Fuchs, S.; Azevedo, J.C.R. Emerging contaminants and antibiotic resistance in the different environmental matrices of Latin America. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.S.; Zhang, T.; Gillings, M.R.; Su, J.Q. Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, P.; Zang, Y.G.; Liu, X. Antibiotics in aquatic environments of China: A review and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 199, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, S.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Wu, M.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Xu, G. Antibiotics in the surface water of Shanghai, China: Screening, distribution, and indicator selecting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9836–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-J.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Liu, S. Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Feng, Q.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, M.; Guo, X. Risk assessment and source identification of coastal groundwater nitrate in northern China using dual nitrate isotopes combined with Bayesian mixing model. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhao, H. Persistence and risk of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in major mariculture sites in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxall, A.B.A.; Sinclair, C.J.; Fenner, K.; Kolpin, D.; Maud, S.J. When synthetic chemicals degrade in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 368A–375A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.; Li, H.; Xu, N.; Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Wen, D.; He, S.; Pan, J.; et al. Antibiotics in water and sediments of rivers and coastal area of Zhuhai City, Pearl River estuary, south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.B.; Di Paolo, C.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.; Seiler, T.B.; Hollert, H. Optimization of screening-level risk assessment and priority selection of emerging pollutants-The case of pharmaceuticals in European surface waters. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.C.G.; Howard, P.H. Are there other persistent organic pollutants? A challenge for environmental chemists. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7157–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.N.; Chen, Y.A.; Lin, Y.J.; An, D. Occurrence, spatial distribution, and seasonal variation of emerging trace organic pollutants in source water for Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinqin, Z.; Ai, J.; Yi, W.; Hong, L.; Kunping, W.; Hui, P.; Zhaomin, D.; Jianying, H. Occurrences of three classes of antibiotics in a natural river basin: Association with antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14317–14325. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, B.D.; Crago, J.P.; Hedman, C.J.; Klaper, R.D. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products found in the Great Lakes above concentrations of environmental concern. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollenberger, L.; Halling-Sorensen, B.; Kusk, K.O. Acute and chronic toxicity of veterinary antibiotics to Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.J.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhong, J.Y.; Lou, Q.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y.Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandoa, M.D.; Mezcuaa, M.; Fernández-Albaa, A.R.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Bao, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.H.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.L.; Feng, C.P.; Wen, D.H. Identification of the priority antibiotics based on their detection frequency, concentration, and ecological risk in urbanized coastal water. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.-T.; Pang, X.-R.; Zeng, H.-H.; Liang, Y.-P.; Mo, L.-Y.; Wang, D.-Q.; Dai, J.-F. Ecological and human health risk of sulfonamides in surface water and groundwater of Huixian karst wetland in Guilin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, P.R.; Beatriz, A.; Macarena, F.; Luis, T.J. Analysis of macrolide antibiotics in water by magnetic solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 146, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.; Zheng, S.; Yin, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, L. Aqueous photolysis of tetracycline and toxicity of photolytic products to luminescent bacteria. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Liu, M.; Li, J.J.; Yang, S.S.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Q.Y.; Wang, W.S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, K.X.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. A review on pollution situation and treatment methods of tetracycline in groundwater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinska, A.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Felis, E.; Bajkacz, S.; Jachimowicz, P.; Niestepski, S.; Konopka, I. Small-scale wastewater treatment plants as a source of the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in the aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Sodhi, K.K.; Shree, P.; Singh, D.K.; Agrawal, P.K.; Shukla, P. Antibiotics bioremediation: Perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.M.; Guan, F.L.; Chen, B.W.; Luo, P.Y.; Guo, C.F.; Wu, G.Q.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, Q.B.; Fang, H.S. Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotics in the surface waters of Poyang Lake in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, H.C.; Pan, Y.F.; Xu, X.R. Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes and ecological risks in the coral reef regions adjacent to two typical islands in South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoob, K.; Singer, H.P.; Mueller, S.R.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Stamm, C.H. Dissipation and transport of veterinary sulfonamide antibiotics after manure application to grassland in a small catchment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7349–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zarin, K. Occurrence, distribution, and source track of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the main rivers of Chongqing city, southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, T. Removal mechanisms and kinetics of trace tetracycline by two types of activated sludge treating freshwater sewage and saline sewage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3024–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Qu, J.; Yang, M. Photodegradation of tetracycline and formation of reactive oxygen species in aqueous tetracycline solution under simulated sunlight irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 197, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wammer, K.H.; Korte, A.R.; Lundeen, R.A.; Sundberg, J.E.; McNeill, K.; Arnold, W.A. Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water Res. 2013, 47, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Kong, L.Y.; Jin, M.; Yang, X.D.; Wu, Q.L.L. Trends in the occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in shallow lakes in the lower-middle reaches of the Yangtze River basin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anke, G.; Angela, T.; McArdell, C.S.; Adriano, J.; Walter, G. Occurrence and sorption behavior of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in activated sludge treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar]
- Kafaei, R.; Papari, F.; Seyedabadi, M.; Sahebi, S.; Tahmasebi, R.; Ahmadi, M.; Sorial, G.A.; Asgari, G.; Ramavandi, B. Occurrence, distribution, and potential sources of antibiotics pollution in the water-sediment of the northern coastline of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Chen, H.J.; Reinhard, M.; Mao, F.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and removal of multiple classes of antibiotics and antimicrobial agents in biological wastewater treatment processes. Water Res. 2016, 104, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Li, M.X.; Guo, C.S.; An, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B.D. Distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a typical effluent-receiving river (Wangyang River) in north China. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasquillo, A.J.; Bruland, G.L.; Mackay, A.A.; Vasudevan, D. Sorption of Ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracycline Zwitterions to Soils and Soil Minerals: Influence of Compound Structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7634–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, T.L.; Li, M.; Liu, X. Organic contaminants in the effluent of Chinese wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26852–26860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerker, F.; Hanna, S.; Lindberg, R.H.; Chau, P.; Mats, T.; Joakim, L.D.G. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.J.; Li, N.; Zheng, H.L.; Lin, H.Y. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in river water in Hong Kong. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 125, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Takada, H.; Mutoh, K.; Hosoda, H.; Harada, A.; Nakada, N. Nationwide monitoring of selected antibiotics: Distribution and sources of sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and macrolides in Japanese rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Hu, J.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Peng, H.; Wu, S.M.; Dong, Z.M. Occurrence and Source Apportionment of sulfonamides and Their Metabolites in Liaodong Bay and the Adjacent Liao River Basin, North China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Liu, Q.; Ru, X.L.; Xi, N.N.; Sun, J.H. Occurrence and distribution of priority pharmaceuticals in the Yellow River and the Huai River in Henan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16816–16826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Carlson, K. Temporal and spatial trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in aqueous and river sediment matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, H.Y.; Cao, Y.X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, B.B.; Sweetman, A.; Lin, C.Y.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotics in river waters in the Haihe River Catchment in China and ecotoxicological risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Alliot, F.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Eurin, J.; Chevreuil, M.; Labadie, P. Measurement of trace levels of antibiotics in river water using on-line enrichment and triple-quadrupole LC-MS/MS. Talanta 2011, 85, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngumba, E.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Occurrence of selected antibiotics and antiretroviral drugs in Nairobi River Basin, Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Ogo, M.; Koike, T.; Takada, H.; Newman, B. Sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in total- and culturable-bacterial assemblages in South African aquatic environments. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.A.; Berglund, B.; Khan, K.M.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Fick, J. Occurrence and abundance of antibiotics and resistance genes in rivers, canal and near drug formulation facilities--a study in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2017, 8, e62712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, R.; Ternes, T.; Haberer, K.; Kratz, K.L. Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Tan, Q.; He, J. Distribution of antibiotics in lake water-groundwater-Sediment system in Chenhu Lake area. Environ. Res. 2022, 204 Pt C, 112343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.F.; Liang, H.; Gao, D.W. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the Songhua River in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19282–19292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sanchez-Melsio, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barcelo, D.; Balcazar, J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Lu, S.Y.; Guo, W.; Xi, B.D.; Wang, W.L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of lakes, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Cao, X.H.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Sediment of Honghu Lake and East Dongting Lake, China. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Miao, J.R.; Wen, H.X.; Li, T.H.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.X. The occurrence and spatial distribution of typical antibiotics in soils along the Fenhe River in Shanxi Province. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, C.S.; Lv, J.P.; Hou, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Spatiotemporal profile of tetracycline and sulfonamide and their resistance on a catchment scale. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Jing, L.J.; Teng, Y.G.; Wang, J.S. Characterization of antibiotics in a large-scale river system of China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Qin, L.T.; Xie, C.; Liu, H.X.; Wang, Y.X.; Guan, C.A.; Huang, S.B. Distribution of antibiotics in alluvial sediment near animal breeding areas at the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tang, Y.Y.; Sun, F.J.; Chen, L.M. Detection and characterization of integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs)-positive Vibrio cholerae isolates from aquacultured shrimp and the environment in Shanghai, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.L.; Yin, D.Q.; Zhang, H.C.; Yu, Z.Y. Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Nie, M.; Shi, H.; Gu, L. Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenwen, G.; Xinhui, L.; Hui, H.; Liang, W.; Guohua, D. Quantitatively modeling soil-water distribution coefficients of three antibiotics using soil physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, M.; Lauwigi, C.; Heinkele, G.; Murdter, T.E.; Letzel, M. Fate of the Antibiotic Sulfamethoxazole and Its Two Major Human Metabolites in a Water Sediment Test. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3135–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.M.; Chen, B.W.; Nie, X.P.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.P.; Li, X.D. The distribution and partitioning of common antibiotics in water and sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; Ke, Y.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. A duodecennial national synthesis of antibiotics in China’s major rivers and seas (2005–2016). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Occurrence and Transport of Tetracycline, Sulfonamide, Quinolone, and Macrolide Antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-L.; Xiang, L.; Yan, Q.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-N.; Li, Y.-W.; Huang, X.-P.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H. Distribution and risk assessment of quinolone antibiotics in the soils from organic vegetable farms of a subtropical city, Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, K.; Wu, W.; Guo, M. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in the Xi’an section of the Weihe River, northwestern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.Z.; You, M.T.; Zhang, R.J.; Kuang, Y.Z.; Dang, C.Y.; Sun, W.L.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wang, W.J.; Ni, J.R. Antibiotics in water and sediments of Danjiangkou Reservoir, China: Spatiotemporal distribution and indicator screening. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, E.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.L. Occurrence and ecological hazard assessment of selected antibiotics in the surface waters in and around Lake Honghu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.S.; Hu, E.; Liu, S.W.; Wen, L.; Yang, F.; Li, M. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of certain antibiotics in 51 urban wastewater treatment plants in the transition zone between North and South China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, J.F.; Sandberg, K.D.; Engstrom, D.R.; LaPara, T.M.; Arnold, W.A. Sedimentary record of antibiotic accumulation in Minnesota Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbiolles, F.; Malleret, L.; Tiliacos, C.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Laffont-Schwob, I. Occurrence and ecotoxicological assessment of pharmaceuticals: Is there a risk for the Mediterranean aquatic environment? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
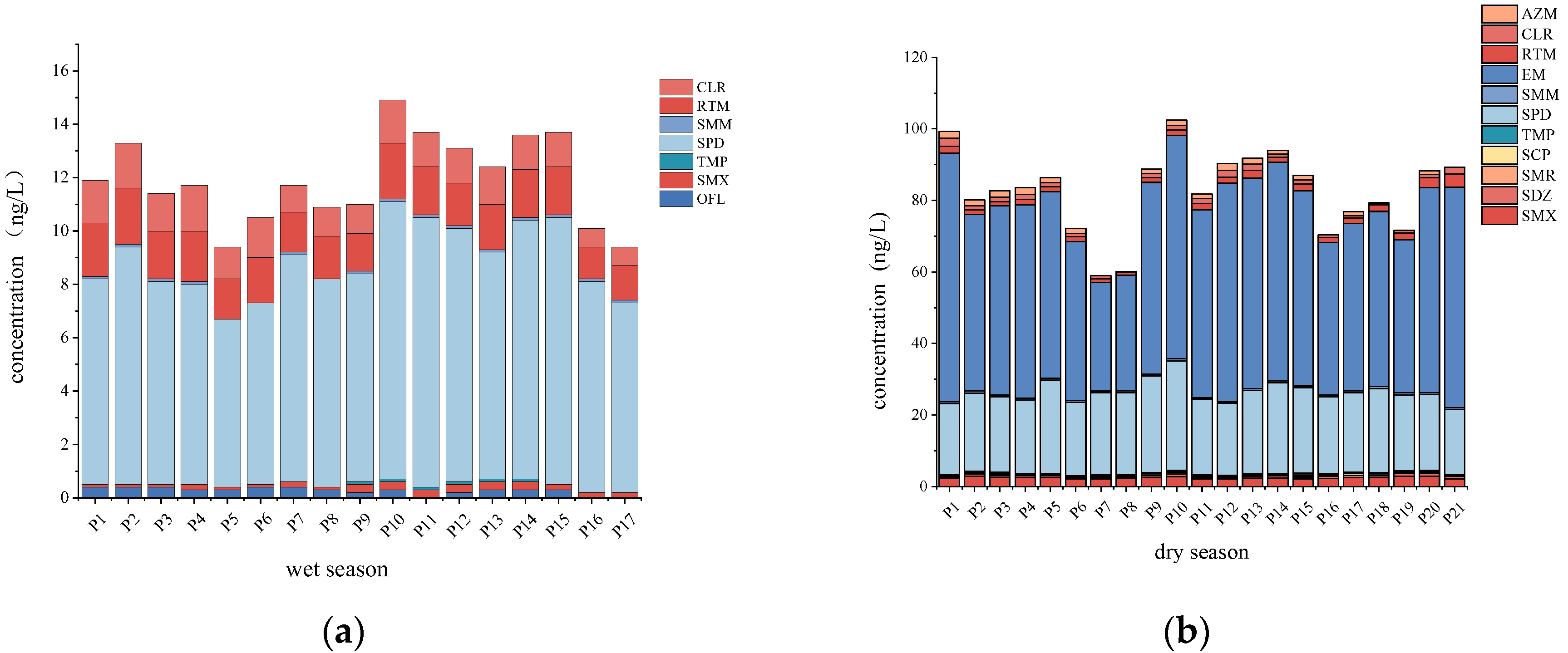
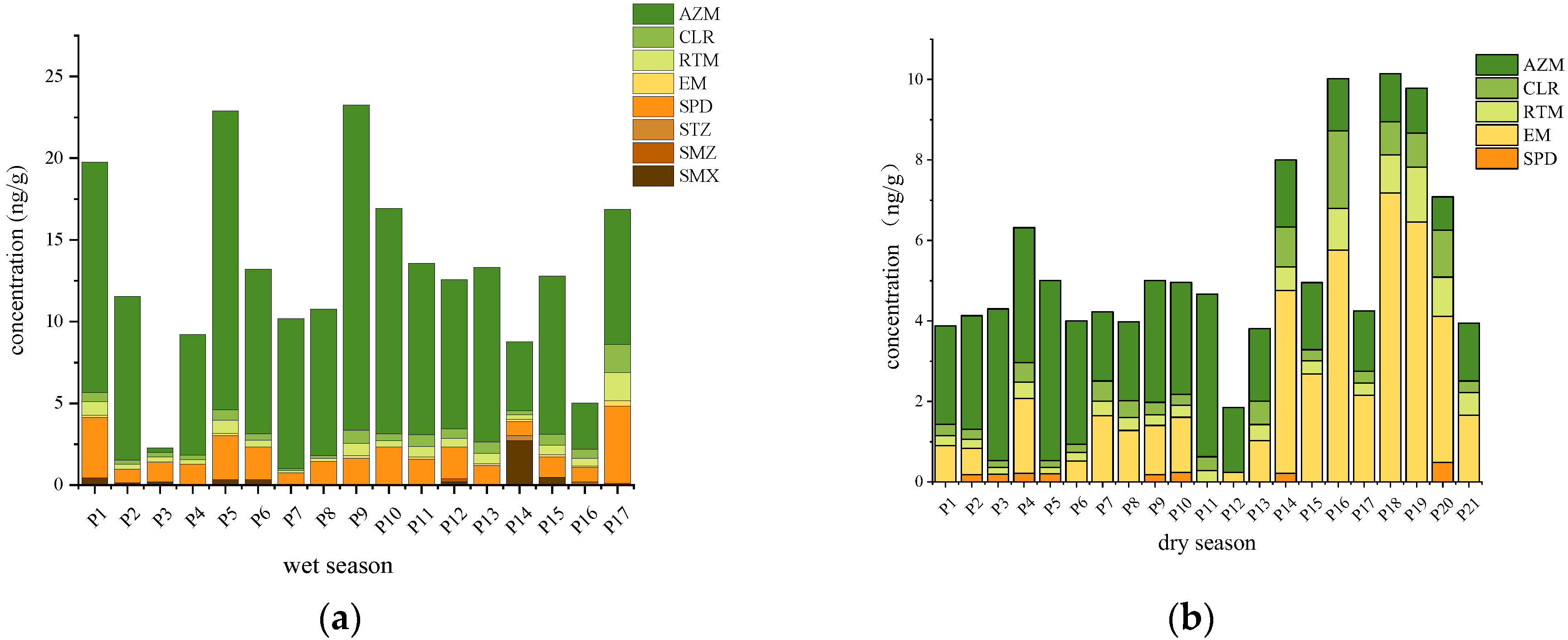

| Compounds | Wet Season (ng/L) | Dry Season (ng/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq. | Median | Mean | Max | Freq. | Median | Mean | Max | |
| OFL | 82% | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | ||||
| SMX | 100% | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 100% | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.9 |
| TMP | 35% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 100% | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| SPD | 100% | 7.9 | 8.4 | 10.4 | 100% | 21.8 | 22.6 | 30.6 |
| SMM | 82% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 100% | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| RTM | 100% | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 100% | 1.5 | 1.7 | 3.7 |
| CLR | 100% | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 100% | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2.3 |
| SDZ | 100% | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.9 | ||||
| SMR | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | ||||
| SCP | 100% | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | ||||
| EM | 100% | 52.9 | 51.9 | 69.5 | ||||
| AZM | 71% | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.9 | ||||
| Compounds | Wet Season (ng/g) | Dry Season (ng/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq. | Median | Mean | Max | Freq. | Median | Mean | Max | |
| EM | 53% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 86% | 1.4 | 2.1 | 7.8 |
| RTM | 100% | 0.4 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 95% | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| CLR | 100% | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 95% | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.9 |
| AZM | 100% | 9.7 | 9.8 | 19.9 | 100% | 1.8 | 2.7 | 4.5 |
| SPD | 100% | 1.4 | 1.8 | 4.7 | 38% | 0 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| SMX | 47% | 0 | 0.3 | 2.7 | ||||
| SMZ | 18% | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | ||||
| STZ | 6% | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Occurrence, Comparison and Priority Identification of Antibiotics in Surface Water and Sediment in Urbanized River: A Case Study of Suzhou Creek in Shanghai. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148757
Li X, Yuan Y, Zhang D, Li X, Li D, Wang X. Occurrence, Comparison and Priority Identification of Antibiotics in Surface Water and Sediment in Urbanized River: A Case Study of Suzhou Creek in Shanghai. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148757
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuhui, Yuan Yuan, Dou Zhang, Xiao Li, Dehuan Li, and Xiangrong Wang. 2022. "Occurrence, Comparison and Priority Identification of Antibiotics in Surface Water and Sediment in Urbanized River: A Case Study of Suzhou Creek in Shanghai" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148757
APA StyleLi, X., Yuan, Y., Zhang, D., Li, X., Li, D., & Wang, X. (2022). Occurrence, Comparison and Priority Identification of Antibiotics in Surface Water and Sediment in Urbanized River: A Case Study of Suzhou Creek in Shanghai. Sustainability, 14(14), 8757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148757






