Analysis of the Relationship between Beijing Rail Transit and Urban Planning Based on Space Syntax
Abstract
:1. Introduction
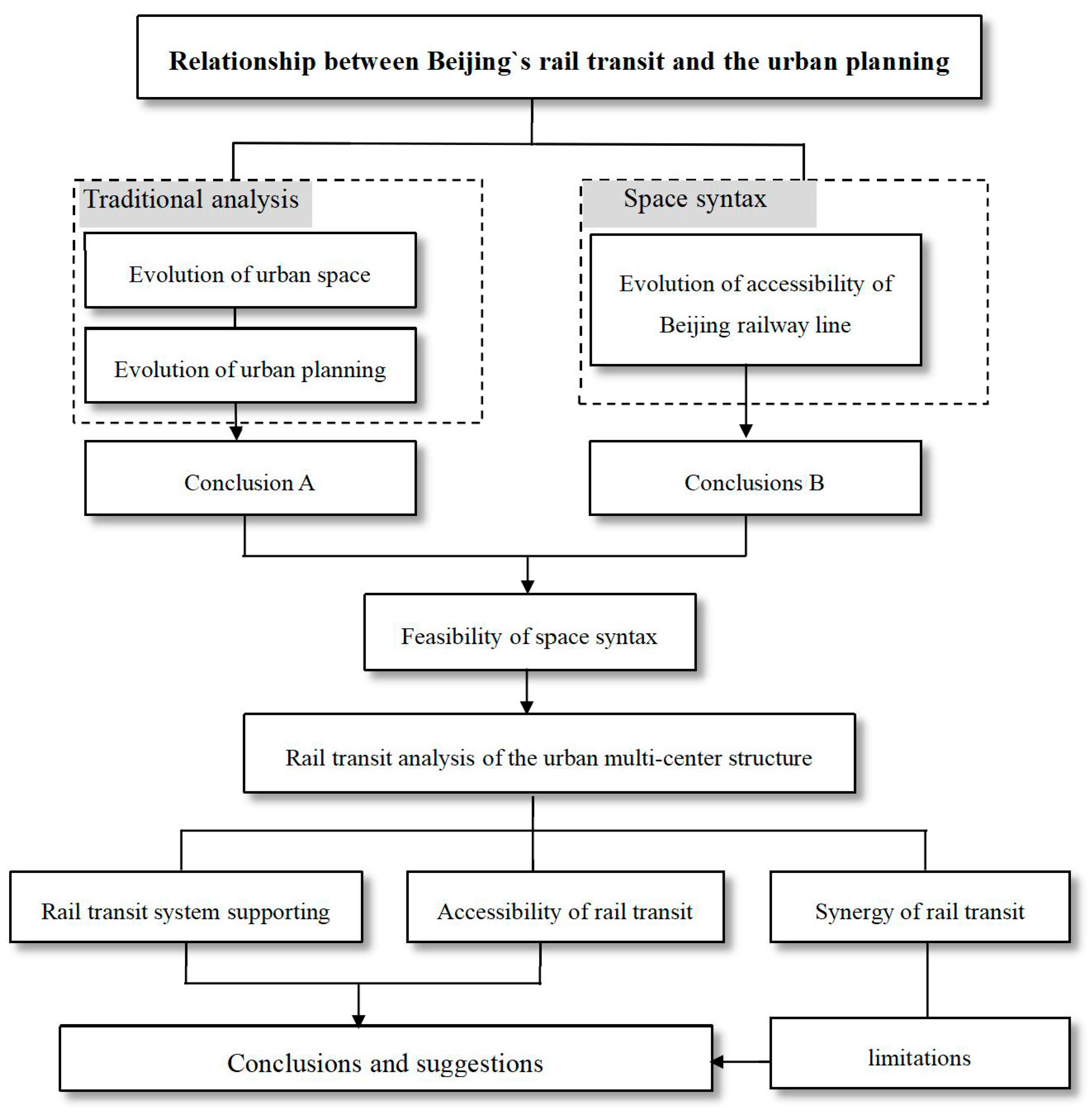
2. Research Framework and Methods
2.1. Research Framework
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Accessibility Based on Topological Relation
2.2.2. Application of Space Syntax in the Beijing Rail Transit Line
3. Results
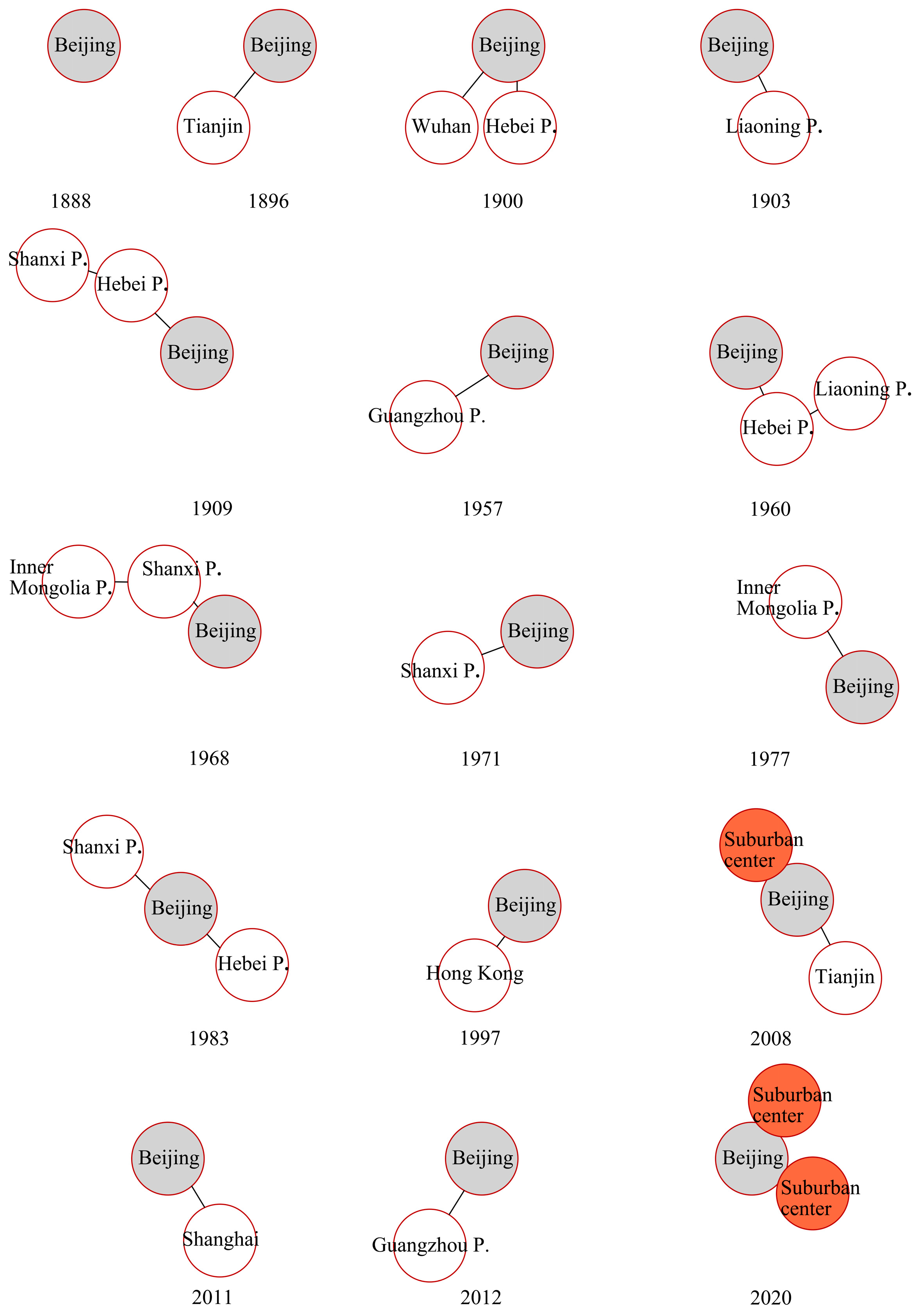
3.1. Evolution of Urban Space and Urban Planning
3.1.1. Evolution of Urban Space
3.1.2. Evolution of Urban Planning
3.2. Feasibility of Space Syntax
3.3. Rail Transit Analysis of the Urban Multi-Center Structure
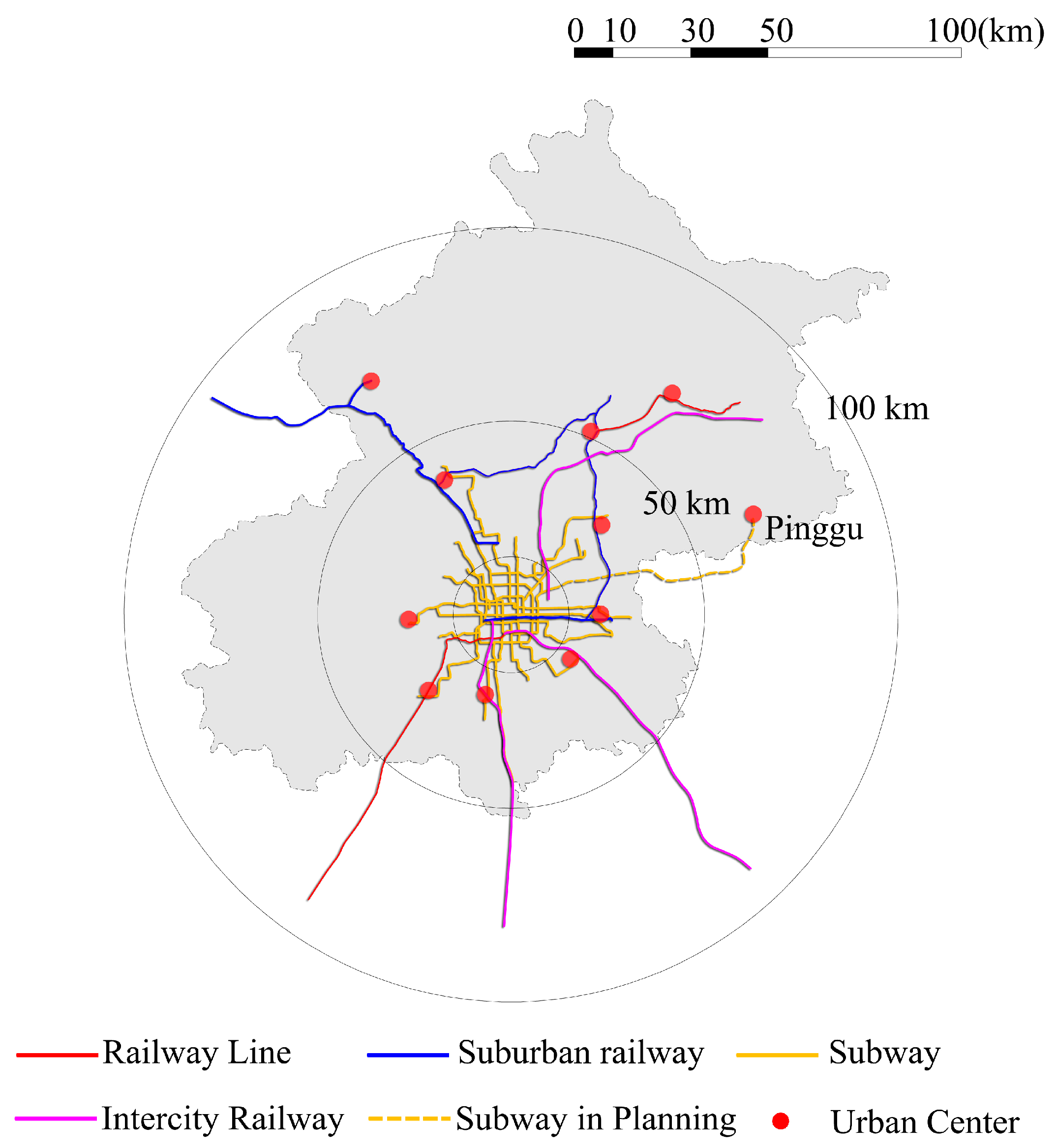
3.3.1. Rail Transit System Supporting
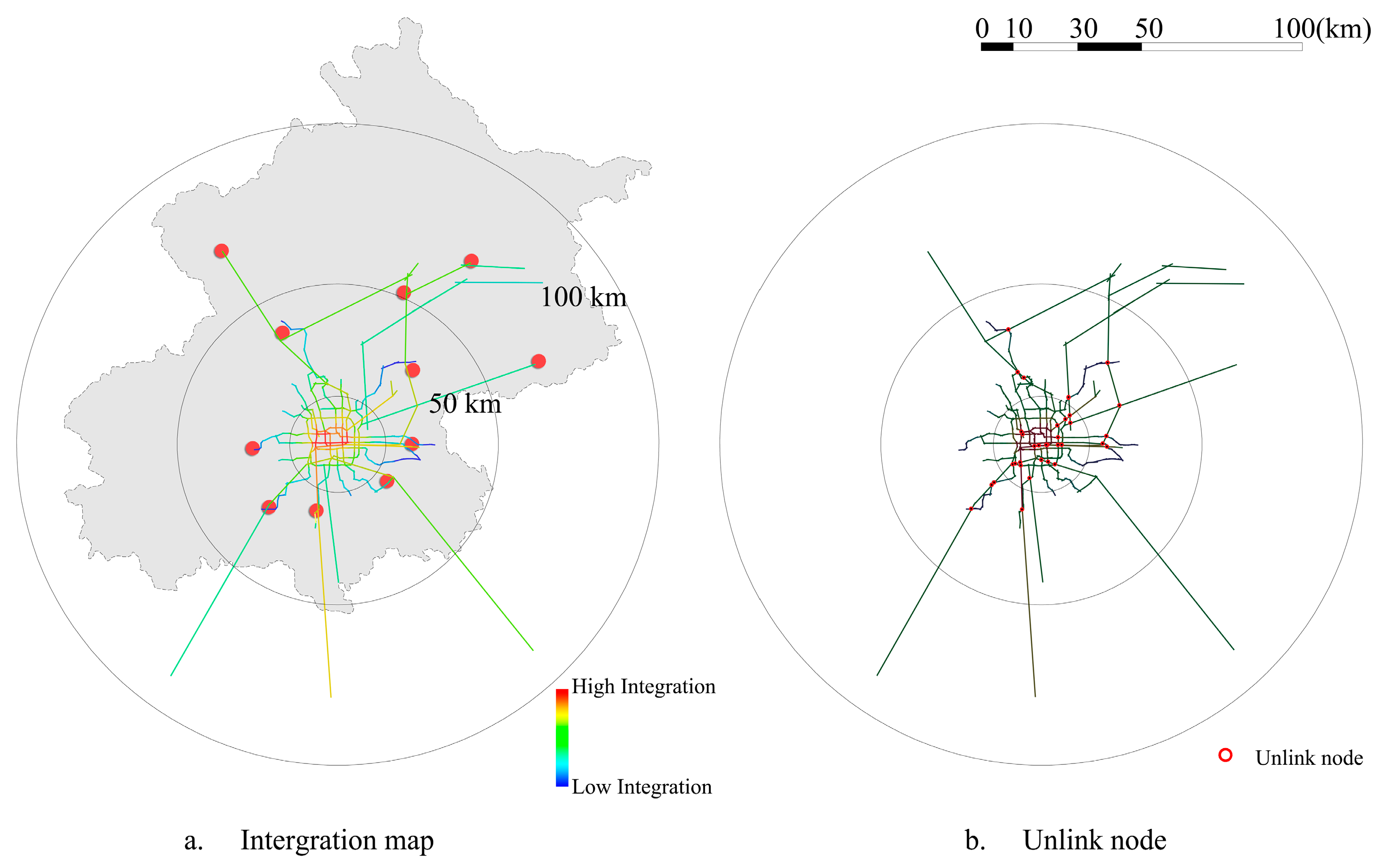
3.3.2. Accessibility of Rail Transit
3.3.3. Synergy of Rail Transit
4. Discussion
- (1)
- After analyzing Beijing’s multi-center and multi-circle rail transit structure, it is concluded that the current division of labor in rail transit in the latest version of Beijing urban planning is unclear. There are inconsistencies between the graphics and texts of Beijing’s urban planning that need to be corrected.
- (2)
- Analysis using space syntax shows that connecting suburban centers using suburban railways improves accessibility better than subways can. Extending subway lines to outer suburbs is not suitable.
- (3)
- The application of space syntax in rail transit structures has been verified. However, the analysis result of the space syntax needs to be examined in combination with the situation on the ground. There may be limitations to the analysis of various rail transit network structures using space syntax. When the rail transit network is dominated by one type of rail transit, the synergy index may not reflect the pros and cons of the actual rail transit structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China’s Low-Carbon Strategy a Boost for Global Green Development. Available online: http://english.www.gov.cn/news/internationalexchanges/202112/05/content_WS61abfc11c6d0df57f98e60c8.html (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Notice of the State Council on Printing and Distributing the Action Plan for Carbon Peak before 2030. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Li, C.; Meng, L.; Zhang, T. Study on the Influence of Multi Railway Stations on Urban Spatial Structure. Urban Plan. Int. 2018, 33, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Gao, H. The impact of urban morphology on urban transportation mode: A case study of Tokyo. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2018, 8, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Shi, R.; Ru, X.; Zhang, S. Research on “multi network integration” of Beijing Rail Transit. J. Transp. Eng. 2020, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Shen, C. Characteristics of suburban railways in Tokyo Metropolitan Area and Its Enlightenment to China. China Railw. 2017, 9, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Early planning and construction of suburban and intercity railways in China. J. Railw. Eng. Soc. 2014, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, C.; Luo, J. A Study on the Experiences of Japan National Railway’s Tokyo Five-prong Strategy for Commuting Service. Railw. Transp. Econ. 2020, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Tao, Y.; Pan, J.; Xiao, Y. A Comparison of Analytical Methods for Urban Street Network: Taking space syntax, sDNA and UNA as examples. Urban Plan. Forum 2020, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Influence Analysis of Intercity Railway Network on Traffic Network and Spatial Structure of Jingjinji Urban Agglomeration; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.J.; Kan, X.D. Coordination Analysis for Urban Underground Space and Rail Transit Based on Space Syntax; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 170, pp. 1388–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.A.; Li, X. Topology Analysis and Comparison of Beijing and Shanghai’s Mass Transit Networks Based on the Space Syntax Theory. J. Jiamusi Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 29, 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Study on Beijing’s Urban Planning and Building Practice in 1900–1949; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research on the Evolution of Chinese Urban Macro-Spatial Planning since 1949; Lanzhou University: Lanzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xia, H.; Yu, X. Spatiotemporal Response of Synergy Development between Rail Transit and Urban Space: A Case Study of Beijing. City Plan. Rev. 2020, 44, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Yu, Z.; Dai, T. Evaluation of Fare Schemes Selection of Beijing Urban Rail Transit based on Space Cost Distribution. Railw. Transp. Econ. 2020, 42, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fang, L.; Yong, K.; Hu, L. Evaluation of spatial performance of metro-led urban underground public space: A case study in Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104484. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L. Study on the Accessibility Evaluation of Regional Railway Network Based on Space Syntax; Southwest Jiaotong University: Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.N.; Karimi, K. Analysis and Modelling of the Multilevel Transport Network: The Metro and Railway System in Greater London. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference Proceedings of the XXVIII International Seminar on Urban Form: “Urban Form and the Sustainable and Prosperous City”, Glasgow, UK, 29 June–3 July 2021; pp. 354–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bill, H.; Julienne, H. The Social Logic of Space; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, W.G. How accessibility shapes land use. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1959, 25, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R. Beijing Historical Atlas: Humanities and Society Volume; Beijing Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. History of Contemporary Beijing Railway; Contemporary China Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, L. Research on the Coupling Development of Rail Transit and Urban Space Based on Time-Space Perspective; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.; Liu, X. Beijing: From Traditional Capital to the Chinese World City; Social Sciences Academic Press (China): Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning. Master Plan for Urban Construction in Beijing (1982); Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning: Beijing, China, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Urban Planning Commission. Beijing Urban Master Plan (1991–2010); Beijing Urban Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Urban Planning Commission. Beijing Urban Master Plan (2004–2020); Beijing Urban Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Urban Planning Commission. Beijing Urban Master Plan (2016–2035); Beijing Urban Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. Spatial Structure Evolution and Dynamic Mechanism Analysis of Beijing Central City and New Town; Capital University of Economics and Business: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X. Three changes in the concept of urban traffic development. Beijing Plan. Rev. 2006, 5, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Construction of Commuter Rails in Metropolitan Areas: A Powerful Engine for Stable Growth and Domestic Demand Expansion of China’s Economy. China Soft Sci. 2015, 12, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bill, H. Space is the Machine: A Configurational Theory of Architecture; Space Syntax: London, UK, 1996; pp. 99–101. [Google Scholar]
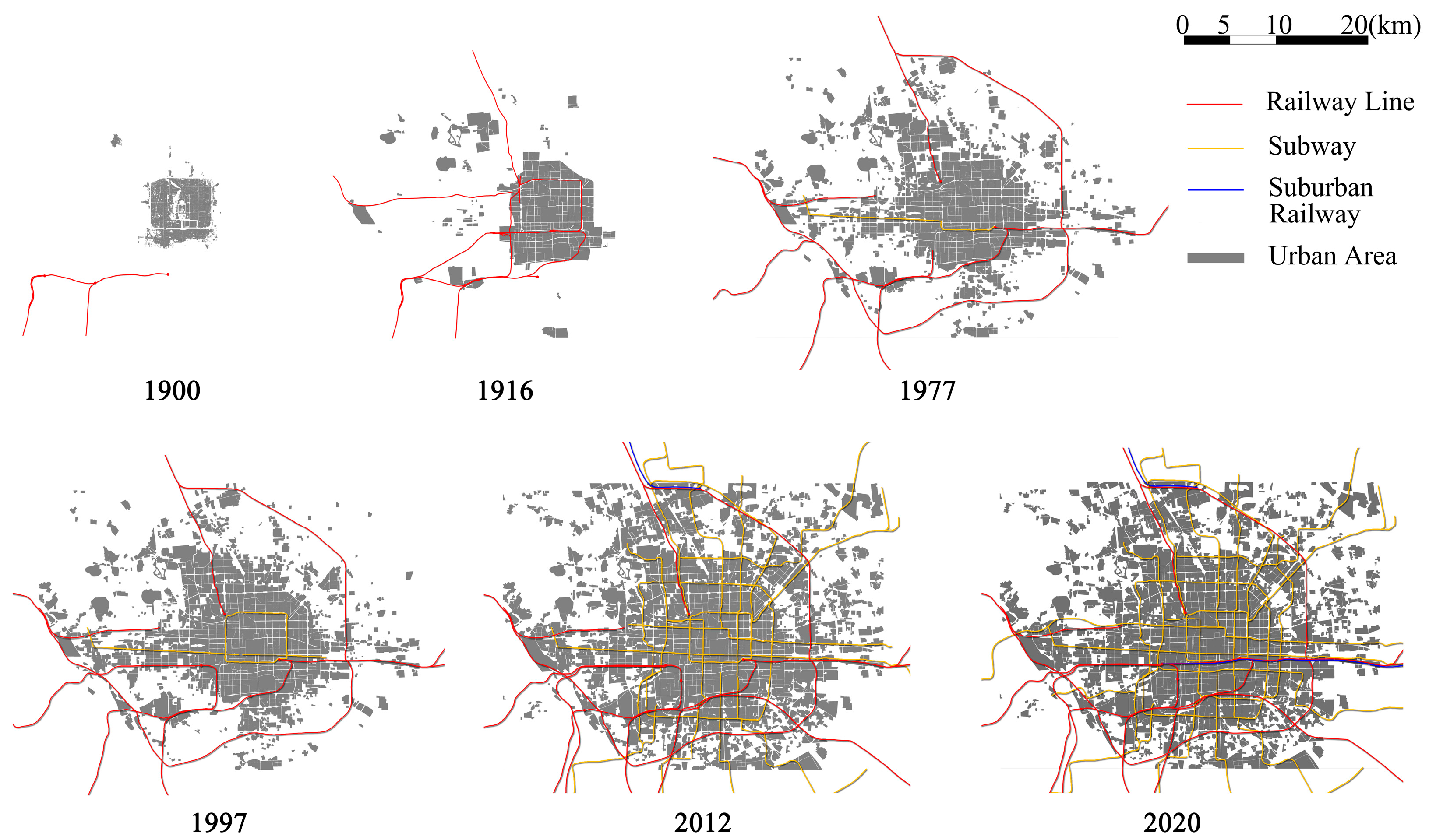
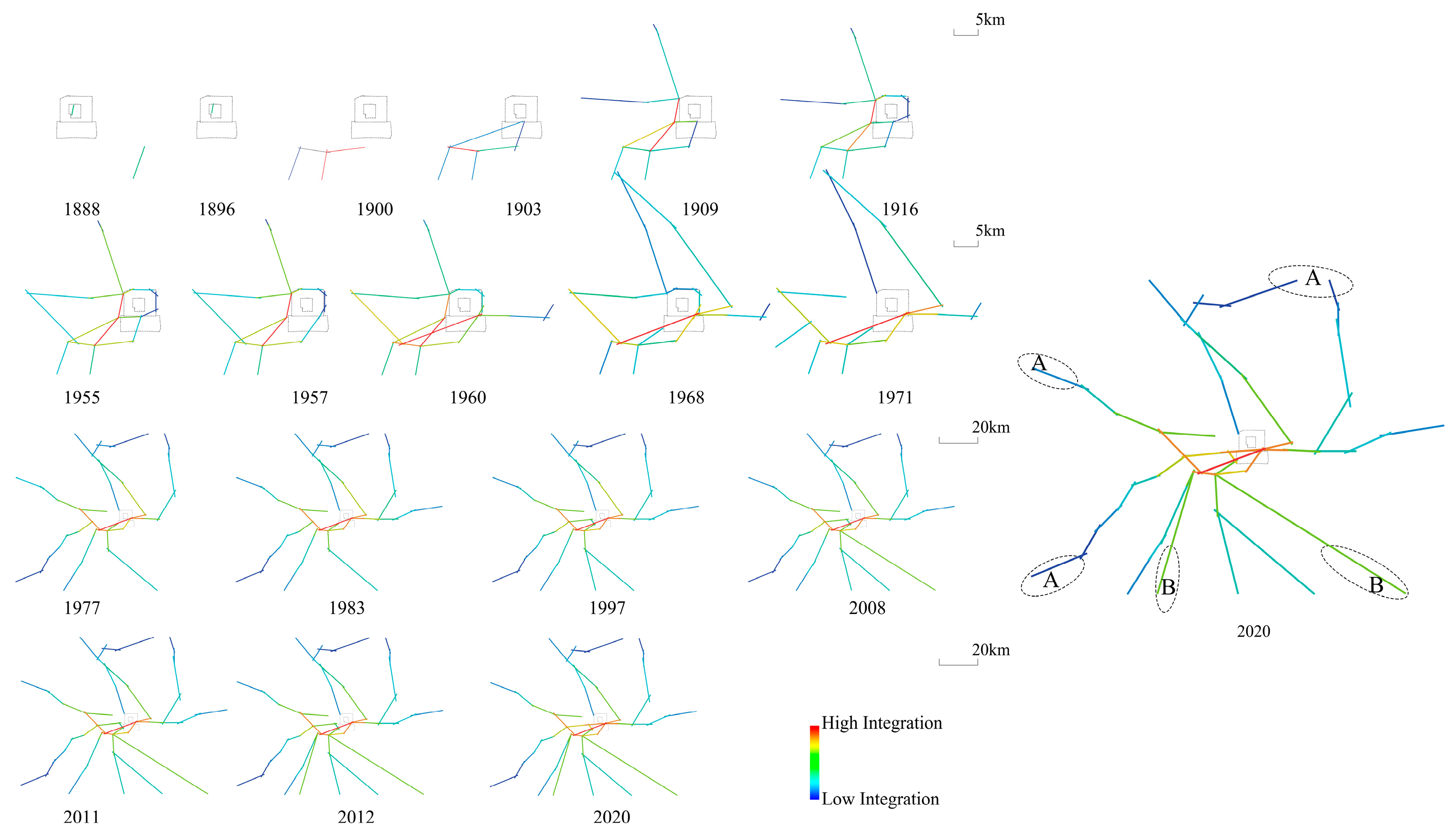

| Year | 1900 | 1916 | 1955 | 1977 | 1983 | 2008 | 2017 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Railway line name | Luhan and Jingshan railway | Circle railway | Fengsha railway | Jingyuan railway | Jingqin railway | Jingjin intercity high-speed railway and S2 suburban railway | S1 | Huairou-Miyun Line, Tong-Mi Line |
| Construction objectives | Passive acceptance and construction | To solve the problem of grain and coal transportation | To solve the problem of coal outward transportation channel in Shanxi Province and ensure Beijing’s energy supply | To form a North Road channel for the coal outward transportation of Shanxi Province | To form an important transportation line for the coal transportation of Shanxi Province to the East | Jingjin: To reduce the space-time distance between the two megacities and provided strong traffic support for the Bohai economic circle.S2: To strengthen the connection between the central urban area and the suburban center. | To strengthen the connection between the central urban area and the suburban center. Huairou-Miyun/Tong-Mi: The existing railway is transformed into suburban railway. | |
| Urban Planning | Outline of the First Phase Plan of Beiping New City | Preliminary Plan of Beijing Urban Master Plan | Master Plan for Urban Construction of Beijing | Beijing Urban Master Plan (1991–2010) | Beijing Urban Master Plan (2004–2020) | Beijing Urban Master Plan (2016–2035) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1947 | 1953 | 1982 | 1992 | 2004 | 2017 |
| Unresolved Issues | Urban spatial pattern | The urban suburbs and outer suburbs develop unevenly. | The construction of the satellite city and flow of population to the outer suburban regions were restricted. | The railway support system of suburban center has not been formed. | - | |
| Rail Transit Construction | Construction of trunk and circle railways | Construction of trunk railway | The main line railway was improved; however, suburban railways were not built. | Subway lines and S1 and S2 suburban railways were constructed. | Establishing the traffic development mode of different circles | |
| Urban Planning Objectives | Reconstruction of urban pattern or restoration of urban space | Suburban area: “decentralized group style” outer suburban regions: satellite cities | Plan involved satellite cities and decentralized group layout | Construction of the spatial layout of the multicenter metropolis, and alleviation of the noncapital function | Building a multi-core urban spatial structure | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Ishida, T. Analysis of the Relationship between Beijing Rail Transit and Urban Planning Based on Space Syntax. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148744
Meng L, Ishida T. Analysis of the Relationship between Beijing Rail Transit and Urban Planning Based on Space Syntax. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148744
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Leilei, and Toshikazu Ishida. 2022. "Analysis of the Relationship between Beijing Rail Transit and Urban Planning Based on Space Syntax" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148744
APA StyleMeng, L., & Ishida, T. (2022). Analysis of the Relationship between Beijing Rail Transit and Urban Planning Based on Space Syntax. Sustainability, 14(14), 8744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148744






