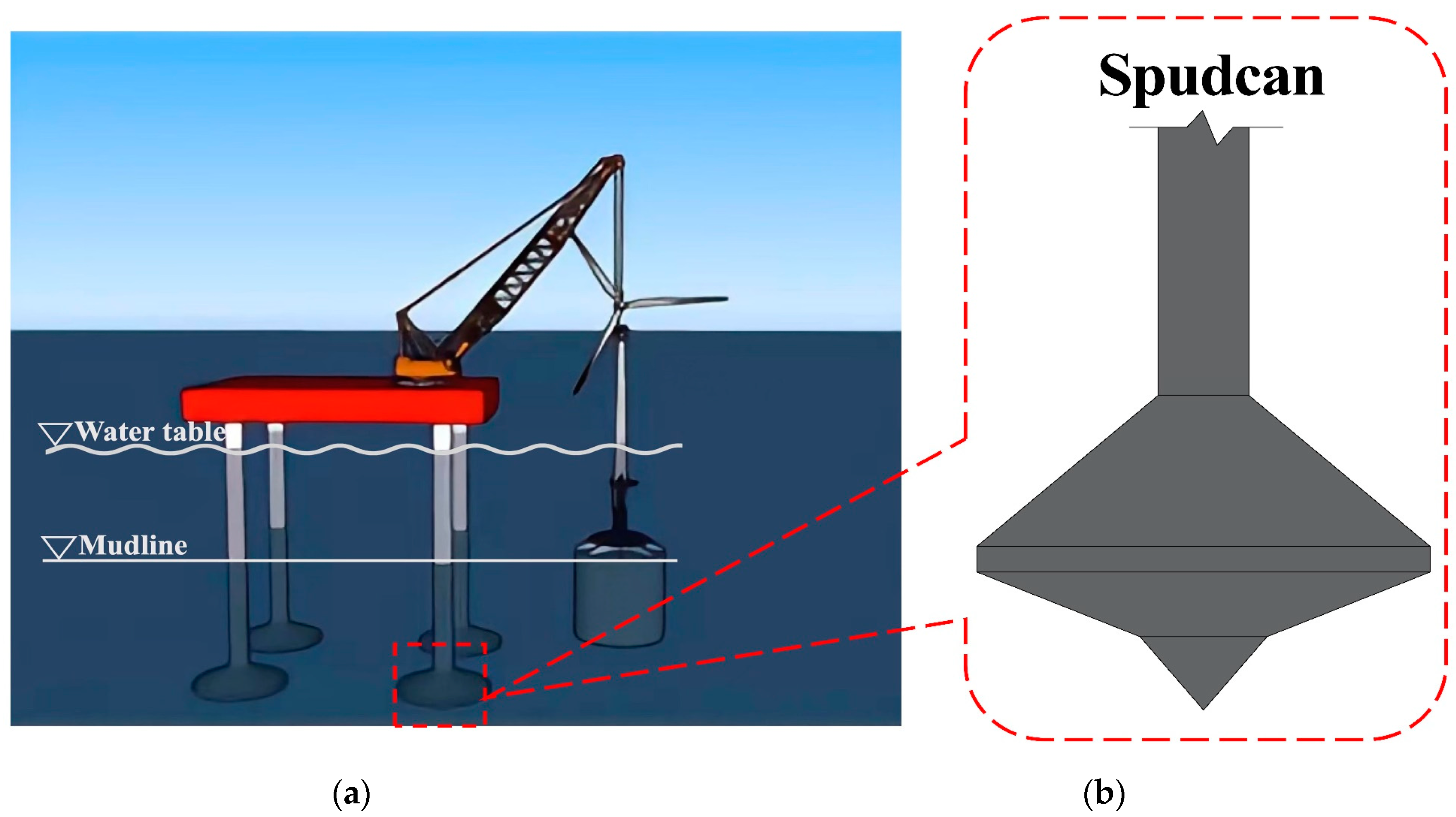
Penetration Behavior of the Footing of Jack-Up Vessel of OWTs in Thin Stiff over NC Clay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Steps and Methods of Jack-Up Vessel Installation
1.2. Previous Work
1.3. Objective of the Present Study
2. Method: LDFE Analyses
2.1. Soil Profile
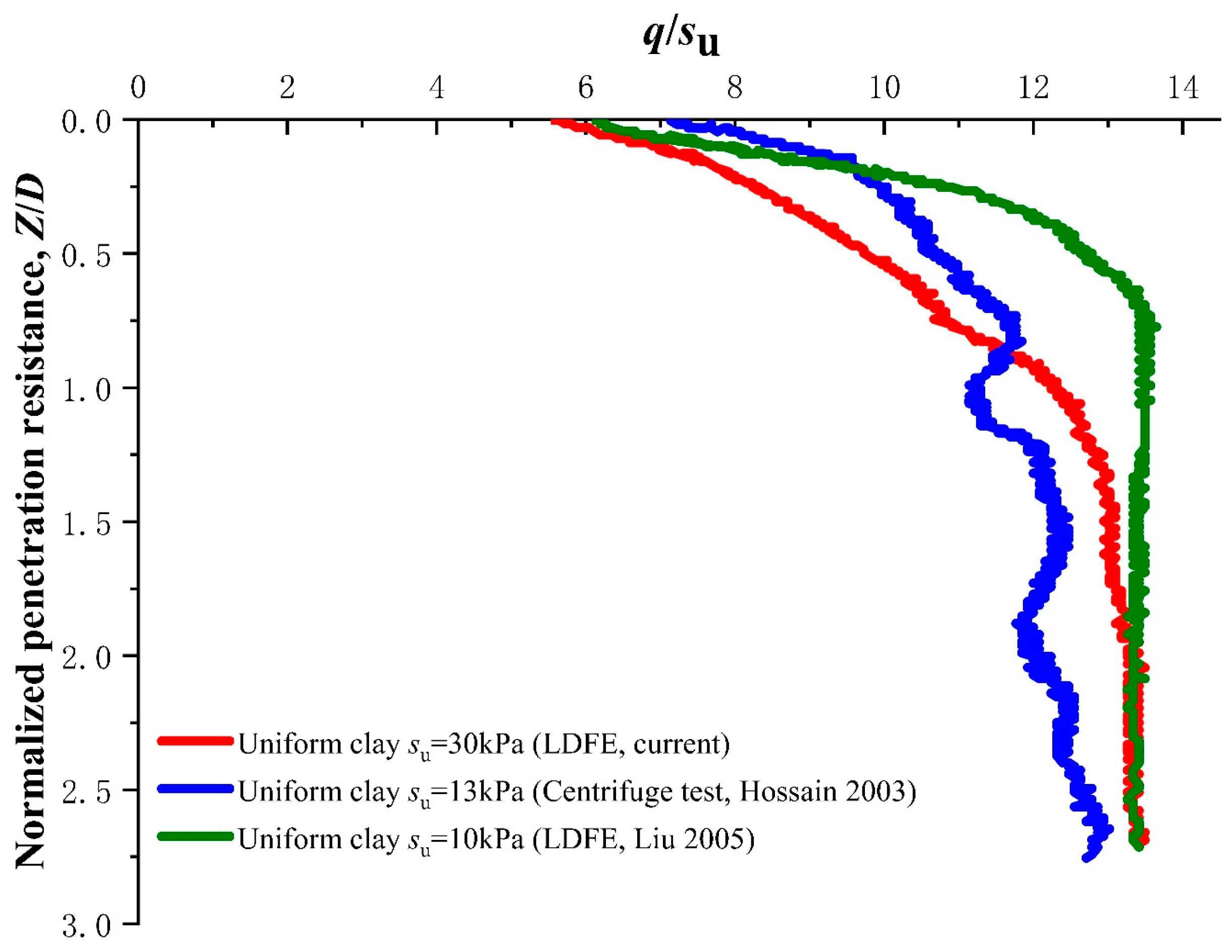
2.2. Model Validation
3. Results
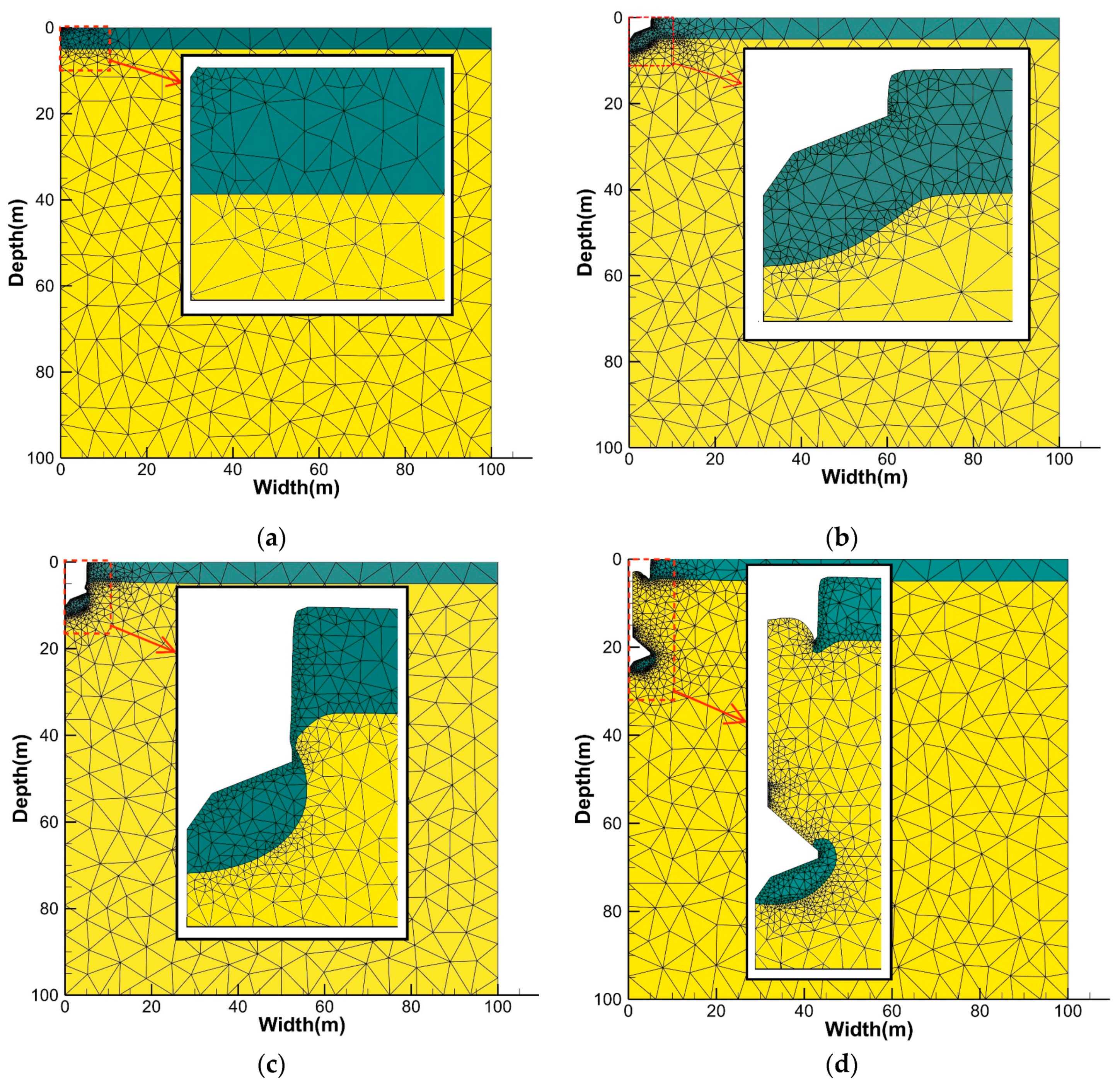
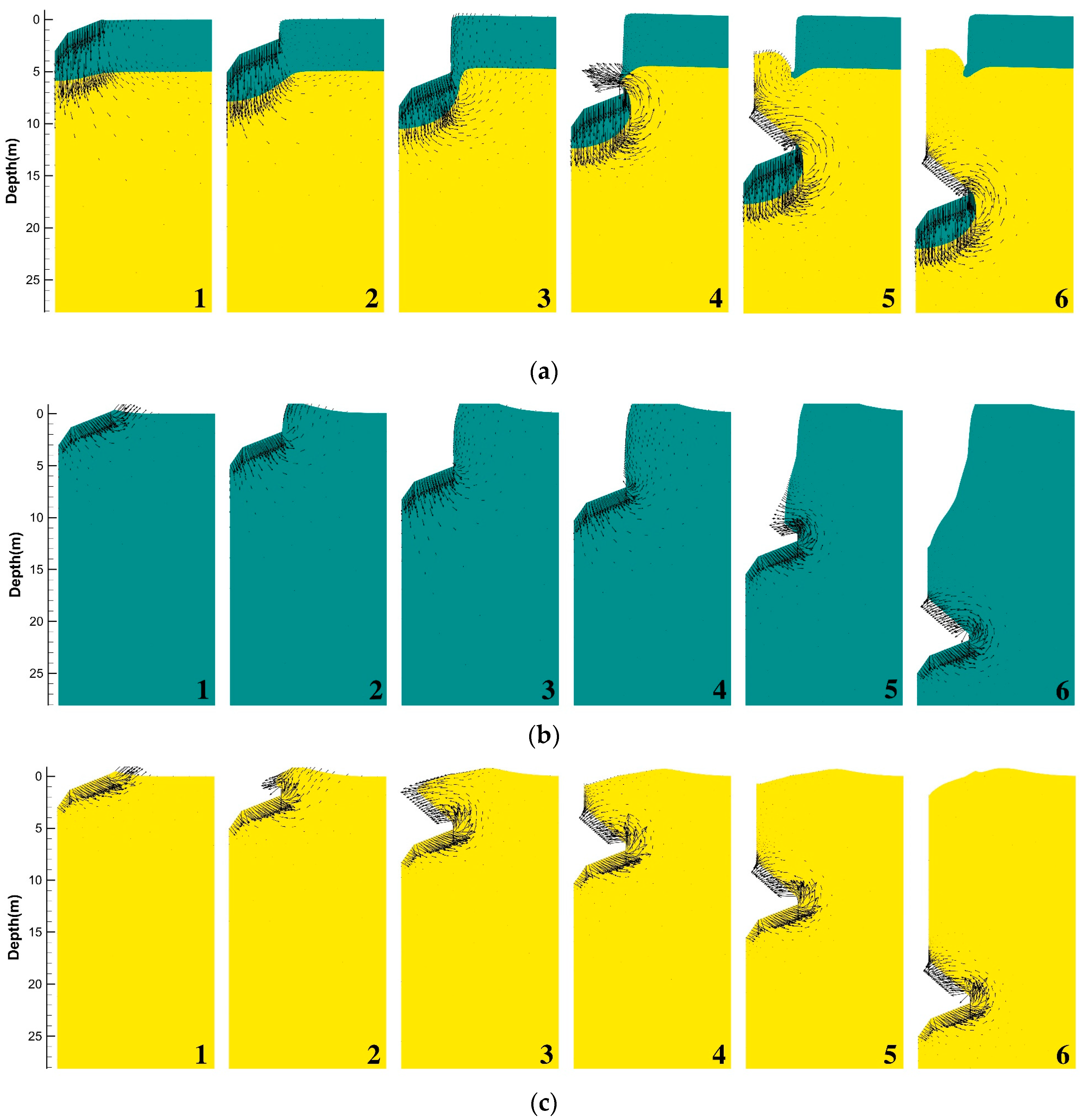
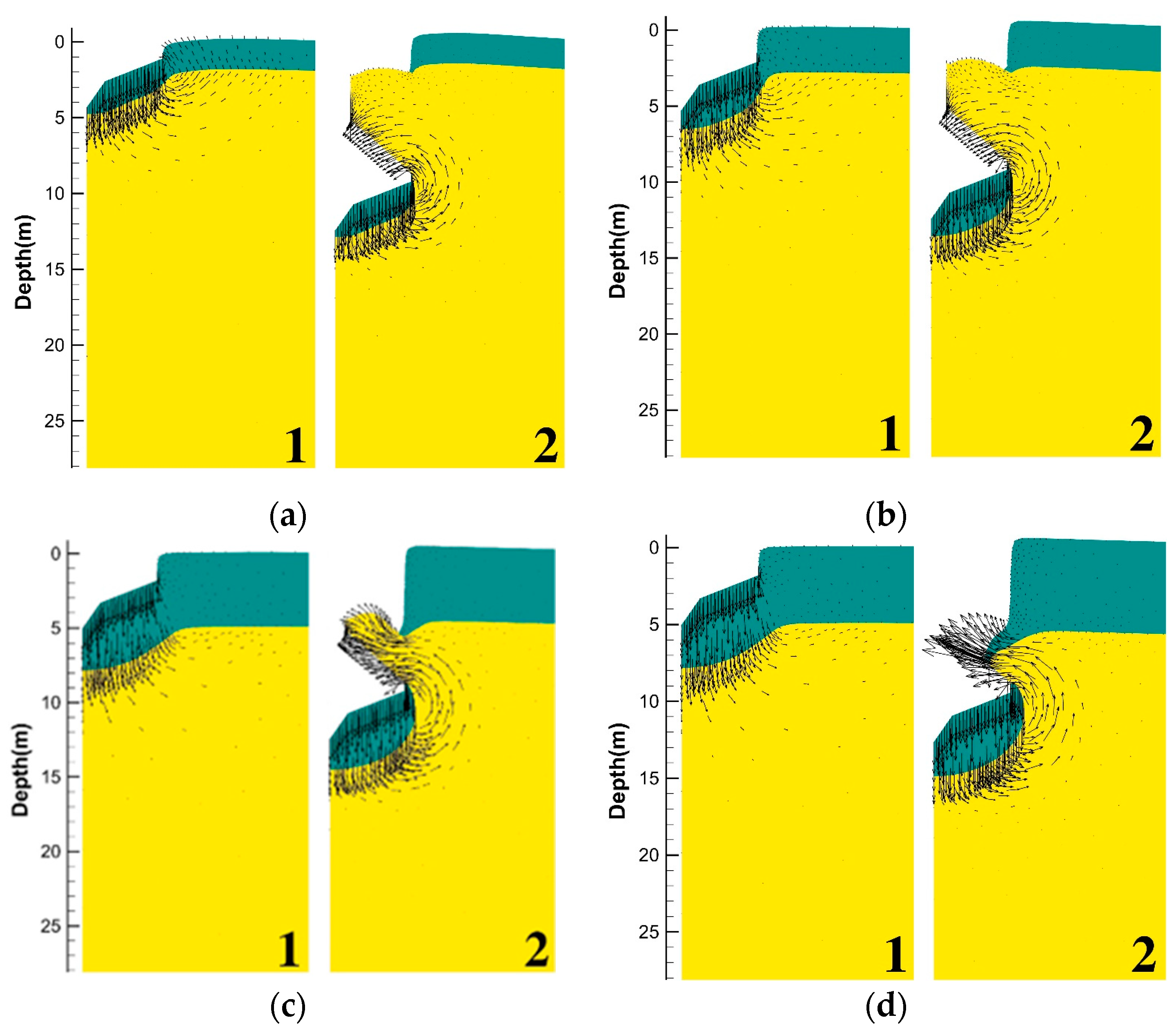
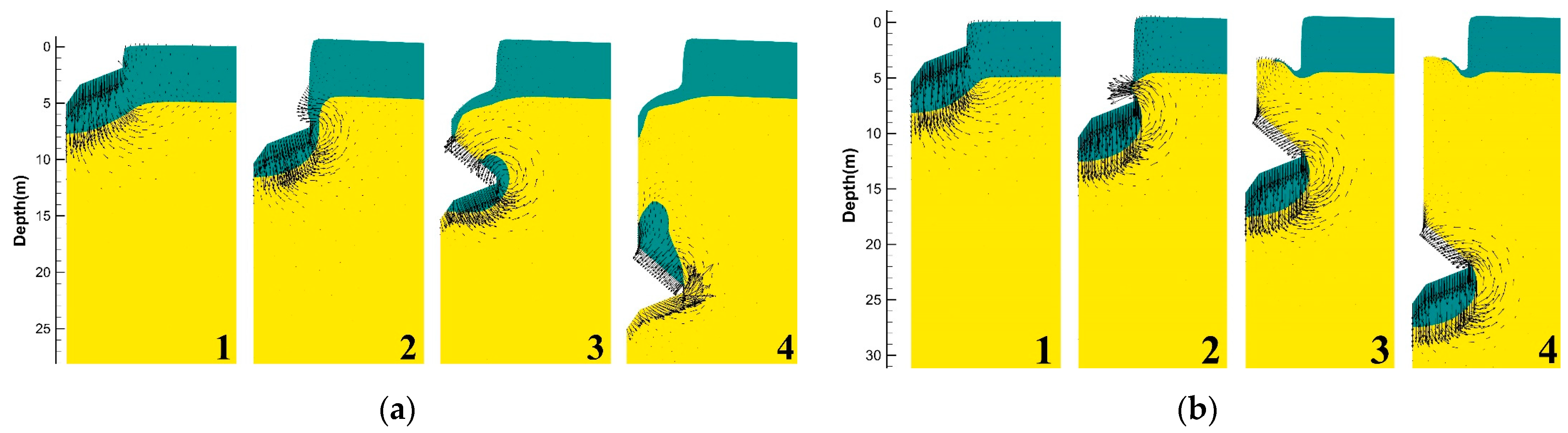
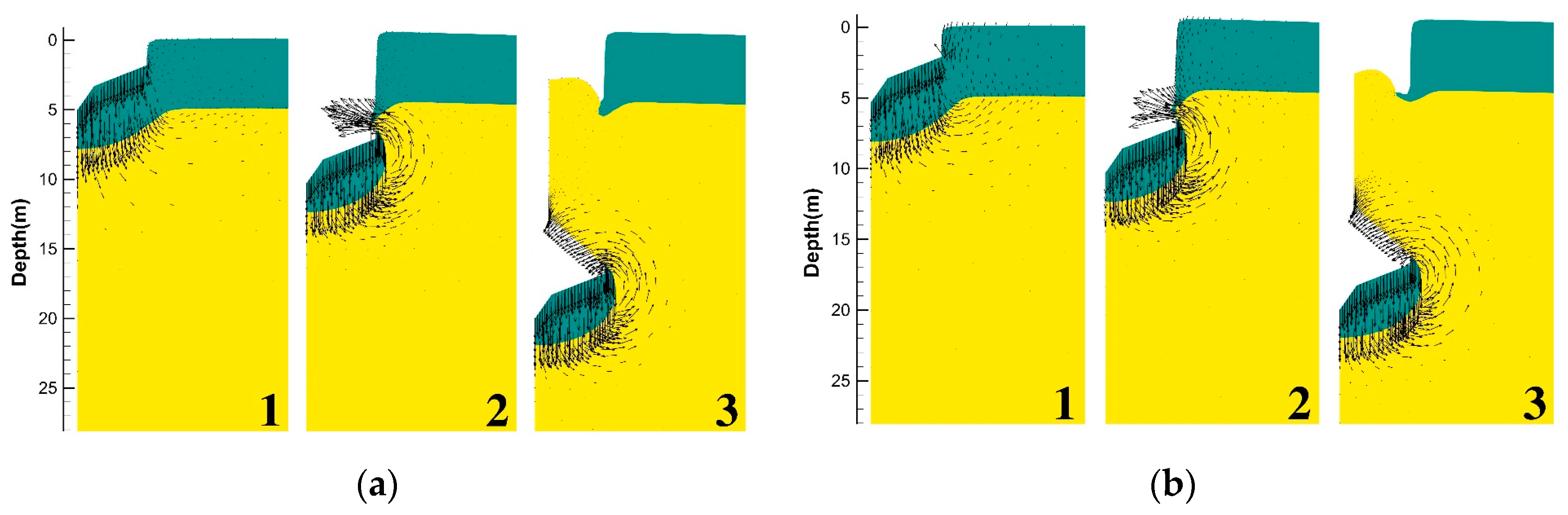
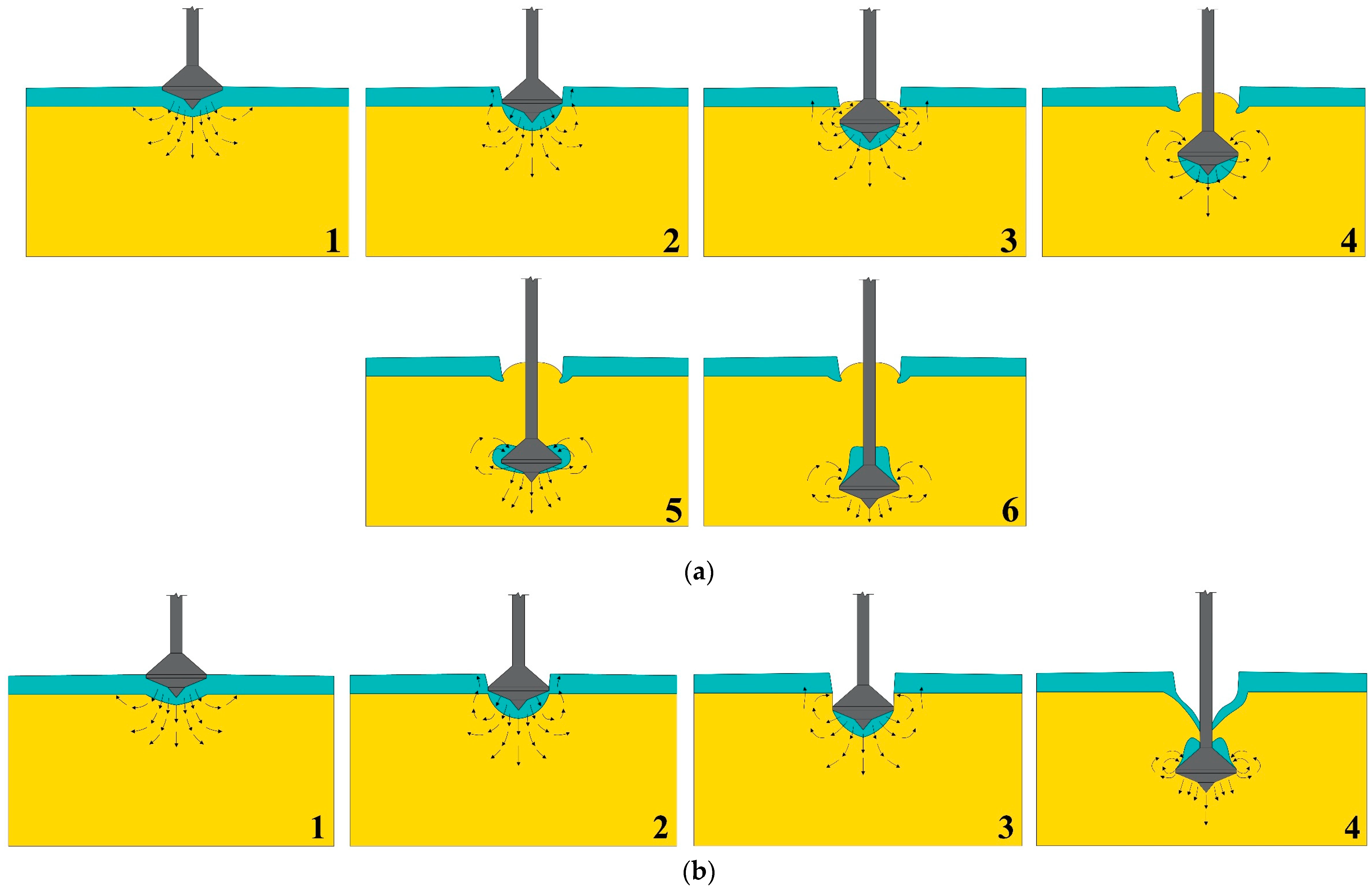
3.1. Typical Soil Failure Mechanism
3.2. Influence of H/D
3.3. Influence of sut /γ’D
3.4. Influence of kD/sui
3.5. Influence of sut/sui
3.6. Influence of α
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of the Soil Failure Mechanism
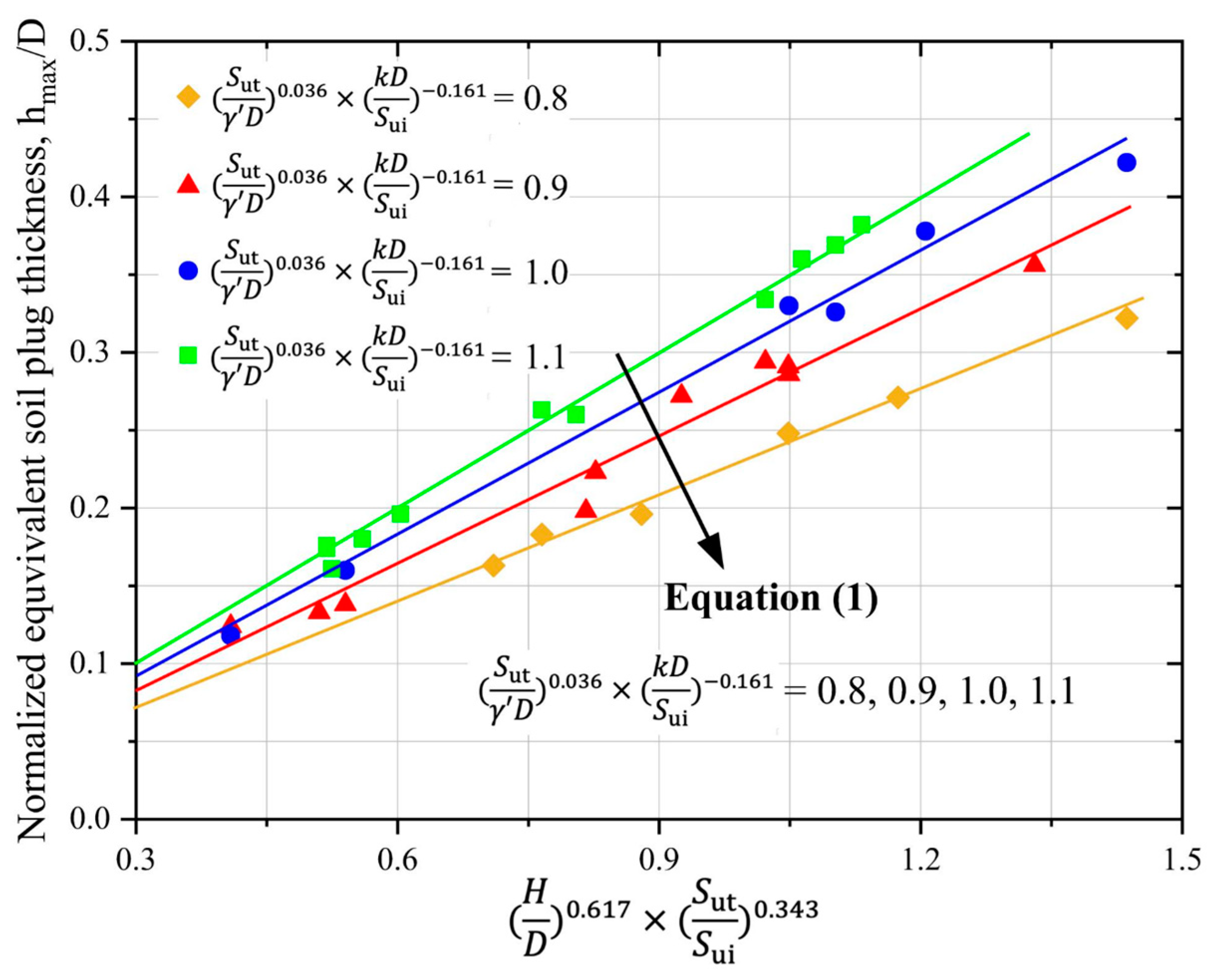
4.2. hmax of Trapped Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Notations
| D | diameter of spudcan |
| H | thickness of top layer(stiff soil) |
| hmin | the minimum element size |
| hmax | maximum thickness of soil plug |
| k | gradient shear strength of bottom layer |
| K0 | geostatic stress condition |
| qu | soil resistance of spudcan penetration |
| R | coefficient of association |
| sub | undrained shear strength of bottom layer |
| sui | undrained shear strength of interface |
| sut | undrained shear strength of top layer |
| Z | depth below soil surface |
| α | coefficient of interface friction |
| γ′ | effective unit weight of soil |
| ν | Poisson’s ratio |
| φ | friction angle |
| ψ | dilation angle |
References
- Huang, Y.; Wan, D. Investigation of interference effects between wind turbine and spar-type floating platform under combined wind-wave excitation. Sustainability 2019, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, J.; Cai, O.; Dong, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Health monitoring and safety evaluation of the offshore wind turbine structure: A review and discussion of future development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassar, W.M.; Anaya-Lara, O.; Ahmed, K.H.; Campos-Gaona, D.; Elgenedy, M. Assessment of multi-use offshore platforms: Structure classification and design challenges. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, J.-S.; Liao, P.-C.; Yeh, C.-D. Risk Analysis and Management of Construction and Operations in Offshore Wind Power Project. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.; Leary, D. Current developments and future prospects of offshore wind and ocean energy. Appl. Energy 2012, 90, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wu, B.; Xu, D.; Zargari, N. Overview of offshore wind farm configurations. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Kunming, China, 22 September 2017; p. 012009. [Google Scholar]
- Aust, T. Accident to the Mobile Offshore Drilling Unit Maersk Victory on November 16 1996; Mines and Energy Resources: Adelaide, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Maung, U.M.; Ahmad, C.K.M. Swiss cheesing to bring in a jack-up rig at Anding location. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Asia Pacific Drilling Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 11 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, R.; Diana, H.; Stonor, R.; Hoyle, M.; Cheng, C.-P.; Roper, R. Installing jackups in punch-through-sensitive clays. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 1 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, K.; Cassidy, M.; Leung, C.; Chow, Y.; Randolph, M.; Quah, C. Revealing the bearing capacity mechanisms of a penetrating spudcan through sand overlying clay. Géotechnique 2008, 58, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, K.; Leung, C. Centrifuge model study of spudcan penetration in sand overlying clay. Géotechnique 2010, 60, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jang, B.-S.; Duan, M. On spudcan deep penetration using Eulerian finite element in multi-layer sediments: Soil plug mechanism. Ships Offshore Struct. 2017, 12, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Snyder, B.F. Empirical models of jackup rig lightship displacement. Ships Offshore Struct. 2013, 8, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Chen, X.J.; Huang, Y.X.; Wang, B. Influence of the legs underwater on the hydrodynamic response of the multi-leg floating structure. Ships Offshore Struct. 2014, 9, 578–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.; Chua, K. Deep penetration of spud-can foundations on sand and clay. Géotechnique 1990, 40, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Hu, Y.; Randolph, M. Spudcan foundation penetration into uniform clay. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Randolph, M.F. New mechanism-based design approach for spudcan foundations on single layer clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, Y.-X.; Kong, X.-J. Deep penetration of spudcan foundation into double layered soils. China Ocean Eng. 2005, 19, 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Randolph, M.F. Deep-penetrating spudcan foundations on layered clays: Numerical analysis. Geotechnique 2010, 60, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, P.; Wang, D.; Cassidy, M.J.; Stanier, S.A. Predicting the resistance profile of a spudcan penetrating sand overlying clay. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Hossain, M.S.; Wang, D. New design approach for spudcan penetration in nonuniform clay with an interbedded stiff layer. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Randolph, M.F. Deep-penetrating spudcan foundations on layered clays: Centrifuge tests. Geotechnique 2010, 60, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.; Balaam, N. AFENA Users’ Manual; Centre for Geotechnical Research, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Randolph, M. A practical numerical approach for large deformation problems in soil. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1998, 22, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Kikuchi, N. An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian finite element method for large deformation analysis of elastic-viscoplastic solids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1991, 86, 127–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, L.R. Finite element analysis of contact problems. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1978, 104, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. Experimental investigation of spudcan penetration in multi-layer clays with interbedded sand layers. Géotechnique 2014, 64, 258–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Randolph, M.F. Numerical investigations into cycling of full-flow penetrometers in soft clay. Géotechnique 2009, 59, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienen, B.; Qiu, G. Numerical analysis of large penetration of a cone and a large diameter footing into dense sand overlying clay. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference of the International Association for Computer Methods and Advances in Geomechanics, Kyoto, Japan, 22 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.; Take, W.; Bolton, M. Soil deformation measurement using particle image velocimetry (PIV) and photogrammetry. Geotechnique 2003, 53, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hossain, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H. Behaviour of ball penetrometer in uniform single-and double-layer clays. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H. Scale issues and interpretation of ball penetration in stratified deposits in centrifuge testing. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hossain, M.S.; Zhou, M. Effect of trapped cavity mechanism on interpretation of T-Bar penetrometer data in uniform clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Analysis | H/D | sut/γ’D | kD/sui | sut/sui | α | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 1 | 0.45 | 0 | 1.6 | 1 | Validation model 1 |
| Group 2 | 1 | 0.31 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | Validation model 2 |
| Group 3 | 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.6 | 0.83 | 1.2 | 10 | 0.3 | Investigation of the effect of the top layer thickness |
| Group 4 | 0.5 | 0.33, 0.5, 0.67, 0.83, 1 | 1.2 | 10 | 0.3 | Investigation of the effect of the top layer shear strength |
| Group 5 | 0.5 | 0.83 | 1.2, 2, 4 | 10 | 0.3 | Investigation of the effect of the gradient strength of the bottom layer |
| Group 6 | 0.5 | 0.83 | 1.2 | 10, 5, 3.33 | 0.3 | Investigation of the effect of the shear strength ratio |
| Group 7 | 0.5 | 0.83 | 1.2 | 10 | 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.8 | Investigation of the effect of the coefficient of friction |
| Group 8 | 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.6 | 0.33, 0.5, 0.67, 0.83, 1 | 1.2, 2, 4 | 10, 5, 3.33 | 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.8 | Random cases |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, D.; Peng, W. Penetration Behavior of the Footing of Jack-Up Vessel of OWTs in Thin Stiff over NC Clay. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8618. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148618
Xie S, Wang X, Zhou M, Wang D, Peng W. Penetration Behavior of the Footing of Jack-Up Vessel of OWTs in Thin Stiff over NC Clay. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8618. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148618
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Shen, Xinggang Wang, Mi Zhou, Deyong Wang, and Weiping Peng. 2022. "Penetration Behavior of the Footing of Jack-Up Vessel of OWTs in Thin Stiff over NC Clay" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8618. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148618
APA StyleXie, S., Wang, X., Zhou, M., Wang, D., & Peng, W. (2022). Penetration Behavior of the Footing of Jack-Up Vessel of OWTs in Thin Stiff over NC Clay. Sustainability, 14(14), 8618. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148618