Impact of Resource-Based Economic Transformation Policy on Sulfur Dioxide Emissions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methodology
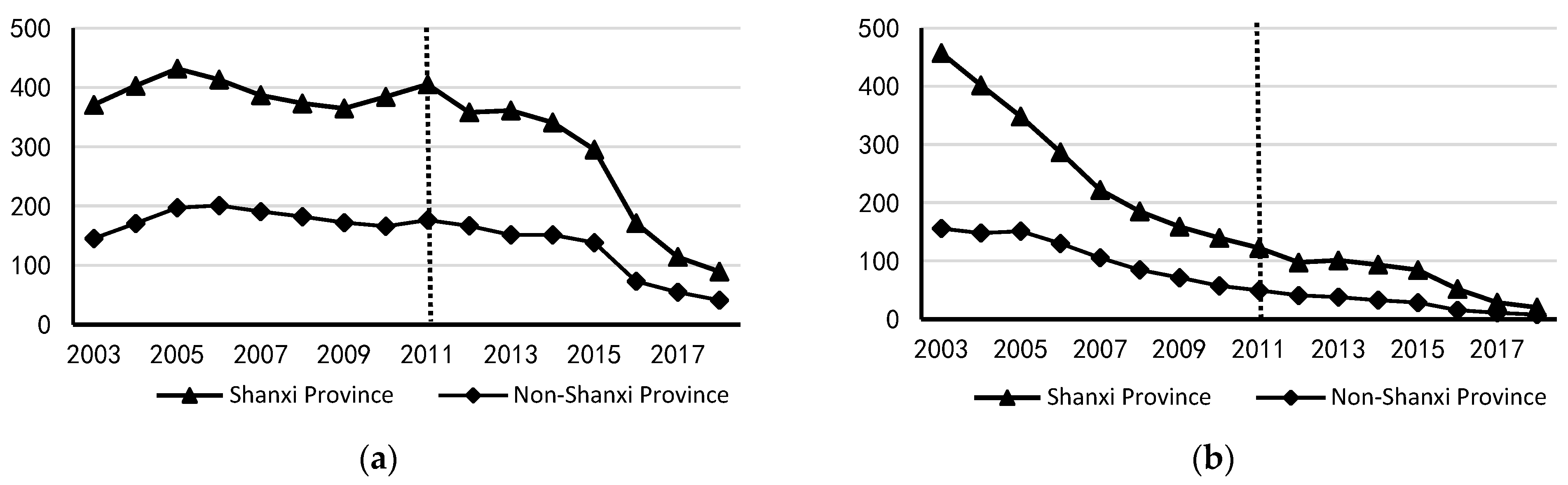
3.2. Variables and Data
4. Results and Discussion
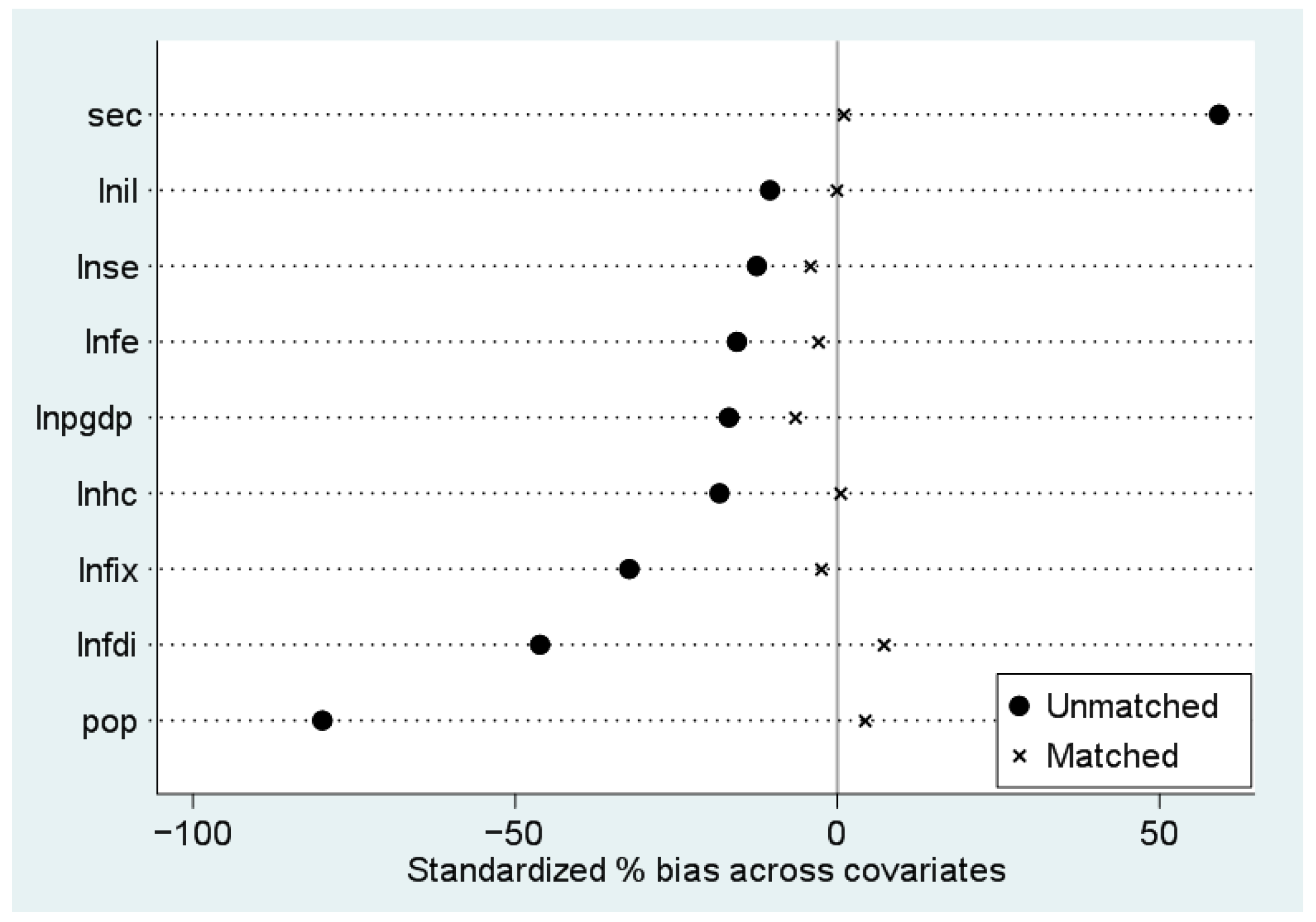
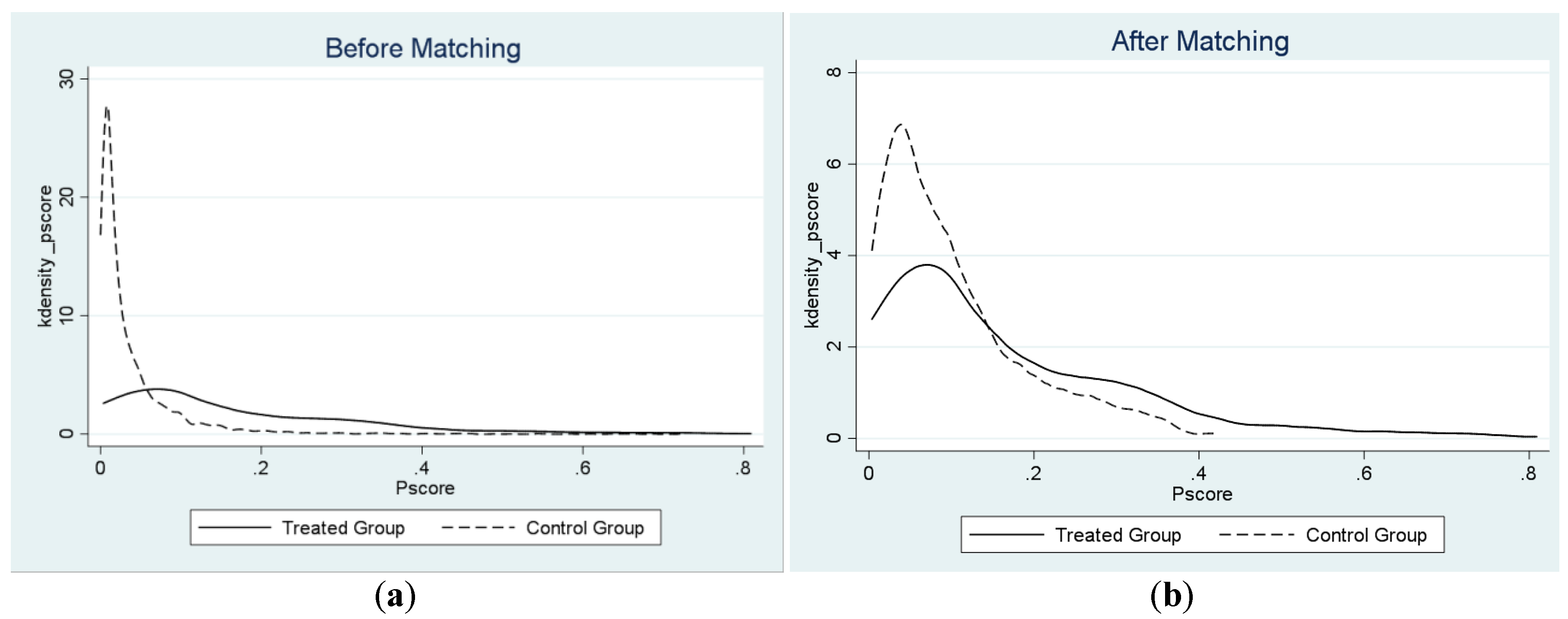
4.1. Propensity Score Matching
4.2. Benchmark Regression Results
4.3. Placebo Test
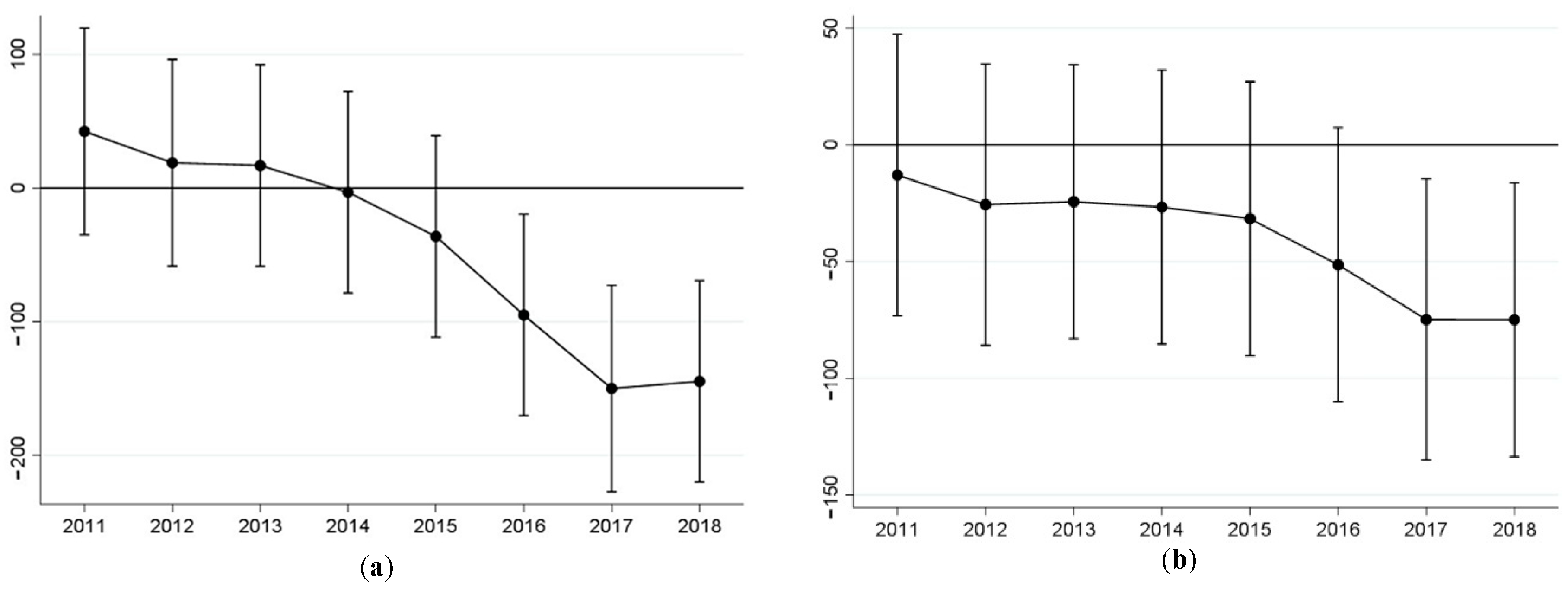
4.4. Dynamic Effects Test
4.5. Mechanism Analysis
4.6. Discussion
4.6.1. Discussion of the Benchmark Regression Results
4.6.2. Discussion of the Dynamic Effects Test
4.6.3. Discussion of the Mechanism Analyses
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Y.Y.; Cao, Y.F.; Qiao, X.; Seyler, B.C.; Tang, Y. Air pollution reduction in China: Recent success but great challenge for the future. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, L.; Poncet, S. Environmental policy and exports: Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 296–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ye, X.; Ge, X. The Impacts of Technical Progress on Sulfur Dioxide Kuznets Curve in China: A Spatial Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2017, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, J.; Han, X.; Li, F.; Bai, Y.; Yu, Y. Contribution of demand shifts to industrial SO2 emissions in a transition economy: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H. Impacts of GDP, Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption, Energy Consumption Intensity, and Economic Structure on SO2 Emissions: A Multi-Variate Panel Data Model Analysis on Selected Chinese Provinces. Sustainability 2018, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wendling, Z.A.; Emerson, J.W.; de Sherbinin, A.; Esty, D.C. Environmental Performance Index; Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy: New Haven, CT, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.X.; Li, P.; Wang, H.Q.; Song, M.L. Quantifying the effects of air pollution control policies: A case of Shanxi province in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Wang, Y.N.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.J.; Ning, S.Y. Evaluating the transformation of China’ s resource-based cities: An integrated sequential weight and TOPSIS approach. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 77, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrik, D.; Rosenzweig, M.R. Preface: Development policy and development economics: An introduction. In Handbook of Development Economics; Rodrik, D., Rosenzweig, M.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 5, pp. xv–xxvii. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A. Trilateral association between SO2/NO2 emission, inequality in energy intensity, and economic growth: A case of Indian cities. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, R. An analysis of the driving forces behind pollutant emission reduction in Chinese industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xiong, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.B. The Analysis of Factors Affecting SO2 Emission of Chinese Industry. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer and Management (CAMAN), Wuhan, China, 19–21 May 2011; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zou, Y. Impacts of energy consumption, energy structure, and treatment technology on SO2 emissions: A multi-scale LMDI decomposition analysis in China. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.Y. A simultaneous estimation of environmental Kuznets curve: Evidence from China. China Econ. Rev. 2006, 17, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodha, M.; Zaghdoud, O. Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: An empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Kubota, J. Is there an environmental Kuznets curve for SO2 emissions? A semi-parametric panel data analysis for China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Liu, T.K.; Wang, H. Thoughts on the economic transformation and upgrading path of China’s Resource-based Cities. Resour. Ind. 2017, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.T.; Yan, W.T. Impact of internet commerce on SO2 pollution: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25801–25812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Shen, H.; Yun, X.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Y.A.; Xu, H.; Shen, G.; Du, W.; Meng, J.; Li, W.; et al. Global sulfur dioxide emissions and the driving forces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6508–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tuygun, G.T.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of urban ambient air pollution characteristics and causes in henan province in the 11th five-year plan period. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2012, 37, 102–105+121. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, T. Air quality and public health: A case study of sulfur dioxide emissions from thermal power plants. Econ. Res. 2014, 49, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Dai, H.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, D.; Masui, T. Impacts of low-carbon power policy on carbon mitigation in Guangdong Province, China. Energy Policy 2016, 88, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. Emissions trading and firm innovation: Evidence from a natural experiment in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 155, 119989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xie, R.; Ma, C.; Fu, Y. Market-based environmental regulation and total factor productivity: Evidence from Chinese enterprises. Econ. Modell. 2021, 95, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Shen, Z.; Song, M.; Zhu, Z. Impact of sulfur dioxide emissions trading pilot scheme on pollution emissions intensity: A study based on the synthetic control method. Energy Policy 2022, 161, 112730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Luo, C.H. Influence of energy exploitation on the economic growth of Yunnan-considerations based on resource curse coefficient. Resour. Sci. 2013, 35, 991–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Auty, R.; Warhurst, A. Sustainable development in mineral exporting economies. Resour. Policy 1993, 19, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.W.; Zhai, X.Y. Is financial development hampering or improving the resource curse? New evidence from China. Resour. Policy 2020, 67, 101676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Yang, L.L. Natural resource dependence, human capital accumulation, and economic growth: A combined explanation for the resource curse and the resource blessing. Energy Policy 2014, 74, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atil, A.; Nawaz, K.; Lahiani, A.; Roubaud, D. Are natural resources a blessing or a curse for financial development in Pakistan? The importance of oil prices, economic growth and economic globalization. Resour. Policy 2020, 67, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Study on economic growth effect and transmission mechanism of environmental regulation in resource-based cities: A dual perspective on innovation compensation and industrial structure upgrading. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.; Leszek, S. Experience in the transformation process of “coal city” to “beautiful city”: Taking Jiaozuo City as an example. Energy Policy 2021, 150, 112164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.A. Evaluation of economic transformation and upgrading of resource-based cities in Shaanxi province based on an improved TOPSIS method. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Zhang, P.Y.; Li, H. Characteristics and evaluation methods of economic transition performance of resource-based cities—based on empirical research in northeast China. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Fluctuation in the transformation of economic development and the coupling mechanism with the environmental quality of resource-based cities—A case study of Northeast China. Resour. Policy 2021, 72, 102128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.G.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.W. What Is the Mechanism of Resource Dependence and High-Quality Economic Development? An Empirical Test from China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Mao, J.Q.; Wang, D.L. Exploring the dilemma and influencing factors of ecological transformation of resource-based cities in China: Perspective on a tripartite evolutionary game. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41386–41408. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-021-18450-x (accessed on 28 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fei, X.Y.; Fang, H. Design and Construction of Evaluation Index System of Regional Innovation Policy Based on a Multi-perspective. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2016, 33, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.S.; Ying, S. How does gender affect the quality of employment?—An empirical study based on the employment evaluation index system of female college students. Res. Financ. Econ. Issue 2012, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.H.; Li, X.M. The shortage of high-end industry in China and the policy deficiencies of traditional overcapacity and countermeasures. Sci. Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, C.H.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, H.B.; Sun, Q.F. Deficiencies and countermeasures of economic policy on rural living environment remediation. Ecol. Res. 2015, 31, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Li, Y. China’s high-speed railway construction and urban economic growth. J. Financ. Res. 2017, 11, 18–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.Q.; Tan, R.P. China’s economic agglomeration and green economy efficiency. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 54, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ebenstein, A.; Greenstone, M.; Li, H. Evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China’s Huai River policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12936–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.B.; Zhang, K.X. The Impact of Air Pollution on Enterprise Productivity: Evidence from Chinese Industrial Enterprises. Manag. World 2019, 35, 95–112, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, C.L. Has the national high-tech zone promoted the transformation and upgrading of China’s industrial structure? China Ind. Econ. 2018, 8, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Qiu, S.L. Can “energy saving and emission reduction” demonstration city selection actually contribute to pollution abatement in China? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1882–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.J.; Wei, W. The Impact of R&D Investment on Enterprise Performance—Research Based on Propensity Score Matching Method. Contemp. Financ. Econ. 2016, 3, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.H.; Jiang, D.C.; Jiang, X.T. The “productivity effect” of China’s technology R&D-oriented outward FDI: Evidence from industrial enterprises. Manag. World 2013, 9, 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.R.; Zhang, A.X.; Tang, Y. Impact of integrated development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt on urban ecological efficiency——An empirical analyse based on PSM-DID model. Soft Sci. 2021, 35, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.P. Does the establishment of national-level poverty-stricken counties promote local economic development? An empirical study based on the PSM-DID method. China. Rural Econ. 2018, 5, 98–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Yang, X.D.; Wang, W.L.; Wu, H.T.; Ran, Q.Y.; Luo, R.D. The impact of innovative city construction on ecological efficiency: A quasi-natural experiment from China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1724–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.D.; Wang, D.; Lu, N. Research on the Impact Mechanism of Carbon Emissions Trading on Low-Carbon Innovation in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.W. Study on the Effectiveness of the Low-Carbon Policy—Evidence from the Synthetic Control Method. Soft Sci. 2017, 31, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Chen, Z.C. Impact evaluation on China’s Western Development policy. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.M.; Zhao, R.J. Western Development: Growth drive or policy trap—Research based on PSM-DID method. China Ind. Eco. 2015, 6, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.N. Research on policy evaluation and promotion path of northeast revitalization strategy——based on empirical estimation of PSM-DID method. Inq. Econ. Issues 2018, 12, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.Z.; Xu, J.X.; Zhang, M.L. Evaluation of the effect of Northeast Revitalization policy. Shanghai Econ. Res. 2017, 4, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Fan, H.W. Evaluation and analysis of the effect of the implementation of the strategy for the rise of central china. Hubei Soc. Sci. 2016, 11, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, J.M.; Shen, Y.B. On the influence of the industrial transfer on the environment in the center region of China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 24, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, C.Q.; Sun, P. Does the construction of low-carbon cities promote local green development? Empirical evidence from quasi-natural experiments. Financ. Trade Res. 2021, 32, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Sun, Y.J.; Chen, D.K. Assessment for the effect of government air pollution control policy: Empirical evidence from “low-carbon city” construction in China. Manag. World 2019, 35, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Zhou, F.N.; Wang, X.Q. Impact of low-carbon pilot policy on the performance of urban carbon emissions and mechanism. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 546–556. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Long, R. Can a carbon emission trading scheme generate the Porter effect? Evidence from pilot areas in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 25, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Chen, S. Could campaign-style enforcement improve environmental performance? Evidence from China’s central environmental protection inspection. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckman, J.J.; Ichimura, H.; Todd, P. Matching as an econometric evaluation estimator. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1998, 65, 261–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Zheng, M.N. Governance mechanism of air pollution and its effects-evidence from Chinese prefecture-level cities. China Ind. Econ. 2016, 4, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum, P.R.; Rubin, D.B. Constructing a control group using multivariate matched sampling methods that incorporate the propensity score. Am. Stat. 1985, 39, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Z.; Hao, Y. Does government expenditure affect environmental quality? Empirical evidence using Chinese city-level data. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, Q.; Shao, S.; Cao, J. Environmental non-governmental organizations and urban environmental governance: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Sun, R.; Dong, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Ni, G. Environmental Kuznets curve for PM2.5 emissions in Beijing, China: What role can natural gas consumption play? Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Identifying the spatial effects and driving factors of urban PM2.5 pollution in China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Huang, S.; Song, M. The influence of increased population density in China on air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Kakinaka, M.; Huang, X. Foreign direct investment, human capital and environmental pollution in China. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2012, 51, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkos, G.E.; Paizanos, E.A. The effect of government expenditure on the environment: An empirical investigation. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 91, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Xu, H.; Draz, M.U.; Ozturkc, I.; Chandio, A.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D. The case of China’s fiscal decentralization and eco-efficiency: Is it worthwhile or just a bootless errand? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, K. Industrial structure, urban governance and haze pollution: Spatiotemporal evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 139228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.L.; Wang, L.P. High investment rate, institutional environment quality and innovation-driven development. J. Guangdong Univ. Financ. Econ. 2016, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Markusen, J.R.; Venables, A.J. Foreign direct investment as a catalyst for industrial development. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1999, 43, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, D.; Li, J. Does foreign direct investment affect environmental pollution in China’s cities? A spatial econometric perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, Y.F.; Lopez, M.F.; Blanco, B.O. Innovation for sustainability: The impact of R&D spending on CO2 emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3459–3467. [Google Scholar]
- You, H.; Chi, R. Informatization and the industrial upgrading in China. Serv. Sci. 2012, 3, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Spatiotemporal PM2.5 variations and its response to the industrial structure from 2000 to 2018 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J. Spatio-temporal variation and influence factors of PM2.5 concentrations in China from 1998 to 2014. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Does flattening government improve economic performance? Evidence from China. J. Dev. Econ. 2016, 123, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, D.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Yuchtman, N.; Zhang, Y.J. Curriculum and Ideology. J. Policy Econ. 2017, 125, 338–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.F.; Li, C.D.; Zhou, S.B. Hopf bifurcation and chaos in macroeconomic models with policy lag. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2005, 25, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anish, S.; Ritesh, B.; Vishal, K.; Unmi, l. How can Indian power plants cost-effectively meet the new sulfur emission standards? Policy evaluation using marginal abatement cost-curves. Energy Policy 2018, 121, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, K.; Akmal, T.; Ahmad, T.; Abbas, Q. Investigating the nexus among sulfur dioxide emission, energy consumption, and economic growth: Empirical evidence from Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 7214–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chor, F.T.; Salah, A.; Navaz, N. Does the quality of institutions and education strengthen the quality of the environment? Evidence from a global perspective. Energy 2021, 218, 119303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu, B.A. Do international investment contribute to environmental pollution? Evidence from 20 African countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 41627–41637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, B.; Khan, M.K.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, S. Impact of foreign direct investment, natural resources, renewable energy consumption, and economic growth on environmental degradation: Evidence from BRICS, developing, developed and global countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21789–21798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Var | Treat Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Max | Min | Std.dev. | Mean | Max | Min | Std.dev. | |
| PCSO2 | 328.83 | 965.84 | 19.89 | 221.33 | 148.46 | 2749.71 | 0.20 | 202.82 |
| PGSO2 | 1.75 | 892.27 | 1.93 | 1.63 | 0.70 | 1599.31 | 0.19 | 1.08 |
| lnpgdp | 10.05 | 11.76 | 8.21 | 0.66 | 10.17 | 15.68 | 7.77 | 0.83 |
| pop | 5.68 | 6.28 | 4.83 | 0.40 | 5.91 | 7.14 | 3.73 | 0.61 |
| lnhc | 3.06 | 6.10 | −1.12 | 1.36 | 3.31 | 6.99 | −2.99 | 1.36 |
| lnfe | 9.13 | 10.90 | 5.55 | 1.20 | 9.32 | 12.43 | 5.22 | 1.29 |
| sec | 53.73 | 73.71 | 36.12 | 8.75 | 48.08 | 85.92 | 14.40 | 10.27 |
| lnfix | 5.98 | 7.62 | 3.63 | 0.92 | 6.32 | 9.04 | 2.81 | 1.19 |
| lnfdi | 6.09 | 8.80 | 0.000 | 1.64 | 6.90 | 11.36 | 1.60 | 1.84 |
| lnse | 7.71 | 9.27 | 5.57 | 0.85 | 7.83 | 11.01 | 4.37 | 1.06 |
| lnil | 5.56 | 7.59 | 1.64 | 0.98 | 5.68 | 8.94 | −1.44 | 1.18 |
| Treatment Assignment | Off Support | On Support | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 20 | 3772 | 3792 |
| Treated | 7 | 169 | 176 |
| Total | 27 | 3941 | 3968 |
| Var | Mean | % Bias | % Bias Reduction | t-Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treated | Control | t | p | ||||
| lnpgdp | U | 10.046 | 10.172 | −16.8 | - | −2.00 | 0.046 |
| M | 10.064 | 10.113 | −6.6 | 61.0 | −0.61 | 0.544 | |
| pop | U | 245.24 | 429.66 | −79.9 | - | −7.90 | 0.000 |
| M | 247.64 | 237.79 | 4.3 | 94.7 | −0.64 | 0.524 | |
| lnhc | U | 3.062 | 3.311 | −18.3 | - | −2.38 | 0.018 |
| M | 3.072 | 3.066 | 0.5 | 97.4 | 0.05 | 0.962 | |
| lnfe | U | 9.129 | 9.322 | −15.6 | - | −1.96 | 0.05 |
| M | 9.161 | 9.198 | −3.0 | 80.8 | −0.29 | 0.774 | |
| sec | U | 53.732 | 48.082 | 59.2 | - | 7.18 | 0.000 |
| M | 53.214 | 53.121 | 1.0 | 98.3 | 0.08 | 0.936 | |
| lnfix | U | 5.980 | 6.323 | −32.3 | - | −3.77 | 0.000 |
| M | 5.998 | 6.025 | −2.5 | 92.2 | −0.24 | 0.807 | |
| lnfdi | U | 6.090 | 6.900 | −46.2 | - | −5.70 | 0.000 |
| M | 6.129 | 6.003 | 7.2 | 84.4 | 0.65 | 0.515 | |
| lnse | U | 7.711 | 7.831 | −12.5 | - | −1.48 | 0.138 |
| M | 7.714 | 7.754 | −4.2 | 66.3 | −0.42 | 0.677 | |
| lnil | U | 5.562 | 5.676 | −10.5 | - | −1.26 | 0.208 |
| M | 5.575 | 5.577 | −0.1 | 98.7 | −0.01 | 0.989 | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCSO2 | PGSO2 | PCSO2 | PGSO2 | |
| −64.905 *** (−4.65) | −1.131 *** (−10.34) | −47.803 *** (−3.48) | −113.935 *** (−10.41) | |
| 80.226 ** (2.27) | 1.398 *** (5.05) | −32.062 (−0.72) | 0.643 ** (1.80) | |
| −108.982 *** (−13.63) | −1.555 *** (−24.78) | −250.598 *** (−7.93) | 0.496 * (1.97) | |
| lnpgdp | 63.081 *** (6.84) | −0.523 *** (7.11) | ||
| pop | 0.122 *** (−3.42) | 0.00058 ** (2.05) | ||
| lnhc | −34.211 *** (−6.65) | 0.034 (0.82) | ||
| lnfe | 33.673 *** (5.69) | −0.031 (−0.65) | ||
| sec | 76.307 ** (1.99) | 1.101 *** (3.61) | ||
| lnfix | 28.416 *** (4.67) | 0.044 (0.91) | ||
| lnfdi | −1.401 (−0.81) | −0.049 *** (−3.55) | ||
| lnse | −34.136 *** (−3.36) | −0.251 *** (−3.09) | ||
| lnil | −10.206 ** (−2.43) | 0.186 *** (−5.57) | ||
| cons | 152.773 *** (6.69) | 1.482 *** (8.28) | −342.966 *** (−3.38) | 8.636 *** (10.67) |
| N | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 |
| R2 | 0.8170 | 0.6219 | 0.8299 | 0.6370 |
| (1) PCSO2 | (2) PGSO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 42.423 (1.08) | −12.970 (−0.42) | |
| 18.970 (0.48) | −25.574 (−0.83) | |
| 16.914 (0.44) | −24.360 (−0.81) | |
| −3.133 (−0.08) | −26.650 (−0.89) | |
| −36.214 (−0.94) | −31.655 (−1.06) | |
| −95.012 ** (−2.47) | −51.371 * (−1.72) | |
| −150.020 *** (−3.80) | −74.821 ** (−2.44) | |
| −144.701 *** (−3.76) | −74.906 ** (−2.50) | |
| cons | 152.534 *** (6.72) | 142.617 *** (8.06) |
| Control | YES | YES |
| N | 3941 | 3941 |
| R2 | 0.8190 | 0.6313 |
| Var | lnpgdp | pop | lnhc | lnlf | sec | lnfix | lnfdi | lnse | lnil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| Treatedit | −0.592 *** (−7.96) | −0.947 ** (−43.93) | −3.092 *** (−27.69) | −0.870 *** (−8.03) | 0.192 *** (10.51) | −1.756 *** (−14.7) | −2.47 *** (−7.23) | −0.775 *** (−12.66) | −1.909 *** (−13.59) |
| 1.799 *** (106.7) | 0.093 *** (18.95) | 1.142 *** (45.14) | 3.320 *** (135.3) | −0.016 *** (−3.95) | 2.634 *** (97.12) | 1.237 *** (15.98) | 2.479 *** (178.8) | 2.624 *** (82.47) | |
| −0.110 *** (−3.81) | −0.006 (−0.69) | 0.112 ** (2.55) | −0.118 *** (−2.76) | −0.064 *** (−8.84) | −0.122 *** (−2.59) | 0.460 *** (3.41) | 0.162 *** (6.70) | −0.026 (−0.46) | |
| cons | 9.343 (194.2) | 6.829 *** (490.19) | 5.098 *** (70.62) | 8.112 *** (115.9) | 0.441 *** (37.36) | 6.187 *** (79.94) | 7.34 *** (33.21) | 7.383 *** (186.6) | 6.007 *** (66.15) |
| N | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 | 3941 |
| R2 | 0.9485 | 0.9925 | 0.9577 | 0.9549 | 0.7946 | 0.9354 | 0.7809 | 0.9786 | 0.9093 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Su, B.; Eric, T.M. Impact of Resource-Based Economic Transformation Policy on Sulfur Dioxide Emissions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148253
Li W, Xiang B, Zhang R, Li G, Wang Z, Su B, Eric TM. Impact of Resource-Based Economic Transformation Policy on Sulfur Dioxide Emissions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148253
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Baichuan Xiang, Rongxia Zhang, Guomin Li, Zhihao Wang, Bin Su, and Tossou Mahugbe Eric. 2022. "Impact of Resource-Based Economic Transformation Policy on Sulfur Dioxide Emissions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148253
APA StyleLi, W., Xiang, B., Zhang, R., Li, G., Wang, Z., Su, B., & Eric, T. M. (2022). Impact of Resource-Based Economic Transformation Policy on Sulfur Dioxide Emissions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Sustainability, 14(14), 8253. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148253






