Towards Human-Scale Competitiveness: Priority Challenges for Triple Helix towards 2030
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Emergence of the Triple Helix
1.2. Challenges That the Triple Helix Must Face to Achieve a Human-Scale Competitiveness by 2030
1.2.1. Lifelong Learning
1.2.2. The Triple Transition (Climate, Digital, and Demographic)
1.2.3. Gender Equality
1.2.4. Employment of the Future and the Future of Employment
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. State of Art Review
2.2. Focus Group
2.3. Online Quantitative Questionnaire
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identified Challenges That the Triple Helix Must Address
3.1.1. Triple Transition
- Develop alternative energy sources to fossil fuels; renewable, robust, and efficient, based on digital solutions and economically competitive;
- Promote and achieve energy savings through education of citizens and optimisation of consumption;
- Manage generational change in the productive system by integrating youth in an orderly handover; boosting digitalisation to fill demographic gaps (thereby covering the future shortage of employees); and employing and integrating migrants;
- Manage and achieve a healthy ageing population, generating socio-economic opportunities;
3.1.2. Lifelong Learning
- Identify and resolve training needs and matching skills between supply and demand, focused on tackling the transformation of work and industry (digitalisation, robotisation, and automation);
- Promote the creation of networks, integrating the education system and companies so as to encourage specialisation in training programmes for lifelong learning;
- Promote highly specialised training to position the Basque Country not as an eternal follower, but (in some areas, sectors or companies) as a technological leader;
- Increase the participation of Basque society in continuous training actions, especially in the segments of the population with fewer qualifications or that are immersed in risk factors;
3.1.3. Future Employment
- Promote the integration of young people into the labour market in decent conditions, thus developing the capacity to attract and retain highly qualified technical profiles and thereby avoiding the flight of talent from the territory, both to other Autonomous Regions and to Europe;
- Favour the establishment of companies in the territory (incentives, legal measures, recognition, etc.);
- Promote strategic cooperative projects and cross-border (European) collaboration. Boost research and transfer (R&D) activity in collaboration with Europe to improve competitiveness;
- Encourage technological entrepreneurship (start-up), intra-entrepreneurship, and diversification;
- Promote the reconciliation of personal, family, and working life. Encourage positive parenting and co-responsibility. Encourage teleworking and flexible working, adapting the dynamics of companies;
3.1.4. Gender Equality
- Publicise and raise awareness in society of the importance of the work and spaces in which women play the majority role for collective and social well-being. Recognise and give value to care work as an indispensable condition for the sustainability of life;
- Tackle the pay gap;
- Transform the economy and society to achieve equality and strengthen social recognition of equality as part of sustainable human development;
- Promote the presence of women in the field of science and technology. Promote STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) vocations;
- Increase the presence of women in public positions of social and political representation and/or decision making;
- Eradicate gender-based violence.
3.2. Quantitative Assessment of the Challenges
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Limitations and Future Lines
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diputación Foral de Guipúzcoa. Bases Reguladoras y Convocatoria 2021 de Las Subvenciones del Programa Para Promover la Calidad del Empleo en el Tejido Empresarial y el Ecosistema Socio-Económico en Gipuzkoa; Diputación Foral de Guipúzcoa: Donostia, Spain, 2021.
- World Economic Forum. Annual Report 2020–2021; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Hülsbeck, M.; Lehmann, E.E. Regional Competitiveness, University Spillovers and Entrepreneurial Activity. Small Bus. Econ. 2012, 39, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzkowitz, H. The Evolution of the Entrepreneurial University. Int. J. Technol. Glob. 2004, 1, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyarra, E. Conceptualizing the Regional Roles of Universities, Implications and Contradictions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2010, 18, 1227–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, A.; Perkmann, M.; Goddard, J.; Kempton, L. Measuring the Impact of University-Business Cooperation; Final Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014; 100p. [Google Scholar]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. The Dynamics of Innovation: From National Systems and ‘Mode 2’ to a Triple Helix of University-Industry-Government Relations. Res. Policy 2000, 29, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, C. Reframing the Role of Universities in the Development of Regional Innovation Systems. J. Technol. Transf. 2006, 31, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Etzkowitz, H. Theorizing the Triple Helix Model: Past, Present, and Future. Triple Helix 2020, 7, 189–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M.; Urbano, D. The Impact of Triple Helix Agents on Entrepreneurial Innovations’ Performance: An inside Look at Enterprises Located in an Emerging Economy. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 119, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, A.; Radziwon, A. Efficient Triple Helix Collaboration Fostering Local Niche Innovation Projects—A Case from Denmark. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 123, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, W.; Yang, T. The Effect of the Triple Helix System and Habitat on Regional Entrepreneurship: Empirical Evidence from the U.S. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, T.; Meerman, A.; Galán-Muros, V.; Orazbayeva, B.; Baaken, T. The State of University-Business Cooperation in Europe; Final Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vivar-Simon, M.; Errasti, N.; Markuerkiaga, L. An Analysis of the Organisational Factors That Determine Education-Related University-Business Cooperation Activities in Manufacturing SMEs. Stud. High. Educ. 2022, 47, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, K.A. From Sustainable Development Goals to Basic Development Goals. Ethics Int. Aff. 2020, 34, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahi, A.; Dervishi, A. Triple Helix, as an Acceleration Model of Sustainable Development Goals. Eur. J. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2019, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- OECD. Higher Education in Regional and City Development: Basque Country, Spain 2013; OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- KPMG. Universidad y Empresa En El País Vasco; KPMG: Madrid, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. Universities and the Global Knowledge Economy: A Triple Helix of University- Industry-Government Relations. In Universities and the Global Knowledge Economy: A Triple Helix of University-Industry-Government Relations; Pinter: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Laukkanen, M. Exploring Academic Entrepreneurship: Drivers and Tensions of University-based Business. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2003, 10, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterton, P.; Goddard, J. The Response of Higher Education Institutions to Regional Needs. Eur. J. Educ. 2000, 35, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markuerkiaga, L.; Errasti, N.; Ochoa, C.; Arcelus, M. UNEK, an Academic Entrepreneurship Maturity Model for Technological Faculties. Dir. Organ. 2017, 61, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gieryn, T.F. Boundary-Work and the Demarcation of Science from Non-Science: Strains and Interests in Professional Ideologies of Scientists*. Am. Sociol. Assoc. 1983, 48, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Education, Youth, Sport and Culture. Measuring the Contribution of Higher Education to Innovation Capacity in the EU: Study; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Davey, T.; Meerman, A.; Orazbayeva, B.; Riedel, M.; Galán-Muros, V.; Plewa, C.; Eckert, N. The Future of Universities. Thoughtbook; University Industry Innovation Network: Amsterdan, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 148, ISBN 9789491901324. [Google Scholar]
- Galan-Muros, V.; Davey, T. The UBC Ecosystem: Putting Together a Comprehensive Framework for University-Business Cooperation. J. Technol. Transf. 2019, 44, 1311–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biney, I.K. Continuing Education and Employment Creation: Investment in Entrepreneurship Matters. Community Dev. 2021, 52, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhards, P. The Notion of Continuing Education in Local Education Reports in Germany—An Analysis of Regional Disparities in Topics, Data, and Governance Recommendations. Educ. Sci. 2021, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstykh, T.O.; Vasin, S.M.; Gamidullaeva, L.A.; Nedelko, S.; Eremina, E.; Koshevoj, O. The Control of Continuing Education Based on the Digital Economy; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-79988-734-8. [Google Scholar]
- Eynon, R.; Malmberg, L.-E. Lifelong Learning and the Internet: Who Benefits Most from Learning Online? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2021, 52, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Navarrete, C.; Noguez, J.; Molina-Espinosa, J.-M.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.-S.; Navarro-Tuch, S.A.; Bustamante-Bello, M.-R.; Rosas-Fernández, J.-B.; Molina, A. The Core Components of Education 4.0 in Higher Education: Three Case Studies in Engineering Education. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gento, A.M.; Pimentel, C.; Pascual, J.A. Lean School: An Example of Industry-University Collaboration. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 32, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkin, G.W. Reshaping University Continuing Education: Leadership Imperatives for Thriving in a Changing and Competitive Market. Am. J. Distance Educ. 2022, 36, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X. Innovation of Undergraduate Talents Cultivation in Continuing Education—Taking Engineering Management as an Example. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd Asia-Pacific Conference on Image Processing, Electronics and Computers, Dalian, China, 14–16 April 2021; pp. 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, J.; Holm, J.R. Firm Innovation and Tertiary Continuing Education. In Globalisation, New and Emerging Technologies, and Sustainable Development; Routledge: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, D.; May, J.; Andrade, J.; Jones, R. Delivering Digital Health: The Barriers and Facilitators to University-Industry Collaboration. Health Policy Technol. 2021, 10, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.; O’Sullivan, D. Benefits Management in University-Industry Collaboration Programs. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2021, 39, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Jayme, B. The handbook of adult and continuing education. Can. J. Study Adult Educ. 2021, 33, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- de Barba, M.L.F.; Vaccarezza, G.F.; Brandão, C.F.S.; Junior, N.C. Continuing education: Experience in the SUS network in the central region of São Paulo. Rev. Int. Educ. Saúde 2020, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Anosova, A.; Drachuk, O.; Semenog, O.; Vaidych, T.; Leshchenko, N.; Ruskulis, L. Current Trends in Training in Continuing Education: Theoretical Principles. Laplage Rev. 2021, 7, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.H.; You, J.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J. Instructional Design for Adult and Continuing Higher Education: Theoretical and Practical Considerations; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Report of the UN Economist Network for the UN 75th Anniversary Shaping the Trends of Our Time; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UN Women. UN Women Strategic Plan 2022–2025; UN Women: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Economic Forum. The Global Competitiveness Report: How Countries Are Performing on the Road to Recovery; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anghel, B.; Conde-Ruiz, J.I.; de Artíñamo, I.M. Brechas salariales de género en España. Hacienda Publica Española/Rev. Public Econ. 2019, 229, 87–119. [Google Scholar]
- Diputación Foral de Gipuzkoa. III Plan Foral Para la Igualdad de Mujeres y Hombres en Gipuzkoa; Diputación Foral de Guipúzcoa: Donostia, Spain, 2020.
- Emakunde. VII Plan para la Igualdad de Mujeres y Hombres en la CAE; Gobierno Vasco: Vitoria-Gazteiz, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, C.B. The Future of Work: A Guide to a Changing Society; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1994; ISBN 0-631-14277-0. [Google Scholar]
- Arboníes, A.L.; Moso, M. Basque Country: The Knowledge Cluster. J. Knowl. Manag. 2002, 6, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barandiaran-Irastorza, X.; Pena-Fernandez, S.; Unceta-Satrustegui, A. The Archipelago of Cultural and Creative Industries: A Case Study of the Basque Country. Economies 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Tola, E.; de la Cal, M.L.; Larrañaga, M.; Jubeto, Y. Highs and Lows in Implementing Work-Life Balance at Companies in the Basque Country. Womens Stud. Int. Forum 2019, 77, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M. Colaboración Regional Transfronteriza y RIS3 2018. Available online: https://www.orkestra.deusto.es/images/investigacion/proyectos/RIS3/PB_ColaboracionRegional_ES.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Azanza, G.; Campos, J.; Moriano, J. Entrepreneurial Intention and Values in the Basque Country. In Proceedings of the ISBE Conference, Dublin, Germany, 7–8 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, K. Collective Entrepreneurship: The Basque Model of Innovation. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2016, 24, 1544–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basque Government Universidades e Investigación. Available online: https://www.euskadi.eus/informacion/sistema-universitario-vasco-universidades/web01-a2hunib/es/ (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Kariker, W.; Frasch, T.; Duckworth, T.; Cox, D.G. Combating the Dislocation Effects of International Trade Through Worker Retraining Programs: A Preliminary Examination of Displaced Workers in the Midwest. Reg. Bus. Rev. 2008, 27, 38–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Laso, A.; McLaughlin, S.J.; Urdaneta, E.; Yanguas, J. Defining and Estimating Healthy Aging in Spain: A Cross-Sectional Study. Gerontologist 2018, 58, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudaha, R.; van Rest, E. Envisioning Pathways to 2030: Megatrends Shaping the Future of Global Higher Education and International Student Mobility; Studyportals: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- International Labour Organization. Global Employment Trends for Youth 2020: Technology and the Future of Jobs; International Labour Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, R.R.; Oyelere, R.U. Global Migration of Talent: Drain, Gain, and Transnational Impacts. In International Scholarships in Higher Education: Pathways to Social Change; Dassin, J.R., Marsh, R.R., Mawer, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 209–234. ISBN 978-3-319-62734-2. [Google Scholar]
- Selva, C.; Recorda, A. Spanish Youth Is Emigrating: A Bibliometric Approach to the Media Coverage. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurofound. Living, Working and COVID-19; COVID-19 Series; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Buomprisco, G.; Ricci, S.; Perri, R.; De Sio, S. Health and Telework: New Challenges after COVID-19 Pandemic. Eur. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 5, em0073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyumba, T.O.; Wilson, K.; Derrick, C.J.; Mukherjee, N. The Use of Focus Group Discussion Methodology: Insights from Two Decades of Application in Conservation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W.; Creswell, J.D. Projeto de Pesquisa: Métodos Qualitativo, Quantitativo e Misto; Penso Editora; Sage Publications: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2021; ISBN 6581334197. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, S.; Roussos, A. El Focus Groups Como téCnica de Investigación Cualitativa; Universidad de Belgrano-Facultad de Humanidades: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2010; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, R.A.; Gullone, E. Why We Should Not Use 5-Point Likert Scales: The Case for Subjective Quality of Life Measurement. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Quality of Life in Cities, Singapore, 8–10 March 2000; pp. 74–93. [Google Scholar]
- Basque Government. Estrategia Vasca de Empleo 2030; Basque Government: Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 2021.
- Carifio, J.; Perla, R. Resolving the 50-Year Debate around Using and Misusing Likert Scales. Med. Educ. 2008, 42, 1150–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, G. Likert Scales, Levels of Measurement and the “Laws” of Statistics. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2010, 15, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, S. Likert Scales: How to (Ab)Use Them. Med. Educ. 2004, 38, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, J. Do Data Characteristics Change According to the Number of Scale Points Used? An Experiment Using 5 Point, 7 Point and 10 Point Scales. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2008, 50, 61–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Artino, A.R. Analyzing and Interpreting Data from Likert-Type Scales. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2013, 5, 541–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, M.; Lewis, P.; Thornhill, A. Research Methods for Business Students, 5th ed.; FT Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780273716860. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Mota, J. Utilização Do Google Forms Na Pesquisa Acadêmica. Humanid. Inovação 2019, 6, 371–373. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics; SAGE: New Delhi, India, 2013; ISBN 1446274586. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Smart Specialisation Platform. Available online: https://s3platform.jrc.ec.europa.eu/regional-benchmarking (accessed on 12 February 2021).
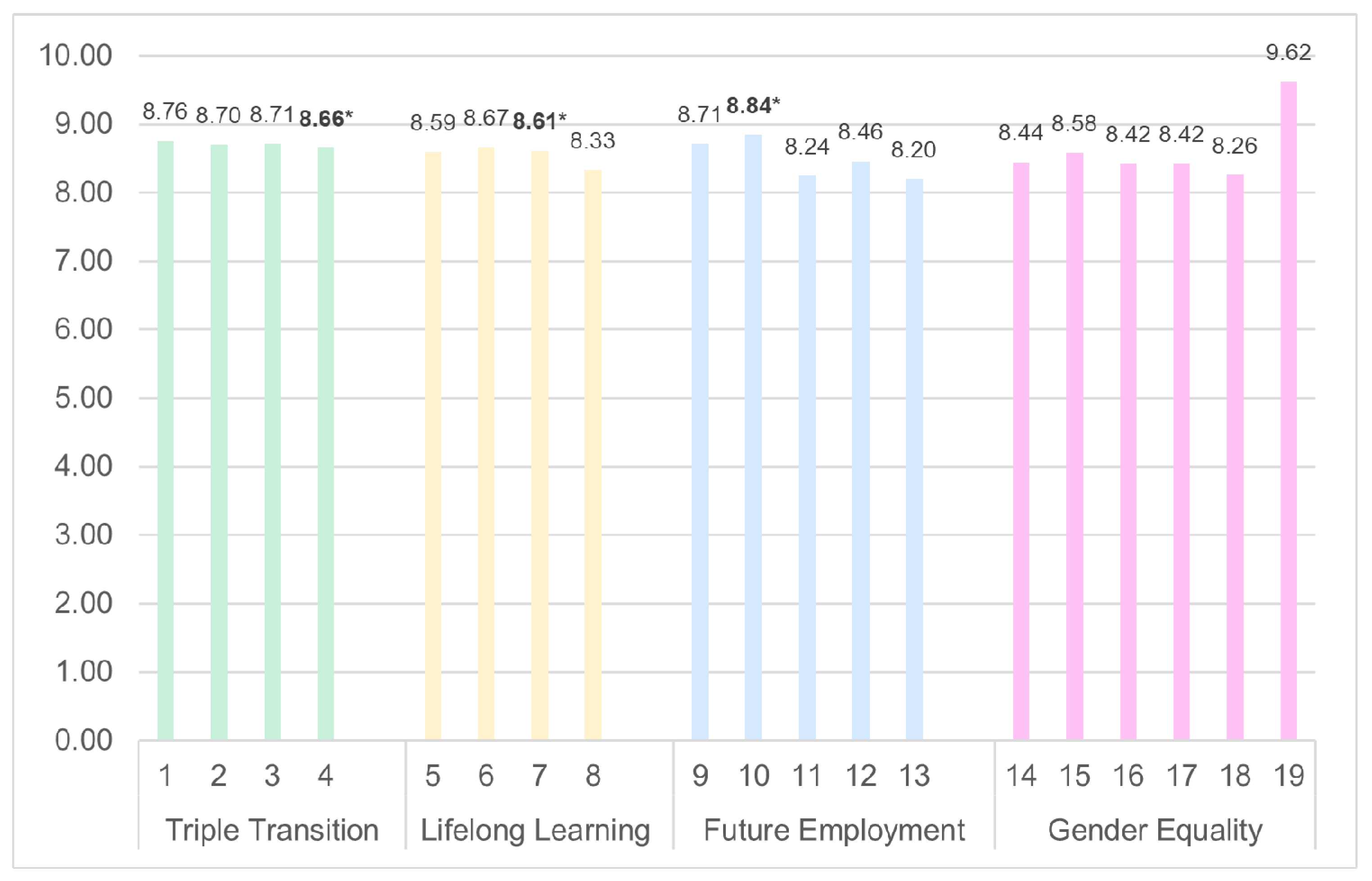
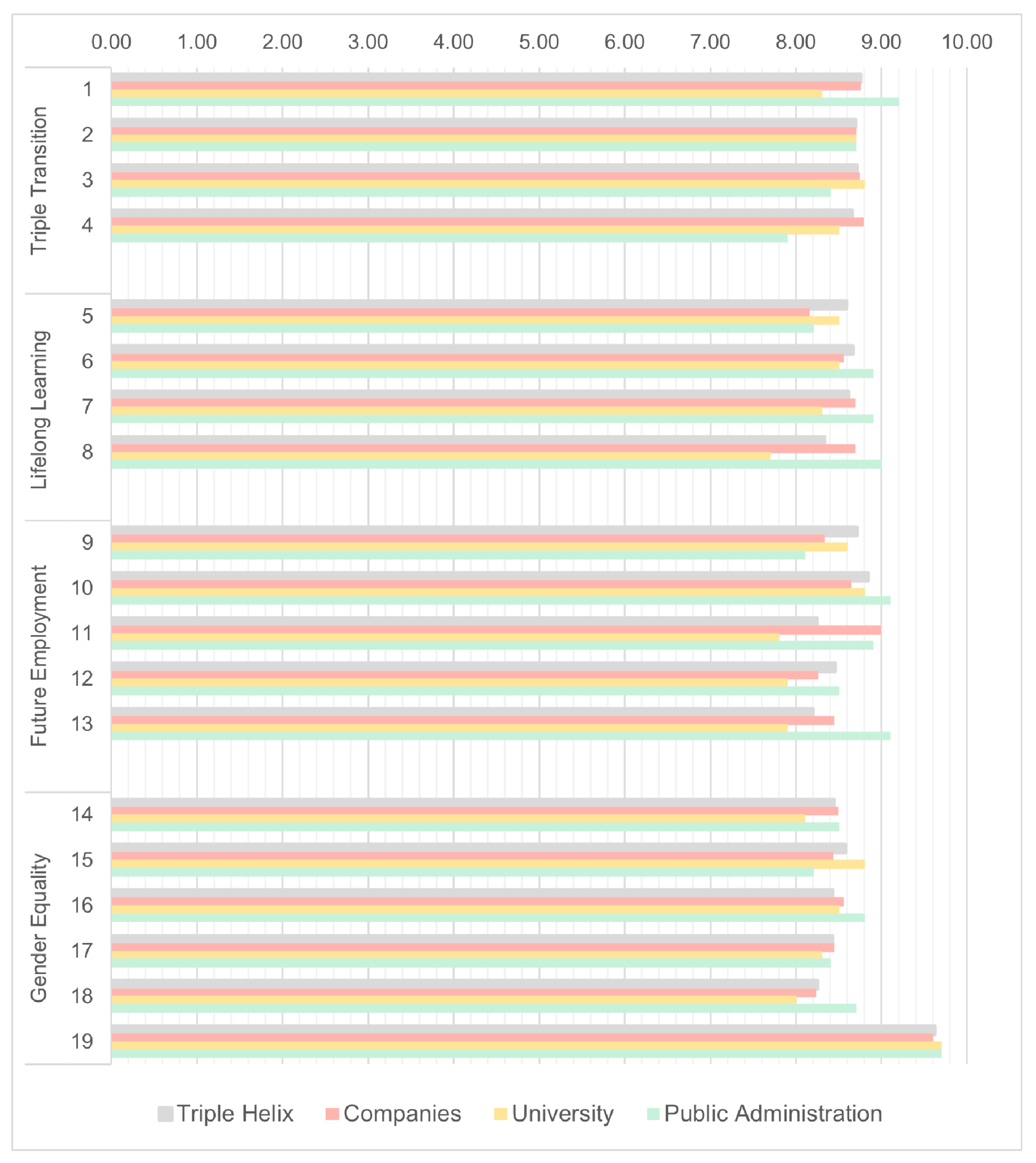
| Topic | Triple Transition | Lifelong Learning | Future Employment | Gender Equality | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| Average | 8.76 | 8.70 | 8.71 | 8.66 | 8.59 | 8.67 | 8.61 | 8.33 | 8.71 | 8.84 | 8.24 | 8.46 | 8.20 | 8.44 | 8.58 | 8.42 | 8.42 | 8.26 | 9.62 |
| SD | 1.38 | 1.28 | 1.15 | 1.06 | 1.04 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.20 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.28 | 1.31 | 1.64 | 1.15 | 1.22 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.29 | 0.80 |
| CI 95%–UL | 8.47 | 8.43 | 8.47 | 8.43 | 8.37 | 8.44 | 8.38 | 8.08 | 8.48 | 8.62 | 7.98 | 8.18 | 7.86 | 8.20 | 8.32 | 8.15 | 8.15 | 7.98 | 9.45 |
| CI 95%—LL | 9.04 | 8.97 | 8.95 | 8.88 | 8.81 | 8.89 | 8.84 | 8.58 | 8.94 | 9.07 | 8.51 | 8.73 | 8.54 | 8.69 | 8.83 | 8.70 | 8.70 | 8.53 | 9.79 |
| Range | 8 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vivar-Simon, M.; Zabaleta, N.; De La Torre, J.; Basañez, A.; Urruzuno, A.; Markuerkiaga, L. Towards Human-Scale Competitiveness: Priority Challenges for Triple Helix towards 2030. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138141
Vivar-Simon M, Zabaleta N, De La Torre J, Basañez A, Urruzuno A, Markuerkiaga L. Towards Human-Scale Competitiveness: Priority Challenges for Triple Helix towards 2030. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138141
Chicago/Turabian StyleVivar-Simon, Maria, Noemi Zabaleta, Juan De La Torre, Aimar Basañez, Aner Urruzuno, and Leire Markuerkiaga. 2022. "Towards Human-Scale Competitiveness: Priority Challenges for Triple Helix towards 2030" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138141
APA StyleVivar-Simon, M., Zabaleta, N., De La Torre, J., Basañez, A., Urruzuno, A., & Markuerkiaga, L. (2022). Towards Human-Scale Competitiveness: Priority Challenges for Triple Helix towards 2030. Sustainability, 14(13), 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138141






