Abstract
This paper is an interpretive reanalysis of 17 in-depth case studies of community-based climate adaptation sponsored by the Kresge Foundation between 2014–2016. Drawing from the political science and international relations literature, we use the policy regime construct to characterize U.S. federal policies and programs that drive and enable climate adaptation at the local scale. While the regime construct has been used to evaluate the international governance of climate change mitigation, it has not been used in the context of climate adaptation. We find that numerous federal policies are used by localities to pursue adaptation objectives. We find that local adaptation initiatives based on federal policy tend to be non-prescriptive, are situational in their application, utilize common policy tools, and adopt a de-centered mode of governance. While a truly sustainable and resilient society may entail fundamental “transformation”, we suggest that such a paradigm shift might be constructively cultivated through the blueprint laid out in the 17 case studies examined here—using existing know-how and tools. Based on our analysis and characterization of a federal climate adaption policy regime, we propose that the enterprise of climate services may need to move beyond existing models of co-production to embrace an ‘apprenticeship’ model, immersing technical information providers in the milieu of policy and governance in order that they might learn to recognize factors that influence the applicability, usefulness, and uptake of climate products and services.
Keywords:
climate change; climate services; adaptation; policy regime; governance; local; co-production 1. Introduction and Background
Climate change has become one of the most pressing issues of our time. Due to the global nature of greenhouse gas emissions, political attention and policy efforts related to climate change have principally focused on the need for international and national scale policy interventions. But the impacts of climate variability, extreme events, and climate change are often local in nature—affected by accidents of microclimate, geography, development, demographics, and governance. Because of this, climate adaptation scholars and professionals have come to recognize the fundamental necessity and validity of local scale efforts to adapt to climate change.
In the United States, localities have taken proactive steps to address climate change, both in terms of mitigation and adaptation to emerging and potential impacts [1,2,3]. Local governments exercise extensive authority over a wide range of day-to-day decisions that influence greenhouse gas emissions as well as climate impacts. This realm of municipal decision making utilizes a broad array of policy, fiscal, and administrative tools to implement and maintain programs and projects to reduce vulnerability to climate variability, extreme events, and climate change. A meaningful proportion of local scale adaptation activities have been crafted to fall under the purview of federal laws, programs, and policy. Because so much progress reducing vulnerability and building resilience occurs at this local scale, it is important to track, characterize, and as appropriate integrate this experience into our evolving map of how decisions about climate impacts and adaptation are made and how to best support and accelerate such decision making.
Most calls for government action on climate impacts and adaptation have followed the climate mitigation policy playbook by focusing on a “top-down” model, for example, enacting Presidential Executive Orders or proposing omnibus legislation at the national level. However, while climate mitigation activities entrain only a few sectors (i.e., energy production, transportation, buildings), climate impacts play out across many more sectors with a much wider range of legal, administrative, and management rules and norms. Because of this breadth of relevance and potential impacts, a wide range of federal policies either drive and/or enable adaptive initiatives at the local scale. With so much adaptation and resilience activity currently happening at the local scale, we submit that better understanding the scope and nature of federal policies that currently facilitate this ongoing activity should be foundational to proposals for additional federal level adaptation policy, and perhaps should lead us to contemplate whether working at the national level is the most direct path to support and accelerate resilience at the community level. The key, we think, is to identify policy and governance arrangements with potential to enhance and expand local uptake of resilience measures, and then use those lessons to help guide the development and deployment of climate services.
2. Technical Approach
This paper is an interpretive re-analysis of 17 in-depth case studies of community-based climate adaptation sponsored by the Kresge Foundation [3]. The authors were senior members of the research team that designed and conducted the overall project, including the case studies, a literature review, thought leader interviews, and a cross case analysis. The original case studies were developed by five core researchers under the supervision of two senior researchers subject to the guidance of a 16-member project advisory committee. As described in the Kresge case study report, the project developed a systematic process for empirical inquiry into the cases dubbed its ‘research protocol’ (https://kresge.org/sites/default/files/library/climate-adaptation-the-state-of-practice-in-us-communities-full-report.pdf, accessed on 25 June 2022, see page 14). This protocol guided the core researchers across all primary data collection and case study development steps, including literature review and desk-top research, site visits, in-person interviews, draft case study development, follow-up email or telephone interviews, review by the senior researchers, and review by the interviewees in each case. The methodology is extensively covered in a chapter of Applied Policy Research [4]. The case studies systematically identified and characterized factors that shaped policy actions that tangibly reduced vulnerability in each community.
It is important to emphasize that this project was selective rather than comprehensive or randomized. The research team “select [ed] only cases with distinct outcomes that already have resulted or are likely to result in tangible reductions of vulnerability to climate variability, extreme events, or climate change” [3], p. 15. Summarized in Table 1, the 17 cases were winnowed from a universe of 93 candidate localities identified through literature review and thought leader interviews. The outcomes identified in these cases included community-level practices that reduced exposure, reduced sensitivity, or enhanced adaptive capacity [5]. The locales differ, however, in terms of size, demographics, economic base, political orientation, geography, and types of relevant climate impact variables.

Table 1.
Case Study Summaries, Associated Federal Policy, and Partners in Governance.
For this reanalysis, the case studies and their supporting information were culled by means of formal rubric to characterize and assess (1) the role—if any—played by federal law, policy, or programs; (2) the organizations and agencies involved in formulation and implementation; and (3) the manner and degree to which technical scientific data, methods, and information were utilized in planning, project design, and decision making. We follow the lead of local actors as illustrated in the Kresge case studies by addressing ‘climate impacts’ broadly and inclusive of expected climate variability (e.g., drought years), extreme events (e.g., severe floods), as well as climate change (e.g., sea level rise).
This interpretive reanalysis begins by building off the empirical foundation of the 17 Kresge case studies to address two basic research questions: (1) do federal policies influence climate adaptation at the local scale; and (2) how do federal climate adaptation policy regimes drive and enable local adaptation initiatives? In this paper, we address these questions through a four-step process. First, we draw from political science and international relations literature to characterize federal influence on local scale climate adaption activities through application of the concept of ‘policy regimes’. Second, utilizing the policy regime construct, we provide a summary of the federal adaptation policy regime as it played out in each of the 17 Kresge case studies to illustrate a federal climate adaptation policy regime. This analysis is augmented through a literature review to summarize federal adaption policies that did not appear to impact the direction or nature of adaptation initiatives in the case study communities, but which help to illustrate the broader relevance of defining federal climate adaptation policy regimes in different policy or management contexts. Third, we provide a descriptive summary of specific federal policies and the role they played in the Kresge case communities. Fourth, we draw upon and integrate across the first three steps to explore implications for the ongoing enterprise of climate services. In the final section we outline several limitations in our analytical approach and articulate potential areas for further research.
3. Policy Regimes Defined
Rarely is an environmental, resilience, or sustainability issue simple enough to address with a single policy. Multi-dimensional, or wicked problems [6] such as urban renewal, health insurance reform, and global climate change tend to be addressed through multiple policies using a variety of tools, something that political scientists and scholars of international relations refer to as ‘policy regimes’. Policy regimes are constructs that depict the mix of institutional mechanisms that make up the governing arrangements addressing a particular problem [7,8,9,10,11,12]. A regime may be comprised of multiple laws, rules, and administrative actions that together specify the contours of governance with respect to an issue or topic. It is important to emphasize that the impact of a regime may or may not be wholly consistent with the stated policy positions of a given administration or agency. Perhaps countering or tangential to political rhetoric, platform statements, or even the titles and captions of legislative acts, the regime construct provides a way to characterize and evaluate the on-the-ground, situational, and empirical impact of federal policies. Academic analysis of regimes typically considers factors such as stated or inferred objectives, strategic focus, scope of mandate, prescribed policy tools, implementation preferences (e.g., legalistic, corporatist, market-based), implementing agencies, and institutional actors. Policy scientists use the concept of regimes to analyze current dynamics, but also to help illuminate historical trends and changes in governance.
Policy regimes vary significantly from issue-to-issue. They can be centralized and tightly linked or loosely coordinated and disjointed across multiple agencies, statutory authorities, and/or jurisdictions. For example, while U.S. monetary policy is the centralized province of the Federal Reserve Board, U.S. health care policies are scattered among as many as 15 departments, bureaus, institutes, and agencies [13]. Regimes can be comprehensive or piecemeal, addressing most or only limited aspects of a problem. They are sometimes characterized as a continuum: “At one end are fully integrated institutions that impose regulation through comprehensive, hierarchical rules. At the other extreme are fragmented collections of institutions with no identifiable core and weak or nonexistent linkages between regime elements” [14], p. 4. In some cases, the term ‘regime complex’ is used to describe loosely coupled arrangements located somewhere in the middle of the continuum.
Policy regimes can be the intentional product of policy design or accretions that form over a span of disassociated activity. As described by Thelen, Mahoney, and others, historical and circumstantial change within regimes can be characterized in terms of various processes, including exhaustion, replacement, layering, and drift [15,16]. ‘Exhaustion’ is a condition under which a policy is no longer effective and requires change. ‘Replacement’ is a state of affairs in which most elements of an institutional arrangement are replaced. ‘Layering’ occurs when new elements are added to the extant complex without abandonment or material alteration of incumbent policies. Finally, ‘drift’ is a situation in which some aspects of a policy mix are maintained even as major aspects of the overall policy environment shift [9].
While the regime construct has been used to evaluate the international governance of climate change mitigation [14,17], we know of no other efforts to characterize national-scale policy clusters as they pertain to climate adaptation at the local scale. In the next section, we apply the regime lens to assess the role played by federal law and policy with respect to climate adaption efforts at the local scale.
4. Do Federal Policies Influence Climate Adaptation at the Local Scale?
It is common to hear that the United States lacks a meaningful or ‘transformational’ climate adaptation policy [18,19,20]. There is no law, program, or suite of governmental activities that can be described as an omnibus vehicle that defines a nation-wide strategy or prescribes an enforceable state-by-state or sector-by-sector implementation approach. There is no bureau or agency with a mission charter centered on adaptation to climatic impacts. Nor is there even an executive proclamation in support of preferred tools of adaptation.
However, if reviewed through a regime lens, it can be demonstrated that the U.S. has already implemented and maintains a wide range of public policy that bears in a substantive way upon local efforts to adapt to climate impacts. Informed by review of the Kresge case studies, Table 2 provides a summary of 26 federal policies that have been utilized in local efforts to plan for and adapt to climate impacts. While none of the vehicles in Table 2 include specific textual enunciation of climate adaptation as a policy objective in the title or caption of its statutory charter, all have been implemented, operationalized, and/or enforced in a manner that drives on-the-ground, empirical consideration of projected climate impacts. It is this use-based symmetry of application that—in our estimation—qualifies the cluster of programs and policies listed in Table 2 as a pragmatic, de facto federal climate adaptation policy regime.

Table 2.
Components of the Federal Adaptation Policy Regime Associated with Local Adaptation Initiatives Profiled in Kresge Case Studies.
In some cases, implementation of laws or programs with a putative, textualist focus on other topics are used to drive climate adaptation initiatives at the local scale. For instance, EPA stormwater discharge permit applications and renewals may be denied if a utility or municipality fails to demonstrate adequate consideration of potential operational deficits due to precipitation changes or the changing likelihood of extreme storm events. Similarly, economic development plans may be scrapped or reformulated due to excessive flood insurance premiums if a municipality allows unchecked siting in federally designated floodplains. In other cases, federal statutes and associated programs provide resources that are used to enable local adaptation initiatives. Federal enablement can come in the form of funding, technical assistance, or promotional support. And in nearly all cases, federal policy is used as an authoritative mechanism through which to structure deliberation and translate sentiment for change into revisions in the structure and/or processes of local governance.
Per their statutory language or statements of programmatic charter, these vehicles were intended to address policy issues other than climate adaptation, such as water pollution abatement, provision of safe drinking water, construction of publicly owned water treatment infrastructure, usage restrictions and protections over public lands, preservation of endangered species, stewardship of National Forests, wise use of coastal zones, and disaster mitigation or recovery. However, agency implementation of these policies has come to allow their routine application in the service of climate adaptation, with formalization occurring not as articles of black letter law, but rather by means of administrative and operational mechanisms such as guidance documents or guidebooks, memoranda of interpretation or implementation, annual workplans from agencies to the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), technical specifications documents, docket notations, circulars, and a wide range of informational materials on agency websites [10,21].
With respect to change over time, the federal climate adaptation policy regimes outlined in this paper cannot be characterized in terms of ‘exhaustion’ or ‘replacement’. The policies through which local scale adaption is being addressed did not take the place of earlier mechanisms due to recognition of a need to adapt to climatic impacts. The cluster of policies outlined in Table 2 was not comprehensively designed but emerged over a period of approximately five decades due to many political actions, initiated by different administrations, at different times, and in response to different issues. Most of the policies summarized in Table 2 are environmental protection, resource management, or disaster response vehicles that have come to be utilized in the context of local scale climate adaptation. In other words, the federal influence on local climate adaptation has resulted from ‘layering’ and ‘drift’, with new conditions being addressed through existing agencies, policy vehicles, and programmatic activities.
We emphasize that the federal climate adaptation policy regime outlined through reanalysis of the Kresge case studies is a contingent, situational, and incidental ‘snap-shot’ of the potentially applicable policy domain. The literature review indicates other federal policies with potential to drive and/or enable climate adaptation at the local scale [1,2]. For example, conservation provisions within the five-year ‘Farm Bill’ have been used by Conservation Districts to support adaptation programs in rural counties [22]. And the Superfund provision of the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA) has been used to reduce the exposure and vulnerability of urban toxic waste sites [23]. Owing to its origins within a single series of case studies, it can only be said that this analysis characterizes a federal climate adaptation policy regime, but not the federal climate adaptation policy regime. We encourage further exploration into the practical boundaries of federal climate adaptation policy regimes. Because climate adaptation is an issue that crosses many policy domains at the local scale, it is likely that it will prove useful to describe multiple regimes that affect particular domains, e.g., a federal water resources adaptation policy regime, a federal land management adaptation policy regime, a federal infrastructure adaptation policy regime, etc. Provisos and scope limitations aside, the Kresge case study reanalysis indicates a pervasive, ongoing, and formative role being played by federal policies with respect to the incidence and nature of local adaptation policies and programs.
It is important to note that the complex of policies summarized in Table 2 differs markedly from recent literature-based inventories of U.S. federal adaptation policy. Reviews conducted by [18,20] include only policy vehicles with an explicit, textually enunciated focus on climate adaptation, sometimes even more narrowly defined as climate change to the exclusion of climate variability and extreme events. These inventories treat an Obama-era Executive Order [24] as the administrative and strategic center of the federal climate adaptation mission. Revoked under the Trump Administration but largely restored by President Biden [25], this order establishes a high-level adaptation planning and coordination task group and directs all federal agencies to develop mission-specific adaptation plans. These Executive Orders spawned a variety of interagency working groups and resulted in a number of sector- and geography-specific planning activities and technical support programs. While it is clearly possible that the Biden EO and associated planning activities will—at some point—alter the fundamental contours of U.S. climate adaptation policy, we emphasize that this set of activities was not in play and did not impact adaptation initiatives undertaken by the Kresge case localities.
5. How Do Federal Climate Adaptation Policy Regimes Drive and Enable Local Adaptation Initiatives?
As summarized in the third column of Table 1, all local adaptation initiatives profiled in the 17 Kresge case studies were influenced by federal policy. In some cases, this influence was relatively incidental, certainly not a necessary factor in the local decision process. Examples of such incidental influence include reference to a federal study or information exchange through a voluntary program. However, the bulk of the cases involved a substantive federal role, often through application of multiple policies. For example,
- Avalon, New Jersey developed a Comprehensive Shoreline Protection Strategy driven partially by the need to reduce flood insurance premiums due to a high rating under the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). The Avalon comprehensive strategy also included beach nourishment and creation of a system of breakwaters and protective dunes, enabled in part by planning, technical assistance, and subsidization by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Maintenance of the artificial dune system is conducted in compliance with a Corps of Engineers ‘dune template’. Avalon’s actions were the subject of high-profile recognition in the form of a Hurricane Mitigation Award, sponsored in part by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). But in an interesting twist, city officials note that dune maintenance activities are constrained due to the presence of a federally listed endangered species (piping plover), subject to protection by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services under the Endangered Species Act.
- In Spartanburg, South Carolina, a major initiative was driven by a requirement to update a FEMA All-Hazards Plan, and to do so in a manner that maintained compliance with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) wastewater regulations. This two-pronged planning process was enabled through use of EPA-developed analytical and decision-support tools and was promoted to local stakeholders through an EPA outreach program called WaterSense. The planning process was enabled through application of U.S. Global Change Research Program future scenarios.
- In the Southwest Crown region of Montana, a coalition of local governments and stakeholders conducted a major forest restoration initiative that included forest thinning and prescribed burns to reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire. This activity was conducted pursuant to a periodic U.S. Forest Service Forest Management Plan update process and subject to Council on Environmental Quality guidance and applicable provisions of the National Environmental Policy Act.
- The El Paso, Texas Water Utility worked in partnership with the U.S. Department of Defense to design and construct a desalinization facility on the grounds of Fort Bliss. The initiative was driven in part by EPA Stormwater Master Planning requirements and the need to maintain compliance with Clean Water Act and Safe Drinking Water Act regulations. Since the facility is sited on a federal property, design activities were overseen by the Corps of Engineers and enabled by the U.S. Geological Survey through development of specialized hydrological modeling capabilities. Planning and development activities were subject to the National Environmental Policy Act.
As described above, most of the federal policies that affected the Kresge case study communities were originally enacted to address environmental protection, resource management, or disaster response concerns. Nevertheless, these federal laws and policies constitute a legal framework that circumscribes appropriate or feasible local policy activity as well as providing technical and fiscal resources beyond what any individual locality could muster on its own.
While the federal climate adaptation policy regime identified and characterized through the Kresge case studies exhibits a clear influence on local adaptation initiatives, it would be wrong to say that these efforts to increase adaptive capacity and reduce vulnerability were top-down impositions by federal agencies or authorities. In response to the question ‘How are communities implementing adaptation actions?’ the Kresge project illustrates a variety of localized strategies, including community-level leadership, consciously building community support, tailoring discussions of ‘climate change’ to local politics and attitudes, generating grassroots and community organization support, engaging vulnerable populations, engaging in peer-to-peer networking, and a focus on dialogue, learning, and collaboration, among others—a list of implementation strategies with a distinctly local flavor [3].
That said, it is also clear that cognizant federal agencies could—if so inclined—have acted to disincentivize, stagnate, or even prohibit use of elements of the regime to support adaption initiatives at the local scale. It is easy to imagine how a hostile Congress or Executive could use tools such as appropriations riders, budget cuts or reprograming, OMB regulatory reviews, or executive orders to limit agency discretion when it comes to use of environmental protection, resource management, or disaster response statutes in the context of climate adaptation at the local scale. This is reminder that the regime construct is not immutable, but rather an active, emergent, and sometimes contested policy space.
It should be emphasized that nearly all the Kresge case studies include reference to tensions between stakeholders, strategic disagreements among partners, and conflicts between champions and affected parties. None of the Kresge initiatives could be described as a bed of roses. This acknowledged, it is nevertheless the case that participants found ways to work past their differences. Given this context, it is interesting to note that the applied policy analysis and public administration literature is replete with references to factors believed to render climate adaptation difficult—perhaps impossible—to achieve. As cataloged by Biesbroek and others [26], these include (1) fragmentation among actors and agencies with a stake in an adaptive project, (2) institutional voids due to a lack of an established, authoritative adaptation policy, (3) the short time horizons of politicians, and (4) a lack of governmental motivation to begin activities to address climate change. It is beyond the scope of this paper to explore—or even explicate—any of these factors. And while we acknowledge the pervasive problematicity of factors such as these within the literature of public policy and government administration, we remind that none of these factors derailed efforts to design and implement adaptation initiatives in the 17 Kresge case localities.
None of the local adaptation initiatives were a simple act of government implemented by and through a lone agency or entity. As summarized in Table 1, all the Kresge initiatives were formulated and implemented by multiple partner organizations under a more or less collaborative model of interaction. It is our sense that the federal climate adaptation policy regime complex suggested through reanalysis of the Kresge case studies bears the hallmarks associated with theories of adaptive governance [27,28,29,30,31,32]. Adaptive governance is characterized by decentralized decision making, a reliance on procedural rationality, and a highly contextual application of science and technical information. Adaptive models of governance are often impelled by perceived stagnation under incumbent top-down patterns of governance controlled by centralized authorities relying on technically rationalized methods and metrics. As Milward and Provan explain, “government refers to the formal institutions of the state—the executive, legislative, and courts—and their monopoly of legitimate coercive power. Governance is a more inclusive term, concerned with creating the conditions for ordered rule and collective action, often including agents in the private and nonprofit sectors as well as within the public sector” [32]. p. 360. “Whereas government refers to political institutions, governance refers to processes of rule wherever they occur” [33], p. 3. The idea of governance, then, includes relationships between government and society, including means through which networks of private actors influence policy decisions and self-organize to mediate their own actions and behavior. As summarized by Ruhl and others, “the role of law and government in adaptive governance is to leave space for local innovation and private governance” [28], p. 1688.
In addition to its adaptive utilization of federal law and statutes, the federal climate adaptation policy regime we identified can be characterized as:
- Non-prescriptive: For the most part, the federal climate adaptation policy regime does not impose specific actions or outcomes on units of local government. With respect to climate adaptation, it mandates no methods, tools, or strategic orientations. Except for NFIP rate determinations, it does not designate enforceable actions or measures. Unlike the environmental protection, resource management, and disaster response statutes from which it is derived, it includes no standards, minimum requirements, or technological stipulations.
- “Situational” in its applicability [10,27]: Adaptation initiatives driven or enabled through the federal policy regime do not necessarily apply to all jurisdictions in the same way. Rather, contingencies and circumstances determine the degree to which governance models, experienced extreme events, or anticipated changes in climate parameters will impact resources or service streams addressed through a given policy or approach to governance.
- De-centered: Local scale adaptation initiatives are not coordinated among cognizant agencies or framed for consistency by means of an overarching strategy or vision. As already emphasized, adaptive governance by local entities is derivative to the original mission of nearly all regime components.
- Scope-limited application of existing policy tools: Local scale adaptation initiatives enabled by federal policy tend not to be synoptic or expansive in nature. Quite the opposite. Limited by the scope of the authorizing statute or program, adaptation initiatives tend merely to operationalize a policy provision or modify a particular service stream or sphere of activity (e.g., planning process, permit renewal, grant review process). Local adaptation initiatives tend to be operationalized by means of familiar tools of local governance such as ordinances, permits, bond issues, easements and property buy-outs, utility fees, comprehensive plans, disaster mitigation plans, zoning, and community or municipal staff capacity-building.
The Kresge case studies and other research efforts reveal a significant amount of adaptation work being conducted by U.S. localities [2,3,34]. Insufficient attention has been paid to the pragmatic role that federal policy plays in community resilience through existing elements of federal climate adaptation policy regimes. For example, the Kresge case reanalysis suggests this role tends to be a ‘bottom-up’ effort to take advantage of available policy tools to accomplish local policy objectives as they emerge through adaptive governance. However, this does not preclude the possibility of using federal climate adaptation policy regimes in a ‘top-down’ effort to incentivize or drive community resilience, for example, through climate projection requirements set by FEMA for hazard mitigation plans.
6. Some Implications for the Ongoing Enterprise of Climate Services
Having characterized a federal climate adaptation policy regime and described how it plays out at the local scale, we turn our attention to what these insights might imply for the enterprise of climate services. We stated earlier that it would be valuable to identify types of policy with potential to improve local uptake of resilience measures, and then to apply this information to help guide the development and deployment of climate services. It is crucial then to note that the evidence from the Kresge case studies and this reanalysis points to many disassociated local scale decisions that are improving the resilience of specific components of individual communities. Taken individually, any one of these actions may seem like a stand-alone case, when in fact they can be understood as part of a larger pattern of adaptive governance focused on community resilience. This section first reviews what the evidence from the Kresge case studies and this reanalysis suggests about common assumptions in the literature about climate services. We then turn to a discussion of how the specific needs articulated by the Kresge case communities suggest augmentation of the path forward for climate services.
As conventionally conceived, the enterprise of climate services has arisen due to the confluence of two phenomena: (1) continued improvement in the predictive capacity, scaling, and applicability of climate data and information; and (2) the fact that improved information has not always translated into effective adaptation [35,36,37,38,39,40]. Owing to this gap, leading researchers, government program administrators, and political leaders have called for significant organizational and strategic overhauls to the ways in which national governments and international agencies produce and deliver climate information and services [41,42,43]. Indeed, it is not uncommon to hear that such change must be “paradigm shifting” or “transformational” in nature [29,44,45,46,47]. In the U.S., this perspective has led to calls for a national climate service, recently amplified through Executive Order 14008 which directs the Office of Science and Technology Policy, NOAA, and FEMA to study and report on ways to expand and improve the delivery of climate services to the American public [48].
The literature on climate services takes it as almost an article of faith that local scale adaptation is being impeded, constrained, or blocked entirely by mismatches and incongruities between available information and the perceived needs of local decision makers and stakeholders [44,46,49]. Our reanalysis of the Kresge case studies suggests that these perspectives are not fully consistent with the observed experience of local communities working to adapt to climate impacts. None of the Kresge case studies revealed the clear and stark bifurcation between knowledge producers and knowledge users that has become a fixture of the climate services literature, certainly nothing as dramatic or lurid as the so-called “valley of death” described by Buontempo and others [50]. Stakeholder interviews that inform the cases studies do not suggest a debilitating distraction due to tension between “answerable” and “unanswerable” questions [44]. None of the cases hinged upon the often-discussed dynamic wherein policy actors insist upon answers to questions that the scientific community is unable to provide [46,51]. There was no evidence of unrealistically “deterministic” views of future change or so-called “projection shopping”. And none of the adaptation champions interviewed for the case studies seemed to harbor unrealistic expectations that action should be delayed because—given time—science would provide a much better characterization of climate impacts upon their specific “neck of the woods” [44].
As illustrated with Figure 1, all the policy initiatives chronicled in the Kresge case studies were framed in terms of some type of data acquisition or assessment process. In many cases, the assessment component was limited and informal. Other cases, such as El Paso, TX; Seattle, WA; and Miami-Dade County, FL involved comprehensive, formalized vulnerability assessments, including provision of tailored climate information products. In nearly all cases, actors seemed capable of seeking information, assessing its relevance, recognizing and appreciating uncertainties, and moving ahead accordingly. We found decision makers and stakeholders willing to “span boundaries” or “make do” with available information [52]. What might explain such a noticeable departure from the climate services orthodoxy?
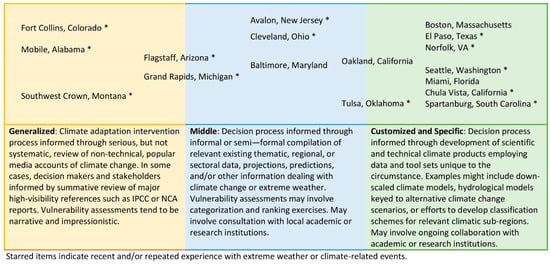
Figure 1.
Conceptualizing Climate Change Vulnerability: Lived Experience, Sources of Information, and Locality-specific Analysis.
As we have already discussed, in most of the cases included in the Kresge study, climate adaptation or resilience actions were in some way associated with one or more federal policy mandates, none of which had an explicit textual focus on climate adaption or the idea of climate services. As per their statutory origins, regulatory actions undertaken by EPA, FEMA and other agencies must be grounded upon the “best available science”, a condition that flows down to primacy agencies at the state and municipal level, and ultimately to regulated entities. In other words, local policy objects such as All-Hazard Plans, permit applications, and environmental impact assessments must be based on the best available science, but nothing more. This means that municipalities, public utilities, and other bodies of local governance are under no compunction to conduct original research, trade in “cutting edge” science, or somehow advance the state of the science in a particular field. It may also be significant that most of the localities covered through the Kresge case studies had experienced extreme weather events. As shown in Figure 1, all but 3 of the 17 case localities were impelled to some extent by recent stakeholder experience—sometimes repeated—with high-impact weather and climate events. Owing to this experience, decision makers and stakeholders may have been unusually motivated to act, adopting mental models animated by regulatory pragmatism and a perceived need to avoid known, experiential threats rather than the calculated output of rationalized, expert-produced, scenario-driven, and risk-optimized projections of future conditions [53].
As emphasized in a classic study by Rayner, Lach, and Ingram, the operational environment of municipalities, utilities, and other regulated entities can be complex, a-rational, programmatically oriented, and dependent upon craft skills and knowledge of localized systems [54]. Climate service developers need to understand and learn how to navigate this milieu; to become connoisseurs of practices and “rules” that explain things like “who and what sources of evidence to trust” and other factors that influence patterns of power and influence at the local scale [55], p. 42. It stands to reason that climate services provision may be especially helpful if conceptualized, framed, and delivered in a manner that is consistent with the concepts, parlance, operational environment, and/or institutional rationalities present in the parent activity.
In this regard, it would seem reasonable for climate service providers to adopt a regime perspective such as outlined in this paper to inventory and map federal policies that regulate resources and/or service streams subject to climatic disruption. This accomplished, would-be climate services providers can proceed in one—or both—of two directions: (1) work directly with communities to navigate applicable federal policy regimes to enable desired changes in local adaptation policy and governance, or (2) engage with federal mission agencies that administer existing regimes of environmental protection, resource management, or disaster response policy to learn how driving and/or enabling policies are being implemented to achieve climate resilience at the local scale, in order to help to expand the uptake and use of such practices. Whichever route is pursued, it seems to us that standard models of information production and provision may need to be modified or augmented in light of the adaptive governance dynamics and regimes described in this paper.
Building on the work of Meadow and colleagues [56], we suggest that co-productive methods such as Action Research (AR) or the Rapid Assessment Process (RAP) could be tailored to address and fit within the epistemic and operational confines of the regulatory context in which local scale initiatives of adaptive governance seem often to be couched. As described by Lather, these techniques are “openly ideological” in the sense that they are undertaken not to discover new knowledge, but rather to alleviate a known and bounded problem [57]. Under this conceptualization, climate products and services would be configured to “plug into” the practices, guidance, tools, and methods used within incumbent service streams. We worry that some co-productive models—such as Participatory Integrated Assessment, transdisciplinarity, or interaction with boundary organizations—may be too focused on open-ended research to be effective within extant federal climate adaptation policy regimes at the local scale.
Meadow and colleagues designate three primary “modes” of deliberative co-production: collegial, consultative, and collaborative. It may be that a distinct, fourth co-productive modality would help to assure better utilization of climate services at the local scale. Specifically, we are suggesting that there may be circumstances when climate service producers would benefit through something like an apprenticeship with local resource or service stream managers, enabling the “experts” at climate services or boundary organizations to learn and appreciate the nuance of place-specific regulatory processes, institutional rationalities, and operational environments at the nexus of federal policy and local governance. We think a similar dynamic could apply if climate service providers sought to work with federal regulatory and oversight agencies to identify procedural and/or functional policy objects that might be impacted by climatic change or extreme weather events.
In both cases, would-be climate service providers would need to become immersed in the culture and operational minutia of the service recipient in order to learn things like whether a particular action requires better information, why a contemplated activity may not need state-of-the-science inputs in order to proceed, and how such information would need to be configured in order to assure up-take through incumbent policy or governance modalities. Before attempting to engage in deliberative, co-productive activities, climate service providers need to “learn how, when, and where” it might be productive to build climate information into existing decision tools, best practices, and applications—or whether sufficient information already exists to support community action now [54], p. 224. We are suggesting that localized adaptations of federal policy may provide an especially rich culture for the inculcation of effective climate services, but that would-be providers of such services need to develop a robust, empathetic appreciation of these operational environments before attempting to engage in the co-productive role [58].
Due to the magnitude of some projected impacts, it is common to hear that climate change policies—both mitigation and adaptation—must be synoptic and transformational in character. Indeed, it has even been suggested that climate change could necessitate new forms of governance [59]. The Kresge case studies and this reanalysis suggest the viability of an alternative perspective [3]. As we have discussed, many of the case communities demonstrate that climate adaptation can be, indeed is being, addressed by collaborative bodies of governance under an extant legal regime using common policy tools. Appropriate application of climate services can help to fuel this emergent movement.
7. Analytical Limitations and Potential Research Needs
We believe it is significant that each of the 17 Kresge case localities exhibit a federal policy influence upon their climate adaptation initiatives. It is our position that the regime construct provides an important tool with which to characterize and evaluate the status of adaptation policy in the United States. However, we acknowledge several limitations in our line of analysis and suggest opportunities to advance research in this important arena.
Constraints of case selection: Our study focused on 17 communities that were able to undertake adaptive initiatives consistent with the scope of specified federal policies (although the federal role was not a factor considered in the original case selection). As with all case-based research, our observations could be an accident of case selection rather than evidence of a broader trend. For example, had the population of Kresge case communities included mostly small municipalities (population less than 300,000), we likely would have found fewer proactive climate adaptation-related initiatives due to limited resources alone. We do not believe that lesser peer learning opportunity or relative exclusion from national adaptation networks (which are also evident in small municipalities; will prove as significant a limitation in part because many of the Kresge case communities were motivated more by recent existential threats from weather or climate events than by a principled prioritization of climate change or adaptation to climate impacts—rendering such networks and peer learning largely beside the point [60]. Alternatively, a case population drawn from politically conservative localities might have exhibited ideological reluctance to build upon federal authorities rooted in environmental protection or resource management in particular, although perhaps less-so for those rooted in disaster response, and may consequently have resisted altogether the idea of addressing climate resilience through those authorities [3,61]. And finally, none of the Kresge case communities were animated by strong religious or faith-based motivations; another factor that could lead to differing approaches and policy outputs [62]. Moreover, it could be argued that had we focused on different localities, we might have found that federal policy actually served to constrain or even prevent adaptation activities envisioned by local actors. We doubt this argument because original case interviews and archival research did not suggest such a dynamic, but nevertheless acknowledge the logical possibility of alternative interpretations. A broader program of policy research could help to illuminate this topic and substantiate our observations.
Our research is U.S. specific: The Kresge case communities are all in the United States. And while tools such as the regime construct have international bona fides and have been used outside the U.S., it could be argued that the bulk of our evidence is unique to the distributed federalist nature of contemporary U.S. environmental protection, resource management, and disaster response policy and therefore of limited applicability. We note however, a literature base that includes influential studies assessing factors affecting climate adaptation policy initiatives in non-U.S. settings, including Western Europe, Scandinavia, Australia, Canada, Russia, and parts of South-Central Asia [63,64,65,66,67]. While none of this research builds on the regime perspective adapted for this paper, it does consider factors that are broadly relevant to our analysis such as the relationship between central and local units of governance; applicability of alternative policy tools; dominant regulatory perspectives; and perhaps most importantly, the role of climate-related data and information. This acknowledged, we nevertheless suggest that our finding of a national level climate adaptation policy regime complex with significant implications for local resilience activity is ripe for further international research.
Assuming effective outcomes: It could be argued that the ultimate effectiveness of the initiatives described in the case studies is unknown. Only time will tell if the actions undertaken by the Kresge case communities will materially reduce vulnerabilities or enhance adaptive capacity.
Promoting the adequacy of the status quo: Climate change is a highly contested and politicized topic. We have suggested that the Kresge case reanalysis points to the viability of a broadly incrementalist approach to climate change adaptation. This could be interpreted as a foil for ideological conservatism, as support for arguments that we do not need to address climate change in a concerted and aggressive manner. We reject the notion that an incrementalist strategic orientation suggests inaction or a passive acceptance of current rates of resilience uptake at the local level. But we acknowledge that some may argue—wrongly in our view—that this strategic orientation amounts to a defense of the status quo.
Policy design and the influence of regime layering: As we have already noted, the literature on policy regimes includes an important focus of the phenomena of layering and drift. There is ample recognition that policy design activities often occur upon the legacy of past decisions [68,69]. This means that new policy elements may or may not be fully consistent with the incumbent portfolio of policy tools. Our reanalysis of the Kresge case studies shows how climate impacts can be successfully layered onto existing environmental protection, resource management, and disaster response policies, but we did not address the question of whether new climate foci either augmented or degraded incumbent policy performance. We see this as a potentially fruitful area of research.
The role of states: Many federal policies are administered and enforced by state-level primacy agencies. Moreover, state constitutions typically delineate areas of allowed local governmental authority and activity. Further, there are several U.S. states that have taken aggressive policy action to promote resilience and adaptation to climate impacts [70]. While the Kresge case materials did not reveal or suggest determinate state roles in local climate decision making, there is clearly a basis in experience and literature to suggest non-trivial state-level involvement. Indeed, application of the regime lens could reveal unexpected and important patterns of state-level policy influence on local adaptation decision making and policy design. This is clearly an area in which focused research could prove illuminating.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, C.H. and J.V.; Investigation, C.H. and J.V.; Methodology, C.H. and J.V.; Writing—original draft, C.H. and J.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- EcoAdapt. Climate Adaptation Knowledge Exchange. 2022. Available online: https://www.cakex.org/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Georgetown Climate Center (GCC). Adaptation Clearinghouse; Georgetown University: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: www.adaptationclearinghouse.org/about.html (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Vogel, J.; Carney, K.; Smith, J.; Herrick, C.; Stults, M.; O’Grady, M.; St Juliana, A.; Hosterman, H.; Giangola, L. Climate Adaptation: The State of Practice in U.S. Communities; The Kresge Foundation: Detroit, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, J.; Herrick, C.; Hosterman, H. Climate change adaptation: An assessment of accomplishments at the community level. In Applied Policy Research: Concepts and Cases; Springer, J.F., Haas, P., Porowski, A., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rittle, H.; Webber, M. Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sci. 1973, 4, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, C. A review of the U.S. invasive species policy mix: Questioning the prospect of an integrated regime. Environ. Policy Gov. 2019, 29, 262–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.; Jochim, A. Policy regime perspectives: Policies, Politics, and Governing. Policy Stud. J. 2013, 41, 426–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, J.; Howlett, M. Introduction: Understanding integrated policy strategies and their evolution. Policy Soc. 2009, 28, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.; Lenschow, A. Environmental policy integration: A state of the art review. Environ. Policy Gov. 2010, 20, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Eckerberg, K. (Eds.) Environmental Policy Integration in Practice; Earthscan: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Underdal, A. Integrated marine policy. What? Why? How? Mar. Policy 1980, 4, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congressional Research Service (CRS). Public Health Service Agencies: Overview and Funding (FY2016-FY2018); Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Keohane, R.; Victor, D. The Regime Complex for Climate Change. Discussion Paper 2010-33; Harvard Project on International Climate Agreements: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thelen, K. How institutions evolve: Insights from comparative historical analysis. In Comparative Historical Analysis in the Social Sciences; Mahoney, J., Rueschmeyer, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, J.; Thelen, K. (Eds.) Advances in Comparative-Historical Analysis; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, R.D. Science and the Climate Change Regime. Policy Sci. 2001, 34, 1–33. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/4532520 (accessed on 10 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bierbaum, R.; Smith, J.; Lee, A.; Blair, M.; Carter, F.; Flemming, P.; Ruffo, S.; Stults, M.; McNeely, S.; Wasley, E.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Climate Adaptation in the United States: More Than before, But Less Than Is Needed. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2013, 18, 361–406. Available online: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11027-012-9423-1#page-2 (accessed on 3 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.; Richmond, T.; Yohe, G. (Eds.) Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment; U.S. Global Change Research Program, U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.; Gregg, R.; Arroyo, V.; Ellsworth, S.; Jackson, L.; Snover, A. The State of Adaptation in the United States: An Overview. A Report for the John D. and Catherine T; MacArthur Foundation: Chicago, IL, USA; EcoAdapt: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kerwin, C. Rulemaking: How Government Agencies Write Law and Make Policy; Congressional Quarterly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, S.; Hanson, L.; Horan, C.; Jacobs, W.; Goho, S.; Opportunities to Address Climate Change in the Farm Bill. Harvard Law School: Emmett Environmental Law and Policy Clinic. 2017. Available online: http://www.farmbilllaw.org/report/climate-change/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Dailey, A. Integrating Climate Change Adaptation into the Superfund Program. In Climate Change Adaptation Webinar; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Available online: https://clu-in.org/conf/tio/climatechange_040115/slides/Dailey.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Executive Order (EO) 13514. Federal Leadership in Environmental, Energy, and Economic Performance; Executive Office of the President: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Executive Order (EO) 14008. Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad; Executive Office of the President: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Biesbroek, R.; Termeer, C.; Kabat, P.; Klostermann, J. Institutional governance barriers for the development and implementation of climate adaptation strategies. In Proceedings of the Working Paper for the International Human Dimensions Programme Conference “Earth System Governance: People, Places, and the Planet”, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2–4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman, N.; Hill, K. Climate change, adaptation planning and institutional integration: A literature review and framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, J.; Cosens, B.; Soininen, N.; Gunderson, L. Designing Law to Enable Adaptive Governance of Modern Wicked Problems. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2020, 73, 1687. Available online: https://scholarship.law.vanderbilt.edu/faculty-publications/1189 (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Granberg, M.; Bosomworth, K.; Moloney, S.; Kristianssen, A.-C.; Funfgeld, H. Can regional-scale governance and planning support transformative adaptation? A study of two places. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, R.; Lynch, A.H. Adaptive Governance and Climate Change; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, R.; Steelman, T.; Coe-Juell, L.; Cromley, C.; Edwards, C.; Tucker, D. Adaptive Governance: Integrating Science, Policy, and Decision Making; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Milward, H.B.; Provan, K. Governing the hollow state. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2000, 10, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevir, M. Governance: A Very Short Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carmin, J.; Nadkarni, N.; Rhie, C. Progress and Challenges in Urban Climate Adaptation Planning: Results of a Global Survey; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, K.; Daly, M.; Scannell, C.; Leathes, B. What can climate services learn from theory and practice of co-production? Clim. Serv. 2018, 12, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail-Zadeh, A.; Cutter, S.; Takeuchi, K. Forging a paradigm shift in disaster science. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrels, A.; Le, T.-T.; Cortekar, J.; Hoa, E.; Stegmaier, P. How much unnoticed merit is there in climate services? Clim. Serv. 2012, 17, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, C.; Dessai, S. Climate services for society: Origins, institutional arrangements, and design elements for an evaluation framework. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilling, L.; Lemos, M. Creating usable science: Opportunities and constraints for climate knowledge use and their implications for science policy. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, A. Meeting the challenge of climate service in the 1980s. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1984, 65, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- WMO. Global Framework for Climate Services. 2022. Available online: https://gfcs.wmo.int/node/1276 (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Lucio, F.D.F.; Grasso, V. The global framework for climate services (GFCS). Clim. Serv. 2016, 2–3, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hewitt, C.; Mason, S.; Walland, D. Commentary: The global framework for climate services. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.; Street, R.B. The next generation of climate services. Clim. Serv. 2020, 20, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.; Forland, E.; Piniewski, M. Challenges for developing climate services—Poland and Norway. Clim. Serv. 2017, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buizer, J.; Jacobs, K.; Cash, D. Making short-term climate forecasts useful: Linking science and action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4597–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickards, L. Transformation is adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of Science and Technology Policy, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and Federal Emergency Management Agency. Opportunities for Expanding and Improving Climate Information and Services for the Public—A Report to the National Climate Task Force. 2021. Available online: https://downloads.globalchange.gov/reports/eo-14008-211-d-report.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Cortekar, J.; Bender, S.; Brune, M.; Groth, M. Why climate change adaptation in cities needs customized and flexible climate services. Clim. Serv. 2016, 4, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buontempo, C.; Hewitt, C.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Dessai, S. Climate service development, delivery and use in Europe at monthly to inter-annual timescales. Clim. Risk Management 2014, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNie, E. Delivering climate services: Organizational strategies and approaches for producing useful climate-science information. Weather. Clim. Soc. 2013, 5, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guston, D. Boundary organizations in environmental policy and science: An introduction. Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 2001, 26, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, C. Self and place constructs in climate change vulnerability assessments: Gaps and recommendations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, S.; Lach, D.; Ingram, H. Weather forecasts are for wimps: Why water resource managers do not use climate forecasts. Clim. Chang. 2005, 69, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, P. The Politics of Evidence-Based Decision Making; Palgrave Pivot: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meadow, A.; Ferguson, D.; Guido, Z.; Horangic AOwen, G.; Wall, T. Moving toward the deliberate coproduction of climate science knowledge. Weather. Clim. Soc. 2015, 7, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lather, P. Issues of validity in openly ideological research: Between a rock and a soft place. Interchange 1986, 17, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, C.; Pratt, J. Sustainability in the water sector: Enabling lasting change through leadership and cultural transformation. Nat. Cult. 2012, 7, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, M.; Jamieson, D. Climate change and the challenges to democracy. Univ. Miami Law Rev. 2018, 72, 369. [Google Scholar]
- Lioubimtseva, E. The role of inclusion in climate vulnerability assessment and equitable adaptation goals in small American municipalities. Discov. Sustain. 2022, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, W. All adaptations are local. Issues Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagwat, S.; Economou, A.; Thornton, T. The idea of climate change as a belief system: Why climate activism resembles a religious movement. GAIA 2016, 25, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkeley, H.; Kern, K. Local government and the governing of climate change in Germany and the UK. Urban Stud. 2006, 43, 2237–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.; Forsyth, T. Community-based adaptation to climate change. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2009, 51, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.B.; Alexander, M.; Dessai, S. Sectoral use of climate information in Europe: A synoptic overview. Clim. Serv. 2018, 9, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachmany, M.; Byrnes, R.; Surminski, S. Policy Brief: National Laws and Policies on Climate Change Adaptation: A Global Review; Grantham Research Institute on Climate Chane and the Environment: London, UK; London School of Economics and Political Science: London, UK; University of Leeds: Leeds, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Swart, R.; Celliers, L.; Collard, M.; Garcia Prats, A.; Huang-Lachmann, J.T.; Llario Sempere, F.; de Jong, F.; Manez Costa, M.; Martinez, G.; Pulido Velazquez, M.; et al. Reframing climate services to support municipal and regional planning. Clim. Serv. 2021, 22, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Ingram, H. Policy Design for Democracy; University Press of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Howlett, M.; Mukherjee, I. Policy Design and Non-Design: A Continuum of Formulation Modalities. In Routledge Handbook of Policy Design; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/soss_research/2760 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Institute for Sustainable Communities (ISC). Regional Collaboratives for Climate Change—A State of the Art. 2019. Available online: https://us.sustain.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Regional-Collaboratives-for-Climate-Change-FINAL-1-pdf (accessed on 15 June 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).