Cactus Cladode Juice as Bioflocculant in the Flocculation-Thickening Process for Phosphate Washing Plant: A Comparative Study with Anionic Polyacrylamide
Abstract
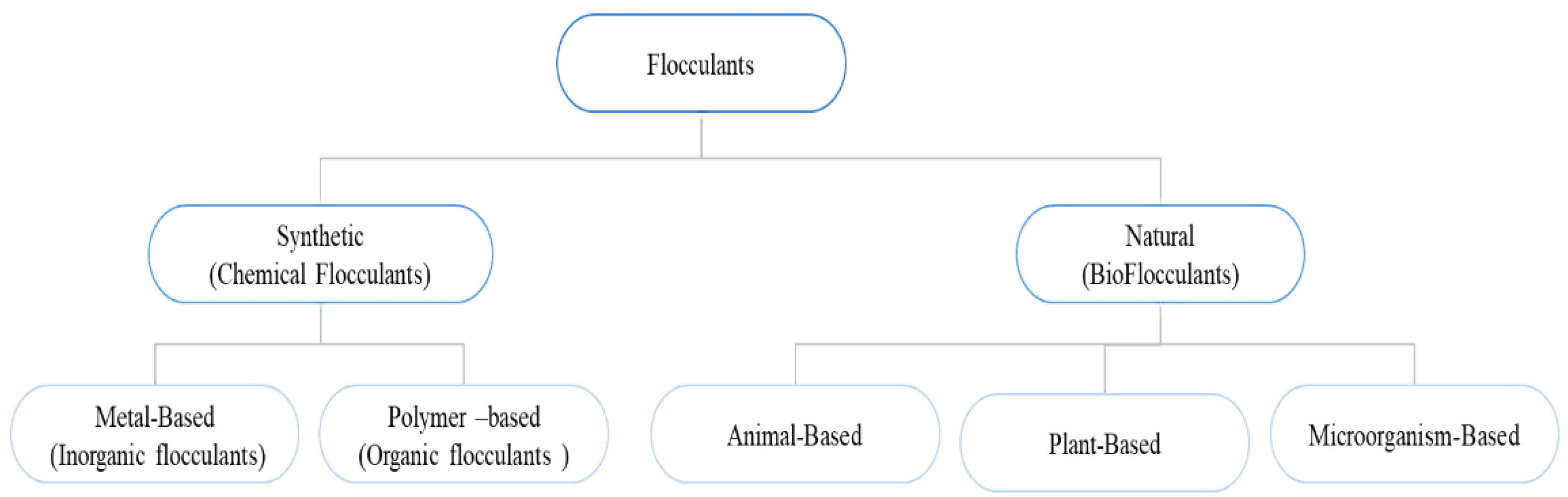
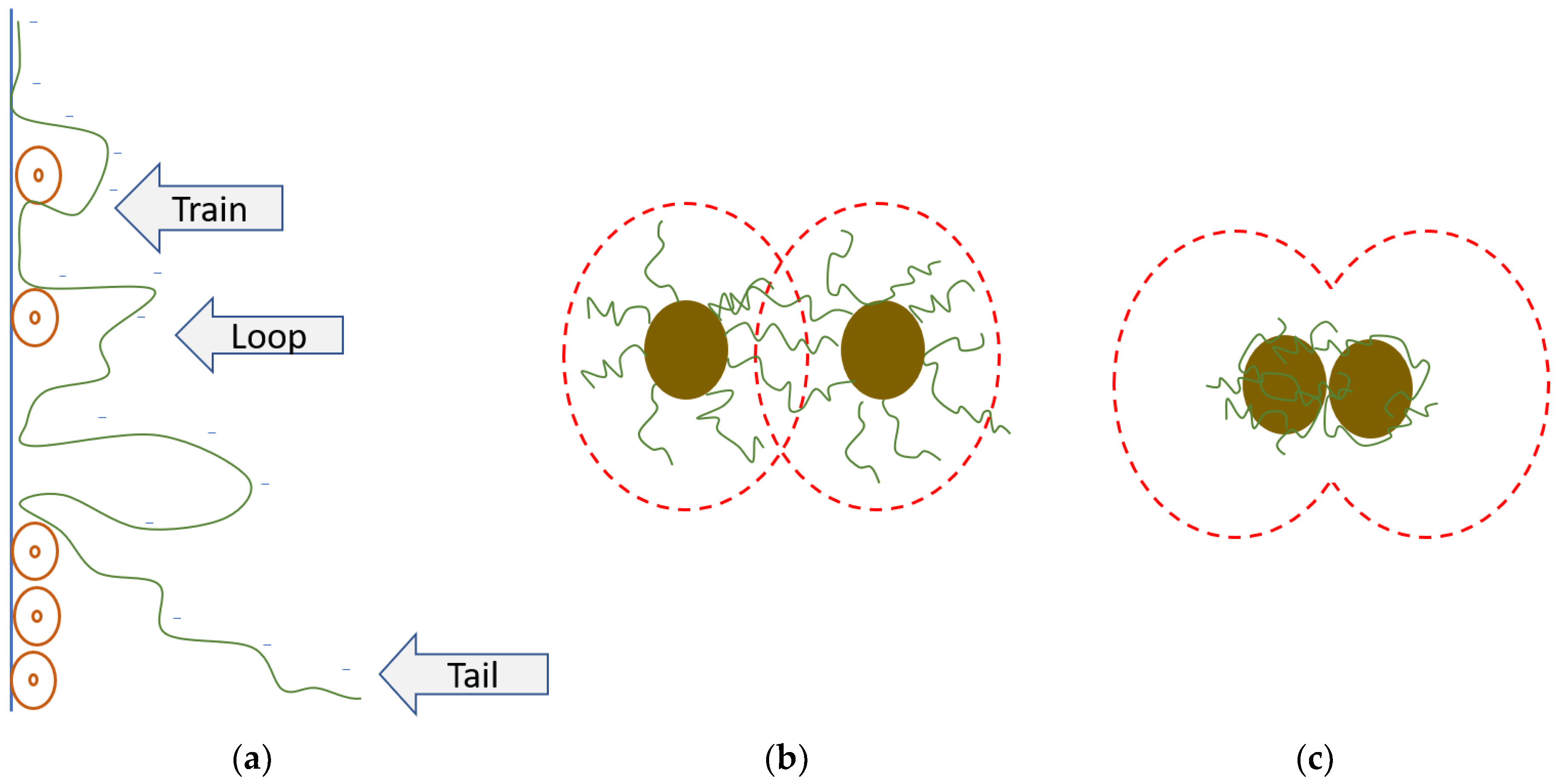
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
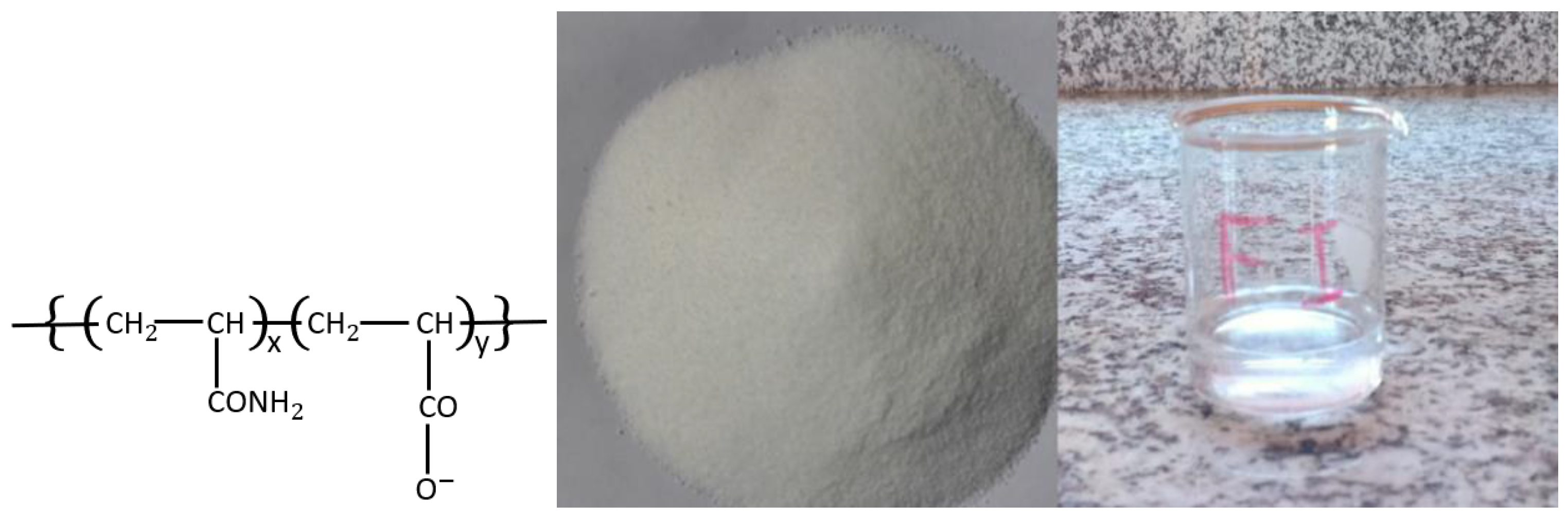
2.1. Industrial Flocculant
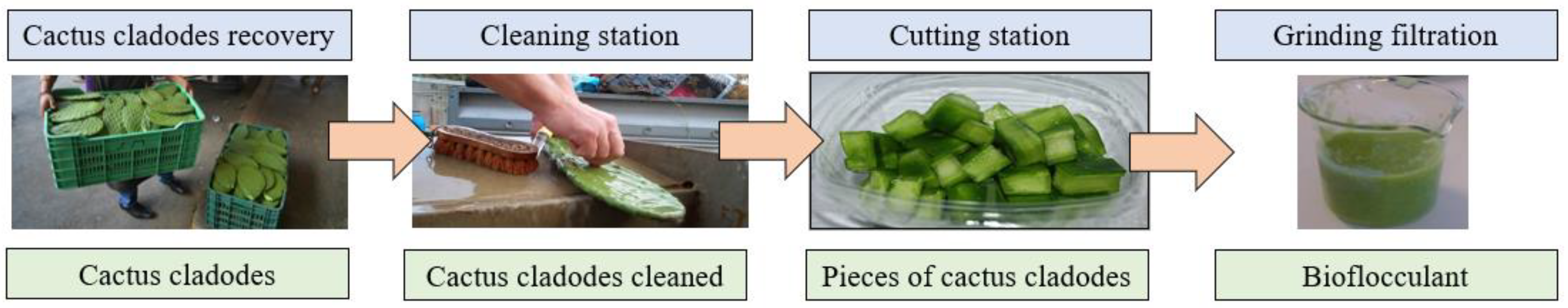
2.2. Bioflocculant Preparation
2.3. Preparation of the Phosphate Sample
2.4. Sedimentation Test
3. Results and Discussion
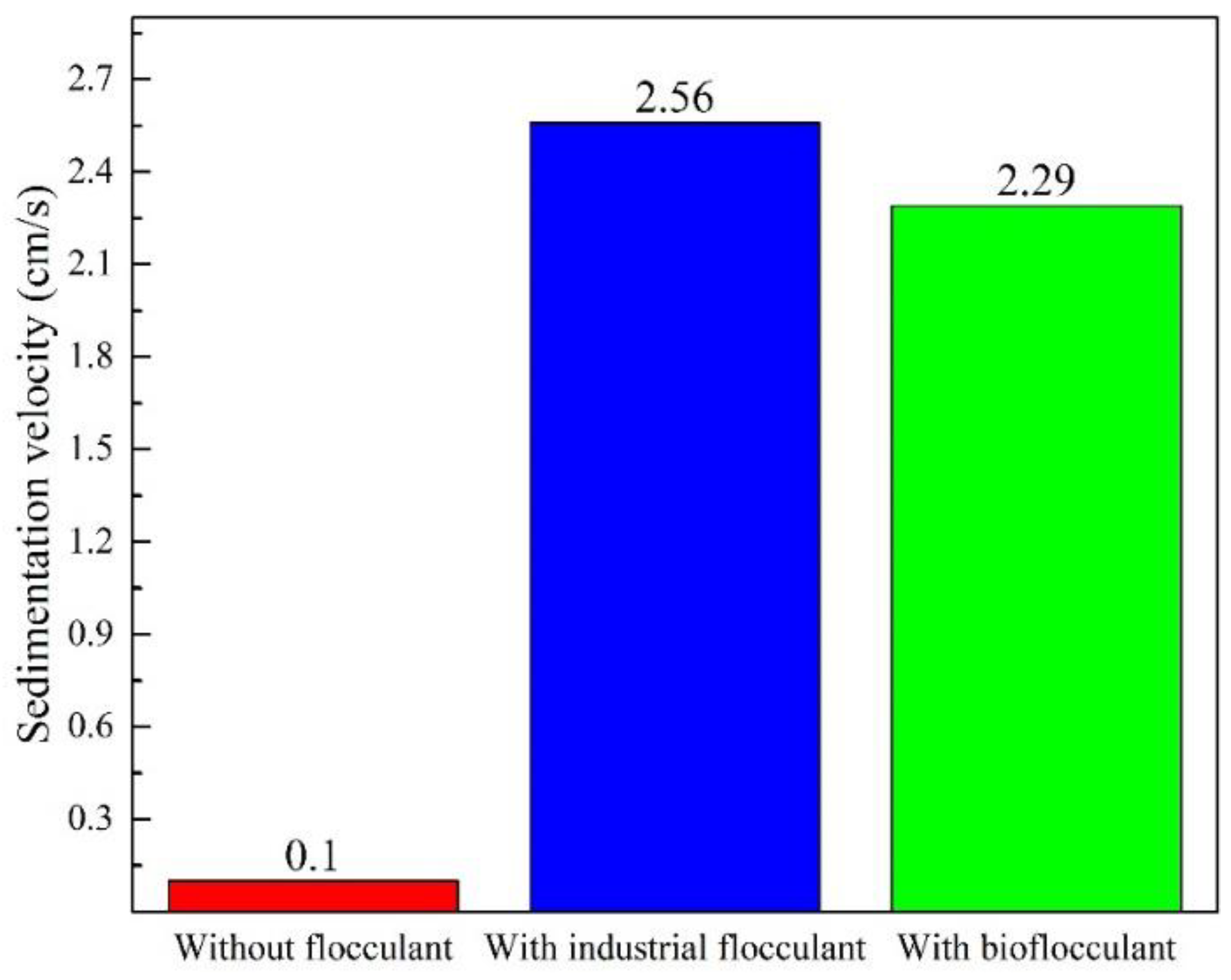
3.1. Bioflocculant Activity
3.2. Optimal Specific Consumption of the Biofloculant
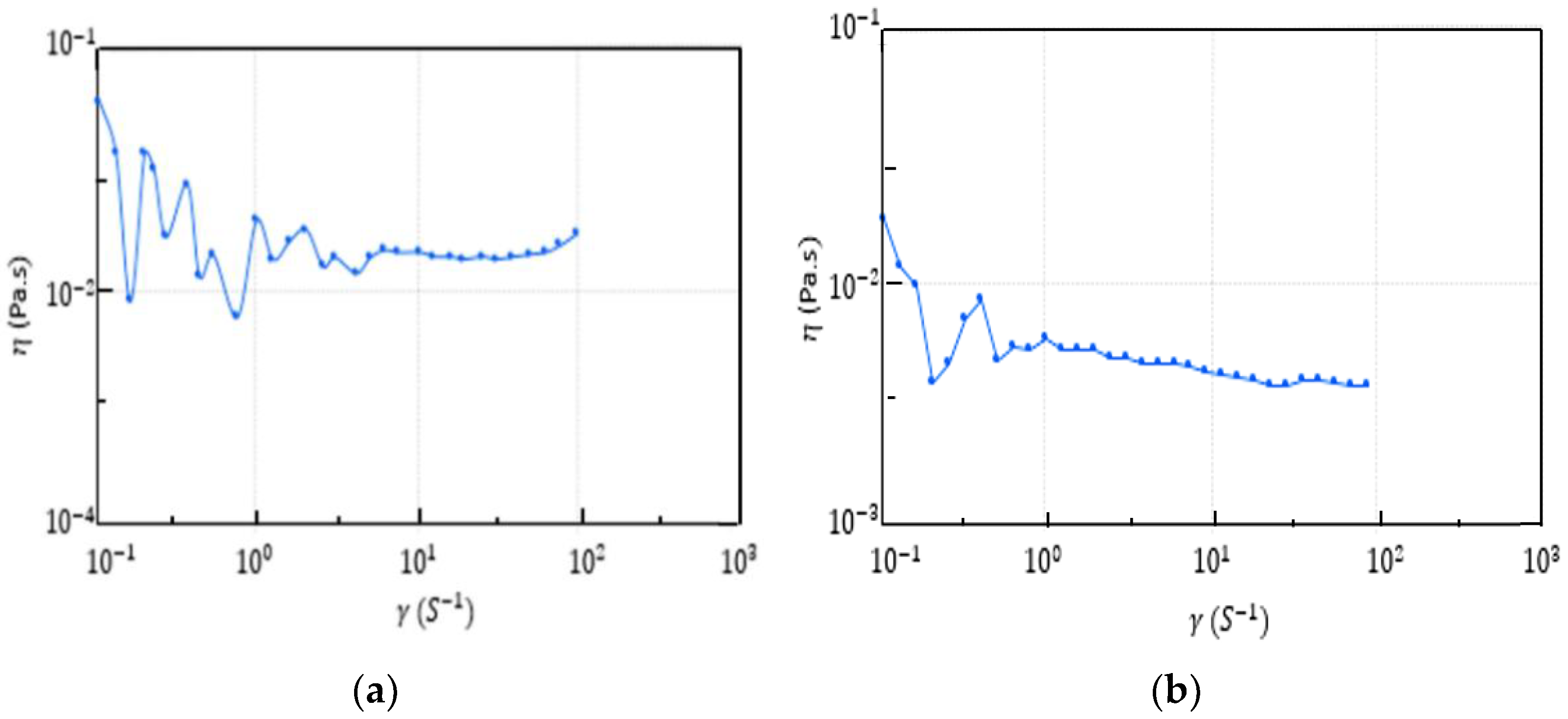
3.3. Bioflocculant Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lifi, M.; Lorenzo, J.; Aguilar, F.; Muñoz-Rujas, N.; Montero, E.A.; Chhiti, Y.; Alaoui, F.E.M. Excess Enthalpy, Density, Speed of Sound and Refractive Index of Binary Mixtures {2-(2-Ethoxyethoxy)Ethanol + 1-Hexene, or Cyclohexane, or Methylcyclohexane at (298.15 and 313.15) K: Application of the PPR-78 Cubic Equation of State, NRTL and UNIQUAC Models. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2021, 153, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abala, I.; M’hamdi Alaoui, F.E.; Chhiti, Y.; Sahib Eddine, A.; Munoz Rujas, N.; Aguilar, F. Experimental Density and PC-SAFT Modeling of Biofuel Mixtures (DBE + 1-Heptanol) at Temperatures from (298.15 to 393.15) K and at Pressures up to 140 MPa. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmen, Y.; Chhiti, Y.; M’Hamdi Alaoui, F.E.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Duquesne, S.; Bensitel, M. Thermal Performance of PEG-MWCNTs Composites as Shape-Stabilised Phase Change Materials for Thermal Energy Storage. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2021, 29, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmen, Y.; Chhiti, Y.; M’Hamdi Alaoui, F.E.; Bentiss, F.; El Khouakhi, M.; Jama, C.; Duquesne, S.; Bensitel, M.; Deshayes, L. Thermal and Energetic Behaviour of Solid-Solid-Liquid Phase Change Materials Storage Unit: Experimental and Numerical Comparative Study of the Top, Bottom and Horizontal Configurations. J. Energy Storage 2021, 33, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svarovsky, L. Introduction to Solid-Liquid Separation. In Solid–Liquid Separation, 3rd ed.; Svarovsky, L., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-0-408-03765-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mineral Processing Handbook PDF (Free|224 Pages). Available online: http://www.pdfdrive.com/mineral-processing-handbook-e176115990.html (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- Ding, C.; Xie, A.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Tang, N.; Wang, X. Treatment of Water-Based Ink Wastewater by a Novel Magnetic Flocculant of Boron-Containing Polysilicic Acid Ferric and Zinc Sulfate. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglio, Y.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Prado, H.J.; Matulewicz, M.C. Paramylon and Synthesis of Its Ionic Derivatives: Applications as Pharmaceutical Tablet Disintegrants and as Colloid Flocculants. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 484, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehizadeh, H.; Yan, N.; Farnood, R. Recent Advances in Polysaccharide Bio-Based Flocculants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapper, D.R.; Krishnan, S.S.; Quittkat, S. Aluminium, Neurofibrillary Degeneration and Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 1976, 99, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, H.; Natsuda, O.; Hirose, J.; Hayashi, S.; Takasaki, Y. Characteristics of a Biopolymer Flocculant Produced by Bacillus Sp. PY-90. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1995, 79, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehizadeh, H.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Removal of Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Polysaccharide Produced from Bacillus Firmus. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4231–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. Production of a Novel Polygalacturonic Acid Bioflocculant REA-11 by Corynebacterium Glutamicum. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 94, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Ike, M.; Kim, S.M.; Fujita, M. Production of a Novel Bioflocculant by Fed-Batch Culture of Citrobacter sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, I.-L.; Van, Y.-T. The Production of Poly-(γ-Glutamic Acid) from Microorganisms and Its Various Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 79, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Ye, H.-F. Characterization and Flocculating Properties of an Extracellular Biopolymer Produced from a Bacillus Subtilis DYU1 Isolate. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.-X.; Wang, S.-G.; Sun, X.-F.; Liu, X.-W.; Yue, Q.-Y.; Gao, B.-Y. Bioflocculant Production by Culture of Serratia Ficaria and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4668–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Li, C.-H.; Wen, J.-P.; Du, L.-X. A Novel Bioflocculant Produced by Enterobacter Aerogenes and Its Use in Defecating the Trona Suspension. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ike, M.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Hirao, T. Bioflocculation Production from Lower-Molecular Fatty Acids as a Novel Strategy for Utilization of Sludge Digestion Liquor. Water Sci Technol 2001, 44, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.T.F.; Ambrosio, E.; de Almeida, C.A.; de Souza Freitas, T.K.F.; Santos, L.B.; de Cinque Almeida, V.; Garcia, J.C. The Use of a Natural Coagulant (Opuntia Ficus-Indica) in the Removal for Organic Materials of Textile Effluents. Env. Monit Assess 2014, 186, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatay, F.; Mhenni, F. Use of the Cactus Cladodes Mucilage (Opuntia Ficus Indica) As an Eco-Friendly Flocculants: Process Development and Optimization Using Stastical Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Development of Production Sectors, Ministry of Agriculture and Maritime Fisheries, Kingdom of Morocco, National Catalog. Edition 2014. Available online: https://www.agriculture.gov.ma/sites/default/files/produits_terroir_edition2014_fr.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Othmani, B.; Rasteiro, M.G.; Khadhraoui, M. Toward Green Technology: A Review on Some Efficient Model Plant-Based Coagulants/Flocculants for Freshwater and Wastewater Remediation. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, C.; Sepúlveda, E.; Matsuhiro, B. Opuntia Spp Mucilage’s: A Functional Component with Industrial Perspectives. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, M.; Zarai, Z.; Khadhraoui, M.; Jdidi, N.; Leduc, R.; Ben Rebah, F. Cactus Juice as Bioflocculant in the Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Comparative Study with Polyacrylamide. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Properties | Industrial Flocculant |
|---|---|
| Polymer type | Polyacrylamide |
| Approximate bulk density | 0.80 |
| Stability of Dl water solution (days) | 1 |
| Color | White |
| Ionic character | Anionic |
| Molecular | Very high |
| Soluble in water | Yes |
| Properties | Bioflocculant |
|---|---|
| Polymer type | Polygalacturonic acid |
| Approximate bulk density | 1 |
| Stability of Dl water solution (days) | 2 |
| Color | Green |
| Ionic character | Anionic |
| Molecular | Very high |
| Soluble in water | Yes |
| Vibration Type | Molecules/Components | Wave Number (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl and Amines (O–H and N–H stretching) | Carbohydrates Glycoproteins | 3400 |
| Alkyl (C–H stretching) | Carbohydrates Glycoproteins | 2931 |
| Asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of ionized carboxylic acid groups (COO−), | Galacturonic Acid | 1623 and 1425 |
| Carboxyl (C=O stretching of non-ionized COOH groups) | Galacturonic Acid | 1730 |
| Methoxyl (C–O stretching alcohol/ether groups) | Carbohydrates | 1050–1150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ennawaoui, A.; Lalam, K.; Harmen, Y.; El Morabit, A.; Chhiti, Y.; Chebak, A.; Benssitel, M. Cactus Cladode Juice as Bioflocculant in the Flocculation-Thickening Process for Phosphate Washing Plant: A Comparative Study with Anionic Polyacrylamide. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138054
Ennawaoui A, Lalam K, Harmen Y, El Morabit A, Chhiti Y, Chebak A, Benssitel M. Cactus Cladode Juice as Bioflocculant in the Flocculation-Thickening Process for Phosphate Washing Plant: A Comparative Study with Anionic Polyacrylamide. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138054
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnnawaoui, Amine, Khadija Lalam, Yasser Harmen, Abdelaziz El Morabit, Younes Chhiti, Ahmed Chebak, and Mohammed Benssitel. 2022. "Cactus Cladode Juice as Bioflocculant in the Flocculation-Thickening Process for Phosphate Washing Plant: A Comparative Study with Anionic Polyacrylamide" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138054
APA StyleEnnawaoui, A., Lalam, K., Harmen, Y., El Morabit, A., Chhiti, Y., Chebak, A., & Benssitel, M. (2022). Cactus Cladode Juice as Bioflocculant in the Flocculation-Thickening Process for Phosphate Washing Plant: A Comparative Study with Anionic Polyacrylamide. Sustainability, 14(13), 8054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138054






