Sustainable Land Use and Livelihood Dynamics in Henan County on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau—A Transdisciplinary Systems Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
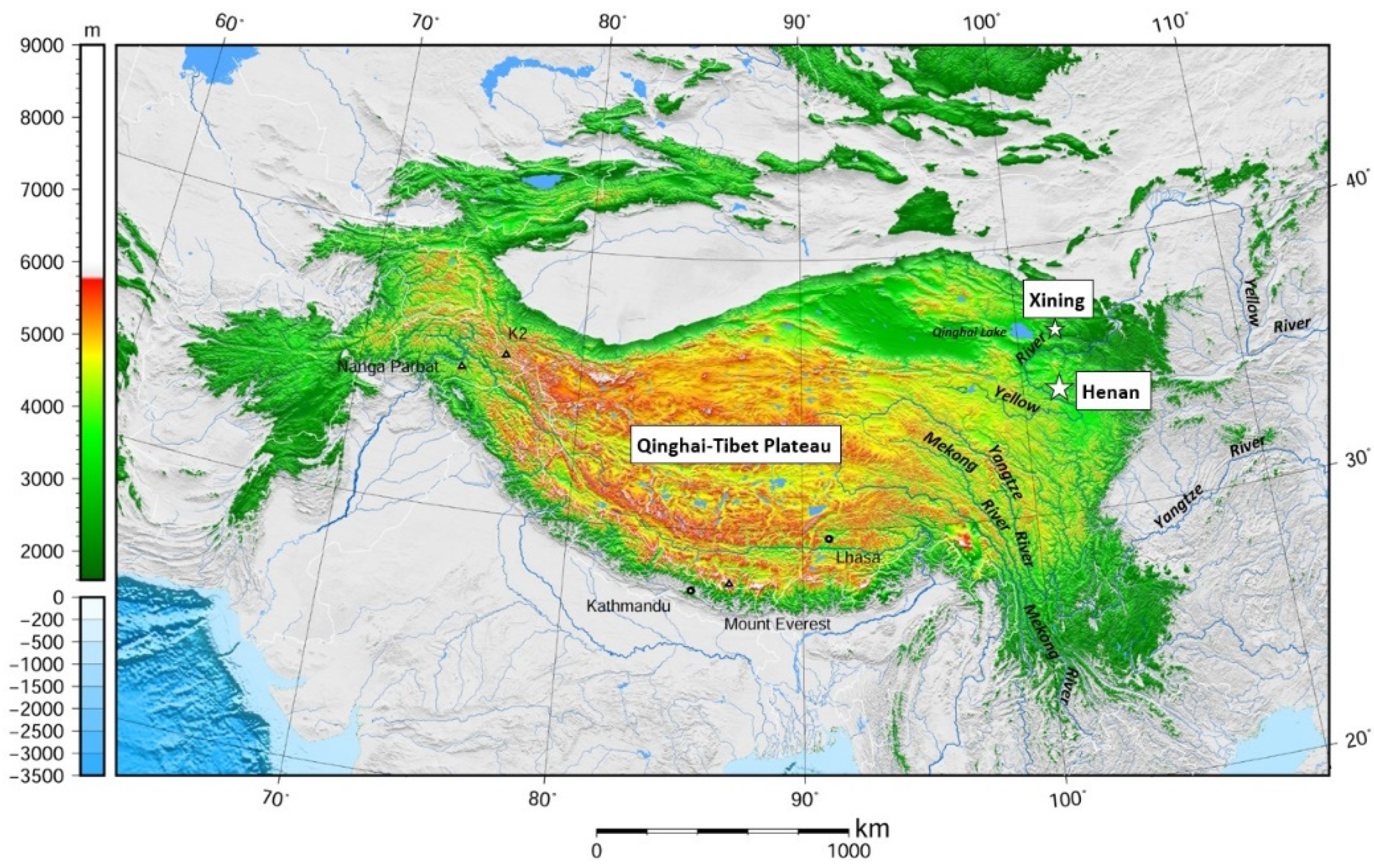
1.1. The Contextual Background
1.2. The History
1.3. Traditional Farming
1.4. Land Use Policy Changes
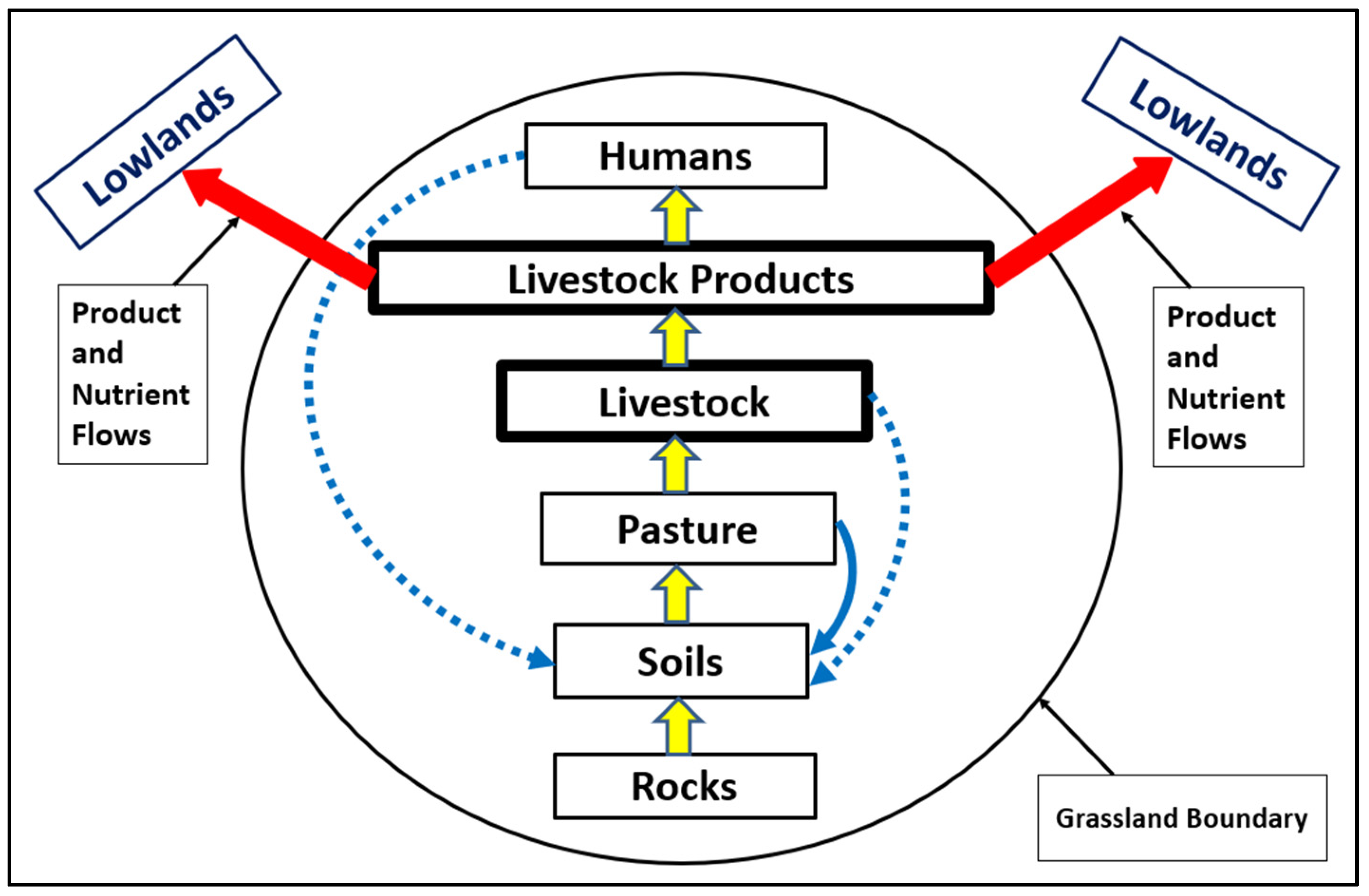
1.5. Environmental Deterioration
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results–Changes in Henan County
3.1. The Changing Landscape
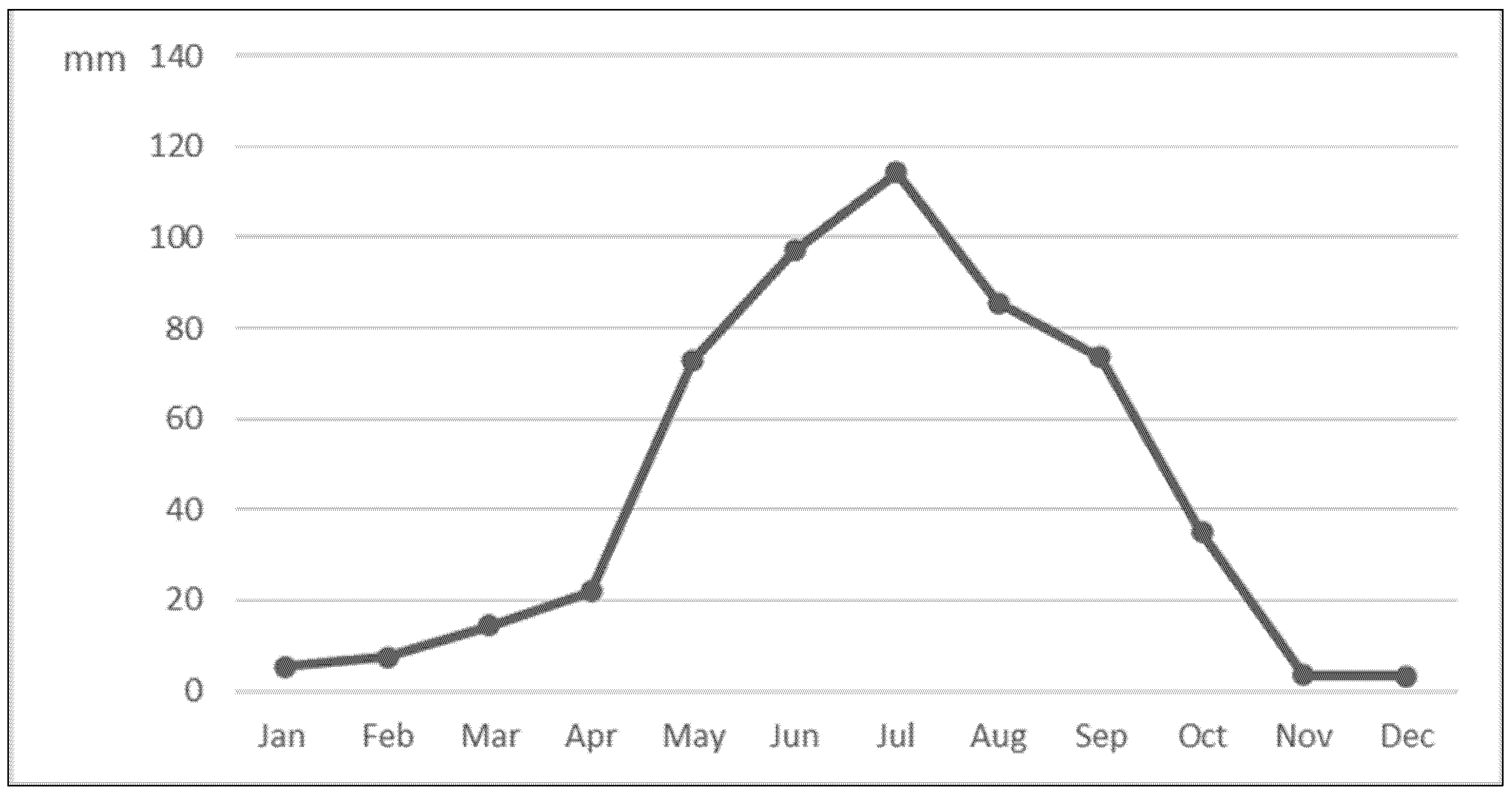
3.1.1. Physical Climate
3.1.2. Demographics
3.1.3. Livestock Numbers
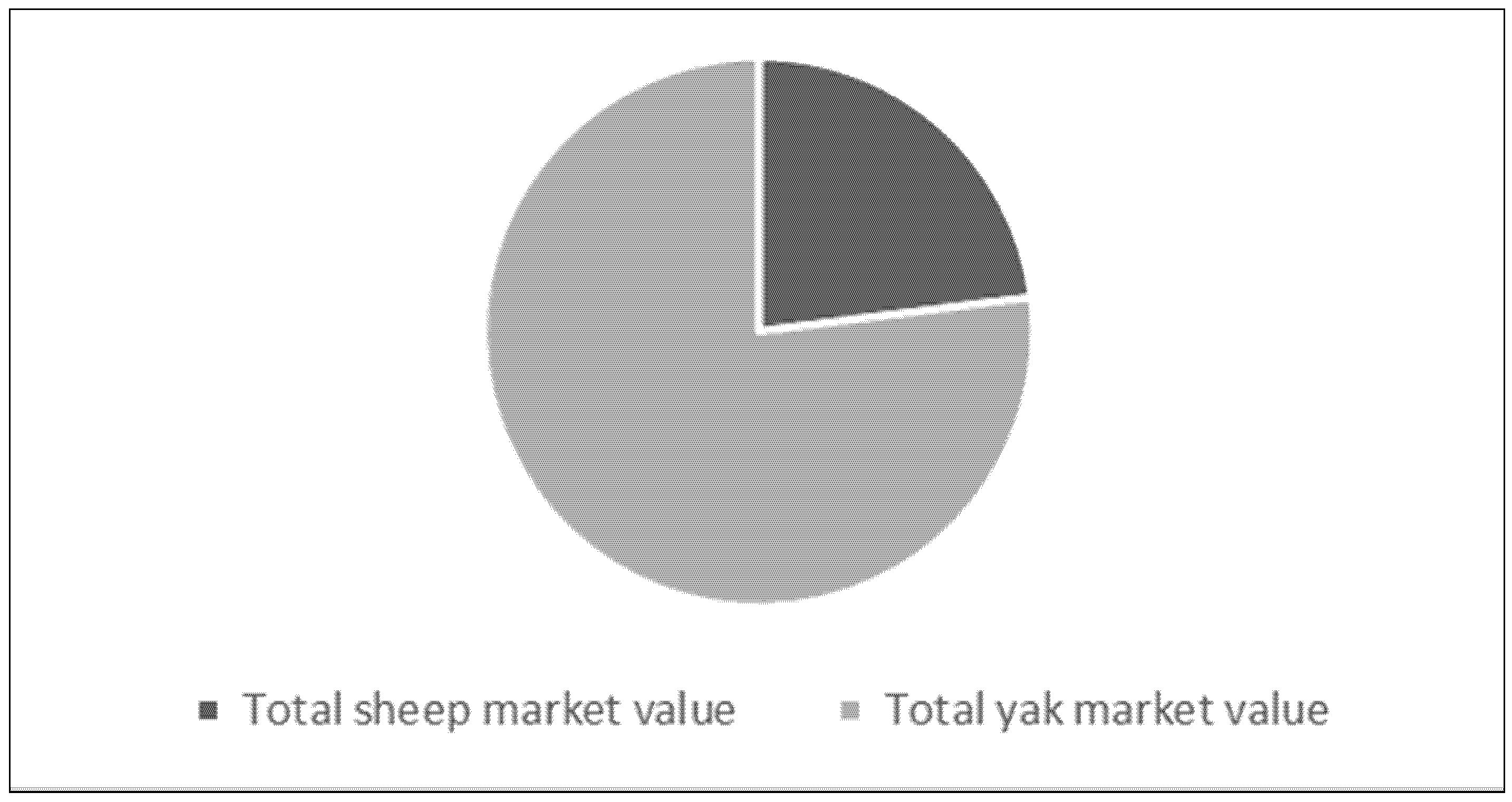
3.1.4. Livestock Productivity and Values
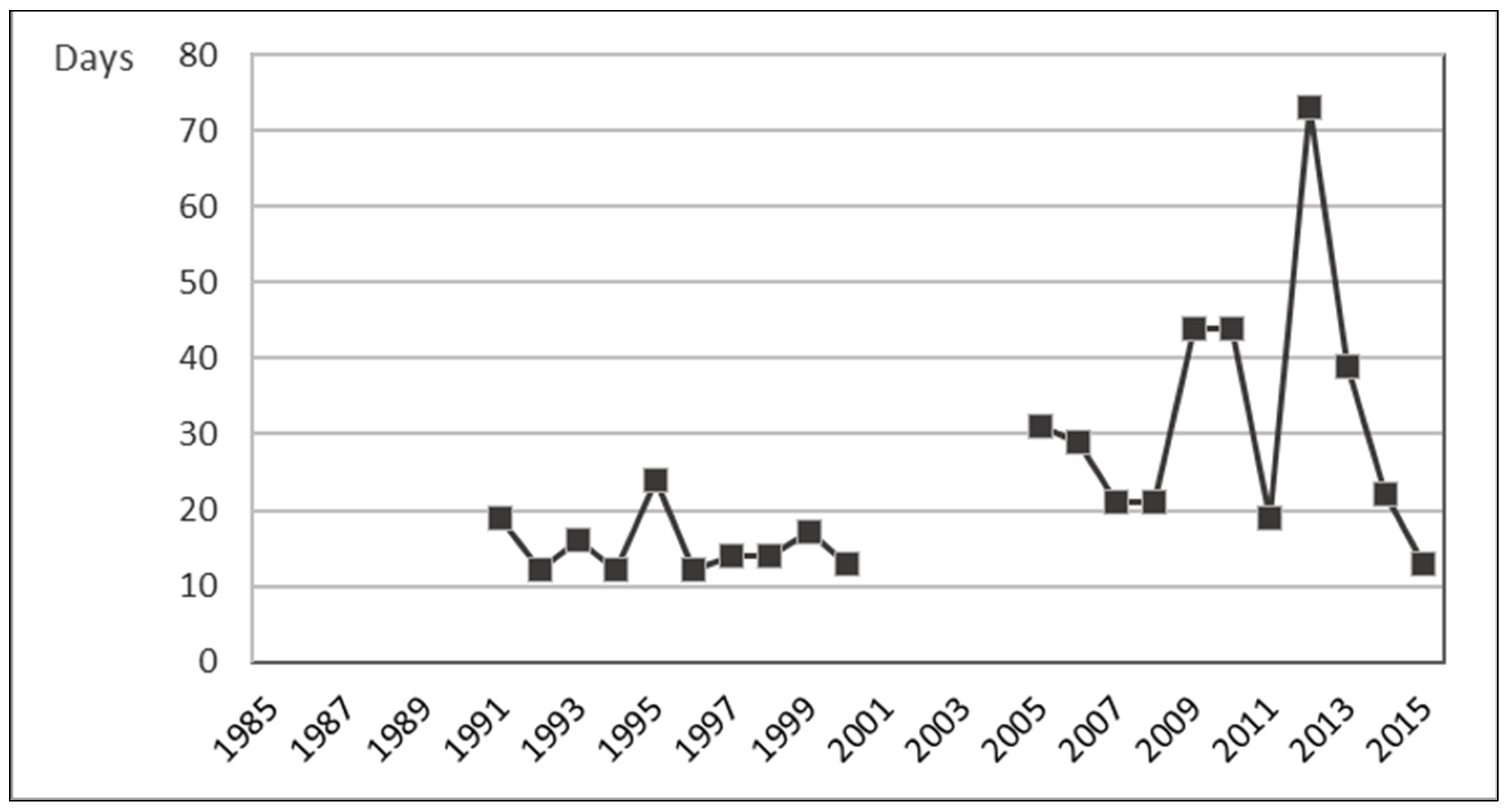
3.1.5. Animal Pests
3.1.6. Grassland Sustainability
3.2. Changing Livelihoods
3.2.1. On-Farm Infrastructure and Assets
3.2.2. The Towns
3.2.3. Transport and Communications
3.2.4. Diet
3.2.5. Market Demand for Henan’s Pastoral Products
3.2.6. Life on Farm
4. Discussion—A Transdisciplinary Systems Perspective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Piquer-Rodríguez, M.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide research trends on sustainable land use in agriculture. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Xing, Z. Challenges and Solutions for Sustainable Land Use in Ruoergai-the Highest Altitude Peatland in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Energy Procedia 2011, 5, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yeh, E.T.; Holden, N.M.; Yang, Y.; Du, G. The effects of enclosures and land-use contracts on rangeland degradation on the Qinghai–Tibetan plateau. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 97, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Trouble in Tibet. Nature 2016, 529, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, S.; Brown, C.; Longworth, J. Grassland degradation and livelihoods in China’s western pastoral region: A framework for understanding and refining China’s recent policy responses. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2010, 2, 298–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, D. Climate adaptation, institutional change, and sustainable livelihoods of herder communities in northern Tibet. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adaptation strategies to pasture degradation: Gap between government and local nomads in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.T. Green governmentality and pastoralism in western China: ‘Converting pastures to grasslands’. Nomadic Peoples 2005, 9, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.; Li, X.; Chen, G. Landscape and Environment Science and Management in the Sanjiangyuan Region; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ptackova, J. Sedentarisation of Tibetan nomads in China: Implementation of the nomadic settlement project in the Tibetan Amdo area; Qinghai and Sichuan Provinces. Pastor. Res. Policy Pract. 2011, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.T. Tibetan Range Wars: Spatial Politics and Authority on the Grasslands of Amdo. Dev. Chang. 2003, 34, 499–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongbuzeren; Zhuang, M.; Li, W. Market-based grazing land transfers and customary institutions in the management of rangelands: Two case studies on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Bruemmer, B.; Huntsinger, L. Technical efficiency and the impact of grassland use right leasing on livestock grazing on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, G.; Adamowski, J.F.; Holden, N.M.; Deo, R.C.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, G.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q. Suitable exclosure duration for the restoration of degraded alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Gongbuzeren; Zhang, J.; Li, W. Community-based seasonal movement grazing maintains lower greenhouse gas emission intensity on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. Land Use Policy 2019, 85, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Barriers and requirements to climate change adaptation of mountainous rural communities in developing countries: The case of the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucock, X.; Woodford, K. Pastoral farming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Agric. Manag. 2018, 6, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.J. Tough times for Tibetan nomads in western China: Snowstorms, settling down, fences and the demise of traditional nomadic pastoralism. Nomadic Peoples 2000, 4, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, D. Boundries and areas of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Res. 2002, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.J. Nomads of the Tibetan Plateau rangelands in western China. Part Two. Pastoral production practices. Rangel. Arch. 1999, 21, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- China Insitute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research. Introduction on Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve. Available online: http://www.iwhr.com/zgskyww/ztbd/qhdy/bjcl/webinfo/2012/08/1342498799296495.htm (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Kmusser. Map of Ü-Tsang Amdo and Kham. 2011. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tibet_provinces.png (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Manderscheid, A. Decline and re-emergence of nomadism: Tibetan pastoralists revive a nomadic way of life and production. GeoJournal 2001, 53, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croquant. Location of Henan County (pink) and Huangnan Prefecture (yellow) within Qinghai Province of China. 2007. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henan_Mongol_Autonomous_County#/media/File:Location_of_Henan_within_Qinghai_(China).png (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Cairang, Z. Mongolian Records on South of Yellow River; Gansu Ethnic Publishing House: Gansu, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dhondup, Y. Writers at the Crossroads: The Mongolian-Tibetan Authors Tsering Dondup and Jangbu. Inner Asia 2002, 4, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenböck, U. Marginalisation at China’s Multi-Ethnic Frontier: The Mongols of Henan Mongolian Autonomous County in Qinghai Province. J. Curr. Chin. Aff. 2016, 45, 149–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Beall, C.M.; Cincotto, R.P. Traditional nomadic pastoralism and ecological conservation on Tibet’s Northern Plateau. Natl. Geogr. Res. 1990, 6, 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.J.; Schaller, G.B. Rangelands of the Chang Tang Wildlife Reserve in Tibet. Rangelands 1996, 18, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Z.; Gibb, M.; Long, R. Effect of snow disasters on livestock farming in some rangeland regions of China and mitigation strategies—A review. Rangel. J. 2012, 34, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Childs, G.; Wangdui, P. “Going for income” in village Tibet. Asian Surv. 2008, 48, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tashi, G.; Foggin, M. Resettlement as development and progress? Eight years on: Review of emerging social and development impacts of an ‘ecological resettlement’ project in Tibet Autonomous Region, China. Nomadic Peoples 2012, 16, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, T. Amdo Tibetans in Transition: Society and Culture in the Post-Mao Era: PIATS 2000: Tibetan Studies: Proceedings of the Ninth Seminar of the International Association for Tibetan Studies, Leiden 2000; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid. Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Brierley, G. Wetland Types and Evolution and Rehabilitation in the Sanjiangyuan Region; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Xining, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Angelo, J. The sedentarization of Tibetan nomads: Conservation or coercion? In Ecological Economics from the Ground Up; Healy, H., Martínez-Alier, J., Temper, L., Walter, M., Gerber, J.-F., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 309–333. [Google Scholar]
- Su, D.X.; Meng, Y.D.; Wu, B.G. Agricultural Industry Standards of P.R.China—Calculation of Proper Carrying Capacity of Rangelands (NY/T 635–2002); Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Building Theories from Case Study Research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Better Stories and Better Constructs: The Case for Rigor and Comparative Logic. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1991, 16, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M.; Graebner, M.E. Theory building from cases: Opportunities and challenges. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M.; Graebner, M.E.; Sonenshein, S. Grand challenges and inductive methods: Rigor without rigor mortis. Acad. Manag. J. 2016, 59, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruegger, R.A.; Jigjsuren, O.; Fernández-Giménez, M.E. Herder Observations of Rangeland Change in Mongolia: Indicators, Causes, and Application to Community-Based Management. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 67, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherren, K.; Darnhofer, I. Precondition for Integration: In Support of Stand-alone Social Science in Rangeland and Silvopastoral Research. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 71, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmer, H.; Fernández-Giménez, M.E. Voices of Change: Narratives from Ranching Women of the Southwestern United States. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 69, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics. Henan County Yearbook 2006; Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics: Henan Mongolian Autonomous County, China, 2007.
- Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics. Henan County Yearbook 2014; Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics: Henan Mongolian Autonomous County, China, 2015.
- Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics. Henan County Yearbook 2015; Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics: Henan Mongolian Autonomous County, China, 2016.
- Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics. Henan County Yearbook 2018; Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Bureau of Statistics: Henan Mongolian Autonomous County, China, 2019.
- Henan Mongolian Autonomous County People’s Government. South to the Heaven River; Qinghai People’s Publishing House: Qinghai, China, 2009.
- Henan Mongolian Autonomous County Yearbook Editorial Committee. Henan County Yearbooks 1991–2000; Gansu People’s Publishing House Lanzhou: Gansu, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Henan Mongonlian Autonomous County Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Planning Committee. Henan Mongonlian Autonomous County Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Planning; Henan Mongonlian Autonomous County Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Planning Committee: Henan Mongol Autonomous County, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 15–3 Length of Transport Routes at Year-end by Region (End of 2000). In China Statistical Yearbook 2001; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 15–29 Number of Private-owned Vehicles. In China Statistical Yearbook 2001; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 4–3 Total Population and Sex Ratio by Region. In China Statistical Yearbook 2001; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 16–42 Main Communication Capacity of Telecommunications (Year-end). In China Statistical Yearbook 2005; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2–6 Population at Year-end by Region. In China Statistical Yearbook 2018; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 16–4 Length of Transport Routes at Year-end by Region (2017). In China Statistical Yearbook 2018; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 16–34 Main Communication Capacity of Telecommunications at Year-end. In China Statistical Yearbook 2018; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 16–21 Possession of Private Vehicles. In China Statistical Yearbook 2018; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China. Ethnic and population profile of Tibet Autonomous Region. Available online: http://www.scio.gov.cn/ztk/dtzt/04/08/5/Document/392015/392015.htm (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- FAOSTAT. Annual Population, China; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh, T.; Zhu, W.X. The one child family policy: The good, the bad, and the ugly. BMJ 1997, 314, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenderfer, M. Peopling the Tibetan Plateau: Insights from Archaeology. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2011, 12, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steelman, T.; Nichols, E.G.; James, A.; Bradford, L.; Ebersöhn, L.; Scherman, V.; Omidire, F.; Bunn, D.N.; Twine, W.; McHale, M.R. Practicing the science of sustainability: The challenges of transdisciplinarity in a developing world context. Sustain. Sci. 2015, 10, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucock, X.; Woodford, K.; Li, X. Sustainable Land Use and Livelihood Dynamics in Henan County on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau—A Transdisciplinary Systems Perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7785. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137785
Lucock X, Woodford K, Li X. Sustainable Land Use and Livelihood Dynamics in Henan County on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau—A Transdisciplinary Systems Perspective. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7785. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137785
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucock, Xiaomeng, Keith Woodford, and Xilai Li. 2022. "Sustainable Land Use and Livelihood Dynamics in Henan County on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau—A Transdisciplinary Systems Perspective" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7785. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137785
APA StyleLucock, X., Woodford, K., & Li, X. (2022). Sustainable Land Use and Livelihood Dynamics in Henan County on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau—A Transdisciplinary Systems Perspective. Sustainability, 14(13), 7785. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137785





