Abstract
Understanding demographic structures, production constraints, and trait preferences is essential for setting up crop breeding goals and enhancing adoption strategies for new varieties. The objective of this study was to document the sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) production constraints and preferred sorghum traits to guide breeding in Sierra Leone. A participatory rural appraisal was used to collect data from 210 farmers across seven districts in Sierra Leone in 2019. Results showed that all sorghum varieties in cultivation are landraces. Poor access to fertilizer (91%), lack of suitable varieties (85%), poor agronomic knowledge (79%), low yielding varieties (78%), storage pests (75%), field pests (67%), low soil fertility (52%), lack of market (49%), sorghum disease (43%), drought (16%), and heavy rainfall (12%) are key production constraints limiting sorghum production. Farmers expressed interest in adopting new varieties with high yield (99%), disease (84%) and pest (81%) resistance, drought tolerance (50%), white grain (59%), and short height (53%). The prioritized traits will form the basis for farmer-oriented sorghum breeding.
1. Introduction
Globally, Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench, 2n = 2x = 20) is the fifth most produced grain [1,2]. The crop is widely grown for food, beverage, feed, and bioenergy [3,4]. The grains are processed into several industrial products such as baked food, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages, starch, and syrup [3]. The stalk is used to make fibers, papers, fencing, and construction materials. Sorghum is gluten-free and ideal for people with celiac disease [5]. In 2018 alone, 59 million tons of sorghum were produced from 42 million hectares of land [2]. The top three sorghum producers in that year were the USA, followed by Nigeria and Sudan with 9.3, 6.9, and 4.95 million tons, respectively. Other countries accounting for the global sorghum production in that year include Ethiopia (4.93 million tons), India (4.8 million tons), Mexico (4.5 million tons), China (2.9 million tons), and Argentina (1.6 million tons) [2]. The ranks have not changed much over the years. Meanwhile, Sierra Leone in 2018 contributed only 50,000 tons of sorghum from 52,416 ha of land with an average yield of 954 kg/ha, which was below the world average of 1.4 ton/ha [2].
The most important cereal crops grown in Sierra Leone from 2010 to 2019 include rice, sorghum, millet, and maize in terms of areas and quantity harvested [2]. The areas allocated to sorghum in Sierra Leone have been increasing in the same period more than maize, for instance. This indicates that sorghum is an integral part of the farming system and perhaps diet among the farming community in Sierra Leone. However, the local on-farm sorghum yields of 926 kg/ha remain far below the global average of two tons in the same period. Paramount among the yield-reducing factors is the predominant cultivation of inherently low-yielding varieties, poor soil fertility, drought, Striga, pests, and diseases [6,7]. There are also weeds, poor agronomic practices, limited mechanization, and limited access to improved varieties [7]. The relative importance of these factors in causing significant sorghum yield reduction varies even within the same region [8].
Sorghum research in sub-Saharan Africa has successfully diffused many new cultivars onto farmers’ fields [7]. However, adopting improved varieties by farmers is slow [9,10], especially if farmers were not consulted for specific traits they preferred [8]. Farmers need assurance on the performance of improved sorghum varieties before they can take them [10]. For instance, West African states have adopted a single variety catalog where varieties bred in any member state can be used by all members farmers; however, the sorghum released in other West African nations have not successfully been taken up by farmers in Sierra Leone; hence they continue to grow landraces. One of the reasons for the lack of adoption of sorghum from other member countries is the lack of Sierra Leone farmers’ preferred traits and poor seed delivery mechanism. Introducing farmers’ preferred traits in new cultivars is a start to improve acceptability and adoption by farmers. However, assessing the socioeconomic status of farmers’, variety preferences, and agro-ecological factors affecting crop productivity through participatory rural appraisal (PRA) is paramount in designing breeding solutions [8].
Participatory rural appraisal (PRA) approaches have been helpful in the priority setting of technologies for transforming agriculture production from communal to commercial enterprise in sub-Saharan Africa [11]. Plant breeders use PRAs to gather information such as varietal and trait preferences to breed consumer-accepted cultivars. Farmers provide helpful information on plant types, desired traits, and insight into trade-offs they are willing to make among traits in cultivars [8]. Adoption rates of improved varieties are low because farmers’ views are often excluded in the decision when defining breeding priorities [12].
The “objective of this study was to assess the sorghum farming system, sorghum production constraints, and farmers’ preferences for sorghum variety in Sierra Leone to guide breeding.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Sites
The survey was undertaken in four administrative provinces of Sierra Leone, namely Eastern, Northern, North-Western, and Southern Provinces (Figure 1). The Western province that hosts the capital, Freetown, was left out. Each region is subdivided into districts, and the districts are further divided into Chiefdoms.
Figure 1.
Map of Sierra Leone showing districts where farmers were sampled for interviews.
Agriculture is the largest sector in the Sierra Leone economy, providing jobs for over 65% of the labor force and contributing 35–47% of the GDP [13] and about 10% of exports. Crop production is carried upon the upland where slash and burn land clearing is commonly practiced. The majority (85%) of households own poultry livestock [13]. Other livestock includes goats, sheep, and ducks. Very few farmers own cattle. Only 1% own bulls and cows [13], and consequently, dominant land preparation is manual. Sierra Leone’s rice consumption per person is 104 kg and highest in the South of Sahara region, but rice production has been below consumption demand since 1970 [13]. This likely explains why sorghum is part of the diet as an alternative for rice or as a supplement.
These regions are also known for crop production for the country, particularly cereals and legumes. The intention was to cover as wide a geographical area as possible since Sierra Leone is a small country.
2.2. Sampling Method
A multistage sampling procedure was used for this study. The first stage included a purposive selection of four administrative provinces of Sierra Leone, namely Eastern, Northern, North-Western, and Southern Provinces, followed by districts considered very key for sorghum production, then Chiefdoms within the districts and lastly, villages, the smallest units of administrations. The ruralness of the districts dictated the number of villages/respondents interviewed so Port Loko and Tonkolili districts had more respondents.
In the last sampling stage, farmers from the selected villages that farmed sorghum at least once in the last 5 years were randomly selected from the list of all smallholder farmers presented by the village chief. Overall, the survey team reached 210 sorghum farmers selected from 52 villages within seven districts of four provinces (Figure 1). The districts reached include Bo, Bombali, Kambia, Kenema, Moyamba, Port Loko, and Tonkolili. The survey tool was pretested in December 2018, but the actual study was conducted between January and March 2019.
2.3. Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection was through structured interviews, observations on sorghum fields, and discussions with focus groups. For this write-up, only results from the structured questionnaire are presented and discussed. The structured questionnaires were designed to get information on the general socioeconomic characteristics of the respondents and household characteristics, farming system, sorghum genetic diversity, sorghum utilization and business performance, sorghum production constraints, and lastly, farmers’ preferred traits in sorghum for Sierra Leone. Sorghum traits were predefined from literature and through discussion with farmers. Quantitative and qualitative data collected through questionnaires were coded and subjected to statistical analysis using IBM SPSS Statistics [14,15].
3. Results
3.1. Household and Demographic Characteristics
The results of the basic socio-demographic profile of the respondents in each district are summarized in Table 1. More males (62%) than females (38%) were interviewed, but females were engaged in field observations and group discussions to ensure their views were well represented. Most respondents (58%) were 28–47, 6% of respondents were below 27 years old, whereas 17% were above 58 years old. Most respondents (88%) were married and living with their spouses, while only 12% of respondents were without a spouse (single or never married, divorced/separated, or widow/widower). Most of the respondents (57%) had no formal education. Meanwhile, 26%, 13%, and 3% of the educated attained primary, secondary, and tertiary education, respectively.

Table 1.
Demographic description of the respondents by province (N = 210).
Seventy-six percent of the respondents live in households with a family size of at least five members. Families are large because most of the households live under one roof with related and unrelated people. About 47% of the respondents said in their households, only four or fewer members are of the productive age group of 15–64 years. Most members are either too young or too old to do garden work, and the result is that farm sizes are too small or crops are generally not well managed.
3.2. Land Ownership, Land Size, and Access for Sorghum Farmers in Sierra Leone
Of 210 farmers interviewed, 71% own land that they can freely use for their agriculture activities. Fifty-five percent own between 5 and 20 hectares of land. Despite holding this big chunk of land, most of it remains unfarmed. The farmers, therefore, have enough space to allow a more extended period of land fallowing. The 29% of respondents who do not own land have access through lending (67%) or hire (33%). Land hiring is more common in the North-west (61%) than in other regions. Proportions of respondents on land ownership, land size, and access are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Assessment of land ownership, land size, and access among respondents.
3.3. Farming Systems
Detailed descriptions of the sorghum systems in the study areas are presented in Table 3. Of all the 210 farmers sampled, 61% practice mixed farming, and only 39% strictly crop production. Farming is the primary source of food, feed, and income. Most farmers had a mix of livestock, including small ruminants (sheep, goats) and birds (chicken and ducts). None of the respondents had cattle and donkeys. Crops grown in the study zones include cereals (rice, sorghum, maize, and pearl millet), oil crops (groundnuts and sesame), tubers (cassava and sweet potatoes), pulses (cowpea and pigeon pea), and several vegetables (okra, jute mallow, and pepper). However, rice is mentioned as the main and staple food crop.

Table 3.
Assessment of farming system among respondents.
Sorghum is predominantly grown in a mixed cropping system (98% of the respondents). The atypical upland field had all kinds of crops mixed in varying proportions. Most of the fields inspected had mixed crops of rice, sorghum, pearl millet, maize, cassava, cowpea, jute mallow, and okra. The fields are in the broadcast arrangement of sowings. A farmer field in Sierra Leone is the most diverse field, with all kinds of crop types in one single season/sowing. According to the various discussions during the survey, the reasons for mixed cropping are various. This reason ranges from lack of modern agronomic knowledge to socioeconomic factors of poverty hindering large-scale field openings, so a farmer must have all his needed crops in one field he can manage within one rainy season. The farming system does not show the slightest exposure of farmers to modern agronomic practices. The crop varieties cannot be traced to a seedhouse/breeder, and the ratio of crops in mixed culture does not follow any recommended agronomic standard.
In all study zones, field preparations are done between January and late April. The standard practice starts with bush clearing, followed by bush burning, then tillage with hand hoes. There is no animal-aided field traction and there is limited use of tractors. Individuals believe that the timing of sowing is crucial in achieving reasonable yield, and they say the onset of rainfall is a perfect time. Overall, 51% of the respondents indicated the month of May as the most suitable for upland sowing of the mixed crops. Very few respondents do sowings in late April (20%) or July (21%). Crop management is manually done by family labor since almost zero mechanization and chemical crop protection is practiced.
3.4. Sorghum Productivity and Seed System
For 95% of the respondents, the quantity of sorghum grain harvested is only 50–250 kg (1–5 bags) per year (Table 4). All respondents reported having no access to mechanization, especially tractors for land preparation. All respondents do not use herbicides and pesticides due to lack of knowledge, and limited access due to price or availability. The farmers also depend strictly on rain as a water source to do their agriculture.

Table 4.
Assessment of use of fertilizer, sorghum yield, seed source, and seed rate among respondents in the study zones.
In the discussions, the respondents showed minimal knowledge of modern agronomic practices of the recommended plant population, sowing distance, use of improved varieties, seed rate, pest, and disease control in sorghum. Most farmers use a very low seed rate of between 0.2 to 1.5 kg (a few panicles to 7 cups) of sorghum seed per season. The predominant seed source in all regions is the own saved seed of local varieties of sorghum (landraces). None of the interviewed individuals ever acquired improved sorghum varieties. The Sierra Leone Agricultural Research Institute has not officially registered any single improved sorghum variety. The farmers have no choice but to conserve their seed or buy from the local market. None of the interviewed farmers have ever seen any new sorghum varieties other than their communities’ landraces or farmer varieties. They admit to having obtained new varieties of rice. There is more investment in rice research in government research institutions. Rice is the staple food, and is one of the government’s priority crops. Sorghum is strictly traded in the informal seed system. According to this survey, a sorghum farmer is likely to get sorghum seed from their harvest (55%), market (10%), relatives (8%), or all three ways (25%). To prepare home save seed, sorghum panicles are harvested, the peduncle tied together, and the whole bundles hung over a fireplace or roof or treetop in the dry season.
The use of fertilizer is one significant single factor that can increase farm crop yield and profitability of a crop farming enterprise by a substantial margin over a season. The proportion of farmers interviewed who use fertilizer is only 9%. The rest said they do not use fertilizers for reasons such as lack of money to buy or that fertilizer is not available locally, or basically that they have no knowledge. Some believe their soil is still fertile, so there is no need to use fertilizers.
3.5. Sorghum Production Constraints
The sorghum production constraints identified by respondents are summarized in Table 5. Among the key constraints are poor access to fertilizer (91%), lack of suitable varieties (85%), poor agronomic knowledge (79%), low yielding varieties (78%), storage pests (75%), field pests, particularly the stalk borer (67%), low soil fertility (52%), lack of market (49%), high disease pressure (43%), drought (16%), and heavy rainfall (12%). The Chi-square test showed that the relative importance of the constraints varied significantly between study provinces (i.e., the association between constraints and regions exists).

Table 5.
‘Farmers’ assessment of major sorghum production constraints.
While transecting various sorghum fields, we noticed the typical damage symptom of stem borers on sorghum characterized by dead hearts and holes near the nodes. We also observed insects such as aphids head bugs in the field and the store; we observed weevils and lesser grain borer (Rhizopertha dominicus) beetles. Some common foliar diseases recognized were gray leaf spots (Cercospora sorghi), leaf blight (Exserohilum turcicum), zonate leaf spot (Gloeocercospora sorghi), and anthracnose (Colletotrichum graminicola). There were incidences of head sterility in several fields and this sterility was not expected for local sorghum.
The farmers are growing sorghum without reference to any modern agronomic knowledge source. This was seen in the production fields and their stories about sorghum production over the years. The basic agronomic knowledge of seed rate, fertilizer use, row planting, source of improved seeds, pests, and disease management is lacking.
3.6. Local Sorghum Genetic Diversity
Nine traits were used to describe existing sorghum varieties with the farmers interviewed in Sierra Leone. These include growth duration, plant height, pest and disease response, yield level, reaction to drought, intercropping ability, response to rainfall, bird attack, and grain seed size (Table 6).

Table 6.
‘Farmers’ assessment of characteristics of sorghum being grown in the study areas.
The respondents described their sorghum as long cycle (99%), tall (96%), low yielding (61%), small grains (91.4%), resistant to pests and diseases (42%), susceptible to drought (74.8%), and tolerance to heavy rainfall (75.2%). They further said their local varieties are not good as intercrop(76.8%) because of severe tillering ability, and that the varieties experience minor birds attack (63.3%). We confirmed most of the phenotypic descriptions during field inspections. In addition to farmers’ descriptions of their sorghum, we observed that it bears very loose/open panicles (15–60 cm) and tiny seeds are generally elliptically exposed out of the glume at maturity. The glumes are of three colors, i.e., red, black, and tan, but the seeds are of two colors, white and red (Figure 2). Our observation is that the morphological diversity of cultivated sorghum in Sierra Leone is narrow.
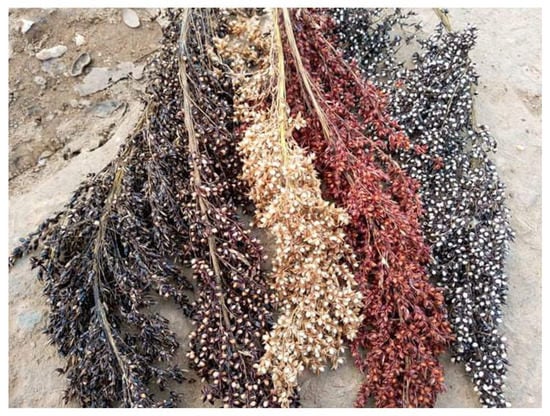

Figure 2.
Panicles of sorghum collected from Sierra Leone.
3.7. Farmers’ Preferences of Sorghum Traits in Sierra Leone
The farmers’ perceptions regarding characteristics of sorghum are summarized in Table 7. The Chi-square test showed that farmers’ preferences varied significantly between study provinces (i.e., the association between constraints and regions exists).

Table 7.
Assessment of perceptions of respondents regarding selected sorghum traits.
Overall, traits of great interest among the respondents were high yield, adaptability to a specific environment, disease resistance, and pest resistance with 99, 85, 84, and 81% of respondents, respectively. Over 74% of the respondents consider earliness attractive; however, they have never seen a variety maturing as early as 90 days after sowing. The choice of earliness is out of curiosity and the hope of growing sorghum twice a season. Traits with 50–60% proportions of respondents agreeing to importance include drought tolerance (50%), white grain (59%), and short growth height (53%). White sorghum is particularly gaining importance because of the growing sorghum trade due to industrial use by Sierra Leone breweries. Regional analysis shows that respondents’ preferences differ for all traits.
3.8. Sorghum Utilization and Business Performance
Assessment of various sorghum utilization and business options is summarized in Table 8. There are minimal options for the utilization of sorghum in Sierra Leone homes. Overall, 98% of the respondents cook sorghum in whole grain form. The clean grains are also roasted and eaten as snacks. The whole grain is sometimes pounded into powder used to make porridge for babies. There is no use for straws in the communities. Most of the sorghum produced on the farm is for home consumption. Only 34% of the respondents sold part of their previous season’s harvest. Of the respondents who sold a portion of their harvest, only 15% sold directly to agents of Sierra Leone Brewery. The rest have little knowledge of who the buyers are or where their produce would end up. The lack of market information is very prominent. Of the respondents who sold, 77% complained of marketing challenges, meager price (84%), and low demand (16%). Only 58% sold a kilogram of sorghum grain above Le1000 (0.1 USD).

Table 8.
Assessment of sorghum utilization and business performance.
In Sierra Leone, a recent development in the sorghum industry is the inclusion of sorghum as an ingredient in many beer and energy drink brands by Sierra Leone Breweries, and this is an expanding marketing option. According to Deters 2011, the Sierra Leone breweries started local sourcing of white sorghum recently and was awarded the UNDP world business development award in 2010. The brewery requirement is particular, and farmers must meet the requirements so that they can trade.
4. Discussion
4.1. Household and Demographic Characteristics of Sorghum Farmers in Sierra Leone
The present study assessed sorghum production system and pattern to identify farmers’ major sorghum production constraints, varietal, and trait preferences to guide breeding of improved sorghum varieties in Sierra Leone. This study reports the first case effort to understand sorghum production constraints and trait preferences in the country. The demographic structure of sorghum farmers revealed by this study concurs with the 2015 population census and other records for Sierra Leone. For instance, the mean household size was 6.9 persons according to global data lab [16] and 6 persons according to the 2015 census report [17]. Our research showed that 76% of the households have five or more persons, and all households are extended ones. A household is defined as a person or group of persons who live together and make joint cooking arrangements [17]. Household sizes have a direct effect on the availability of household labor and food security. In our case, 47% of households interviewed had less than 4 members in the productive age brackets. Like most African countries, Sierra Leone has its population below the 15 years bracket.
The 2015 census also supports our finding that the main economic activity in Sierra Leone is agriculture, comprising crops, livestock, forestry, and fishing activities [17]. Agriculture contributed 66.8% to GDP in 2016 [17]. The economy of Sierra Leone falls within the category of least developed nation [18]. The importance of agriculture has not changed much since then.
A large proportion of sorghum farmers interviewed had no formal education (57%); the 2015 census shows that 61.6 percent of Sierra Leoneans do not send their children to schools because they do not value education [17]. Education levels are expected to influence knowledge that can help improve farmers’ adoption of agricultural technologies and farming systems. Demographic characteristics of farming communities influence production and adoption. In Kenya, for example, Chepng’etich et al. (2015) [19] found that the technical efficiency of sorghum production was influenced positively by the formal education level of the household, and access to training in farmers’ associations, use of hired labor, and negatively by the household size. A large household size does not automatically result in increased labor access as members may be outside the productive age brackets [19]. The mean years of schooling in Sierra Leone is only 3.5 [20]. The level of education of a household and number of workforce greatly affects farm productivity.
4.2. Land Ownership, Land Size, and Access for Sorghum Farmers in Sierra Leone
This research showed that 71% of farmers have access to family land for farming activities. Because the majority of people are engaged in farming, access to land is very important. The 2018 Sierra Leone integrated household survey indicates that out of 1,247,942 agricultural households that gave information on owning or cultivating land during 2018, 792,425 (64%) households used either agriculture or non-agriculture land during the year at the national level [20]. The land is one of the most critical assets for rural households, and lack of access to land is often a key constraint preventing rural households from emerging from poverty [21]. Access to land influences agricultural and economic activities that can be carried out by a farmer [22]. Land in the country is held in communal ownership under customary tenure. It is controlled by traditional rulers who administer it on behalf of their communities according to established customary principles and usage. However, absolute interest in land is vested in land-owning families that deal in all lands [23].
4.3. Farming Systems
This study showed mixed farming as the primary source of food and income for farmers in Sierra Leone. With mixed farming, a farmer keeps a few domestic birds and animals and does crop farming simultaneously. This practice has been reported in Ethiopia [8], Uganda [24], Kenya, and many other countries in Africa.
Our finding is that sorghum is a minor cereal compared to rice, and that rice is the staple food and main cereal crop as well. Sorghum is cultivated as an intercrop in upland rice. This finding concurs with the Sierra Leone Household survey 2018, which found that rice is the staple food in Sierra Leone [20]. Countries such as Ethiopia [8] and Uganda [24] now have a reasonable number of farmers sowing sorghum as monocrop. Farmers do intercropping or mixed cropping for various reasons. The reasons are maximizing land use, controlling pests and diseases, improving ecological protection, and maximizing crop output from available land [25]. However, intercropping systems may have negative or positive effects on crop yield. Interspecific competition for light and nutrients has been reported in various intercropping systems [26,27]. Comparing monoculture and intercropping of cereals and legumes revealed that intercropping is more profitable than monoculture [28]. Yield and nutrient acquisitions by intercropped wheat, maize, and soybean were significantly greater than for sole wheat, maize, and soybean. Intercropping advantages in yield (40–70% for wheat intercropped with maize and 28–30% for wheat intercropped with soybean) [29].
Our finding on cropping calendar matches those of other studies. In all study zones, field preparations start by late January through bush burning. The month of May is when most sowings of mixed crops is done. Very few respondents do sowings in late April (20%) or July (21%). Crop management is manually done by family labor with minimal mechanization and use of chemicals [20].
4.4. Sorghum Seed, Seed Source, and Seed System
The sorghum seed system is mainly informal and with seed source being own harvest (55%), market (10%), relatives (8%), and all three ways (25%) for a given cropping season. This study confirms the common knowledge that smallholder farmers always save their seeds of varieties of interest for the subsequent production and transfer to the next generation. In 2018, out of 1,630,694 agricultural households that responded to the different sources of obtaining seeds for planting in Sierra Leone, 946,433 (58%) save from the last harvest [20]. The practice of saving one’s own seed can be at the expense of adopting improved varieties and has a negative effect on the formal seed trade [30]. Farmers sticking to their landrace varieties is not only in Sierra Leone. For instance, Gebretsadik et al. (2014) in Ethiopia showed that 86% of farmers preferred to grow sorghum landraces than improved varieties. This present study showed that all sorghum varieties in Sierra Leone are landraces traded in the informal seed system. This presents an opportunity for new sorghum varieties from seed companies but also a challenge. The ability of seed companies to breed new varieties and trade effectively is directly linked to the seed system [30].
Access to seed is crucial for successful and profitable farming [31]. Yet, a crop that is primarily sold dominantly in the informal seed system is a high-risk crop for a commercial seed company because variety dissemination is slow and requires a lot of investment to market.
A lot of farmers’ awareness campaigns are required in Sierra Leone to sensitize farmers to the values of improved varieties from seed companies and this will directly contribute to the development of the seed industry. The seed industry should be market-oriented and competitive so that high-quality seed of improved varieties can be available from investors/seed companies. The European Cooperative for Rural Development (EUCORD) project under Sierra Leone Brewery has supported sorghum breeding and seed multiplication of landraces in a kind of community seed system while working closely with a formal seed business called Genesis Farms since 2009 [32].
The formal seed system is just starting to develop. As of 2018, six index seed companies, namely Corteva Agriscience, Bejo, NAFASO, Pop Vriend Seeds, Sakata, and Technisem, operate in Sierra Leone, but none carries out seed production and crop breeding locally. Only Genesis Farms, the predecessor of the African Seed Company, was constantly engaged in mainly rice seed production and sales. The new entrant African Seed Company is doing seed production and breeding in the country for the first time for field crops.
4.5. Sorghum Productivity
Agricultural productivity is measured as the ratio of agricultural outputs to agricultural inputs [33]. The factors of agriculture productivity include mechanization, improved varieties, fertilizers, liming, irrigation, herbicides, pesticides, and improved agronomy to the farm [33]. We reveal that only 9% of the farmers use fertilizer on their farms. This study concurs with the 2018 Sierra Leone sierra_leone_integrated_household_survey report that showed that only 134,665 (8.3%) out of 1,614,867 agricultural households interviewed used inorganic fertilizer in the 12 months. The only available kind of fertilizer is NPK 15:15:15. The use of fertilizer is one significant single factor that can increase farm crop yield and profitability of a crop farming enterprise by a considerable margin over a season.
The farmers do not use herbicides and pesticides on sorghum farms. The low use of productivity enhancement factors such as fertilizers and improved seed is related to lack of money to buy or fertilizer being not available locally, or basically that they do not know how (Table 4). In order to increase productivity, specific interventions can be helpful. For instance, the quantity of sorghum produced by EUCORD project beneficiaries increased from 0.8 bags (50 kg) before the project to 5.9 bags per household after the project [32]. This indicates that intervention in such productivity enhancement areas is necessary.
Using the global agro-ecological zones, sorghum production in Sierra Leone can be classified as a very low input system. The farming system is mainly subsistence-based, where production is based on local cultivars, labor intensive, and zero use of fertilizers and chemicals for pests and disease control. If improved cultivars are used, they are treated in the same way as local cultivars [34]. Long-term productivity growth requires continuous improvement in farmers’ production efficiency and steady introduction of agricultural technologies [33].
4.6. Sorghum Production Constraints
Globally, sorghum yield remains below its potential because of various production constraints [1]. In this study, farmers identified poor access to fertilizer as the most significant constraint to sorghum production, followed by lack of suitable varieties, poor agronomic knowledge, low yielding varieties, storage pests, field pests, particularly the stalk borer, low soil fertility, lack of market, high disease pressure, drought, and heavy rainfall (Table 5). This finding is in agreement that it is always multiple factors occurring simultaneously in most sorghum production ecologies [1]. It also agrees that factors differ in relevance with regards to geography on the map. For instance, similar studies in Ethiopia [8] and Uganda [35] ranked striga as the number one sorghum production constraint in those countries. There are no striga weed in Sierra Leone.
Our studies showed that Sierra Leone had no in country bred sorghum variety. This leaves the farmers with no choice except to use the low-yielding and available landraces. Lack of access to improved sorghum varieties is a significant constraint in even more developed seed industries such as Ethiopia [8] and Uganda [24].
Insect pests are key sorghum production constraints, we observed midge (Stenodiplosis sorghicola Coquillett), green bug (Schizaphis graminum Rondani), aphids, shootfly (Atherigona soccata Rondani), and stem borer (Chilo partellus Swinhoe) and these were already reported as key sorghum pests in West Africa [36].
On the abiotic production constraints, i.e., drought, strong wind, heavy rainfall, and poor soil fertility, incidences of El Niño resulting in a storm of rains have been reported in Sierra Leone [37]. Wadsworth et al. (2019) [37] indicated that El Niño was more frequent in the southeast of Sierra Leone. It is known that West and Central Africa have some of the most highly weathered soil with shallow organic matter and low soil fertility [38]. Sorghum production is significantly affected when plant-available phosphorus is low in the soil [38]. However, sorghum still yields much more than maize in such conditions making it an essential part of crop culture in Sierra Leone.
4.7. Description of Sorghum Varieties Being Grown Now by the Farmers
This study reveals that the sorghum grown by Sierra Leone farmers is 100% landraces. The farmers described their sorghum as long cycle, tall height, small seed size, and low yielding. From the many fields we inspected, we assessed that the sorghum types are characteristically grassy, with many root tillers. The panicles are primarily loose and open, measuring 15–60 cm in length. The glumes colors are purple, tan, black, and red (Figure 2). The seed is of two colors, i.e., white and red. All the farmer fields inspected had a mixture of varieties in terms of seed and glume colors. Our observation is that the morphological diversity of cultivated sorghum in Sierra Leone is narrow. The landrace sorghum varieties in Sierra Leone flower in mid-October across the country in response to changes in photoperiod.
Our finding of the limited diversity of sorghum landraces in Sierra Leone contradicts the belief that the diversity of cultivated sorghum is high on the African continent [38]. The limited diversity of sorghum in Sierra Leone compared to other West African states of Mali, Burkina Faso, and Cameroon is likely because the country lies outside the 500- and 1200-mm rainfall isohyets. These isohyets are the major sorghum varietal adaptation zones [38]. Heavy rainfall affects seed set in sorghum hence the ability to select against all sorghum types that do not fit in the heavy rain. The incidences of head mold are not reported on the local sorghum because the grains are formed when the conditions for head molds are not favorable anymore. The sorghum landraces in Sierra Leone are unique to the country.
4.8. Sorghum Varietal Preferences in Sierra Leone
Farmers who participated in this study preferred sorghum varieties with high grain yield, good adaptability, good disease resistance, and good pest resistance. They also consider earliness, drought tolerance, white grain, and short growth height (Table 6). Interestingly, the farmers have never seen a variety maturing as early as 90 days after sowing. The choice of earliness is out of curiosity and the hope of growing sorghum twice a season. Meanwhile, white sorghum is particularly gaining importance because of the growing sorghum trade due to industrial use by Sierra Leone Breweries [32]. Often farmers choose varieties to optimize outputs in the face of variation in the growing environment [39]. Aspects such as time to maturity, market, and consumer preferences, adaptation to agroecology, changes in environmental, and climatic conditions, and responses to various biotic and abiotic challenges have affected farmers’ choice of a sorghum cultivar [39]. Improved understanding of farmers’ varietal choices can contribute to collaboration between farmers and formal plant breeders [39].
Drought resistance was surprisingly mentioned by 50% of the respondents. The farmers sometimes experience extreme weather events, including heat waves and heavy precipitation. According to Wadsworth et al., there is evidence for a significant reduction in annual rainfall in the North-west Sierra Leone [37]. The farmers also think the rainy seasons are becoming more erratic every year. Farmers say sometimes the dry period occurs soon after seedlings emerge but also that newly emerged seedlings are sometimes damaged by heavy rainfall. There is, however, only limited support for this widely held belief [37].
The farmers who participated in this study also expressed willingness to try modern varieties with traits they never knew existed. Such new traits include short cycles, short height, and large thousand-grain weight; however, such traits will have to meet the biophysical and socioeconomic environments for acceptability. The analysis, conducted with Tobit models of modern sorghum and rice varietal technologies in Burkina Faso and Guinea, strongly supports the hypothesis that farmers’ perceptions of technology characteristics significantly affect their adoption decisions [40]. Consumers generally have subjective preferences for attributes of products, and that their demand for products is significantly affected by their perceptions of the product’s characteristics [40].
This study revealed the perceptions of Sierra Leone farmers on several traits of sorghum for the first time.
4.9. Sorghum Utilization and Business Performance
Sorghum is majorly grown for food by all respondents interviewed. A review by Weltzien et al. (2018) [38] confirms that sorghum is grown majorly for food throughout West and Central Africa. Only the grain is utilized among the Sierra Leone community. However, sorghum is used worldwide as livestock feed, human food, fuelwood, stalk for making furniture or shelter, and even fences [41].
In Sierra Leoneans’ homes, the grain preparation for food is limited to boiling whole grains and eating with a sauce (98%). The grains are crushed in a mortar with a pestle to make fine flour for baby porridge in a few instances. The utilization options are very narrow compared to countries such as Uganda, where the grains are milled into flour, used for baking pancakes, porridge, whole grains cooked, and even used in traditional local brewing. The Sierra Leone sorghum grain is not farinaceous but vitreous, unlike many sorghums from other regions.
Because farmers are part of the cash economy and sorghum grain is increasingly being taken up by the brewery and poultry industry in Sierra Leone, farmers have started apportioning part of their production for sales. Multiple sorghum users are coming up in Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone brewery has increased the content of sorghum in its major products since 2009. For instance, Star beer now has 16% sorghum, Guinness 10%, and Maltina has 17% sorghum [32]. From 2006 until 2008, the SLB could consume a maximum of 230 MT of sorghum per year, but they could only access supplies of 20, 40, and 65 MT in 2006, 2007, and 2008 respectively [32]. The demand pushed production up in the following years to 174 and 675 MT in 2009 and 2010, respectively [32]. The SLBL has since increased its consumption capacity and added more products that require sorghum.
5. Conclusions
To understand the sorghum farming system in Sierra Leone, farmers were interviewed across four provinces. The study identified that sorghum farmers are mostly 18–47 married men and women. They live in extended families of at least five members. Most of these households have less than four members in the productive age group of 15–64 years, and the majority do not have formal education. The farmers have access to farmland through ownership, hire, or free. The farmers practice mixed farming as their primary source of food, feed, and income. The sorghum crop is a minor crop compared to rice and is cultivated as an intercrop. The sorghum seed moves through an informal seed system (own save, neighbors, local market, or both within a season). There are no improved sorghum varieties with farmers, and therefore all sorghum varieties in cultivation in Sierra Leone are landraces.
These landrace sorghum in cultivation are described as long cycle, tall, small seeded, and low yielding. Furthermore, the sorghum is grassy, with many root tillers and loose and open panicles of 15–60 cm long. The glumes are red, black, and tans and the seeds are red or white. We therefore state here that the phenotypic diversity in Sierra Leone landrace sorghum is narrow.
Sorghum utilization is limited to grain as human food in households. However, because farmers are part of the cash economy, sorghum grain is increasingly sold to various buyers, including brewery agents and poultry farmers. In homes, sorghum is prepared into a few food products, for example, boiled whole grain, porridge, and roasted grains. There is no use for straws in the communities.
Poor access to fertilizer, lack of suitable varieties, poor agronomic knowledge, low yielding varieties, storage pests, field pests, low soil fertility, lack of market, high disease pressure, drought, and heavy rainfall have been identified as main sorghum production constraints. Farmers are willing to take in new varieties if they are of high yield, have good adaptability, and are disease and pest resistant. They are also attracted to earliness, drought tolerance, white grain, and short growth height. This research on the diagnostic appraisal of the sorghum farming system is the first of such studies in Sierra Leone and provides a good base for a future similar study.
Therefore, we conclude that sorghum improvement for Sierra Leone should be directed toward developing sorghum cultivars with enhanced yield potential combined with adaptability to Sierra Leone’s high rainfall, low inputs, low fertility, low pH environment, and high pest and disease pressure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.O.; Formal analysis, F.O.; Investigation, F.O.; Supervision, M.L., H.S. and W.A.J.d.M.; Writing—original draft, F.O.; Writing—review & editing, M.L., H.S. and W.A.J.d.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the African Seed Company Sierra Leone. https://www.africanseed.sl/.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study is publicly available online https://www.narcis.nl/dataset/RecordID/oai%3Aeasy.dans.knaw.nl%3Aeasy-dataset%3A239091.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank African Seed Company Sierra Leone for funding the research. The University of KwaZulu-Natal is thanked for Ph.D. study placement to the first author. Sorghum farmers in Sierra Leone are thanked for making this study possible. Francis Okot conducted the surveys, data curation, formal analysis, and writing of the original draft of the manuscript. Hussein Shimelis, Mark Laing, Walter A.J de Milliano, and Admire Isaac Tichafa Shayanowako contributed to the supervision and review of this work. Special thanks to Hans Lemkes and Jean-Francois Luoisa for paying keen interest and supporting the research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mundia, C.W.; Secchi, S.; Akamani, K.; Wang, G. A regional comparison of factors affecting global sorghum production: The case of North America, Asia and Africa’s Sahel. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. FAOSTAT Statistical Database; FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations): Rome, Italy, 2019; Available online: http.faostat.fao.org (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Berenji, J.; Dahlberg, J. Perspectives of sorghum in Europe. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2004, 190, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, C.T.; Dahlberg, J.A.; Kresovich, S. The gene pool of Sorghum bicolor and its improvement. In Genomics of the Saccharinae; Paterson, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya, H.D.; Reddy, K.N.; Vetriventhan, M.; Ahmed, M.I.; Krishna, G.M.; Reddy, M.T.; Singh, S.K. Sorghum germplasm from West and Central Africa maintained in the ICRISAT genebank: Status, gaps, and diversity. Crop J. 2017, 5, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Milliano, W.A.J. Sorghum diseases in southern Africa. In Sorghum and Millet Diseases: A Second World Review; De Milliano, W.A.J., Frederiksen, R.A., Bengston, G.D., Eds.; ICRISAT: Patancheru, AP, India, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Olembo, K.N.; M’mboyi, F.; Kiplagat, S.; Sitieney, J.K.; Oyugi, F.K. Sorghum Breeding in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Success Stories; The African Biotechnology Stakeholders Forum (ABSF): Nairobi, Kenya, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gebretsadik, R.; Shimelis, H.; Laing, M.D.; Tongoona, P.; Mandefro, N. A diagnostic appraisal of the sorghum farming system and breeding priorities in Striga infested agroecologies of Ethiopia. Agric. Syst. 2014, 123, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatoe, J.B.D.; Al-Hassan, R.M.; Abatania, L.N. Factors affecting the adoption of improved sorghum varieties among farm households in Northwest Ghana: A probit analysis. J. Dev. Stud. 2005, 2, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kaliba, A.R.; Mazvimavi, K.; Gregory, T.L.; Mgonja, F.M.; Mgonja, M. Factors affecting adoption of improved sorghum varieties in Tanzania under information and capital constraints. Agric. Food Econ. 2018, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R. Participatory rural appraisal as qualitative research: Distinguishing methodological issues from participatory claims. Hum. Organ. 2001, 60, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witcombe, J.R.; Gyawali, S.; Sunwar, S.; Sthapit, B.R.; Joshi, K.D. Participatory plant breeding is better described as highly client-oriented plant breeding. II. Optional farmer collaboration in the segregating generations. Exp. Agric. 2006, 42, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalloh, A.; Nelson, G.C.; Thomas, T.S.; Zougmoré, R.B.; Roy-Macauley, H. (Eds.) West African Agriculture and Climate Change: A Comprehensive Analysis; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- SPSS. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; Version 20.0; IBM Corp: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, S.; Everitt, B.S. A Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using SPSS; Chapman & Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Smits, J.; van Geffen, A.; Huisman, J.; Wildeman, J. Sierra Leone Average Household Size. GDL Area Database. 2015. Available online: https://globaldatalab.org/areadata/hhsize/SLE/ (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Statistics Sierra Leone. Sierra Leone 2015 Population and Housing Census. Provisional Results. 2016. Available online: https://www.statistics.sl/images/StatisticsSL/Documents/final-results-2015populationandhousingcensus.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- United Nations. Profiles of Least Developed Countries. 2018. Available online: https://www.un.org/ohrlls/content/profiles-ldcs (accessed on 16 July 2020).
- Chepng’etich, E.; Nyamwaro, S.O.; Bett, E.K.; Kizito, K. Factors that influence technical efficiency of sorghum production: A case of small holder sorghum producers in Lower Eastern Kenya. Adv. Agric. 2015, 2015, 861919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra Leone Integrated Household Survey (SLIHS) Report. 2018. Available online: https://www.statistics.sl/images/StatisticsSL/Documents/SLIHS2018/SLIHS_2018_New/sierra_leone_integrated_household_survey2018_report.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Deininger, K.; Savastano, S.; Xia, F. ‘Smallholders’ land access in Sub-Saharan Africa: A new landscape? Food Policy 2017, 67, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogeto, R.M.; Cheruiyot, E.; Mshenga, P.; Onyari, C.N. Sorghum production for food security: A socioeconomic analysis of sorghum production in Nakuru County, Kenya. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 6055–6067. [Google Scholar]
- Ahene, R.; Bagdonavicius, A.; Barra, A.F.; Galpin, C. Support to the Sierra Leone Land Agenda: Policy Note; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Andiku, C.; Shimelis, H.; Laing, M.; Shayanowako, A.I.T.; Ugen, M.A.; Manyasa, E.; Ojiewo, C. Assessment of sorghum production constraints and farmer preferences for sorghum variety in Uganda: Implications for nutritional quality breeding. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malézieux, E.; Crozat, Y.; Dupraz, C.; Laurans, M.; Makowski, D.; Ozier-Lafontaine, H.; Rapidel, B.; de Tourdonnet, S.; Valantin-Morison, M. Mixing plant species in cropping systems: Concepts, tools and models: A review. In Sustainable Agriculture; Lichtfouse, E., Navarrete, M., Debaeke, P., Véronique, S., Alberola, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 329–353. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, D.T.; Bastiaans, L.; Goudriaan, J.; Van Laar, H.H.; Kropff, M.J. Analysing crop yield and plant quality in an intercropping system using an eco-physiological model for interplant competition. Agric. Syst. 2002, 73, 173–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Ambus, P.; Jensen, E.S. Interspecific competition, N use and interference with weeds in pea–barley intercropping. Field Crops Res. 2001, 70, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, Z.; Dong, S. Interspecific competitiveness affects the total biomass yield in an alfalfa and corn intercropping system. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Rengel, Z. Wheat/maize or wheat/soybean strip intercropping: I. Yield advantage and interspecific interactions on nutrients. Field Crops Res. 2001, 71, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J.G.; Conner, A.J.; Boelt, B.; Chastain, T.G.; Rolston, P. Climate change: Seed production and options for adaptation. Agriculture 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.J. Securing access to seed: Social relations and sorghum seed exchange in eastern Ethiopia. Hum. Ecol. 2008, 36, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deters, A. Sorghum Supply Chain Sierra Leone–A Sustainable Project. Bachelor’s Thesis, Stenden University, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Australia, F. Australian Government Department Agriculture. Fisheries and Forestry. 2021. Available online: https://www.awe.gov.au/abares/research-topics/productivity (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Maltsoglou, I.; Kojakovic, A.; Rincon, L.E.; Felix, E.; Branca, G.; Valle, S.; Gianvenuti, A.; Rossi, A.; Thulstrup, A.; Thofern, H. Combining bioenergy and food security: An approach and rapid appraisal to guide bioenergy policy formulation. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 79, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, O.J. Genetic Analysis of Striga Hermonthica Resistance in Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor) Genotypes in Eastern Uganda. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Kwazulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nwanze, K.F. Sorghum insect pests in West Africa. In Proceedings of the International Sorghum Entomology Workshop, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 15–21 July 1984; Volume 15, p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth, R.; Jalloh, A.; Lebbie, A. Changes in Rainfall in Sierra Leone: 1981–2018. Climate 2019, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltzien, E.; Rattunde, H.F.W.; Van Mourik, T.A.; Ajeigbe, H.A. Sorghum cultivation and improvement in West and Central Africa. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Sorghum. Volume 2: Sorghum Utilization around the World; Rooney, W., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, S.M.; Cleveland, D.A.; Soleri, D. Farmer choice of sorghum varieties in southern Mali. Hum. Ecol. 2006, 34, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A.A.; Baidu-Forson, J. ‘Farmers’ perceptions and adoption of new agricultural technology: Evidence from analysis in Burkina Faso and Guinea, West Africa. Agric. Econ. 1995, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karper, R.E.; Quinby, J.R. Sorghum—Its production, utilization and breeding. Econ. Bot. 1947, 1, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).