Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Water Using MXene (Ti3C2) Nanosheets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of MXene Nanosheets
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Adsorption Experiment
3. Results and Discussions
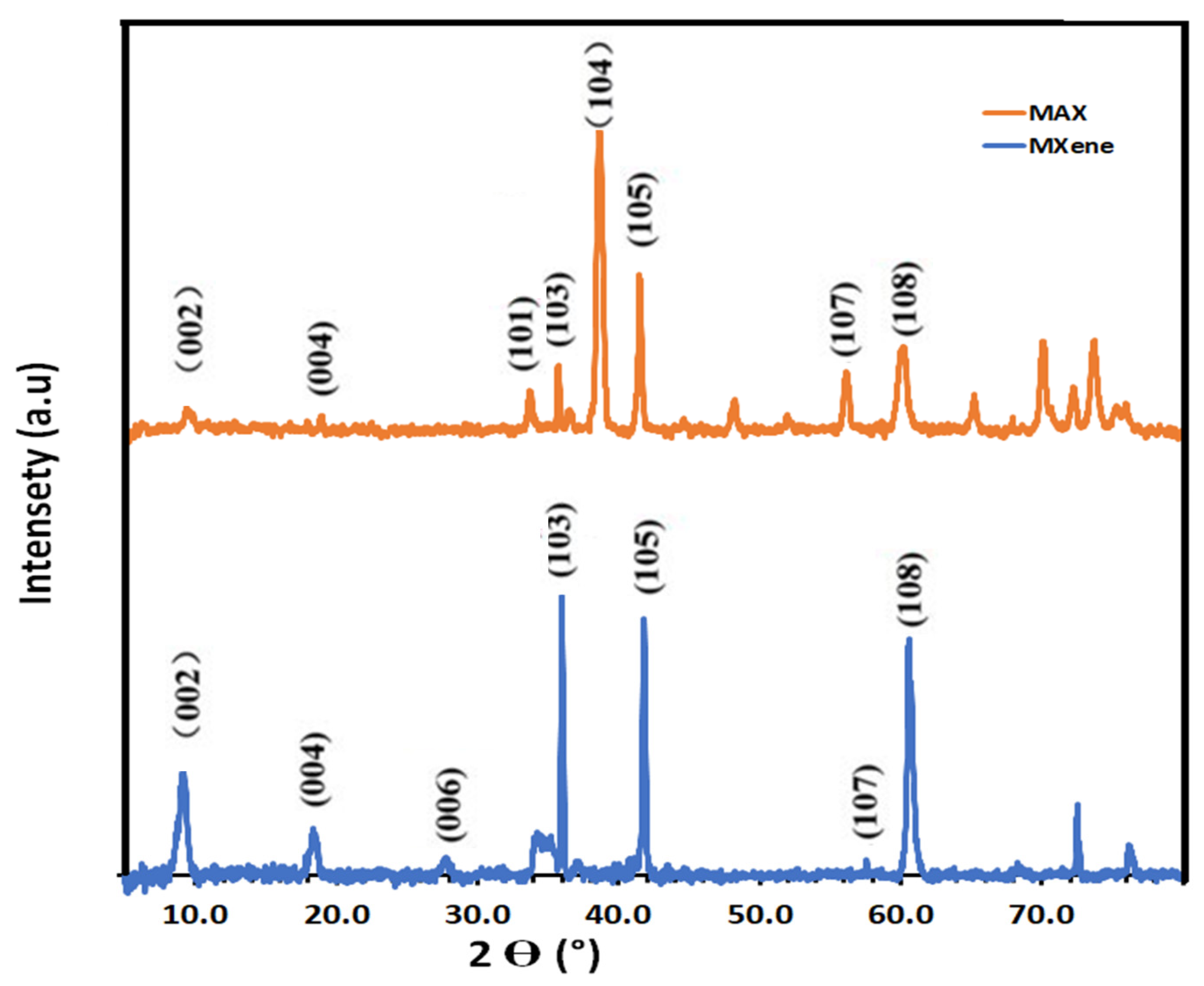
3.1. Characterization of MXNS
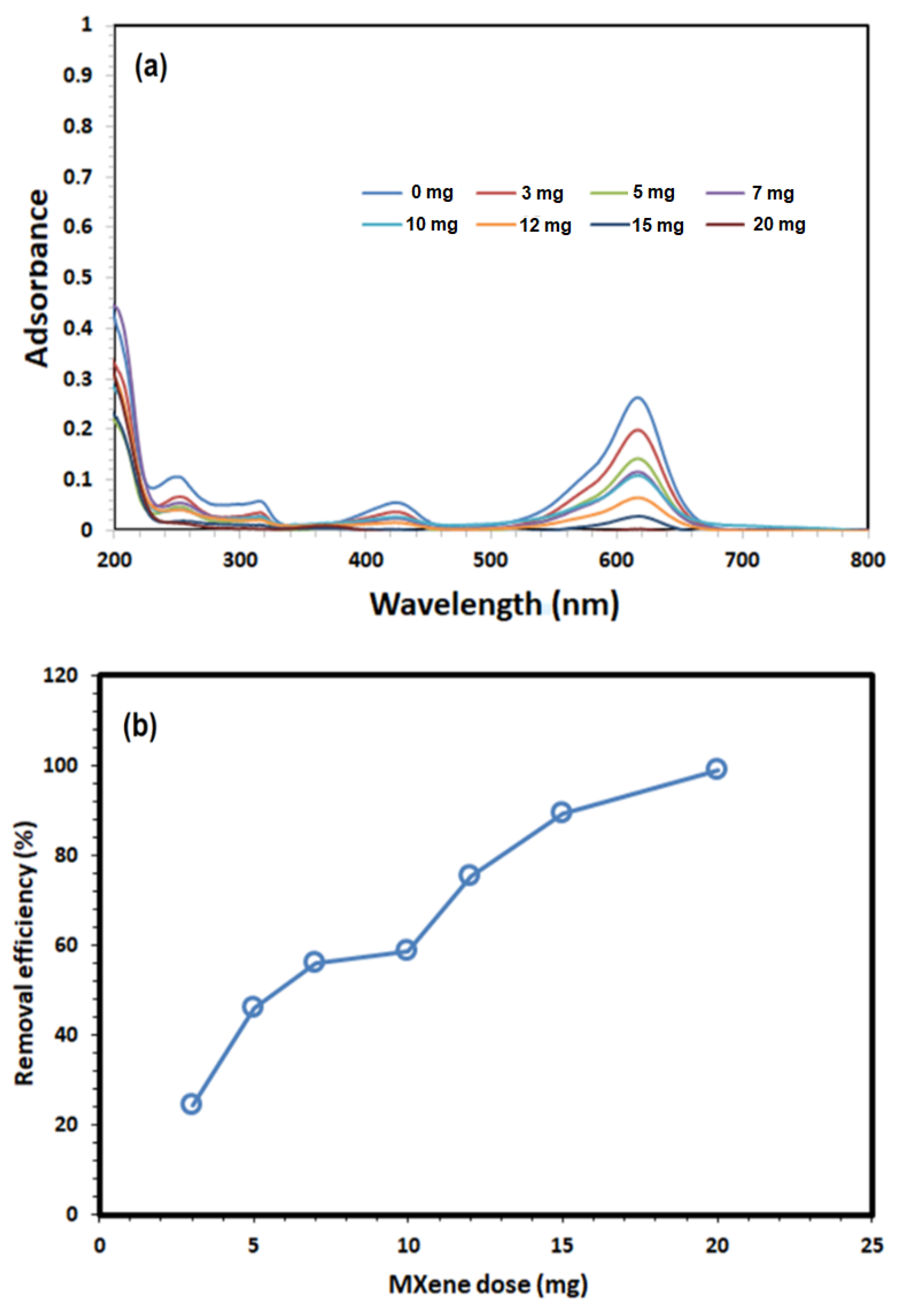
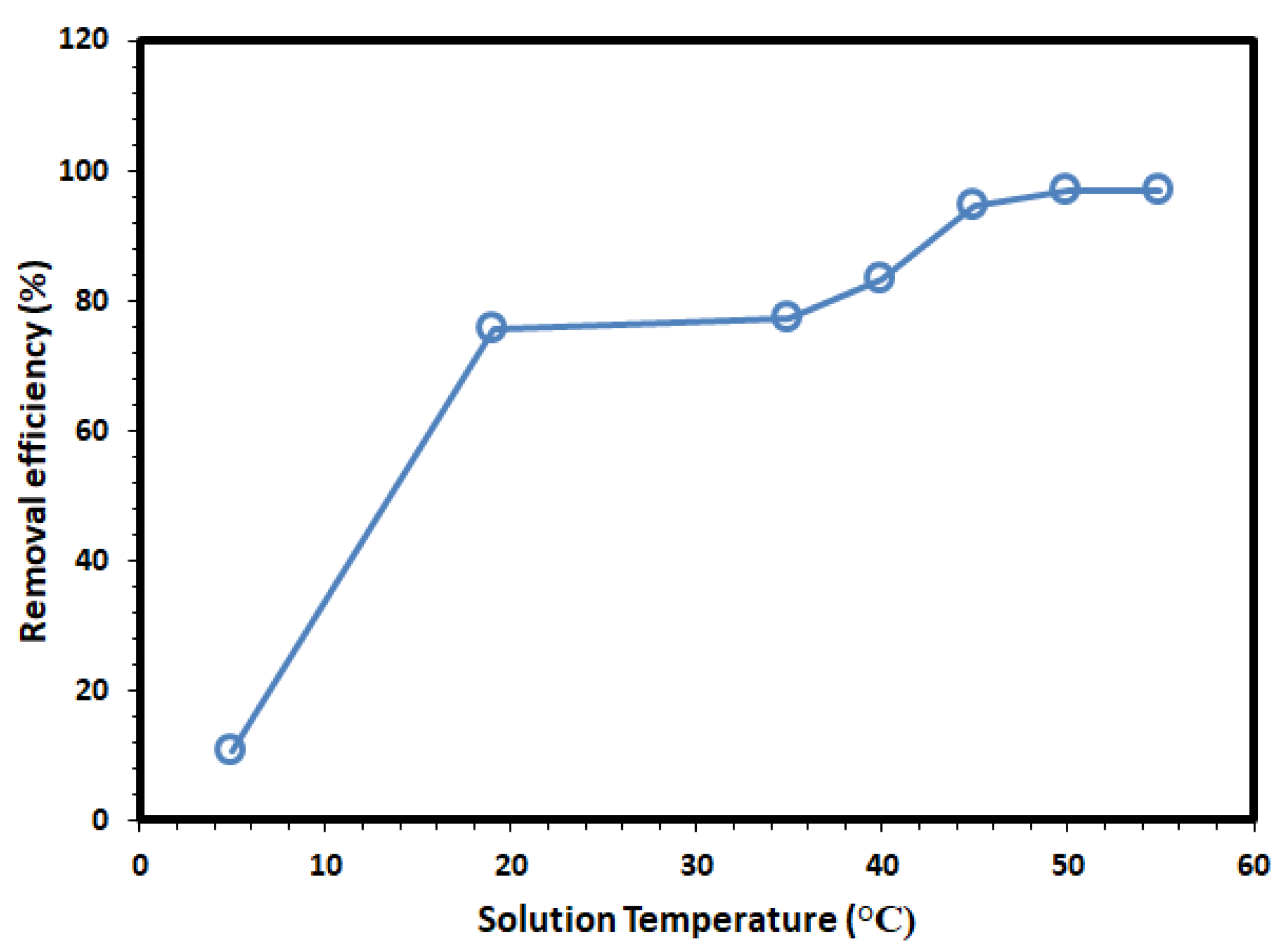
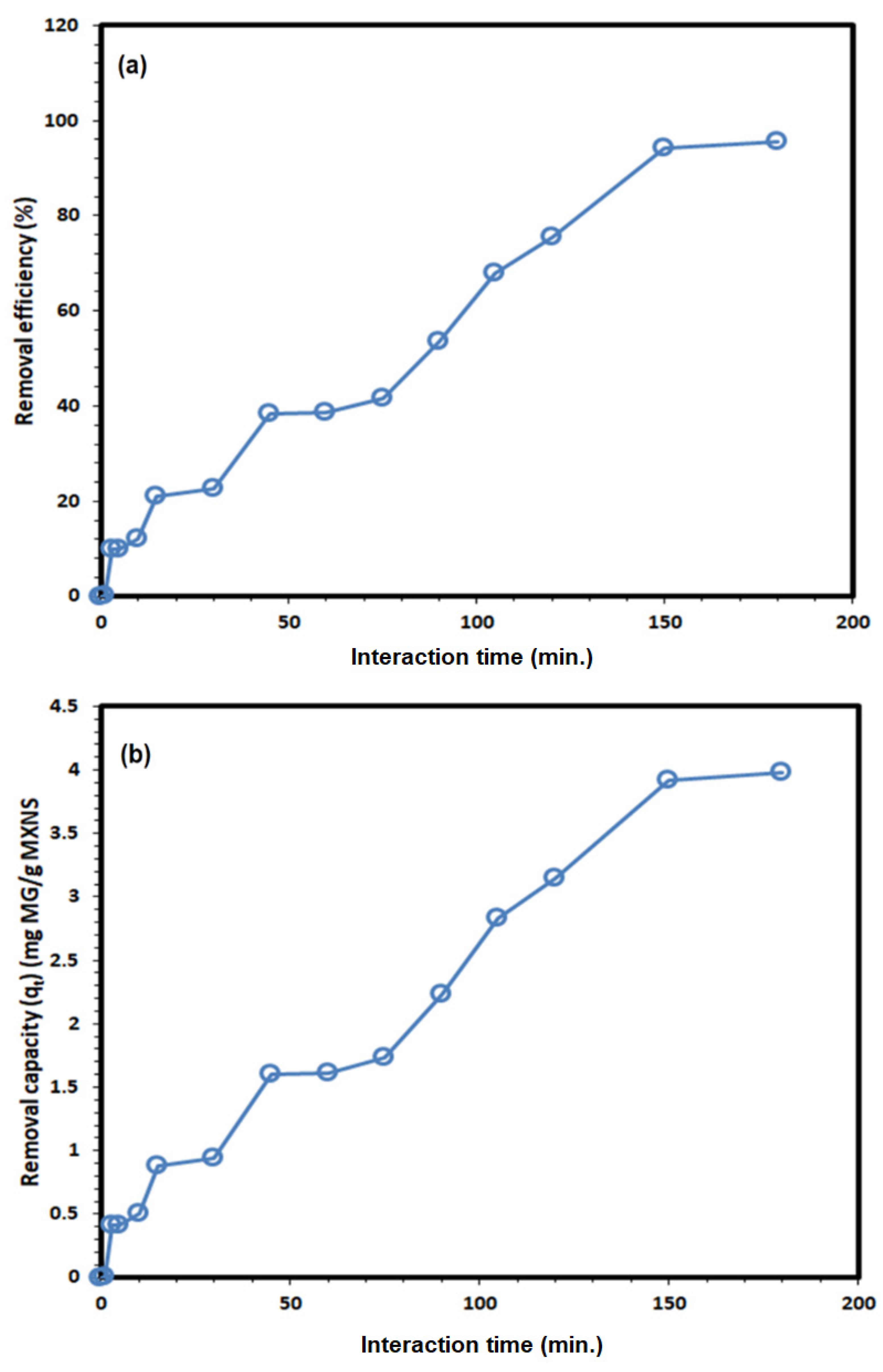
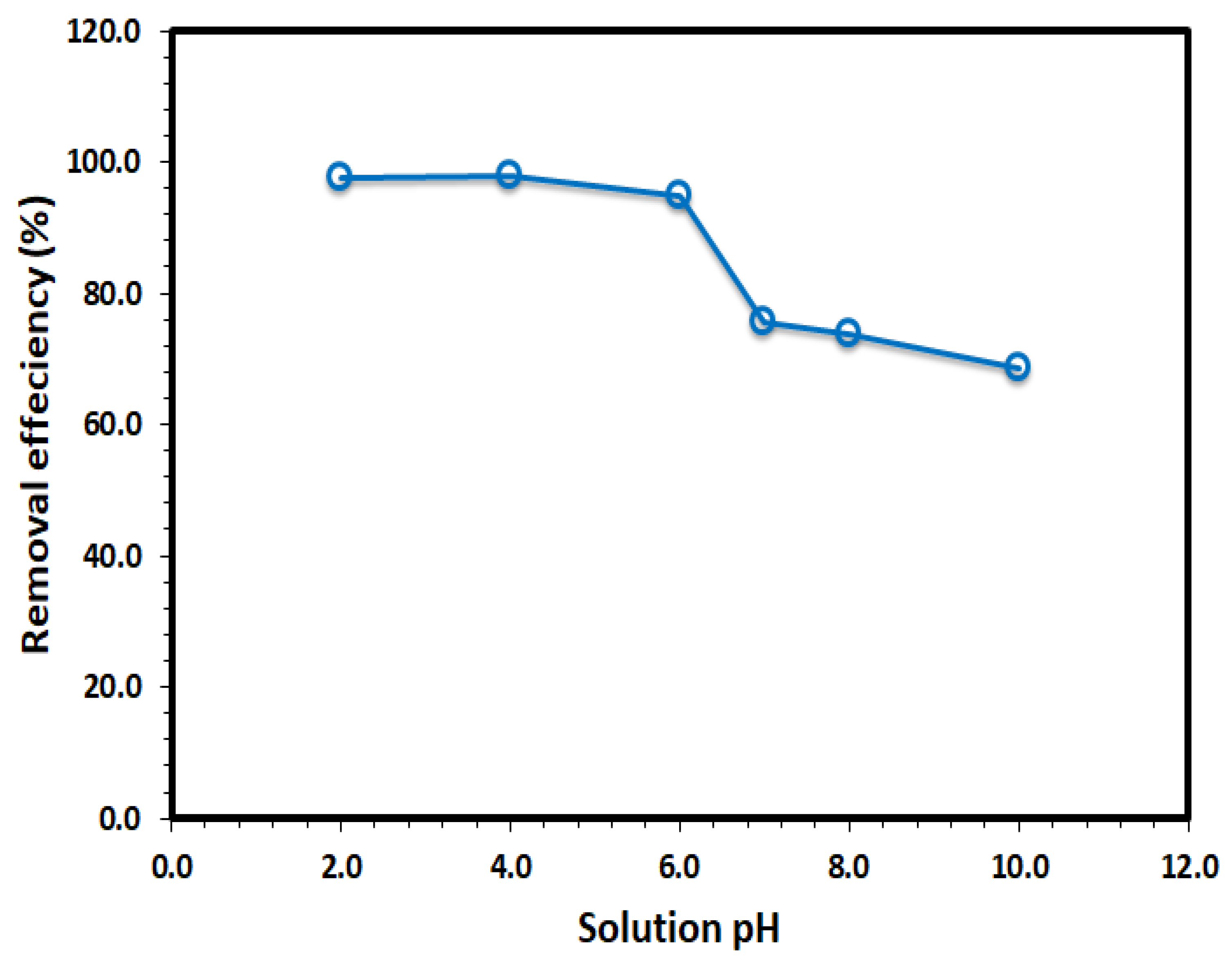
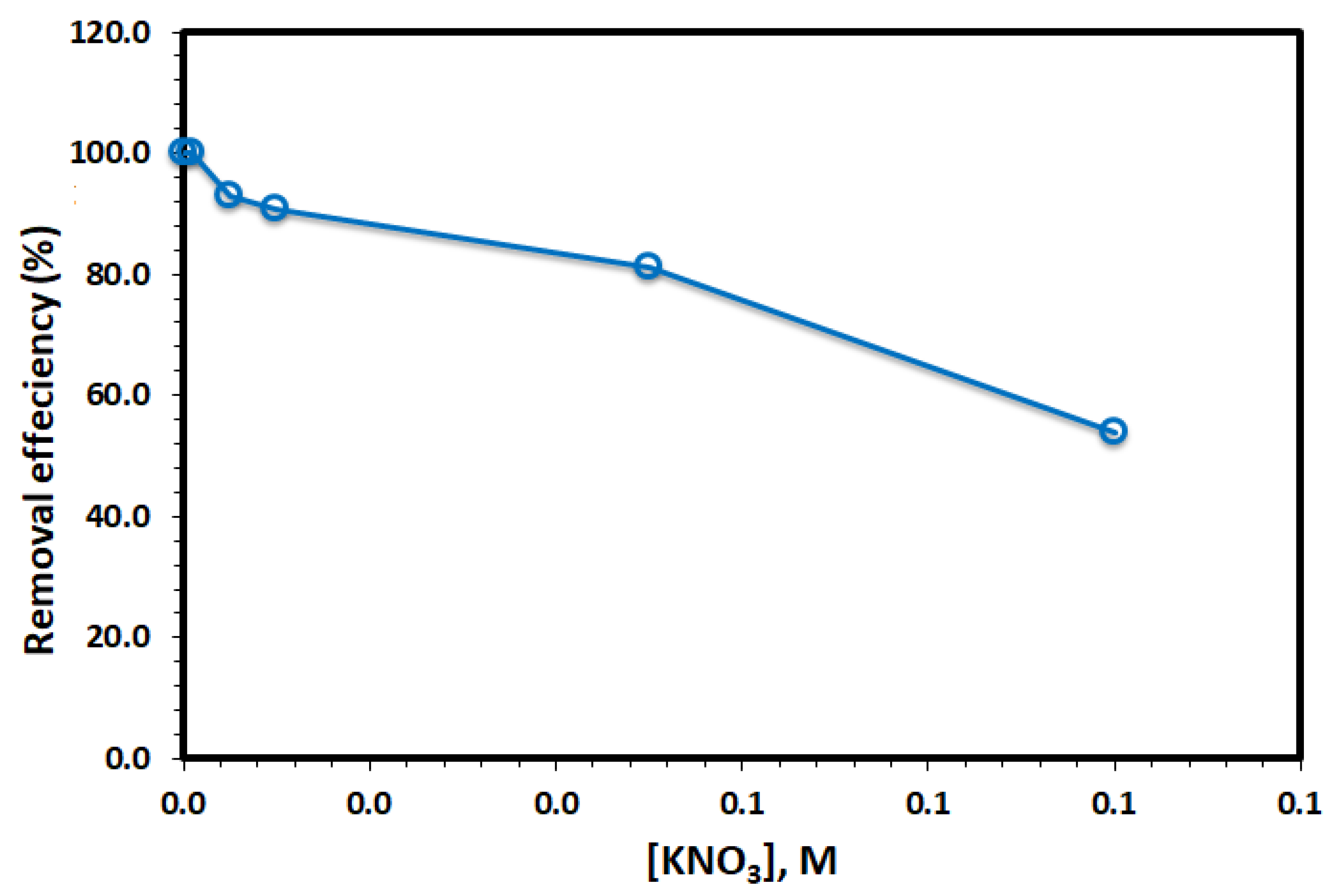
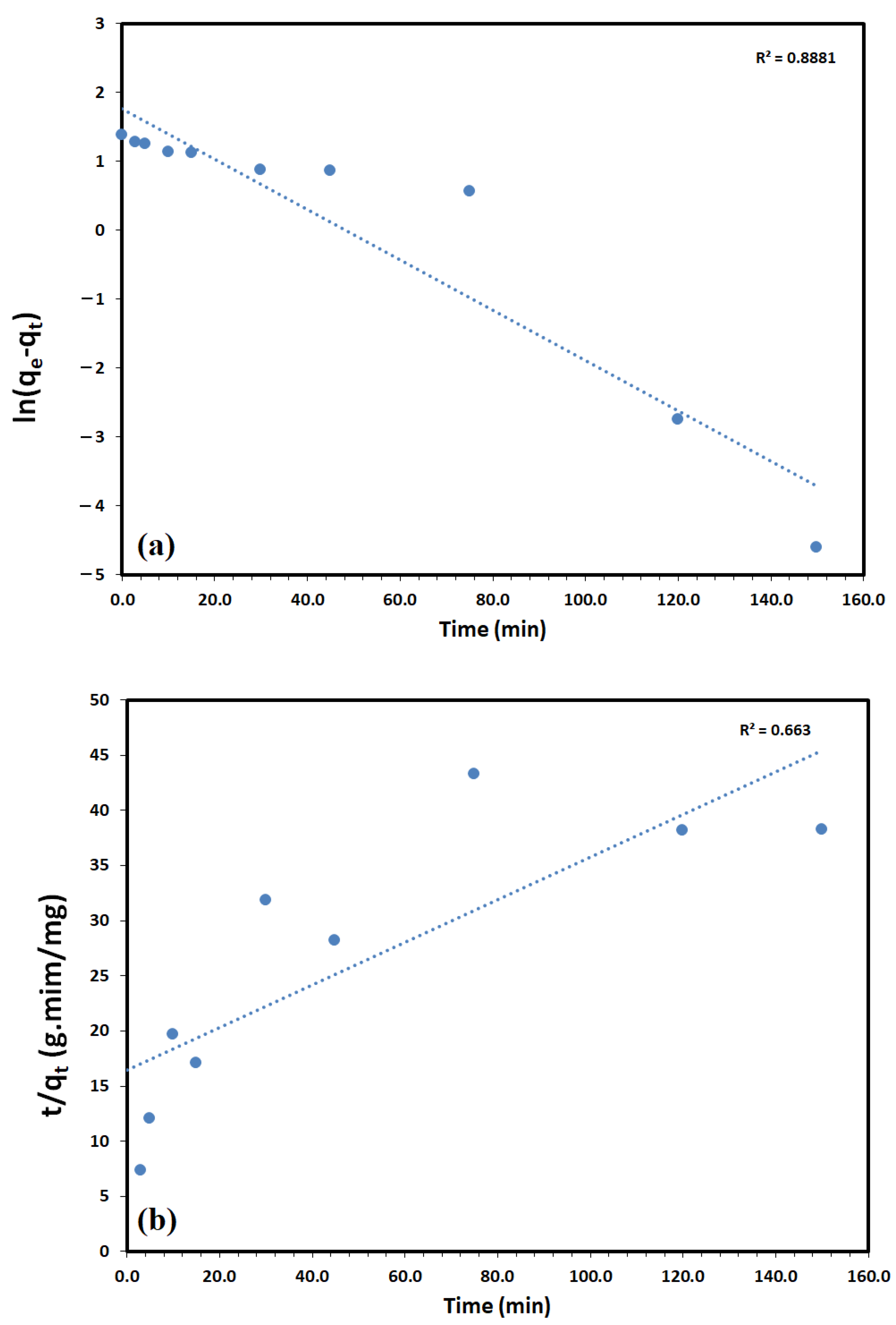
3.2. Adsorption Studies
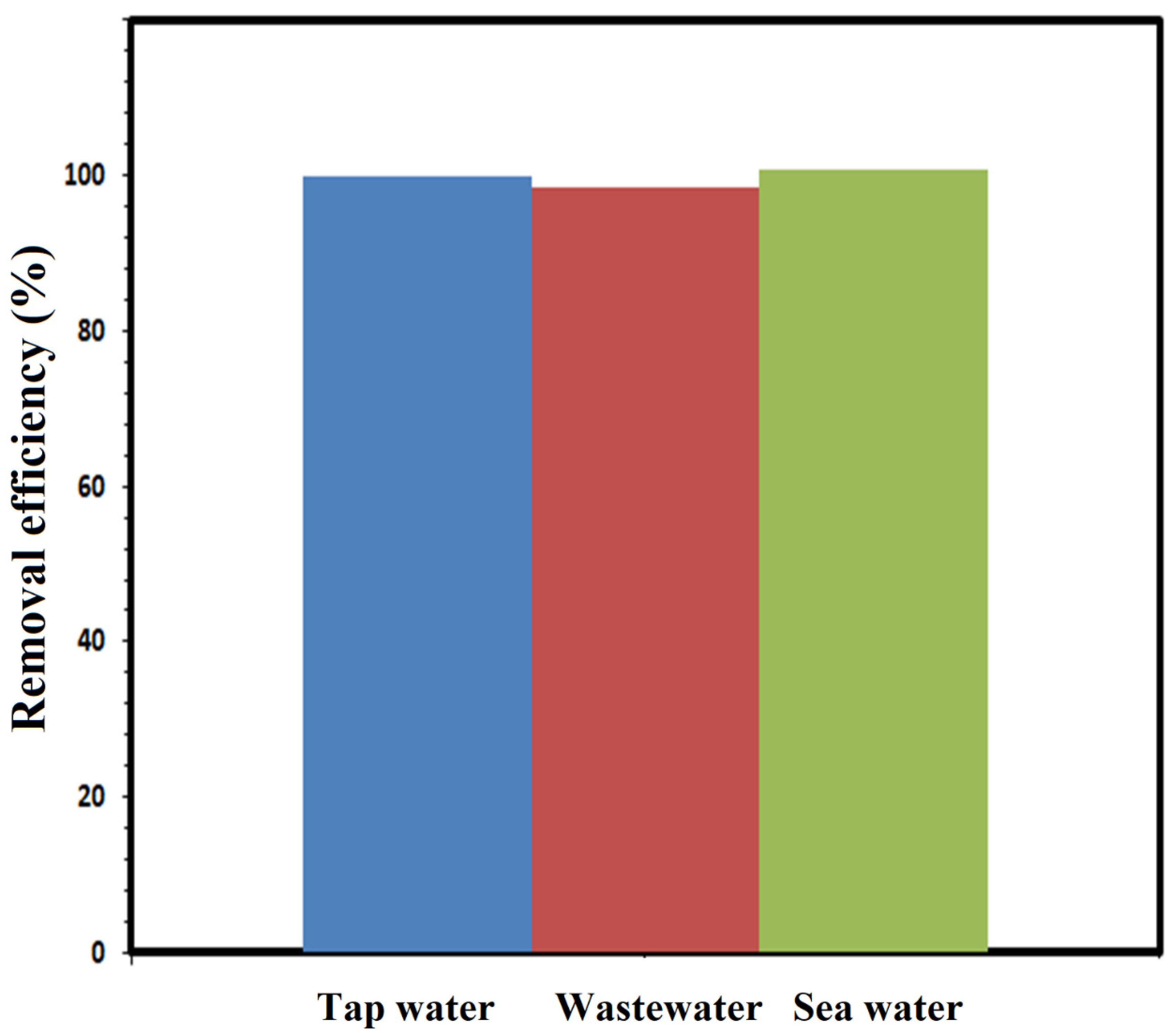
3.3. Environmental Samples
3.4. Reusability Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anju, A.; Ravi, S.P.; Bechan, S. Water pollution with special reference to pesticide contamination in India. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dechnik, J.; Janiak, C.; De, S. Aluminium fumarate metal-organic framework: A super adsorbent for fluoride from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 303, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rasalingam, S.; Peng, R.; Koodali, R.T. Removal of hazardous pollutants from wastewaters: Applications of TiO2-SiO2 mixed oxide materials. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 617405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniel, P. Investing in Tomorrow’S Liquid Gold. 2006. Available online: http://finance.yahoo.com/columnist/article/trenddesk/pp3748 (accessed on 16 November 2013).
- Barlow, M.; Clarke, T. Blue Gold: The Battle Against Corporate Theft of the World’s Water; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Sinha, R.; Roy, D. Toxicological effects of malachite green. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, S.-G.; Lu, L.; Gong, W.-X.; Liu, X.-W.; Gao, B.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y. Removal of malachite green (MG) from aqueous solutions by native and heat-treated anaerobic granular sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyai, S.; Tetana, Z.; Mathipa, M.; Ntsendwana, B.; Hintsho-Mbita, N. Green synthesis of Cadmium Sulphide nanoparticles for the photodegradation of Malachite green dye, Sulfisoxazole and removal of bacteria. Optik 2021, 247, 167851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qusti, A.H.; Malkhasian, A.Y.; Salam, M.A. Enhancement of CdS nanoparticles photocatalytic activity by Pt and In2O3 doping for the degradation of malachite green dye in water. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 255, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.L.; Koe, A.Z.Y.; Chan, Y.Y.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. Enhanced Sonocatalytic Performance of Non-Metal Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4)/Coconut Shell Husk Derived-Carbon Composite. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-W.; Yang, C.W.; Chao, W.L.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chang, B.V. Biodegradation of malachite green in milkfish pond sediments. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, H.; Wu, T.; Yu, L.; Liu, G.; Yu, Y. Insight into performance and mechanism of tea polyphenols and ferric ions on reductive decolorization of malachite green cationic dye under moderate conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, K.; Sherugar, P.; Rao, S.; Lavanya, C.; Balakrishna, G.R.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Padaki, M. Prolific approach for the removal of dyes by an effective interaction with polymer matrix using ultrafiltration membrane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, W.; Meng, M.; Hu, L.; Gan, W. Adsorption of Malachite Green and Pb2+ by KMnO4-Modified Biochar: Insights and Mechanisms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, G.; Chu, F.; Kong, Z. Lignin-inspired porous polymer networks as high-performance adsorbents for the efficient removal of malachite green dye. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 643, 128760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Abukhadra, M.R.; Adlii, A. Insight into the adsorption and photocatalytic behaviors of an organo-bentonite/Co3O4 green nanocomposite for malachite green synthetic dye and Cr (VI) metal ions: Application and mechanisms. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, X.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, Y.; Bu, D.; Cheng, D. Adsorption of dyes methyl violet and malachite green from aqueous solution on multi-step modified rice husk powder in single and binary systems: Characterization, adsorption behavior and physical interpretations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, D.; Kerkez Kuyumcu, Ö.; Bayazit Ş, S.; Abdel Salam, M. Adsorptive removal of malachite green and Rhodamine B dyes on Fe3O4/activated carbon composite. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymaniha, M.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Rafieerad, A.R.; Maleki, A.; Amiri, A. Promoting role of MXene nanosheets in biomedical sciences: Therapeutic and biosensing innovations. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamil, F.; Ali, H.M.; Janjua, M.M. MXene based advanced materials for thermal energy storage: A recent review. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, T.; Tran, D.T.; Le, H.T.; Nguyen, D.C.; Van Hoa, H.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in MXene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Liu, B.; Qiu, H.; Shi, X.; Cao, D.; Gu, J. MXenes for polymer matrix electromagnetic interference shielding composites: A review. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I. Potential of MXenes in Water Desalination: Current Status and Perspectives. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chirica, I.M.; Mirea, A.G.; Neaţu, Ş.; Florea, M.; Barsoum, M.W.; Neaţu, F. Applications of MAX phases and MXenes as catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 19589–19612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T. MXenes as emerging two-dimensional analytical modalities for potential recognition of hazardous environmental contaminants. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 24, 100859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Kausar, F.; Rizwan, K.; Adeel, M.; Sher, F.; Alwadai, N.; Alshammari, F.H. Two dimensional MXenes as emerging paradigm for adsorptive removal of toxic metallic pollutants from wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Gholamirad, F.; Yu, M.; Park, C.M.; Jang, A.; Jang, M.; Taheri-Qazvini, N.; Yoon, Y. Enhanced adsorption performance for selected pharmaceutical compounds by sonicated Ti3C2TX MXene. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I. MXenes (two-dimensional metal carbides) as emerging nanomaterials for water purification: Progress, challenges and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanweer, M.S.; Chauhan, H.; Alam, M. Advanced 2D Nanomaterial Composites: Applications in Adsorption of Water Pollutants and Toxic Gases. In 2D Nanomaterials for Energy and Environmental Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 97–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, G.P.; Soon, C.F.; Morsin, M.; Ahmad, M.K.; Nayan, N.; Tee, K.S. Synthesis, characterization and antifungal property of Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 20306–20312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Mashtalir, O.; Carle, J.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Husnain, S.M.; Shahzad, F.; Mujtaba-ul-Hassan, S.; Mehmood, M.; Ahmad, J.; Rahman, S.; Mehran, M.T. Two-dimensional transition metal carbide (Ti3C2Tx) as an efficient adsorbent to remove cesium (Cs+). Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 11803–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Removal of Rhodamine B with Fe-supported bentonite as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst under visible irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 178, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoc, E.; Nuhoglu, Y. Potential of tea factory waste for chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solutions: Thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.; Nawaz, H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.; Adeoye, I.O.; Bello, O.S. Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, Q.; Li, M.; Du, S.; Huang, Q.; Lee, J.; Han, Y.-H. Facile preparation of in situ coated Ti3C2Tx/ Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composites and their electromagnetic performance. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gel.oster Stoffe-About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rudzinski, W.; Plazinski, W. On the applicability of the pseudo-second order equation to represent the kinetics of adsorption at solid/solution interfaces: A theoretical analysis based on the statistical rate theory. Adsorption 2009, 15, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owija, N.Y.; Kosa, S.; Abdel Salam, M. Removal of the toxic cadmium ions from aqueous solutions by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.L.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kang, S.-W.; Cho, J.-S.; Jeon, J.-R.; Lee, Y.-B.; Seo, D.-C. Sorption behavior of malachite green onto pristine lignin to evaluate the possibility as a dye adsorbent by lignin. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albukhari, S.M.; Abdel Salam, M.; Aldawsari, A.M.M. Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Water Using MXene (Ti3C2) Nanosheets. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105996
Albukhari SM, Abdel Salam M, Aldawsari AMM. Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Water Using MXene (Ti3C2) Nanosheets. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105996
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbukhari, Soha M., Mohamed Abdel Salam, and Ahad M. M. Aldawsari. 2022. "Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Water Using MXene (Ti3C2) Nanosheets" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105996
APA StyleAlbukhari, S. M., Abdel Salam, M., & Aldawsari, A. M. M. (2022). Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Water Using MXene (Ti3C2) Nanosheets. Sustainability, 14(10), 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105996






