Using Lean to Improve Operational Performance in a Retail Store and E-Commerce Service: A Portuguese Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
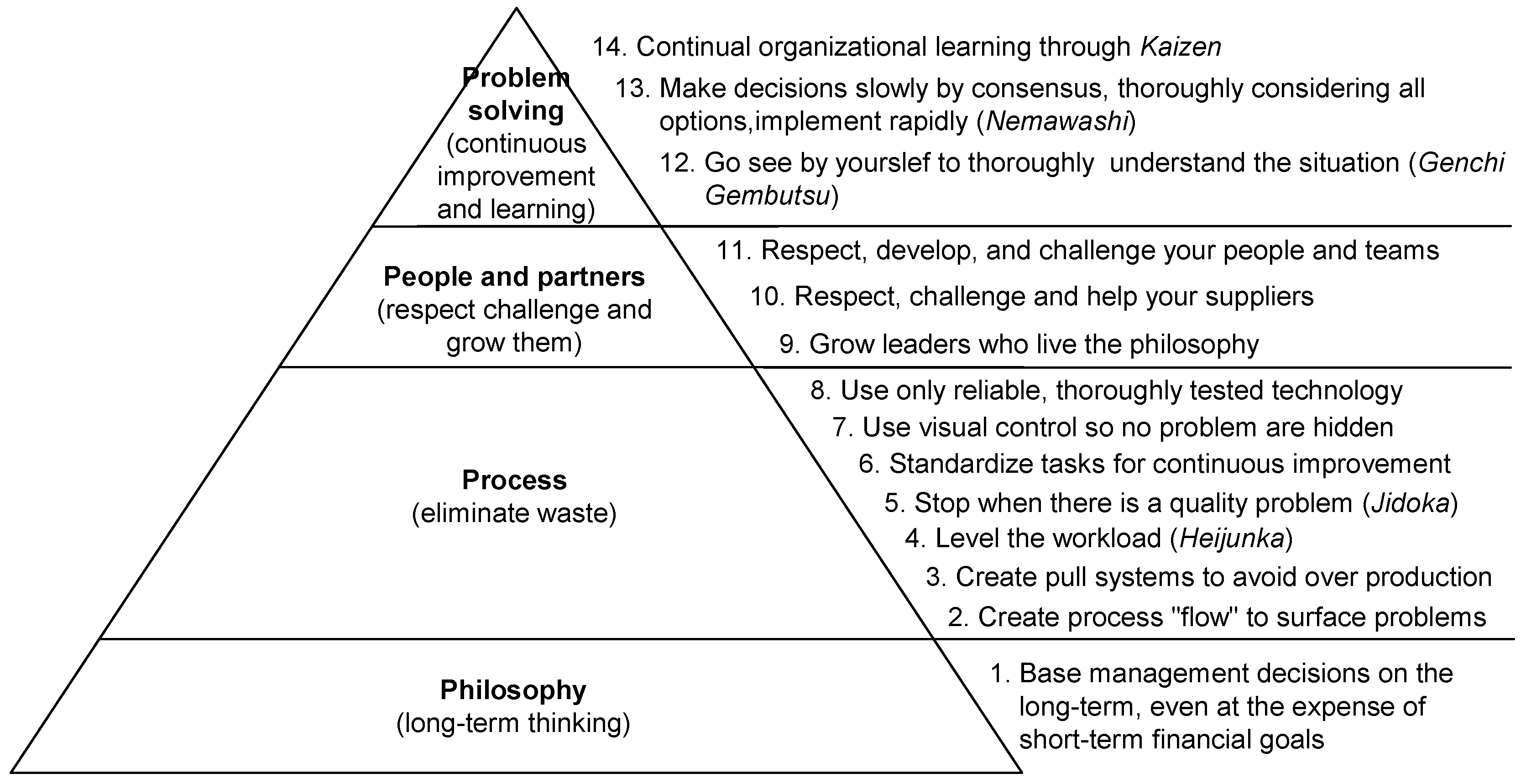
2.1. Lean Management
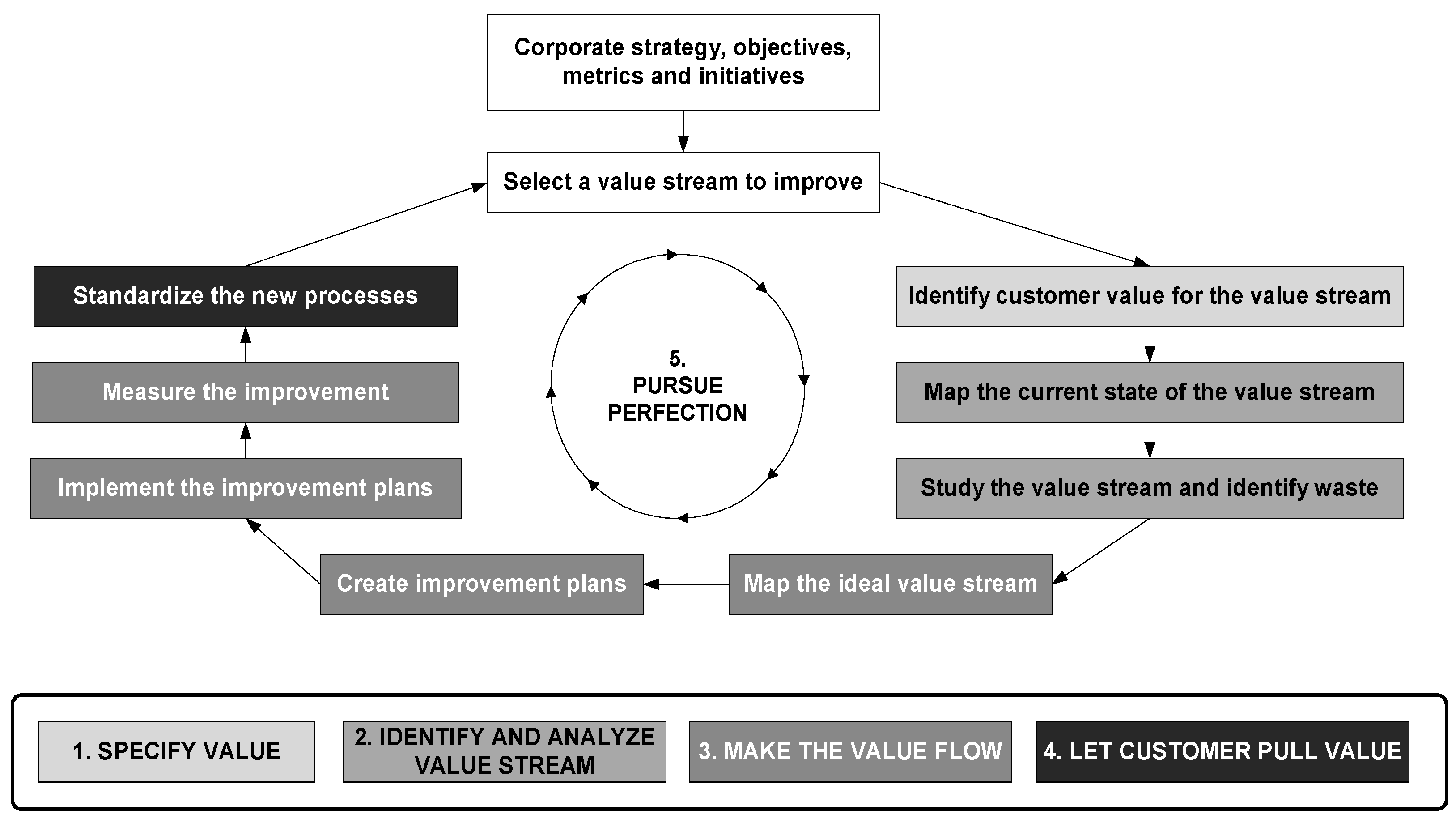
2.1.1. Value Stream Management—VSM
- Specify value. Understand who the customer is, determine what their needs are and define what is “value” for the customer.
- Identify and analyze the value stream. Map the flow of value, perform value-added analysis and identify existing waste factors in the value stream.
- Make the value flow. Design, develop and implement a future state, with less waste factors, where value will flow continuously in the direction of the customer.
- Let the customer pull value. Standardize the value stream and initiate the flow when the customer pulls their needs.
- Pursue perfection. Repeat the cycle towards the creation of new future-state maps and continuously improve in order to seek perfection.
2.1.2. Kanban
2.2. Lean Management in the Retail Sector
3. Case Study
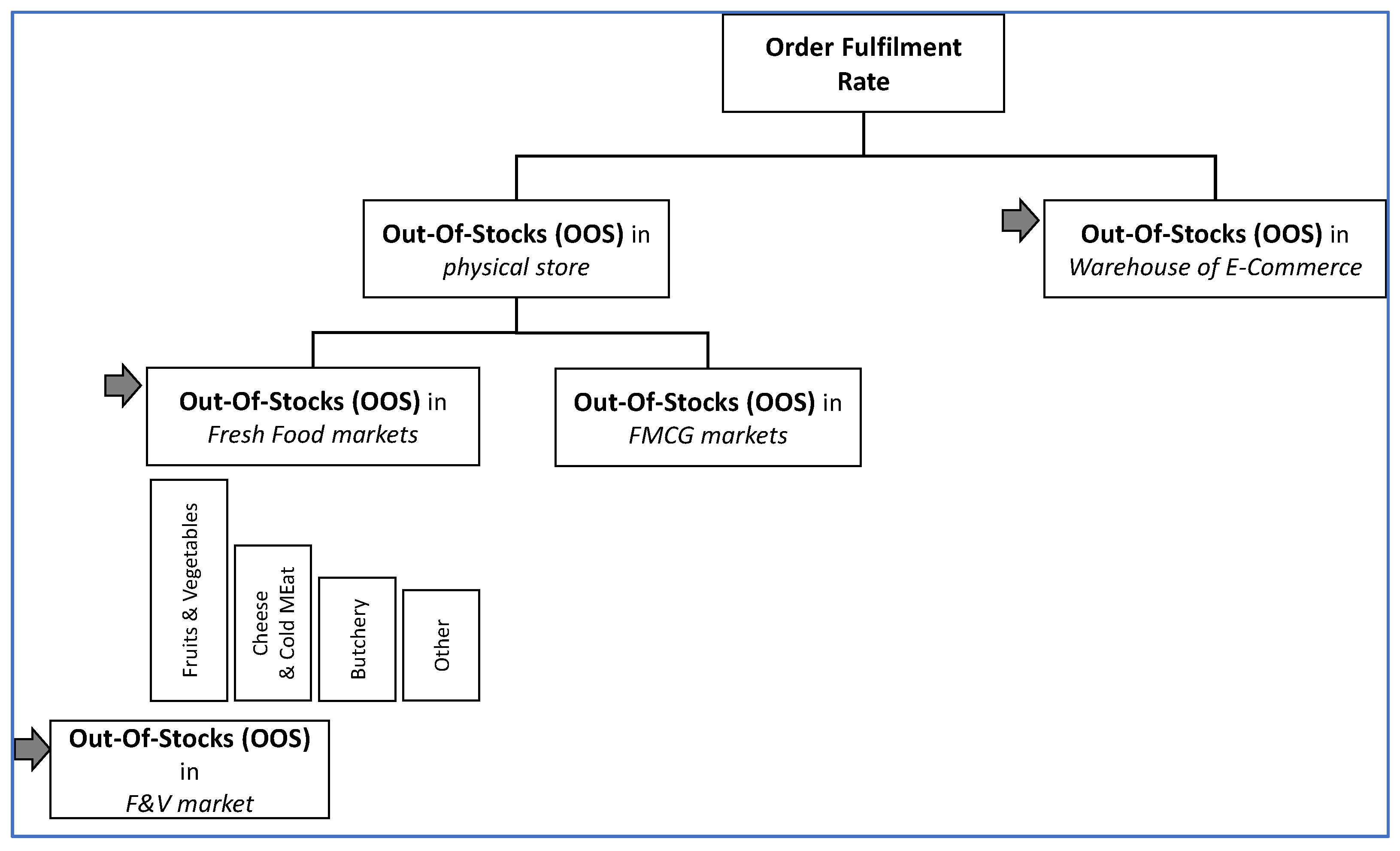
3.1. Problem Statement
- The warehouse of E-Commerce.
- The market of F V in the physical store.
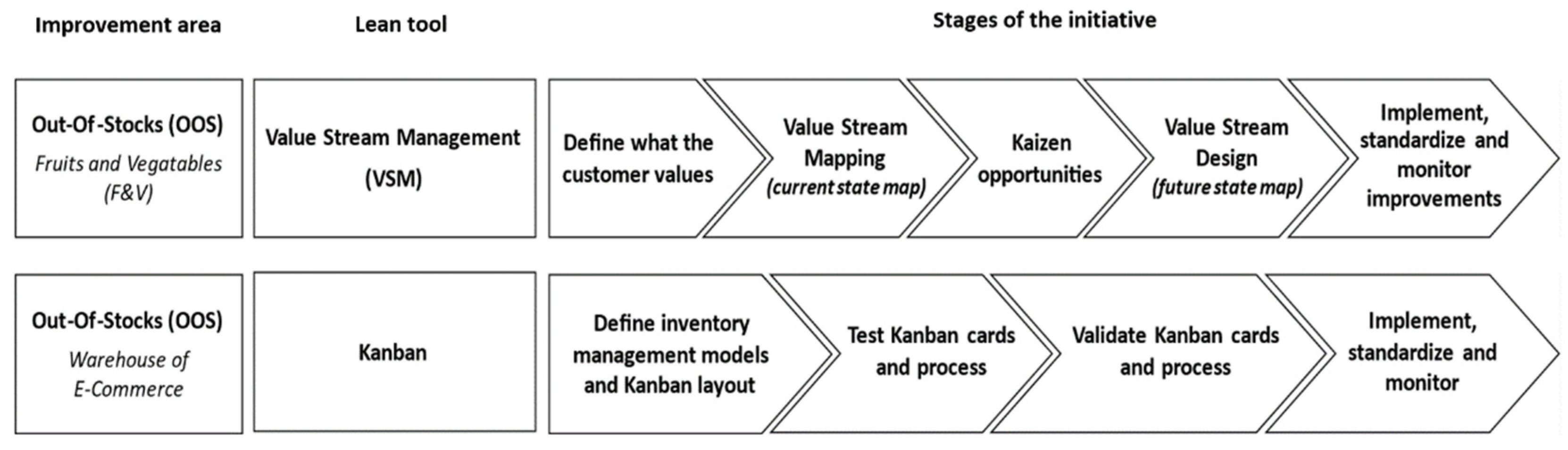
3.2. Methodology
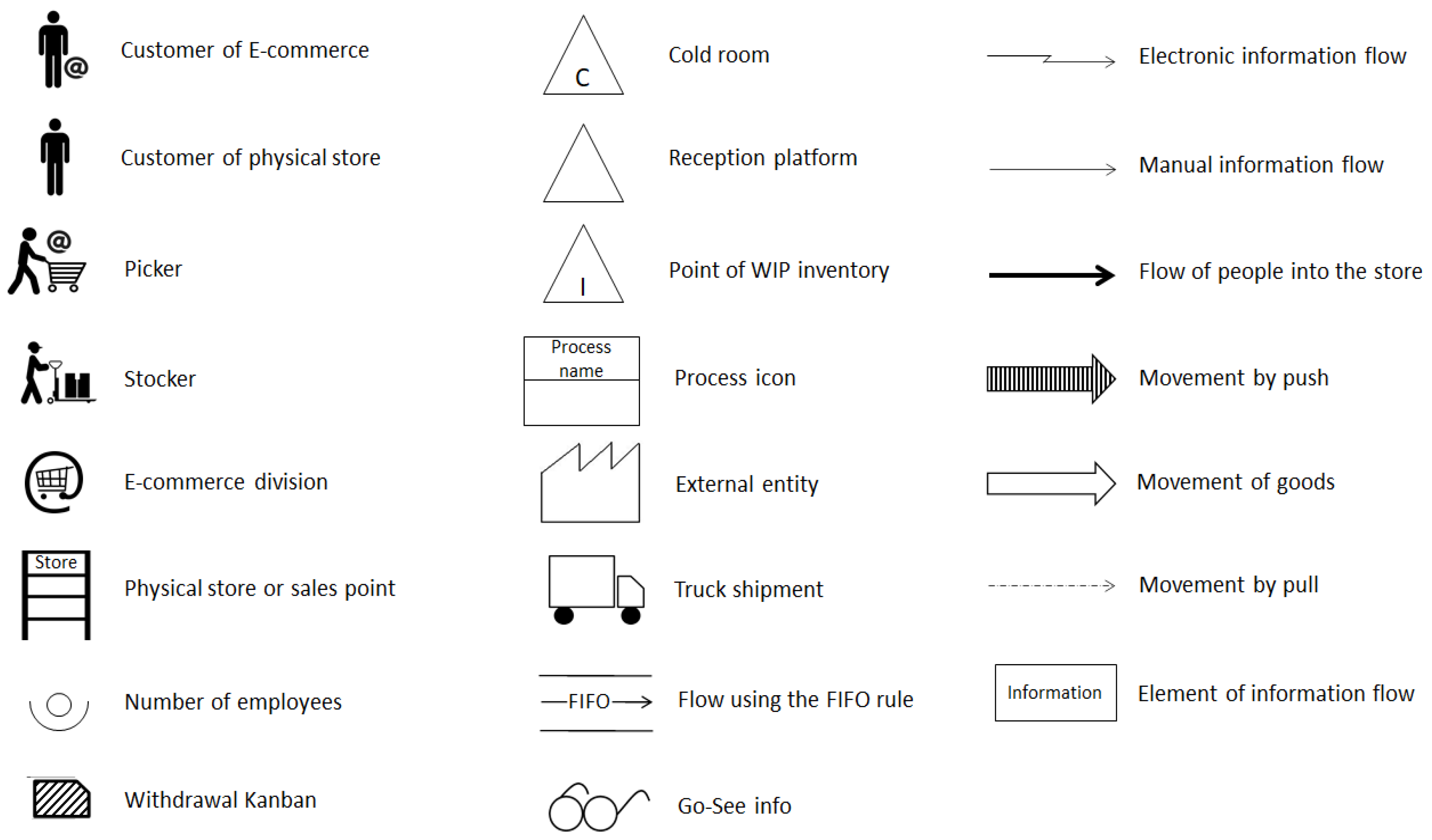
3.3. Value Stream Mapping
3.3.1. Stage 1—Define What the Customer Values
- The consumer that ordered online.
- The client that buys in the physical store.
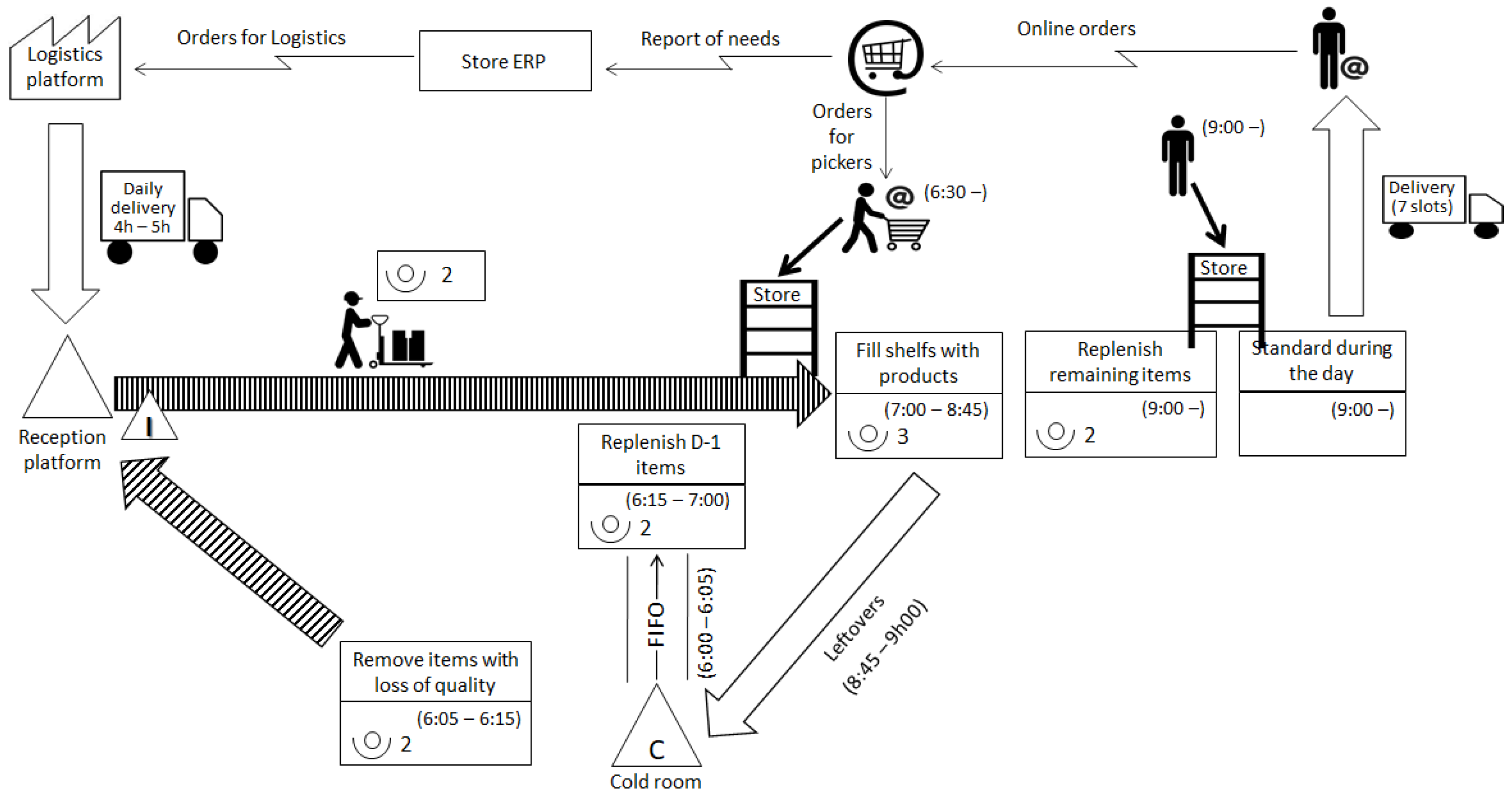
3.3.2. Stage 2—Value Stream Mapping (Current State Map)
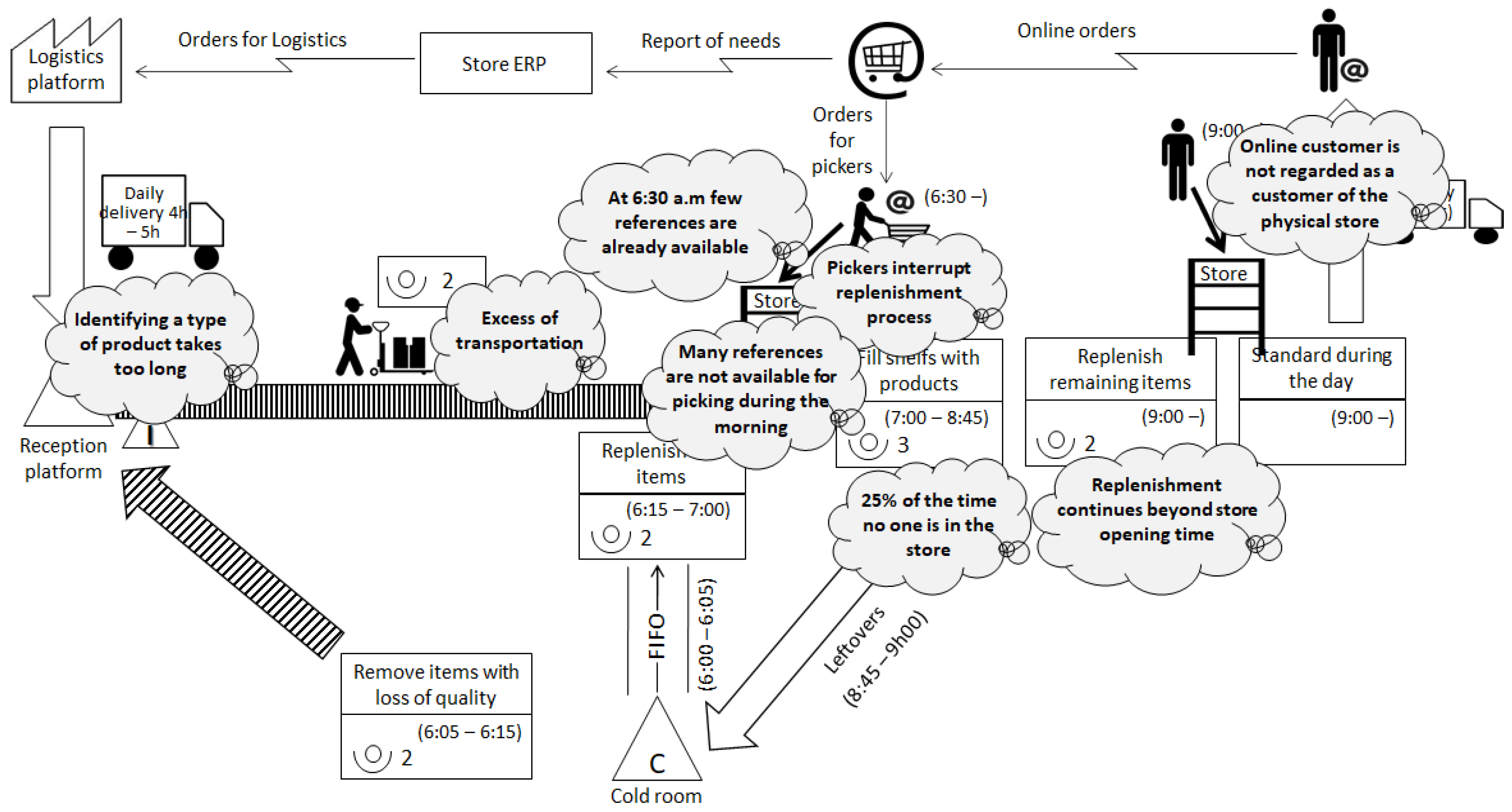
3.3.3. Stage 3—Kaizen Opportunities
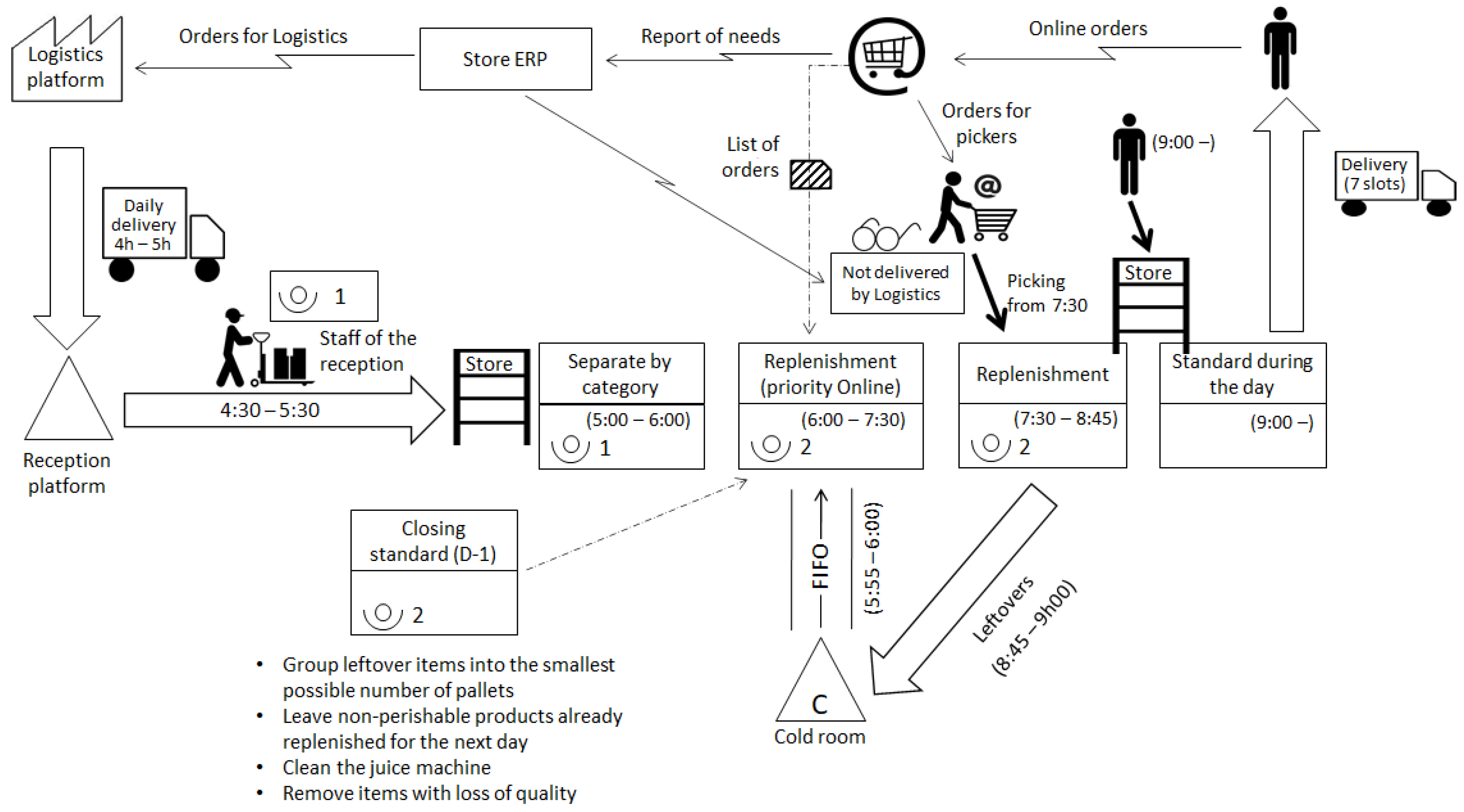
3.3.4. Stage 4—Value Stream Design (Future State Map)
- Instead of remaining in the reception, the pallets are moved by the personnel of this area into the corridor of the store nearby the FV market area. A stocker from the FV market arrives 1 h earlier at 5 a.m. to dismantle the pallets and sort the products by category.
- The other two stockers of the FV market arrive at 6 a.m. to start refilling the shelves. Unlike what happened before, these two people remain in the store and do not need to move to the backroom of the store nor to the reception area. Any necessary transportation or movement is exclusively performed by the worker that arrived earlier, who also has the role of supplying all the goods to be replenished and to remove pallets and empty boxes. Lean calls to this role “Mizusumashi” [106].
- To leverage the workload among work shift, it was decided that the evening shift (responsible for closing the store) would advance the replenishment process by refilling all the products that do not need to remain at a controlled temperature. This takes away needed work time for the tasks necessary to prepare the store opening.
- The managers of the store and of the E-Commerce division agreed that the pickers would only go to the FV section from 7:30 onwards. Between 6 a.m. and 7:30 a.m. the priority for the stockers is to refill all the product references required by the customer that ordered online. Every day, the E-Commerce division communicates to the store the list of products to be picked, so this is similar to a withdrawal kanban system. It avoids unnecessary interruption in the work performed by both the pickers and stockers.
- The pickers will have access to the list of goods that are not available in the store because they were not delivered by the truck that arrived from the logistics platform. This will avoid pickers wasting further time.
3.3.5. Stage 5—Implement, Standardize and Monitor Improvements
3.4. Kanban
3.4.1. Stage 1—Define Inventory Management Models and Kanban Layout
- Conversion Factor (number of product items contained in a supplied box of product);
- Photo and description of the product;
- Product European Article Number (EAN) code—a type of barcode that encodes an article number;
- Name of the supplier;
- Days of the week to place an order;
- Days of the week provided for receiving orders.
3.4.2. Stage 2—Test the Kanban Cards and Process
3.4.3. Stage 3—Validate the Kanban Cards and Process
3.4.4. Stage 4—Implement, Standardize and Monitor
3.5. Research Results
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aastrup, J.; Kotzab, H. Forty years of out-of-stock research—And shelves are still empty. Int. Rev. Retail Distrib. Consum. Res. 2010, 20, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.H.; Oliva, R.; Liu, S. On-shelf availability, retail performance, and external audits: A field experience. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2016, 25, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benrqya, Y. An examination of the effects of cross-docking on retail out of stock. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2021, 49, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, A.C.; Mendes, D.; Nababteh, M. In-store logistics: An analysis of on-shelf availability and stockout responses for three product groups. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2007, 10, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.H. Assessment of the effect of out-of-stock on customers purchasing behavior. Int. J. Transp. Eng. Technol. 2019, 5, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Lewis, M. Stockouts in online retailing. J. Mark. Res. 2011, 48, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; De Leeuw, S.; Dullaert, W.E.H. Consumer behaviour and order fulfilment in online retailing: A systematic review. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2018, 20, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Sergi, B.S.; Esposito, M. Literature review of emerging trends and future directions of E-Commerce in global business landscape. World Rev. Entrep. Manag. Sust. Dev. 2019, 15, 226–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabius, V.; Kohli, S.; Veranen, S.M.; Timelin, B. How COVID-19 is changing consumer behavior—Now and forever. McKinsey Perspect. Retail Consum. Goods 2020, 8, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie, C.; Fosso-Wamba, S.; Arnaud, J.B. Online consumer resilience during a pandemic: An exploratory study of E-Commerce behavior before, during and after a COVID-19 lockdown. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 61, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Briel, F. The future of omnichannel retail: A four-stage Delphi study. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 132, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, M.; Kwan, S.K.; Mitronen, L. From the store to omnichannel retail: Looking back over three decades of research. Int. Rev. Distrib. Consum. Res. 2021, 31, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, L. The impact of cross-channel integration on retailers’ sales growth. J. Retail. 2015, 91, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Lim, E.T.K.; Goh, J.M.; Yang, F.; Lee, M.K.O. Customer’s reaction to cross-channel integration in omnichannel retailing: The mediating roles of retailer uncertainty, identity attractiveness, and switching costs. Decis. Support Syst. 2018, 109, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tweed, T.; Al-Hussein, M.; Nasseri, R. Development of Lean model for house construction using value stream mapping. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2009, 135, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturiale, L.; Scuderi, A. The marketplaces and the integration between physic and virtual in the business models of fruit and vegetables E-Commerce. HAICTA Comput. Sci. Bus. 2017, 2030, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Van Donselaar, K.H.; Peters, J.; De Jong, A.; Broekmeulen, R.A.C.M. Analysis and Forecasting of Demand During Promotions for Perishable Items. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 172, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Woensel, T.; Van Donselaar, K.; Broekmeulen, R.; Fransoo, J. Consumer responses to shelf out-of-stocks of perishable products. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2007, 37, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.; Minvielle, A. A fresh take on food retailing. McKinsey Perspect. Retail Consum. Goods 2014, 2, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Chaudhuri, A.; Srivastava, R.K. Propagation of risks and their impact on performance in fresh food retail. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2015, 26, 568–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirci, M.; Biçer, I.; Seifert, R.W. Optimal replenishment cycle for perishable items facing demand uncertainty in a two-echelon inventory system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, R. The effects of application of Lean concept in retail. Econ. Ser. Manag. 2012, 15, 88–98. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, T. Integration of Lean operation and pricing strategy in retail. J. Mark. Dev. Compet. 2015, 9, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Myerson, P. Lean retail. In The Routledge Companion to Lean Management; Netland, T.H., Daryl, J., Powell, D.J., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 413–421. [Google Scholar]
- Madhani, P.M. Performance optimisation of retail industry: Lean Six Sigma approach. ASBM J. Manag. 2020, 13, 74–91. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.; Braga, A.; Mota, S.; Soares, M.; Ferreira, M.R. A Lean-Kaizen implementation: A case study in the food retail industry. In Reviving Businesses with New Organizational Change Management Strategies; Geada, N., Anunciação, P., Eds.; IGI Global: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 182–195. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, M.; Childerhouse, P. Retail value stream management. Int. J. Electron. Cust. Relatsh. Manag. 2010, 4, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, P.; Holweg, M.; Rich, N. Learning to evolve: A review of contemporary Lean Thinking. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2004, 24, 994–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhasin, S. Clarification of the Lean concept. In Lean Management beyond Manufacturing: A Holistic Approach; Bhasin, S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Netland, T.H.; Powell, D.J. A Lean world. In The Routledge Companion to Lean Management; Netland, T.H., Powell, D.J., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 465–473. [Google Scholar]
- Womack, J.P.; Jones, D.T. Lean consumption. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2005, 83, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruo, S.; Toma, S.G. From Toyota Production System to Lean retailing. Lessons from Seven-Eleven Japan. In Advances in Production Management System; Olhager, J., Perrson, F., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 246, pp. 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, M. Gemba Kaizen: A Commonsense Approach to a Continuous Improvement Strategy, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter, E.D.; Maleyeff, J. The integration of Lean management and Six Sigma. TQM Mag. 2005, 17, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, K.B. Four decades of Lean: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2012, 3, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, W.J.; Spearman, M.S. The lenses of Lean: Visioning the science and practice of efficiency. J. Oper. Manag. 2020, 67, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Jo, H. The mutation of the Toyota Production System: Adapting the TPS at Hyundai Motor Company. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 3665–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Osono, E.; Shimizu, N. The contradictions that drive Toyota’s success. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2008, 86, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cusumano, M.A. Manufacturing innovation: Lessons from the Japanese auto industry. Sloan Manag. Rev. 1988, 30, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Holweg, M. The genealogy of Lean production. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetsch, D.L.; Davis, S.B. Quality Management for Organizational Excellence: Introduction to Total Quality, 8th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 366–395. [Google Scholar]
- Krafcik, J.F. The triumph of the Lean production system. Sloan Manag. Rev. 1988, 30, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Womack, J.P.; Jones, D.T.; Roos, D. The Machine that Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production—Toyota’s Secret Weapon in the Global Car Wars that is Now Revolutionizing World Industry; Rawson Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 17–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tischler, L. Bringing Lean to the office. Qual. Prog. 2006, 39, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C.; Cox, R.A. Value stream management for Lean office—A case study. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2012, 2, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, T.T.; De Oliveira, M.A.; Futami, A.H. A Systematic Literature Review on Lean Office. Ind. Eng. Manag. Syst. 2019, 18, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, M.P.J.; Spedding, T.A. The evolution of Lean Six Sigma. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2010, 27, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Tesai, T.N. Lean Six Sigma: A categorized review of the literature. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2016, 7, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Rathi, R. A structured review of Lean Six Sigma in various industrial sectors. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2019, 10, 622–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T. Toyota Production System: Beyond Large Scale Production; Productivity Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pieńkowski, M. Waste measurement techniques for Lean companies. Lean Think. 2014, 5, 9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S. Muda, Muri and Mura. Six Sigma Forum Mag. 2014, 13, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bicheno, J.; Holweg, M. The Lean Toolbox: A Handbook for Lean Transformation, 5th ed.; PICSIE Books: Buckingham, UK, 2016; pp. 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cusumano, M.A.; Holweg, M.; Howell, J.; Netland, T.; Shah, R.; Shook, J.; Ward, P.; Womack, J. Commentaries on the lenses of Lean. J. Oper. Manag. 2021, 67, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.D. Hearing the Voice of the Shingo Principles: Creating Sustainable Cultures of Enterprise Excellence; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 21–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liker, J.K. The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the World’s Greatest Manufacturer; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 27–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, N.; Baghel, A. An overview of continuous improvement: From the past to the present. Manag. Decis. 2005, 43, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alaskari, O.; Ahmad, M.M.; Pinedo-Cuenca, R. Development of a methodology to assist manufacturing SMEs in the selection of appropriate lean tools. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2016, 7, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, M.; Shook, J. Learning to See—Value Stream Mapping to Add Value and Eliminate Muda; The Lean Enterprise Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Seth, D.; Nitin, S.; Pratik, D. Application of value stream mapping (VSM) for Lean and cycle time reduction in complex production environments: A case study. Prod. Plan. Control 2017, 28, 398–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belokar, R.M.; Vikas, K.; Sandeep, S.K. An application of value stream mapping in automotive industry: A case study. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2012, 1, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Khatri, A.; Mathur, Y.B. Application of value stream mapping in Bhujia Manufacturing. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.A.; Karim, A. A systematic approach to evaluate the process improvement in Lean manufacturing organizations. In Sustainable Manufacturing: Shaping Global Value Creation; Seliger, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Saleeshya, P.G.; Rajan, V.; Premkumar, N. Optimising the financial performance of supply chain—A case study. Int. J. Adv. Oper. Manag. 2019, 11, 232–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanski, G.; Schönemann, M.; Thiede, S.; Andrew, S.; Herrmann, C. An extended energy value stream approach applied on the electronics industry. In Advances in Production Management Systems. Competitive Manufacturing for Innovative Products and Services; Emmanouilidis, C., Taisch, M., Kiritsis, D., Eds.; Spinger: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, P.; Rich, N.; Bicheno, J.; Brunt, D.; Taylor, D.; Butterworth, C.; Sullivan, J. Value Stream Management. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 1998, 9, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlach, K. Value Stream Design: The Way Towards a Lean Factory; Springer: Dortmund, Germany, 2013; pp. 25–96. [Google Scholar]
- Oberhausen, C.; Plapper, P. Value stream management in the Lean manufacturing laboratory. Procedia CIRP 2015, 32, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sony, M. Industry 4.0 and Lean management: A proposed integration model and research propositions. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2018, 6, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, K.; Osterling, M. Value Stream Mapping: How to Visualize Work and Align Leadership for Organizational Transformation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarini, A. Lean Organization: From the Tools of the Toyota Production System to Lean Office; Springer: Bologna, Italy, 2013; pp. 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, M., Jr.; Filho, M.G. Variations of the kanban system: Literature review and classification. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2010, 125, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A.A.; Sharif, S.M.; Esa, M.M. Lean manufacturing case study with kanban system implementation. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2013, 7, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Kusiak, A. Overview of kanban systems. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 1996, 9, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürer, M.; Stevenson, M.; Protzman, C. Card-Based Control Systems for a Lean Work Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 25–56. [Google Scholar]
- Frein, Y.; Mascolo, M.D.; Dallery, Y. On the design of generalized kanban control systems. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1995, 15, 158–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Panneerselvam, R. Literature review of JIT-kanban system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 32, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, K.; Nomura, J.; Takakuwo, S. Module-Based Modeling and Analysis of Just-In-Time Production Adopting Dual-Card Kanban System and Mizusumashi Worker. In Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Esparrago, R.A., Jr. Kanban. Prod. Inventory Manag. J. 1988, 29, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kouri, I.A.; Salmimaa, T.; Vilpola, I. The principles and planning process of an electronic kanban system. In Novel Algorithms and Techniques in Telecommunications, Automation and Industrial Electronics; Sobh, T., Elleithy, K., Mahmood, A., Mohammad, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrech, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.K. Managing a flow line with single-kanban, dual kanban or ConWip. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2000, 9, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akturk, M.S.; Erhun, F. An Overview of design and operational issues of kanban systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1999, 37, 3859–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monden, Y. Review of kanban system principles. In Toyota Production System, 2nd ed.; Monden, Y., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Braglia, M.; Gabbrielli, R.; Marrazzini, L. Rolling kanban: A new visual tool to schedule family batch manufacturing processes with kanban. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 3998–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghi, M.; Rostamzadeh, R.; Mascle, C. Kanban and value stream mapping analysis in Lean manufacturing philosophy via Simulations: A plastic fabrication (case study). Int. J. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2015, 20, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, S.; Robb, D.J.; DeHoratius, N. Retail store operations: Literature review and research directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 265, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, R.; Monzón, A. Mobility restrictions and E-Commerce: Holistic balance in Madrid centre during COVID-19 lockdown. Economies 2021, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmignani, G.; Zammori, F. Lean thinking in the luxury-fashion market: Evidences from an extensive industrial project. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2015, 43, 988–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, J.R.; Manikas, A.S.; Gattiker, T.F. Operational leanness and retail firm performance since 1980. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 197, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaca, C.; Santos, J.; Errasti, A.; Viles, E. Lean thinking with improvement teams in retail distribution: A case study. Total Qual. Manag. 2012, 23, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernathy, F.H.; Dunlop, J.T.; Hammond, J.H.; Weil, D. A Stitch in Time: Lean Retailing and the Transformation of Manufacturing—Lessons from the Apparel and Textile Industries; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 39–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, J.D.; Hinrichs, C.C. The long reach of Lean retailing: Firm embeddedness and Wal-Mart’s implementation of local produce Sourcing in the US. Environ. Plan. 2017, 49, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.; Lund, J. Variations on a Lean theme: Work restructuring in retail distribution. New Technol. Work Employ. 2006, 21, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daine, T.; Winnington, T.; Head, P. Transition from push to pull in the wholesale/retail sector: Lessons to be learned from Lean. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2011, 8, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernie, J.; Grant, D.B. On-shelf availability in UK retailing. In Logistics and Retail Management—Emerging Issues and New Challenges in the Retail Supply Chain, 4th ed.; Fernie, J., Sparks, L., Eds.; Kogan Page: London, UK, 2014; pp. 179–204. [Google Scholar]
- Morcillo-Bellido, J.; Duran, A. Supply chain sustainability in Spanish major retailer through strategic alliances and Lean practices. In Closing the Gap between Practice and Research in Industrial Engineering; Viles, E., Ormazábal, M., Lleó, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- López-González, A.; Lois-González, R.C.; Fernández-Casal, R. Mercadona (Spain): A retail model in expansion. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2013, 41, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J. How Mercadona Fixes Retail’s Last 10 Yards Problem; Research & Ideas; Harvard Business School: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Onetto, M. When Toyota Met E-Commerce—Lean at Amazon. McKinsey Q. 2014, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, N. How Zara Used Lean to Become the Largest Fashion Retailer. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-zara-used-lean-become-largest-fashion-retailer-nathan-robinson/ (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Domingo, T.M. The Adoption of Lean Techniques to Optimize the On-Shelf Availability of Products and Drive Business Performance in the Food Industry: A South African Manufacturing and Retail Case Study. Masters’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.R.; Lindsay, W.M. An Introduction to Six Sigma & Process Improvement, 2nd ed.; CENGAGE Learning: Stamford, CT, USA, 2015; pp. 65–198. [Google Scholar]
- Özkavukcu, A.; Durmuşoğlu, M.B. Product development by Hoshin Kanri approach: An application in retail sector. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2016, 34, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, J. Lean in Retail—Implementation in Stores. In Proceedings of the NES2017 Conference, Lund, Sweden, 20–23 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhadi, A. Applying Lean manufacturing to retail business to prevent the spread of COVID-19. Acad. Strateg. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, E.A. Total Flow Management: Achieving Excellence with Kaizen and Lean Supply Chains; Kaizen Institute: Oporto, Portugal, 2009; pp. 1–277. [Google Scholar]


| Customer of the Physical Store | Customer That Ordered Online | |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery requirements | Have the desired product available in the correct place from the moment the store is opened | Have the desired product available in the correct place when the picking is needed |
| Quality requirements | Have the product looking fresh and within the expiration date | |
| Name of KPI | Baseline | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Out-of-stock (OOS) rate in the fresh food markets | 6.5% | 5.0% |
| Out-of-stock (OOS) rate in FV | 10.0% | 7.5% |
| Name of KPI | Baseline | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Out-of-stock (OOS) rate in the E-Commerce warehouse | 1.50% | 0.50% |
| Name of KPI | Before the Initiative | After the Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Order Fulfilment Rate (overall) | 92.5% | 94.5% |
| Order Fulfilment Rate in F&V | 90.0% | 93.0% |
| OOS in the fresh food markets | 6.5% | 5.8% |
| OOS rate in F&V | 10.0% | 4.2% |
| OOS rate in the E-Commerce warehouse | 1.50% | 0.30% |
| Number Out-Of-Stocks per day (F&V) | 70 stockouts/day | 45 stockouts/day |
| Number Out-Of-Stocks per day (Warehouse) | 10 stockouts/day | 2 stockouts/day |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, P.A.; Jorge, D.; Reis, J. Using Lean to Improve Operational Performance in a Retail Store and E-Commerce Service: A Portuguese Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105913
Marques PA, Jorge D, Reis J. Using Lean to Improve Operational Performance in a Retail Store and E-Commerce Service: A Portuguese Case Study. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105913
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Pedro Alexandre, Diana Jorge, and João Reis. 2022. "Using Lean to Improve Operational Performance in a Retail Store and E-Commerce Service: A Portuguese Case Study" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105913
APA StyleMarques, P. A., Jorge, D., & Reis, J. (2022). Using Lean to Improve Operational Performance in a Retail Store and E-Commerce Service: A Portuguese Case Study. Sustainability, 14(10), 5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105913







