Spatiotemporal Differences and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Roadside Plant Leaves in Baoji City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
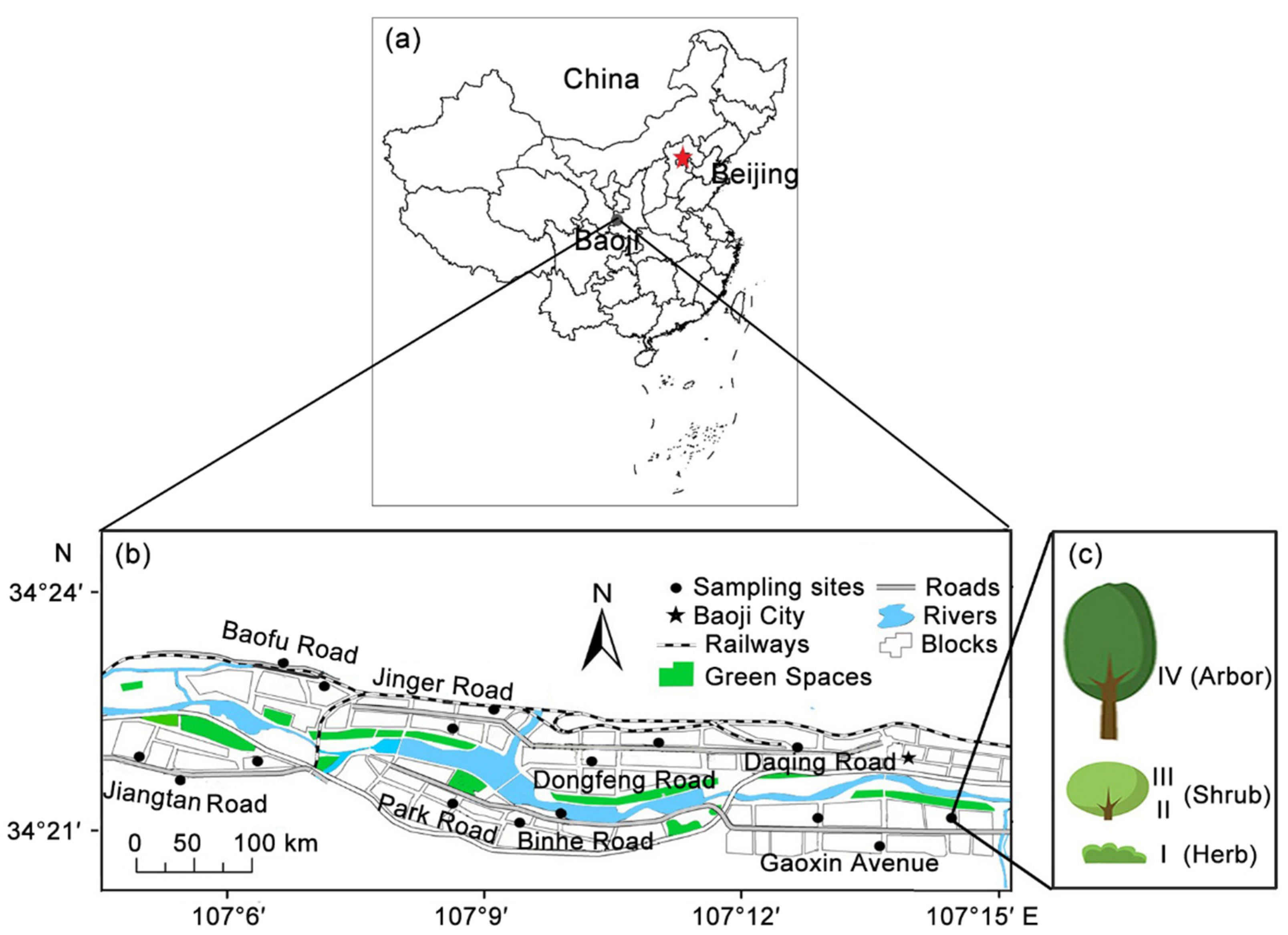
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Determining the Degree of Pollution
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment Method
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
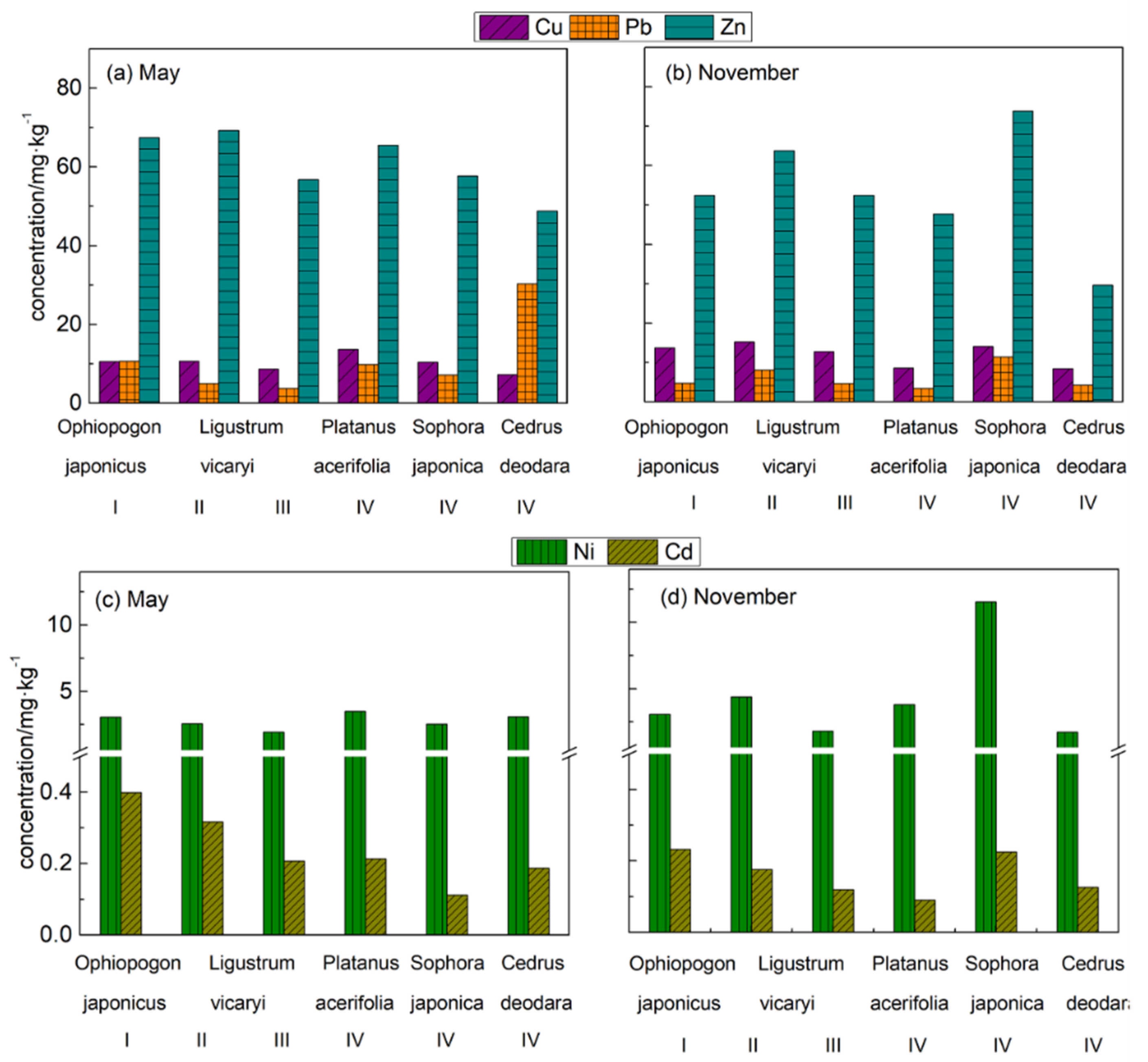
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in Leaves of Different Plants
3.2. Level of Heavy Metal Pollution in Plant Leaves
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Variation of the Heavy Metal Pollution in Plant Species
4.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution of the Degree of Heavy Metal Pollution in Plant Leaves
4.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Plant Leaves
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Marlier, M.E.; DeFries, R.S.; Westervelt, D.M.; Xia, K.R.; Fiore, A.M.; Mickley, L.J.; Cusworth, D.H.; Milly, G. Seasonal impact of regional outdoor biomass burning on air pollution in three Indian cities: Delhi, Bengaluru, and Pune. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 172, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, G.V.; de Lieto, R. Correlation between air pollution and weather data in urban areas: Assessment of the city of Rome (Italy) as spatially and temporally independent regarding pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Hopke, P.; Felton, H.; Frank, B.; Rattigan, O.; Wurth, M.; LaDuke, G. Analysis of major air pollutants and submicron particles in New York City and Long Island. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, B.-K.; Park, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Yeon, S.H.; Ji, B.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, J.-S. Screening of particulate matter reduction ability of 21 indigenous Korean evergreen species for indoor use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkin, V.; Khodzher, T.; Sorokovikova, L.; Tomberg, I.; Netsvetaeva, O.; Golobokova, L. Effect of long-range transport of sulphur and nitrogen oxides from large coal power plants on acidification of river waters in the Baikal region, East Siberia. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 73, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M.; Podsiadlik, D.H.; Chase, R.E. Examination of the size-resolved and transient nature of motor vehicle particle emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, F.; Golasi, I.; Vollaro, R.d.L.; Vollaro, A.d.L. Outdoor thermal comfort in the Mediterranean area. A transversal study in Rome, Italy. Build. Environ. 2016, 96, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargava, P.; Rajagopalan, V. Source prioritization for urban particulate emission control in India based on an inventory of PM_(10) and its carbonaceous fraction in six cities. Environ. Dev. 2015, 16, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürgen, B.; Grantz, D.A. Plants and Atmospheric Aerosols; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Sabin, L.D.; Lim, J.H.; Venezia, M.T.; Winer, A.M.; Schiff, K.C.; Stolzenbach, K.D. Dry deposition and resuspension of particle-associated metals near a freeway in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7528–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Singh, R.; Barman, S.C.; Mishra, D.; Kumar, R.; Negi, M.P.S.; Mandal, S.K.; Kisku, G.C.; Khan, A.H.; Kidwai, M.M.; et al. Comparison of trace metals concentration in PM_(10) of different locations of Lucknow City, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Environmental magnetic studies of participates with special reference to biomagnetic monitoring using roadside plant leaves. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.M.; Gomez, C.D.; Rojas, N.Y.; Acevedo, H.; Aristizabal, B.H. Relative impact of on-road vehicular and point-source industrial emissions of air pollutants in a medium-sized Andean city. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.T.; So, E.S.; Samad, S.C. Strategic guidelines for street canyon geometry to achieve sustainable street air quality—Part II: Multiple canopies and canyons. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, G.C.; Carnielo, E.; Vollaro, R.D.L. Thermal impact of a redeveloped area on localized urban microclimate: A case study in Rome. Energy Build. 2016, 133, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-W.; Vivian, E.; Mohammed, K.; Jakhar, S.; Vaughn, M.; Huang, J.; Zelicoff, A.; Xaverius, P.; Bai, Z.; Lin, S.; et al. Long-term ambient air pollution and lung function impairment in Chinese children from a high air pollution range area: The Seven Northeastern Cities (SNEC) study. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, B.; Moore, C.; Matzka, J. Spatial variation in vehicle-derived metal pollution identified by magnetic and elemental analysis of roadside tree leaves. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cichowicz, R.; Dobrzański, M. Modeling pollutant emissions: Influence of two heat and power plants on urban air quality. Energies 2021, 14, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanhong, W.; Jibiao, L. Capacity of dust uptake by leaf surface of Euonymus Japonicus Thunb and the morphology of captured particle in air polluted city. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 15, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givoni, B. Impact of planted areas on urban environmental quality: A review. Atmos. Environ. Part B Urban Atmos. 1991, 25, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer-Smith, P.; Holloway, S.; Goodman, A. The uptake of particulates by an urban woodland—Site description and particulate composition. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 95, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, F.; Monaci, F.; Blanusa, T.; Bargagli, R. Holm oak (Quercus ilex L.) canopy as interceptor of airborne trace elements and their accumulation in the litter and topsoil. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.; Zhu, N.; Han, H. Dust removal effect of urban tree species in Harbin. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.-T.; Leveque, T.; Austruy, A.; Goix, S.; Schreck, E.; Dappe, V.; Sobanska, S.; Foucault, Y.; Dumat, C. Foliar uptake and metal(loid) bioaccessibility in vegetables exposed to particulate matter. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.K.; Bishop, T.F.A.; Singh, B. Evaluation of spatial variability of soil arsenic adjacent to a disused cattle-dip site, using model-based geostatistics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10463–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harguinteguy, C.A.; Cofré, M.N.; Fernández-Cirelli, A.; Pignata, M.L. The macrophytes Potamogeton pusillus L. and Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdc. as potential bioindicators of a river contaminated by heavy metals. Microchem. J. Devot. Appl. Microtech. Branches Sci. 2016, 124, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Xiong, T.; Castrec-Rouelle, M.; Leveque, T.; Dumat, C. Water extraction kinetics of metals, arsenic and dissolved organic carbon from industrial contaminated poplar leaves. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.X.; Cai, Y.; Dong, L. Dust absorption capacities of eight evergreen broad-leaved plants in Beijing, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-N.; Kong, L.-W.; Lu, S.-W.; Chen, B.; Gao, C.; Shi, Y. Beijing common green tree leaves’ accumulation capacity for heavy metals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 35, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Feng, G.; Jiang, X.; Si, L.; Yang, Y. Analyses of heavy metal accumulation and physiological characteristics in leaves of main arbor and shrub plants in traffic roads of Lanzhou City. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xia, D.-S.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Ma, X. Pollution monitoring using the leaf-deposited particulates and magnetism of the leaves of 23 plant species in a semi-arid city, Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Lu, X.W.; Kai, L. Analysis of content and environmental risk of heavy metal elements in street dust of Baoji City. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 43, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B.; Li, D.X.; Wang, Y.H. Analysis of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment on vegetation leaves in Baoji City. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.X.; Dang, H.B.; Zheng, M.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.Y. Heavy metal pollution assessment of farmland soil in suburb in Zhengzhou City. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2013, 29, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.U. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment for the farmland soil heavy metals in Dali county. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 28, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Hou, Q.; Duan, H.J. Pollution and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface dust on urban kindergartens. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.Y.; Wu, X.Y. Transfer and cycling of heavy metals in and out of the Larch trees before and after leaf fallen. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1998, 18, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoying, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xin, W. Transferring and cycling of heavy metals in and out of poplar tree before and after its leaf fallen. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 7, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.L.; Yu, S.Q.; Hui, L.; Qiu, W.X.; Wen, Y.T. Characteristics of heavy metal enrichment efficiency in different organs of urban green tree Cinnamomum camphora. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Duan, X.M.; Shen, M.J.; Blaha, U.; Roesler, W.; Yan, H.T.; Hoffmann, E.A. Magnetic response to atmospheric heavy metal pollution recorded by dust-loaded leaves in Shougang industrial area, Western Beijing. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.W.; Hu, S.Y.; Erwin, A.; Shi, S.L.; Yin, G. The spatio-temporal variation of magnetic properties of tree leaves in Linfen, China and its indication to the atmospheric pollution of heavy metals. Chin. J. Geophys. 2016, 59, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huayun, X.; She, W.D.; Congguo, T. Review on research on traffic-related heavy metals pollution. Earth Environ. 2012, 40, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.H.; Chen, T.-B.; Song, B.; Yang, J.; Huang, Z.C.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.-C. Emissions of heavy metals from road traffic and effect of emitted lead on land contamination in China: A primary study. Geogr. Res. 2007, 26, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Tang, L.; Liu, D. Monitor and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soils along the main road—A review. Environ. Monit. China 2015, 31, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L. Particulate matter concentrations and heavy metal contamination levels in the railway transport system of Sydney, Australia. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.L. Interactions between fine particulate matter (PM_(2.5)) and vegetation: A review. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi-Yao, L.; Yu-bin, N.; Jin, F.; Hai-long, Y.; Ju-ying, H. Analysis on Dust Retention Capability of Greening Tree Species Surrounding Coal-Fired Power Plant Based on Leaf Surface Micro-Structure. Chin. J. Ecology 2021, 40, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Hui-Min, C.; Xiang-Min, Z. Magnetic response of dust-loaded leaves in parks of Shanghai to atmospheric heavy metal pollution. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 4374–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-ying, C.; Qiu-ying, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhi-yun, J.; Ru-chen, X.; Yuan-mei, G.; Yi-hong, Z.; Da, Z.; Sheng-sheng, S.; Rui-bin, H.; et al. The Effects of Rainfall Partitioning on Heavy Metal Deposition for Three Typical Urban Tree Species in Guangzho. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Eerdun, H.; Lian-you, L.; Shang-Yu, G. Physico-chemical characteristics of ambient particles settling upon leaf surface of six conifers in Beijing. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 18, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zou, R.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z. Experimental examination of effectiveness of vegetation as bio-filter of particulate matters in the urban environment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Xia, D.S.; Fan, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Tang, Z.R.; Ma, S. The influence of roadside trees on the diffusion of road traffic pollutants and their magnetic characteristics in a typical semi-arid urban area of Northwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Z.; Jie, D.; Qingfang, L.; Yani, G.; Wenke, W.; Zhoufeng, W. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of Baoji city. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 32, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Fan, S.X. Risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil in the outskirts of Baoji City. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.L.; Dong, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhu, C.Y. Pollution characteristics, sources analysis and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in different functional zones of Baoji City. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 27, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter Name | Parameter | Parameter Name | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio frequency power | 1550 W | Atomizing chamber temperature | 2.6 ℃ |
| Plasma gas flow | 15 L/min | Analysis time | 0.6 s |
| Carrier gas flow rate | 0.8 L/min | Plasma cooling water velocity | 0.55 L/min |
| Atomizer velocity | 1.1818 L/min | Sampling depth | 5 mm |
| Flow rate of cooler | 13.94 L/min | Determination of the number | 3 |
| Ni (mg·kg−1) | Cu (mg·kg−1) | Cd (mg·kg−1) | Pb (mg·kg−1) | Zn (mg·kg−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Time | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV |
| O. japonicus (I) | May | 3.07 | 0.45 | 10.57 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.88 | 10.60 | 1.15 | 67.49 | 0.35 |
| Nov. | 3.07 | 0.44 | 13.71 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.45 | 4.74 | 1.73 | 52.43 | 0.45 | |
| L. vicaryi (II) | May | 2.55 | 0.45 | 10.65 | 0.57 | 0.32 | 1.42 | 5.00 | 0.95 | 69.31 | 0.39 |
| Nov. | 4.39 | 0.39 | 15.20 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.77 | 8.05 | 0.66 | 63.82 | 0.44 | |
| L. vicaryi (III) | May | 1.92 | 0.28 | 8.63 | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 3.71 | 0.58 | 56.79 | 0.19 |
| Nov. | 1.79 | 0.47 | 12.73 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 4.67 | 0.55 | 52.49 | 0.42 | |
| P. acerifolia (IV) | May | 3.48 | 0.19 | 13.61 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 9.78 | 0.60 | 65.51 | 0.34 |
| Nov. | 3.79 | 1.05 | 8.56 | 1.06 | 0.09 | 1.56 | 3.41 | 1.56 | 47.69 | 0.77 | |
| S. japonica (IV) | May | 2.52 | 0.21 | 10.41 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 7.17 | 0.45 | 57.69 | 0.23 |
| Nov. | 11.55 | 0.89 | 14.03 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 11.37 | 0.37 | 73.82 | 0.07 | |
| C. deodara (IV) | May | 3.08 | 0.98 | 7.25 | 0.66 | 0.19 | 0.46 | 30.28 | 1.47 | 85.43 | 0.74 |
| Nov. | 1.73 | 0.12 | 8.38 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.77 | 4.19 | 0.03 | 29.65 | 0.55 | |
| Herb | Shrub | Shrub | Arbor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | O. japonicus (I) | L. vicaryi (II) | L. vicaryi (III) | P. acerifolia (IV) | |
| Ni (mg·kg−1) | May | 4.83 | 1.29 | 1.05 | 1.33 |
| Nov. | 2.25 | 3.57 | 1.53 | 1.47 | |
| Cu (mg·kg−1) | May | 11.18 | 9.8 | 4.53 | 9.28 |
| Nov. | 10.06 | 11.61 | 6.81 | 6.36 | |
| Cd (mg·kg−1) | May | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| Nov. | 0.69 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| Pb (mg·kg−1) | May | 9.67 | 4.68 | 1.52 | 5.72 |
| Nov. | 7.70 | 4.39 | 2.99 | 2.94 | |
| Zn (mg·kg−1) | May | 52.31 | 33.79 | 27.52 | 23.49 |
| Nov. | 65.74 | 21.22 | 20.09 | 16.44 |
| Ni | Cu | Cd | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height | 0.007 | 0.066 | 0.154 | 0.3 | 0.068 |
| Plant species | 0.001 | 0.22 | 0.988 | 0.046 | 0.696 |
| Time | 0.004 | 0.029 | 0.065 | 0.015 | 0.018 |
| Height: Time | 0.1 | 0.854 | 0.646 | 0.643 | 0.926 |
| Plant species: Time | 0.000 | 0.094 | 0.517 | 0.01 | 0.056 |
| Pi | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Time | Ni | Cu | Cd | Pb | Zn | Psum | Level |
| O. japonicus (I) | May | 0.64 | 0.95 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 1.29 | 1.51 | slight pollution |
| Nov. | 1.36 | 1.36 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.79 | 1.439 | slight pollution | |
| L. vicaryi (II) | May | 1.98 | 1.08 | 1.74 | 1.07 | 2.05 | 2.30 | moderate pollution |
| Nov. | 1.23 | 1.31 | 5.35 | 1.83 | 3.01 | 4.26 | heavy pollution | |
| L. vicaryi (III) | May | 1.82 | 1.90 | 1.33 | 2.43 | 2.06 | 2.48 | moderate pollution |
| Nov. | 1.17 | 1.87 | 4.28 | 1.56 | 2.61 | 3.57 | heavy pollution | |
| P. acerifolia (IV) | May | 2.49 | 1.46 | 11.73 | 1.71 | 2.78 | 8.91 | heavy pollution |
| Nov. | 2.58 | 1.35 | 6.22 | 1.16 | 2.90 | 5.89 | heavy pollution | |
| S. japonica (IV) | May | 1.89 | 1.12 | 6.14 | 1.25 | 2.46 | 4.71 | heavy pollution |
| Nov. | 7.88 | 2.21 | 15.47 | 3.87 | 4.49 | 11.96 | heavy pollution | |
| C. deodara (IV) | May | 2.32 | 0.78 | 10.25 | 5.24 | 3.49 | 7.93 | heavy pollution |
| Nov. | 1.18 | 1.32 | 8.69 | 1.43 | 1.80 | 6.49 | heavy pollution | |
| F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Height | 25.718 | <0.0001 |
| Time | 1.65 | 0.202 |
| Height: time | 0.963 | 0.413 |
| E | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | O. japonicas (I) | L. vicaryi (II) | L. vicaryi (III) | P. acerifolia (IV) | S. japonica (IV) | C. deodara (IV) | |
| Ni | May | 3.18 | 9.88 | 9.11 | 12.44 | 9.47 | 11.58 |
| Nov. | 6.81 | 6.15 | 5.85 | 12.94 | 39.40 | 5.90 | |
| Cu | May | 4.73 | 5.40 | 9.52 | 7.33 | 5.61 | 3.90 |
| Nov. | 6.81 | 6.54 | 9.36 | 6.73 | 11.03 | 6.59 | |
| Cd | May | 35.37 | 52.09 | 39.89 | 351.80 | 184.07 | 307.41 |
| No. | 10.10 | 160.56 | 128.42 | 186.74 | 464.07 | 260.70 | |
| Pb | May | 5.48 | 5.34 | 12.15 | 8.56 | 6.27 | 26.19 |
| Nov. | 3.07 | 9.15 | 7.80 | 5.81 | 19.37 | 7.14 | |
| Zn | May | 1.29 | 2.05 | 2.06 | 2.79 | 2.46 | 3.50 |
| Nov. | 0.80 | 3.01 | 2.61 | 2.90 | 4.49 | 1.80 | |
| RI | May | 53.53 | 79.62 | 77.77 | 425.15 | 276.36 | 468.95 |
| Nov. | 29.25 | 196.81 | 163.51 | 241.66 | 671.82 | 375.57 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Xia, D. Spatiotemporal Differences and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Roadside Plant Leaves in Baoji City, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105809
Zhang J, Guan Y, Lin Q, Wang Y, Wu B, Liu X, Wang B, Xia D. Spatiotemporal Differences and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Roadside Plant Leaves in Baoji City, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105809
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junhui, Yunjiu Guan, Qing Lin, Yaxin Wang, Bowen Wu, Xin Liu, Bo Wang, and Dunsheng Xia. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Differences and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Roadside Plant Leaves in Baoji City, China" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105809
APA StyleZhang, J., Guan, Y., Lin, Q., Wang, Y., Wu, B., Liu, X., Wang, B., & Xia, D. (2022). Spatiotemporal Differences and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution of Roadside Plant Leaves in Baoji City, China. Sustainability, 14(10), 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105809





