Getting Started with Positive Energy Districts: Experience until Now from Maia, Reykjavik, Kifissia, Kladno and Lviv
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Positive Energy Districts (PEDs)
- PED autonomous: a district having clear geographical boundaries that is completely self-sufficient energy-wise. This means the energy demand is covered by renewable energy produced within the district. The district is thus not allowed to import any energy from the external electricity grid or district heating/gas network. Energy generated in excess may be exported;
- PED dynamic: a district having clear geographical boundaries with annual on-site renewable energy generation higher than its annual energy demand. The district may also openly interact with other PEDs as well as the external electricity grid and district heating/gas network;
- PED virtual: a district that makes use of virtual renewable energy systems and energy storage located outside its geographical boundaries. The combined annual energy production of the virtual renewable energy systems and the on-site renewable energy systems must, however, be greater than the annual energy demand of the district.
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Purpose of This Paper
2. Materials and Methods
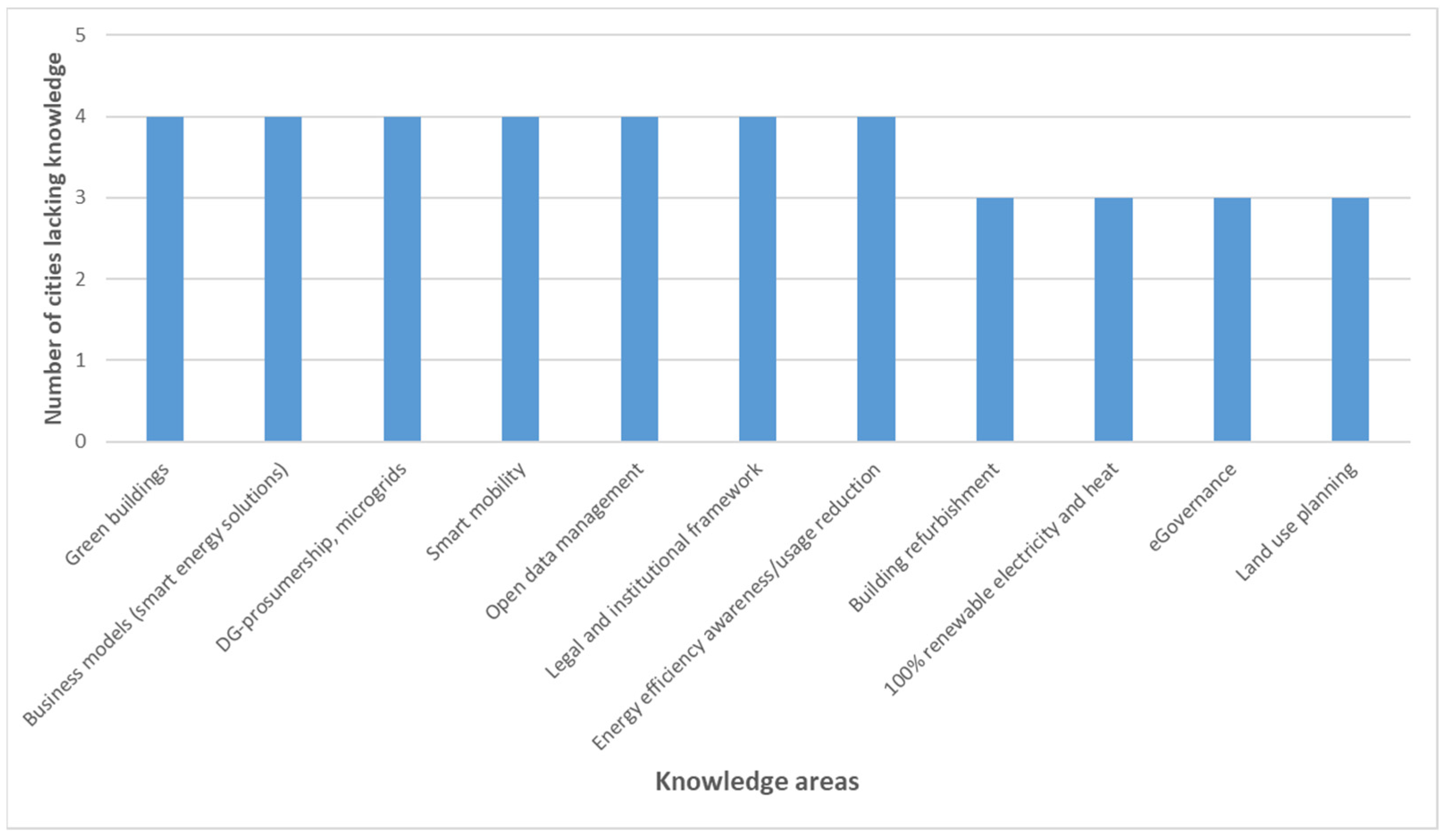
2.1. Knowledge Gap Survey
2.2. City Vision 2050
2.3. City Forum
2.4. Interviews with City Representatives
3. Results
3.1. Maia
3.2. Reykjavik
3.3. Kladno
3.4. Kifissia
3.5. Lviv
3.6. Limitations of the Research
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Category | Knowledge Area | Number of Cities Lacking Knowledge |
|---|---|---|
| Building/infrastructure | Green buildings | 4 |
| Building refurbishment | 3 | |
| Efficiency upgrades in historic districts/general retrofitting | 2 | |
| Life cycle consideration of construction waste | 1 | |
| Energy performance certification (implementation) | 1 | |
| Thermal insulation and passive energy efficiency improvement | 1 | |
| Finance | Business models (smart energy solutions) | 4 |
| Public–private partnerships, investment, cooperation | 2 | |
| Economic modeling of PED/smart cities | 1 | |
| Proving financial viability | 1 | |
| Demand and distribution | Smart metering | 2 |
| EV integration (data-driven)/bidirectional charging/V2G | 2 | |
| Load management/electricity distribution | 1 | |
| Demand-side management | 1 | |
| Flexible hydrogen production… | 1 | |
| Predicting demand/load patterns | 1 | |
| Energy independence versus distribution system investment | 1 | |
| Energy production | DG-prosumership, microgrids | 4 |
| 100% renewable electricity and heat | 3 | |
| Photovoltaics (PV) | 2 | |
| District heating | 1 | |
| PED planning and function overview | 2 | |
| Wind | 1 | |
| Energy storage systems | 1 | |
| Exploring RES potential | 1 | |
| Waste CHP (specifically carbon-neutral) | 1 | |
| Mobility | Smart mobility | 4 |
| Multimodal/active transit | 2 | |
| EV uptake strategies | 2 | |
| Public EV charging | 2 | |
| Public transit investment | 2 | |
| Bike infrastructure | 1 | |
| Shared mobility | 1 | |
| Changing charging behaviour | 1 | |
| Increasing share of foot/bike/public transit trips | 1 | |
| Data | Open data management | 4 |
| Modeling tools for planning | 1 | |
| Kera 5G/city and regional 5G legal implications | 1 | |
| Data integration | 1 | |
| Calculating energy balance of PED | 1 | |
| Artificial Intelligence/IoT | 1 | |
| Smart monitoring system | 1 | |
| Energy burden modeling of buildings/city level | 1 | |
| Efficiency increases in public transit | 1 | |
| Interoperable and integrated data platform | 1 | |
| PED impact assessment | 1 | |
| Governance | Legal and institutional framework | 4 |
| eGovernance | 3 | |
| Land use planning | 3 | |
| Smart city policies | 2 | |
| Coordinating with regional/national reform/regulation | 2 | |
| Knowledge of national policy in energy, renewables, and building efficiency | 1 | |
| Project management unit for energy and sustainability | 1 | |
| General public sector (utilities, etc.) development | 1 | |
| Post-communist innovation process | 1 | |
| Circular economy policies | 1 | |
| Stakeholder management | 1 | |
| Increasing R&D capacity, innovation potential | 1 | |
| Smart city management structure | 1 | |
| Public engagement | Energy efficiency awareness/usage reduction | 4 |
| Industry efficiency/engagement | 2 | |
| Workshops and online surveys | 1 | |
| Focus groups | 1 | |
| Water consumption and rainwater collection | 1 |
References
- International Energy Agency. Energy Transitions Tracking Progress in Clean Energy Transitions through Key Indicators across Fuels and Technologies. 2021. Available online: https://www.iea.org/topics/energy-transitions (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- European Commission. 100 Climate-Neutral Cities by 2030—By and for the Citizens: INTERIM Report of the Mission Board for Climate-Neutral and Smart Cities; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores, A.; Álvarez, L.; Chico, J.; Ramajo, G.; Azabal, I.; Urgel, J.M. The Future of Sustainable Cities: Urban Energy Transition to 2030. 2019. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/eg/en/pages/energy-and-resources/articles/future-of-sustainable-cities-urban-energy-transition-to-2030.html (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- OECD. Managing Environmental and Energy Transitions for Regions and Cities. 2020. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/urban-rural-and-regional-development/managing-environmental-and-energy-transitions-for-regions-and-cities_f0c6621f-en (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- The United Nations. The New Urban Agenda. 2016. Available online: https://habitat3.org/the-new-urban-agenda/ (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Pulselli, R.M.; Broersma, S.; Martin, C.L.; Keeffe, G.; Bastianoni, S.; van den Dobbelsteen, A. Future city visions. The energy transition towards carbon-neutrality: Lessons learned from the case of Roeselare, Belgium. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs. 68% of the World Population Projected to Live in Urban Areas by 2050, Says UN. 2018. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/en/news/population/2018-revision-of-world-urbanization-prospects.html (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Ferrer, J.N.; Taranic, I.; Veum, K.; van den Oosterkamp, P.; Wilson, C. The Making of a Smart City: Replication and Scale-Up of Innovation in Europe. 2017. Available online: https://smart-cities-marketplace.ec.europa.eu/insights/publications/making-smart-city-replication-and-scale-innovation-europe (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Fatima, Z.; Pollmer, U.; Santala, S.-S.; Kontu, K.; Ticklen, M. Citizens and Positive Energy Districts: Are Espoo and Leipzig Ready for PEDs? Buildings 2021, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Urban Agenda for the EU. 2016. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/en/policy/themes/urban-development/agenda/#:~:text=The%20Urban%20Agenda%20for%20the%20EU%20is%20an%20integrated%20and,of%20life%20in%20urban%20areas (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- JPI Urban Europe/SET Plan Action 3.2. White Paper on PED Reference Framework for Positive Energy Districts and Neighbourhoods. 2020. Available online: https://jpi-urbaneurope.eu/ped/ (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Derkenbaeva, E.; Vega, S.H.; Hofstede, G.J.; van Leeuwen, E. Positive energy districts: Mainstreaming energy transition in urban areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 153, 111782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckmans, A.; Karatzoudi, K.; Brigg, D.; Ahlers, D. D9.5: Report on Attendance at Events Held by Other SCC-01 Co-Ordinators 2. 2018. Available online: https://cityxchange.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/D9.5_Report-on-Attendance-at-events-held-by-other-SCC-01-co-ordinators2.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Lindholm, O.; Rehman, H.U.; Reda, F. Positioning Positive Energy Districts in European Cities. Buildings 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavikka, R.; Rehman, H.U.; Reda, F.; Kazi, A.S. Positive Energy Buildings; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkalainen, M.; Reda, F.; Klobut, K. Positive Energy District: Ad New Puzzle Piece for Cities’ Energy Transformation. 2021. Available online: https://cris.vtt.fi/en/publications/positive-energy-district-a-new-puzzle-piece-for-cities-energy-tra (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Zhang, X.; Penaka, S.R.; Giriraj, S.; Sánchez, M.N.; Civiero, P.; Vandevyvere, H. Characterizing Positive Energy District (PED) through a Preliminary Review of 60 Existing Projects in Europe. Buildings 2021, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raworth, K. Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century Economist; Chelsea Green Publishing: White River Junction, VT, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bale, C.S.E.; Varga, L.; Foxon, T.J. Energy and complexity: New ways forward. Appl. Energy 2015, 138, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krangsås, S.G.; Steemers, K.; Konstantinou, T.; Soutullo, S.; Liu, M.; Giancola, E.; Prebreza, B.; Ashrafian, T.; Murauskaitė, L.; Maas, N. Positive Energy Districts: Identifying Challenges and Interdependencies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailova, D.; Schubert, I.; Martinez-Cruz, A.L.; Hearn, A.X.; Sohre, A. Preferences for configurations of Positive Energy Districts—Insights from a discrete choice experiment on Swiss households. Energy Policy 2022, 163, 112824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, N.; Ceseña, E.A.M.; Mancarella, P.; Monti, A.; Pesch, D.; Ellis, K.A. Barriers, Challenges, and Recommendations Related to Development of Energy Positive Neighborhoods and Smart Energy Districts. In Energy Positive Neighborhoods and Smart Energy Districts: Methods, Tools, and Experiences from the Field; Academic Press: Aachen, Germany, 2017; pp. 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Bossi, S.; Gollner, C.; Theierling, S. Towards 100 Positive Energy Districts in Europe: Preliminary Data Analysis of 61 European Cases. Energies 2020, 13, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, S.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Aelenei, L.; Reda, F.; Etminan, G.; Andreucci, M.-B.; Kuzmic, M.; Maas, N.; Seco, O.; Civiero, P.; et al. Ten questions concerning positive energy districts. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 109017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uspenskaia, D.; Specht, K.; Kondziella, H.; Bruckner, T. Challenges and Barriers for Net-Zero/Positive Energy Buildings and Districts—Empirical Evidence from the Smart City Project SPARCS. Buildings 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Hasan, A.; Reda, F. Challenges in reaching positive energy building level in apartment buildings in the Nordic climate: A techno-economic analysis. Energy Build. 2022, 262, 111991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrini, A.; Lentini, G.; Cuman, S.; Bodrato, A.; Marenco, L. From nearly zero energy buildings (NZEB) to positive energy buildings (PEB): The next challenge—The most recent European trends with some notes on the energy analysis of a forerunner PEB example. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl-Wostl, C.; Mostert, E.; Tabara, D. The Growing Importance of Social Learning in Water Resources Management and Sustainability Science. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ison, R.; Watson, D. Illuminating the Possibilities for Social Learning in the Management of Scotland’s Water. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.; Chidambaranathan, M.; Escobar, C.; Wiesmann, U.; Zimmermann, A. Moving from sustainable management to sustainable governance of natural resources: The role of social learning processes in rural India, Bolivia and Mali. J. Rural Stud. 2007, 23, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lave, J.; Wenger, E. Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.S.; Duguid, P. Organizational Learning and Communities-of-Practice: Toward a Unified View of Working, Learning, and Innovation. Organ. Sci. 1991, 2, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bögel, P.; Pereverza, K.; Upham, P.; Kordas, O. Linking socio-technical transition studies and organisational change management: Steps towards an integrative, multi-scale heuristic. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J. Governing Cities for Sustainability: A Research Agenda and Invitation. Front. Sustain. Cities 2019, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SPARCS. H2020 SPARCS Project. Available online: https://www.sparcs.info/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- EU Commission. Smart Cities and Communities Lighthouse Projects. 2016. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/programme/id/H2020_SCC-1-2016-2017 (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- SPARCS. D1.11 City Vision 2050—Draft. 2021. Available online: https://www.sparcs.info/index.php/about/deliverables/d111-city-vision-2050-draft (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Aghamolaei, R.; Shamsi, M.H.; Tahsildoost, M.; O’Donnell, J. Review of district-scale energy performance analysis: Outlooks towards holistic urban frameworks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammen, D.M.; Sunter, D.A. City-integrated renewable energy for urban sustainability. Science 2016, 352, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Maia | Reykjavik | Kladno | Kifissia | Lviv | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate (Köppen–Geiger system) | Warm and temperate (Csb) | Marine West Coast Climate (Cfc) | Warm and temperate (Cfb) | Mediterranean climate (Cfa) | Humid continental (Dfb) |
| Share of energy demand covered by RES (% of end energy demand) | 26.5 | 100 | 1.82 | - | - |
| Share of electricity demand generated by RES (% of electricity demand) | 45 | 100 | 2.05 | - | - |
| Renewable energy sources in use | Hydro, wind, solar | Hydro, geothermal | Solar, partially hydro and wind | - | - |
| Other sources of energy | Natural gas, oil | None | Coal, natural gas | Coal, natural gas, oil | Natural gas (heating) |
| Examples Questions in the Survey | |
|---|---|
| Knowledge Exchange Questions |
|
| City Vision and Civic Engagement |
|
| What challenges are you facing in your city regarding PEDs? |
| What do you wish to learn from other cities? |
| What is your advice to a new a city that wants to plan PEDs? |
| Interviewees | |
|---|---|
| Maia | SPARCS project coordinator—City of Maia (1) Technical experts—City of Maia (1), EDP NEW (1), Porto Energy Agency (2) |
| Reykjavik | SPARCS project coordinator—City of Reykjavik (1) Technical expert—Reykjavik Energy (1) |
| Kladno | SPARCS project coordinator—City of Kladno (1) |
| Kifissia | SPARCS project coordinator—City of Kifissia (1) Deputy Mayor (1) |
| Lviv | SPARCS project coordinator—City of Lviv (1) |
| Topics | Interview Questions |
|---|---|
| Energy transition | How would you describe your energy transition efforts? For example, the starting point and where you are now. |
| PED learnings and value |
|
| Reflection and way forward | What would you do differently, if you could, to change or improve energy transition in your city? |
| Categories | Local Challenges in the Five Cities | Maia | REK | KLD | KFS | Lviv |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governance | Understanding the PED definition and concept | x | x | x | x | x |
| Legislation, regulations and bureaucracy | x | x | x | x | ||
| Political priorities | x | x | x | |||
| Lack of leadership in energy sector | x | |||||
| Weak cooperation between municipality and private service providers | x | x | ||||
| Lack of communication and capacity and high individualism | x | |||||
| Technology | Understanding of technologies (PV, BIPV) and technical implementation | x | ||||
| EV charging stations | x | |||||
| Data availability and use | x | |||||
| Energy infrastructure to maintain load from e-charging | x | |||||
| Energy calculations on housing | x | |||||
| Replicating solutions in a given timeframe | x | |||||
| Lack of trust in new “innovative” solutions | x | |||||
| Low awareness about current technologies for energy modernization and RES potential | x | |||||
| Availability of areas for RES installations | x | |||||
| Lack of access to the best technology | x | |||||
| Lack of qualified personnel | x | x | ||||
| Continuous source of energy supply | x | x | ||||
| Financial and economic | High energy prices | x | x | |||
| Business as usual attitude | x | |||||
| High dependency on private energy companies | x | |||||
| Uncertainty: COVID, war, economic crisis | x | |||||
| Limited financial resources in municipal budget | x | x | x | x | ||
| Social and cultural | Stakeholder engagement (who to involve and how) | x | x | |||
| Citizen engagement and commitment | x | |||||
| Environmental | Behaviour of citizens (non-energy efficient lifestyle) | x | ||||
| Heavy use of private cars | x | x | x | |||
| Heat island effect, flooding, air quality | x | |||||
| Water and waste management | x | x |
| Maia | Reykjavik | Kladno | Kifissia | Lviv | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial Development | x | x | x | x | |
| Mobility | x | x | x | x | x |
| Efficient buildings and materials | x | x | x | ||
| Green energy | x | x | x | x | |
| Digital networks and eServices | x | x | x | ||
| Citizen Education and Participation | x | x | x | ||
| Circular Economy (waste management etc.) | x | x | x | x | |
| Nature-based solutions | x | x |
| Maia | REK | KLD | KFS | Lviv | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learnings from PED development | Scaling up of solutions Understanding the concept of PEDs Realization that the city needs more technical knowledge Better know-how about the city situation | PEDs encouraged new efforts, such as taking the life cycle approach into use in the construction sector. Inspired and motivated the city to fill in the gaps | Understanding the concept of PEDs Technical understanding was missing Concerned about how to raise interest in energy efficiency High energy prices support PED development | Bureaucracy is an underlying issue—this leads to extraordinary delays and consumes much of the city’s time resources. Citizen and stakeholder engagement could also be done more vigorously as citizens seem eager to participate in activities | Understanding the concept of PEDs Which technologies to implement? Resolving issues through interactions with the two Lighthouse Cities and other four cities. |
| Value that PEDs brought | City vision helped realize the challenge in translating the knowledge into the city’s own reality PEDs initiated deeper discussions Better relationship with stakeholders | PED has led the city to think about other sectors that should be developed in parallel. Renewed interest when the stakeholders find out that SPARCS is a large European project with several partners. For example, the city recently attracted 400 applicants for further research into use of electric vehicles and load control. | PED attracted a lot of positive attention. Realizing that PED discussions are not only meant for energy balance, but they are connected to people, economy, urbanism, etc. Allows to attract more stakeholders | The project helped the city create a roadmap for itself. Project webinars and workshops also continuously support the journey and help develop a system approach. The city also shares the gathered knowledge within the city departments for more awareness. The city was able to identify key strategy areas to work upon with the help with city vision workshop Establishing the city’s first public PV system | The city gained new knowledge about existing solutions and how they can be implemented, for example, how should e-mobility be improved through scooters and e-bikes. Became familiar with how to integrate energy, mobility and engage stakeholders. The city is looking into procurement of e-bikes. By being part of the PED project, the city of Lviv believes it could be a leader in energy efficiency in the country. Identifying key strategy areas to work on helped understand how the different sectors can be combined. |
| Checkpoints for Initiating PED Development in a City | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Knowledge about the concept, best technologies, city context, regulatory concerns and baseline assessment |
| 2 | Prepare a clear strategy with goals. Define legal, financial frameworks and other required documents |
| 3 | Avoid large-scale projects in the beginning, start from small pilots that could give you quick wins and motivate |
| 4 | Establish a local task force and governance model |
| 5 | Establish local agreements with relevant stakeholders to assure data interoperability |
| 6 | Define the business models and explore all funding options |
| 7 | Analyse the current situation in your city |
| 8 | Analyse potential locations accurately to implement PED solutions |
| 9 | Ensure good project management from the start |
| 10 | Identify all possible challenges and needs |
| 11 | Have the support of the administration to ensure project ownership and awareness of project purpose |
| 12 | Do resource assessment (finance, employees, funds etc.) |
| 13 | Ensure close collaboration between city + technical partners of your city |
| 14 | Create collaborative ecosystem (colleagues, other departments, other city stakeholders, other partners incl. distributors). Invite business partners, developers, investors, banks from the beginning. Engage the politicians and counsellor. |
| 15 | Provide an open data for planning and implementing solutions |
| 16 | Set up a data software solution and collect data regular or as much as possible |
| 17 | Get information from other projects for examples |
| 18 | Demonstrate advantages of new solutions |
| 19 | Be flexible as local city situations may change abruptly |
| 20 | Collaborate with NGOs and SMEs to reach citizens and better know the needs of citizens |
| 21 | Communicate with other cities |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatima, Z.; Vacha, T.; Swamygowda, K.; Qubailat, R. Getting Started with Positive Energy Districts: Experience until Now from Maia, Reykjavik, Kifissia, Kladno and Lviv. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105799
Fatima Z, Vacha T, Swamygowda K, Qubailat R. Getting Started with Positive Energy Districts: Experience until Now from Maia, Reykjavik, Kifissia, Kladno and Lviv. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105799
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatima, Zarrin, Tomas Vacha, Kavyashree Swamygowda, and Reef Qubailat. 2022. "Getting Started with Positive Energy Districts: Experience until Now from Maia, Reykjavik, Kifissia, Kladno and Lviv" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105799
APA StyleFatima, Z., Vacha, T., Swamygowda, K., & Qubailat, R. (2022). Getting Started with Positive Energy Districts: Experience until Now from Maia, Reykjavik, Kifissia, Kladno and Lviv. Sustainability, 14(10), 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105799







