An Innovative and Interactive Teaching Model for Cultivating Talent’s Digital Literacy in Decision Making, Sustainability, and Computational Thinking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis
2.1. Digital Literacy
2.2. Data Visualization
2.3. Decision Making
2.4. Critical Thinking
3. Research Methods
3.1. Research Hypotheses
3.2. Experimental Design
3.3. Teaching Strategy
3.4. Participants
3.5. Instruments
3.5.1. Quiz
3.5.2. Questionnaire
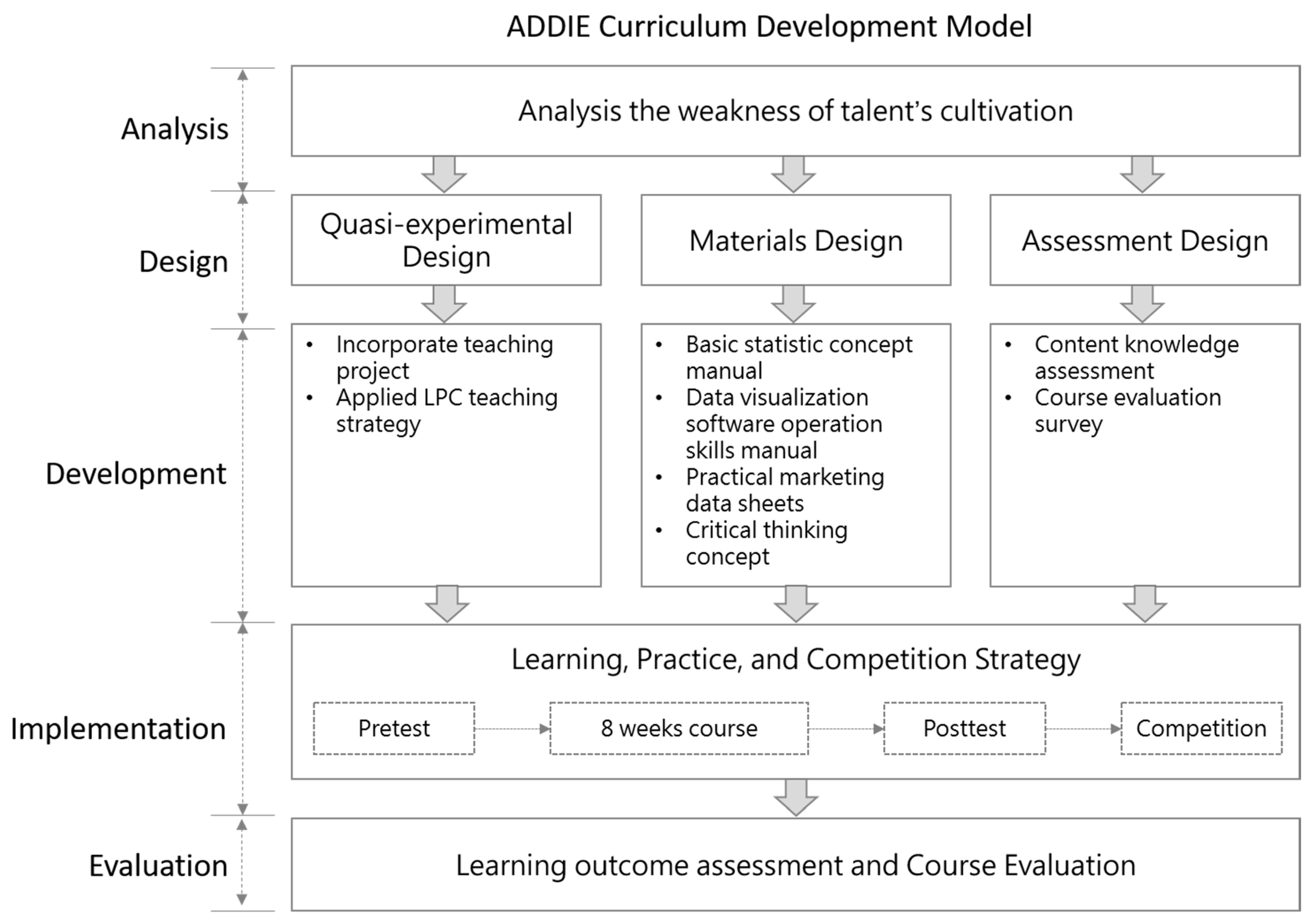
3.6. ADDIE Model as Useful Curriculum Development Strategy
3.7. Data Analysis
3.7.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.7.2. Paired Sample t-Test
3.7.3. ANCOVA
3.7.4. The Effect Check
4. Findings
4.1. The Background of Participants
4.2. The Effects of Experimental Curriculum
4.3. The Pure Effects of Learning Outcome
4.4. Teaching Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jan, S. Investigating the Relationship between Students’ Digital Literacy and Their Attitude towards Using ICT. Int. J. Educ. Technol. 2018, 5, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ratten, V. Coronavirus (covid-19) and entrepreneurship: Changing life and work landscape. J. Small Bus. Entrep. 2020, 32, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ing, H.C.; Yahaya, N.; Kumar, L.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. Examining Learners’ Interaction Pattern in Asynchronous Text-Based Online Learning. i-Manag. J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 16, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nyikes, Z. Contemporary digital competency review. Interdiscip. Descr. Complex Syst. 2018, 16, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gretter, S.; Yadav, A. Computational thinking and media & information literacy: An integrated approach to teaching twenty-first century skills. TechTrends 2016, 60, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Easterbrook, S. From Computational Thinking to Systems Thinking: A conceptual toolkit for sustainability computing. In Ict Sustain; (ICT4S-14); Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Djambong, T.; Freiman, V.; Gauvin, S.; Paquet, M.; Chiasson, M. Measurement of computational thinking in K-12 education: The need for innovative practices. In Digital Technologies: Sustainable Innovations for Improving Teaching and Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 193–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zoller, U. Science education for global sustainability: What is necessary for teaching, learning, and assessment strategies? J. Chem. Educ. 2012, 89, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, D. Defining digital literacy. In Medienbildung in neuen Kulturräumen; VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- OSPI. No Child Left Behind Act of 2001. Available online: www.k12.wa.us/policy-funding/grants-grant-management/every-student-succeeds-act-essa-implementation/elementary-and-secondary-education-act-esea/no-child-left-behind-act-2001 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Ungerer, L. Digital curation as a core competency in current learning and literacy: A higher education perspective. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2016, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatlevik, O.E.; Throndsen, I.; Loi, M.; Gudmundsdottir, G.B. Students’ ICT self-efficacy and computer and information literacy: Determinants and relationships. Comput. Educ. 2018, 118, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltay, T. The media and the literacies: Media literacy, information literacy, digital literacy. MediaCult. Soc. 2011, 33, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Härdle, W.K.; Unwin, A. (Eds.) Handbook of Data Visualization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Telea, A.C. Data Visualization: Principles and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Evergreen, S.; Metzner, C. Design principles for data visualization in evaluation. New Dir. Eval. 2013, 140, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, S.; Poovaiah, R. On defining visual narratives. Des. Thoughts 2010, 3, 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Marchau, V.A.; Walker, W.E.; Bloemen, P.J.; Popper, S.W. Decision Making Under Deep Uncertainty: From Theory to Practice; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 405–458. [Google Scholar]
- Škraba, A.; Kljajić, M.; Leskovar, R. Group exploration of system dynamics models—Is there a place for a feedback loop in the decision process? System Dynamics Review. J. Syst. Dyn. Soc. 2003, 19, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciliska, D.K.; Pinelli, J.; DiCenso, A.; Cullum, N. Resources to enhance evidence-based nursing practice. Aacn Clin. Issues 2001, 12, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineout-Overholt, E.; Johnston, L. Teaching EBP: Asking searchable, answerable clinical questions. Worldviews Evid. Based Nurs. 2005, 2, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahnel, C.; Goldhammer, F.; Kröhne, U.; Naumann, J. The role of reading skills in the evaluation of online information gathered from search engine environments. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 78, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schudel, I.J. Modelling dialectical processes in environmental learning: An elaboration of Roy Bhaskar’s onto-axiological chain. J. Crit. Realism 2017, 16, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Kao, C.H.; Hwang, G.J.; Lin, F.H. From experiencing to critical thinking: A contextual game-based learning approach to improving nursing students’ performance in electrocardiogram training. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2020, 68, 1225–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavdar, G.; Doe, S. Learning through writing: Teaching critical thinking skills in writing assignments. Political Sci. Politics 2012, 45, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Z.H.; Sun, Z.H. The Practical Innovation Teaching Strategy and Implementation for Senior Vocational High School Curriculum of Electronic Commerce. 2016. Available online: Ba.tchcvs.tc.edu.tw/epapers/course/1050525_01.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Licorish, S.A.; Owen, H.E.; Daniel, B.; George, J.L. Students’ perception of Kahoot!’s influence on teaching and learning. Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2018, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Learning Express. Critical Thinking Assessment Practice. AL: Columbia Southern University. 2010. Available online: pdf4pro.com/amp/view/critical-thinking-assessment-practice-quiz-mycsu-5b6cf3.html (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Tan, S. Misuses of KR-20 and Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficients. Egit. Bilim 2009, 34, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Beaton, D.E.; Bombardier, C.; Guillemin, F.; Ferraz, M.B. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine 2000, 25, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fogarty, G.; Cretchley, P.; Harman, C.; Ellerton, N.; Konki, N. Validation of a questionnaire to measure mathematics confidence, computer confidence, and attitudes towards the use of technology for learning mathematics. Math. Educ. Res. J. 2001, 13, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis. Meta-Analysis; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Muthén, B.O.; Curran, P.J. General longitudinal modeling of individual differences in experimental designs: A latent variable framework for analysis and power estimation. Psychol. Methods 1997, 2, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, R.H. (Ed.) Statistical Strategies for Small Sample Research; Sage: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bump, W.M. The Homogeneity of Regression Assumption in the Analysis of Covariance, Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Southwest Educational Research Association. Huston, TX, USA, 31 January–2 February 1992.
- Brunette, D.M. Critical Thinking: Understanding and Evaluating Dental Research; Quintessence: Chicago, IL, USA, 1996; pp. 187–203. [Google Scholar]

| Week | Activities |
|---|---|
| 5th | Pre-test:
|
| 6th | Lecture: Critical thinking concept. Practice: Critical thinking skill assignment. |
| 7th | Lecture: Basic statistical concept I. Practice: Basic statistic assignment: pre-test and post-test by Kahoot! |
| 8th | Lecture: Basic statistical concept II. Practice: Basic statistic assignment: pre-test and post-test by Kahoot! |
| 9th | Lecture: Data visualization software operation skills: infographics. Practice: Software operation with practical marketing data: pre-test and post-test by Kahoot! |
| 10th | Lecture: Data visualization software operation skills: geographic data in map. Practice: Software operation with practical marketing data: pre-test and post-test by Kahoot! |
| 11th | Practice: Discussion and software operation with practical marketing data. |
| 12th | Competition: Data visualization software operation skills and interpretation of the meaning of produced infographics. Post-test:
|
| Variable | Group | n | % | Mean | St.Dev. | Mode | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 49 | 62.0 | 0.38 | 0.488 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Male | 30 | 38.0 | |||||
| Academic | Lower | 14 | 17.7 | 3.11 | 0.734 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Confidence | Middle | 42 | 53.2 | ||||
| Higher | 23 | 29.1 | |||||
| Academic | Lower | 24 | 30.4 | 3.56 | 0.944 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Performance | Middle | 30 | 38.0 | ||||
| Higher | 25 | 31.6 | |||||
| Critical | Lower | 12 | 15.2 | 15.76 | 3.787 | 16.0 | 15.76 |
| Thinking | Middle | 24 | 30.4 | ||||
| Higher | 43 | 54.4 | 3.56 | 0.944 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Unit | Test | Mean | SD | The Difference of Paired Variables | t Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Std. Error of Mean | 95% Confidence Interval | ||||||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Statistic test mean score | Pre | 7.15 | 1.908 | −2.445 | 2.825 | 0.318 | −3.078 | −1.812 | −7.692 *** |
| Post | 9.59 | 2.146 | |||||||
| Infographic test mean score | Pre | 3.46 | 0.698 | −2.629 | 1.027 | 0.116 | −2.859 | −2.398 | −22.739 *** |
| Post | 6.09 | 0.732 | |||||||
| Map test mean score | Pre | 3.13 | 0.865 | −1.898 | 1.486 | 0.167 | −2.231 | −1.565 | −11.352 *** |
| Post | 5.02 | 1.276 | |||||||
| Pre- Test | Post- Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects | Units | Group | n | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| Statistic | High | 23 | 7.18 | 1.711 | 10.14 | 1.893 | |
| Middle | 42 | 7.42 | 1.963 | 9.48 | 2.394 | ||
| Low | 14 | 6.27 | 1.913 | 9.01 | 1.598 | ||
| Infographic | High | 23 | 3.52 | 0.798 | 5.97 | 0.855 | |
| Academic Confidence | Middle | 42 | 3.41 | 0.715 | 6.11 | 0.578 | |
| Low | 14 | 3.50 | 0.462 | 6.21 | 0.939 | ||
| Map | High | 23 | 3.45 | 1.013 | 5.05 | 1.296 | |
| Middle | 42 | 3.03 | 0.720 | 5.08 | 1.197 | ||
| Low | 14 | 2.88 | 0.917 | 4.80 | 1.530 | ||
| Statistic | High | 25 | 8.00 | 2.152 | 10.12 | 1.587 | |
| Middle | 30 | 6.95 | 1.442 | 9.41 | 1.756 | ||
| Low | 24 | 6.50 | 1.902 | 9.27 | 2.940 | ||
| Infographic | High | 25 | 3.52 | 0.778 | 6.10 | 0.733 | |
| Academic Performance | Middle | 30 | 3.43 | 0.505 | 6.10 | 0.761 | |
| Low | 24 | 3.43 | 0.832 | 6.06 | 0.781 | ||
| Map | High | 25 | 3.41 | 0.840 | 5.33 | 1.143 | |
| Middle | 30 | 3.08 | 0.590 | 4.98 | 1.189 | ||
| Low | 24 | 2.89 | 1.100 | 4.76 | 1.484 | ||
| Statistic | High | 25 | 8.00 | 2.152 | 10.12 | 1.587 | |
| Middle | 30 | 6.95 | 1.442 | 9.41 | 1.756 | ||
| Low | 24 | 6.50 | 1.902 | 9.27 | 2.940 | ||
| Infographic | High | 25 | 3.52 | 0.778 | 6.10 | 0.733 | |
| Critical Thinking | Middle | 30 | 3.43 | 0.505 | 6.10 | 0.716 | |
| Low | 24 | 3.43 | 0.832 | 6.06 | 0.781 | ||
| Map | High | 25 | 3.41 | 0.840 | 5.33 | 1.143 | |
| Middle | 30 | 3.08 | 0.590 | 4.98 | 1.189 | ||
| Low | 24 | 2.89 | 1.100 | 4.76 | 1.484 | ||
| Unit | Group | Adj. M | SE | Source | Sum of Squares | df | MS | F | Eta² | Observed Power (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | 10.032 | 0.320 | Contrast | 34.219 | 2 | 17.109 | 3.952 * | 0.095 | 0.693 | |
| Statistic | Middle | 9.546 | 0.426 | Error | 324.720 | 75 | 4.330 | |||
| Low | 8.101 | 0.604 | ||||||||
| High | 6.310 | 0.215 | Contrast | 0.889 | 2 | 0.444 | 0.815 n.s. | 0.021 | 0.185 | |
| Infographic | Middle | 6.117 | 0.152 | Error | 40.894 | 75 | 0.545 | |||
| Low | 6.008 | 0.113 | ||||||||
| High | 5.113 | 0.199 | Contrast | 0.330 | 2 | 0.665 | 0.399 n.s. | 0.011 | 0.112 | |
| Map | Middle | 5.104 | 0.373 | Error | 124.918 | 75 | 1.666 | |||
| Low | 4.823 | 0.267 |
| Items | Responses | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| 5. The teacher is attentively | 92% | 1 |
| 3. This course is designed attentively | 88% | 2 |
| 9. I think my competency to be enhanced via this course in data visualization skills | 84% | 3 |
| 7. I feel the data visualization skills is useful to me | 84% | 4 |
| 8. I agree to learn data visualization skill is important | 84% | 5 |
| 6. I learned marketing management knowledge in this course | 84% | 6 |
| 4. The progress is appropriated for me | 83% | 7 |
| 1. The materials is suited for me for learning | 83% | 8 |
| 2. I can easy to learn by the teaching method | 82% | 9 |
| 10. I enjoy the course which combined theory and practical case and data | 81% | 10 |
| 12. I learned the critical thinking concept | 80% | 11 |
| 11. My learning performance in this course | 78% | 12 |
| The overall evaluated of the course | 88% | ─ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Kuang, S.-S. An Innovative and Interactive Teaching Model for Cultivating Talent’s Digital Literacy in Decision Making, Sustainability, and Computational Thinking. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095117
Yuan Y-H, Liu C-H, Kuang S-S. An Innovative and Interactive Teaching Model for Cultivating Talent’s Digital Literacy in Decision Making, Sustainability, and Computational Thinking. Sustainability. 2021; 13(9):5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095117
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yu-Hsi, Chia-Hui Liu, and Szu-Sheng Kuang. 2021. "An Innovative and Interactive Teaching Model for Cultivating Talent’s Digital Literacy in Decision Making, Sustainability, and Computational Thinking" Sustainability 13, no. 9: 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095117
APA StyleYuan, Y.-H., Liu, C.-H., & Kuang, S.-S. (2021). An Innovative and Interactive Teaching Model for Cultivating Talent’s Digital Literacy in Decision Making, Sustainability, and Computational Thinking. Sustainability, 13(9), 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095117






