Study on the Farmland Improvement Effect of Drainage Measures under Film Mulch with Drip Irrigation in Saline–Alkali Land in Arid Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.1.1. Open Ditch Drainage (ODD)
2.1.2. Subsurface Pipe Drainage (SPD)
2.1.3. Crop Management—Drip Irrigation and Leaching
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Sampling, Measurements, and Calculations
2.3.1. Soil Electrical Conductivity (EC) and Desalination Rate
2.3.2. Drainage Flow and Drainage Water Salt Concentration
2.3.3. Groundwater Level and Mineralization
2.3.4. Crop Growth and Yield
3. Results
3.1. The Spatiotemporal Patterns of Soil EC
3.2. Effectiveness of Soil Desalination
3.3. Dynamic Variation of Drainage Flow and Salt Concentration of the Drainage Water
3.4. Dynamic Variation of Groundwater Level and Salt Concentration of Groundwater
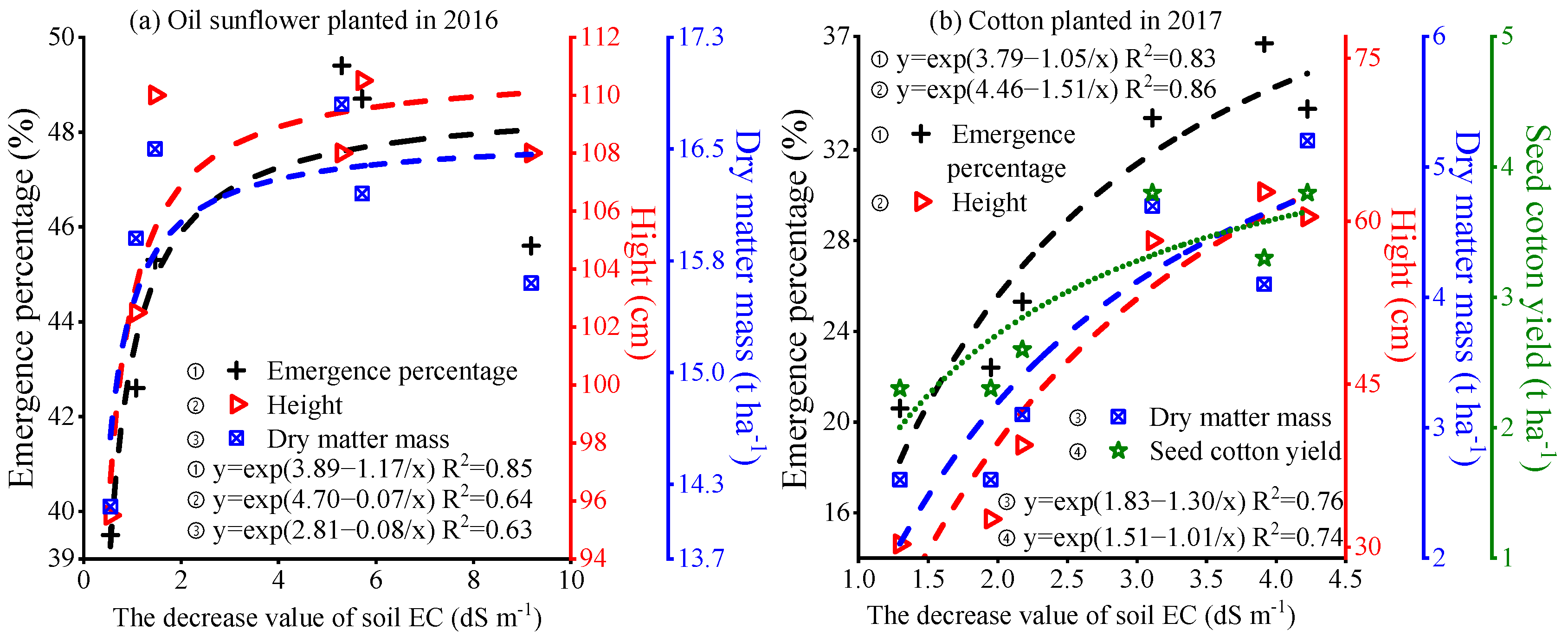
3.5. Crop Growth and Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. The Relationship Between Soil EC, Groundwater Level, and Salt Concentration of Groundwater
4.2. The Relationship between Soil Desalination Rate, Drainage Flow, and Salt Concentration of the Drainage Water
4.3. Effect of Soil EC on Cotton Growth in Saline–Alkali Cultivated Land
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.N.; Cui, W.; Li, W.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Utilization of Water Resources and Ecological Protection in the Tarim River. Acta Geogr. Sinica 2003, 58, 215–222. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Amezketa, E. An integrated methodology for assessing soil salinization, a pre−condition for land desertification. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 67, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrakhimov, M.; Khamzina, A.; Forkutsa, I.; Paluasheva, G.; Lamers, J.P.A.; Tischbein, B.; Vlek, P.L.G.; Martius, C. Groundwater table and salinity: Spatial and temporal distribution and influence on soil salinization in Khorezm region (Uzbekistan, Aral Sea Basin). Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2007, 21, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj, A.Z.; Bouri, S. Subsurface Drainage System Performance, Soil Salinization Risk, and Shallow Groundwater Dynamic Under Irrigation Practice in an Arid Land. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 467–477. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.R.; Ayars, J.E. Strategies for reducing subsurface drainage in irrigated agriculture through improved irrigation. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2002, 16, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.N.; Gibson, R.D. The Economics of Agriculture in the Maricopa−Stanfield Irrigation and Drainage District in Central Arizona. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2000, 14, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshadi, M.; Fahandej, S.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Effects of salinity and irrigation water management on soil and tomato in drip irrigation. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2013, 7, 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Tao, S. Study on Land Use/Cover Changes and Soil Salinization in Dry Areas: A Case Study of Shaya County in Xinjiang. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.; Liao, R.K.; Wang, Z.H. Effects of combined drip irrigation and sub−surface pipe drainage on water and salt transport of saline−alkali soil in Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 932–945. [Google Scholar]
- Naftchali, D.A.; Abdullah, R.H.; Karandish, F.; Bidgoli, M.A.; Nasr, M.G. Alternate wetting and drying for different subsurface drainage systems to improve paddy yield and water productivity in Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukolaee, M.J.; Naftchali, A.D.; Parvariji, L.Z. Investigating long−term effects of subsurface drainage on soil structure in paddy fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, B.; Eash, N.; Freeland, R.; Martinez, L.; Wishart, D.B. Effective and efficient agricultural drainage pipe mapping with UAS thermal infrared imagery: A case study. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Collapsibility of Loess at South Bank of The Yili Trunk Ditch in Xinjiang. J. Eng. Geol. 2008, 16, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.J.; Zhang, R.Z.; Huang, X.; Zheng, H.P.; Xie, K.Z.; Xu, P.Z. Effects of open ditch drainage on soil physical and chemical properties and yield of cold−soaked fields. J. Irrig. Drain. 2014, 33, 114–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bielorai, H.; Levy, J. Irrigation regimes in a semi−arid and their effects on grapefruit yield, water use and soil salinity. Isr. J. Agr. Res. 1971. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/293334457_Irrigation_regimes_in_a_semi-arid_area_and_their_effects_on_grapefruit_yield_water_use_and_soil_salinity (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Eziz, M.; Anwar, M.; Li, X.G. Geostatistical analysis of variations in soil salinity in a typical irrigation area in Xinjiang, northwest China. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2016, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.B.; Li, X.S.; Chi, D.C. The development status and trends of underground pipe drainage at home and abroad. Agric. Technol. 2003, 23, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, G.A. The Assessment of Egypt’s Subsurface Drainage System; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ritzema, H.P.; Nijland, H.J.; Croon, F.W. Subsurface drainage practices: From manual installation to large−scale implementation. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.A. comparative analysis of technological models of saline−alkali land improvement by open ditch and underground pipe drainage. Agric. Inf. China 2016, 13, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.J.; Ma, J.; Yang, B. Stable isotope evidence for a Paleogene high-altitude setting of the Sikeshu drainage basin in the northern Tianshan, western China. Geomorphology 2019, 342, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, H.F.; Valdes, G.S.; Lee, H.C. Mulch effects on rainfall interception, soil physical characteristics and temperature under Zea mays L. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 91, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, H.H.; Rieckh, H.; Sommer, M. Interactions between crop, water, and dissolved organic and inorganic carbon in a hummocky landscape with erosion-affected pedogenesis. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, D.; De, J. Field measurements for tests of soil drainage theory 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1952, 16, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual model part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Yang, H.C.; Wang, K.Y.; Lu, T.; Zhang, F.H. Shallow subsurface pipe drainage in Xinjiang lowers soil salinity and improves cotton seed yield. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.Y.; Grunwald, S.; Beck, H.W.; Jung, Y.; Daroub, S.H.; Lang, T.A.; Morgan, K.T. Ontology-based simulation of water flow in organic soils applied to Florida sugarcane. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.X.; Li, G.S.; Mu, X.B. Different drainage methods in wheat fields and their effects on wheat growth. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 1988. (In Chinese). Available online: http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSNY198811000.htm (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Chapman, A.S.; Foster, I.D.; Lees, J.A.; Hodgkinson, R.A. Sediment delivery from agricultural land to rivers via subsurface drainage. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 19, 2875–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.R.; Grattan, S.R.; Fulton, A. Agricultural Salinity and Drainage, revised ed. Div. Agric. Nat. Resour. Publ. 2006, 3375, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.P.; Letey, J. Development and evaluation of ENVIRO-GRO, an integrated water, salinity, and nitrogen model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.; Hoffman, G. Crop salt tolerance current assessment. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1977, 103, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.V. Salt tolerance of plants. App. Agric. Res. 1986, 1, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Zou, J.; Liu, S. Annual accounting of net greenhouse gas balance response to biochar addition in a coastal saline bioenergy cropping system in China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 158, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, J.; Saqib, Z.; Sarfraz, M.; Saleem, I.; Haq, M.A. Evaluating salt tolerant cotton genotypes at different levels of NaCl stress in solution and soil culture. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H. Technology and field management for controlling soil salinity effects on cotton. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 6, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Ye, W.W.; Zhou, D.Y.; Jun, L.Y.; Song, L.Y. Studies on Germination Characteristics of Different Salinity-resistant cotton under Salt Stress. Cotton Sci. 2007, 19, 315–317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, M.A.; Malik, M.D. Farm production losses in salt affected soils. Proc. Nat. Congr. Soil 1988, 6–8, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ghumman, A.R.; Ghazaw, Y.M.; Niazi, M.F.; Hashmi, H.N. Impact assessment of subsurface drainage on waterlogged and saline lands. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 172, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritzema, H.P.; Satyanarayana, T.V.; Raman, S.; Boonstra, J. Subsurface drainage to combat waterlogging and salinity in irrigated lands in India: Lessons learned in farmers’ fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cotton Growth | Irrigation Date | Irrigation Time (h) | I Quota (m3 ha−1) | Oil Sunflower Growth | Irrigation Date | Irrigation Time (h) | I Quota (m3 ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Squaring | 20 May 10 Jun | 30 24 | 450 600 | Seedling | 8 Jun | 33 | 800 |
| Flowering | 25 Jun 5 Jul 11 Jul | 25 25 24 | 600 600 600 | Squaring | 25 Jun 5 Jul 16 Jul | 30 31 30 | 675 675 675 |
| Bolling | 20 Jul 5 Aug 10 Aug | 24 25 24 | 600 600 600 | Flowering | 25 Jul 8 Aug 13 Aug | 30 31 30 | 675 675 675 |
| Boll opening | 19 Aug | 25 | 600 | Maturity | 26 Aug | 31 | 675 |
| Leaching Scheme | 1st Drip Irrigation Leaching (DL1) | 2nd Drip Irrigation Leaching (DL2) | 3rd Drip Irrigation Leaching (DL3) | ||||
| Leaching date | 8 Jun 2016 | 8 Sep 2016 | 18 Apr 2017 | ||||
| Total quota (m3 ha−1) | 8000 | 7500 | 7500 | ||||
| Leaching time (h) | 60 | 64 | 56 | ||||
| Treatment | 0–20 cm Soil Layer (%) | 20–40 cm Soil Layer (%) | AVG 1 (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | ||
| Subsurface pipe drainage | |||||||||
| P1 | 25.0 a | 35.5 a | 47.6 a | 21.9 a | 38.8 a | 43.6 a | 61.3 a | 8.2 a | 35.2 a |
| P2 | 30.0 a | 34.7 a | 34.9 b | 18.6 a | 27.7 b | 35.0 b | 48.2 b | −11.5 c | 27.6 b |
| P3 | 15.8 b | 17.9 b | 26.4 c | 21.6 a | 26.4 b | 31.1 b | 56.9 b | 10.6 a | 25.8 b |
| Open ditch drainage | |||||||||
| D1 | 4.2 c | 1.7 c | −0.5 d | 3.4 c | 6.5 c | 2.8 c | 1.7 c | 2.4 b | 2.8 c |
| D2 | 1.5 c | 2.3 c | 2.5 d | 10.9 b | 9.5 c | 2.4 c | 8.6 c | 3.7 b | 5.3 c |
| D3 | 3.6 c | 3.2 c | 6.6 d | 12.0 b | 10.7 c | 4.4 c | −0.2 c | 15.6 a | 6.9 c |
| ANOVA (p−value) | |||||||||
| Pa (df1) | 0.041 * | 0.024 * | 0.005 ** | 0.185 | 0.047 * | 0.038 * | 0.029 * | 0.015 * | 0.022 * |
| Da (df2) | 0.075 | 0.083 | 0.067 | 0.036 * | 0.121 | 0.156 | 0.087 | 0.035 * | 0.088 |
| Pa × Da (df2) | 0.021 * | 0.064 * | 0.034 * | 0.069 | 0.284 | 0.076 | 0.097 | 0.041 * | 0.068 |
| Difference Source | Intergroup | Intragroup | Total | Multiple Comparisons | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of squares | 6682.157 | 257.084 | 6939.241 | MD 3 | 51.83167 * |
| df 1 | 6 | 8 | 48 | SEM 4 | 3.29607 |
| RMS 2 | 3341.079 | 25.708 | p-value | 0.001 | |
| F-value | 129.961 | 95% CI 5 | 44.4876 | ||
| F-test | F < F0.01 | 59.1758 | |||
| p-value | 0.004 | ||||
| Treatment | Oil Sunflower (2016a) | Cotton (2017a) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP 1 (%) | Height (cm) | DM 2 (t ha−1) | EP 1 (%) | Height (cm) | DM 2 (t ha−1) | SCY 3 (t ha−1) | |
| Subsurface Pipe Drainage | |||||||
| P1 | 45.6b | 103.5b | 15.6a | 36.7a | 62.7a | 4.1b | 3.3b |
| P2 | 49.4a | 108.0a | 16.8a | 33.4a | 58.2a | 4.7a | 3.8a |
| P3 | 48.7a | 110.5a | 16.2a | 33.8a | 60.4a | 5.2a | 3.8a |
| Open Ditch Drainage | |||||||
| D1 | 39.5b | 95.5c | 14.1a | 21.6b | 30.3c | 2.6c | 2.3c |
| D2 | 42.6b | 102.5b | 15.9a | 22.4b | 32.6c | 2.6c | 2.3c |
| D3 | 45.3b | 110.0a | 16.5a | 25.3b | 39.4b | 3.1c | 2.6c |
| ANOVA (p−value) | |||||||
| Pa (df1) | 0.043 * | 0.034 * | 0.120 | 0.185 | 0.095 | 0.042 * | 0.035 * |
| Da (df2) | 0.076 | 0.009 ** | 0.084 | 0.259 | 0.028 * | 0.162 | 0.295 |
| Pa × Da (df2) | 0.062 | 0.027 * | 0.303 | 0.012 * | 0.035 * | 0.039 * | 0.225 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Heng, T.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Feng, Y. Study on the Farmland Improvement Effect of Drainage Measures under Film Mulch with Drip Irrigation in Saline–Alkali Land in Arid Areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084159
Zhao L, Heng T, Yang L, Xu X, Feng Y. Study on the Farmland Improvement Effect of Drainage Measures under Film Mulch with Drip Irrigation in Saline–Alkali Land in Arid Areas. Sustainability. 2021; 13(8):4159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084159
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li, Tong Heng, Lili Yang, Xuan Xu, and Yue Feng. 2021. "Study on the Farmland Improvement Effect of Drainage Measures under Film Mulch with Drip Irrigation in Saline–Alkali Land in Arid Areas" Sustainability 13, no. 8: 4159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084159
APA StyleZhao, L., Heng, T., Yang, L., Xu, X., & Feng, Y. (2021). Study on the Farmland Improvement Effect of Drainage Measures under Film Mulch with Drip Irrigation in Saline–Alkali Land in Arid Areas. Sustainability, 13(8), 4159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084159






