Mode Choice Change under Environmental Constraints in the Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
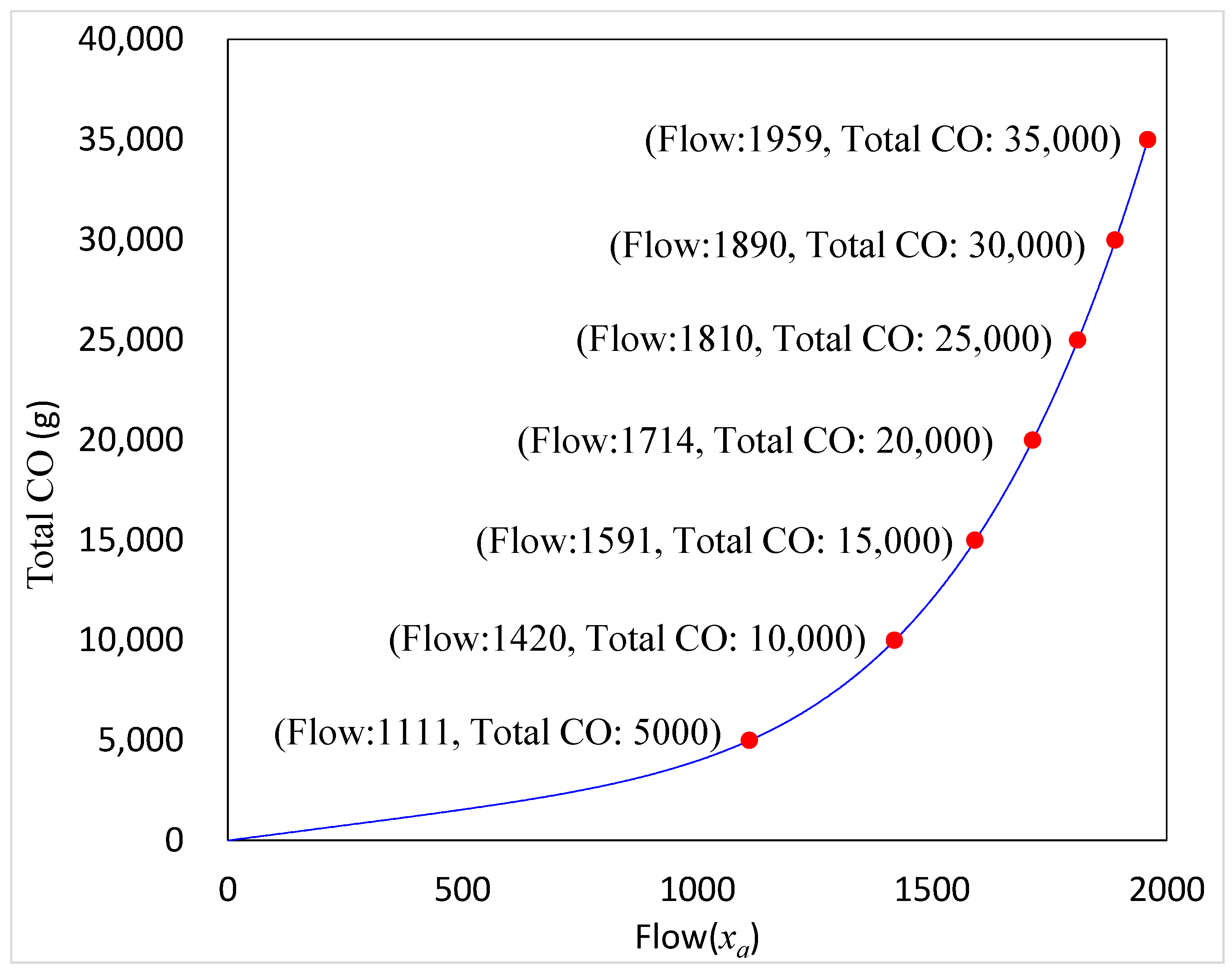
2. Environmental Constraint
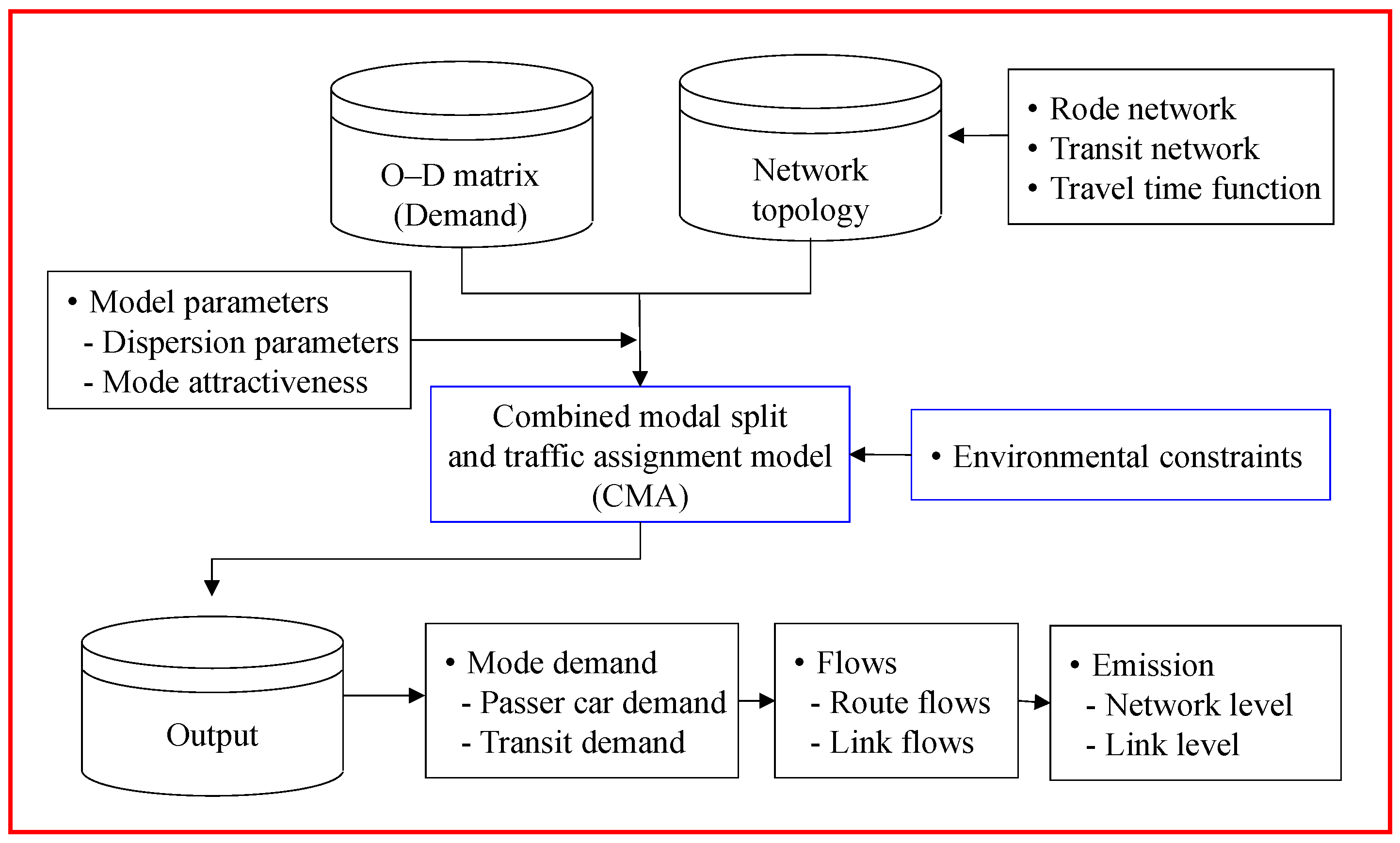
3. Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Problem with the Environmental Constraints
3.1. Review of the Combined Models
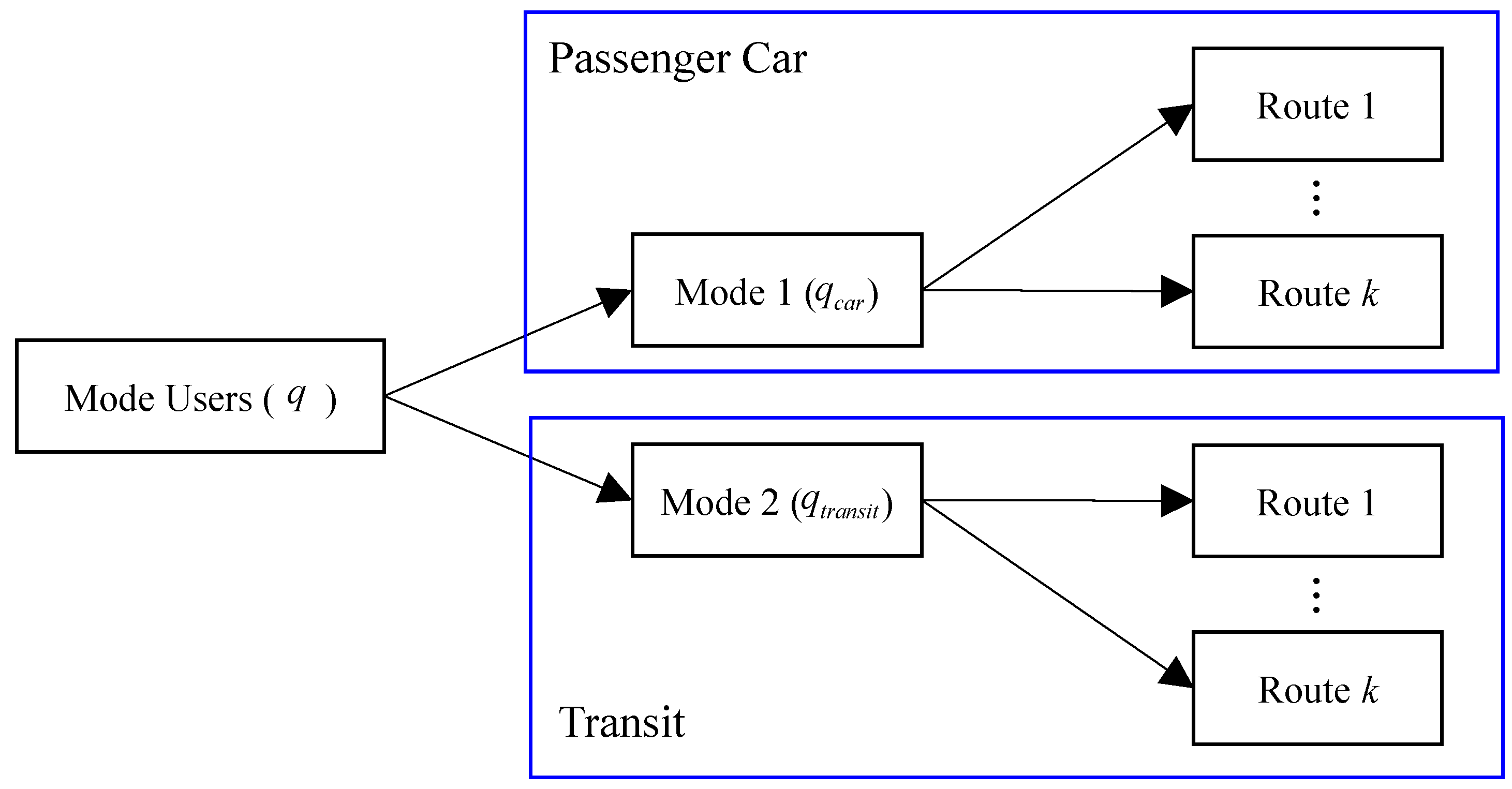
3.2. Combined Mode and Route Choices
- Mode-choice probabilitywhere is the mode-choice probability of choosing mode m, given mode set M between origin–destination pairs (O–D pair) rs; is the demand of mode m between O–D pair rs, is the total demand between O–D pair rs; is the dispersion parameters for mode choice; is the expected received disutility of all routes between O–D pair rs; RS is a set of O–D pairs; is the dispersion parameters for route choice; and is the route cost on route k between O–D pair rs in mode m.
- Route choice probabilitywhere is the route-choice probability of choosing route k, given route set in mode m; is the flow on route k of mode m between O–D pair rs; and is the route set of O–D pairs in mode m.
3.3. Mathematical Programming Formulation with Environmental Constraints
4. Solution Algorithm
4.1. Dual Variable Adjustment
4.2. Solution Procedure
- Initial primal variables: ;
- Initial dual variables: ;
- Initial path set: ;
- Compute: with given , using Equation (4).
- ;
- ;
- .
- and .
- and .
- ;
- ;
- .
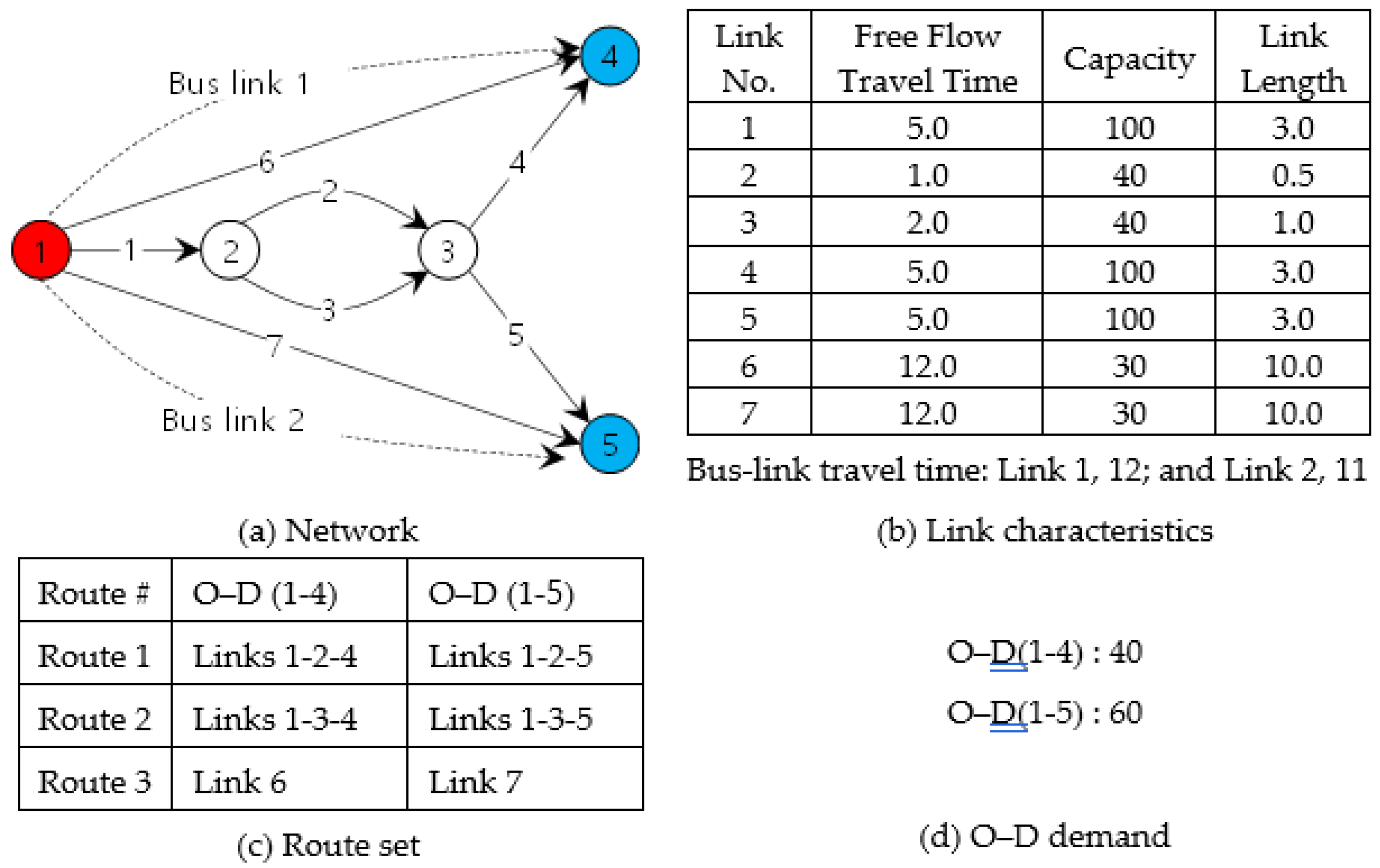
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Small Network
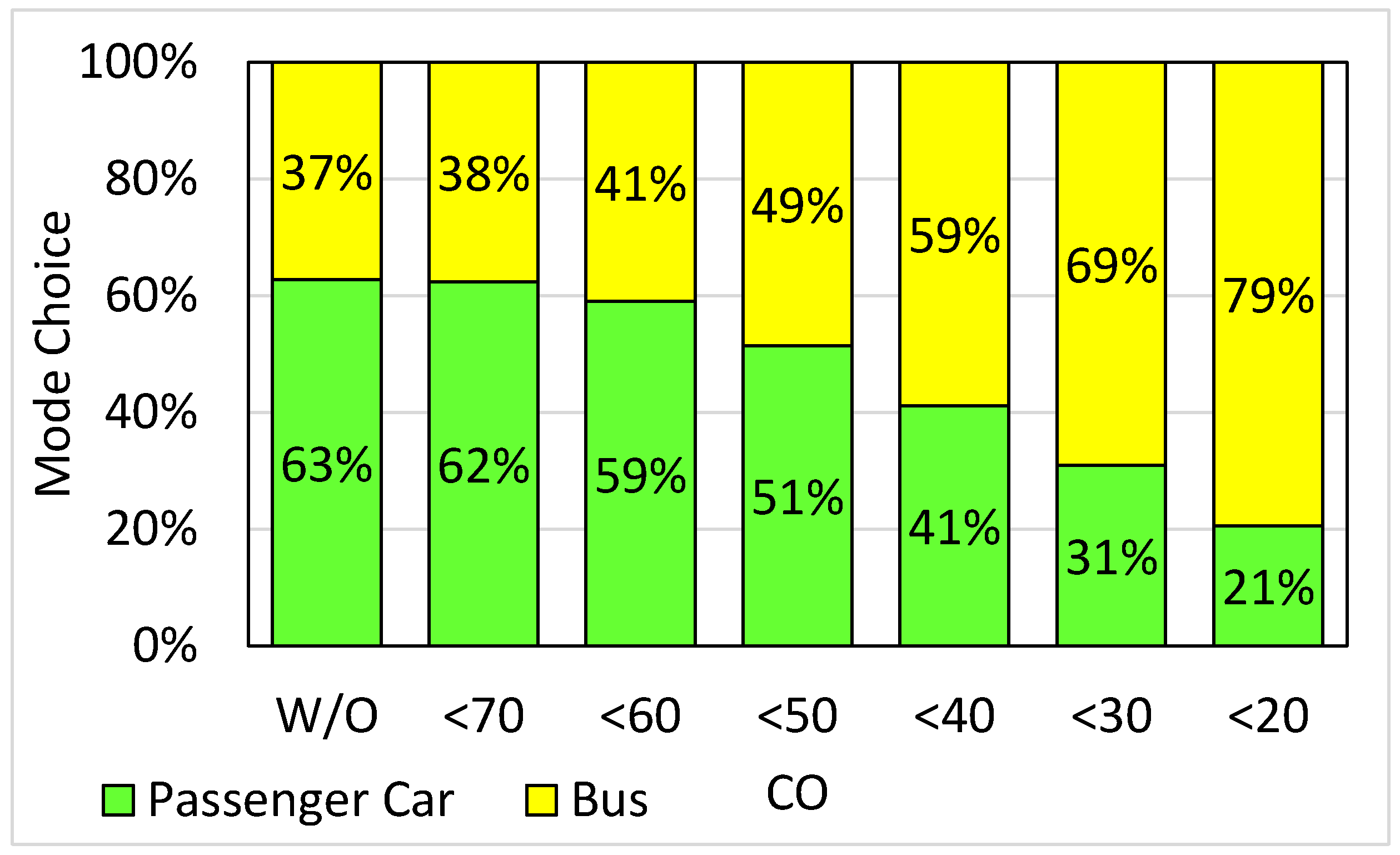
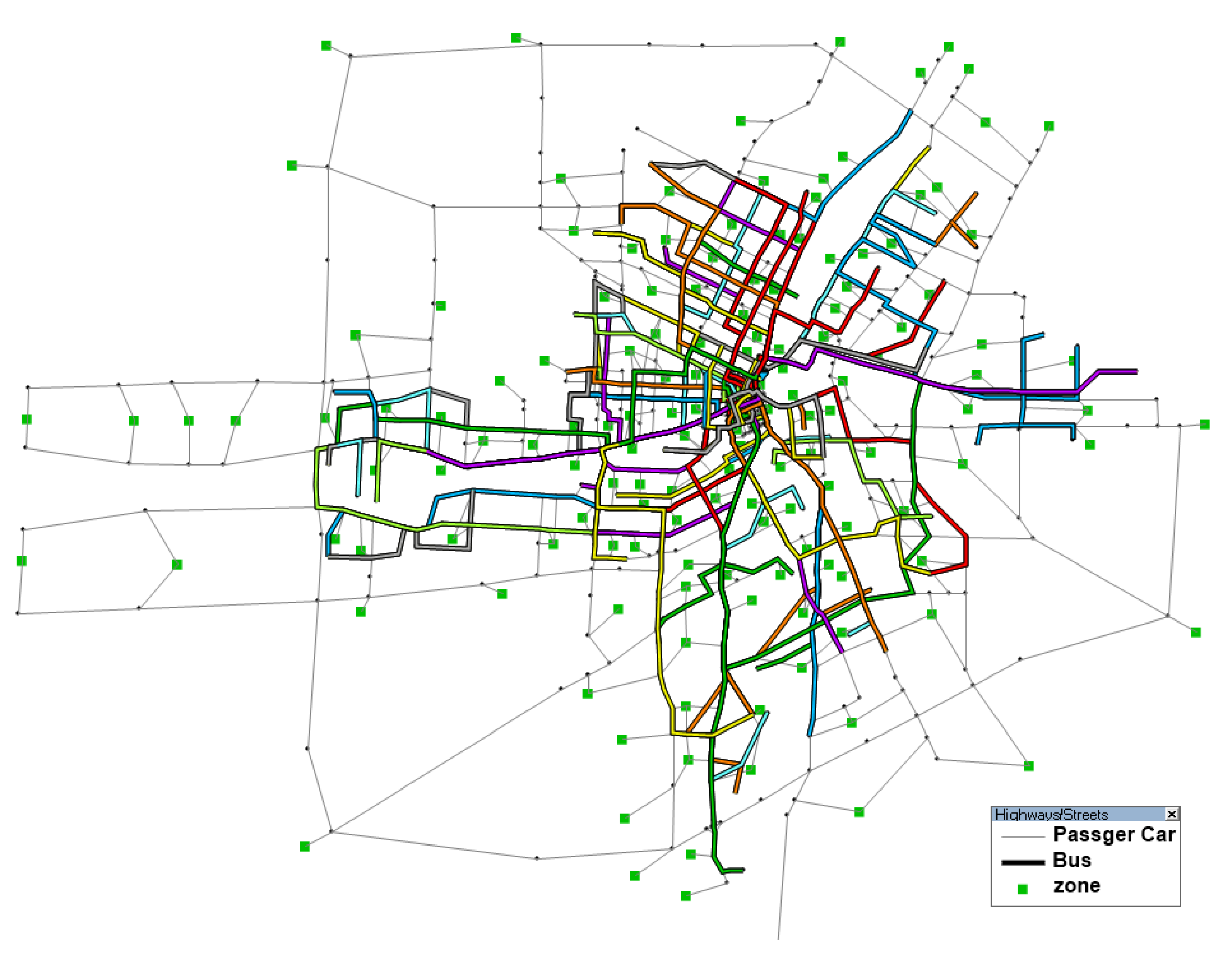
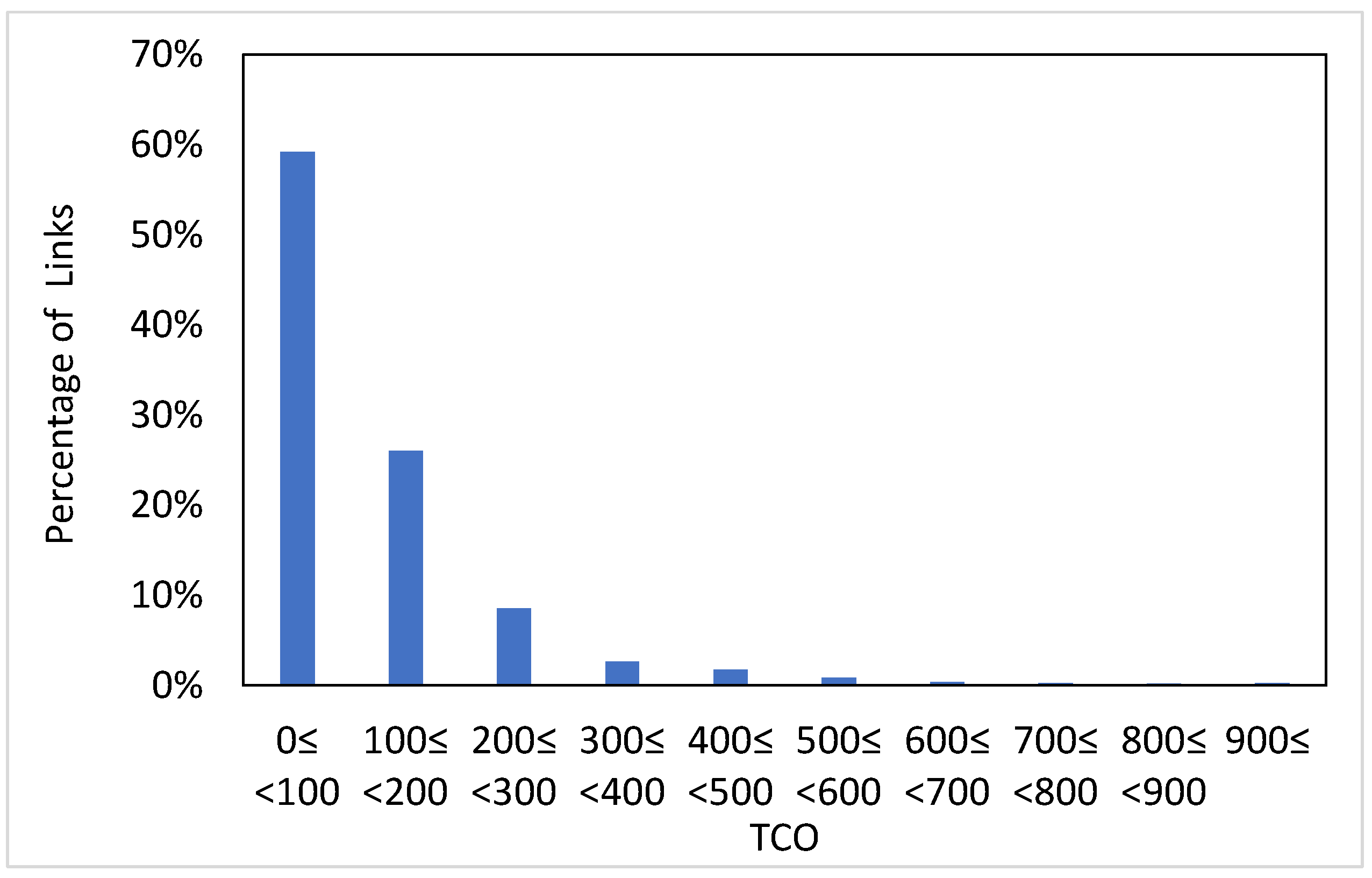
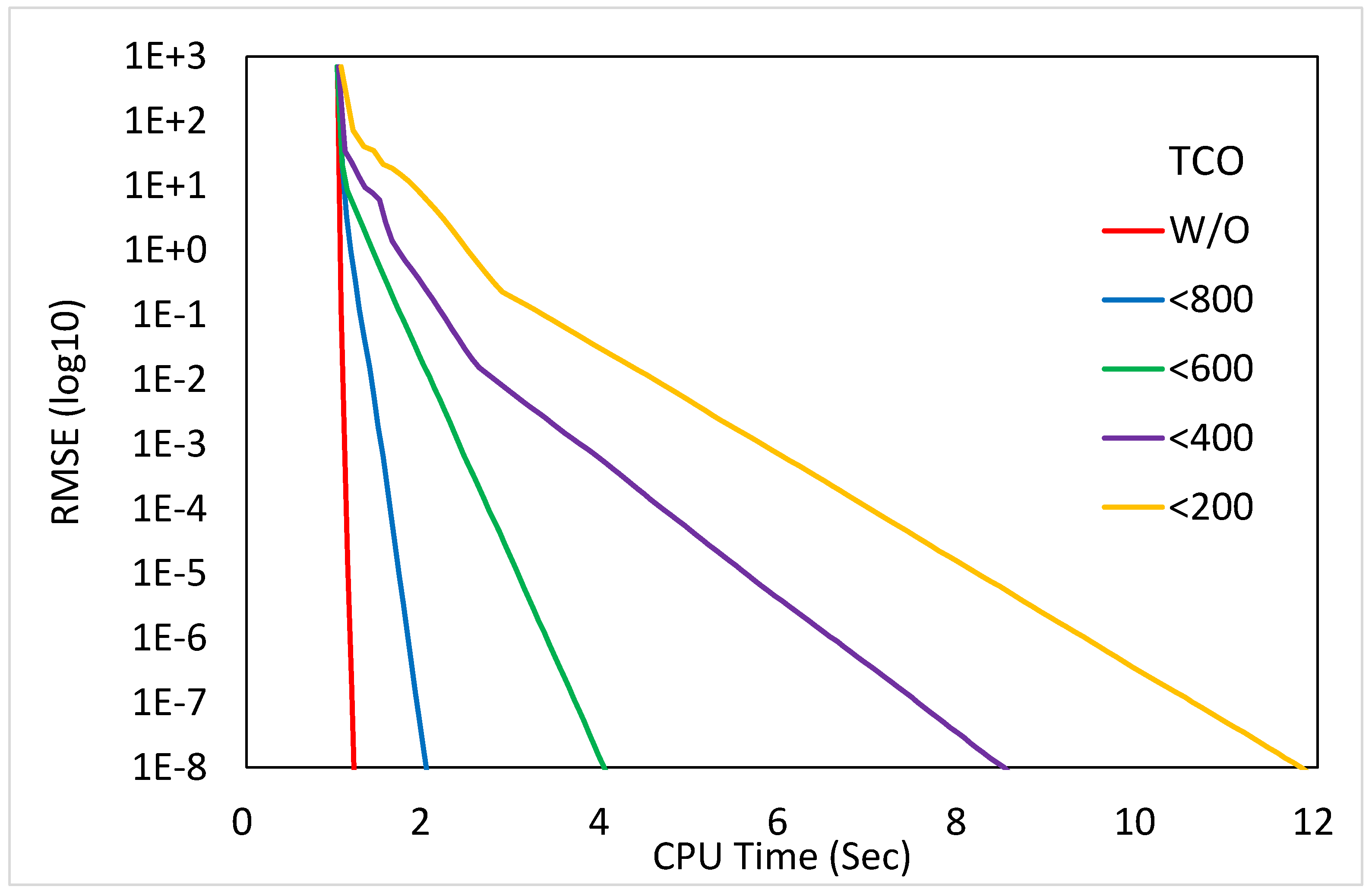
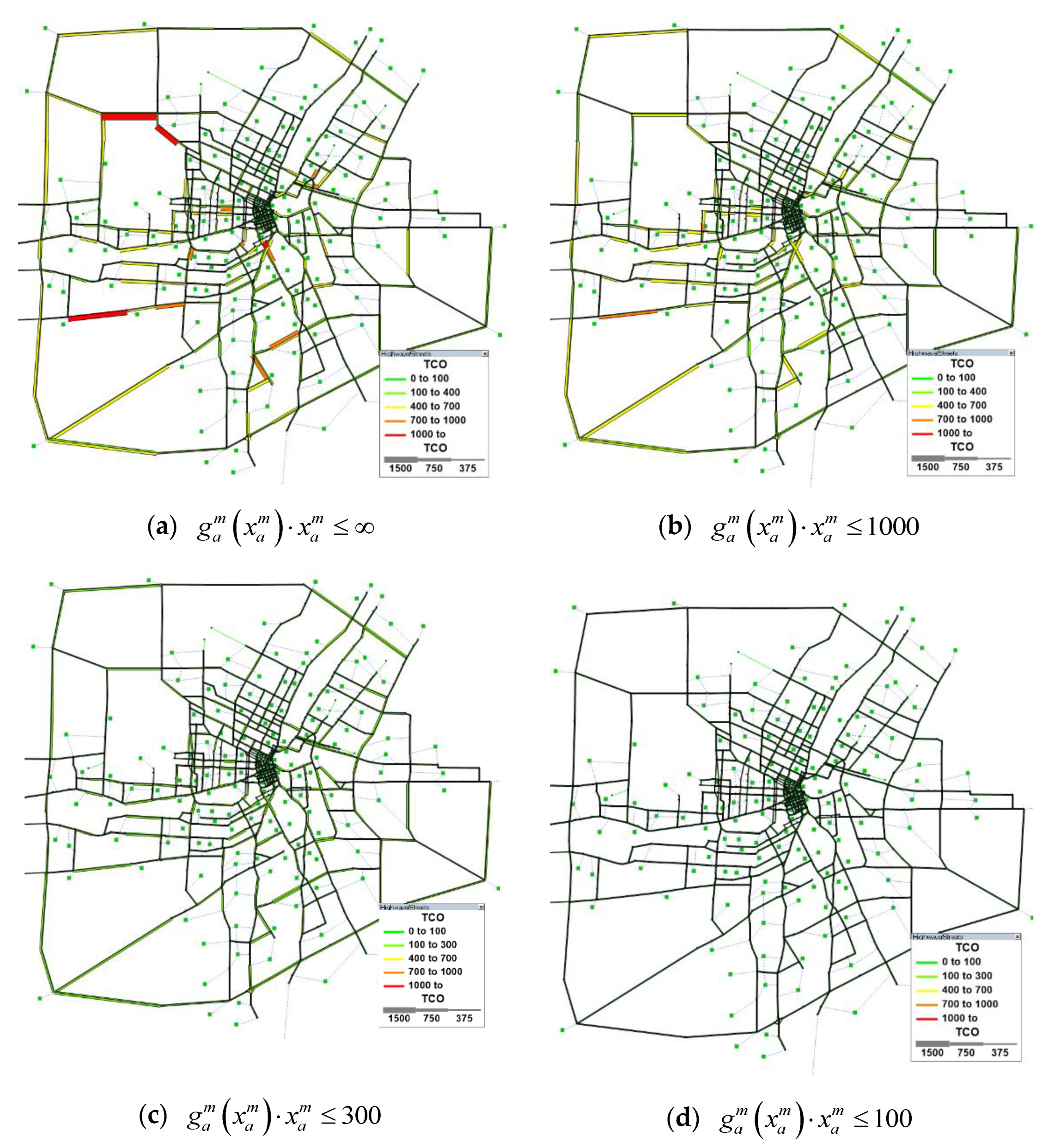
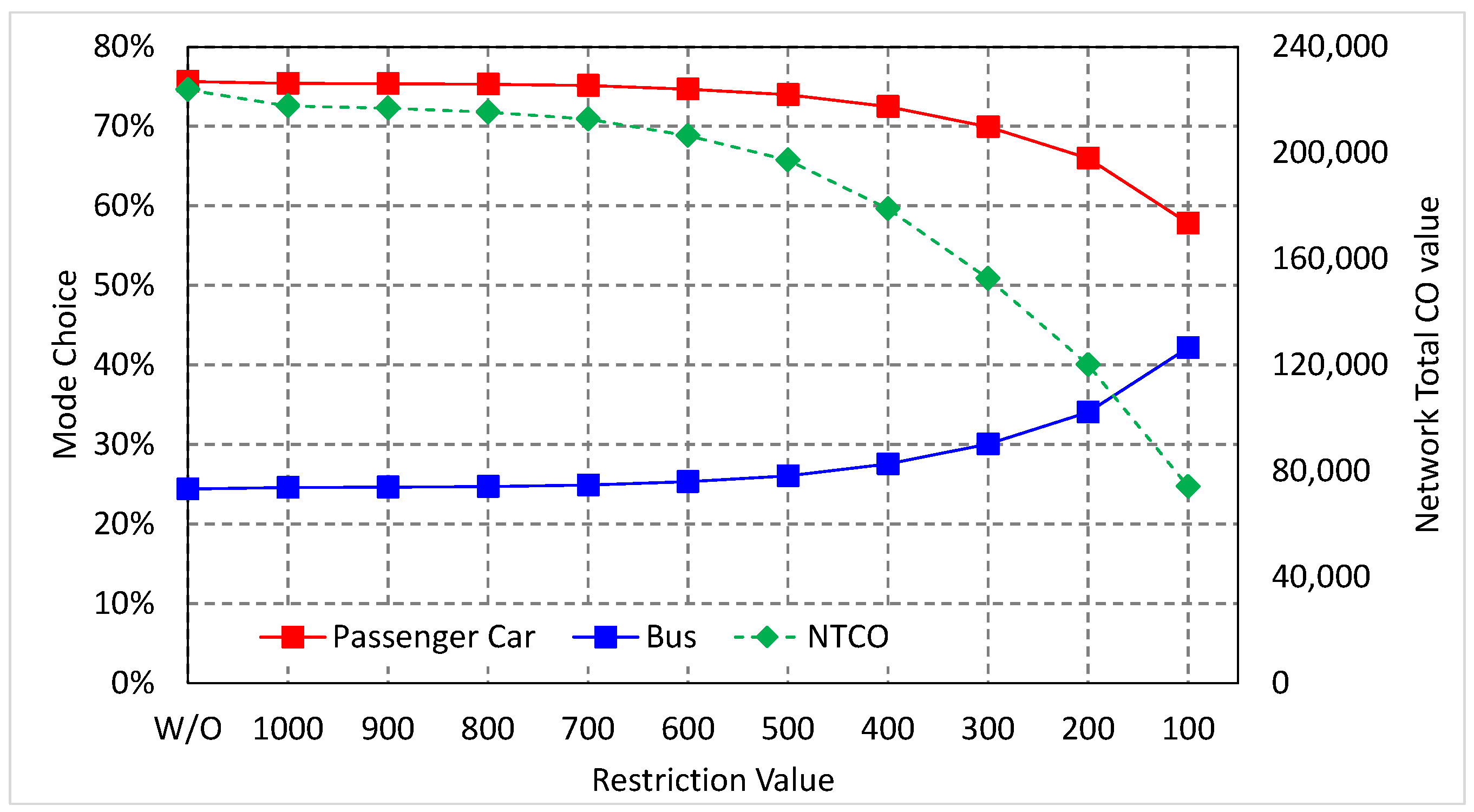
5.2. Winnipeg Network
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). U.S. Greenhouse gas Emissions and Sink. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2021-02/documents/us-ghg-inventory-2021-main-text.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). Basic Information about Carbon Monoxide (CO) Outdoor Air Pollution. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/co-pollution/basic-information-about-carbon-monoxide-co-outdoor-air-pollution (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Kheirbek, I.; Haney, J.; Douglas, S.; Ito, K.; Matte, T. The contribution of motor vehicle emissions to ambient fine particulate matter public health impacts in New York City: A health burden assessment. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Decomposition analysis of greenhouse gas emissions in Korea’s transportation sector. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoto Protocol. 1992. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyoto_Protocol (accessed on 14 March 2020).
- Paris Agreement. 2016. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paris_Agreement (accessed on 14 March 2020).
- The Korea Herald. 2019. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paris_Agreement (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Reuters. 2018. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-germany-emissions-factbox-idUSKCN1NK28L (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Auto.com. 2015. Available online: https://auto.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/passenger-vehicle/cars/ngts-ban-on-diesel-run-vehicles-over-10-years-old-in-delhi-hits-used-cars-hard/46902519 (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- The Korea Herald. 2018. Available online: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20180121000206 (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Xu, X.; Chen, A.; Cheng, L. Reformulating environmentally constrained traffic equilibrium via a smooth gap function. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2015, 9, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, M. A traffic equilibrium model of travel by car and public transit modes. Transp. Sci. 1977, 11, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaal, M.; LeBlanc, L.J. Methods for combining modal split and equilibrium assignment models. Transp. Sci. 1979, 13, 292–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; de Cea, J.; Floria, M.; Cabrera, E. Network equilibrium models with combined modes. Transp. Sci. 1994, 28, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Marin, A. Network equilibrium with combined modes models and solution algorithms. Transp. Res. Part B 2005, 39, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Chen, A.; Choi, K. Solving the combined modal split and traffic assignment problem with two types of transit impedance function. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 257, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, D.W.; Ribera, J. Bounded flow equilibrium problems by penalty methods. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Circuits and Computers, New York, NY, USA, 1–3 October 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, M.L.; Lam, W.H.K. Maximum car ownership under constraint of road capacity and parking space. Transp. Res. Part A 2000, 34, 145–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, M.L.; Lam, W.H.K. Balance for car ownership under user demand and road network supply conditions-case study in Hong Kong. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2004, 130, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Huang, H.J.; Lam, W.H.; Wong, S.C. A model for evaluation of transport policies in multimodal networks with road and parking capacity constraints. J. Math. Model. Algorithms 2006, 6, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Chen, A.; Xu, X.; Choi, K. A dual approach for solving the combined distribution and assignment problem with link capacity constraints. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2014, 14, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, T.; Li, X. A log-exponential smoothing method for mathematical programs with complementarity constraints. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 218, 5900–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green House Online. 2021. Available online: http://www.ghgonline.org/otherco.htm (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Larsson, T.; Patriksson, M. Side constrained traffic equilibrium models-analysis, computation and applications. Transp. Res. Part B 1999, 33, 233–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.G.H. Stochastic user equilibrium assignment in network with queues. Transp. Res. Part B 1995, 29, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lam, W.H.K. Optimal road tolls under conditions of queuing and congestion. Transp. Res. Part A 1996, 30, 319–332. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, T.; Patriksson, M.; Rydegren, C. A column generation procedure for the side constrained traffic equilibrium problem. Transp. Res. Part B 2004, 38, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhou, Z.; Ryu, S. Modeling physical and environmental side constraints in traffic equilibrium problem. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2011, 5, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P. Road pricing and network equilibrium. Transp. Res. Part B 1995, 29, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Bell, M.G.H. Traffic restraint, road pricing and network equilibrium. Transp. Res. Part B 1997, 31, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kim, I. Modelling rail-based park and ride with environmental constraints in a multimodal transport network. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, C.E.; Courage, K.G.; Hadi, M.A.; Gan, A.G. TRANSYT-7 F User’s Guide; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Lawphongpanich, L. Internalizing emission externality on road networks. Transp. Res. Part D 2006, 11, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurney, A.; Qiang, Q.; Nagurney, L.S. Environmental impact assessment of transportation networks with degradable links in an era of climate change. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2010, 4, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Xu, X. Goal programming approach to solving the network design problem with multiple objectives and demand uncertainty. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 4160–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, H. Managing congestion and emissions on road networks with tolls and rebates. Transp. Res. Part B 2012, 46, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.W.; Lo, H.K. Regional air quality conformity in transportation networks with stochastic dependencies: A theoretical copula-based model. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2013, 13, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Lu, H. Designing emission charging schemes for transportation conformity. J. Adv. Transp. 2014, 48, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, A.; Cheng, L. Stochastic network design problem with fuzzy goals. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2399, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, W.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wong, S.C. The chemical reaction optimization approach to solving the environmentally sustainable network design problem. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2014, 29, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, D. Forecasting Travel on congested urban transportation networks: Review and prospects for network equilibrium models. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2007, 7, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, A.; Ryu, S.; Shi, F. A general unconstrained optimization formulation for the combined distribution-assignment problem. Transp. Res. Part B 2014, 59, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Du, M.; Jiang, X.; Chu, Z. The combined distribution and assignment model: A new solution algorithm and its applications in travel demand forecasting for modern urban transportation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Lam, W.H.K. A combined modal split and stochastic assignment model for congested networks with motorized and non-motorized Modes. Transp. Res. Rec. 2003, 1831, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canterella, G.E. A general fixed-point approach to multimode, multiuser equilibrium assignment with elastic demand. Transp. Sci. 1997, 31, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitthamkesorn, S.; Chen, A.; Xu, X.; Ryu, S. Modeling mode and route similarities in network equilibrium problem with go-green modes. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2016, 16, 33–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, M.; Nguyen, S. A combined trip distribution, modal split and trip assignment model. Transp. Res. 1978, 12, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, D.E.; Daskin, M.S. Urban Transportation. In Design and Operation of Civil and Environmental Engineering Systems; ReVelle, C., McGarity, A., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.I.; Wong, S.C.; Wu, J.H.; Yang, H.; Lam, W.H.K. A combined distribution, hierarchical mode choice, and assignment network model with multiple user and mode classes. In Urban and Regional Transportation Modeling; Lee, D.H., Ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltnham, UK, 2004; pp. 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, N. Urban Travel Demand Modeling; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Chen, A.; Xu, X. Improved partial linearization algorithm for solving the combined travel-destination-mode-route choice problem. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2013, 139, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, M.J.; McGuire, C.B.; Winsten, C.B. Studies in the Economics of Transportation; Yale University Press: New Haven, CO, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, C. Some developments in equilibrium traffic assignment. Transp. Res. Part B 1980, 14, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.G.H.; Iida, Y. Transportation Network Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Emme/4 Software. INRO Consultants, Montréal. 2013. Available online: https://www.inrosoftware.com/ (accessed on 10 March 2014).
- Bekhor, S.; Toledo, T. Investigating path-based solution algorithms to the stochastic user equilibrium problem. Transp. Res. Part B 2005, 39, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
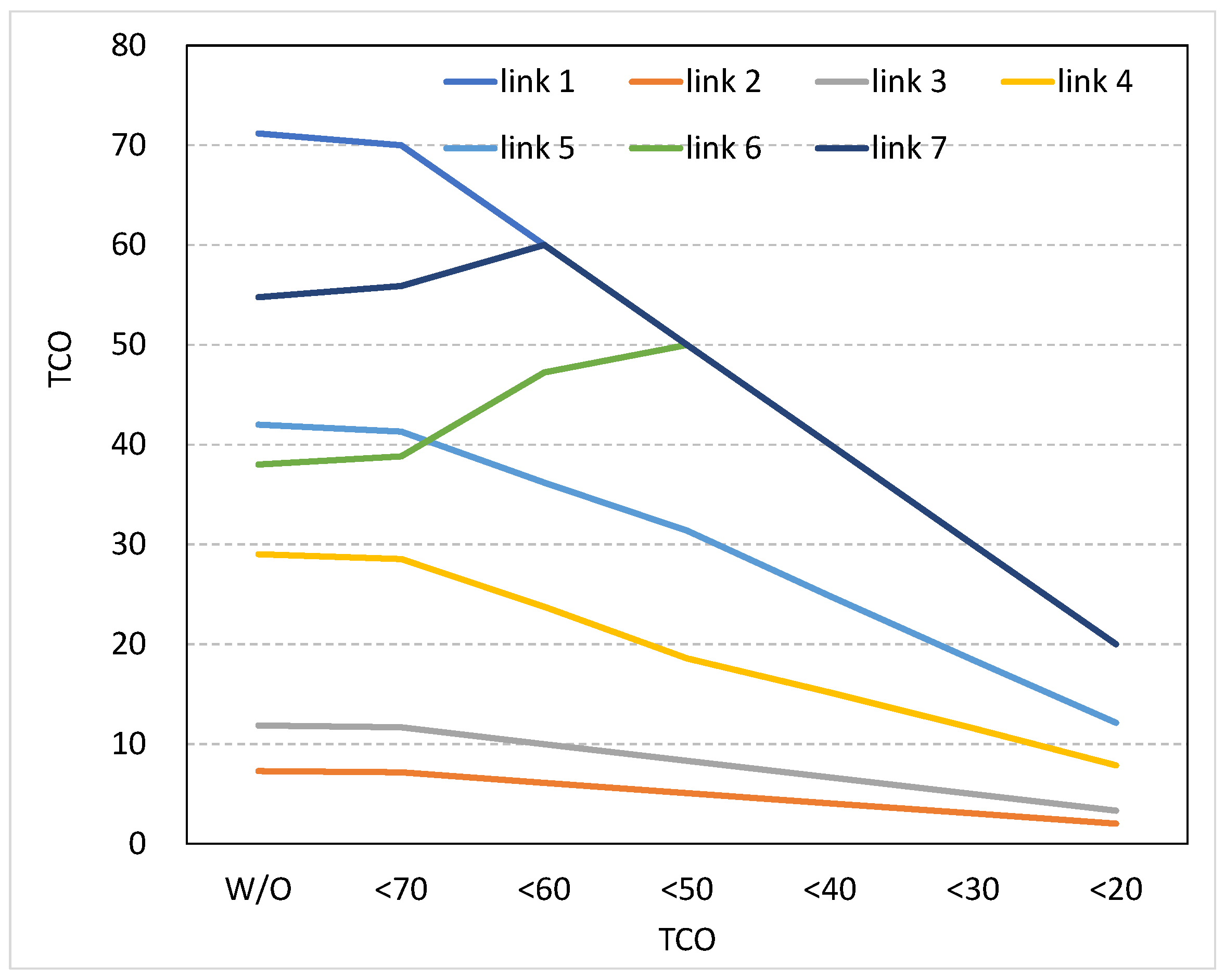
| Constraint | Link 1 | Link 2 | Link 3 | Link 4 | Link 5 | Link 6 | Link 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without constraint | Flow | 43.20 | 23.75 | 19.45 | 17.65 | 25.55 | 8.00 | 11.52 |
| TCO | 71.18 | 7.29 | 11.87 | 29.01 | 41.99 | 38.01 | 54.76 | |
| TCO | Flow | 42.50 | 23.36 | 19.13 | 17.37 | 25.13 | 8.17 | 11.76 |
| TCO | 70.00 | 7.16 | 11.67 | 28.53 | 41.30 | 38.82 | 55.89 | |
| TCO | Flow | 36.47 | 20.05 | 16.42 | 14.45 | 22.02 | 9.94 | 12.62 |
| TCO | 60.00 | 6.12 | 9.99 | 23.75 | 36.18 | 47.23 | 60.00 | |
| TCO | Flow | 30.41 | 16.72 | 13.69 | 11.31 | 19.10 | 10.52 | 10.52 |
| TCO | 50.00 | 5.09 | 8.32 | 18.59 | 31.38 | 50.00 | 50.00 | |
| TCO | Flow | 24.34 | 13.38 | 10.96 | 9.23 | 15.11 | 8.42 | 8.42 |
| TCO | 40.00 | 4.07 | 6.65 | 15.17 | 24.82 | 40.00 | 40.00 | |
| TCO | Flow | 18.26 | 10.04 | 8.22 | 7.05 | 11.21 | 6.32 | 6.32 |
| TCO | 30.00 | 3.05 | 4.99 | 11.59 | 18.41 | 30.00 | 30.00 | |
| TCO | Flow | 12.17 | 6.69 | 5.48 | 4.78 | 7.39 | 4.21 | 4.21 |
| TCO | 20.00 | 2.03 | 3.33 | 7.86 | 12.14 | 20.00 | 20.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, S. Mode Choice Change under Environmental Constraints in the Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073780
Ryu S. Mode Choice Change under Environmental Constraints in the Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Model. Sustainability. 2021; 13(7):3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073780
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Seungkyu. 2021. "Mode Choice Change under Environmental Constraints in the Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Model" Sustainability 13, no. 7: 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073780
APA StyleRyu, S. (2021). Mode Choice Change under Environmental Constraints in the Combined Modal Split and Traffic Assignment Model. Sustainability, 13(7), 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073780






