Abstract
Due to the scarcity of water, raw sewage effluents are often used to irrigate arable suburban soils in developing countries, which causes soil contamination with toxic metals. Soil microorganisms involved in biochemical transformations are sensitive to heavy metals contamination. The study was designed to investigate the effect of organic amendments on the microbial activity of cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) fractions and their bioavailability in soils contaminated with wastewater irrigation. Three metal contaminated soils under wastewater irrigation were collected, ground, sieved and added to incubation jars. Two organic amendments: wheat straw and chickpea straw, were applied (1% w/w) to the soil before incubation for 84 days at 25 °C. The CO2-C evolution after 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10 and 14 days was measured and thereafter was also measured weekly. Soil samples collected at 0, 14, 28, 42, 56, 70 and 84 days after incubation were analyzed for microbial biomass carbon (MBC). Sequential extraction for metal fractionation of samples was carried out collected at 0, 28, 56 and 84 days. Three soils differed significantly in evolved MBC and ∑CO2-C. Chickpea straw addition significantly increased soil MBC as compared to the wheat straw. Organic amendments significantly increased ∑CO2-C evolution from the soils, which was higher from chickpea straw. The addition of crop residues did not affect total Pb, Cd and Zn contents in soils. The concentration of exchangeable, carbonate bound and residual fractions of Pb, Cd and Zn decreased (6–27%), while the organic matter bound fraction increased (4–75%) with straw addition. Overall, the organic amendments improved microbial activity and reduce the bioavailability of toxic metals in wastewater irrigated soils. Furthermore, organic amendments not only reduce economic losses as they are cheap to produce but also minimize human health risks from heavy metals by hindering their entry into the food chain.
1. Introduction
Toxic metals contamination in soils is a key environmental problem because it adversely affects humans, animals and soil health [1]. In recent years, an estimated 12.6 million people have died worldwide from more than 100 diseases caused by unhealthy environments such as contaminated soils [2]. Despite all of the health risks, industries are reluctant to safely dispose of wastewater that needs huge finances. Several studies in South Africa and other regions of the world, including Kenya, Iran, Tunisia, Poland, China and the United States, have documented heavy metal contaminations in soil and aquatic environments [3]. In Nigeria, Senegal and many other countries, young children have died from Pb contaminated soil exposure [4]. It is estimated that globally, approximately 20 million ha of land is irrigated with wastewater, and this practice has intensified in recent years due to scarcity of water [5]. Waste effluents not only contain substantial amounts of organic carbon (OC) and essential plant nutrients to benefit crops but also possess organic and inorganic pollutants, including toxic metals which tend to accumulate in soil [6]. Higher rates of toxic metals in soil are a major concern, as metal ions persist and their negative effects could be long lasting. In particular, the soil microorganisms which play a key role in biochemical transformations essential for soil productivity have been found to be sensitive to heavy metals [1]. A decline in diversity, population size, respiration rate, microbial biomass and the overall activity of soil microbial communities in metal contaminated soils has been reported [7]. Moreover, crop plants grown in contaminated soils uptake metal and leads to their entry into the food-chain, resulting in serious health concerns [8].
Chemical species and relative distribution of heavy metals in soil control the behavior of heavy metals in a soil-plant system. The species and forms of metals are more important to access their bioavailability and potential toxicity in soil rather than their total dissolved concentration [9]. Organic materials play an important role in determining the mobility and eco-toxicity of metals [10]. Total metal content in soil can be divided into the following fractions: (i) water-soluble and exchangeable, (ii) carbonate-bound, (iii) Fe-Mn oxide-bound, (iv) organic matter (OM)-bound, and (v) residual forms [8]. Water-soluble and exchangeable metal fractions are considered to be bio-available and the oxide-, carbonate- and OM-bound fractions might be potentially bio-available, while the residual fraction is not available to either plants or microorganisms [11]. Metal fractions and their bioavailability are strongly influenced by soil properties texture, pH, redox potential, cation exchange capacity (CEC) and OM content [12]. Soils with high OM content comprise a substantial amount of metals in OM-bound fractions [13].
The use of crop residues as a soil amendment is an eco-friendly agronomic practice because it not only lessens environmental pollution but also enhances nutrients availability in soils. It may also improve soil physical conditions and activities of microorganisms and enzymes in soil [14]. According to the International Humic Substances Society (IHSS), dissolved organic carbon (DOC) derived from straw contains 25% to 50% fulvic acid (FA) and humic acids (HA) [15], hydrophilic acids (HY) and a hydrophobic neutral fraction (HON) [16]. Among these fractions, low molecular weight amino acids present in HY and humic substances (HS) containing FA and HA are considered to be the most reactive and strong chelating organic fractions that control metal mobility and bioavailability by forming insoluble metal ion complexes [9,17]. Davias [18] reported that toxic metals like Pb form stable complexes with OM and become less extractable in soil containing a higher content of OC. However, the stability of metal-organic matter complexes and chelates depends upon the quality and quantity of organic substances applied and thus has a pivotal role in determining the bioavailability of metals in soil. Some previous studies demonstrated that OM addition—i.e., manure, peat, municipal solid waste, sewage sludge, compost, biochar and crop residues—has a moderate effect on the mobility of metals [19,20] and improves soil microbial biomass and some enzymatic activities [21]. During the selection of organic amendment, the economic feasibility is an important consideration. Thus, environmentally friendly agricultural crop residues are recommended for remediation of heavy metals from contaminated soils, because of their effectiveness as immobilization agents and soil conditioners, their low-costs, their high applicability and also due to their economic feasibility. With increasing risks to human health posed by contaminated soils, identifying and optimizing soil remediation techniques has become increasingly important. Considerable research work has been carried out regarding toxic metal’s effects on the growth and activities of microbial community and metals speciation in wastewater irrigated soils. The information on the microbial response to organic amendments in the presence of toxic metals and the speciation of toxic metals and their bioavailability due to organic amendments addition is scant. The main objectives of the present study were to: (i) have an insight into the toxic effects of metals (Cd, Pb and Zn) on the size and activity of soil microbial biomass and organic amendments decomposition rate in the contaminated soils, and (ii) to evaluate the organic amendment effect on Cd, Pb and Zn speciation in wastewater irrigated soils.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil and Organic Amendment Sampling
Soil samples of the Rawal soil series (Typic Ustochrepts, Inceptisols) were collected from the surface layer (0–15 cm depth) of three different agricultural sites i.e., (1) Dhoke Hassu (DH) (33°37′48.4″ N 73°01′23.6″ E), (2) Dhoke Ratta site-1 (DR-1) (33°37′00.1″ N 73°02′56.7″ E), (3) Dhoke Ratta site-2 (DR-2) (33°36′38.3″ N 73°02′52.1″ E) of the humid and subtropical areas from northern Punjab, Pakistan. The soils of these areas are well-drained, calcareous and sandy clay to loam in texture. These soils were under wastewater irrigation for the last 15 years. Soil samples collected were handpicked, homogenized and passed through a 2 mm sieve in moist conditions before freezing until the incubation study. For physicochemical analysis, a subsample was air dried and crushed to pass through the 0.25 mm sieve (Table 1).

Table 1.
Physico-chemical analysis of soils indicating variation in properties and heavy metals contents.
The organic amendments (wheat and chickpea straw) used in the study were collected from the farmlands. For the incubation experiment, straw samples were rinsed with water, air dried and chopped to pass through a 5 mm sieve. Samples of both the straws were digested with aqua regia to analyze their chemical composition (Table 2).

Table 2.
Chemical compositions showing variation in macro and micronutrient contents of the organic amendments.
2.2. Experimental Material Characterization
Soil particle size distribution was assessed by sieving and sedimentation, according to the hydrometer method [22]. Soil pH and electrical conductivity (dS m−1) were estimated in a saturated soil paste using a calibrated HANNA-212 pH meter and HANNA HI-8033 conductivity meter, respectively. The total organic carbon (TOC) was measured according to Liu et al. [23] by potassium dichromate oxidation-ferrous sulphate titrimetry. The acid neutralization method was followed for the determination of CaCO3 in soils [24]. The CEC was determined by a method described by Anderson and Ingram [25]. The Kjeldahl method was used to estimate the Total nitrogen in soils [26]. Soil phosphorous was determined calorimetrically using 0.5 M NaHCO3 as an extractant [24]. Total cadmium lead and zinc contents were determined by aqua regia digestion. Metals concentration in the digest was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer.
2.3. Experimental Design
Laboratory incubation experiment was carried out in darkness in a temperature-controlled incubator at 25 °C for 84 days. First of all, soil samples kept in the freezer were equilibrated at room temperature. De-ionized water was added to bring the soil moisture content to up to 50% of its water-holding capacity. Six hundred grams of soil was added to each incubation jar and three treatments were run for each soil: (i) un-amended control soil, (ii) soil amended with chickpea straw at the rate of 1% on a w/w basis, (iii) soil amended with wheat straw at the rate of 1% on a w/w basis. Following the completely randomized design (CRD), all the treatments were replicated in triplicate. Applied straw was thoroughly mixed and homogenized with soils. For the preparation of the control, the same amount of soil was added to the incubation jar without a straw amendment. Soil moisture was maintained by adding distilled water every 2 to 3 days for 84 days. A beaker containing 5 mL of 1 M NaOH was placed inside each incubation vessel to retain the CO2 evolved from the soil samples. Soil respiration was measured by trapping the CO2 evolved from the soil during the incubation in each jar after 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10 and 14 days and thereafter weekly. For the MBC measurement, 60 g of soil was sampled from incubation jars at different aging periods (0, 14, 28, 42, 56, 70 and 84 days). For sequential extraction of Cd, Pb and Zn samples were collected at 0, 28, 56 and 84 days of incubation.
2.4. Microbial Analyses
Soil microbial respiration was measured by trapping the CO2 evolved from the soil during the incubation in a closed system. The CO2 released was captured in 1 M NaOH solution and estimated by back-titration with 1 M HCl [27]. Soil MBC was measured by the chloroform fumigation-extraction method [28]. Ten grams of soil from fumigated and non-fumigated portions was extracted with 40 mL 0.5 M K2SO4 for Cmic and filtered after 30 min of shaking at 200 rev min−1. Organic C in the extracts was measured as CO2 by infrared absorption after combustion at 760 °C using a Shimadzu automatic TOC analyzer and MBC was calculated by using the following equation:
or
where EC is the difference of organic C extracted from the fumigated soils and organic C extracted from non-fumigated soils and kEC is equal to 0.45.
2.5. Fractionation of Cd, Pb and Zn
The sequential extraction method was applied for fractionation and speciation analysis of toxic metals (Cd, Pb and Zn), according to McGrath and Cegarra [29]. The soil samples were taken in 50 mL centrifuge tubes and was treated with different extractant solutions for each sequential extraction step, keeping a soil and solution ratio of 1:10. After each extraction step, suspension was centrifuged for 20 min at 4000 rpm. The Cd, Pb and Zn concentrations in all the extracts were estimated by GBC-932 plus atomic absorption spectroscopy. The detailed scheme of the sequential extraction procedure is explained in the following steps: (i) Metals in solution and exchangeable forms: 16 h shaking with 0.1 M CaCl2, (ii) Metals associated with OM: 16 h shaking with 0.5 M NaOH, (iii) Metals in carbonate form: 1 h shaking with 0.05 M Na2H2EDTA, and (iv) Residual metals: Digestion with aqua regia.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
The experimental data presented in tables are based on arithmetic means of three replicates on an oven-dry weight basis (105 °C, 24 h). Three-way analysis of variance was applied to data to test the significance of main factors (soil, organic amendments and sampling days) using MSTAT-C (statistical software). The treatment mean differences were calculated by using the least significant differences (LSD) test at a 0.05% level of significance.
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characterization of Soils and Organic Amendments
The data of basic physicochemical properties of the soils are given in Table 1. The pH of DH, DR-1 and DR-2 soils was in the range of 7.36 to 7.59 and EC was less than 0.7 dS m−1, which shows that soils were in the near-neutral range and agricultural salinity problem was not observed. The moisture content of these soils was in the range of 23% to 30%. Water holding capacity ranged from 41.8% to 48.1%. Total organic carbon (TOC) and CaCO3 contents of DH soil were 0.63% and 2.65%, respectively, while DR-1 soil was 0.23% and 12.5%, respectively, and DR-2 was 0.58% and 15.3%, respectively. The Dhoke Ratta soils were classified as moderately calcareous. The DH and DR-2 soils were sandy clay with sand, silt and clay percentages of 49%, 15%, 35% and 44%, 15.5%, 37.5%, respectively. The DR-1 was Loam with sand, silt and clay percentages of 44%, 37.5% and 17.5%, respectively. All the soils had low CEC values due to low OM content in the following order: DH < DR-1 < DR-2. The CEC of these soils ranged from 14–18 Cmolc Kg−1, while DR-2 had a higher CEC content (17.7 Cmolc Kg−1). Total Zn and Pb concentrations of all the three soils were within the range of 90–110 (mg kg−1) and 40–90 (mg kg−1), which were within the permissible range limits given by the Council of the European Community [30]. While total Cd content (6–7 mg kg−1) of these soils was higher than the permissible limit.
Crop residues (chickpea straw and wheat straw) varied in their chemical composition. Chickpea straw had a markedly higher content of total C, N, P, K and other essential micro and macronutrients than the wheat straw (Table 2). The chickpea straw also contained lower contents of total metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Mn, Fe) except total Cu. Wheat straw had a higher total C/total N ratio than chickpea straw.
3.2. Soil Microbial Properties Dynamics
3.2.1. Soil Respiration
The effect of organic amendments on the microbial respiration dynamics was estimated in soils at different intervals during the incubation study. Cumulative CO2-C (∑CO2-C) evolution from the soils (DH, DR-1 and DR-2 in response to organic amendments were studied.
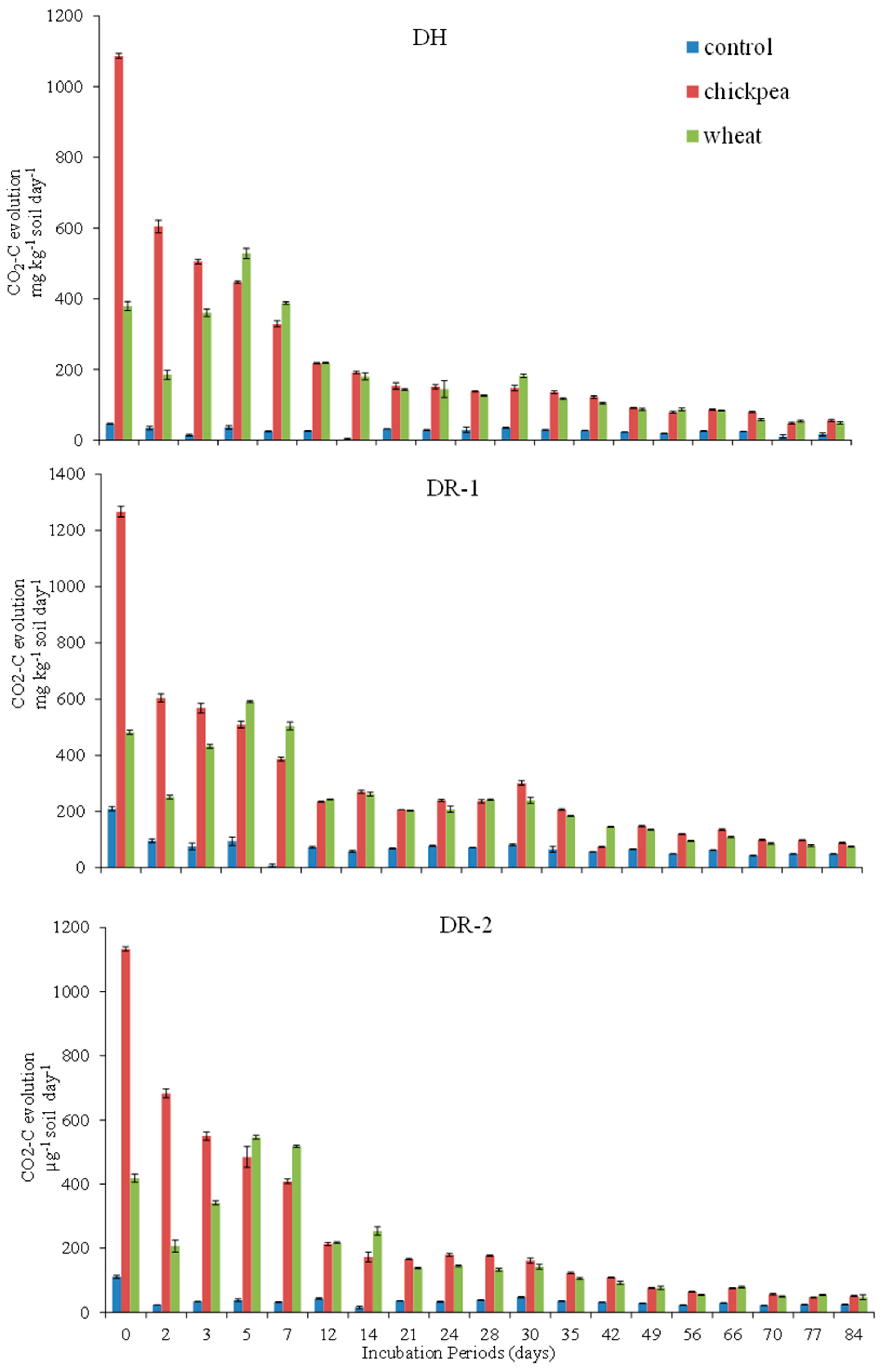
According to the results, the three soils differed significantly from one another in the case that ∑CO2-C evolved. The DR-1 had maximum (11,930 mg kg−1 soil) ∑CO2-C evolution, while the minimum from DH soil (7964 mg kg−1 soil). A significant increase in ∑CO2-C evolution was observed with the addition of chickpea straw and wheat straw; however, soil amended with chickpea straw had greater ∑CO2-C evolution (13,290 mg kg−1 soil) compared to the wheat straw amendment (11,830 mg kg−1 soil). The highest respiration rate was observed immediately after the residue addition and starts decreasing with the maturity of the experiment (Figure 1).
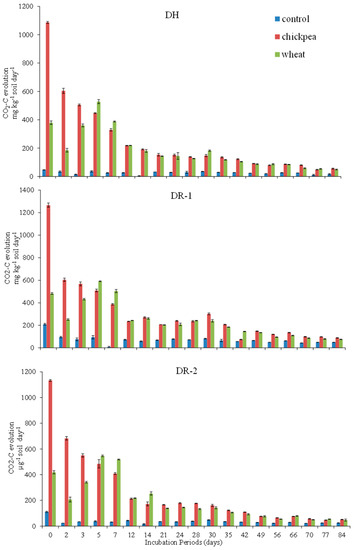
Figure 1.
Dynamics of CO2-C evolution (µg g−1 soil day−1) influenced by different organic amendments in Dhoke Hassu (DH), Dhoke Ratta site-1 (DR-1) and Dhoke Ratta site-2 (DR-2) soils depicting the fluctuation in size and activity of microbial biomass throughout the incubation period.
3.2.2. Microbial Biomass Carbon
The dynamics of soil biomass C were estimated in metal contaminated soils at different intervals during the incubation study as a result of the application of organic amendments. According to the results, MBC in three soils was significantly different from one another (Table 3).

Table 3.
Main effects of soils, organic amendments, and their interaction on cumulative CO2-C evolution (mg kg−1 soil) and microbial biomass C (mg kg−1 soil) in soils at different days after incubation.
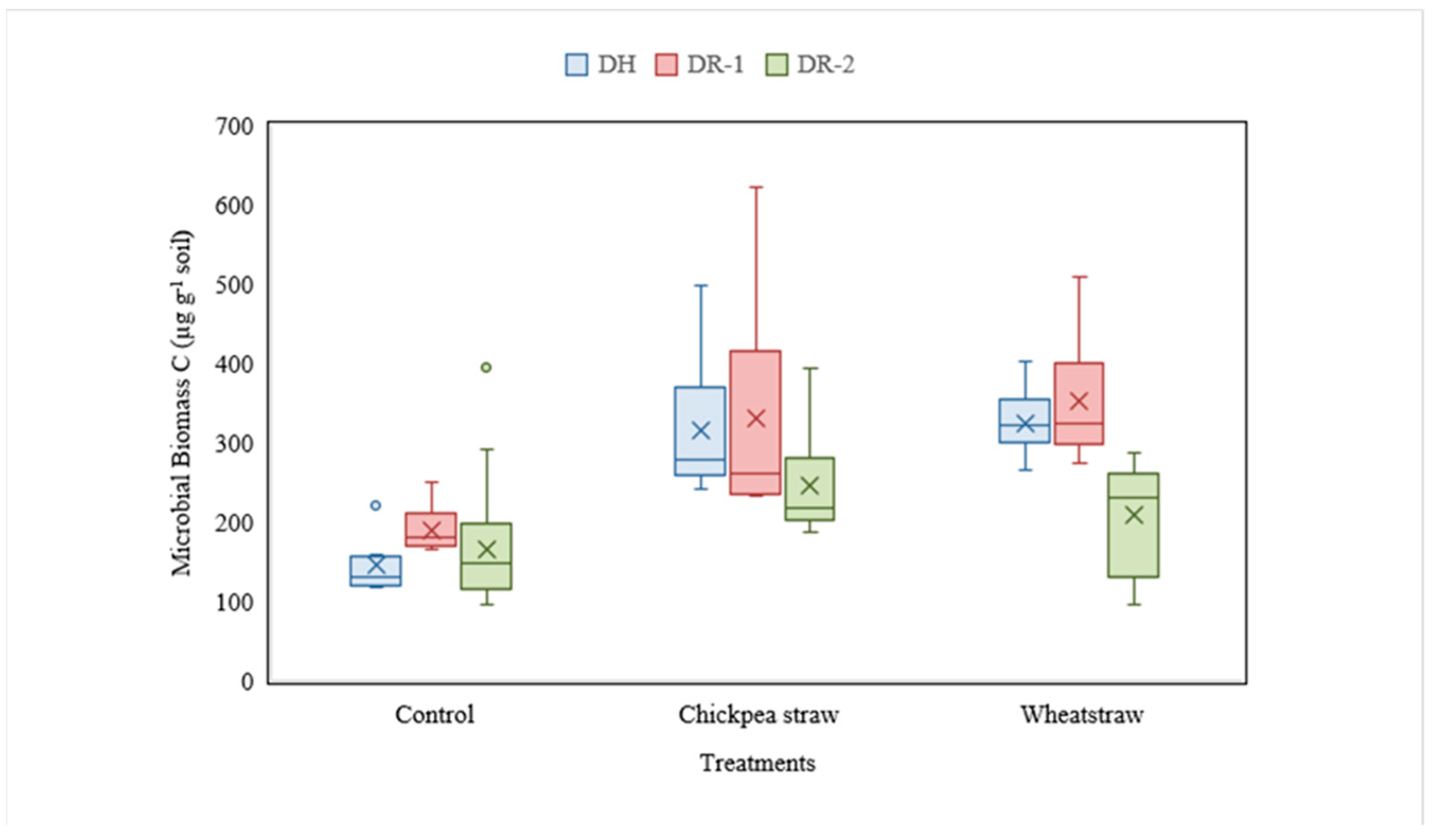
The maximum MBC (459.3 mg kg−1soil) was observed in DR-1, while the minimum MBC content (286.4 mg kg−1soil) was observed in DR-2. The addition of chickpea straw and wheat straw significantly increased MBC in the soils as compared to unamended soils. However, MBC content was significantly higher in chickpea straw amended soil (504.2 mg kg−1soil) compared to wheat straw amended soils (398.3 mg kg−1soil). The lowest MBC (216.1 mg kg−1soil) was observed in unamended control soil (Figure 2).
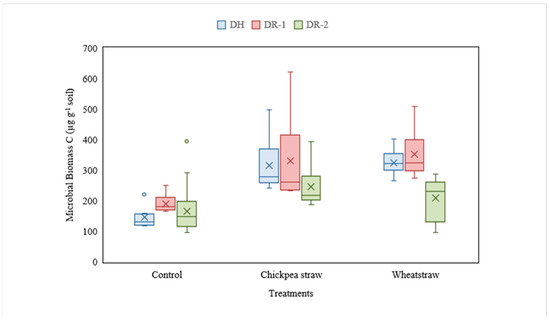
Figure 2.
Dynamics of microbial biomass C (µg g−1 soil) under different organic amendments in DH, DR-1 and DR-2 soils. Variation in the treatment effects on MBC (mg kg−1 soil) in all the three organically amended soils as compared to control was visualized on an average basis by the box and whisker plots. The middle line in each box represents the mean MBC values for each treatment. The box stretches from the first quartile to the third quartile, and the whiskers stretch 1.5 inter-quartile ranges. The organic amendment effect was significantly different in all three soils.
3.3. Metal Fractions Dynamics
3.3.1. Lead
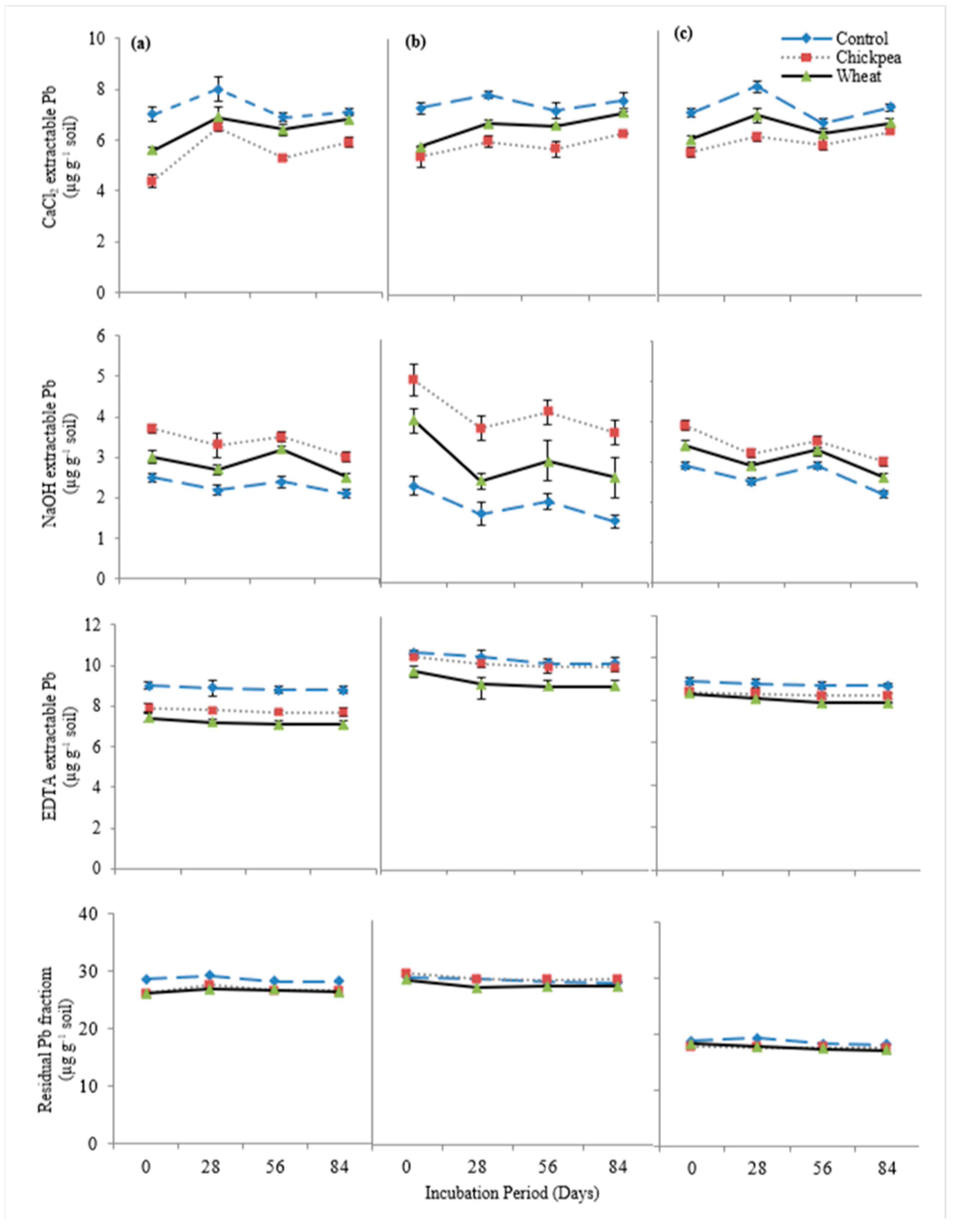
Chickpea straw addition caused a 15.6% reduction in exchangeable (CaCl2-extractable) Pb contents in the soils at the end of the incubation (Figure 3). The application of wheat straw resulted in a 6.4% reduction in exchangeable (CaCl2-extractable) Pb concentration. Chickpea straw caused a 75% increase in OM-bound (NaOH-extractable) Pb content in the soils, while the wheat straw caused a 3.5% increase in OM-bound (NaOH-extractable) Pb. The Carbonate bound (EDTA-extractable) Pb fraction was decreased by 6.7% with the addition of chickpea straw and a 13% decrease was caused due to the addition of wheat straw. Chickpea straw caused a 5% decrease in residual Pb where a 5.7% decrease was caused by the addition of wheat straw.
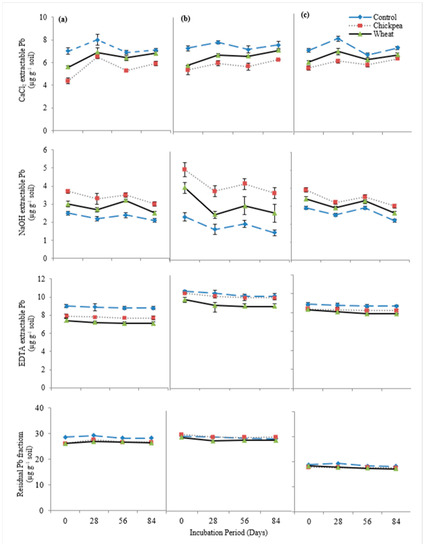
Figure 3.
Pb speciation influenced by organic amendments in (a) DH, (b) DR-1 and (c) DR-2, soils depicting the decrease in bioavailability of Pb fractions throughout the incubation period.
3.3.2. Cadmium
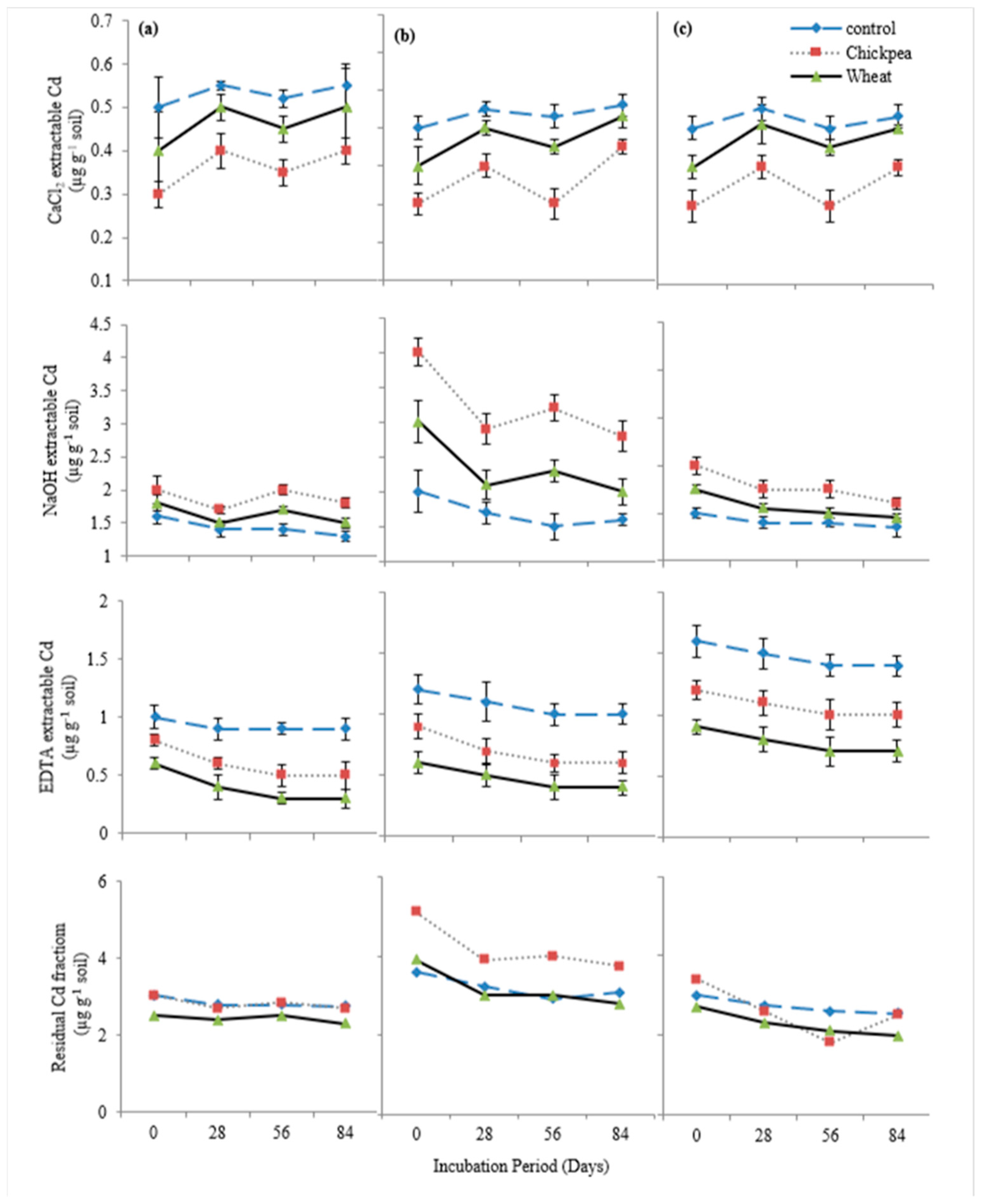
The addition of chickpea straw caused a 27% reduction in exchangeable (CaCl2-extractable) Cd contents in the soils (Figure 4). The application of wheat straw resulted in a 7.5% reduction in the exchangeable (CaCl2-extractable) Cd fraction. Chickpea straw caused a 61.5% increase in the OM-bound (NaOH-extractable) Cd content in the soils while the wheat straw caused a 23% increase in the OM-bound (NaOH-extractable) Cd fraction. The Carbonate bound (EDTA-extractable) Cd fraction was decreased by 37% with the addition of chickpea straw and a 59% decrease was caused due to the addition of wheat straw. Chickpea straw caused a 1.5% decrease in residual Cd fraction of DH soil and DR-2 and a 22.5% increase was caused in DR-1, whereas a 15% decrease was caused by the addition of wheat straw.
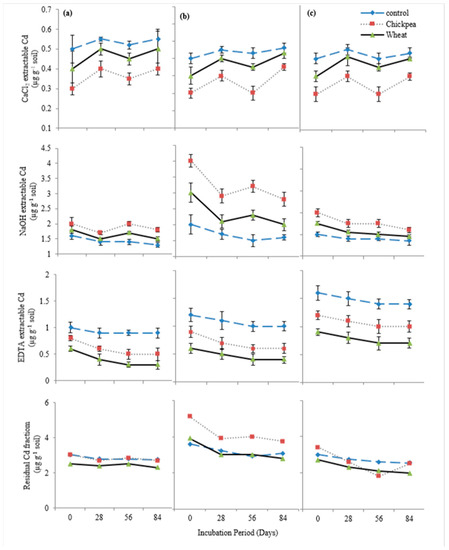
Figure 4.
Effect of organic amendments on Cd speciation in (a) DH, (b) DR-1 and (c) DR-2 soils depicting the decrease in bioavailability of Cd fractions throughout the incubation period.
3.3.3. Zinc
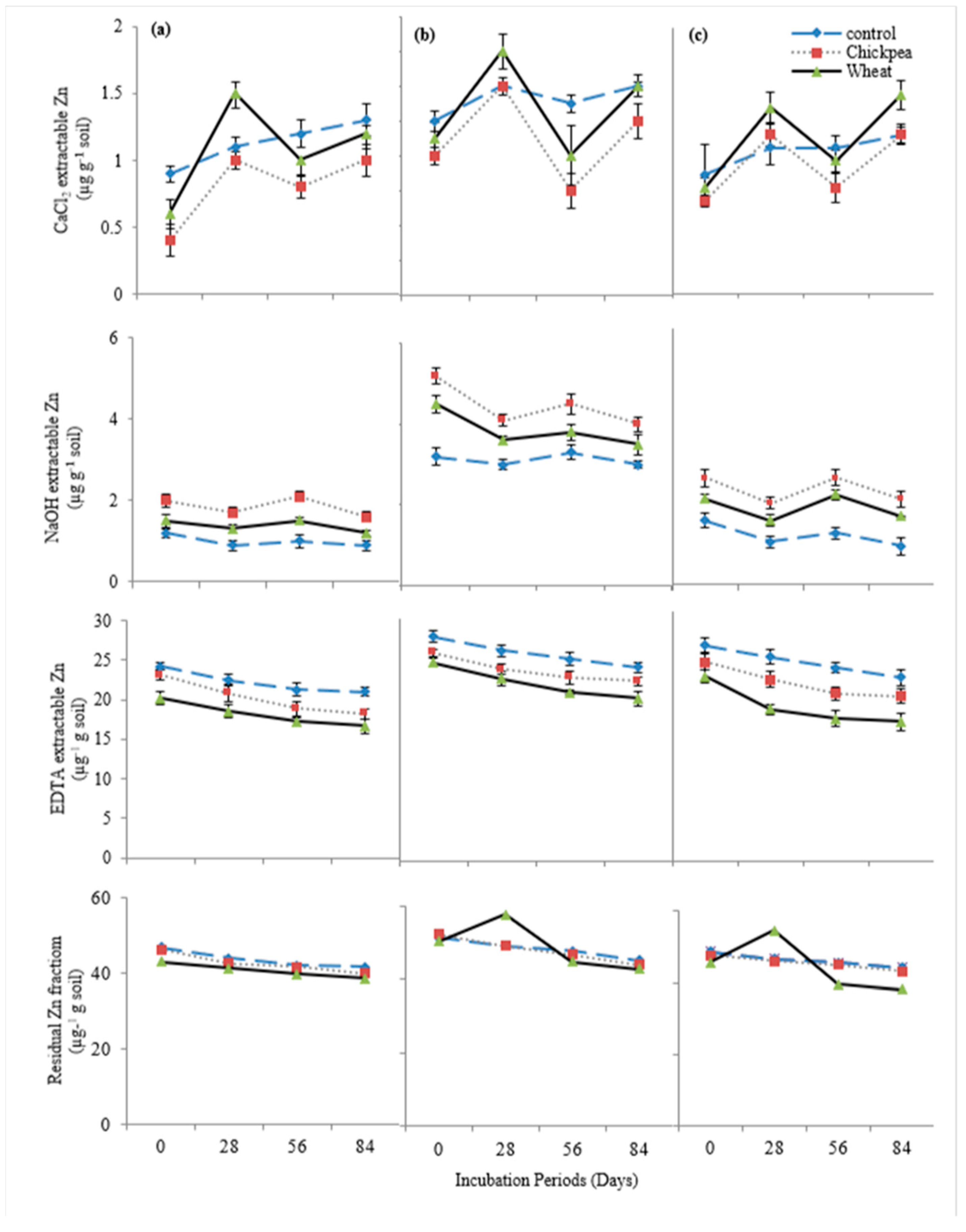
Chickpea straw addition caused an 18.6% reduction in exchangeable (CaCl2-extractable) Zn contents in the soils at the end of the incubation (Figure 5). The application of wheat straw resulted in an 11% reduction in exchangeable (CaCl2-extractable) Zn. Chickpea straw caused a 75% increase in OM-bound (NaOH-extractable) Zn content in the soils while the wheat straw caused a 42% increase in OM bound (NaOH-extractable) Zn. The Carbonate bound (EDTA-extractable) Zn fraction was decreased by 9.8% with the addition of chickpea straw and a 20% decrease was caused due to the addition of wheat straw. Chickpea straw caused a 5.5% decrease in residual Zn where an 8.6% decrease was caused by the addition of wheat straw.
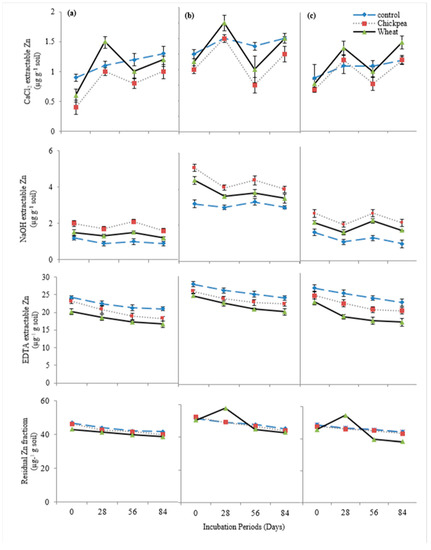
Figure 5.
Effect of organic amendments on Zn speciation in (a) DH, (b) DR-1, (c) DR-2, soils depicting the decrease in bioavailability of Zn fractions throughout the incubation period.
4. Discussion
4.1. CO2-C Evolution
Many advanced techniques are being used for the measurement of the microbial community in the soil but soil respiration is considered as a rapid indicator for evaluating the response of the microbial community to changes in the soil ecosystem and soil quality [31]. Organic materials applied to soils are transformed into CO2, microbial biomass, metabolites and humus components [32]. The composition of the materials, soil physicochemical properties and environmental conditions affect such transformations. The higher levels of heavy metals can adversely affect not only OM decomposition but also other soil biological processes. In polluted soils, respiration rate decreases significantly which is directly related to the microbial activity in the soil. Earlier studies indicated inhibitory effects of toxic metals like Pb, Zn, Cd or Cu on soil respiration [33]. In the present study, plant residues incorporation in soils counterbalanced the negative heavy metals effect by supplying energy in the form of carbon through residue decomposition and complexion mechanism. An increase in the OC and macro element levels in soils was observed due to the application of organic amendments, which accelerated the microbial activity and ultimately increased respiratory activity [34]. Also, the complexation mechanism might be another reason for an increase in CO2 evolution with the addition of organic amendments, which results in toxicity reduction, later as a result of biomass improvement and eventually more CO2 production [35]. The respiration rate, especially in amended soil, was higher at the start of the experiment and with time it decreased significantly. However, in the end, there was no significant difference in CO2 evolution of amended soils and untreated control. The results of the study by Duong et al. [36] also support this finding for the highest respiration rate that occurred immediately after the residue addition. The addition of new OM at the beginning stage of incubation causes a significant increase in the CO2 evolution rate and microbial activity. As the added straw decomposed with time, CO2 production and microbial activity decreased by the end of the experiment (84th day). Therefore, soil microbial respiration is limited by the OC availability [37].
The results showed that soils and organic amendments had a strong interaction (P< 0.0001). A significantly high interaction was observed between chickpea straw and three soils, which ultimately indicated a higher CO2 evolution than wheat straw and control. A study reported that CO2 evolution increased in residue-treated soils as compared to that of non-residue soils and declined at later stages because of the reduction of the substrate [38].
4.2. Microbial Biomass Carbon
For the assessment of long-term soil OM changes, MBC is considered as a sensitive parameter [39]. Heavy metal toxicity has an inhibitory effect on soil-plant systems like plant growth, enzymatic activity, photosynthesis activity and accumulation of other nutrients and microbial activities. The negative effect of heavy metal toxicity on microbial biomass, respiration, their activities and processes has been reported previously [40,41,42]. The decrease in MBC might be due to metals exposure, which results in immediate microbial cell death caused by variation in population size led by poor viability and interruption of essential functions [40]. Soil microorganisms use their energy for cell maintenance function instead of growth under metal stress conditions, which results in the reduction of MBC in metal contaminated soils [4]. The additional energy cost for the survival of soil microbes results in a reduced availability of substrate for their growth, and hence a decrease in microbial biomass [40]. The metabolic requirements of microorganisms in particular are related to their ability to obtain these key nutrients via their extracellular enzymes [43]. However, in this study, substrate addition in metal contaminated soil as organic amendments increased the growth of microbial biomass by supplying the required energy, and also reduced the toxic effects of metals by forming metal chelates in organically amended soils. In the present investigation, organic amendment’s addition showed a significant positive effect on soil microbes and increased their biomass content as compared to control. Microbial biomass carbon was significantly higher in all three chickpea straw and the wheat straw amended soils; however, chickpea straw showed a more significant effect that might be attributed to its high total N and P contents. Likewise, lower ratios of C/N, C/P and lignin contents in chickpea straw than wheat straw might also be the reason for quick chickpea straw residues degradation, which rapidly increased soil microbial biomass. Plant material with a low C/N ratio will decompose faster than materials with a high C/N ratio [44]. Organic carbon is used by the soil microorganism as an energy source and C for microbial organic material production which ultimately increases microbial biomass [45]; however, amendment in the soils with the different compositions follow different mineralization patterns and hence variable soil microbial biomass is produced. These results align with the previously reported studies which showed considerable interactions between microbial activity and added soil OM quality [46]. The added soil organic material in the form of crop residues may be a cheaper source of carbon and may also be helpful for profit maximization through increased soil productivity. However, the profitability through entrepreneurial success is highly dependent on some specific factors like a changing and global environment, a quick response and adaptation to market conditions [47]. However, economic analysis for the use of organic amendments and the resultant net returns due to increased organic carbon of the soil may be helpful in the adoption of the subsequent strategy in the future. For this purpose, it was reported by [48] that both technical and economic strategies altogether create prerequisites for the sustainability of developing agriculture.
4.3. Speciation of Metals
The bioavailability and toxicity of metals to crop plants and soil microbes depend upon the chemical forms of the metals present in the soil. The five forms of metals present in the soil are soluble and exchangeable, carbonate bound phases, Fe and Mn oxides bound (reducible phases), OM and sulfides bound and lattice metals [11]. During this research, the main emphasis was on four major fractions i.e., soluble and exchangeable fraction, OM-bound fraction, carbonate bound fraction and residual fraction.
The exchangeable and carbonate bonded metal fractions are generally considered “bio-available”, as they exhibit mobility in the environment and are potentially available to crop plants. Organic matter influences the mobility of metal species by forming soluble or insoluble organic-metal chelates. Metals immobilized on the complexation with OM become less mobile and less bioavailable and thus result in a decrease of the exchangeable metal fraction [8]. In this study, a significant decrease was observed in exchangeable and carbonate bound fractions in soils throughout the incubation study when soils were organically amended with straws. Chickpea straw amendment showed significant interaction (P < 0.0001) with soils as compared to the wheat straw amendment. The possible reason behind the decrease in metal content can be the formation of soluble and insoluble complexes with metal ions. During the decomposition humic acid and fulvic acids are produced, which play their specific role in metal bioavailability by forming complexes [49]. The heavy metals availability is affected by straw amendments in terms of their correlation with the released organic substance’s solubility and their chelating ability [50]. Insoluble humic substances bind heavy metals, which are relatively immobile. Organic components such as humic carboxylic (-COOH) and phenolic (-OH) groups are mainly responsible for the metal-humic complexes formation. Humic substances can form insoluble Pb complexes, while low molecular weight organic substances tend to form soluble Cd and Zn complexes. More stable Pb and humic acid complexes compared to Cd and Zn complexes have been reported [51]. In this study, wheat straw addition caused a significant decrease in the concentration of exchangeable and carbonate bound fractions of soils, while the OM-bound fraction was increased in the soils. This might be because an increase in OM content allows more and more adsorption mechanisms on the adsorption sites of the OM. Some other studies also revealed that mature compost rich in humified OM can reduce heavy metals bioavailability and mobility in soil [35]. Metal organo-complexes formation and soil organic substances solubilization overall control the metal bioavailability in soils [9]. Organic materials dominated by insoluble humic substances exert a strong influence on heavy metals retention in soils. Thus, metals present in high OM soils are less mobile and bio-available than metals present in low OM soils. Results are in line with the incubation study conducted by Cui et al. [52] to check the effect of rice straw on speciation of Cd in soil. Results showed a decrease in free Cd and soluble Cd concentration in soils amended with rice straw. The study suggested that pH change might be one of the possible reasons for the decrease in Cd concentration in treatment as compared to control. The addition of OM in alkaline soils and their subsequent decomposition may alter the soil pH and indirectly affect the bioavailability of metals, thereby allowing the formation of insoluble complexes [53]. All the treatments showed a positive significant interaction between soils × organic amendments, except that few interactions showed non-significant behavior.
5. Conclusions
The addition of organic amendments (wheat straw and chickpea straw) in the wastewater irrigated soils significantly reduced the bioavailability of metals (Cd, Pb and Zn) while enhancing the microbial community. However, the chickpea straw addition had a more immobilizing effect on the metals than the wheat straw, probably due to its greater ability to form insoluble metal complexes. Microbial biomass and their activity were significantly increased with the addition of straws. Enhancement in the microbial community during incubation caused faster decomposition of added straw, which significantly immobilized the bio-available forms of toxic metals. Based on results, it was concluded that organic amendments like chickpea straw and wheat straw can be used as cost-effective immobilization agents for the remediation of metals (Cd, Pb and Zn) contaminated soils when applied regularly. However, the magnitude of influence varies from soil to soil and with the amendment applied.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, M.B.; Funding acquisition, M.S.A. and M.S.E.; Investigation, S.A. and M.S.E.; Methodology, S.D. and A.K.; Project administration, K.S.K. and K.M.M.; Resources, M.S.E.; Writing—original draft, K.M.M.; Writing—review & editing, S.R. and S.B.; Funding acquisition, Resources, A.A.A.-G. and A.E.-Z.M.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University, grant number RG-1440-054.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The first author gratefully acknowledges the cooperation and support of the laboratory staff of the Institute of Soil Science, PMAS-Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi 46300, Pakistan, for their technical support and cooperation during the analytical work. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the work through the research group No RG-1440-054.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Azarbad, H.; Gestel, C.A.M.V.; Niklin’ska, M.; Röling, W.F.M.; Straalen, N.M.V. Resilience of soil microbial communities to metals and additional stressors: DNA-based approaches for assessing “stress-on-stress” responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. News Release, Geneva, 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/detail/15-03-2016-an-estimated-12-6-million-deaths-each-year-are-attributable-to-unhealthyenvironments (accessed on 11 February 2021).
- Agoro, M.A.; Abiodun, O.A.; Martins, A.A.; Omobola, O.O. Heavy metals in wastewater and sewage sludge from selected municipal treatment plants in eastern cape province, South Africa. Water 2020, 2746, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, B.; Faciano, A.; Tsega, A.; Ehrlich, J. Epidemiologic characteristics of children with blood lead levels ≥45 μg/dL. J. Pediatr. 2017, 180, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Bibi, I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A.H.; Niazi, N.K. A review of environmental contamination and health risk assessment of wastewater use for crop irrigation with a focus on low and high-income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 895–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Ghafoor, A.; Qadir, M.; Owens, G.; Aziz, M.A.; Zia, M.H. Saifullah, Disposal and use of sewage on agricultural lands in Pakistan: A review. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebiewski, M.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Cichosz, M.; Tretyn, A.; Wrobel, B. 16S rDNA Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial community in heavy metals polluted soils. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, V.; Gupta, S.; Dhundhel, R.S.; Matic, N.; Bilinski, S.F.; Devic, N. Determination of total heavy metal by sequential extraction from soil. Int. J. Res. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.L.; Tella, M.; Matthieu, N.B.; Comans, R.N.J.; Dai, J.; Garnier, J.M.; Sivry, Y.; Doelsch, E.; Straathof, A.; Benedetti, M.F. Effect of dissolved organic matter composition on metal speciation in soil solutions. Chem. Geol. 2015, 398, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Safdar, M.E.; Shahzad, S.M.; Aziz, A.; Piracaha, M.A.; Suleman, M.; Ahmad, M.B. Challenges and opportunities for using wastewater in agriculture: A review. J. Appl. Agri. Biotech. 2017, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ideriah, T.J.K.; Ikpe, F.N.; Nwanjoku, F.N. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in crude oil contaminated soils from niger delta, Nigeria. World Environ. 2013, 3, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.M.; Hina, A.; Saeed, A.; Sabahat, S.; Jannat, F.T.; Aslam, M. Impact of heavy metals on plants and animals in relation to sewage water—A review. Sci. Technol. Develop. 2017, 36, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Gong, Z.T.; Zhang, G.L.; Burghardt, W. Concentrations and chemical speciation of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cr of urban soils in Nanjing, China. Geoderma 2005, 115, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xue, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Tang, L.; Cao, S.; Wei, Y.; Yang, C.; Liang, D. Effects of straw amendments on selenium aging in soils: Mechanism and influential factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Kim, S.H.; Jeon, E.K.; Kim, D.H.; Tsang, D.C.; Alessi, D.S.; Kwon, E.E.; Baek, K. Effect of dissolved organic carbon from sludge, Rice straw and spent coffee ground biochar on the mobility of arsenic in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, E.M.; Malcolm, R.L. Preparative isolation of aquatic humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1981, 15, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picollo, A. The supra-molecular structure of humic acids. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 810–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinnes, E. Lead. In Heavy Metals in Soils. Environmental Pollution; Alloway, B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 22, pp. 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, I.; Bocar, A.; Li, M.; Gong, C.; Cai, P.; Al, W.L.E. Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marousek, J.; Marek, V.; Jan, P.; Jaroslav, Z. Glory and misery of biochar. Clean Techn. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Garcia, C.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Hernandaz, M.T. Use of organic amendments as a strategy for saline soil remediation: Influence on the physical, chemical and biological properties of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis by hydrometer: A simplified method for routine textural analysis and a sensitivity test of measurement parameters. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1979, 43, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Xia, N. Rapid determination of organic carbon in marine sediments samples by potassium dichromate oxidation-ferrous sulphate titrimetry. Rock Miner. Anal. 2007, 3, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Rayan, J.; Estefan, G.; Rashid, A. Soil and Plant Analysis Manual; International Center for Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas and National Agriculture Research Center: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2001; pp. 42–165. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Ingram, J.S.I. Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility; Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International: Wallingford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Nitrogen-Total: In Methods of Soil Analysis; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Soceity of Agronomy & Soil Science Society of America: Madison, Wisconsin, 1982; pp. 595–622. [Google Scholar]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Academic Press Inc: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.S.; Heinze, S.; Joergensen, R.G. Simultaneous measurement of S, macronutrients, and heavy metals in the soil microbial biomass with CHCl3 fumigation and NH4NO3 extraction. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, S.P.; Cegarra, J. Chemical extractability of heavy metals during and after long term application of sewage sludge to soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1992, 43, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Communities (CEC). Council directive on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1986, 181, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandas, S.A.P.; Bettiol, W.; Cerri, C.C. Effect of sewage sludg on microbial biomass, basal respiration, metabolic quotient and soil enzymatic activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 30, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.H.; Lodhi, A.; Azam, F. Changes in enzyme activity during the decomposition of plant residues in soil. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 5, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.K.; Yadav, D.V.; Singh, C.P.; Suman, A.; Gaur, A. Effect of heavy metals on soil respiration during decomposition of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) trash in different soils. Plant Soil Environ. 2010, 56, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerling, C.; Liebner, C.; Haubold-Rosar, M.; Katzur, J.; Schroder, D. Impact of application of organic waste materials on microbial and enzyme activities of mine soils in the Lusatian coal mining region. Plant Soil 2000, 220, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordoff, G.M.; Baker, A.J.M.; Willis, A.J. Current approaches to the revegetation and reclamation of metalliferous mine waste. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.T.T.; Baumann, K.; Marschner, P. Frequent addition of wheat straw residues to soil enhances carbon mineralization rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.S.; Bahmanyar, M.A. Impact of organic amendments with and without mineral fertilizers on soil microbial respiration. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.; Khan, A.A.; Sarhad, M. Microbial activity as influenced by crop residues in soils during laboratory incubations. Sarhad J. Agric. 2003, 19, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Smejkalova, M.; Mikanova, O.; Boruka, L. Effect of heavy metals concentrations on biological activity of soil microorganisms. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oijagbe, I.J.; Abubakar, B.Y.; Edogbanya, P.R.O.; Suleiman, M.O.; Olorunmola, J.B. Effects of heavy metals on soil microbial biomass carbon. MOJ Biol. Med. 2019, 4, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Akmal, M.; Jianming, X. Microbial biomass and bacterial community changes by pb contamination in acidic soil. J. Agri. Biol. Sci. 2009, 1, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Wahid, A.; Ahmad, S.S.; Butt, A. Response of soil microbial biomass and respiration in heavy metal contaminated soil of Multan. Int. J. Biosci. 2015, 7, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Maroušek, J.; Otakar, S.; Ladislav, K.; Marek, V.; Marek, K.; Anna, M.; Jana, B.; Milos, P.; Miloslav, Š.; Peter, B.; et al. Advances in nutrient management make it possible to accelerate biogas production and thus improve the economy of food waste processing. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danga, B.O.; Ouma, J.P.; Wakindiki, I.I.C.; Bar-Tal, A. Chickpea-Wheat rotation for higher production in a humid tropical region. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revoredo, M.D.; DeMelo, W.J. Enzymatic activity and microbial biomass in an oxisol amended with sewage sludge contaminated with nickel. Sci. Agric. 2007, 64, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiros, M.C.; Cepede, C.T.; Seoane, S.; Gilsotres, F. Biochemical properties of acid soils under climax vegetation in an area of the European temperate-humid zone (Glacia, N. W. Spain) general parameters. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blažková, I. Sectoral and firm-level determinants of profitability: A multilevel approach. Int. J. Entrep. Knowl. 2018, 6, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Rowland, Z.; Valášková, K.; Král, P. Techno-economic assessment of potato waste management in developing economies. Clean Technol. Environ. 2020, 22, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-de-Mora, A.; Burgos, P.; Madejon, E.; Cabrera, F.; Jaeckel, P.; Schloter, M. Microbial community structure and function in soil contaminated by heavy metals: Effect of plant growth and different amendments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, C.N.; Banta, G.T.; Hansen, P.E.; Jacobsen, O.S. The influence of organic matter on sorption and fate of glyphosate in soil-comparing different soils and humic subatances. Environmen. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2865–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borůvka, L.; Drábek, O. Heavy metal distribution between fractions of humic substances in heavily polluted soils. Plant Soil Environ. 2004, 50, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.S.; Du, X.; Wang, L.P.; Zhu, Y.G. Effect of rice straw on the speciation of cadmium (Cd) and copper (Cu) in soils. Geoderma 2008, 146, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, A.S.; Seaman, J.C.; Mench, M.J.; Vangronsveld, J. Remediation of metal and radionuclides-n. In Environmental Restoration of Metals-Contaminated; Soils, K.I.I., Ed.; Chemical Rubber Company Press Limited Liability Company: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 21–60. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).