Municipal Solid Waste Characterization and Landfill Gas Generation in Kakia Landfill, Makkah
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MSW Sampling and Characterization
2.2. Study Area and Modelling
- MCF = methane correction factor (1 = well managed landfill, assumed in this case 0.7),
- DOC = degradable organic carbon (fraction),
- DOCF = fraction DOC dissimilated, and
- F = fraction of methane in landfill gas (measurement at landfill has indicated a value of 56% CH4 in biogas).
- A = % paper and textiles,
- B = % garden waste, park waste, or other non-food organic putrescibles,
- C = % food waste, and
- D = % wood or straw
- 0.83 = empirical constant;
- 0.028 = empirical constant; and
- LC = lignin content of the VS expressed as a percent of dry weight from leachate sample.
3. Results
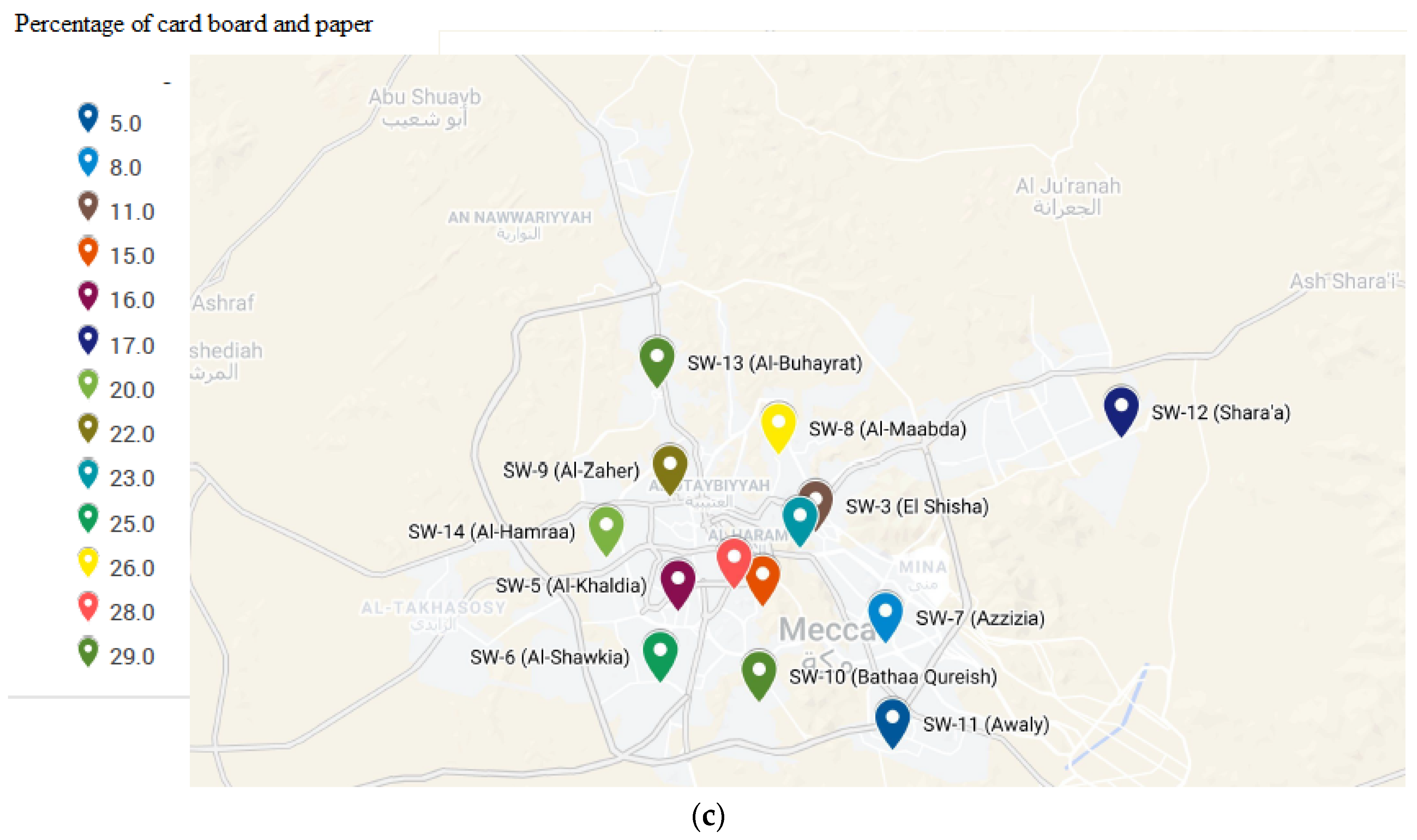
3.1. Characterization of Solid Waste
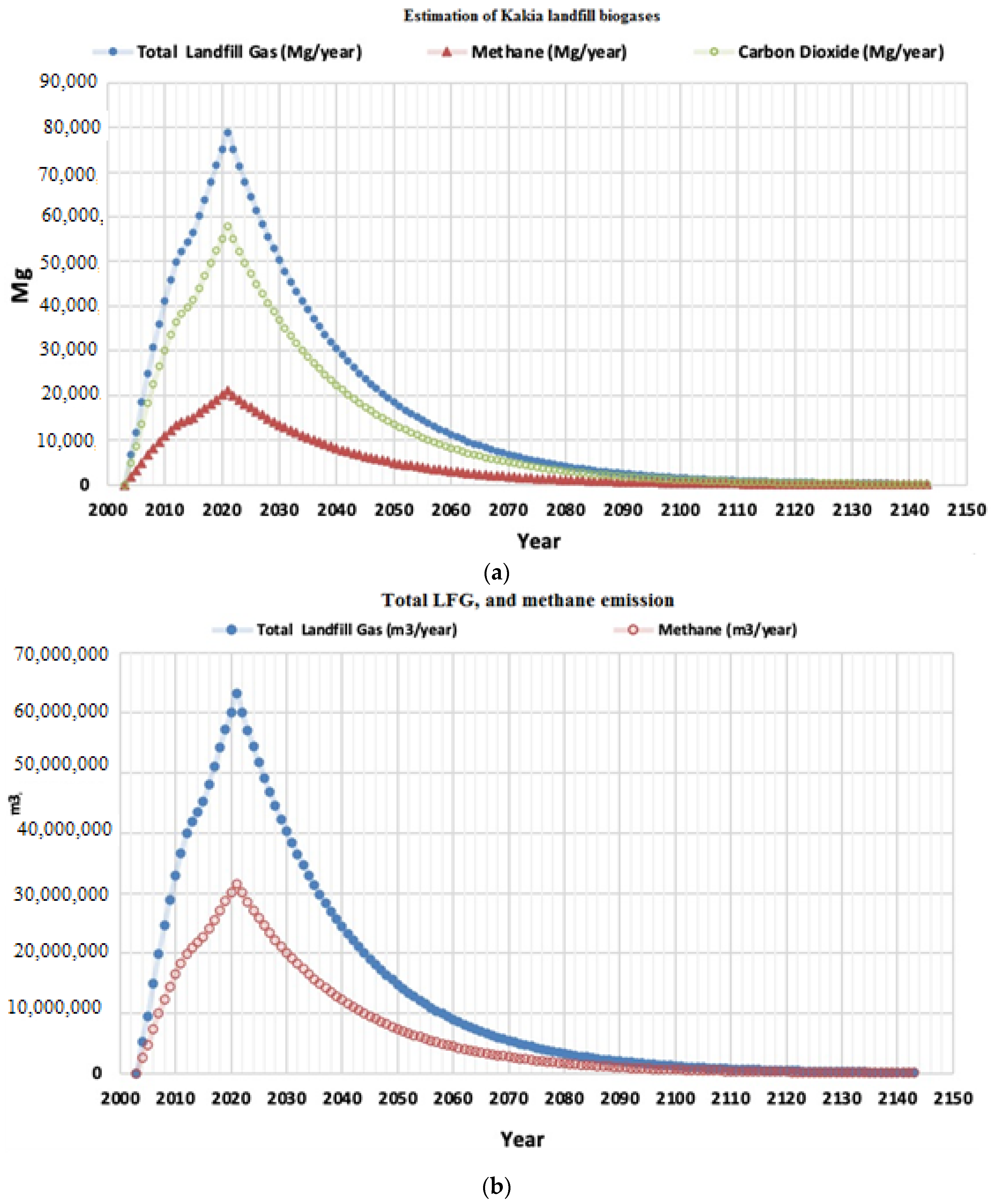
3.2. Estimation of Landfill Gas Production Potential in Makkah
- Sum of landfill total gases = 2,380,203.3 Mg/year and 1,905,957,300 m3/year,
- Sum of methane = 635,791.4 Mg/year,
- Sum of carbon dioxide gas = 1,744,388.6 Mg/year, an
- Sum of landfill total gases = 1,905,957,300 m3/year,
- Sum of methane = 952,996,960 m3/year,
- Sum of carbon dioxide gas = 952,996,960 m3/year, and
4. Comparison
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kontos, T.D.; Komilis, D.; Halvadakis, C.P. Siting MSW landfills with a spatial multiple criteria analysis methodology. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.-H. Municipal solid waste: Review of best practices in application of life cycle assessment and sustainable management techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, S.; Dominguez-Ramos, A.; Irabien, A. From linear to circular integrated waste management systems: A review of methodological approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hipel, K.W. Exploring social dimensions of municipal solid waste management around the globe—A systematic literature review. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laner, D.; Crest, M.; Scharff, H.; Morris, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. A review of approaches for the long-term management of municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocârță, D.M.; Rada, E.; Ragazzi, M.; Badea, A.; Apostol, T. A contribution for a correct vision of health impact from municipal solid waste treatments. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, A.; Atmaca, E. Environmental geological assessment of a solid waste disposal site: A case study in Sivas, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2006, 50, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, I.A.; Arafat, H.A.; Basheer, T.; Shawahneh, H.; Salahat, A.; Eid, J.; Ali, W. Trends and problems of solid waste management in developing countries: A case study in seven Palestinian districts. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Municipal Solid Waste Generation, Recycling, and Disposal in the United States: Facts and Figures for 2010; EPA-530-F-14-001; AM-BRA GmbH: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 1–12.
- Kim, K.-R.; Owens, G. Potential for Enhanced Phytoremediation of Landfills Using Biosolids—A Review. Compr. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, M.; Homaee, M.; Mahmodi, S. An integrated multi criteria approach for landfill siting in a conflicting environmental, economical and socio-cultural area. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breukelman, H.; Krikke, H.; Löhr, A.J. Failing Services on Urban Waste Management in Developing Countries: A Review on Symptoms, Diagnoses, and Interventions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.N.; Noor, Z.Z.; Abba, A.H.; Yusuf, R.O.; Abu Hassan, M.A. Review on life cycle assessment of integrated solid waste management in some Asian countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, T.; Bhagat, R.M.; Bhattacharyya, P. Municipal Solid Waste Generation, Composition, and Management: The World Scenario. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1509–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, G.P.; Gupta, P.K. Sustainable municipal solid waste management in low income group of cities: A review. Trop. Ecol. 2011, 52, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Rada, E.C.; Istrate, I.A.; Panaitescu, V.; Ragazzi, M.; Cirlioru, T.M.; Apostol, T. A comparison between different scenarios of Romanian municipal solid waste treatment before landfilling. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mepaiyeda, S.; Madi, K.; Gwavava, O.; Baiyegunhi, C. Geological and geophysical assessment of groundwater contamination at the Roundhill landfill site, Berlin, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskese, A.; Demir, H.H.; Ozcan, H.K.; Okten, H.E. Landfill site selection using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS: A case study for Istanbul. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, V.R.; Natesan, U.; Sarkar, C. GIS-based approach for optimized siting of municipal solid waste landfill. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2146–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Kashem, S.; Morshed, S. Integrating spatial information technologies and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (F-AHP) approach for landfill siting. City Environ. Interact. 2020, 7, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chembukavu, A.A.; Mohammad, A.; Singh, D.N. Bioreactor landfills in developing countries: A critical review. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 2019, 45, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, E.C.; Ragazzi, M.; Stefani, P.; Schiavon, M.; Torretta, V. Modelling the Potential Biogas Productivity Range from a MSW Landfill for Its Sustainable Exploitation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, A.; Värri, H.; Havukainen, J.; Uusitalo, V.; Horttanainen, M. Enhancing landfill gas recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 55, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, C.; Gökçek, M. A techno-economic assessment of landfill gas emissions and energy recovery potential of different landfill areas in Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatova, T.; Perederii, T.; Hyrchenko, Y. Assessment of electricity generation cost from landfill gas. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Energy Smart Systems (ESS), Kyiv, Ukraine, 12–14 May 2020; pp. 230–233. [Google Scholar]
- Pujotomo, I.; Azzahra, S. Electrical Energy Production Process from Landfill Gas. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 125, 13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purmessur, B.; Surroop, D. Power generation using landfill gas generated from new cell at the existing landfill site. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Temporal and spatial variation of greenhouse gas emissions from a limited-controlled landfill site. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Humer, M.; Gebert, J.; Hilger, H. Biotic systems to mitigate landfill methane emissions. Waste Manag. Res. 2008, 26, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutz, C.; Pedicone, A.; Pedersen, G.B.; Kjeldsen, P. Evaluation of respiration in compost landfill biocovers intended for methane oxidation. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contrera, R.C.; Silva, K.C.D.C.; Da Silva, G.H.R.; Morita, D.M.; Zaiat, M.; Schalch, V. The chemical oxygen demand/total volatile acids ratio as an anaerobic treatability indicator for landfill leachates. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Thangarajan, R.; Seshadri, B.; Jena, U.; Das, K.; Wang, H.; Naidu, R. Landfills as a biorefinery to produce biomass and capture biogas. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.C. Religious tourism and its management: The hajj in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2010, 13, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo-Feng, C.; Jian-Guo, L.; Qing-Xian, G.; Xiao-Qin, N.; Dong, C.; Lan-Cui, L.; Ying, Z.; Zhan-Sheng, Z. Estimation of Methane Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste Landfills in China Based on Point Emission Sources. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2014, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Rouboa, A. Renewable energy from solid waste: Life cycle analysis and social welfare. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 85, 106469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarlat, N.; Fahl, F.; Dallemand, J.-F. Status and Opportunities for Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste in Europe. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2019, 10, 2425–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus, R.G.; Shephard, L.E. Waste-to-energy. In Low-Carbon Energy in Africa and Latin America; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 38, pp. 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, E.C. Energy from municipal solid waste. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 190, 945–958. [Google Scholar]
- Osra, F. Optimizing The Suitable Site(S) for Landfill by Multi-Criteria Decision and Investigating Biogasification Potential of the Waste in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Graduate Studies in Science and Engineering, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sandip, T.M.; Kanchan, C.K.; Ashok, H.B. Enhancement of methane production and bio-stabilisation of municipal solid waste in anaerobic bioreactor landfill. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, H.K.; Smith, R.W.; Azapagic, A. Energy from waste: Carbon footprint of incineration and landfill biogas in the UK. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2012, 18, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- According to Article (seventy) of the Basic Law of Governance, issued by Royal Decree No. (A/90) on 8/22/1412 AH. Available online: https://www.saudiembassy.net/basic-law-governance (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Almeelbi, T.; Ouda, O.K.M. Waste Bio-refinery in Makkah: A solution to convert waste produced during Hajj and Umrah Seasons into wealth. In Proceedings of the 15th Scientific Symposium for Hajj, Umrah and Madinah visit, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, 27–28 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mashat, B. Effective Microorganisms (EM) Technology as a Pathway to Improve Municipal Solid Waste of Makkah City (Saudi Arabia) and as Foul Odor Eliminator’. In Proceedings of the Clute Institute International Academic Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–12 June 2014; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Edjabou, M.E.; Jensen, M.B.; Götze, R.; Pivnenko, K.; Petersen, C.; Scheutz, C.; Astrup, T.F. Municipal solid waste composition: Sampling methodology, statistical analyses, and case study evaluation. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard Test Method for Determination of the Composition of Un-Processed Municipal Solid Waste; ASTM D5231; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ozcan, H.K.; Guvenc, S.Y.; Guvenc, L.; Demir, G. Municipal Solid Waste Characterization According to Different Income Levels: A Case Study. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Theisen, H.; Vigil, S. Integrated Solid Waste Management: Engineering Principles and Management Issues; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Agrawal, A. Recent trends in solid waste management status, challenges, and potential for the future Indian cities—A review. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA, US Environmental Protection Agency. 2012; pp. 1–15. Available online: www.epa.gov (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Kreith, F.; Tchobanoglous, G. Handbook of Solid Waste Management; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, A.; Rashid, M.; Muhammad, W.; Ijaz, A.; Ziad, O.A.A.; Asad, S.A.; Mohamed, A.B.; Tasneem, A. Solid waste management n Saudi Arabia: A review. J. Appl. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kerimov, I.A.; Mintsaev, M.S.; Debiev, M.; Pashaev, M.Y. Basic Stages of Energy Development Program Implementation in the Chechen Republic. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2020, 10, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Hesam, N.M.; Akhiar, A.; Fazril, I.; A Zamri, M.F.M.; Shamsuddin, A.H. Economic Feasibility of Smart City Power Generation from Biogas Produced by Food Waste in Malaysia via Techno-Economic Analysis; IOP Publishing: Langkawi, Malaysia, 2020; Volume 476, p. 012076. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan, G.C.; Gabriel, M.; Ion, V.I.; Florin, P. Energy from Municipal solid wastes: Galati city case study. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences 207, 02001 (2020), Sozopol, Bulgaria, 19–21 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- De Tuesta, J.L.D.; Pantuzza, G.F.; Silva, A.M.T.; Praça, P.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Catalysts Prepared with Matured Compost Derived from Mechanical-Biological Treatment Plants for the Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Pollutants with Different Lipophilicity. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
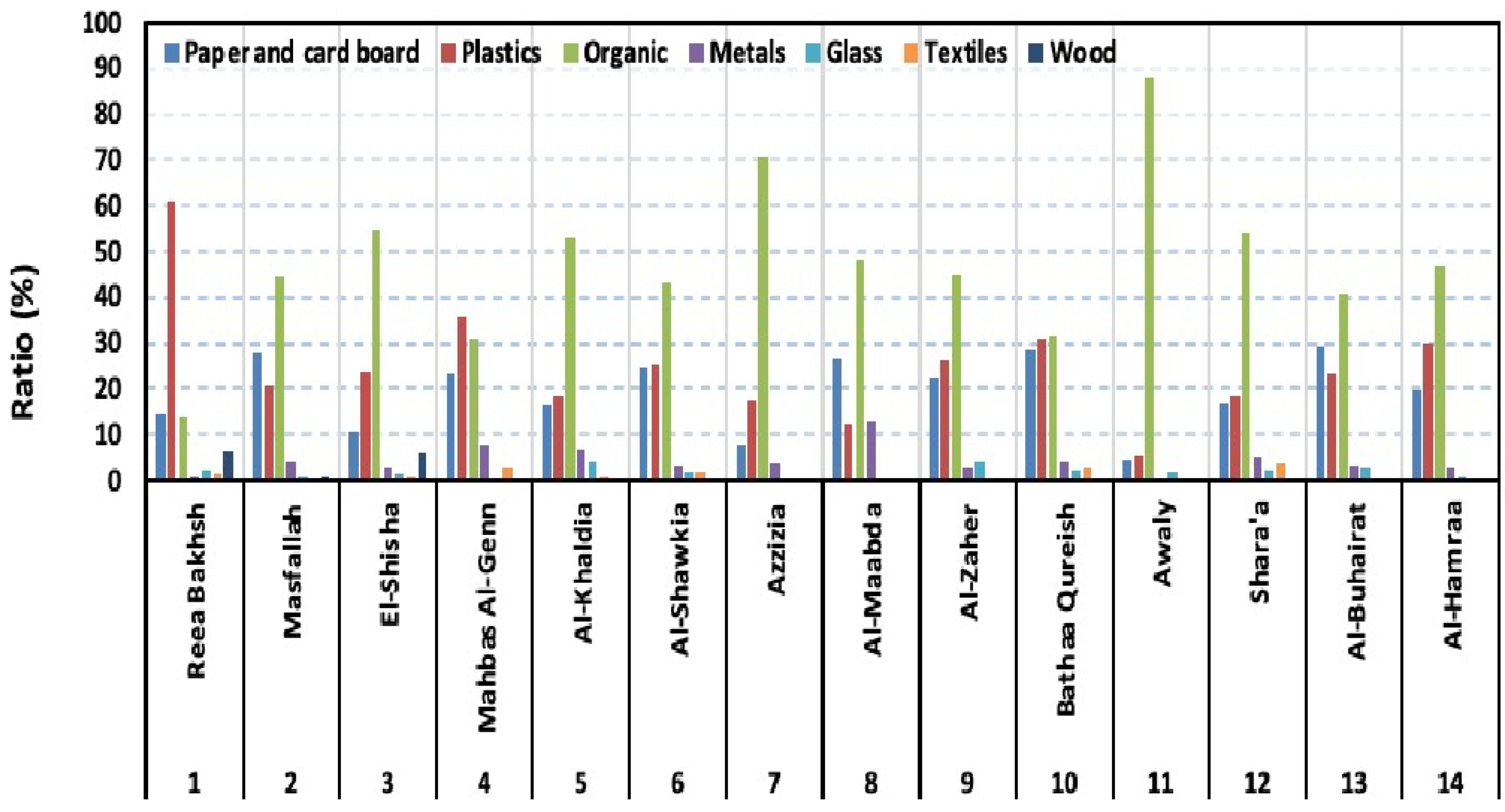
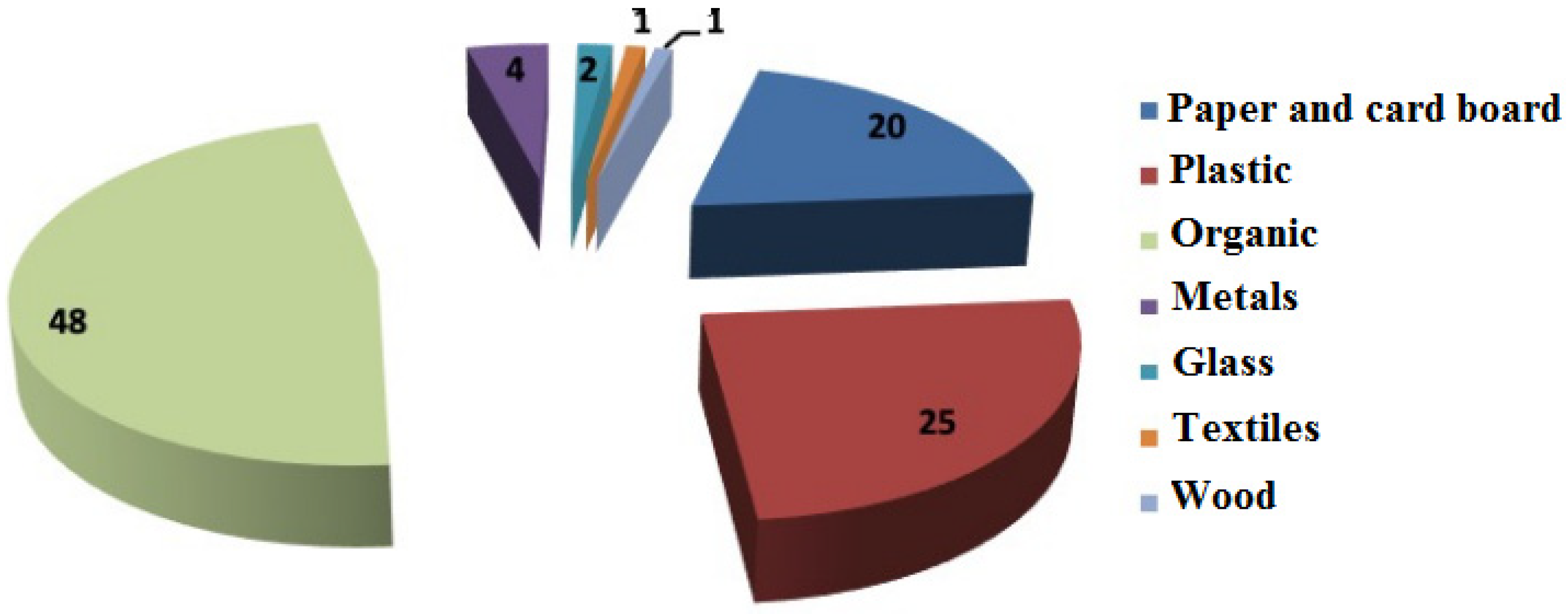
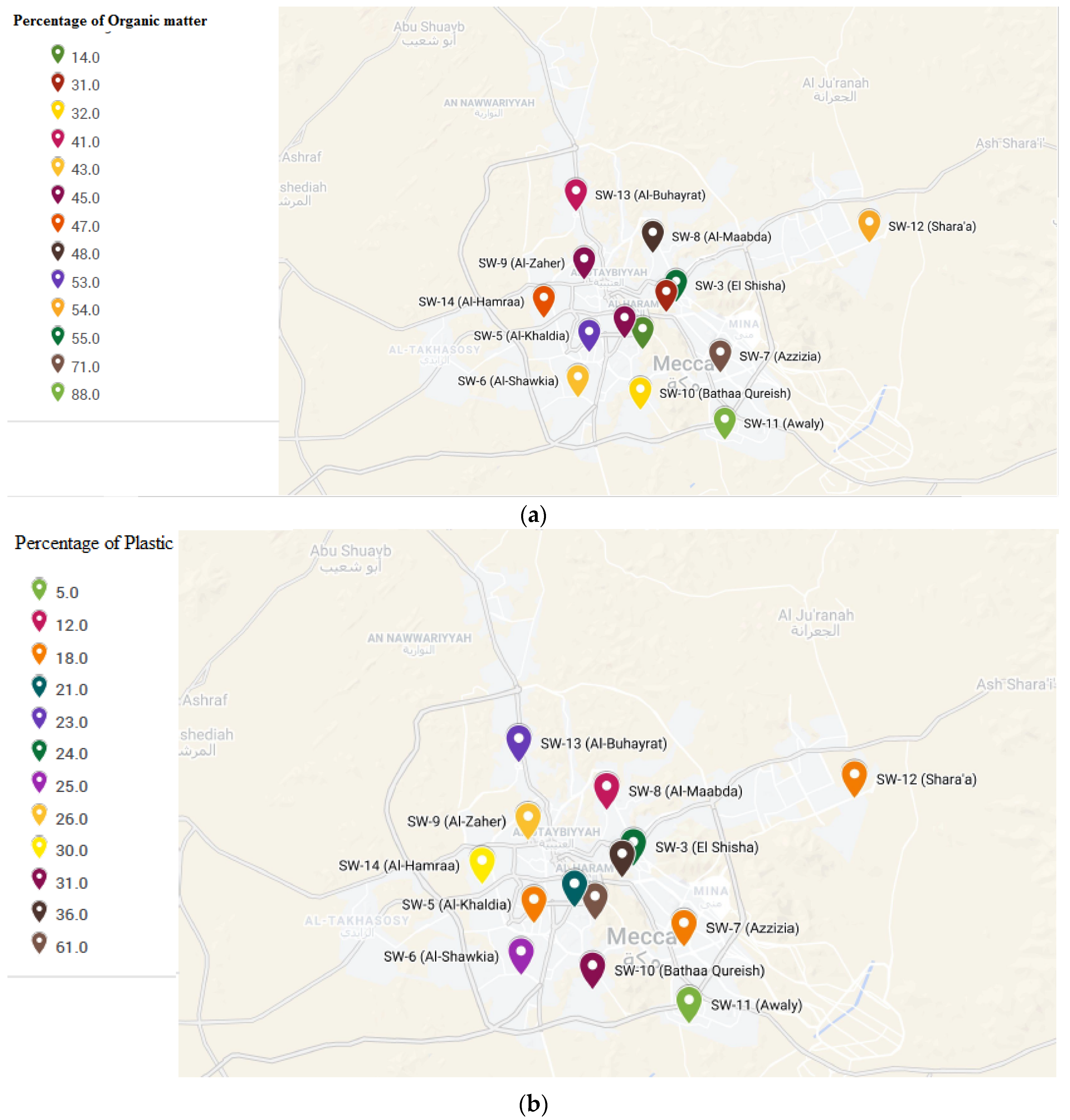
| Waste Fractions | Waste Components |
|---|---|
| Organic matter | Food, animal excrements, vegetables |
| Wood | Wood, garden trimmings |
| Paper | Newspapers, office paper, bills, magazines, sales notes and receipts |
| Cardboard | Corrugated cardboard, boxboard |
| Plastic | HDPE, PVC, Film PE, polyethylene bag, hair, food containers, PS |
| Metal | Ferrous and non-ferrous material, aluminum cans and foils |
| Glass | Soda, beer, wine container, window glass, car glass |
| Textile | Clothes, ropes, sacks, sanitary products, cotton |
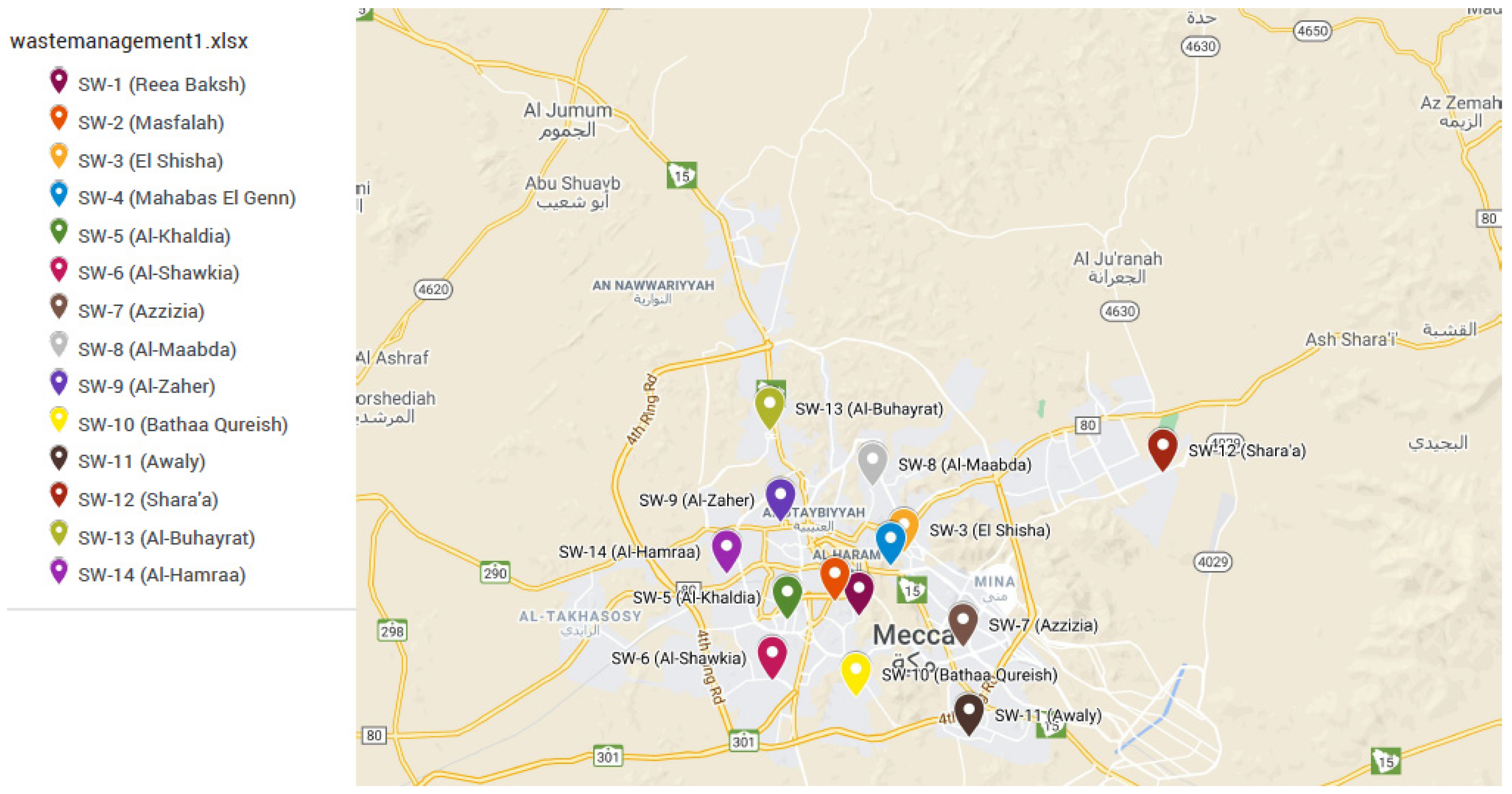
| Sample Name | Geographical Coordinates | Ratio of MSW with Respect to the Container (%) | District | Spatial Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW-1 | N 21° 24′ 7.74″ E 39° 49′ 57.9″ | 60 | Reea Baksh | Central Zone |
| SW-2 | N 21° 24′ 29.70″ E 39° 49′ 18.30″ | 70 | Masfallah | Central Zone |
| SW-3 | N 21° 25′ 44.34″ E 39° 51′ 11.94″ | 60 | El-Shisha | Residential |
| SW-4 | N 21° 25′ 23.58″ E 39° 50′ 50.10″ | 80 | Mahbas Al-Genn | Central Zone |
| SW-5 | N 21° 24′ 01.98″ E 39° 48′ 00.48″ | 90 | Al-Khaldia | Residential |
| SW-6 | N 21° 22′ 29.10″ E 39° 47′ 36.12″ | 90 | Al-Shawkia | Residential |
| SW-7 | N 21° 23′ 19.74″ E 39° 52′ 48.66″ | 80 | Azzizia | Commercial |
| SW-8 | N 21° 27′ 24.12″ E 39° 50′ 20.70″ | 70 | Al-Maabda | Residential |
| SW-9 | N 21° 26′ 30.18″ E 39° 47′ 49.44″ | 60 | Al-Zaher | Residential |
| SW-10 | N 21° 22 04.02″ E 39° 49 52.92″ | 95 | Bathaa Qureish | Residential |
| SW-11 | N 21° 21′ 02.22″ E 39° 52′ 58.74″ | 100 | Awaly | Villas |
| SW-12 | N 21° 27′ 45.54″ E 39° 58′ 16.08″ | 100 | Shara’a | Residential |
| SW-13 | N 21° 28′ 49.50″ E 39° 47′ 31.92″ | 90 | Al-Buhayrat | New Urbanized |
| SW-14 | N 21° 25′ 11.16″ E 39° 46′ 21.42″ | 90 | Al-Hamraa | New Urbanized |
| Input Parameters | Lo (m3 of CH4/tonne of MSW) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF | DOC (%) | DOCF | F(%) | ||
| Result | 0.7 | 0.19488 | 0.82 | 0.56 | 83.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osra, F.A.; Ozcan, H.K.; Alzahrani, J.S.; Alsoufi, M.S. Municipal Solid Waste Characterization and Landfill Gas Generation in Kakia Landfill, Makkah. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031462
Osra FA, Ozcan HK, Alzahrani JS, Alsoufi MS. Municipal Solid Waste Characterization and Landfill Gas Generation in Kakia Landfill, Makkah. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031462
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsra, Faisal A., Huseyin Kurtulus Ozcan, Jaber S. Alzahrani, and Mohammad S. Alsoufi. 2021. "Municipal Solid Waste Characterization and Landfill Gas Generation in Kakia Landfill, Makkah" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031462
APA StyleOsra, F. A., Ozcan, H. K., Alzahrani, J. S., & Alsoufi, M. S. (2021). Municipal Solid Waste Characterization and Landfill Gas Generation in Kakia Landfill, Makkah. Sustainability, 13(3), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031462






