Theoretical Investigation of Equilibrium Dynamics in Braided Gravel Beds for the Preservation of a Sustainable Fluvial Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosley, M.P. Analysis of the effect of changing discharge on channel morphology and instream uses in a braided river, Ohau River, New Zealand. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, W.; Ashmore, P.; Tubino, M. A method for estimating the mean bed load flux in braided rivers. Geomorphology 2009, 103, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Brancati, F.; Pannone, M. An experimental analysis of bed load transport in gravel-bed braided rivers with high grain Reynolds numbers. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 94, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redolfi, M.; Tubino, M.; Bertoldi, W.; Brasington, J. Analysis of reachscale elevation distribution in braided rivers: Definition of a new morphologic indicator and estimation of mean quantities. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 5951–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; De Vincenzo, A.; Pannone, M. Statistical characterization of flow field structure in evolving braided gravel beds. Spat. Stat. 2019, 34, 100268–doi10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P. Channel morphology and bed load pulses in braided, gravel-bed streams. Geogr. Ann. 1991, 73, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanoski, D.; Schumm, S.A. Changes in Braided River Morphology Resulting from Aggradation and Degradation. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitlick, J.; Mueller, E.R.; Segura, C.; Cress, R.; Torizzo, M. Relation between flow, surface-layer armoring and sediment transport in gravel-bed rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Laronne, J.B.; Sala, M. Continuous monitoring of bedload flux in a mountain gravel-bed river. Geomorphology 2000, 34, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habersack, H.; Hauer, C.; Liedermann, M.; Tritthart, M. Modelling and monitoring and management of the Austrian Danube. Proc. Water 2008, 21, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Downs, P.W.; Soar, P.J.; Taylor, A. The anatomy of effective discharge: The dynamics of coarse sediment transport revealed using continuous bedload monitoring in a gravel-bed river during a very wet year. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, B.; Naff, R.L.; Hubbell, D.W. Temporal variations in bedload transport rates associated with the migration of bedforms. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1989, 14, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Fienberg, K.; Jerolmack, D.J.; Marr, J.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Experimental evidence for statistical scaling and intermittency in sediment transport rates. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, F01025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, J.; Mettra, F.; Ma, H.B.; Ancey, C. Statistics of bedload transport over steep slopes: Separation of time scales and collective motion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Heyman, J.; Fu, X.; Mettra, F.; Ancey, C.; Parker, G. Bed load transport over a broad range of timescales: Determination of three regimes of fluctuations. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 2653–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikora, V.; Habersack, H.M.; Huber, T.; McEwan, I.K. On bed particle diffusion in gravel-bed flows. Water Resour. Res 2002, 38, 17/1–17/9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrce, R.S.; Ashmore, P.E. Particle path length distributions in meandering gravel-bed streams: Results from physical models. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, V.; Meerschaert, M.M.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Viparelli, E.; Parker, G. Normal and anomalous diffusion of gravel tracer particles in rivers. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancey, C.; Heyman, J. A microstructural approach to bed load transport: Mean behaviour and fluctuations of particle transport rates. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 744, 129–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, T.B. Temporal variations in bedload transport rates and sediment storage in gravel-bed rivers. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1992, 16, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnle, R.A.; Southard, J.B. Bed load transport fluctuations in a gravel bed laboratory channel. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recking, A.; Frey, P.; Paquier, A.; Belleudy, P. An experimental investigation of mechanisms involved in bed load sheet production and migration. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, F03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, T.B.; Cudden, J.R.; Shvidchenko, A.B. The consequences of unsteady sediment transport in braided rivers. In Gravel-Bed Rivers V.; Mosley, M.P., Ed.; The New Zealand Hydrological Society: Thorndon, Wellington, New Zealand, 2001; pp. 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprak, A.; Wheaton, J.M.; Ashmore, P.E.; Hensleigh, J.W.; Peirce, S. The relationship between particle travel distance and channel morphology: Results from physical models of braided rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberger, R. Direct bedload mesurements on the Danube at Vienna and their results to date. Die Wasserwirtsch. 1931, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mühlofer, L. Investigation into suspended load and bedload of the river Inn, near Kirchbichl, Tirol. Die Wasserwirtsch. 1933, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, H.A. The calibration of bedload trap used in the Rhine. Schweuzerische Bauztg. 1937, 110, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nesper, F. Results of bedload and silt movement observations on the Rhine at the Brugg Bridge. Schweuzerische Bauztg. 1937, 110, 143–148, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Emmett, W.W. The Channels and Waters of the Upper Salmon River Area, Idaho; USGS Professional Paper 870A; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.; Frostick, L.E.; Layman, J.T. The incidence and nature of bedload transport during flood flows in coarse-grained alluvial channels. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1985, 10, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.J.; Dietrich, W.E.; Leopold, L.B.; Drake, T.G.; Shreve, R.L. Bedload sheets in heterogeneous sediment. Geology 1988, 16, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudden, J.R.; Hoey, T.B. The causes of bedload pulses in a gravel channel: The implications of bedload grain-size distributions. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 1411–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, T.B.; Sutherland, A.J. Channel morphology and bedload pulses in braided rivers: A laboratory study. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1991, 16, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedermann, M.; Tritthart, M.; Habersack, H. Particle path characteristics at the large gravel-bed river Danube: Results from a tracer study and numerical modelling. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla Pittaluga, M.; Luchi, R.; Seminara, G. On the equilibrium profile of river beds. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.L.; Shimizu, Y. Numerical simulation of relatively wide, shallow channels with erodible banks. J. Hydraulic Eng. 2005, 131, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahnestock, R.K. Morphology and hydrology of a glacial stream—White River, Mount Rainier, Washington. U.S. Geol. Surv. 1963, 422, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A.; Khan, H.R. Experimental study of channel patterns. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1972, 83, 1755–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, J.C.; Ashley, G.M. Processes, bar morphology, and sedimentary structures on braided outwash fans, Northeastern Gulf of Alaska. In Glaciofluvial and Glaciolacustrine Sedimentation; Jopling, A.V., McDonald, C., Eds.; Special publication—Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1975; pp. 193–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ergenzinger, P. Chaos and order: The channel geometry of gravel bed braided rivers. In Geomorphological Models; Ahnert, F., Ed.; Catena Verlag: Cremlingen-Destedt, Germany, 1987; Catena Suppl. 10; pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, G.E. Critical flow constrains flow hydraulics in mobile-bed streams. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viparelli, M.; Pica, M. Streams in Large Alluvial Beds of High Slope, xii iahr. International Congress, Fort Collins. 1967. Available online: http://www.diia.unina.it/collana02.html (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Young, W.; Davies, T. Bedload transport in braided gravel-bed river model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1991, 16, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarn, B. Einfluss der flussbettbreite auf die wechselwirkung zwischen abfluss, morphologie und geschiebetransportkapazität. In VAW Mit-Teilung 154; Vischer, D., Ed.; Laboratory of Hydraulics, Hydrology and Glaciology (VAW): ETH Zurich, Switzerland, 1997. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Church, M.; Rood, K. Catalogue of alluvial river channel regime data, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. Rep. Dept. Geol. Univ. Br. Columbia 1983. Available online: http://www.nced.umn.edu/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Hey, R.D.; Thorne, C.R. Stable channels with mobile gravel beds. J. Hydraulic Eng. 1986, 112, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viparelli, C. Corsi d’acqua naturali e leggi che ne regolano il modellamento. In Quaderno n.4; Istituto di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche: Napoli, Italy, 1972. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Peter, E.; Müller, R. Formulas for bed-load transport. In Meeting of the International Association for Hydraulic Structures Research, 2nd ed.; International Association Hydraulic Research: Stockholm, Sweden, 1948; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker, R.P. Fraktionsweiser Geschiebetransport. Mitteilungen der Versuch-sanstalt fur Wasserbau. In Hydrologie und Glaziologie, 138; Eidgenossische Technische Hochschule (ETH): Zurich, Switzerland, 1995; p. 209. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.; Parker, G. Re-analysis and correction of bed-load relation of Meyer-Peter and Muller using their own database. J. Hydraulic Eng. 2006, 132, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T. Open-Channel Hydraulics; Mc Graw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959; p. 680. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, G.; Andrews, E.D. Sorting of bed load sediment by flow in meandering bends. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tealdi, S.; Camporeale, C.; Ridolfi, L. Long-term morphological river response to hydrological changes. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1643–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Transient Hydrodynamic Dispersion in Rough Open Channels: Theoretical Analysis of Bed-Form Effects. J. Hydr. Eng. 2010, 136, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Longitudinal Dispersion in River Flows Characterized by Random Large-Scale Bed Irregularities: First-Order Analytical Solution. J. Hydr. Eng. 2012, 138, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M.; De Vincenzo, A.; Brancati, F. A mathematical model for the flow resistance and the related hydrodynamic dispersion induced by river dunes. J. Appl. Math. 2013, 432610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Saint-Venant, B. Comptes Rendus De L’académie Des Sciences; Sciences Academy of France Institute: Paris, France, 1871; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pannone, M. Effect of nonlocal transverse mixing on river flows dispersion: A numerical study. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W08534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Predictability of tracer dilution in large open channel flows: Analytical solution for the coefficient of variation of the depth-averaged concentration. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2617–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M.; De Vincenzo, A. Stochastic numerical analysis of anomalous longitudinal dispersion and dilution in shallow decelerating stream flows. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 2087–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M.; Mirauda, D.; De Vincenzo, A.; Molino, B. Longitudinal Dispersion in Straight Open Channels: Anomalous Breakthrough Curves and First-Order Analytical Solution for the Depth-Averaged Concentration. Water 2018, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, L.B.; Wolman, M.G. River channel patterns: Braided, meandering, and straight. U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1957, 282-B, 39–84. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. Patterns of alluvial rivers. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1985, 13, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosgen, D.L. A Classification of Natural Rivers. Catena 1994, 22, 169–199. Available online: http://www.science.earthjay.com/instruction/HSU/2016_fall/GEOL_332/labs/lab_04/Rosgen_1994_Classification_Rivers.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Buffington, J.M. Channel-reach morphology in mountain drainage basins. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1997, 109, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M. Bed material transport and the morphology of alluvial rivers. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006, 34, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialik, R.J.; Nikora, V.I.; Rowinski, P.M. 3-D Lagrangian modeling of saltating particles diffusion in turbulent water flow. Acta Geophys. 2012, 60, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The dispersion of matter in turbulent flow through a pipe. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1954, 223, 446–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. On the exact analytical solution for the spatial moments of the cross-sectional average concentration in open channel flows. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W08511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; De Vincenzo, A.; Pannone, M. Simplified entropic model for the evaluation of suspended load concentration. Water 2018, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Molino, A.J.; Molino, B.; Scorpio, V. Reservoir rehabilitation: The new methodological approach of Economic Environmental Defence. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Covelli, C.; Molino, A.J.; Pannone, M.; Ciccaglione, M.; Molino, B. Long-Term Management Policies of Reservoirs: Possible Re-Use of Dredged Sediments for Coastal Nourishment. Water 2019, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assani, A.A.; Petit, F. Impact of hydroelectric power releases on the morphology and sedimentology of the bed of the Warche River (Belgium). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2004, 29, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ock, G.; Gaeuman, D.; McSloy, J.; Kondolf, G.M. Ecological functions of restored gravel bars, the Trinity River, California. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Shi, L.; Wen, L.; Chen, J.; Duo, H.; Lei, G. Gravel Bars Can Be Critical for Biodiversity Conservation: A Case Study on Scaly-Sided Merganser in South China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rempel, L.L.; Healey, M.; Richardson, J.R. Macroinvertebrate community structure along gradients of hydraulic and sedimentary conditions in a large gravel-bed river. Freshwat. Biol. 2000, 45, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilvear, D.; Francis, R.; Will, N.; Gurnell, A. 26 Gravel bars: A key habitat of gravel-bed rivers for vegetation. Dev. Earth Surf. Process. 2007, 11, 677–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
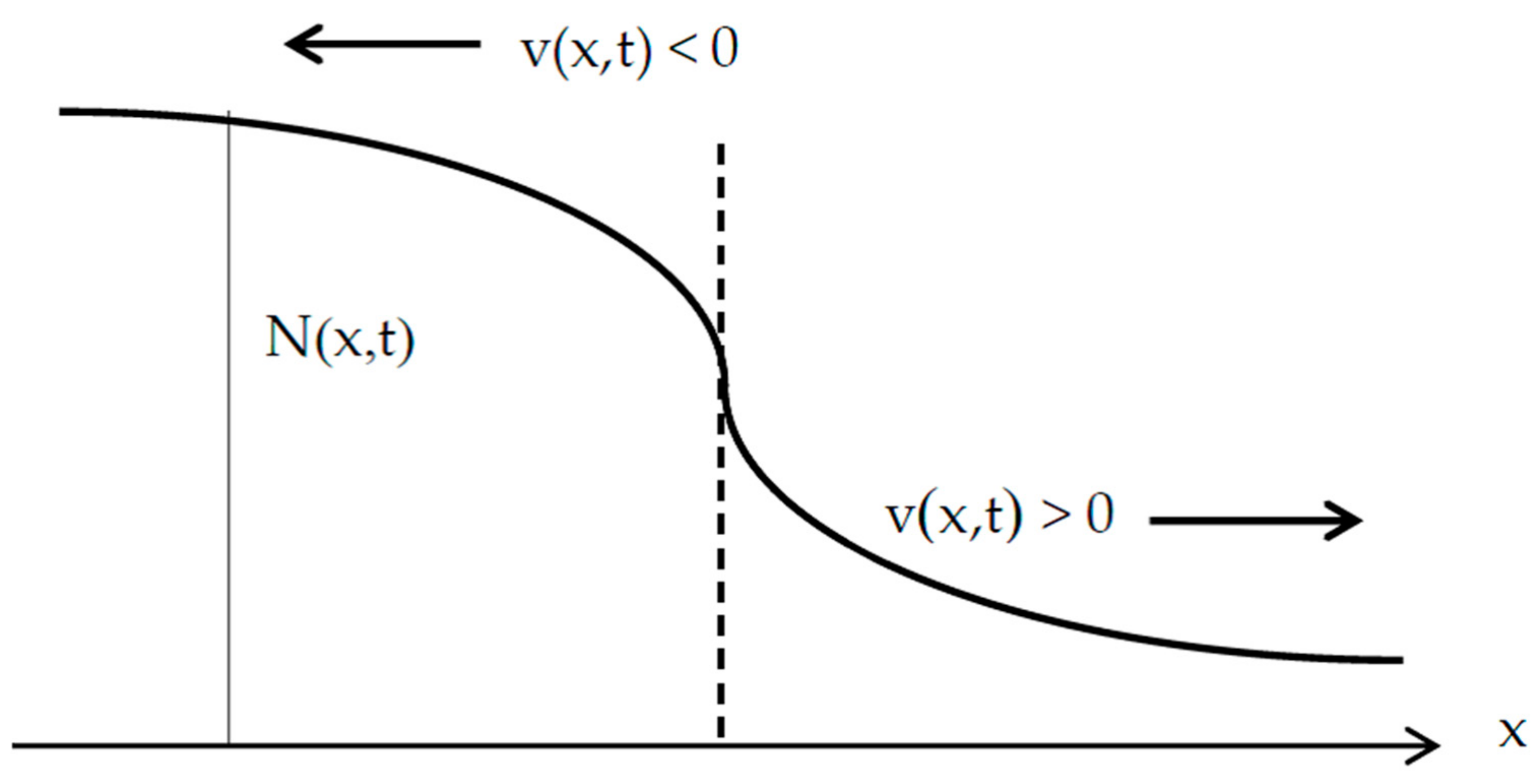
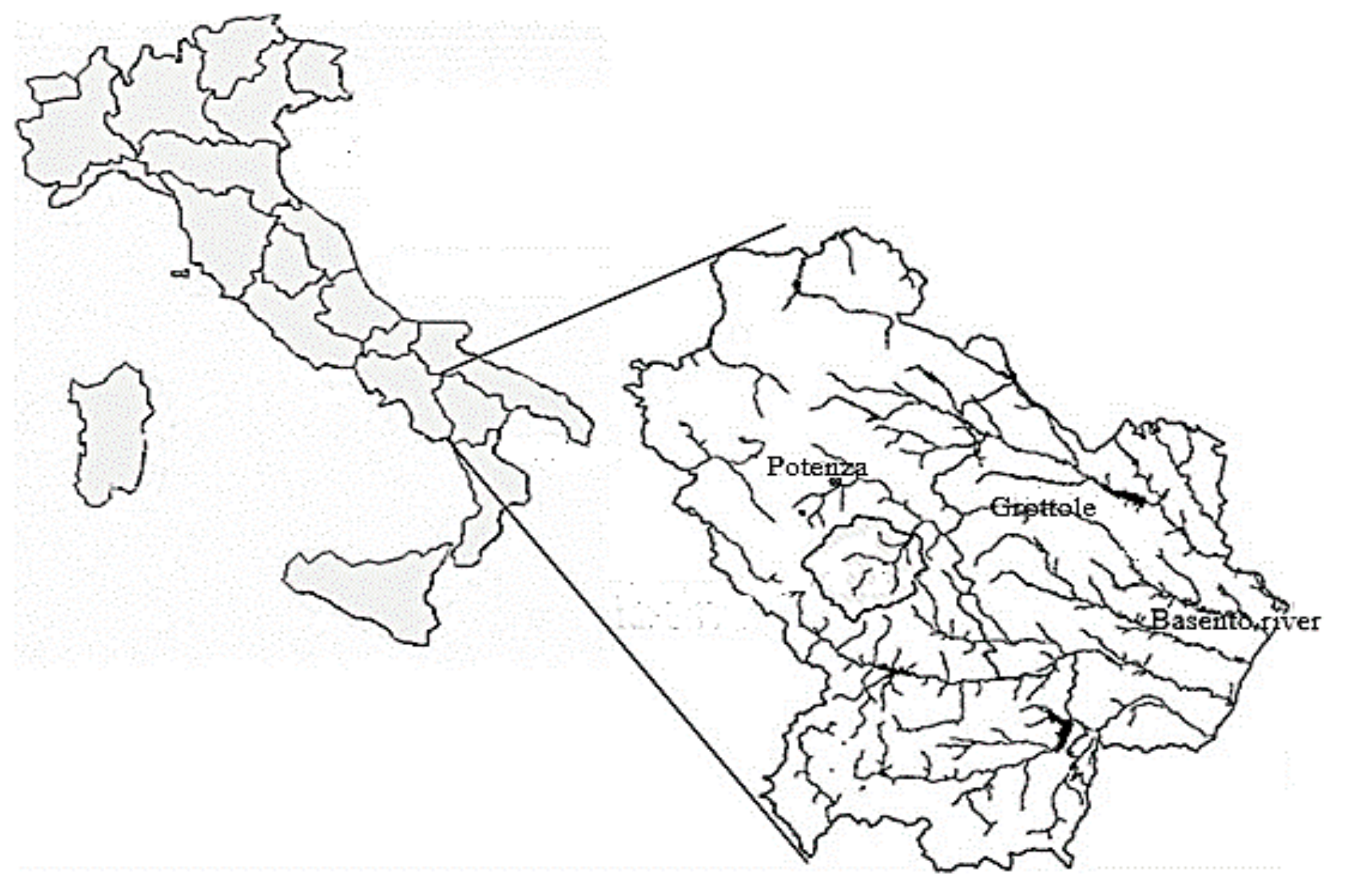

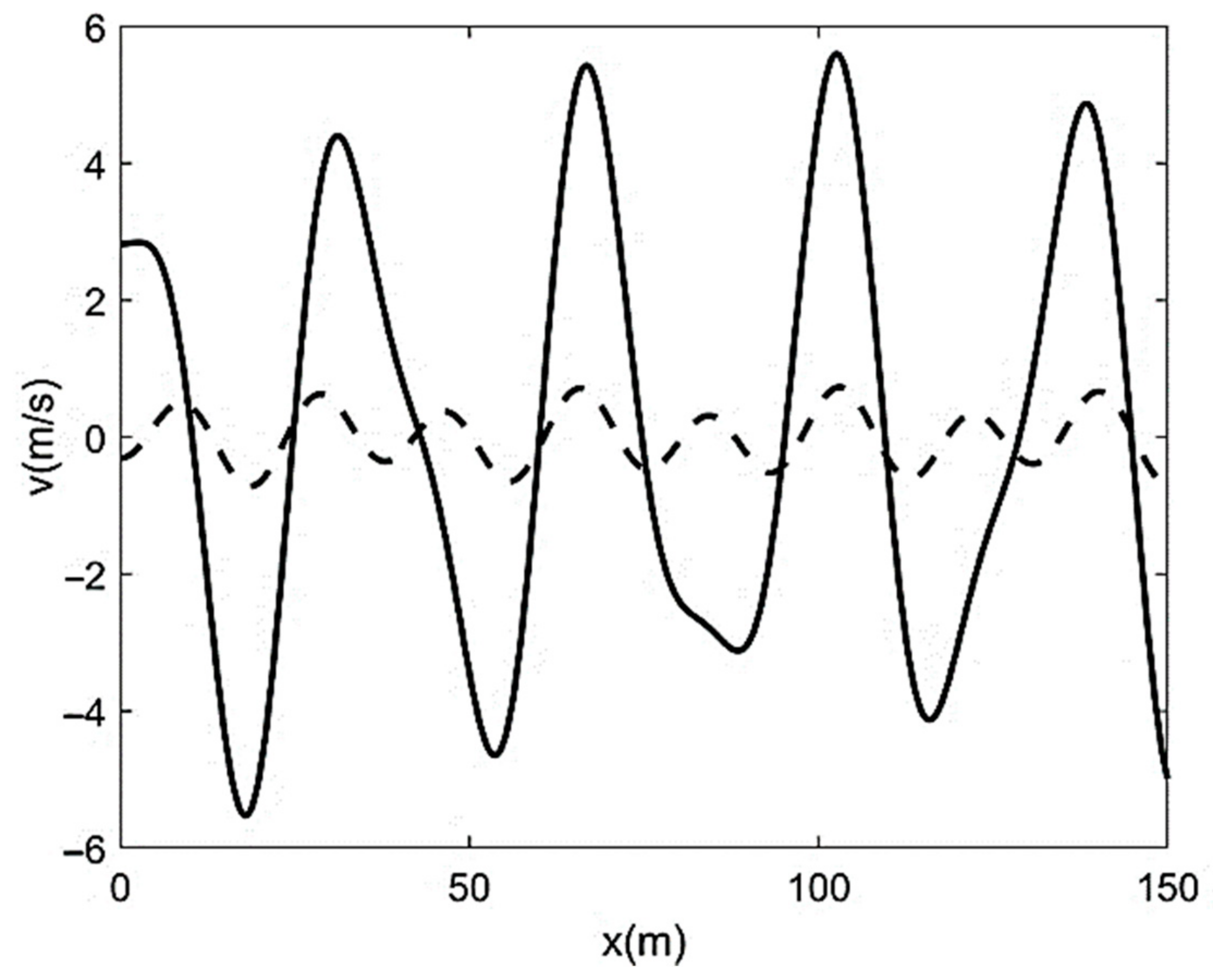
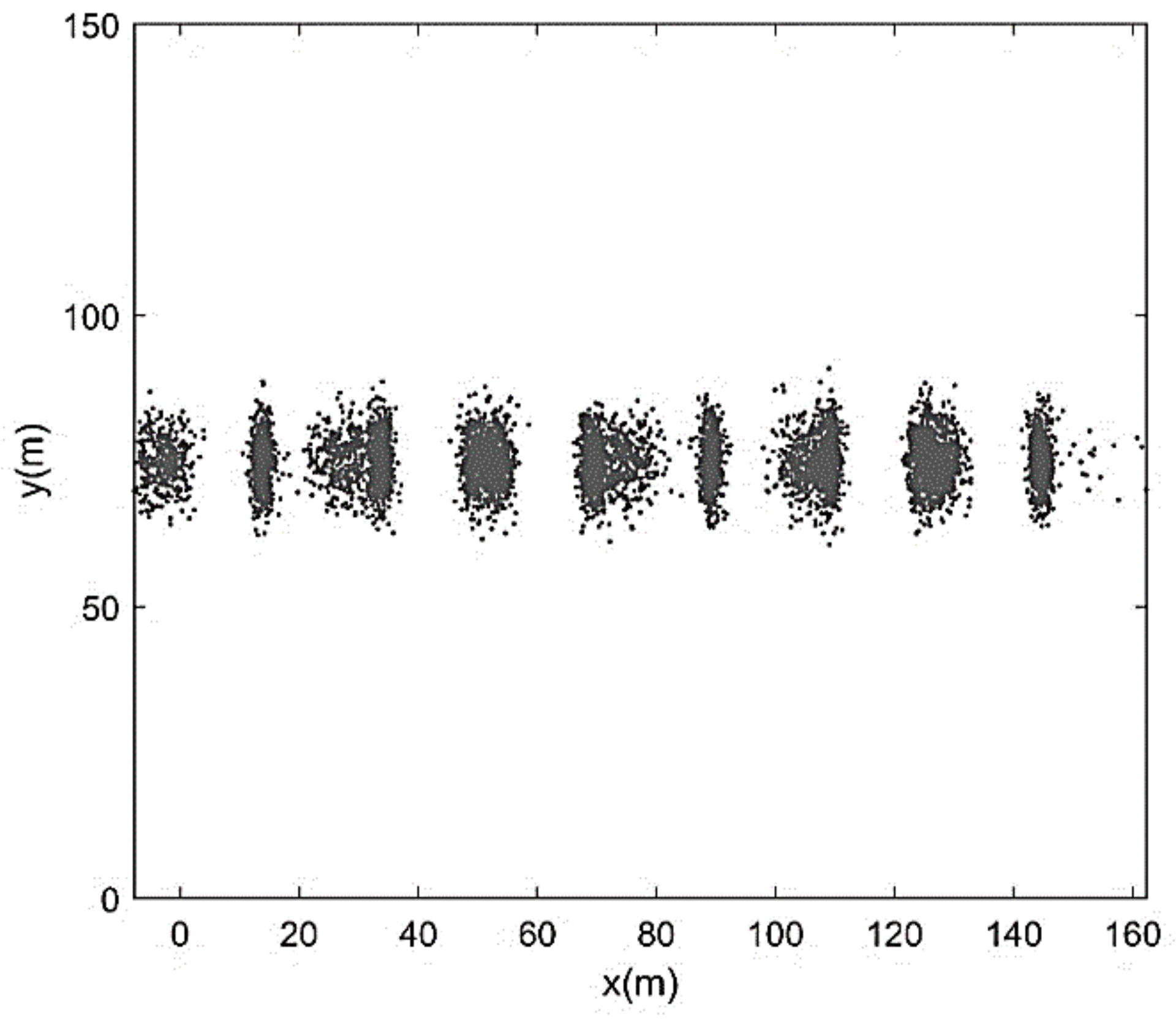
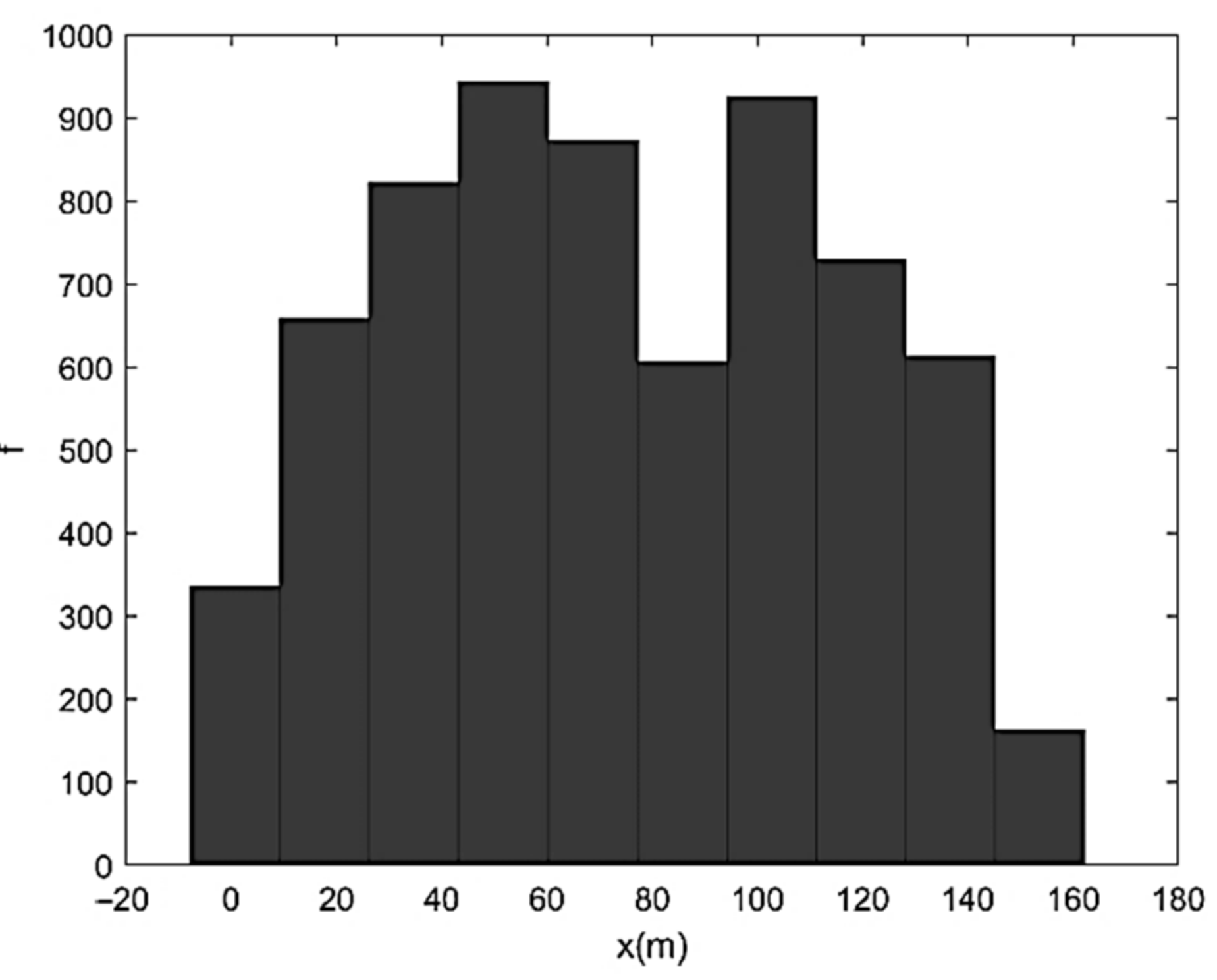
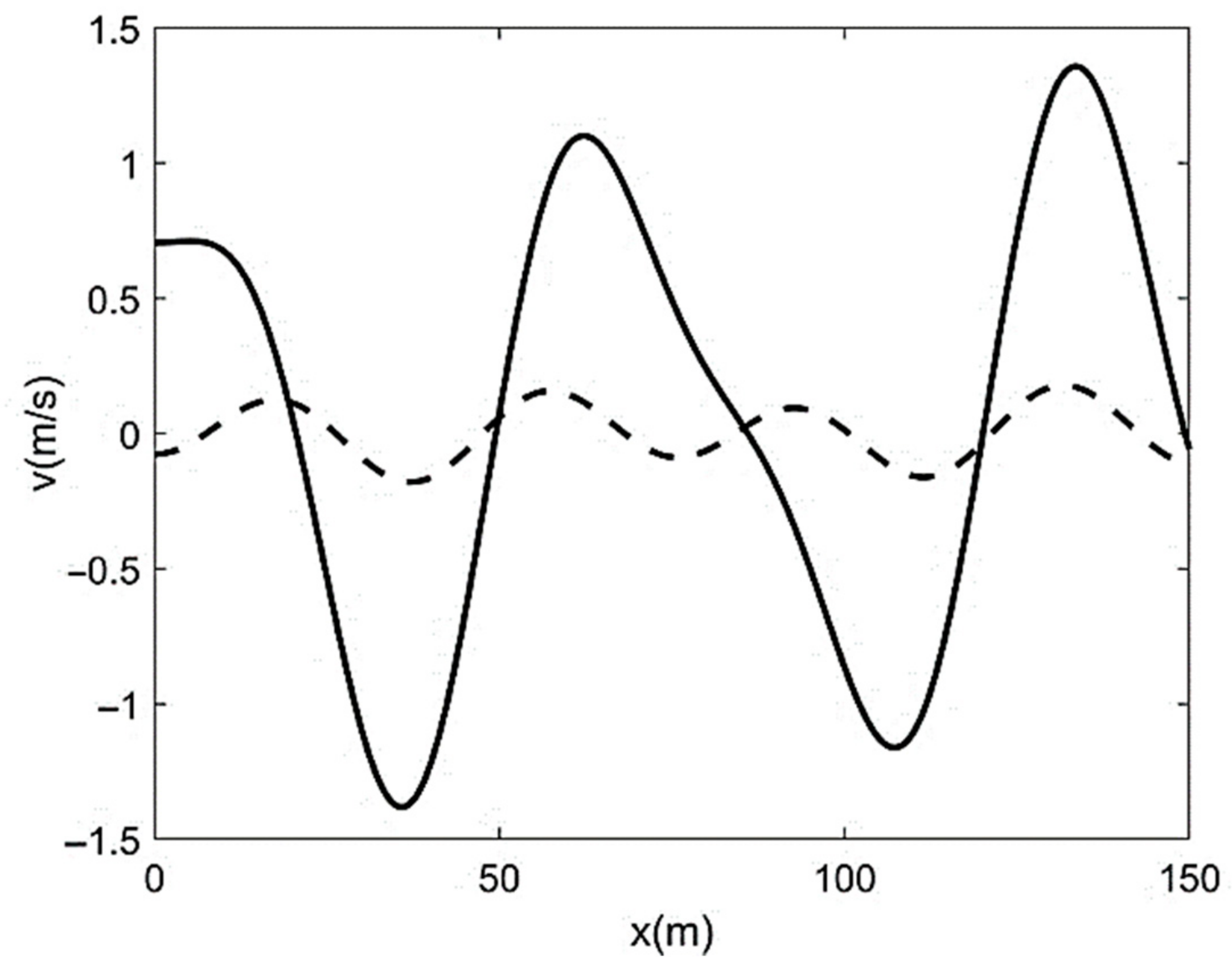
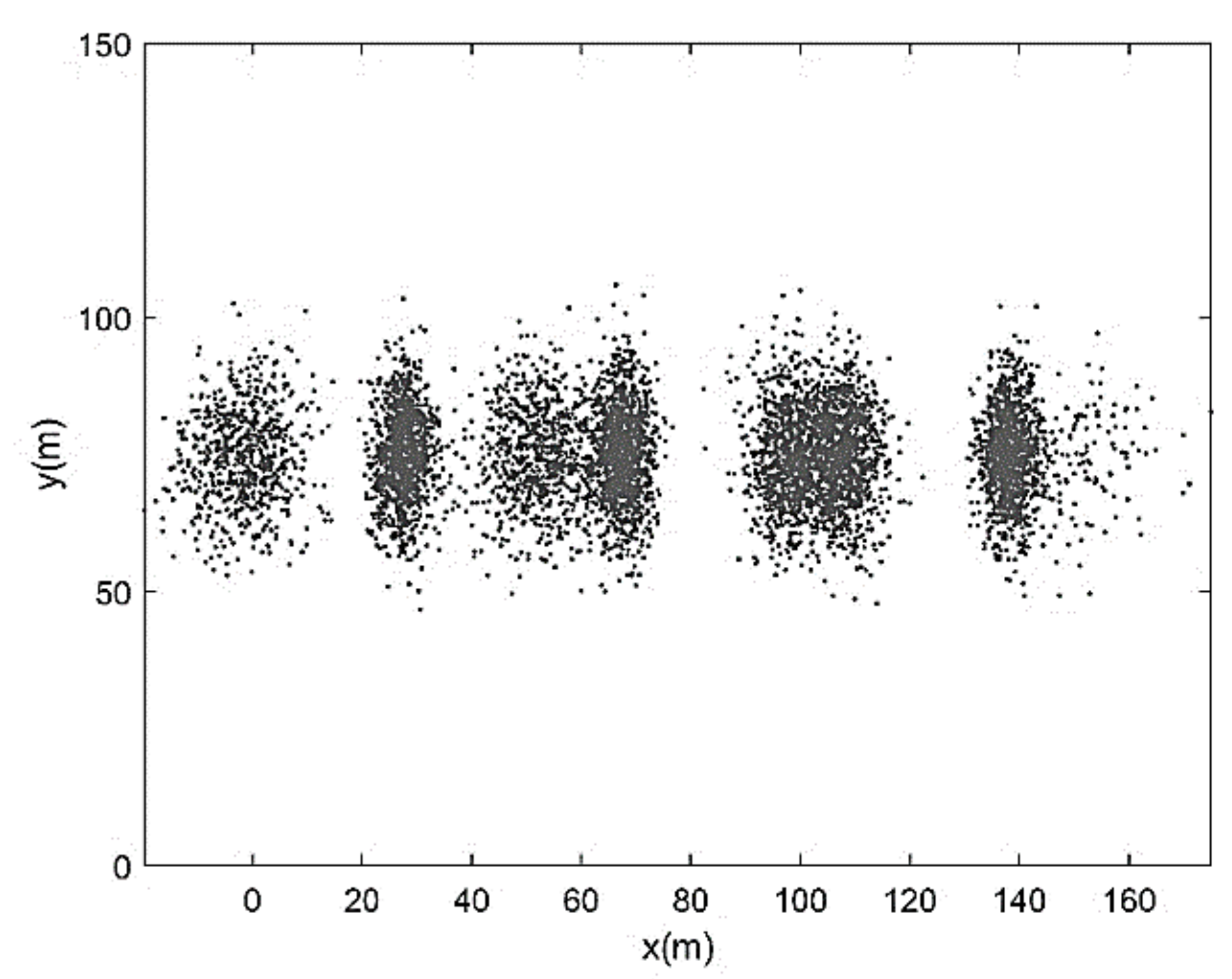
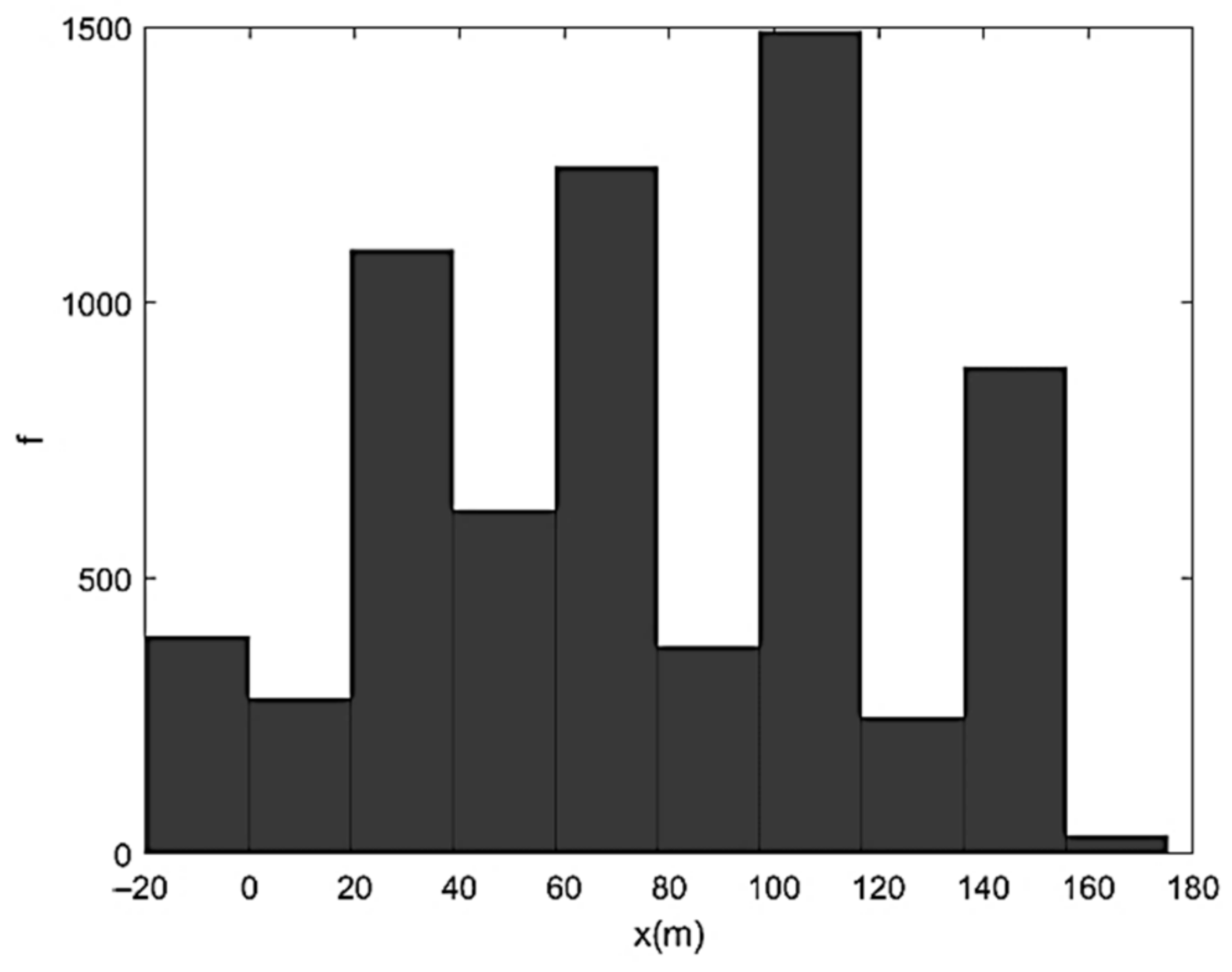
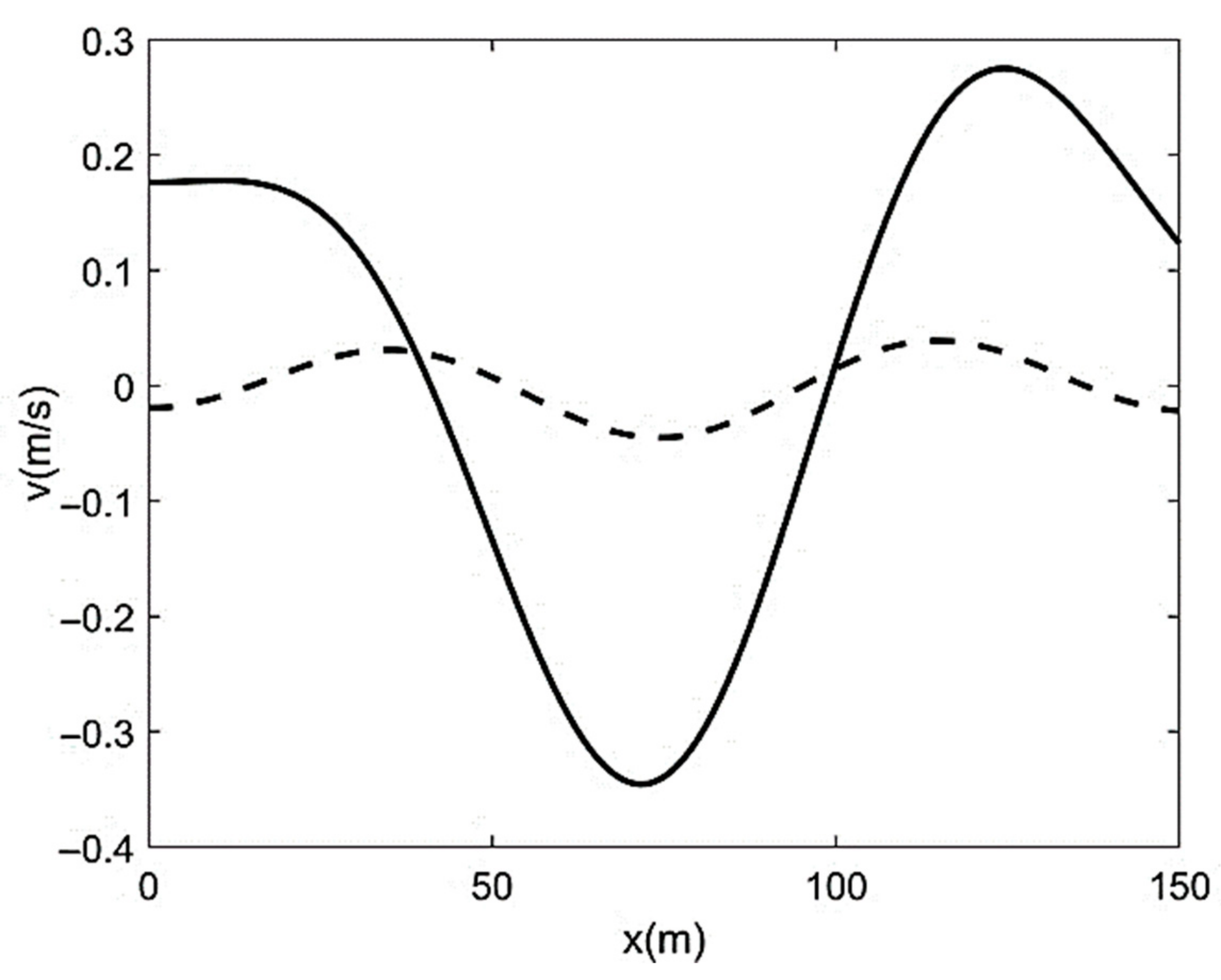
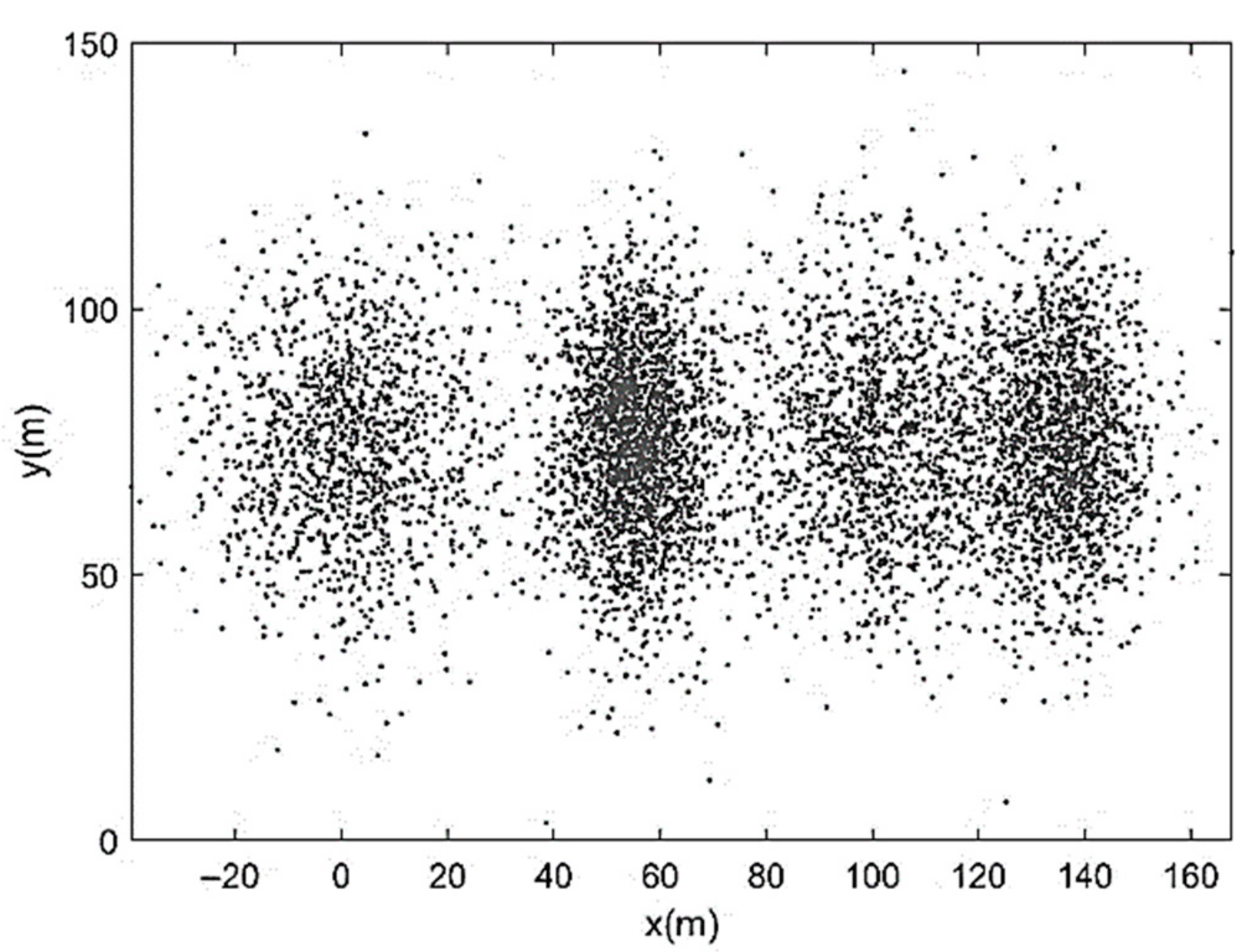
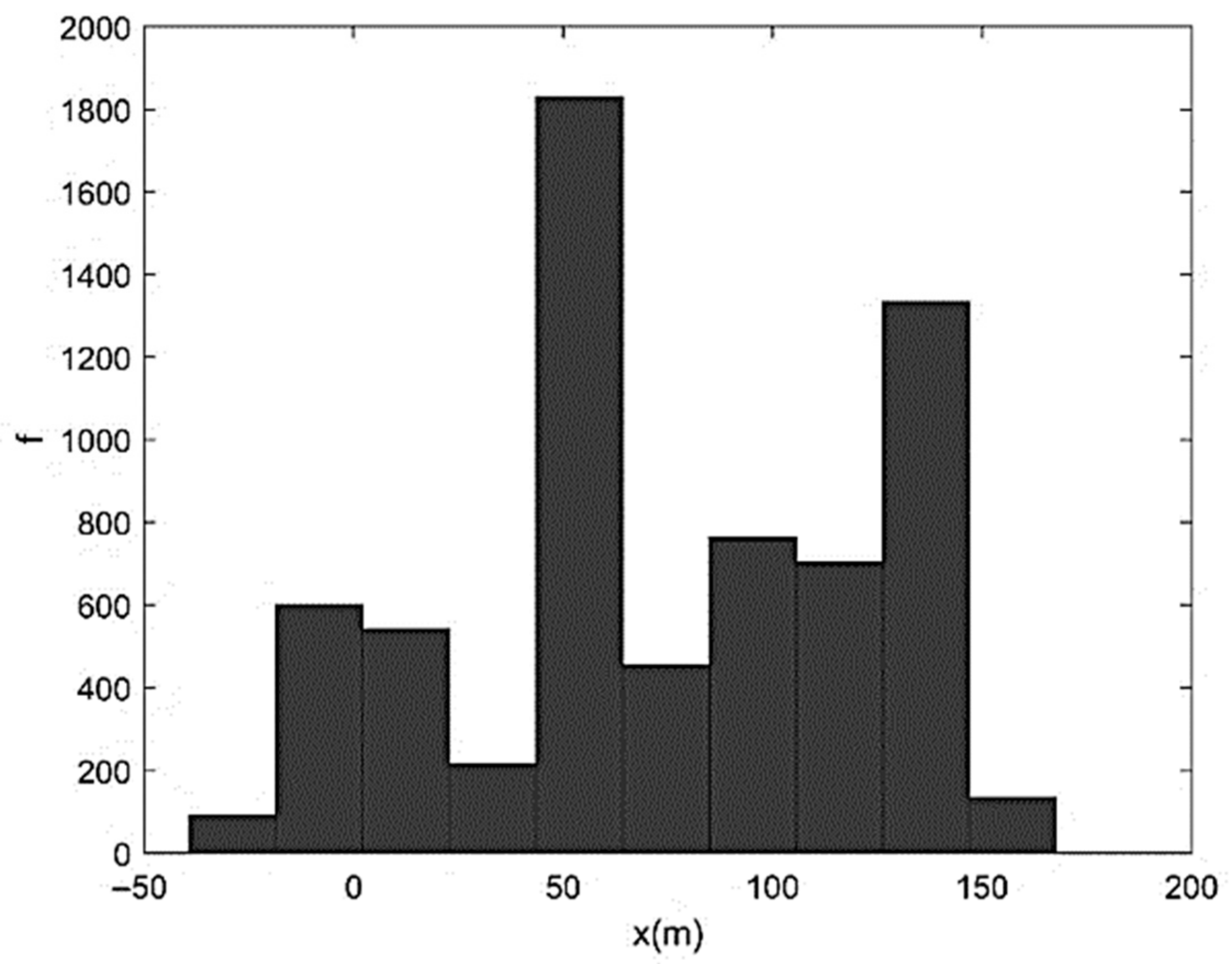

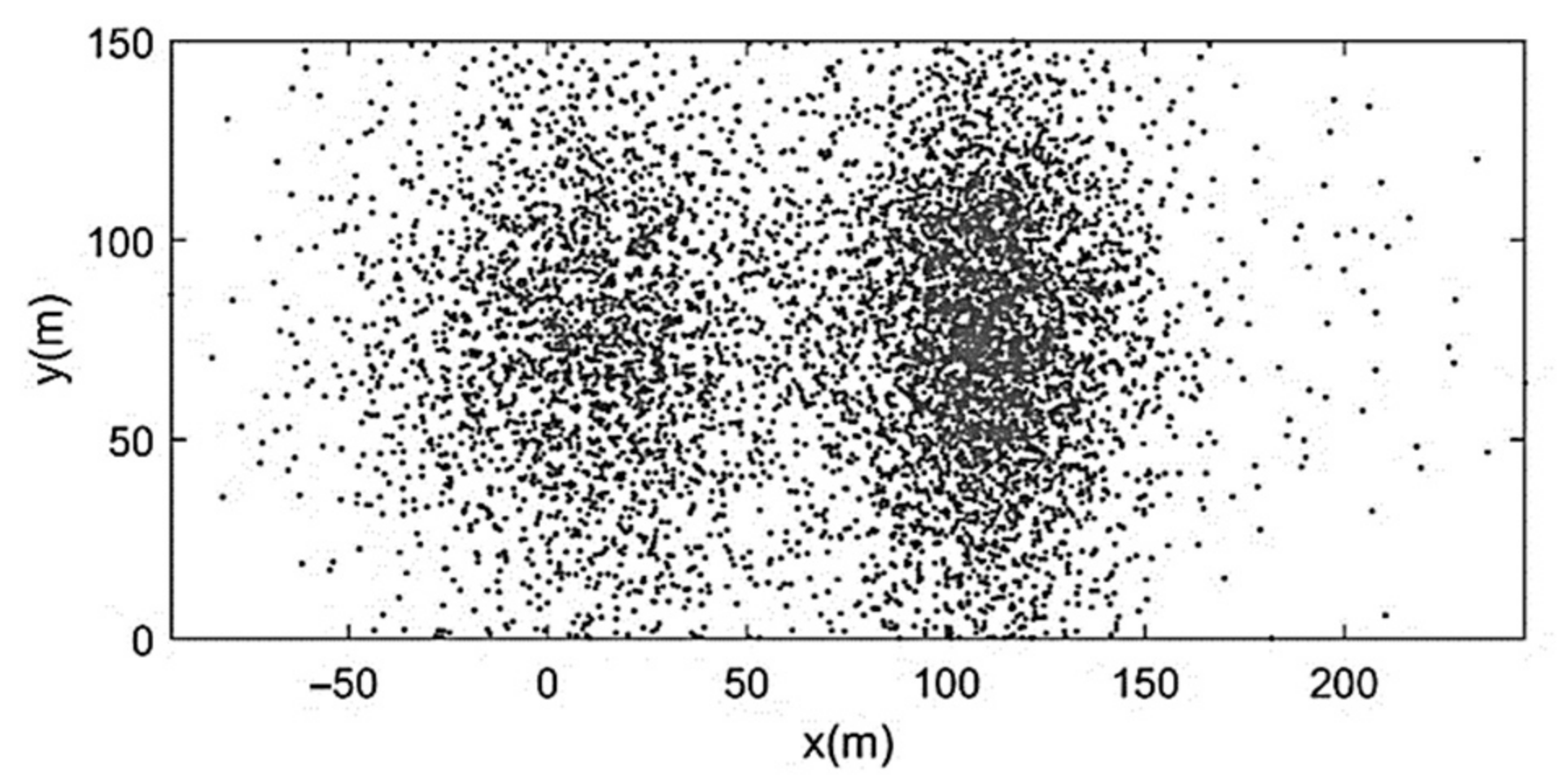
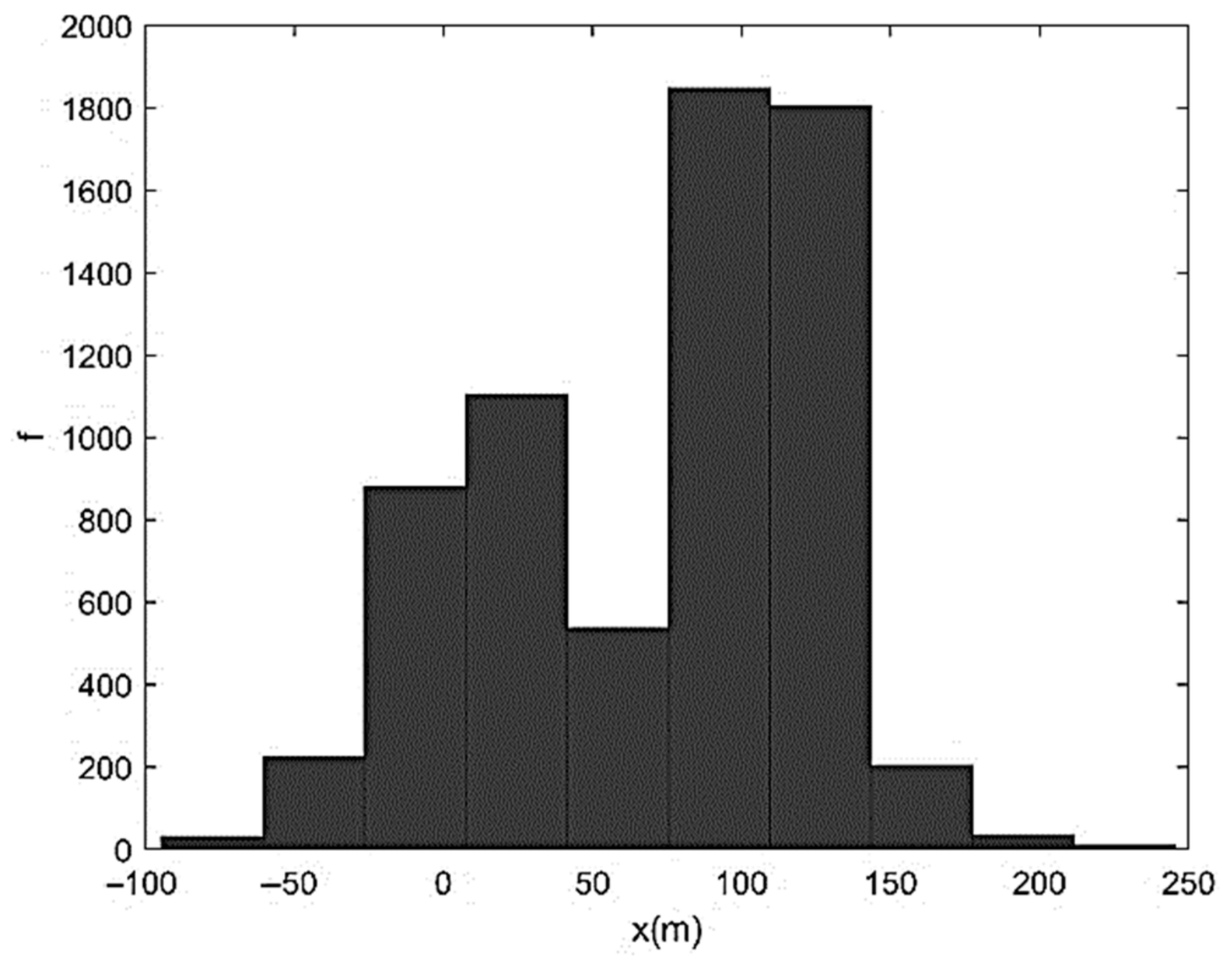
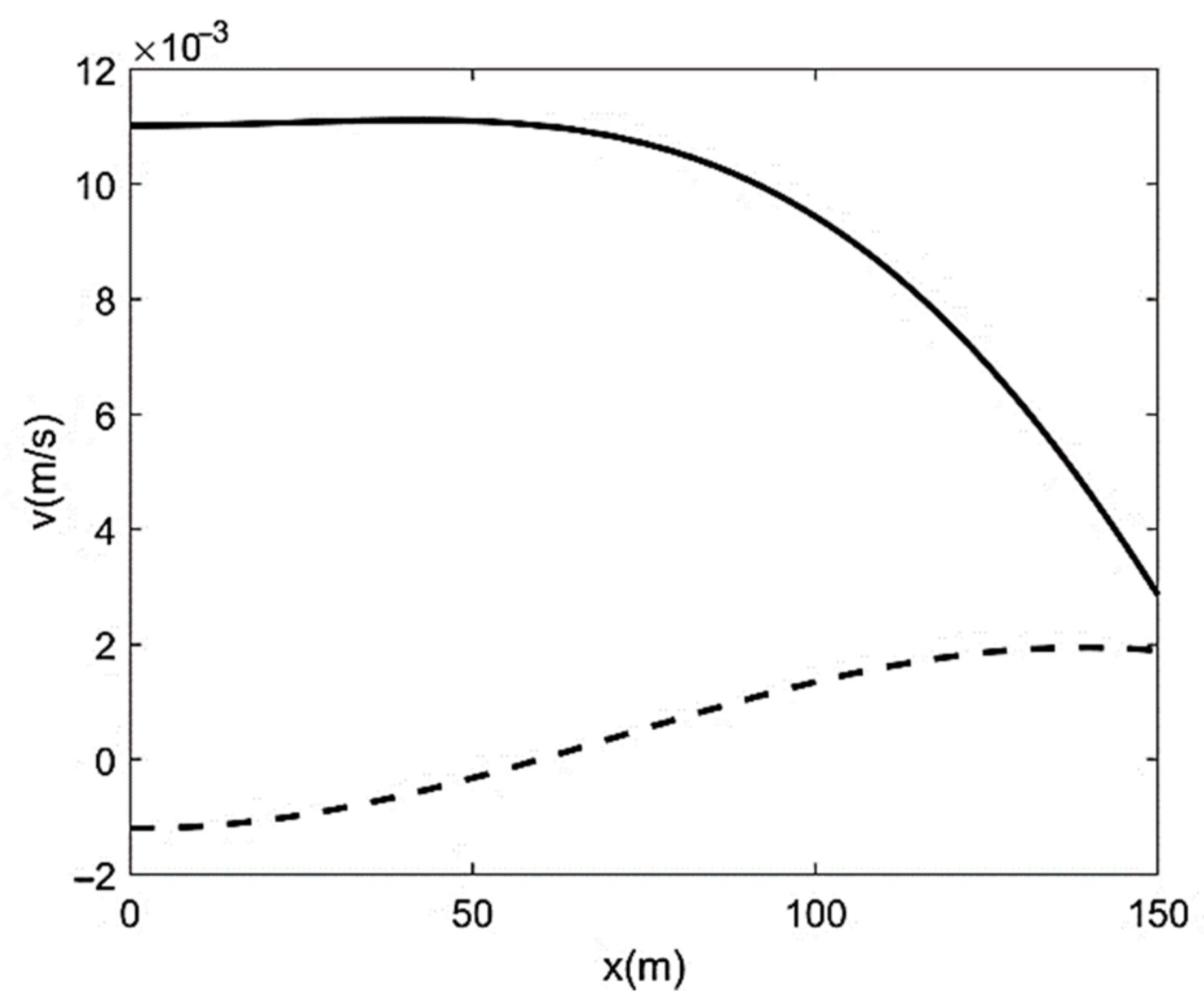
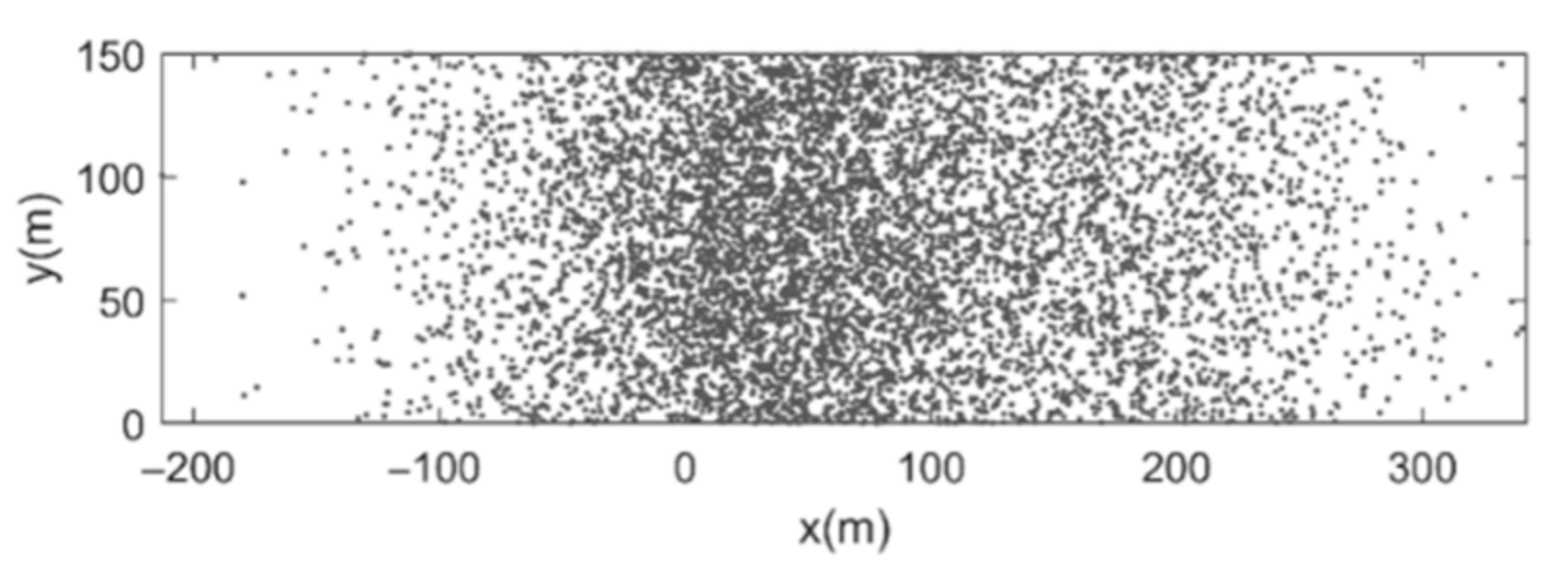

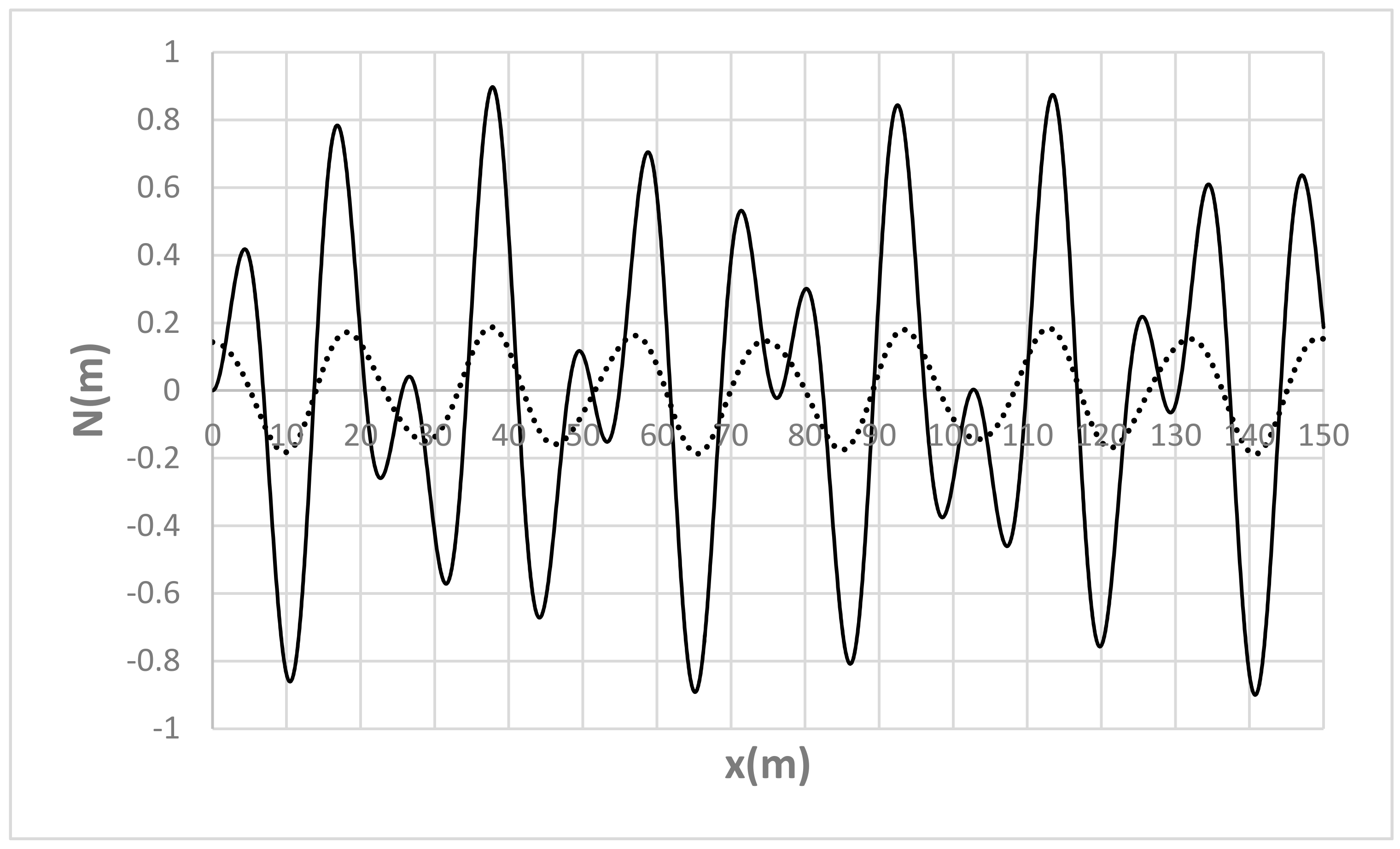
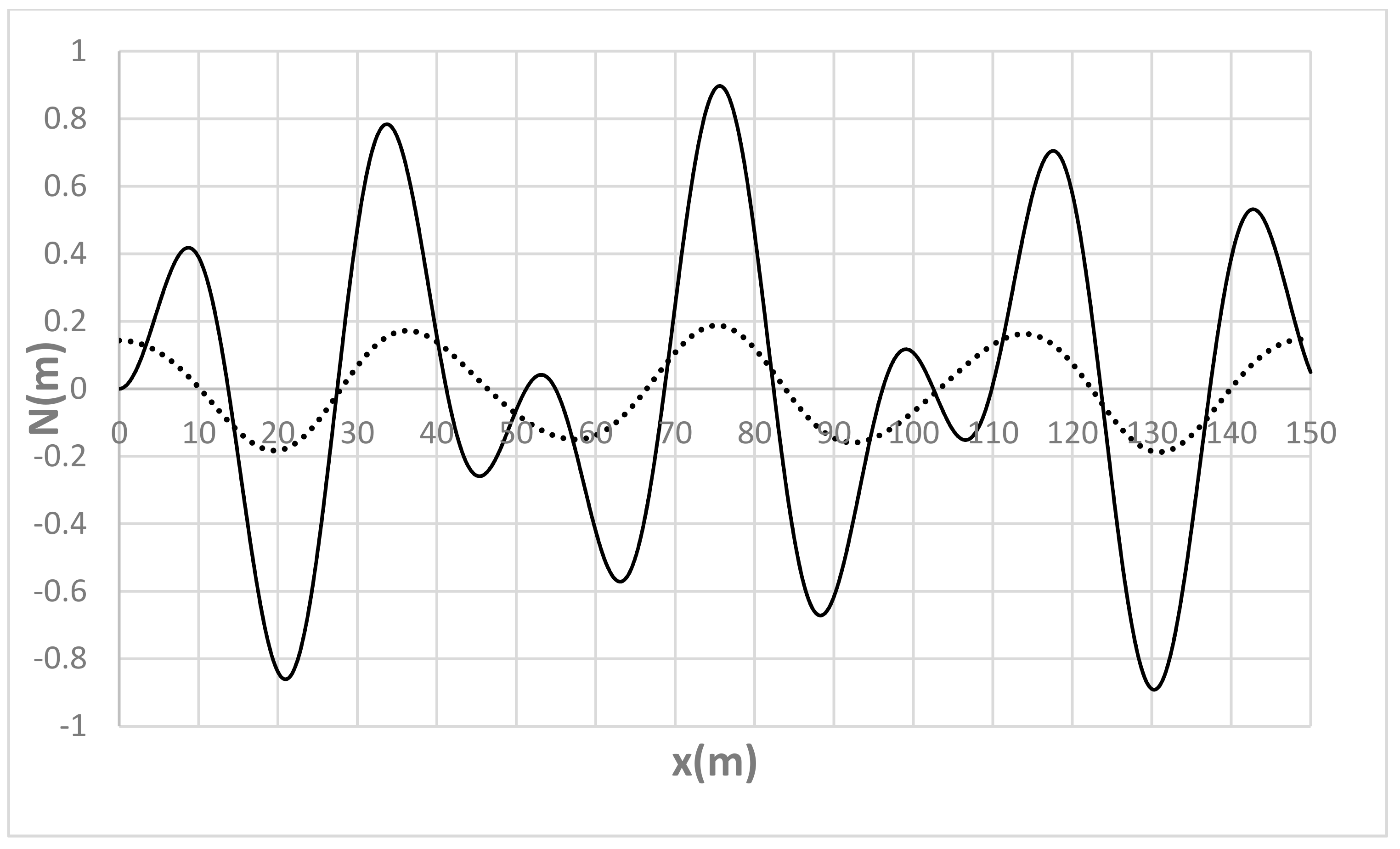
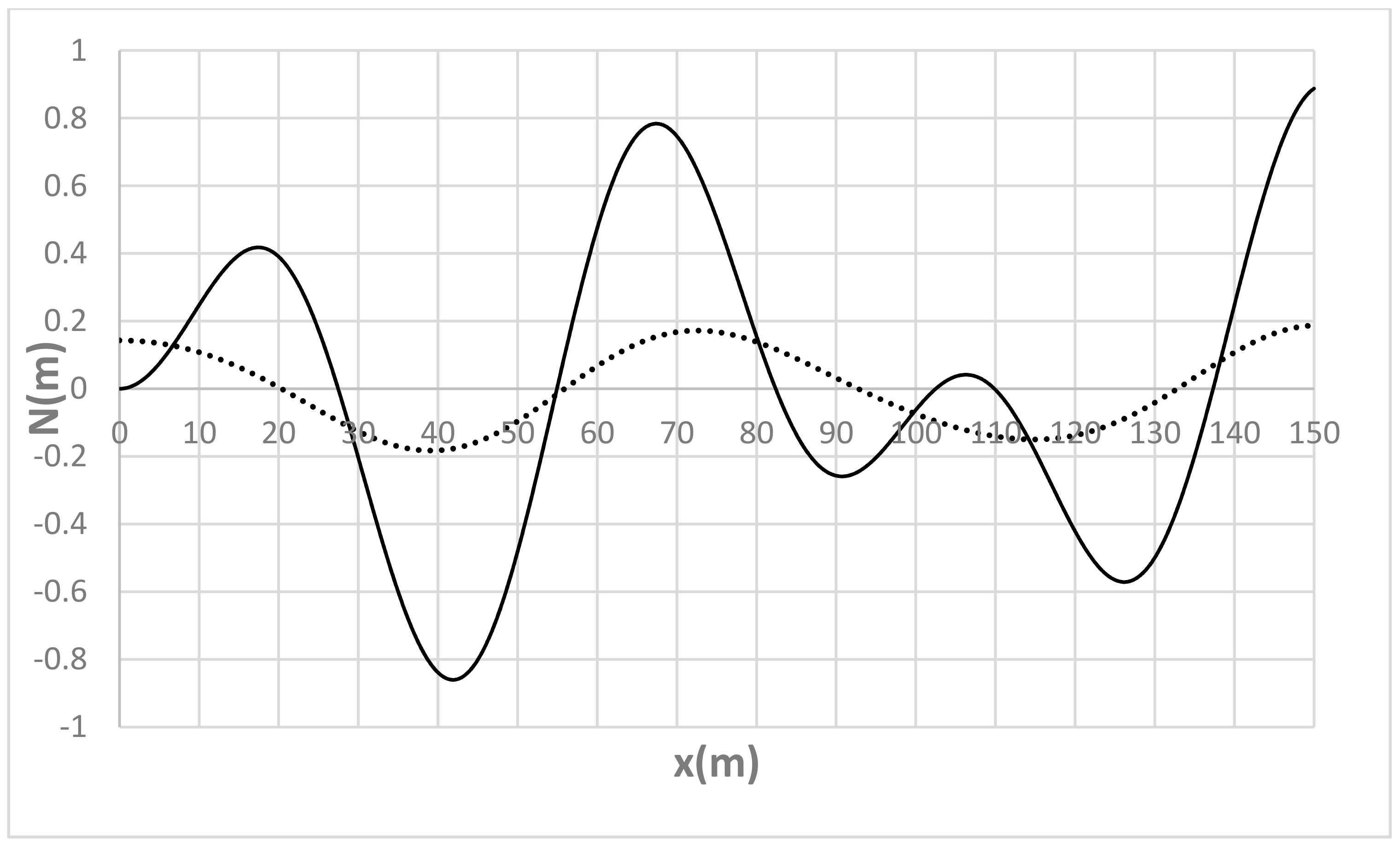
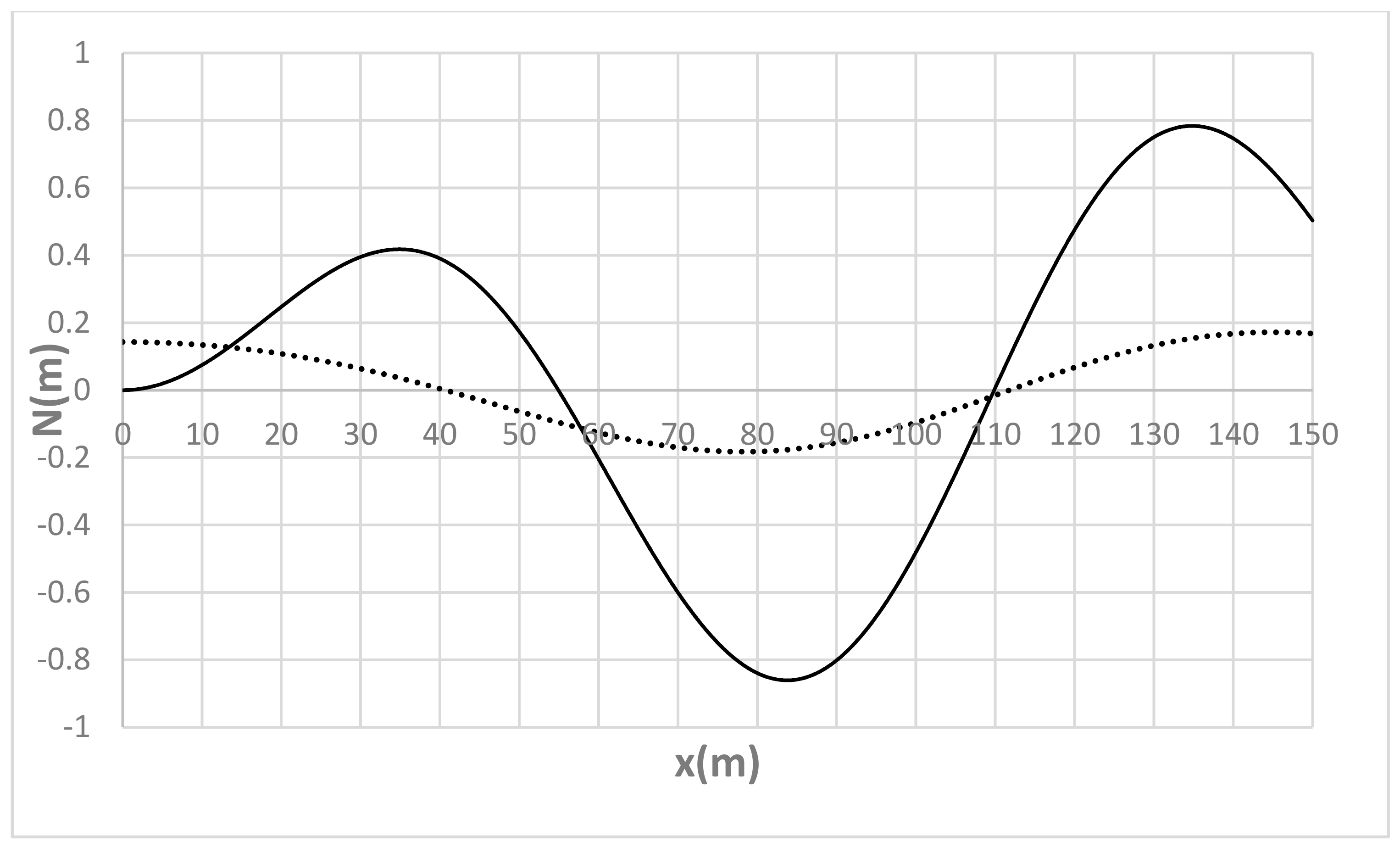
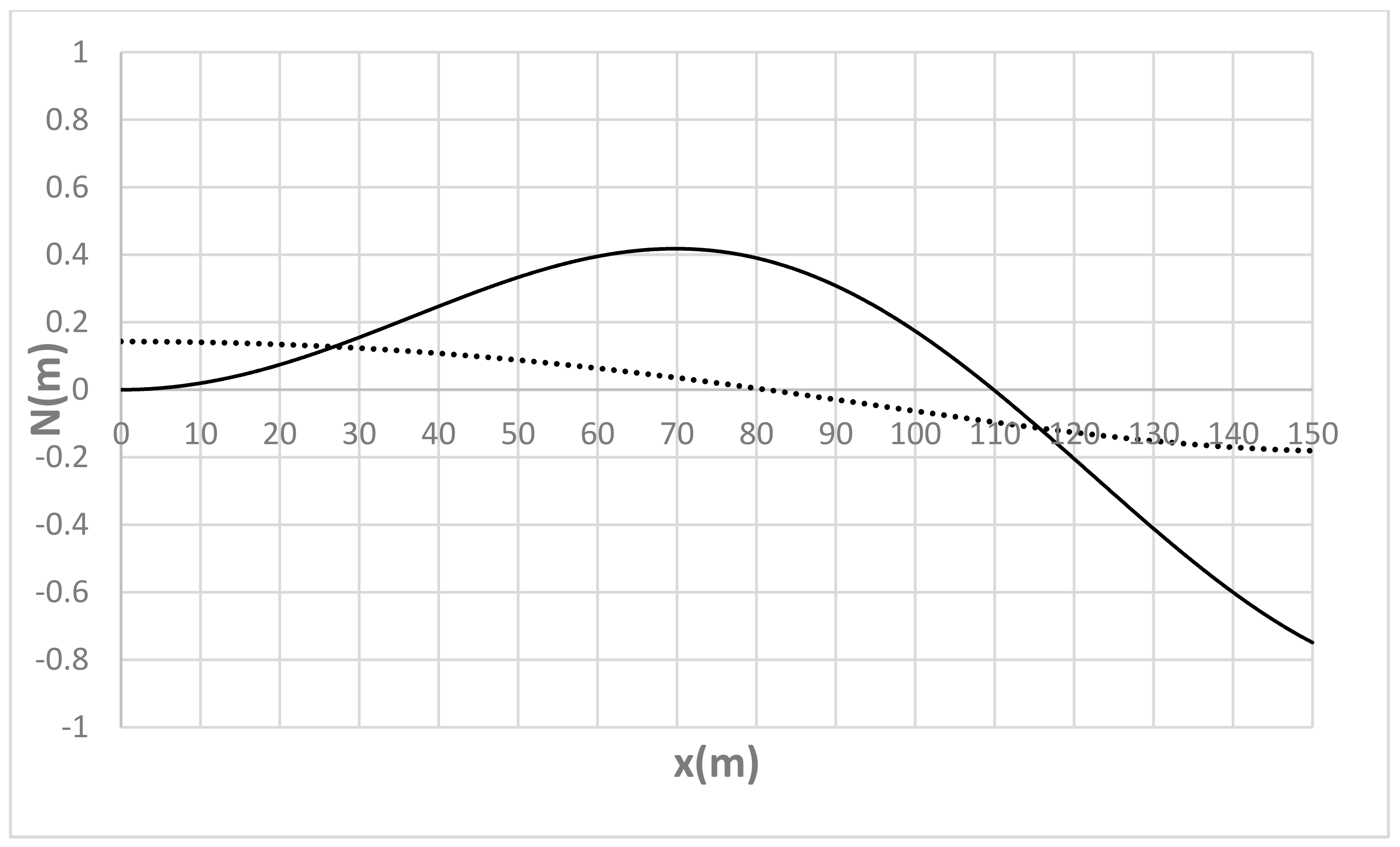
| Run | Q (m3/s) | S0 | S0SB | Seq | teq (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 0.0444 | 0.014 | 0.084 | 0.007 | 46 |
| R2 | 0.031 | 0.013 | 0.067 | 0.012 | 167 |
| R3 | 0.036 | 0.0135 | 0.067 | 0.011 | 168 |
| R4 | 0.0254 | 0.027 | 0.0566 | 0.015 | 261 |
| R5 | 0.0304 | 0.014 | 0.041 | 0.015 | 208 |
| R6 | 0.040 | 0.01 | 0.0331 | 0.012 | 96 |
| R7 | 0.045 | 0.0192 | 0.0491 | 0.009 | 144 |
| R8 | 0.048 | 0.01 | 0.0331 | 0.011 | 197 |
| R9 | 0.053 | 0.0104 | 0.032 | 0.01 | 261 |
| R10 | 0.035 | 0.022 | 0.0145 | 0.015 | 72 |
| Run | Λ/B | τd (s) | Pe | BI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1/8 | 32.74 | 210.52 | 8.8 |
| R2 | 1/4 | 130.96 | 105.33 | 4.5 |
| R3 | 1/2 | 523.83 | 52.67 | 2.8 |
| R4 | 1 | 2095.34 | 26.47 | 2.3 |
| R5 | 2 | 8381.35 | 13.24 | 1.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pannone, M.; Vincenzo, A.D. Theoretical Investigation of Equilibrium Dynamics in Braided Gravel Beds for the Preservation of a Sustainable Fluvial Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031246
Pannone M, Vincenzo AD. Theoretical Investigation of Equilibrium Dynamics in Braided Gravel Beds for the Preservation of a Sustainable Fluvial Environment. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031246
Chicago/Turabian StylePannone, Marilena, and Annamaria De Vincenzo. 2021. "Theoretical Investigation of Equilibrium Dynamics in Braided Gravel Beds for the Preservation of a Sustainable Fluvial Environment" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031246
APA StylePannone, M., & Vincenzo, A. D. (2021). Theoretical Investigation of Equilibrium Dynamics in Braided Gravel Beds for the Preservation of a Sustainable Fluvial Environment. Sustainability, 13(3), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031246





